Neurophysiology- PNS Afferent AQ'S
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
What are the anatomical components of the peripheral nervous system(PNS)?
The components of the PNS are the cranial and spinal nerves
What is the functional organization of the PNS? In other words, can you schematically explain the organization of the efferent division and the afferent division of the PNS?
There are two divisions of the PNS. The afferent division consists of sensory innervation which include somatosensory, special sensory, and visceral innervation. The efferent division consists of somatic and autonomic innervation. Autonomic innervation includes cardiac, smooth muscle, glandular, and adipose innervation. The autonomic system also breaks down into the sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric nervous systems.
Sensory information enters the afferent division of the PNS. What are exteroceptors?
Exteroceptors are sensory receptors that receive external stimuli for both special and somatic senses, and send the sensory information to the CNS.
What are proprioceptors and what type of information do they send to the CNS?
Proprioceptors are sensors that provide information about joint angle, muscle length, and muscle tension, which is integrated to give information about the position of the limb in space
What are interoceptors and what type of information do they send to the CNS?
Interoceptors are receptors that receive stimuli of internal organs (i.e., visceral senses)
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there and are these nerves mixed? In other words, do all cranial nerves contain both sensory and motor nerve fibers?
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves. Some, but not all, are mixed.
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves
What are the different types of intervertebral disc abnormalities that can occur and how can these issues relate to spinal stenosis?
Intervertebral disc deterioration and herniation are intervertebral disc abnormalities that can occur. These can lead to spinal stenosis, causing a narrowing of the open spaces within your spine. This can put pressure on your spinal cord and spinal nerves
What is a ventral root composed of?
A ventral root is composed of motor neurons.
What is a dorsal root composed of?
A dorsal root is composed of sensory neurons
What is a dorsal root ganglion composed of?
A dorsal root ganglion contains the cell bodies of unipolar neurons.
What is a ventral ramus?
A ventral ramus is the anterior division of a spinal nerve
What is a dorsal ramus?
A dorsal ramus is the posterior division of a spinal nerve
What are the sympathetic chain ganglia?
Sympathetic chain ganglia are paired bundles of nerve fibers, and aggregations of nerve cell bodies, that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. They are part of the autonomic nervous system.
What two components of the PNS combine to form a spinal nerve?
Ventral and dorsal roots combine to form a spinal nerve
Can you draw a spinal reflex arc?
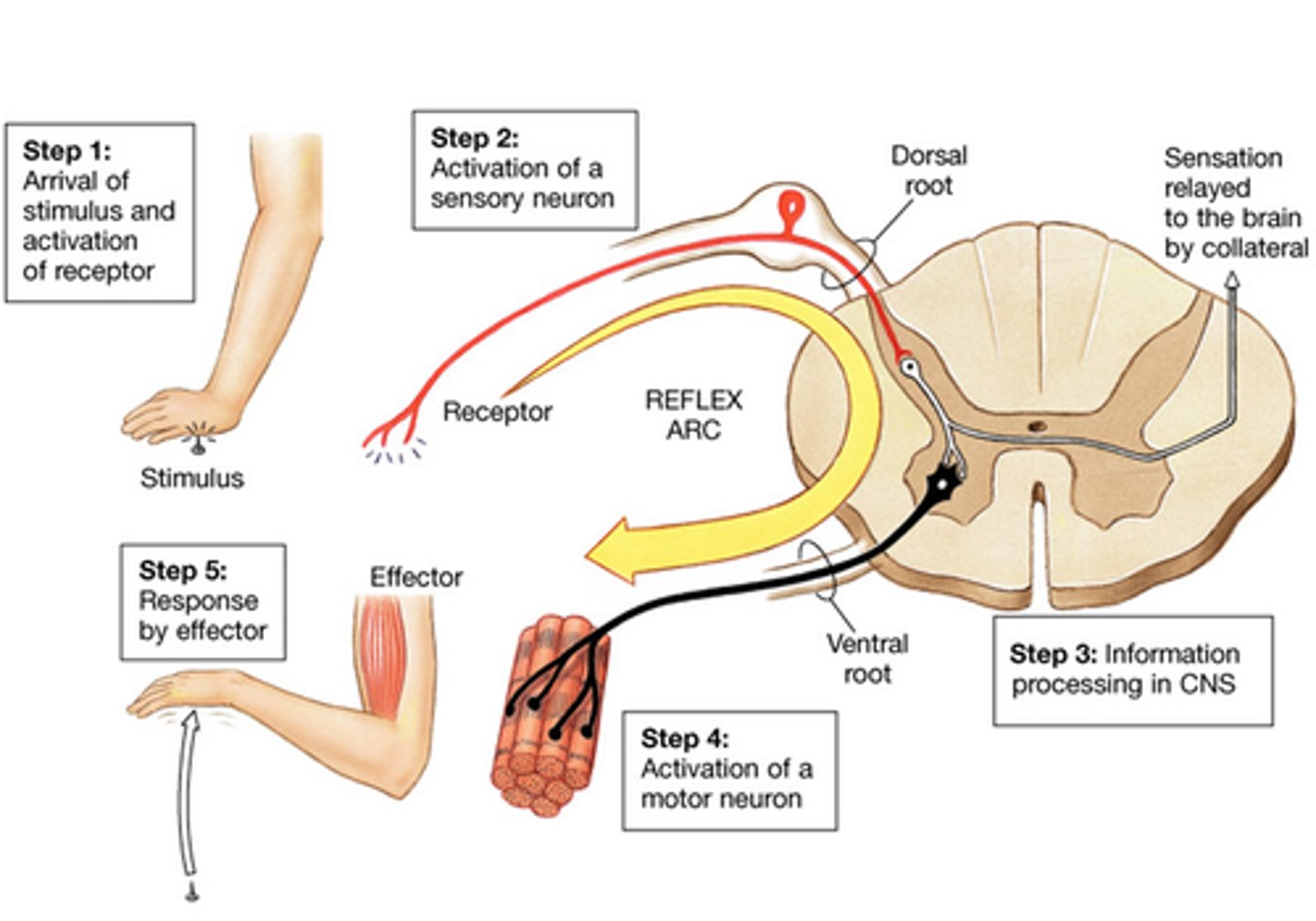
What are the three neurons involved and how do they communicate with one another?
