Kin 100 midterm (L4 scapula landmarks - 9 distal radioulnar)
1/354
Earn XP
Description and Tags
continue from page 17 lecture 5 latissimus dorsi
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
355 Terms
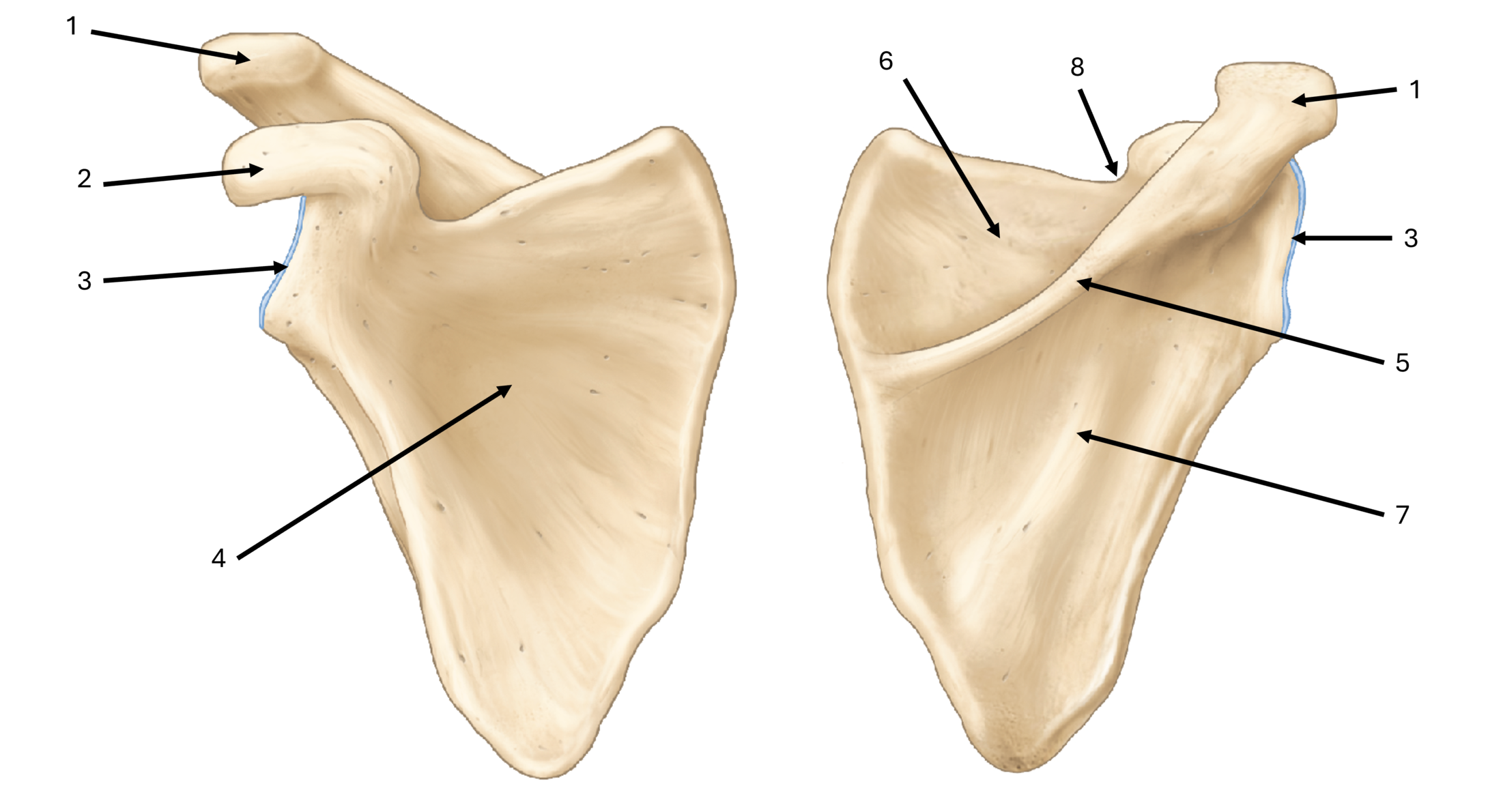
what is label #1
acromion
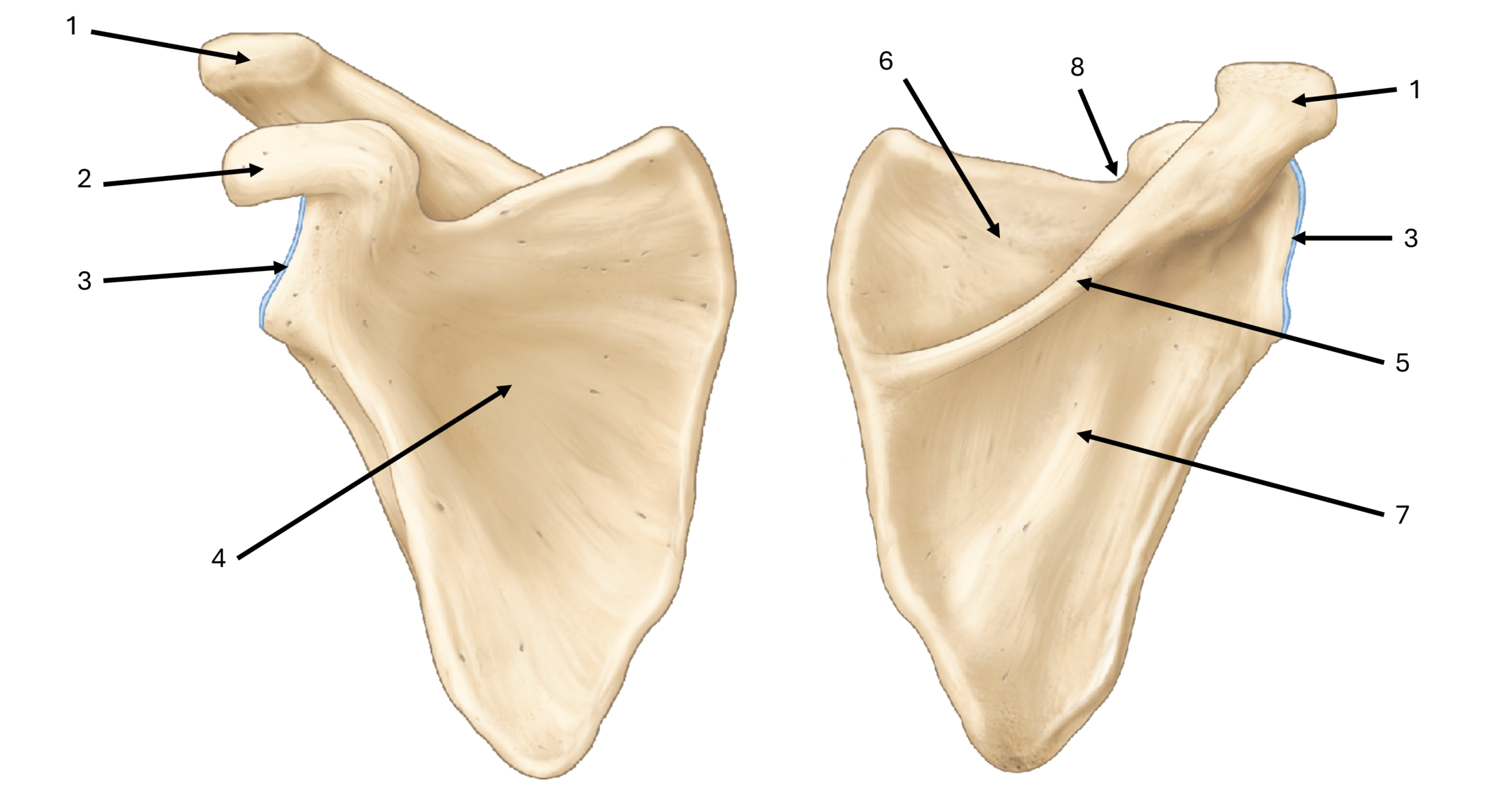
what is label #2
coracoid process
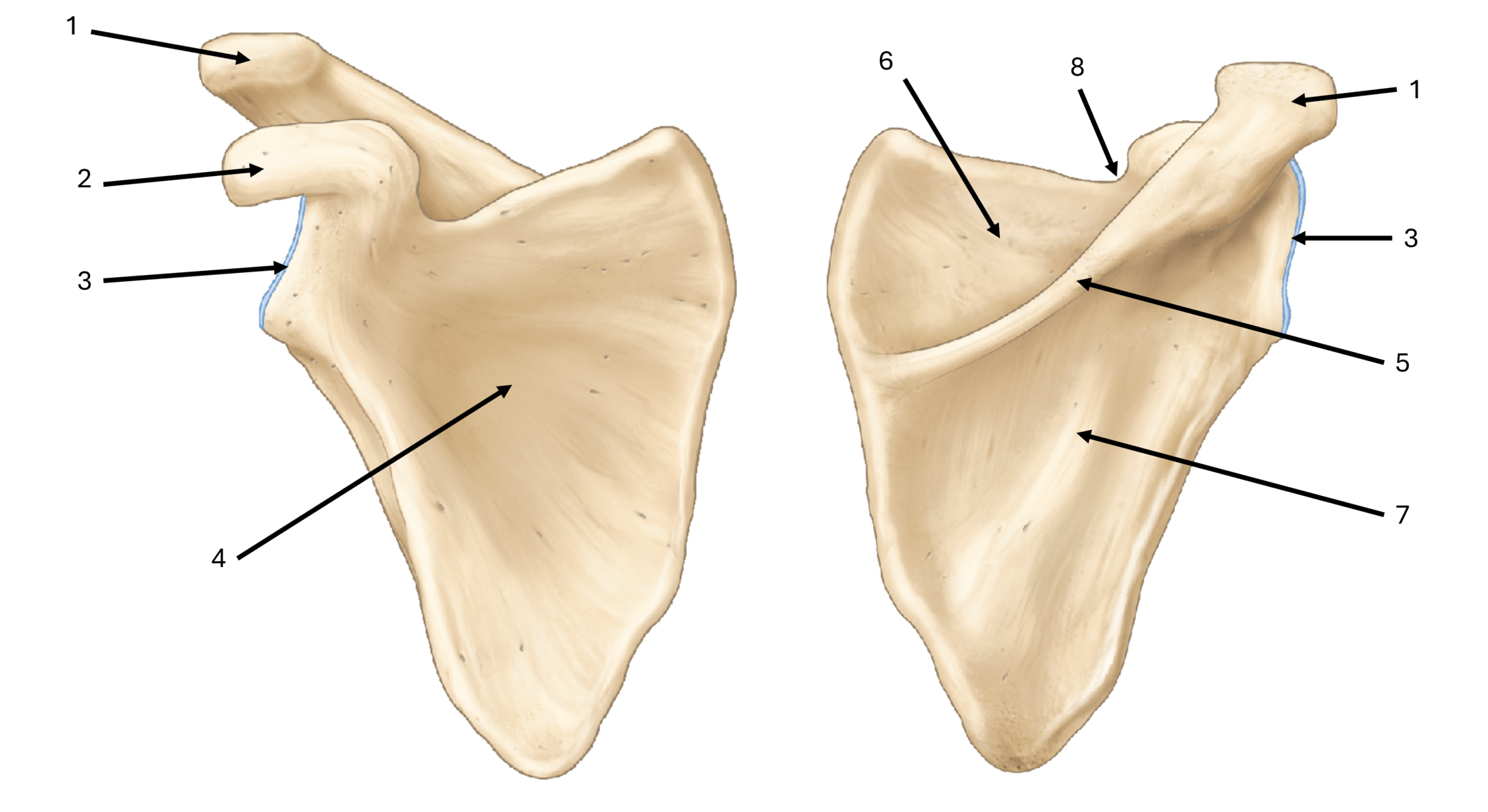
what is label #3
glenoid fossa/cavity
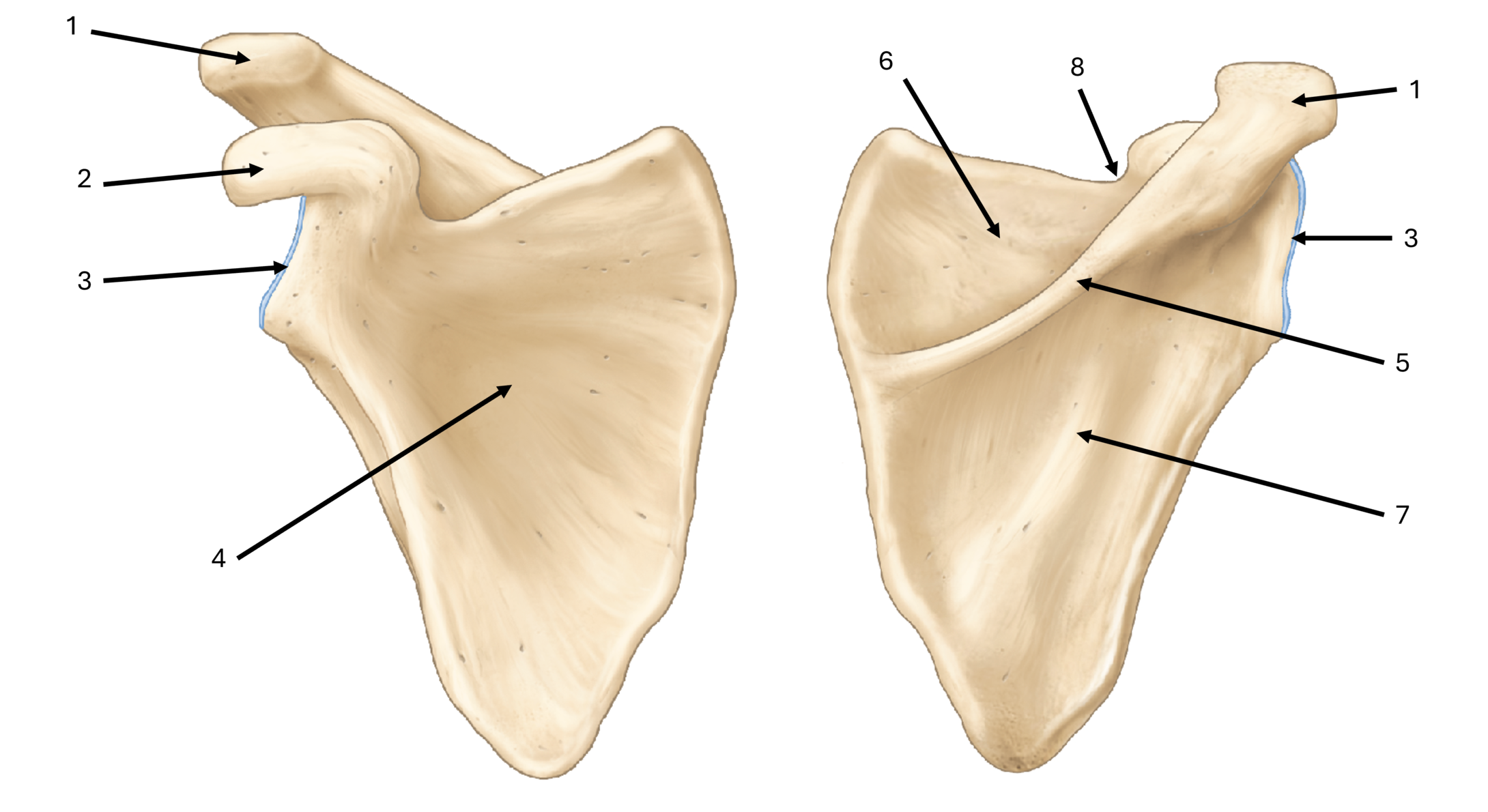
what is label #4
subscapular fossa
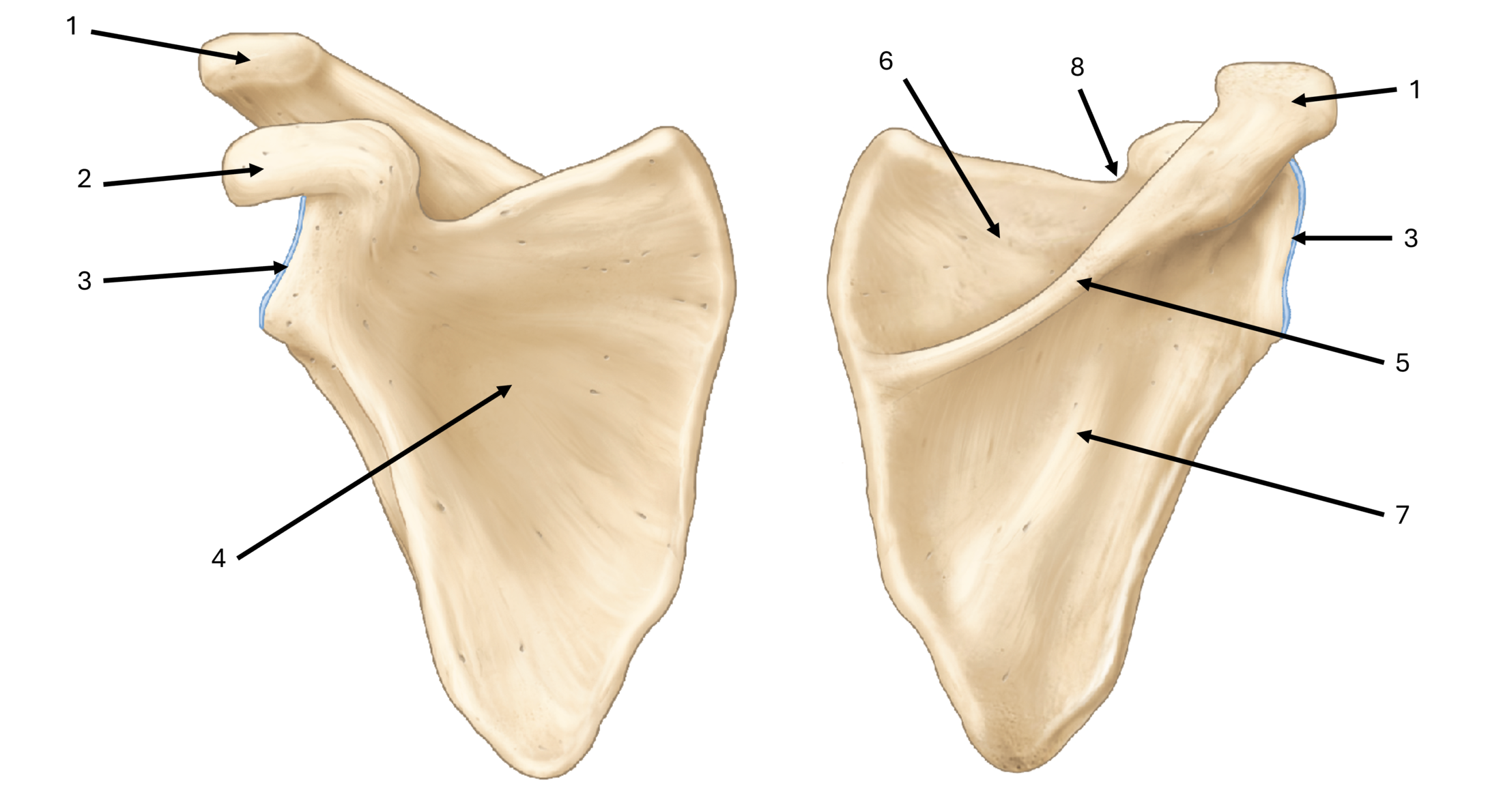
what is label #5
spine
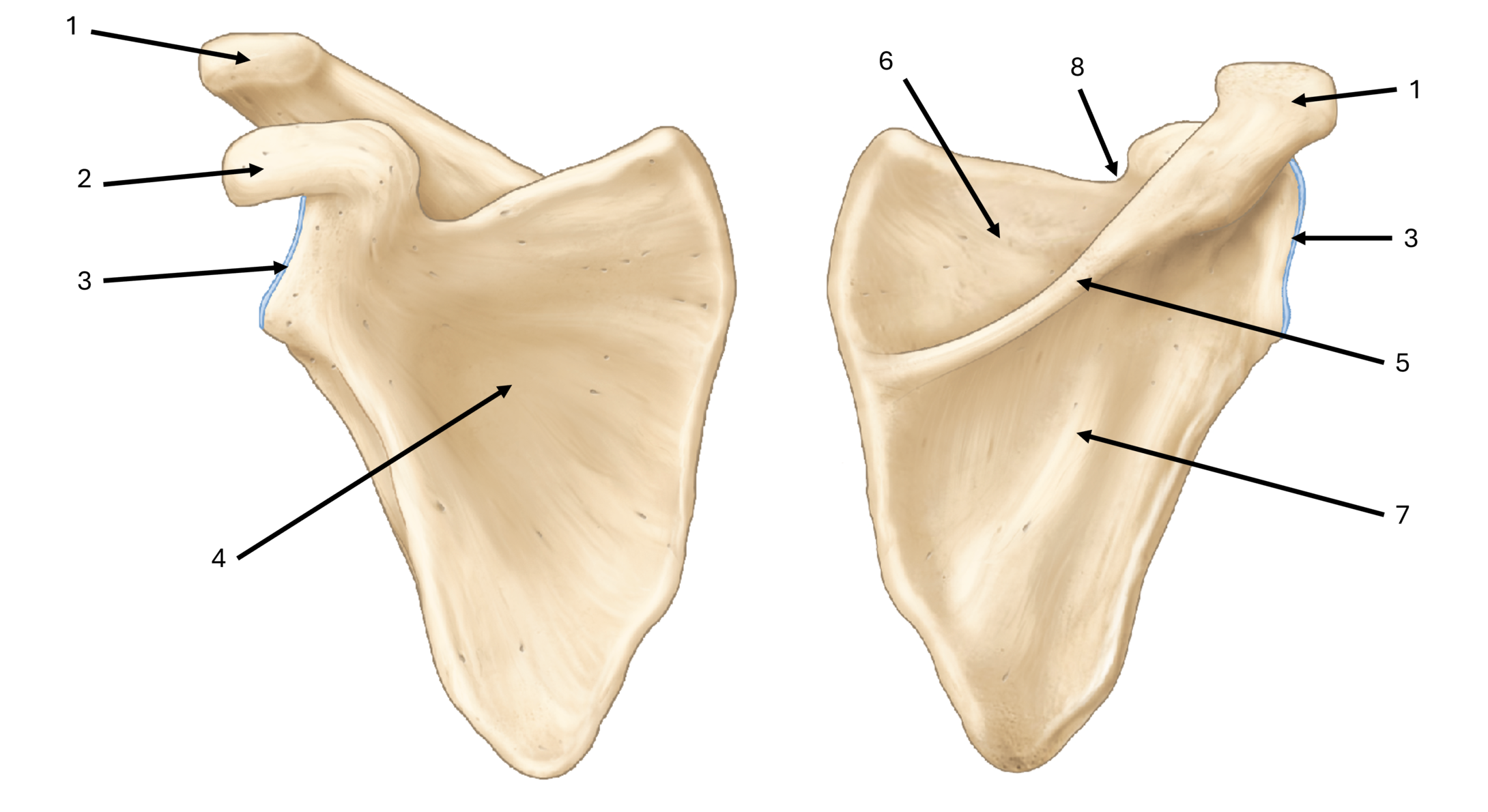
what is label #6
supraspinous fossa
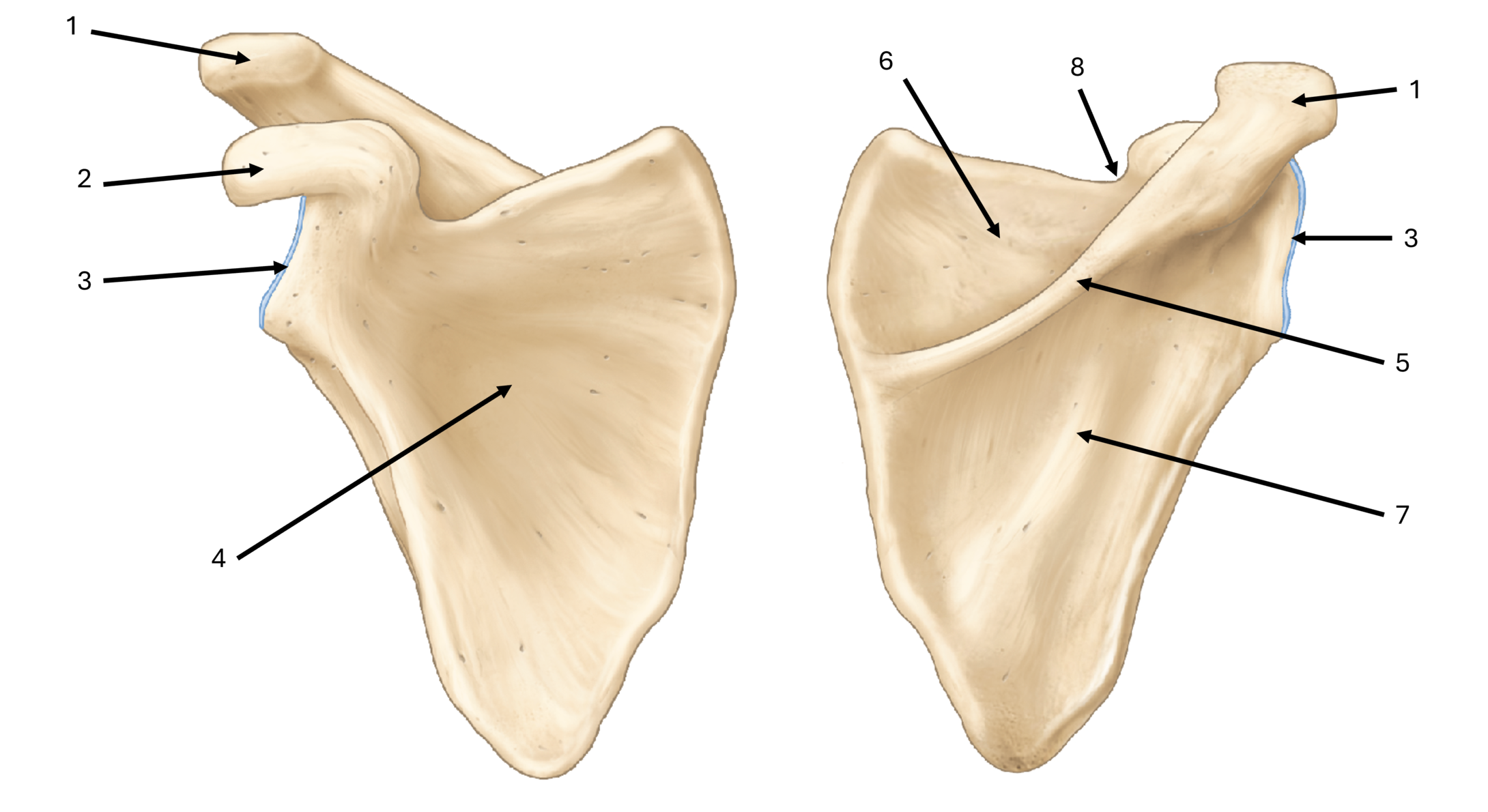
what is label #7
infraspinous fossa
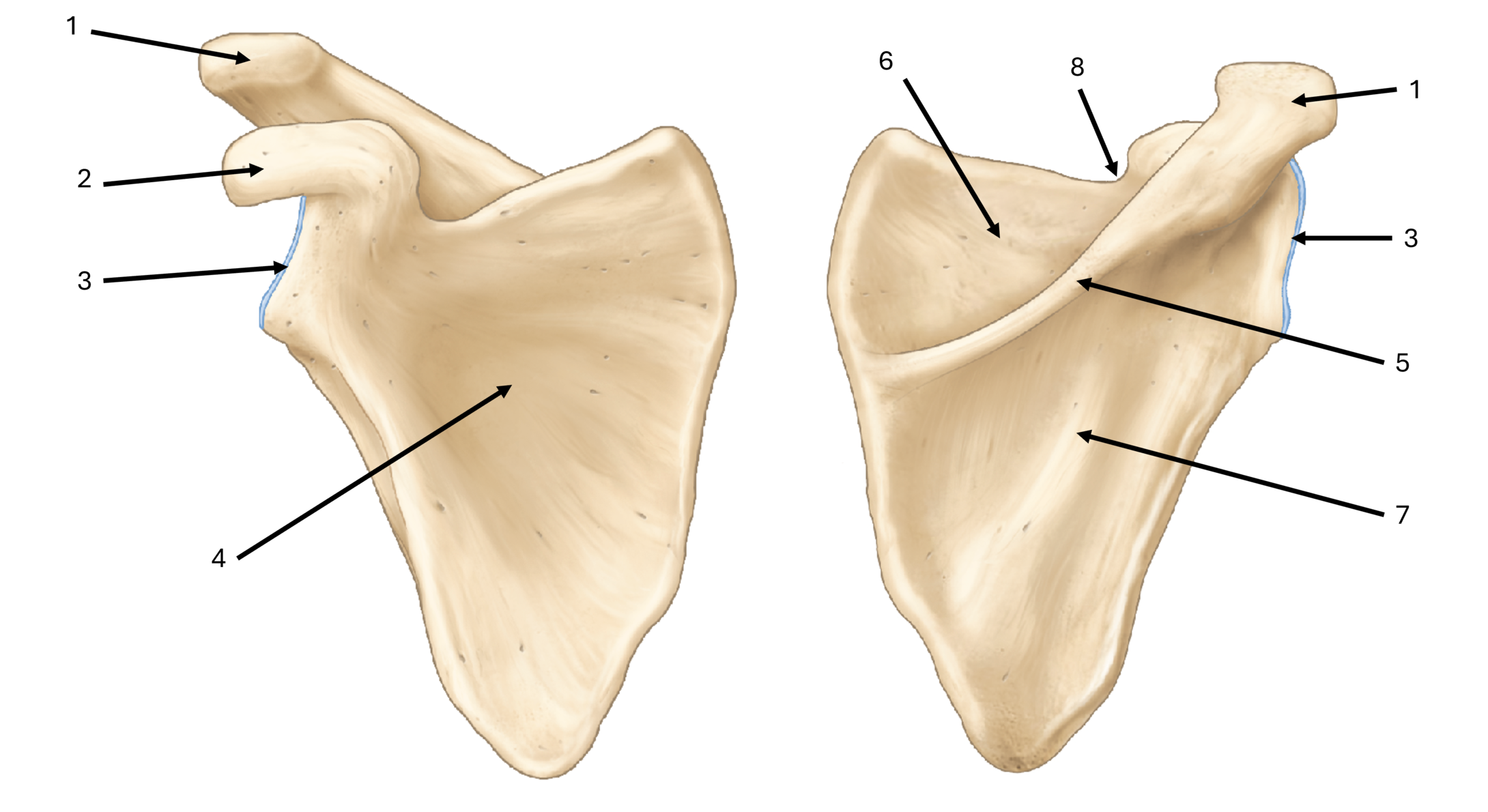
what is label #8
subscapular notch
how is the scapula held in place
by muscles
what type of bone is the humerus
a long bone
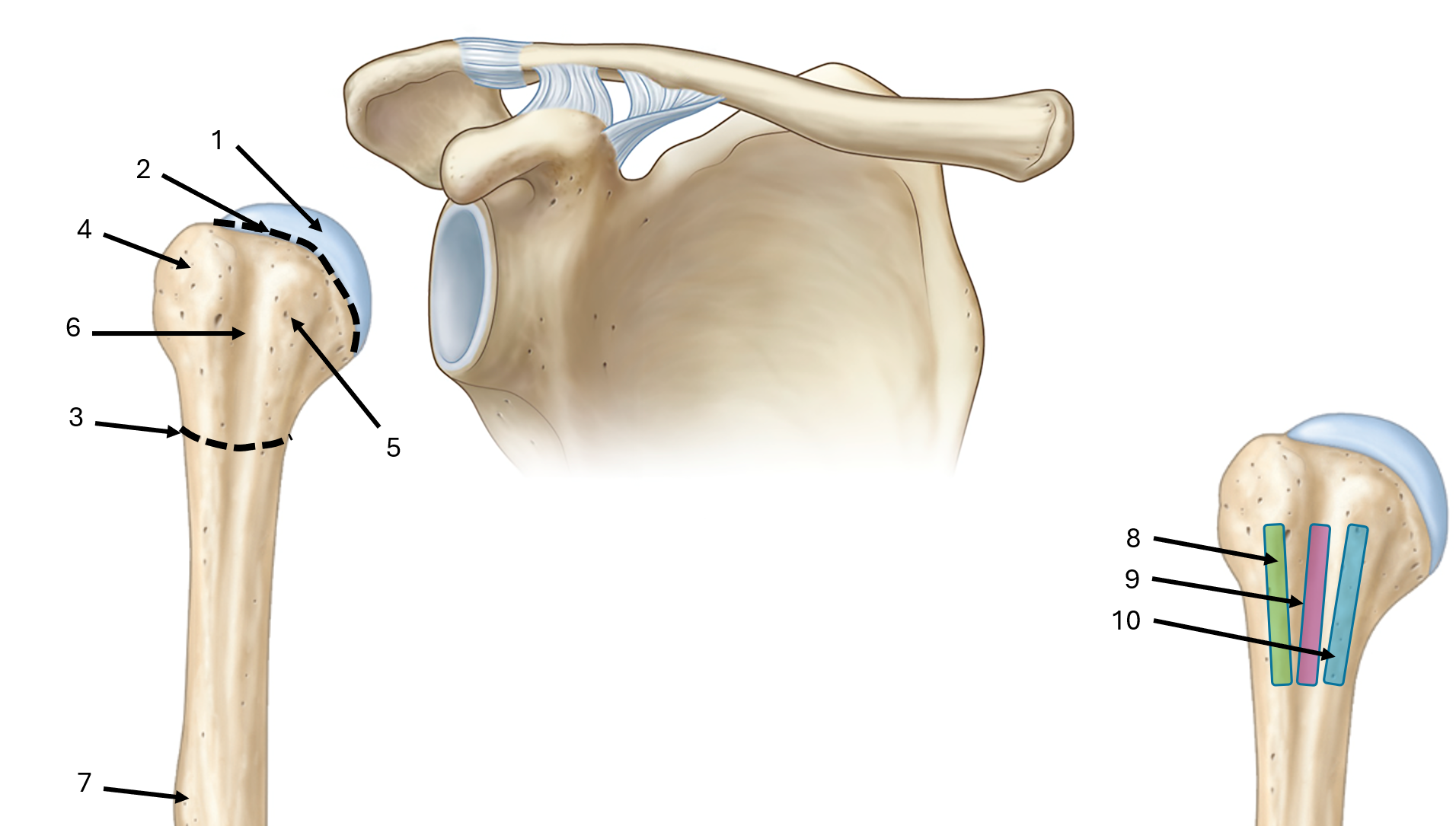
what is label #1
head
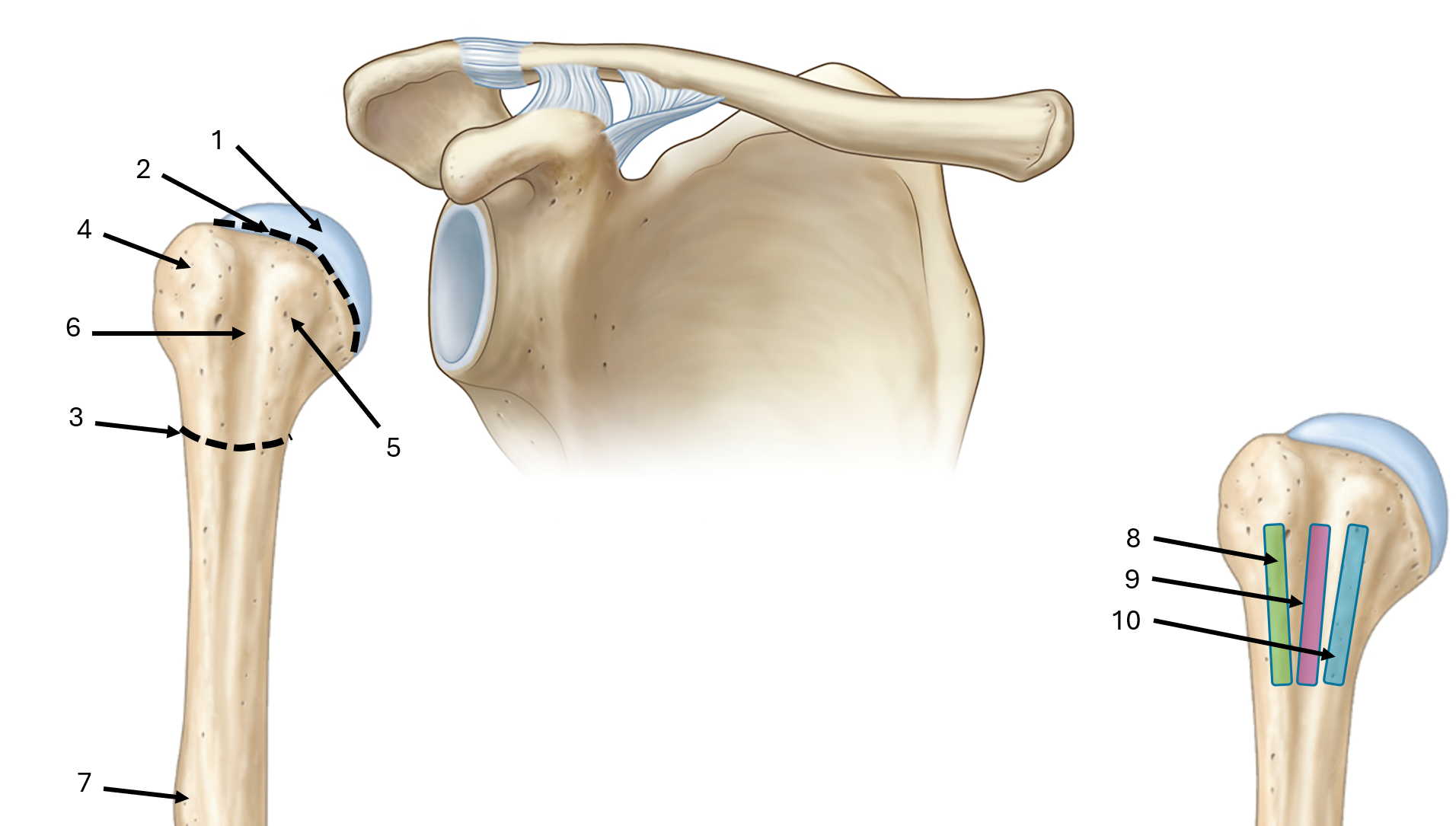
what is label #2
anatomical neck
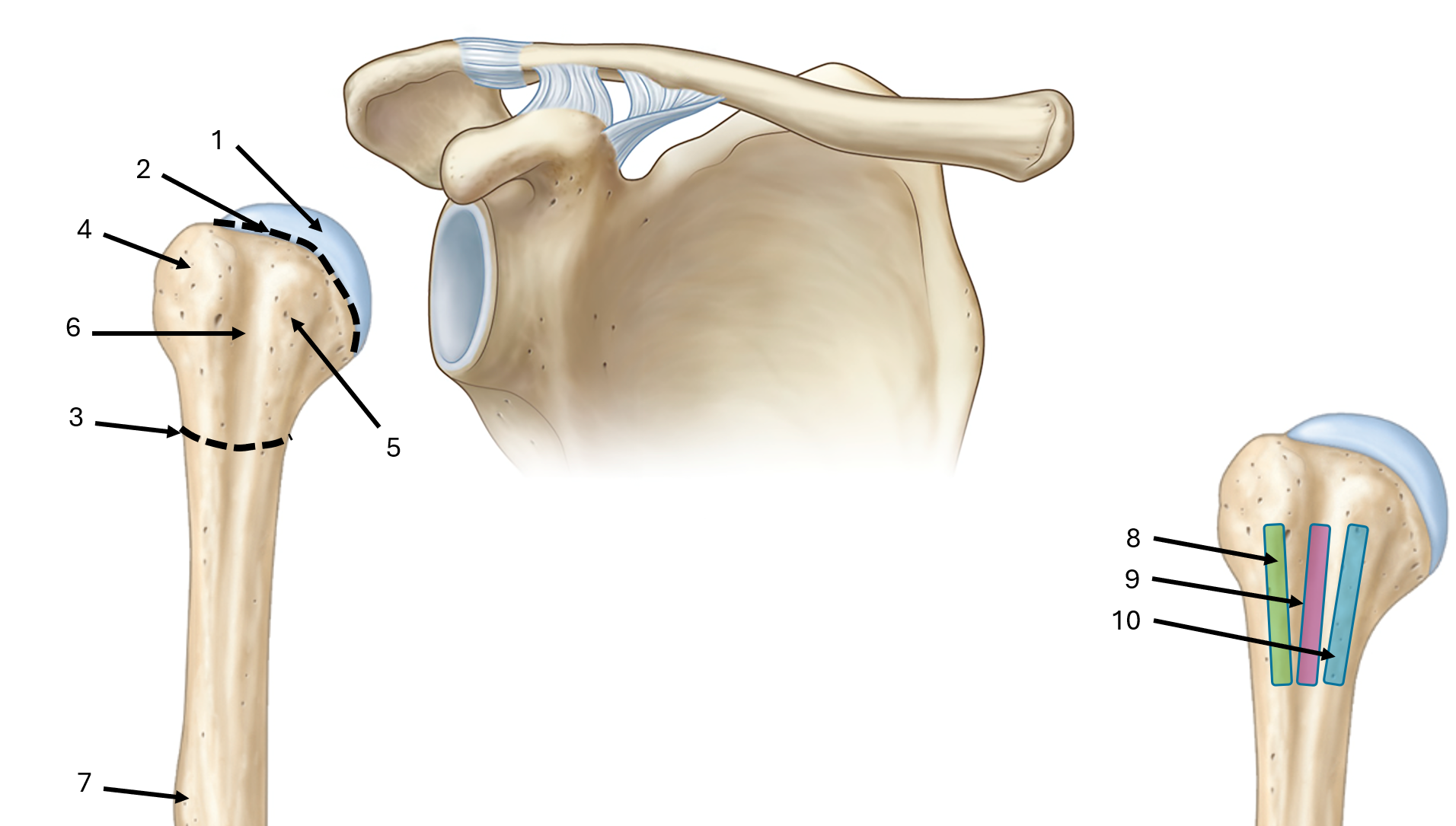
what is label #3
surgical neck
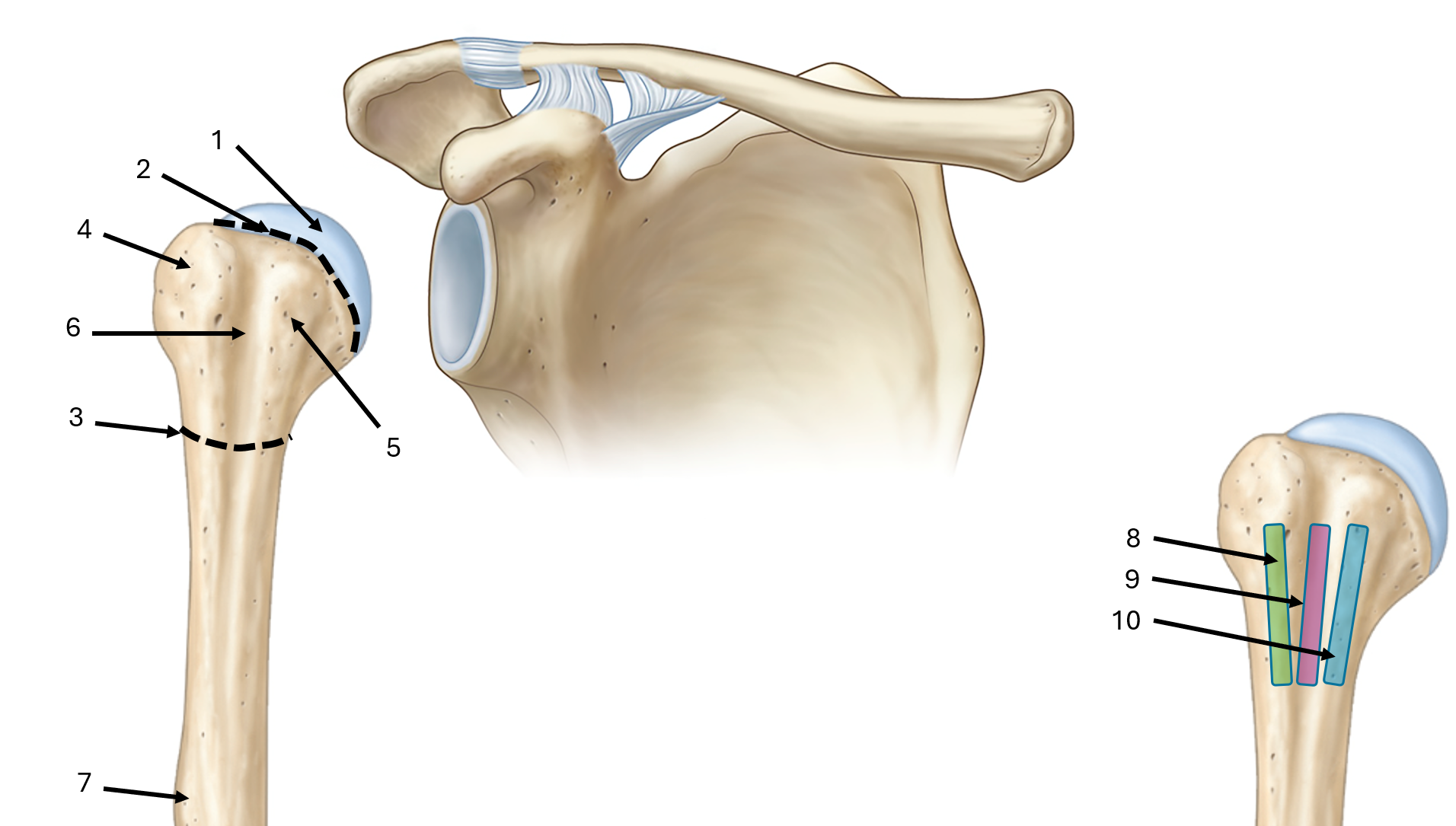
what is label #4
greater tubercle
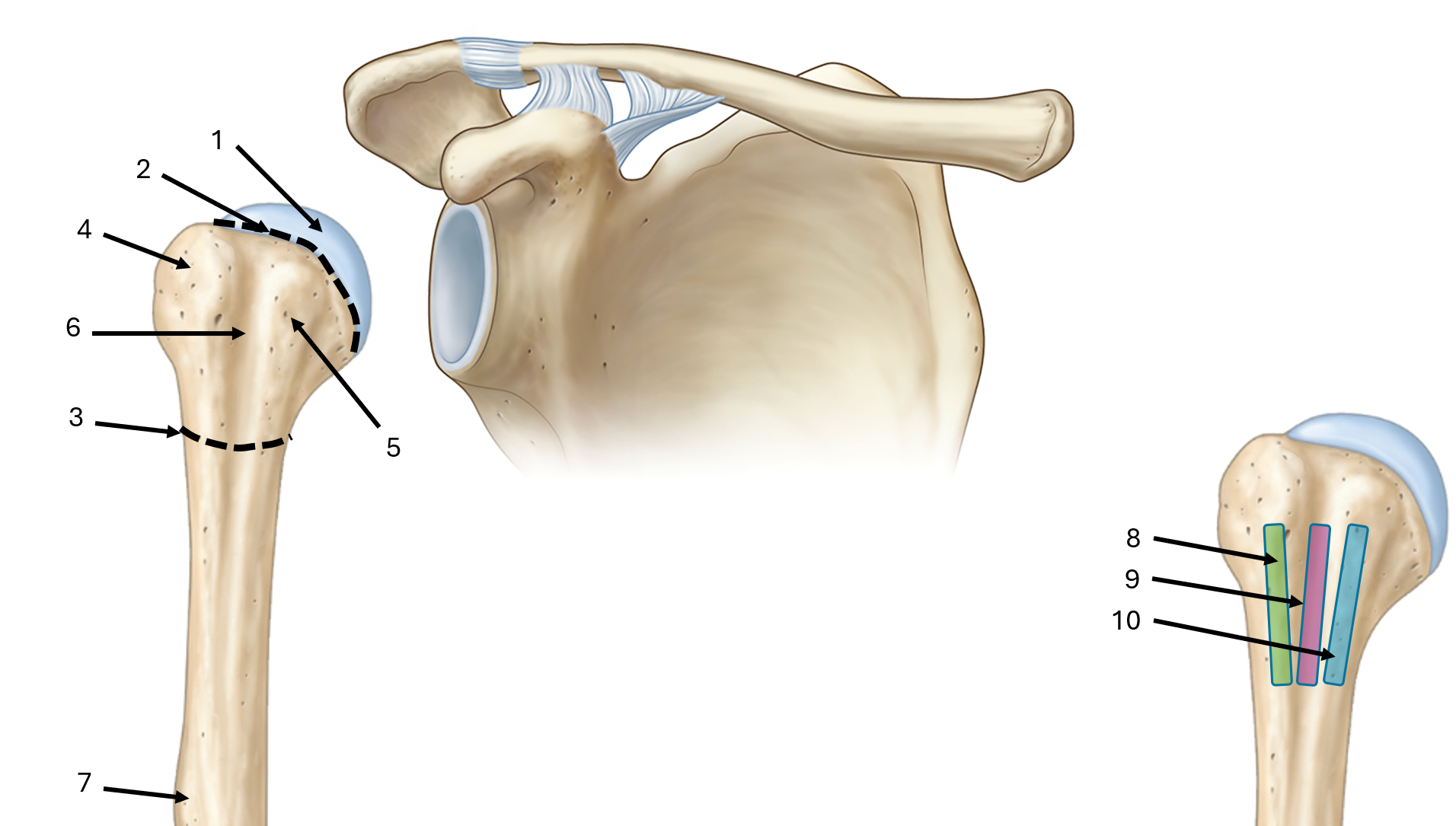
what is label #5
lesser tubercle
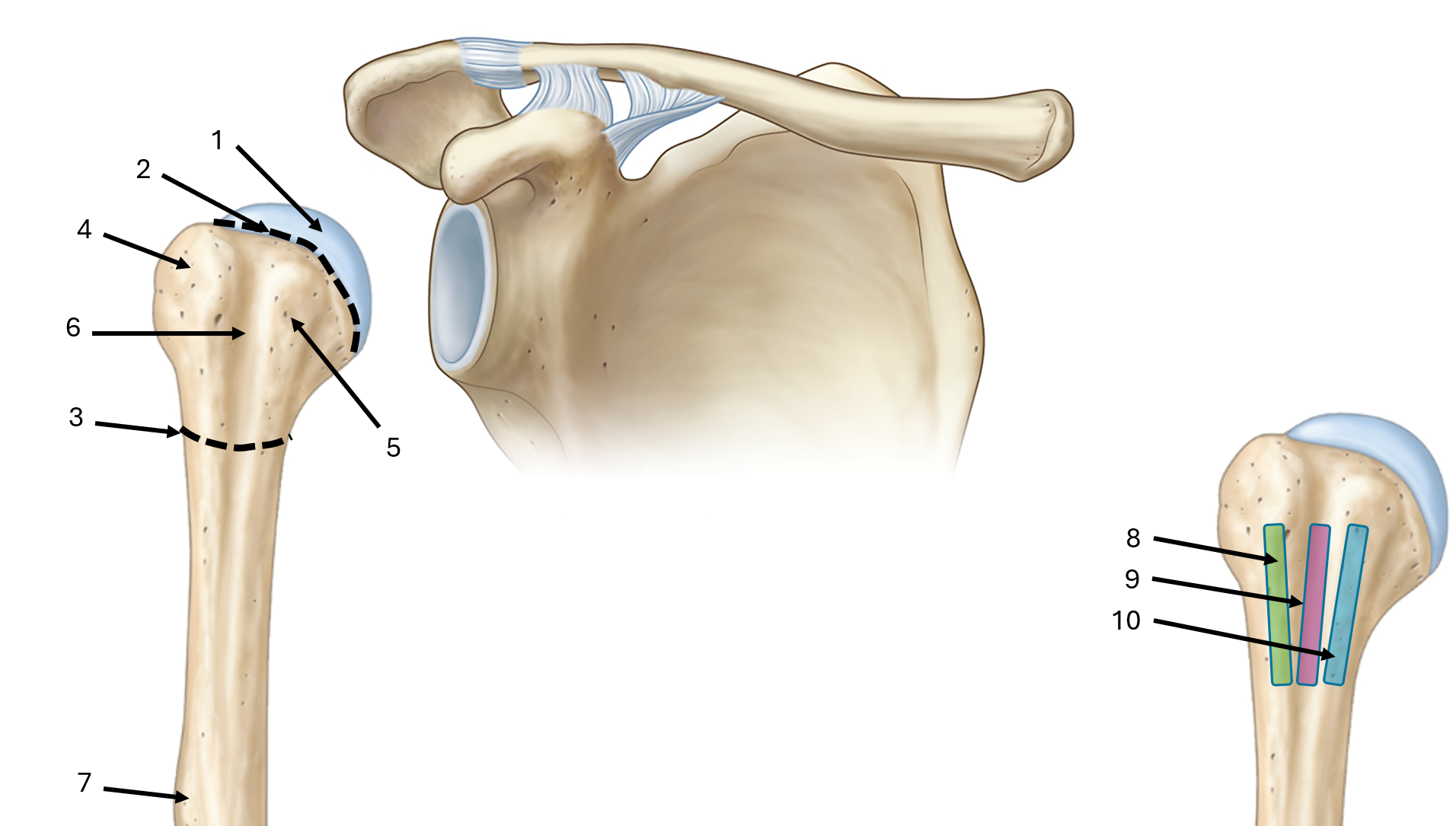
what is label #6
