chem 112 unit 2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
reversible, equilibrium
all reactions are ______ and will reach ______ if given enough time
equal
at equilibrium, forward and reverse reaction rates are _____
concentration
after equilibrium is reached, the _________ of reactants and products do not change
reaction quotient

equilibrium constant
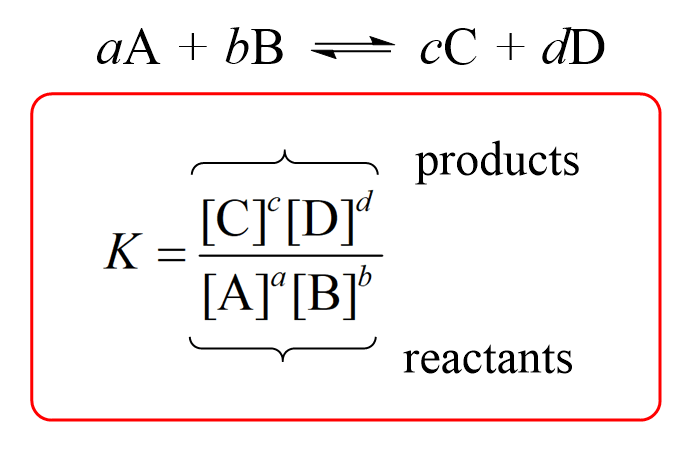
at equilibrium
if Q=K, reaction is __ _____________
right (forward), products
if Q<K, reaction moves to the _____ and forms ______
left (reverse), reactants
if Q>K, reaction moves to the _____ and forms ______
homogenous equilibria
occurs when all products and reactants are present in a single solution
Le Chatelier’s principle
a system in equilibrium will adjust to a stress by shifting to minimize or alleviate the stress
concentration changes, volume/pressure changes, temperature changes
3 types of stress
gases, gas molecules
pressure changes only have an effect when dealing with ______ and only when the reaction has a change in total number of ___ ______
acid
a substance that will yield or liberate H+ ions when dissolved in water (Arrhenius definition)
base
a substance that will yield or liberate OH- ions when dissolved in water (Arrhenius definition)
acid
a compound that donates a proton to another compound/proton donor (Bronsted-Lowry definition)
base
a compound that accepts a proton from another compound/proton acceptor (Bronsted-Lowry definition)
conjugate base
deprotonated form of original acid in reaction
conjugate acid
newly protonated form of original base in reaction
amphoteric
