AP BIO: Chemistry of life
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 1 test...
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Covalent bonds
when two or more atoms share
electrons (usually between two nonmetals)
Nonpolar covalent:
Electrons are shared equally between two atoms
Polar covalent
Electrons are not shared equally between two atoms
ex: oxygen is negative charges & Hydrogen is positive
Ionic bonds
The attraction between oppositely charged atoms (ions)
Hydrogen bonds
the partially positive hydrogen atom in one polar covalent molecule will be
attracted to an electronegative atom in another polar covalent molecule
Polarity
polar covalent bonds created by unequal sharing of electrons between oxygen and
hydrogen within the molecule of water
Cohesion
attraction of molecules or other molecules of the same kind
-Allows for the transport of H2O and nutrients against gravity in plants
ex:H2O toH2O
Adhesion
the attraction to other molecules that are polar or have charge
-In plants, this allows water to
cling to the cell walls to resist
the downward pull of gravity
Capillary Action
the upward movement of water due to the forces of cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension
- Occurs when adhesion is greater than cohesion
-Important for transport of
water and nutrients in plants
Functional groups
chemical groups attached to the carbon skeleton that participate in chemical reactions
ex:Amino acid group,Carboxyl group,hydroxyl group etc
Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Nucleic Acid
Lipids
Polymers
chain like macromolecules of similar or identical repeating units that are covalently bonded together
Monomers
the repeating units that make up
polymers
Dehydration reaction
covalently bonds two monomers with the loss of H2O
ex:AB + H2O → A+B
Hydrolysis
breaks the covalent bonds in a polymer by adding H2O
ex:AB + H2O → A+B
Carbohydrates
Composed of C,H,& O
Includes sugars and polymers of sugars
-contains a hydroxyl and carbonyl group
Carbohydrate Monomer
Monosaccharide
Carbohydrate Polymer
polysaccharide
Examples of Carbohydrates
Glucose,fructose,and sucrose
Dissaccharides
Two monomers
ex:sucrose
bond:Glycoside linkage
Polyssaccharides
polymers with many sugars
Carbohydrate structural
Cellulose: Found in plant cell walls
Chitin: Forms exoskeleton of arthropods
Carbohydrate storage
Starch: Found in plants
Glycogen: Found in animals
Proteins
composed of C,H,O,N,& S
molecule consisting of polypeptides,folded into 3D shape
-shape determines function
Bond: peptide bond (between Carboxyl & amino acid )
Protein Monomer
Amino Acid
Protein Polymer
Polypeptide
Primary Structure
Bond: peptide bonds between amino acids
structure: string of amino acids

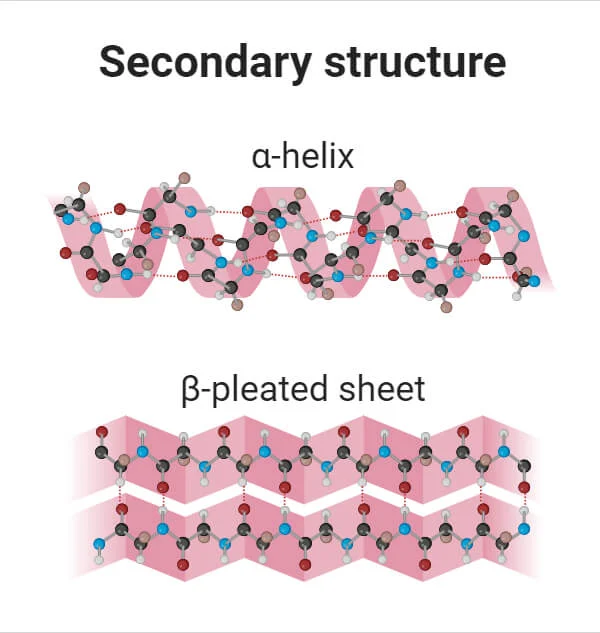
Secondary Structure
Bond: Hydrogen bonds between backbone
Structure: alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
Tertiary Structure
Bond: Any (Hydrogen,Covalent,Ionic) between R groups
structure: Final 3D structure

Quaternary
Bond: Any (Hydrogen,Covalent,Ionic) between R groups or different polypeptides

Function of proteins
Antibody-help protect the body from disease
Enzyme- carry out chemical reactions or assist
in creating new molecules
Messenger- transmit signals (ie hormones)
Structural- provide structure and support
Transport/storage- bind to and carry small
atoms and molecules through the body
Nucleic Acid
Composed of C,H,O,N,& P
-Polymers made of nucleotide monomers
Directionality 5’—> 3’ ; anti-parallel
TWO FORMS:DNA & RNA
Nucleic Acid monomers
Nucleotide
Nucleic Acid Polymer
DNA & RNA
Nucleic Acid Function
Store,transmit,& express heredity info
Purines
Double ring (A & G)
Pyrimidine
single ring (C,U,T)
Lipids
Composed of C,H,O,& P
Class of molecules that do not include true polymers
*ALL LIPIDS ARE NON-POLAR (aka hydrophobic)
Types of Lipids
Fats
Phospholipids
Steroids
Cholesterol
Function of Lipids
Provide energy storage
support cell function
provide insulation to keep mammals warm
Lipids Monomer
Glycerol: classified as an alcohol
Fatty acid: long carbon chains
*LIPIDS HAS NO POLYMERS
Saturated fatty acid
all single bonds
-each carbon is saturated by hydrogen
unsaturated fatty acid
at least one double bonds
-Not all carbons are saturated by hydrogen
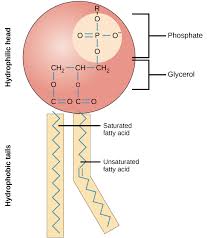
Phospholipids
Major component of cell membrane
-TWO fatty acids attached to a glycerol and a phosphate
Hydrophillic head (attracted to water )
Hydrophobic tail (repelled by water)
Steroids
hormones that support physiological functions like growth, development, energy,metabolism, and homeostasis
ex: testosterone, or estrogen
Cholesterol
Provides structural stability to animal cell membranes