intertubercular sulcus or bicipital groove
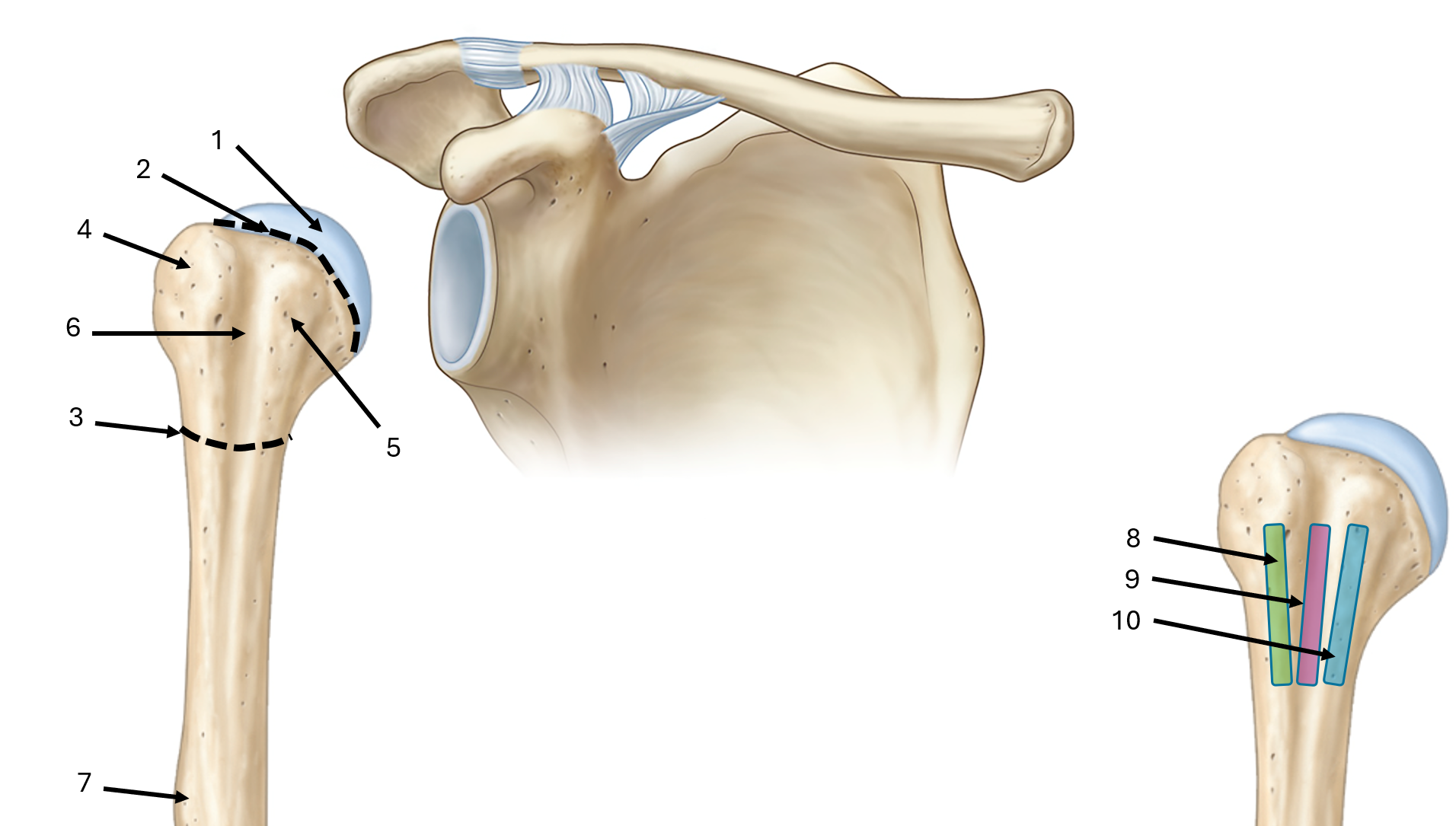
what is label #7
deltoid tuberosity
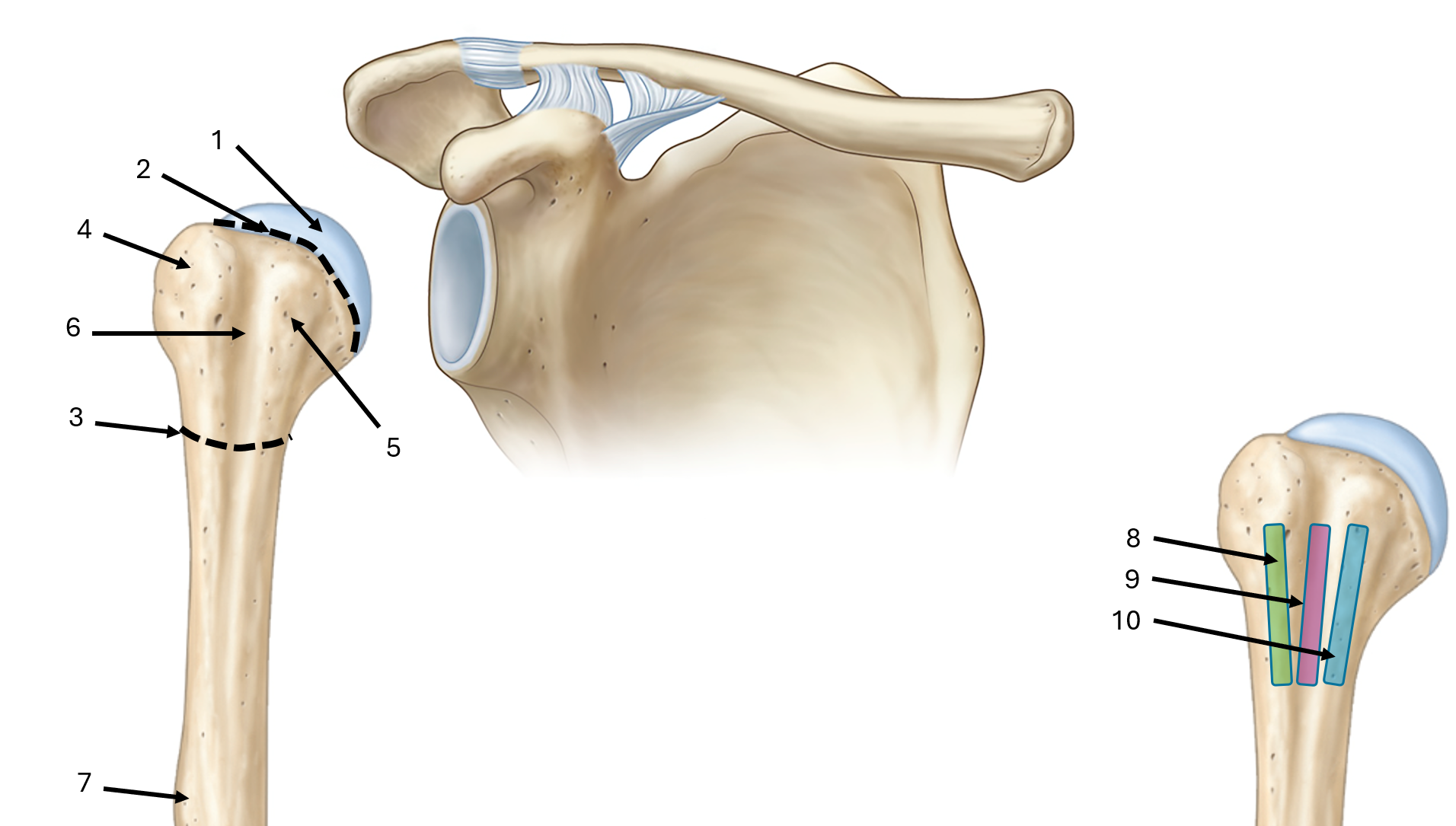
what is label #8
lateral lip of bicipital groove
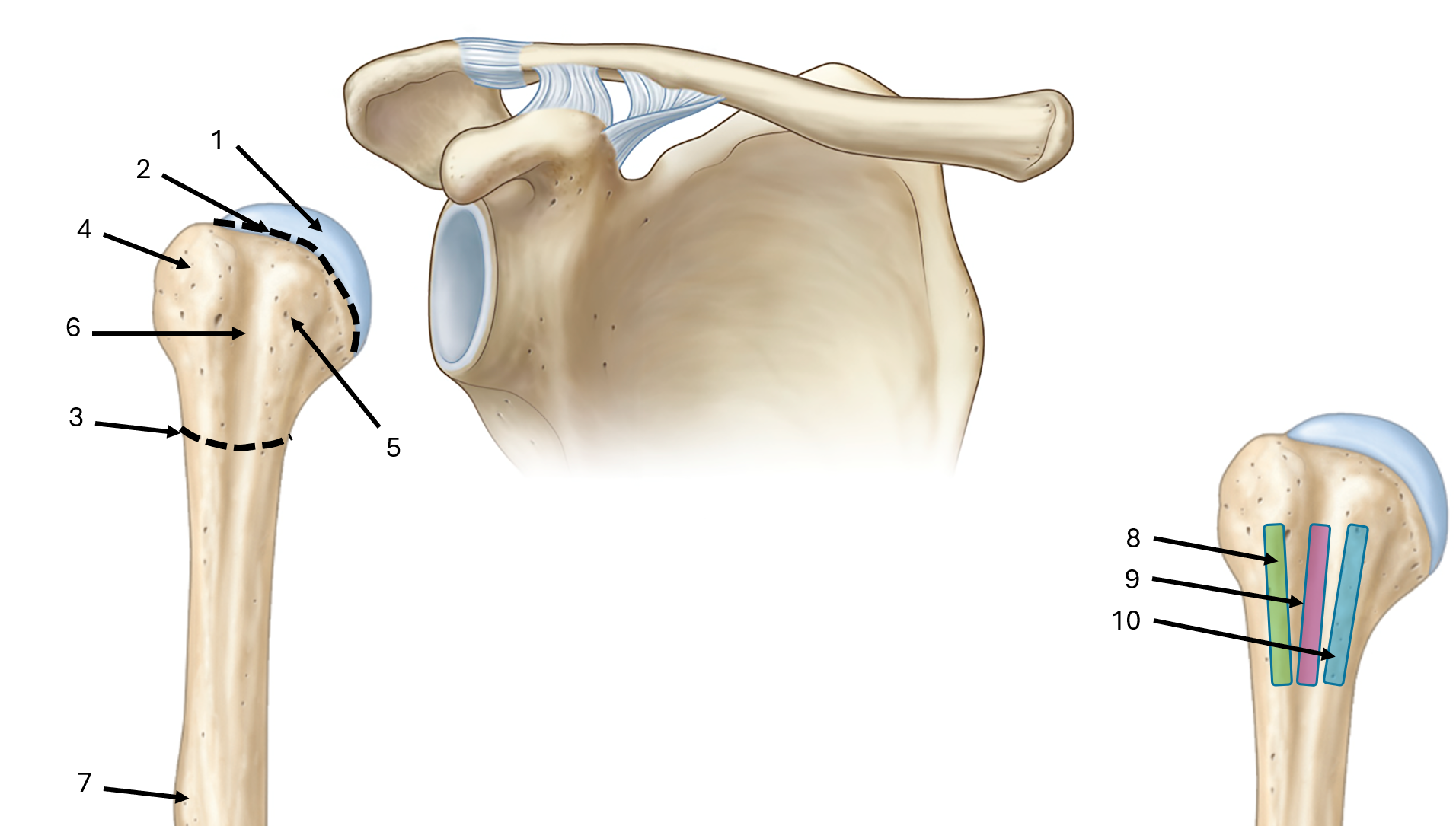
what is label #9
floor of bicipital groove
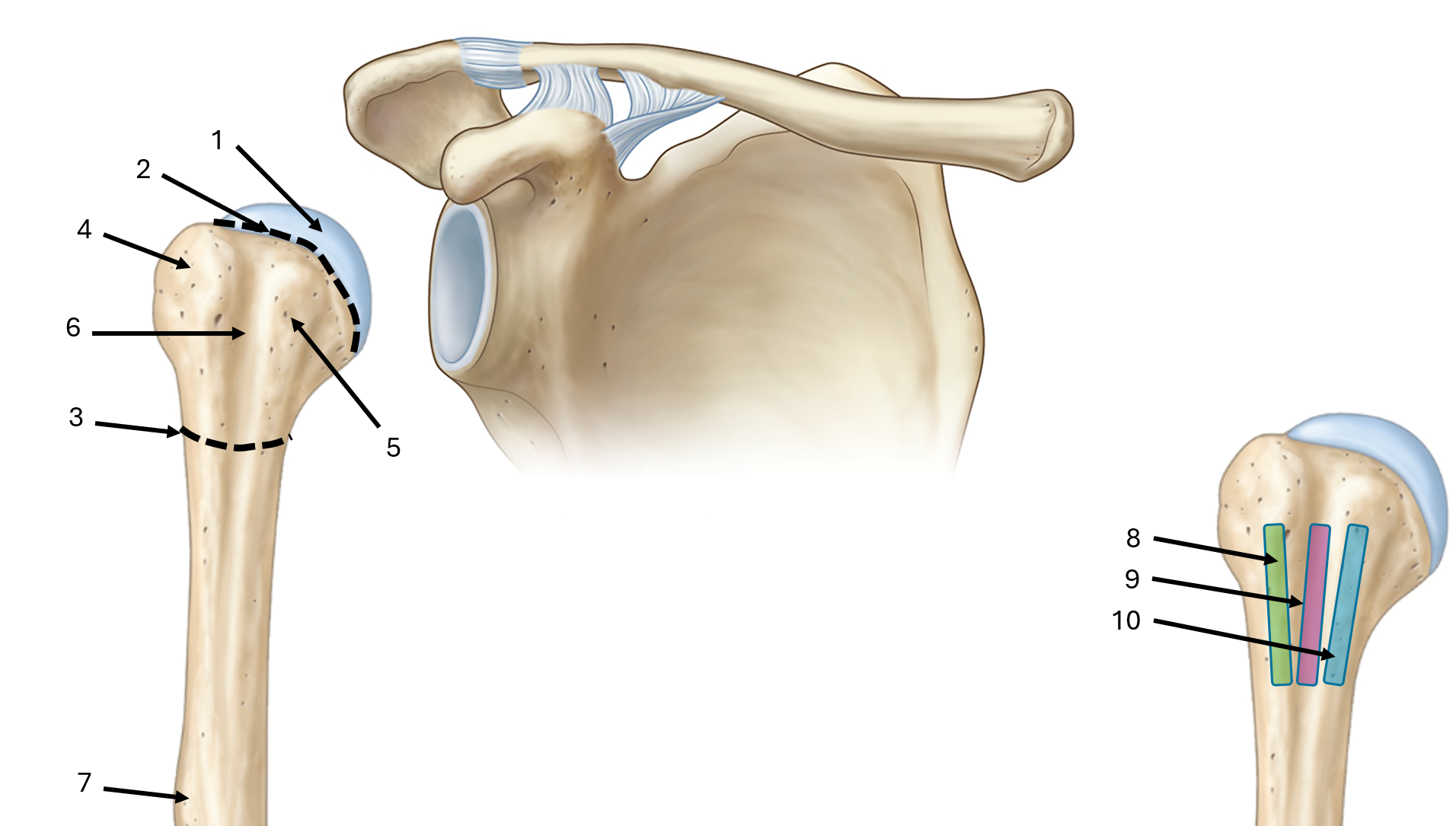
what is label #10
medial lip of bicipital groove
what is an intrinsic ligaments
thickenings of the joint capsule
what is an extrinsic ligament
a supporting ligament for a joint located some distance away from the joint capsule
what type of joint is the sternoclavicular joint
saddle joint
what are the articulations of the sternoclavicular joint
the sternal end of the clavicle articulates with the manubrium
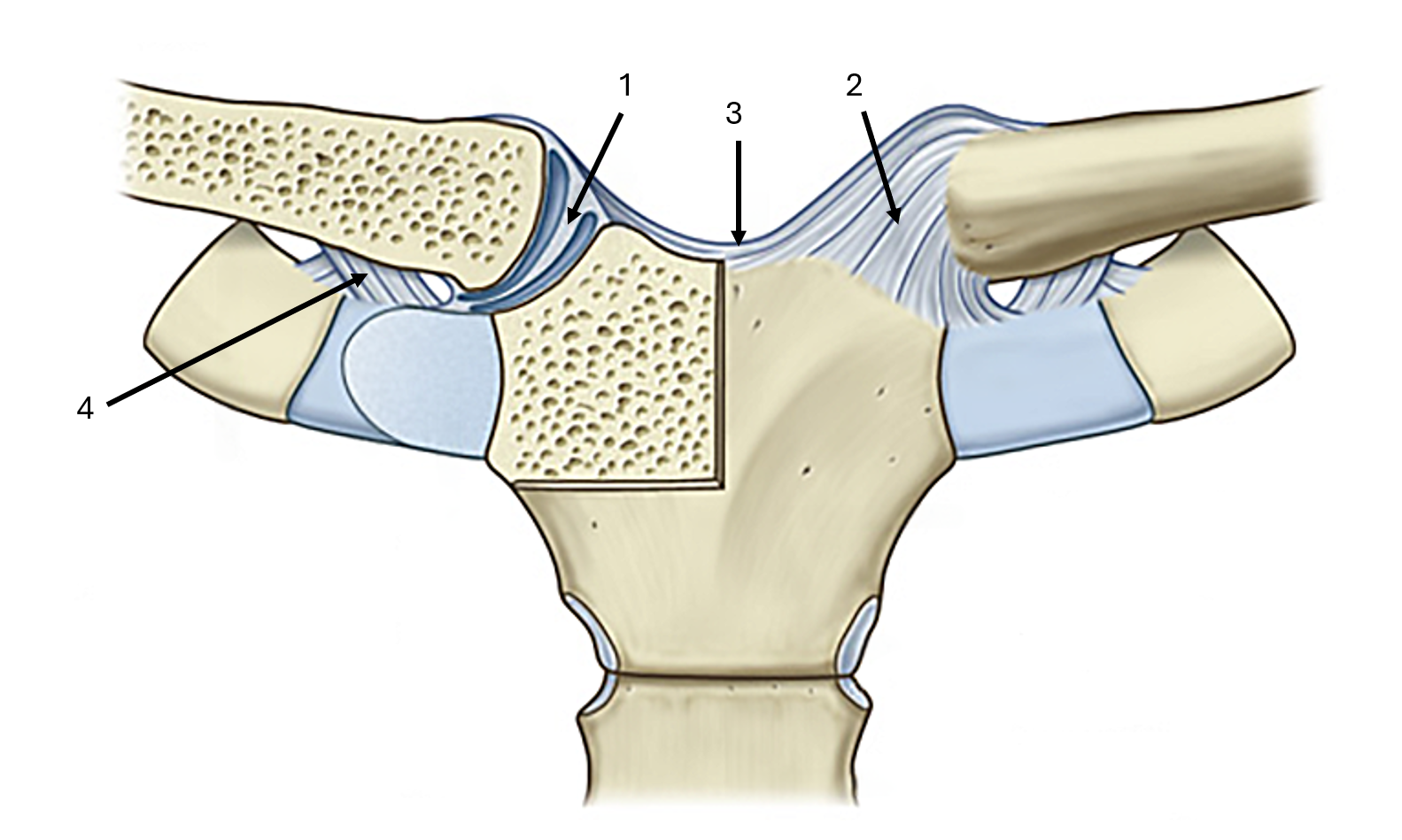
what is label #1
articular disc
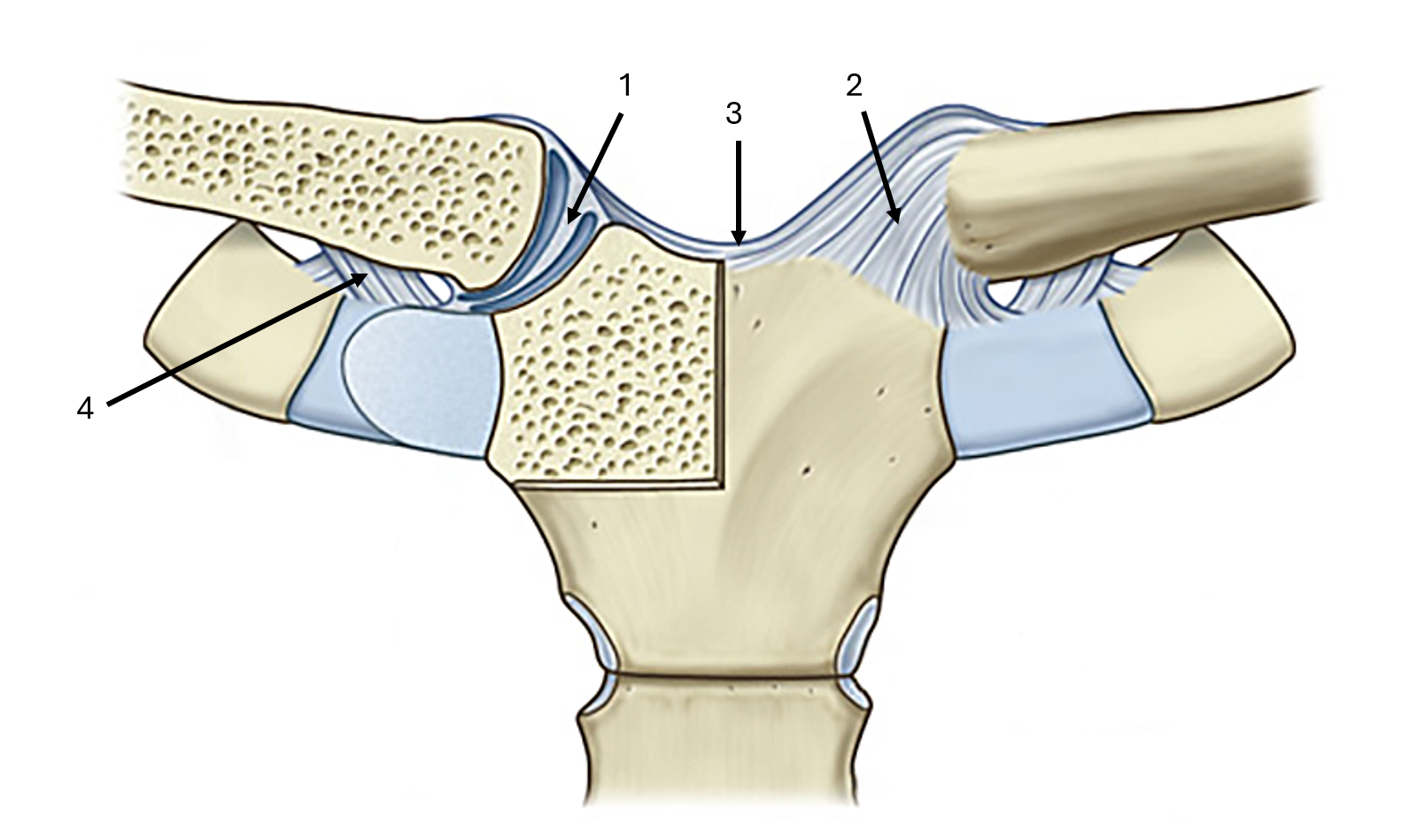
what is label #2 and its classification
anterior sternoclavicular ligament
intrinsic ligament
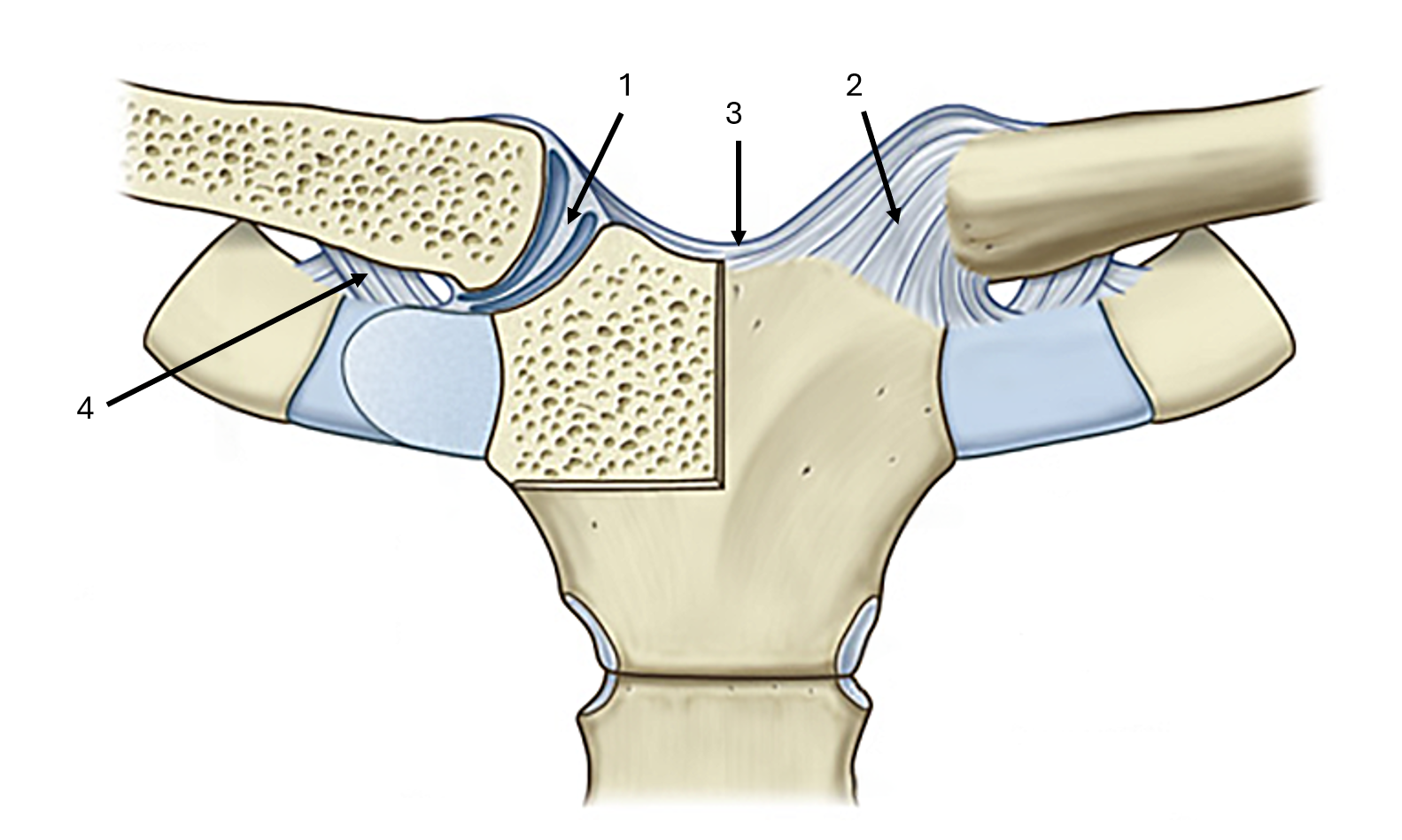
what is label #3 and its classification
interclavicular ligament
extrinsic ligament
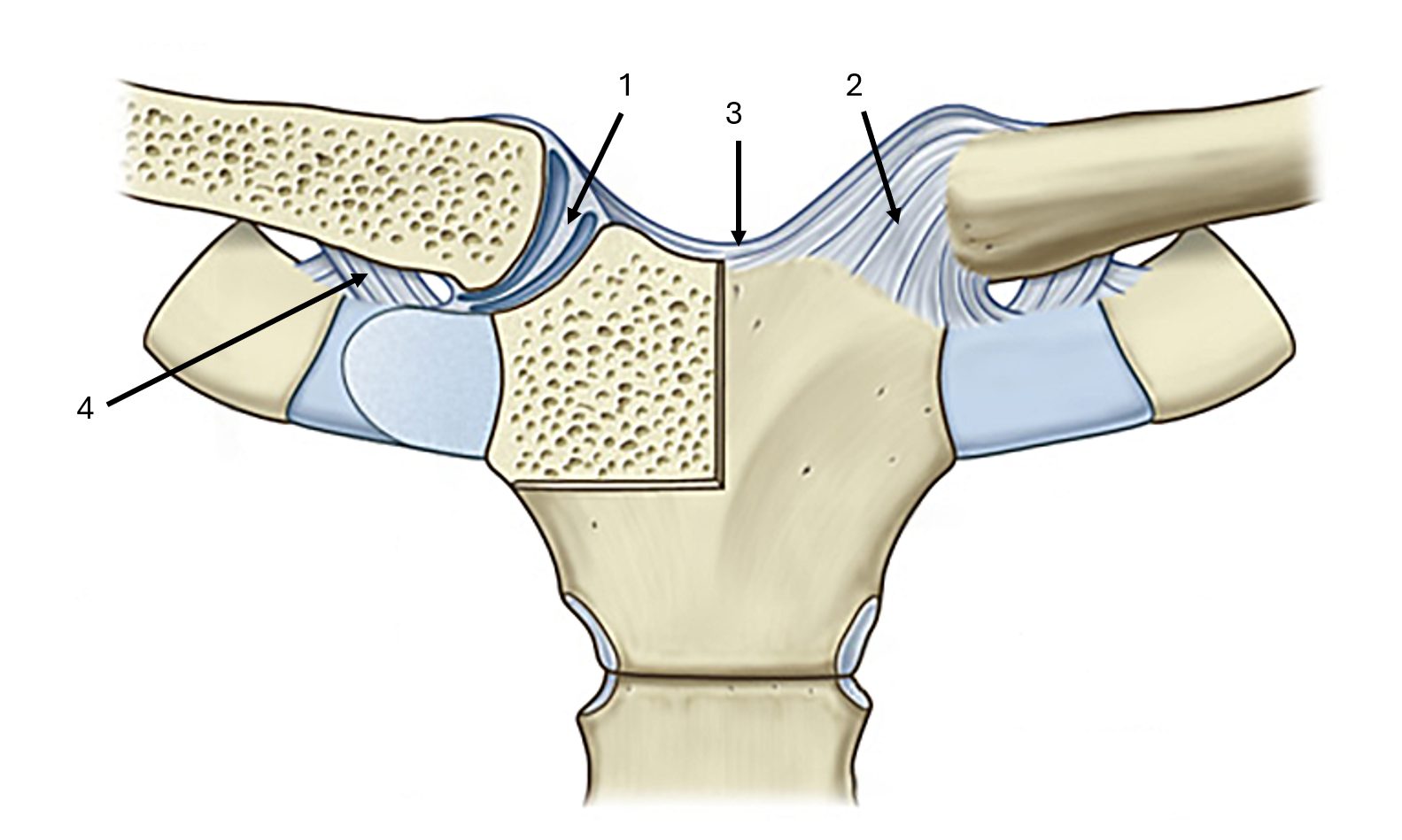
what is label #4 and its classification
costoclavicular ligament
extrinsic ligament
during abduction of the arm, what is the approximate angle the clavicle elevates
60 degrees