molecules or ions that can either gain or lose a proton under appropriate conditions (also known as amphiprotic)
pH
common way to express concentration of hydronium ions in solution
acidic
pH<7
basic
pH>7
neutral
pH=7
acid-ionization constant
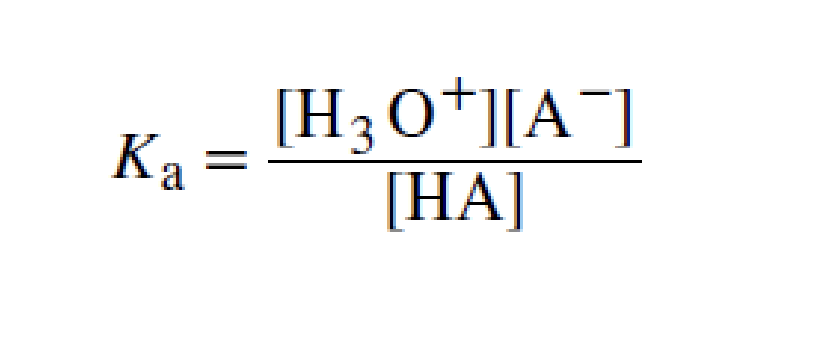
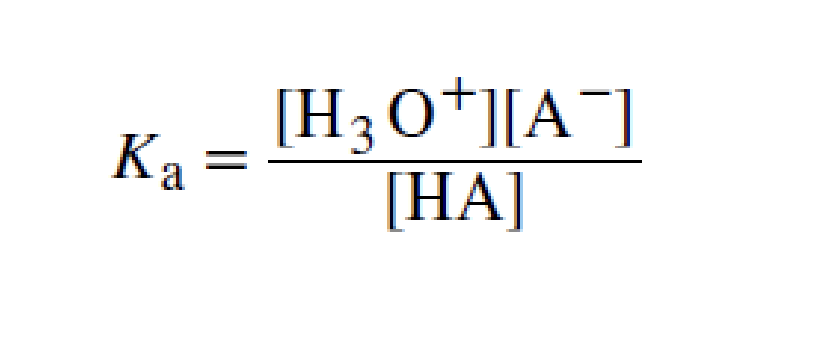
larger
the stronger the acid, the _____ the ionization constant
ions
ability of a solution to conduct electricity is related to number of ____ available to carry charge
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2
6 strong bases
HClO4, HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4
6 strong acids
base-ionization constant
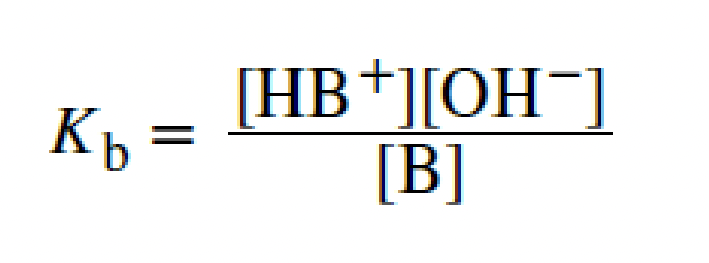
protons
we classify acids by the number of _____ they can transfer per molecule
neutral
conjugate partners of strong acids and bases are _____
weak
conjugate partners of weak acids and bases are ____
neutralization reaction
acid + base —>salt + (water)
neutral
strong acid + strong base =
slightly basic
weak acid + strong base=
slightly acidic
strong acid + weak base=
acidic
weak acid + weak base= if Ka>Kb
basic
weak acid + weak base= if Ka<Kb
buffer
mixture of weak acid/base with its conjugate partner
Henderson-Hasselbach equation
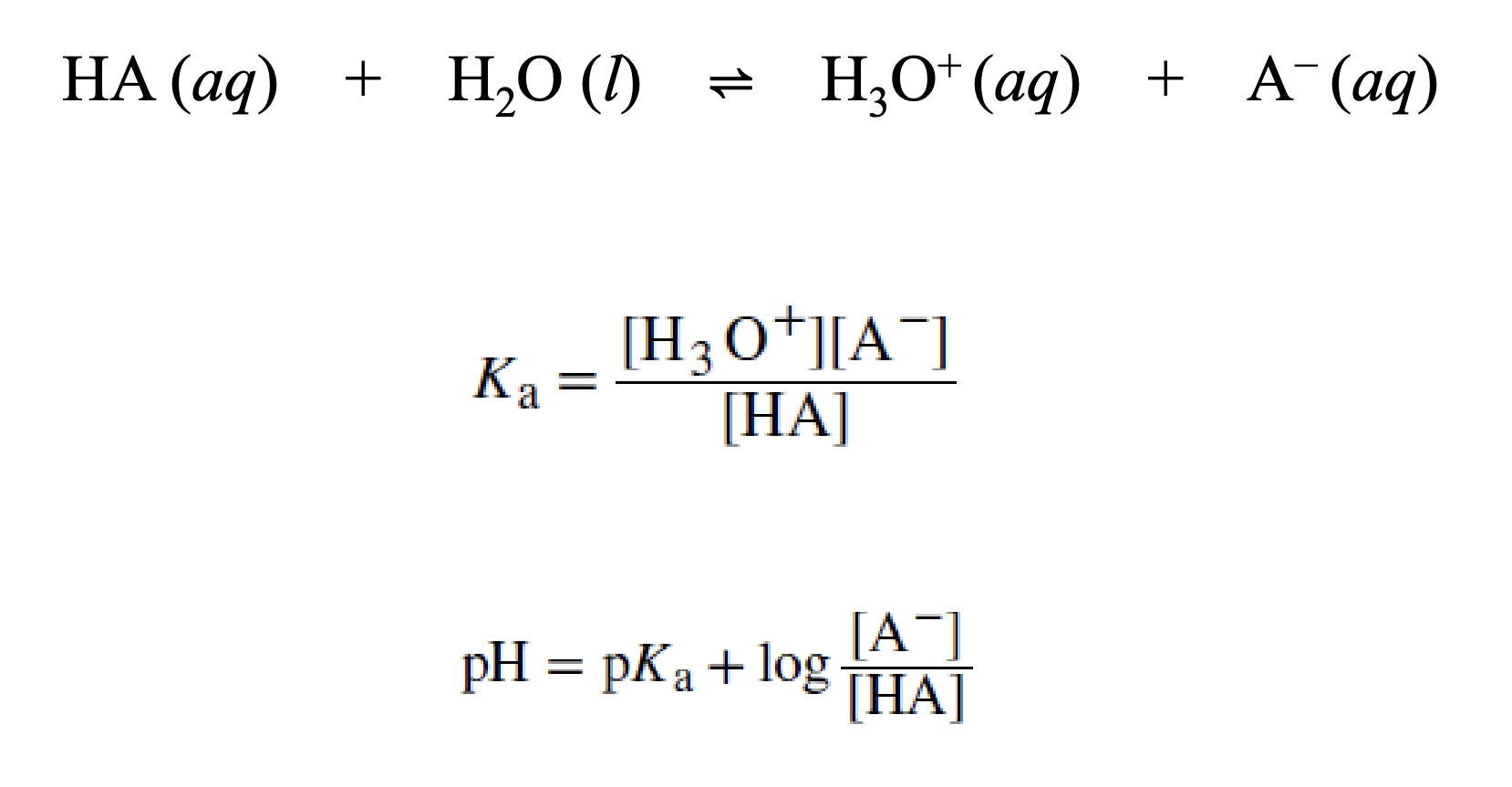
capacity
greater concentration of acid and base form result in higher ________
titration
addition of acid or base of known concentration to determine concentration of an unknown via a neutralization reaction
titration curve
data obtained from an experimental titration that looks at pH vs. volume of titrant added
indicators
weak acids or bases that change color to help determine pH of solution