what movements can the sternoclavicular joint preform
elevation, depression, protraction, retraction and posterior rotation
does the sternoclavicular joint dislocate
very rarely, normally the clavicle will fracture before
what are the articulations of the acroioclavicular joint
the acromion articulates with the acromial end of the clavicle
what type of joint is the acromioclavicular joint
plane
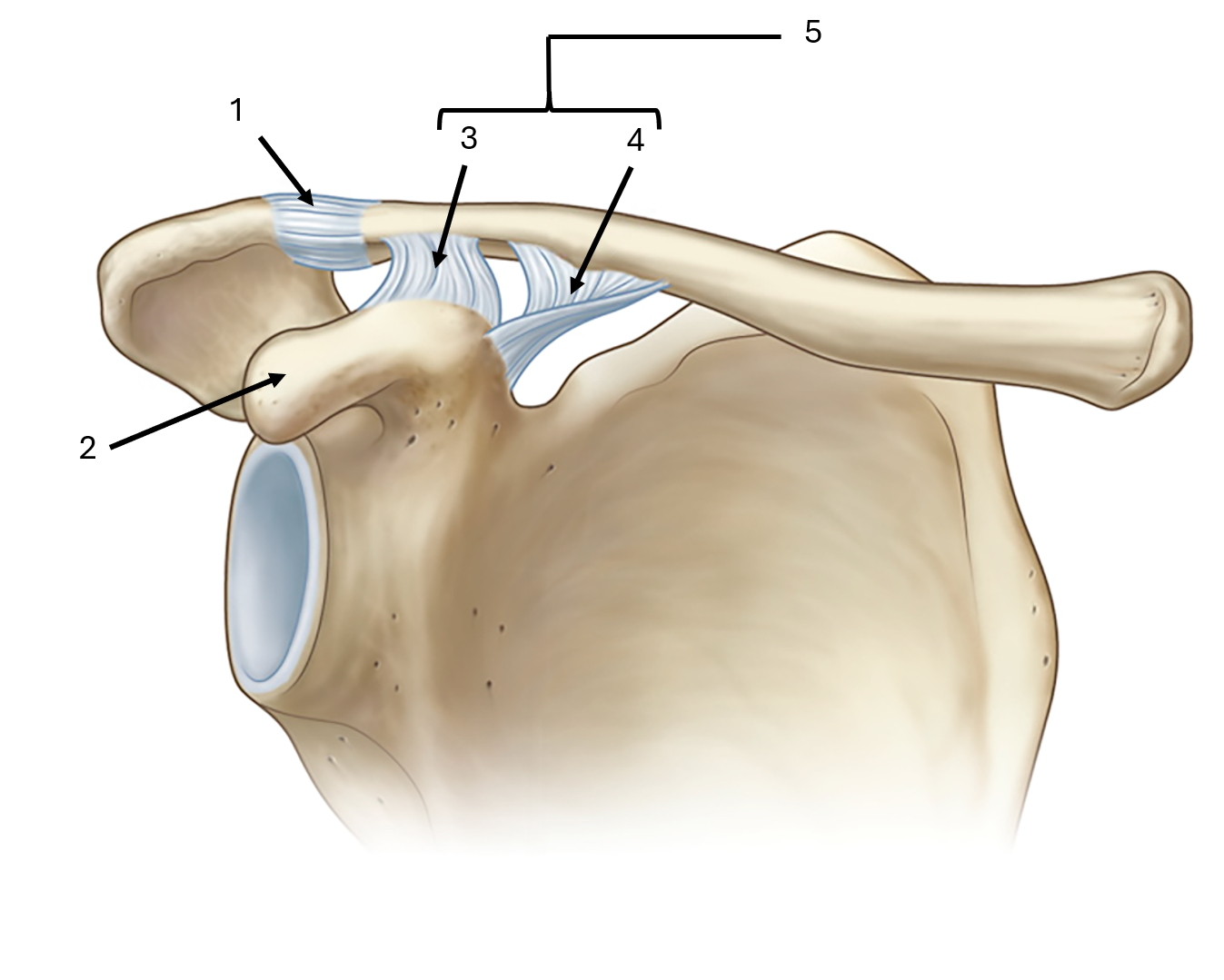
what is label #1 and its classification
acromioclavicular ligament
intrinsic ligament
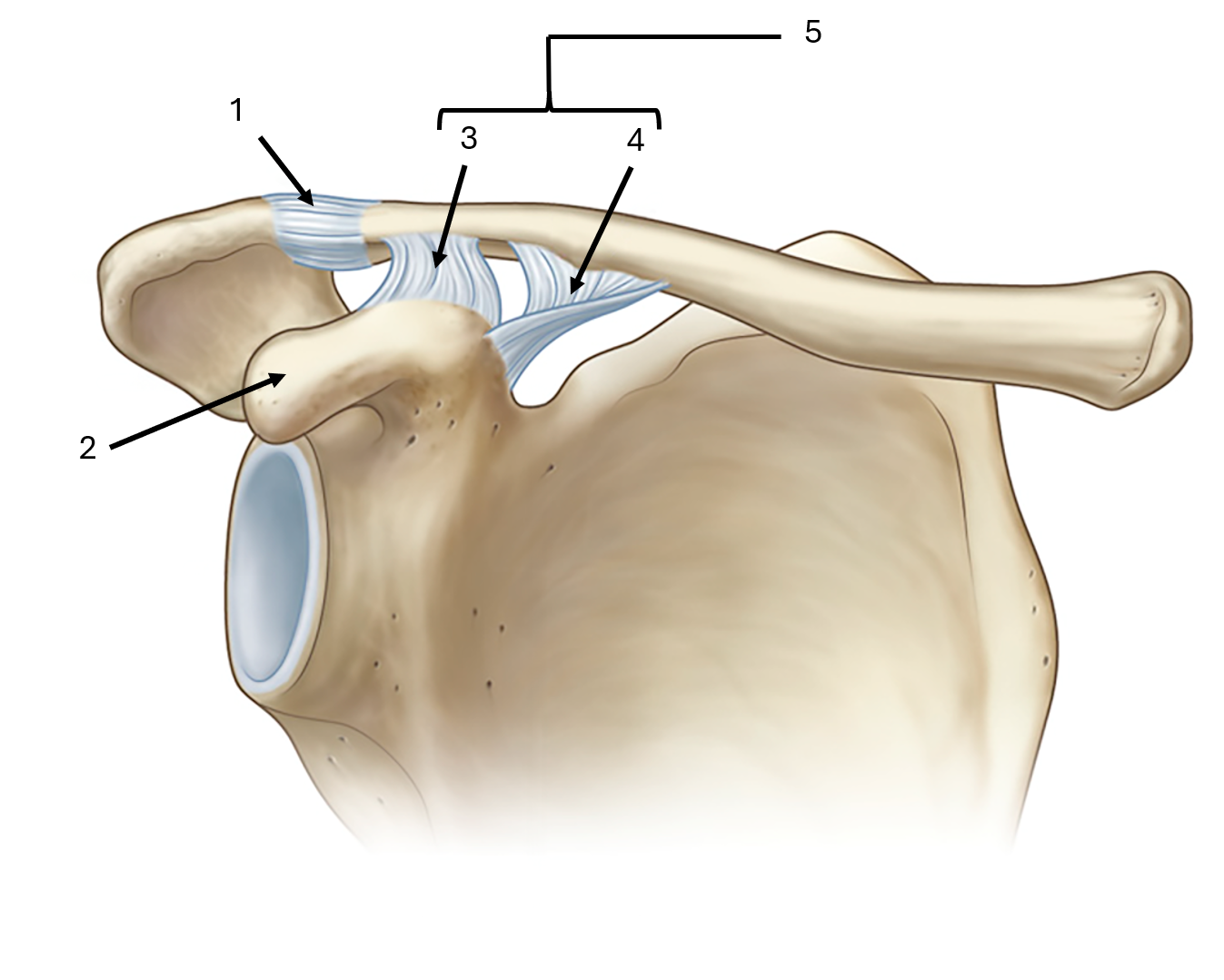
what is label #2
coracoid process
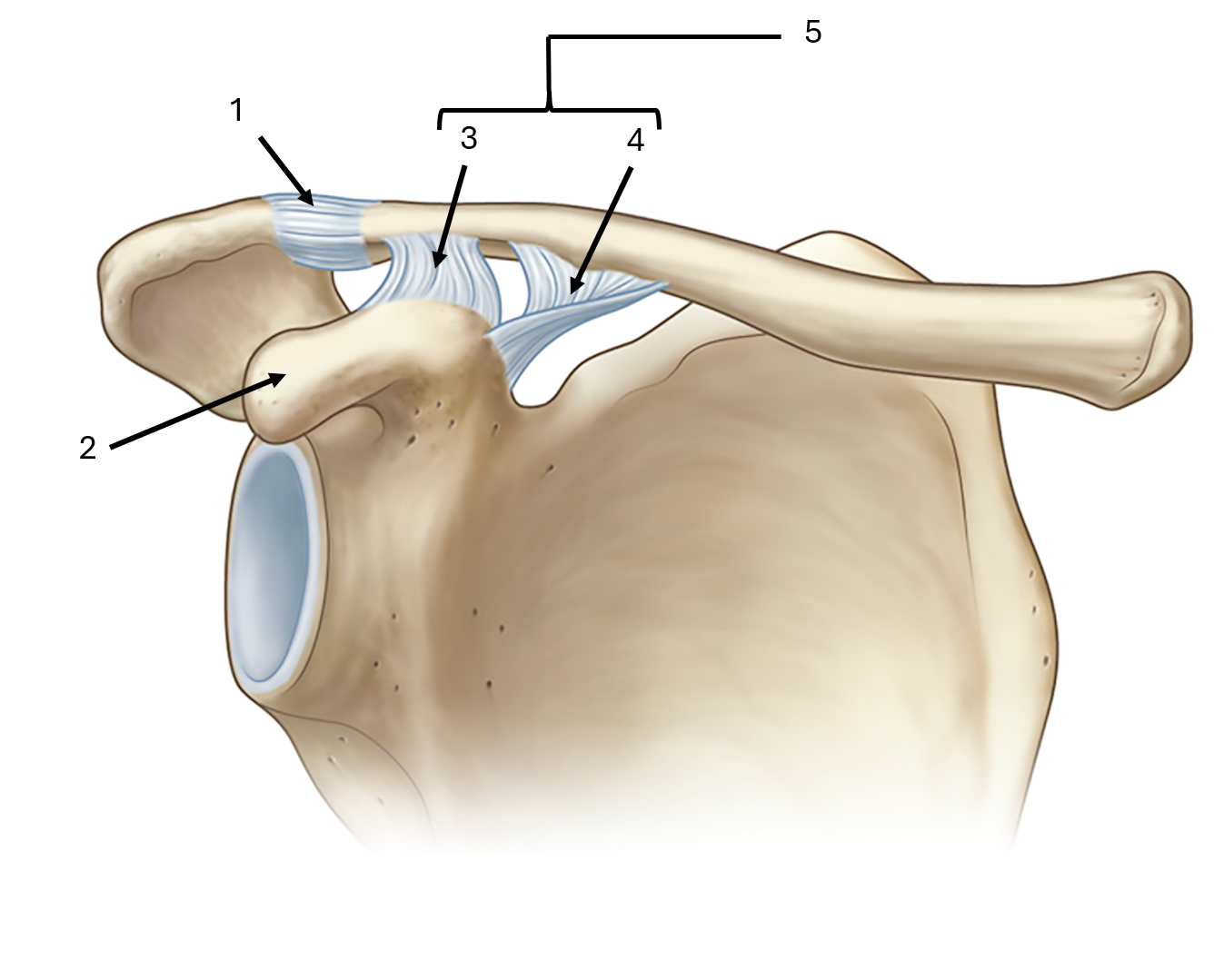
what is label #3 and its classification
trapezoid ligament
extrinsic ligament
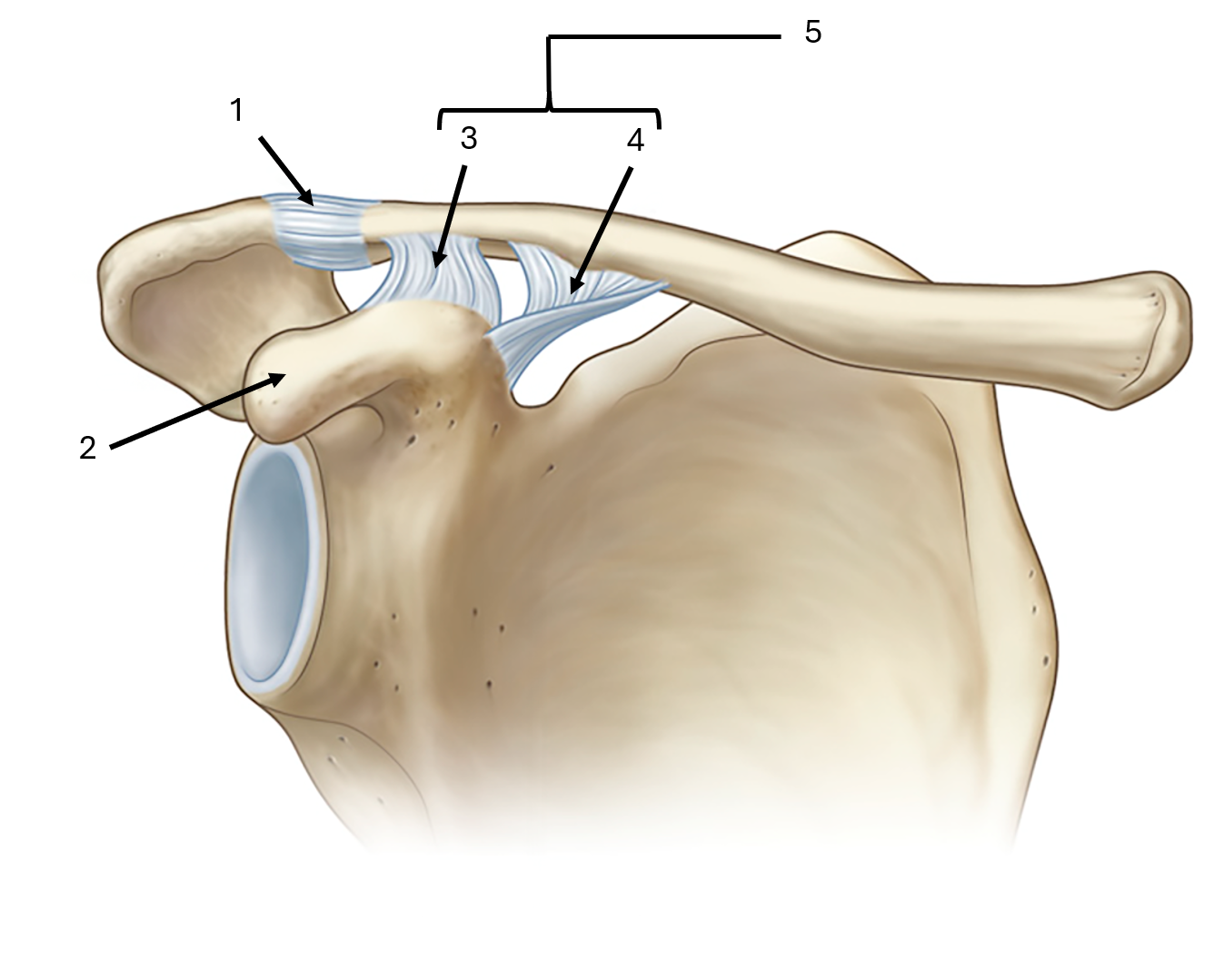
what is label #4 and its classification
conoid ligament
extrinsic ligament
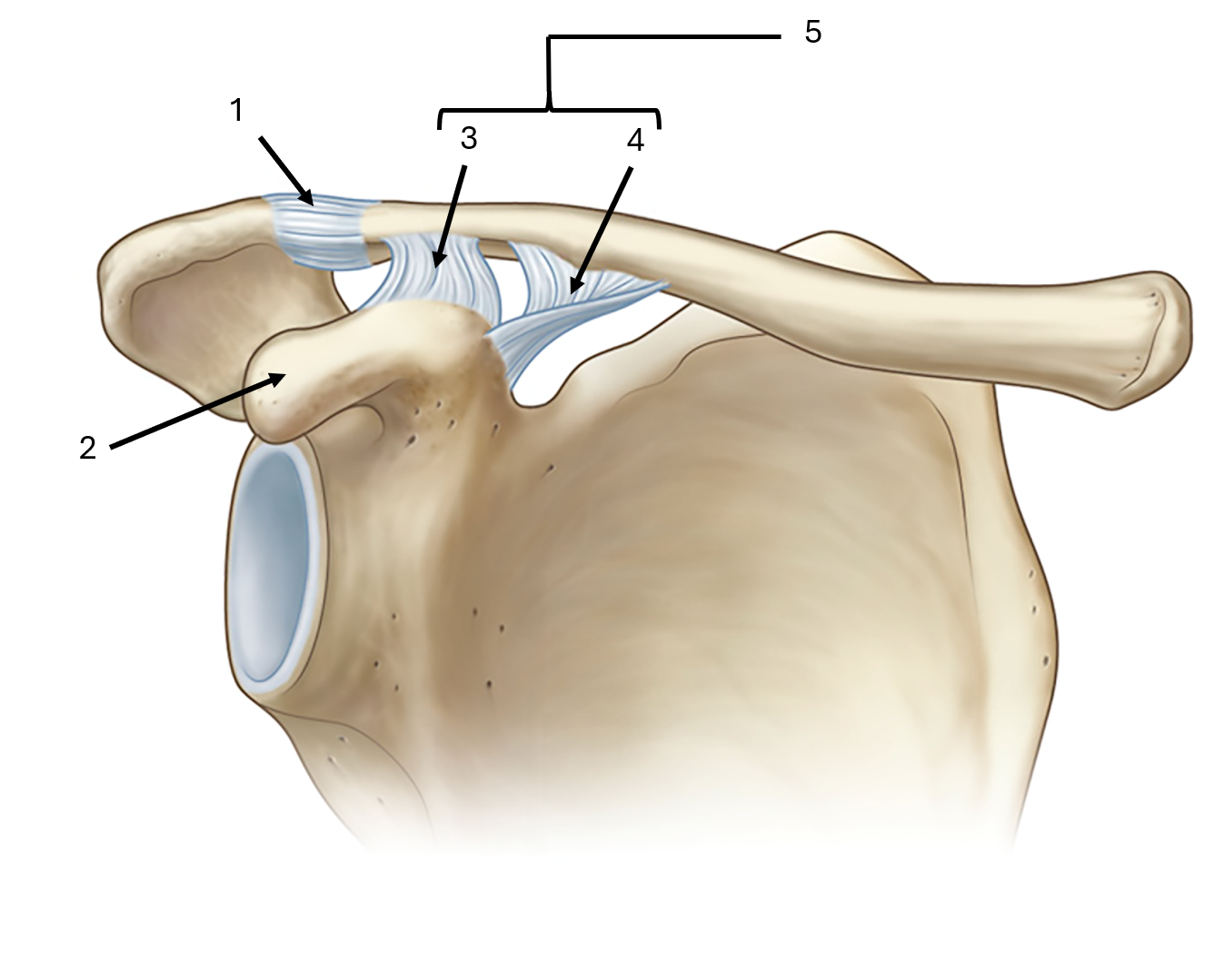
what is label #5 and its classification
coracoclavicular ligament
extrinsic ligament
in layman’s terms what does the dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint refer to
dislocated shoulder
what is the articulations of the glenohumeral joint
the head of humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity/fossa
what type of joint is the glenohumeral joint
ball and socket
what actions can the glenohumeral joint preform
full abduction of the arm
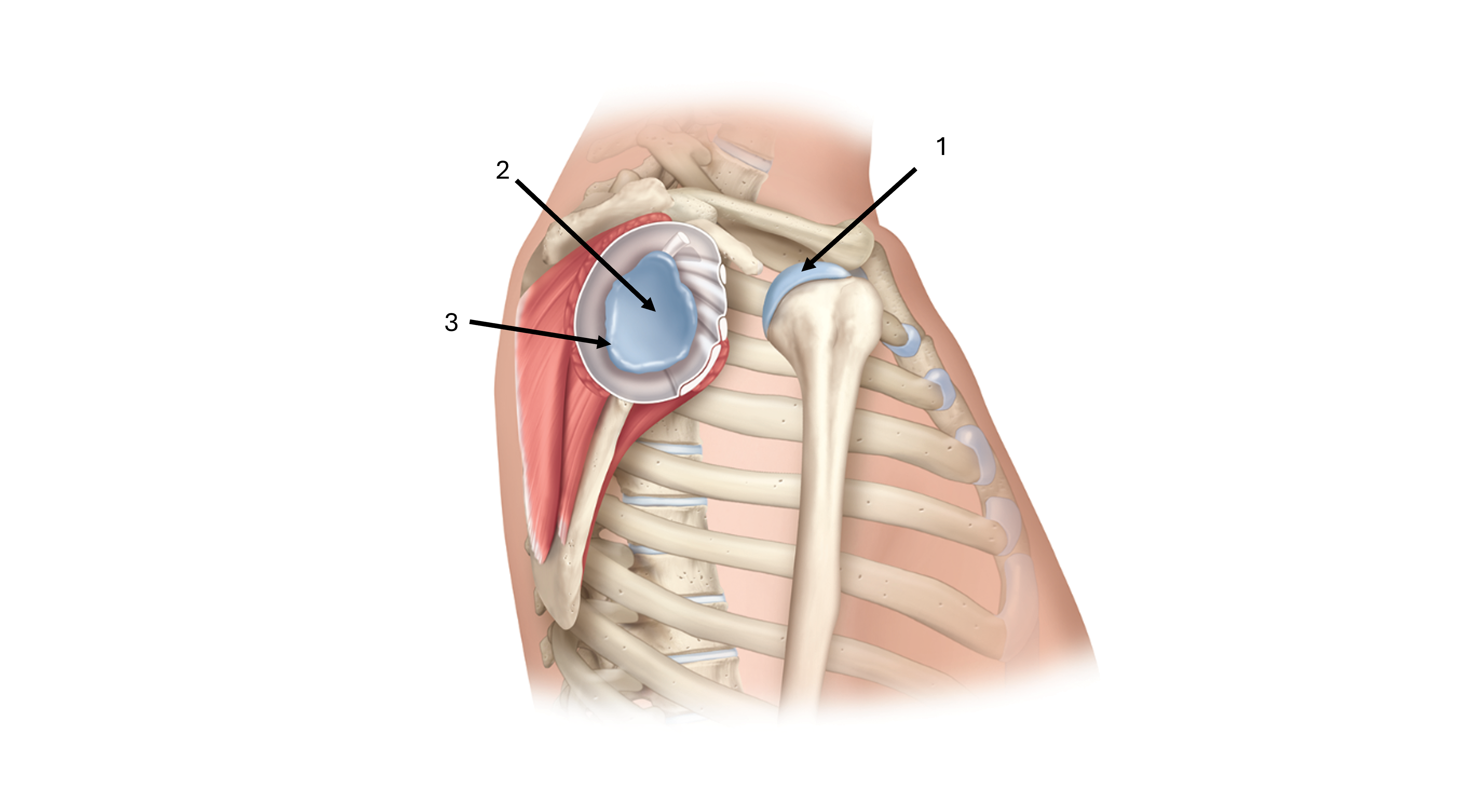
what is label #1
head of humerus
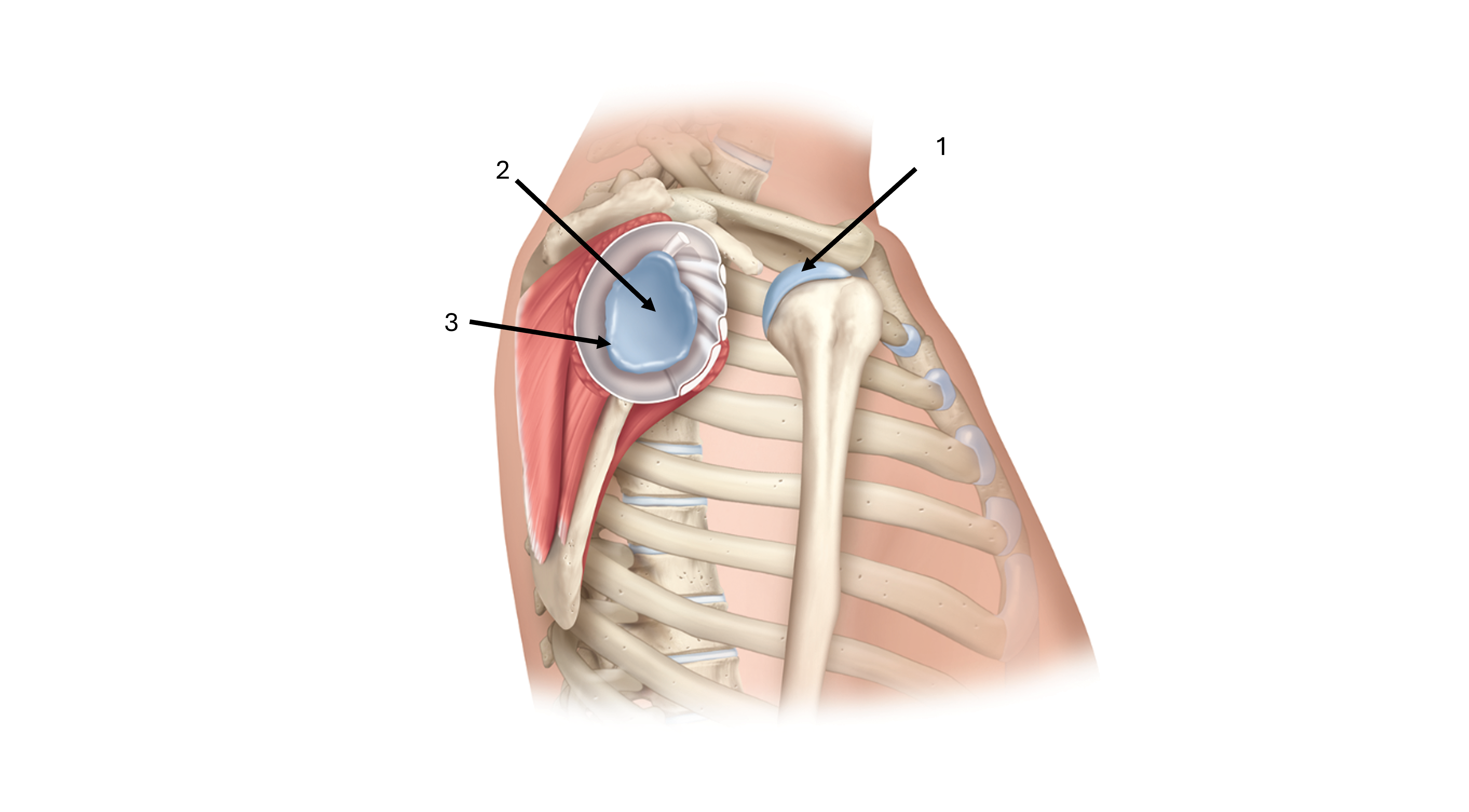
what is label #2
glenoid cavity/fossa
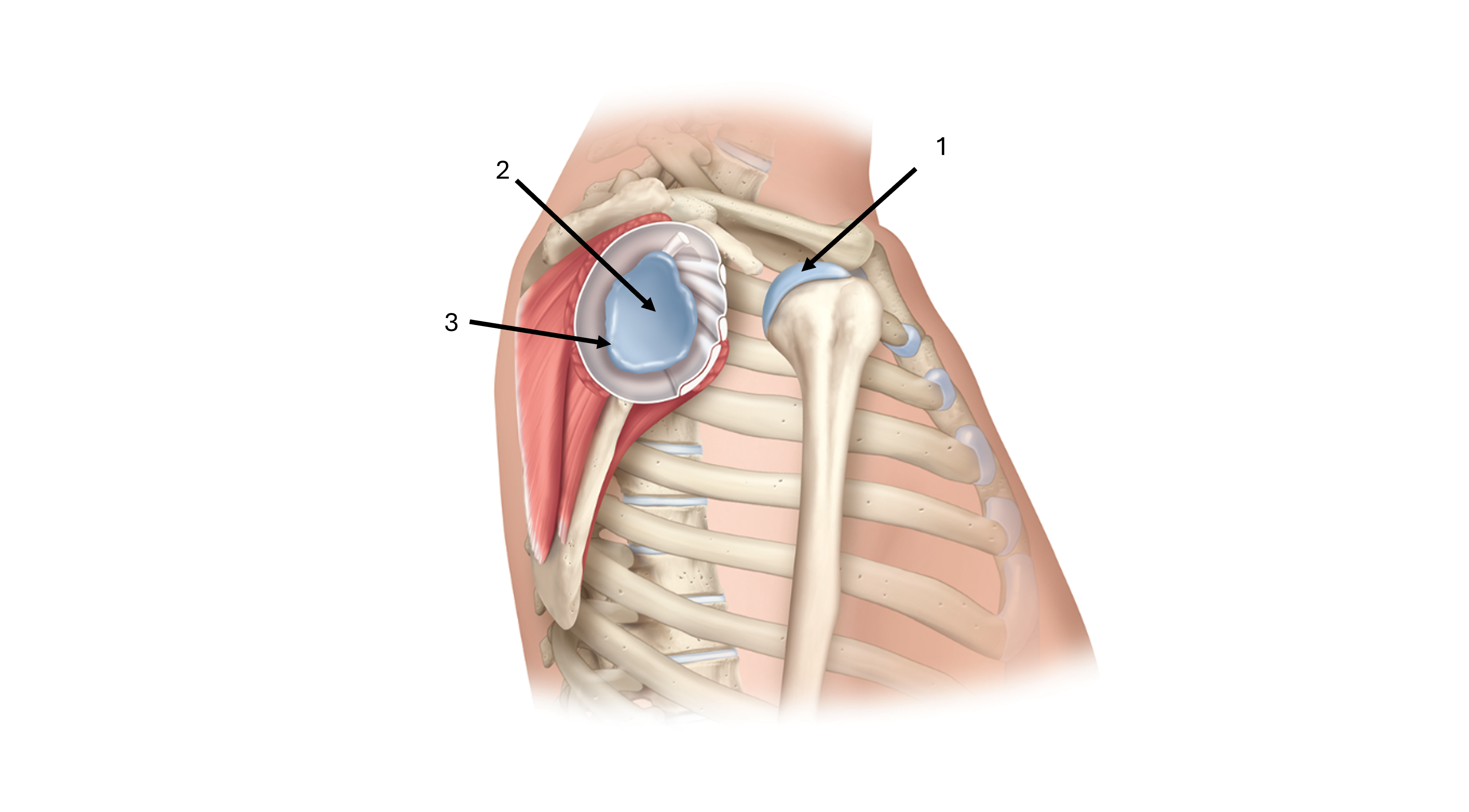
what is label #3
glenoid labrum
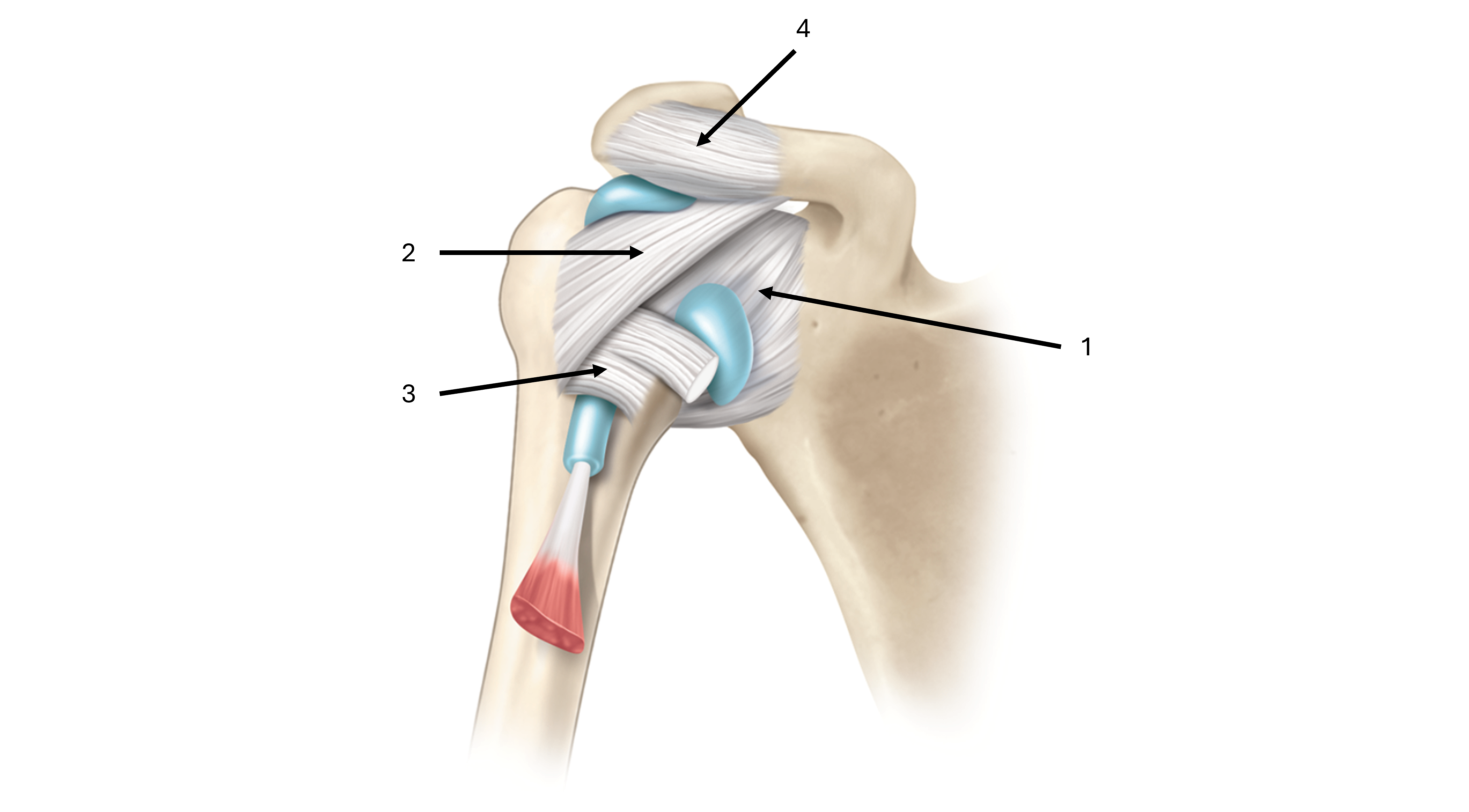
what is label #1 and its classification
glenohumeral ligament
intrinsic ligament
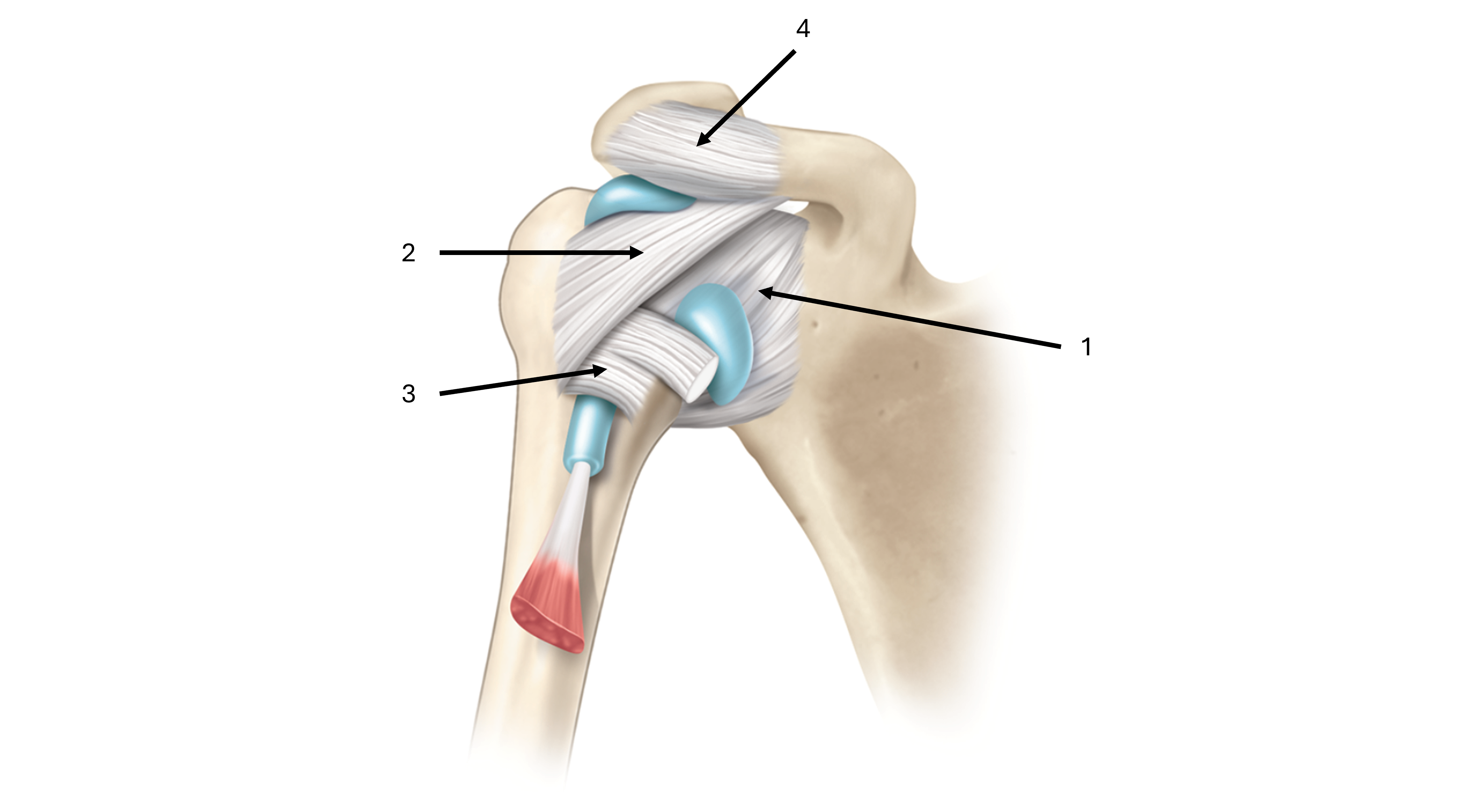
what is label #2 and its classification
coracohumeral ligament
intrinsic ligament
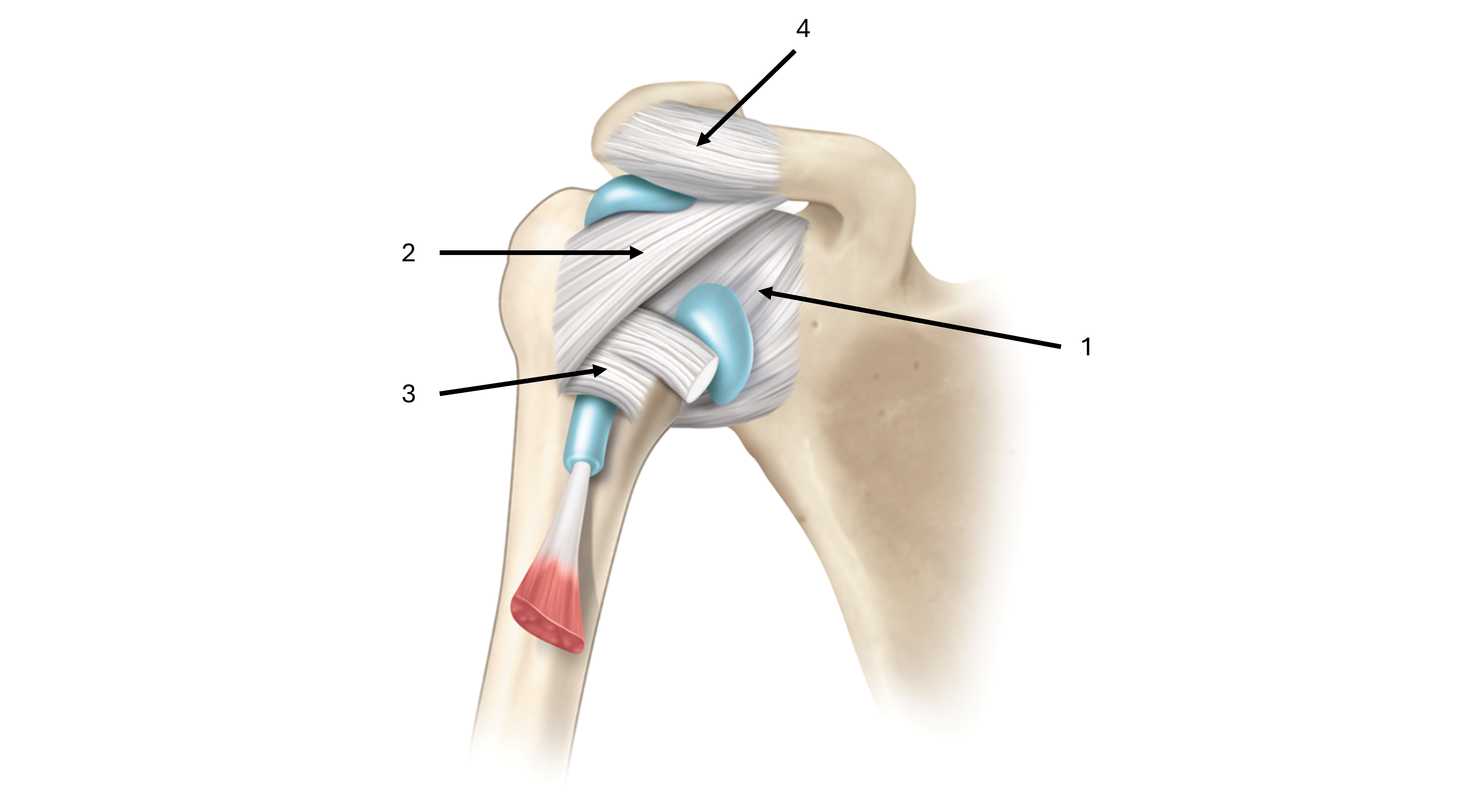
what is label #3 and its classification
transverse humeral ligament
intrinsic ligament
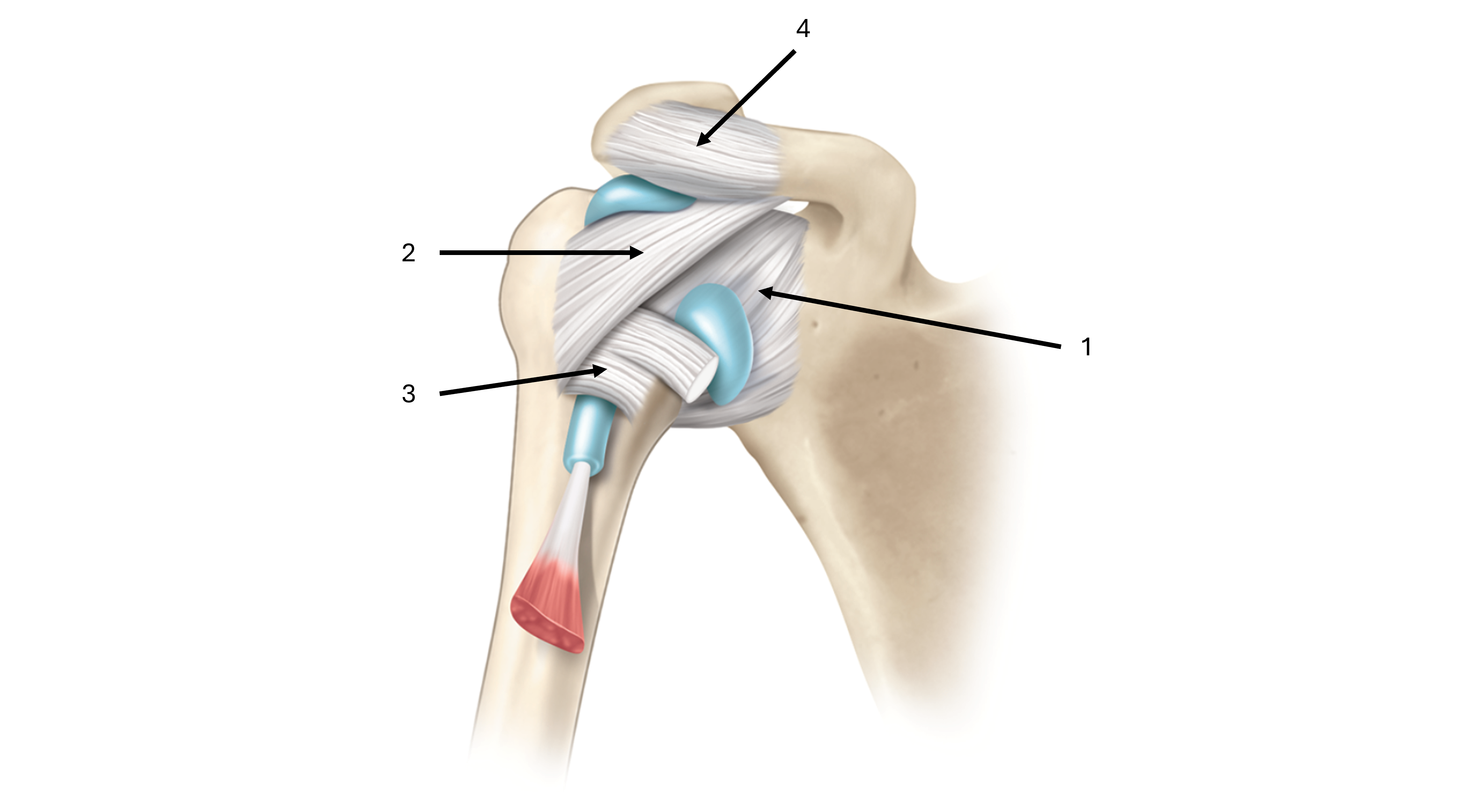
what is label #4 and its classification
coracoacromial ligament
extrinsic ligament
what makes up the coracromial arch
the coracoid process, coracoacromial ligament and the acromionm
what are the 3 types of shoulder dislocations
posterior, anterior and interior
what is the most common type of shoulder dislocation
inferior
does the scapula have direct attachment to the ribcage
no
for every ___ degrees of rotation, ____ comes from the glenohumeral joint and _____ from the scapulothoracic joint
3, 2, 1
what does scapula movement contribute to
extreme flexion and abduction of the humerus
what are axio-appendicular muscles
muscles that attach the appendicular skeleton to the axial skeleton
what are the muscle groups under axio-appendicular muscles
anterior axio-appendicular muscles and posterio axio-appendicular muscles
name the 4 anterior axio-appendicular muscles
pectoralis major
pectoralis minor
subclavius
serratus anterior
name the 4 posterior axio-appendicular muscles
trapezius
latissimus dorsi
levator scapula
rhomboid major and minor
what are the proximal and distal attachment(s) for pectoralis major
proximal: sternum and medial clavical
distal: lateral lip of bicipital groove
what are the inntervation(s) of pectoralis major
the medial and lateral pectoral nerves
what actions preformed by pectoralis major, and what heads preform them
shoulder flexion:clavicular head
shoulder extension: sternal head
should adduction: both heads
shoulder internal/medial rotation: both heads
pectoralis minor lies ____ to pectoralis major
deep
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for pectoralis minor
proximal: ribs 3-5
distal: coracoid process
what are the innervation(s) of pectoralis minor
the medial pectoral nerve
what actions does pectoralis minor preform or assit with
respiration assistents
stabilizing and pinning scapula against the ribcage
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for subclavius
proximal: 1st rib and 1st costal cartilage
distal: inferior surface of the clavicle
what are the innervation(s) of subclavius
nerve to subclavius
what actions are preformed by subclavius
anchoring and depressing the clavicle
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for serratus anterior
proximal: lateral surface of ribs 1-8
distal: medial border of the scapula
what are the innervation(s) of serratus anterior
long thoracic nerve
what action does serratus anterior preform
protraction of scapula
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for trapezius
proximal: base of skull, nuchal ligament and spinous process of throacic vertebrae
distal: lateral clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula
what are the innervation(s) of trapezius
accessory nerve/cranial nerve XI
what actions are preformed by trapezius, and what fibers allow so
scapula elevation: upper fibers
scapula retraction: middle fibres
scapula depression: lower fibers
rotating glenoid cavity/fossa upwards: upper and lover fibers
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for latissimus dorsi
proximal: spinous process of T6-T12 vertebrae, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest
distal: floor of the biciptial groove
what are the innervation(s) of latissimus dorsi
thoracodorsal nerve
what actions does the latissimus dorsi
shoulder extension
shoulder adduction
shoulder internal rotation
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for levator scapula
proximal: transverse processes of cervical vertebra
distal: superior angle of the scapula, the media border of the scapula to the superior root of the spine
what are the innervation(s) of levator scapula
the dorsal scapular nerve
what actions does the levator scapula preform
elevation of the scapula
inferior rotation of the glenoid fossa
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for rhomboid major
proximal: spinous process of T5-T7
distal: medial border of scapula at the root of the spine
what are the innervation(s) for rhomboid major
the dorsal scapular nerve
what actions are preformed by rhomboid major
retracting the scapula
medial rotation of the glenoid fossa
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for rhomboid minor
proximal: spinous process of C7 and T1
distal: medial border of the scapula at the root of the spine
what are the innervation(s) for rhomboid minor
the dorsal scapular nerve
what actions are preformed by rhomboid minor
retraction of the scapula
medial rotation of the glenoid fossa
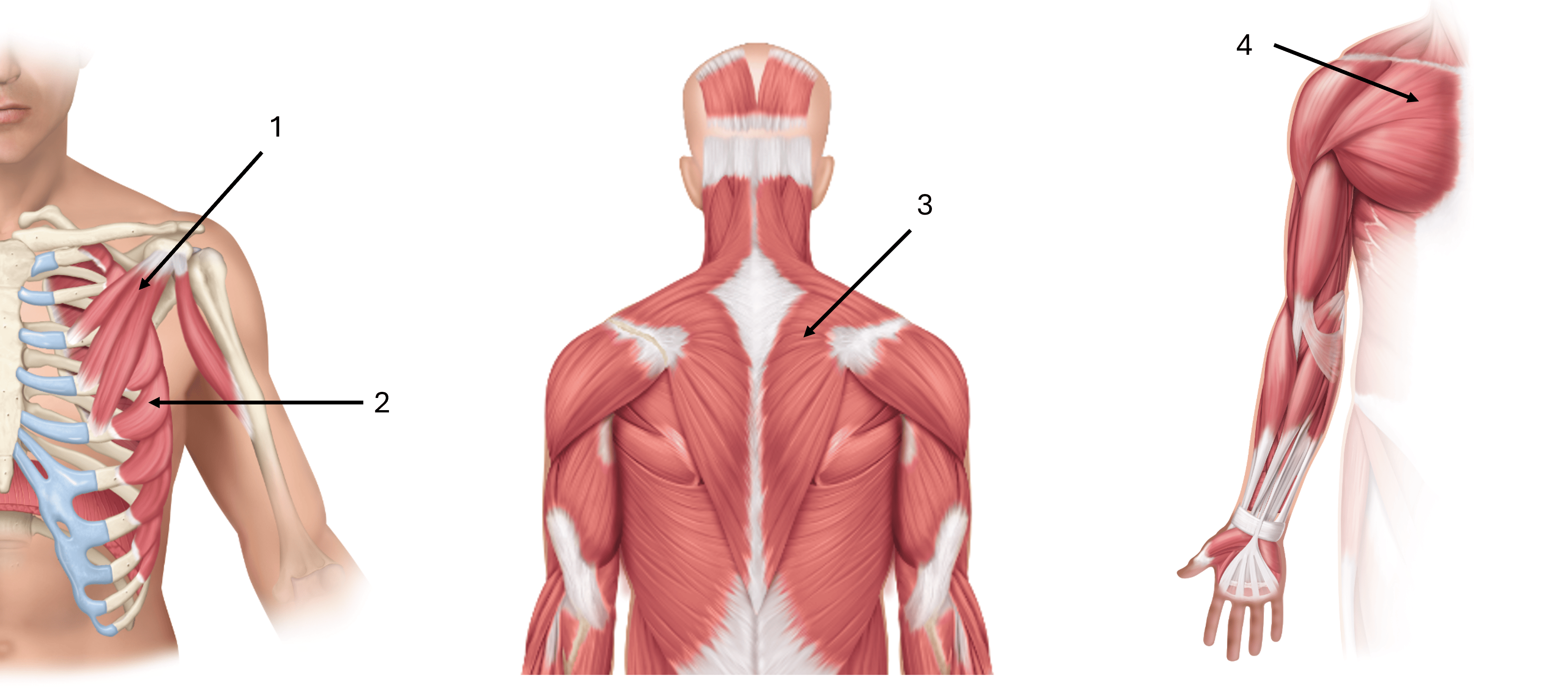
what is label #1
pectoralis minor
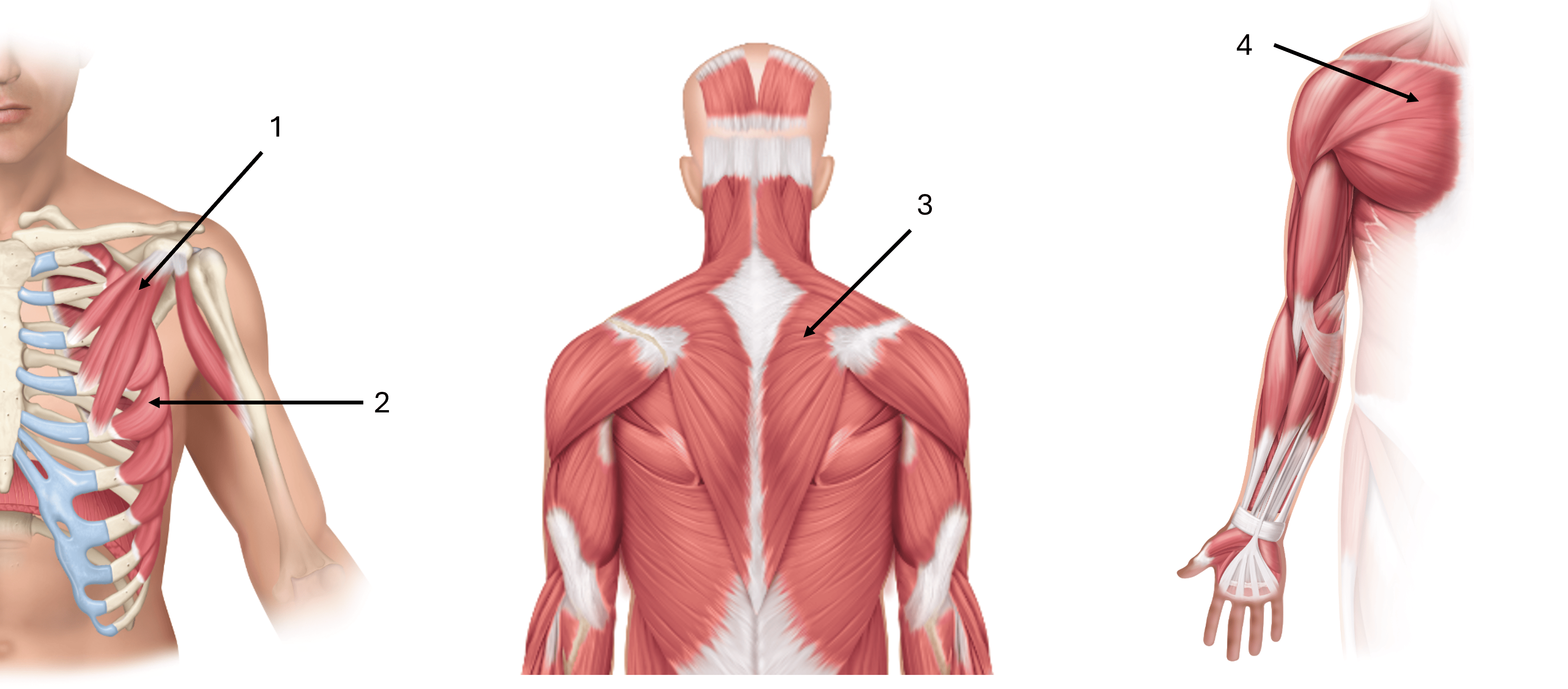
what is label #2
serratus anterior
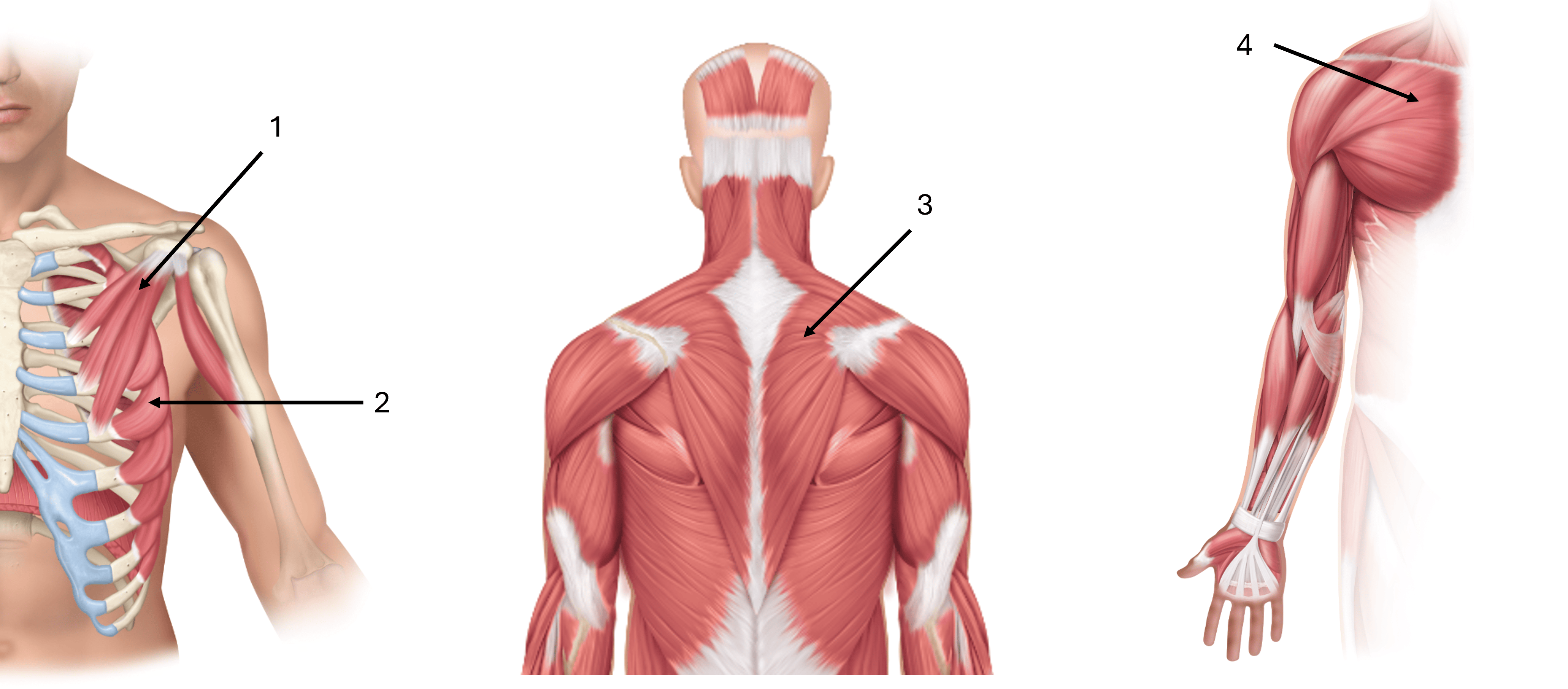
what is label #3
trapezius
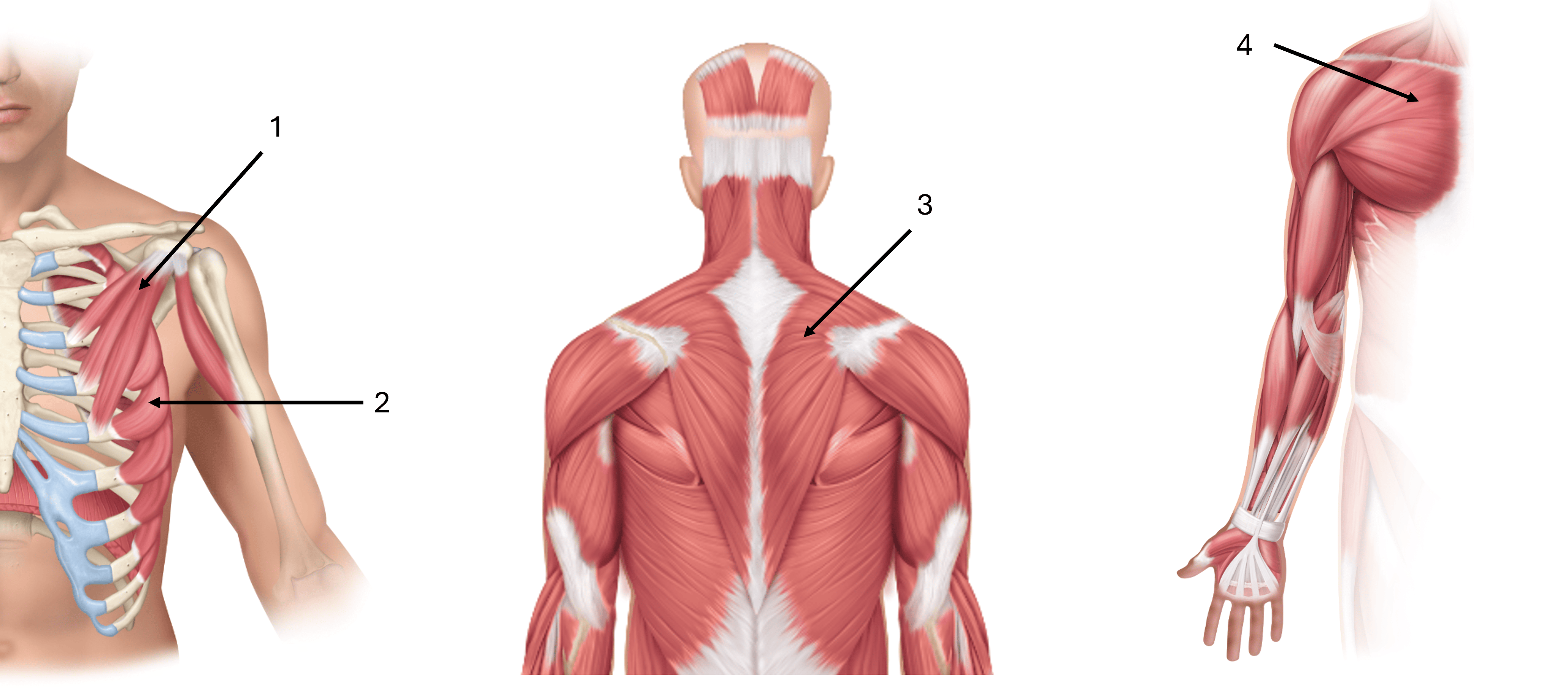
what is label #4
pectoralis major
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for the deltoid
proximal: lateral clavicle, acromion and spine of the scapula
distal: deltoid tuberosity
what are the innervation(s) of the deltoid
axillary nerve
what actions are preformed by the deltoid and by what fibers
shoulder abduction (middle fibers)
shoulder flexion and internal rotation (anterior fibers)
shoulder extension and external rotation (posterior fibers)
shoulder adduction (anterior and posterior fibers)
what is the proximal and distal attachment(s) for teres major
proximal: supraspinous fossa
distal: medial lip of the bicipital groove
what are the innervation(s) of teres major
the lower subscapular nerve
what actions are preformed by teres major
extension, adduction and internal rotation
what muscle preforms the same actions as teres major
latissimus dorsi
what 4 muscles make up the rotator cuff
supraspinatus
infraspinatus
teres minor
supscapularis
what are the two meanings of the word “lat”
lat = lateral (referring to a movement direction)
lat = latissimus dorsi (referring to the muscle)