The three neurons involved include: afferent neurons, interneurons and motor neurons. These neurons communicate through the neurotransmitters that are released in the synaptic clefts between them.
If you touched a hot stove with your hand, you would reflexively remove your hand from the stove. Does the brain regulate this muscle activity required to remove your hand? Do you sense the pain before or after your hand is withdrawn?
No, the brain does not regulate this muscle activity required to remove your hand. The pain is perceived in the brain after the hand is withdrawn
What are mechanoreceptors and what are some general examples?
Mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical stimuli. Some examples of mechanoreceptors include tactile receptors, baroreceptors and proprioceptors.
What are the three examples of tactile receptors in the skin and what do they detect?
Pacinian corpuscles sense deep touch, while Meissner's corpuscles and Merkel cells sense light touch.
What do ipsilateral and contralateral mean?
Senses that are processed ipsilaterally converge at the level of the brain stem. Senses that are processed contralaterally converge at the level of the spinal cord
Which receptors would inform you of an ice cube that was just placed on your arm?
Thermoreceptors
Which receptors would inform you of the taste of a cup of coffee?
Chemoreceptors.
Which receptors would inform you of the pain of stepping on a nail?
Nociceptors and mechanoreceptors
Are nociceptors tonic or phasic receptors?
Nociceptors are tonic (slowly adapting)
When you put on your shirt/top/blouse in the morning, you can feel it on your skin; however, several hours later the feeling is "gone." Based on this fact, are tactile receptors tonic or phasic?
Tactile receptors are phasic (quickly adapting).
Are odorant receptors phasic or tonic?
Odorant receptors are phasic
The receptor portion of tactile receptors (e.g., Meissner's and Pacinian corpuscles) is literally a modification of what portion of the neuron?
The receptor portion of one of these sensory neurons is a modification of a dendrite
What happens to the membrane of the receptor as a result of receiving a stimulus?
As a result of receiving a stimulus, ion channels open, allowing sodium to enter, leading to the generation of the first action potential at the initial segment of the neuron
If you had a lesion on your arm, what medications could you take to reduce the activity of prostaglandins, histamine and substance P?
To reduce the activity of prostaglandins, you would take anNSAID (e.g., ibuprofen, aspirin); to reduce the activity of histamine, you would take an antihistamine (e.g., Benadryl); to reduce the activity of substance P, you would take capsaicin
What do opiates mimic?
Heroin and prescription opioids chemically resemble the brain's natural opioids (i.e., endorphins)
Does nociceptive information travel to the brain contralaterally or ipsilaterally?
Nociceptive information travels to the brain contralaterally
The phenomenon of referred pain is thought to exist as the result of "cross-talk" between neurons. Where is it believed that this cross-talk occurs?
Cross-talk occurs in the spinal cord gray matter or dorsal root ganglia
Can you use this information to explain how an individual can experience pain in the arm when they are having chest pain due to a heart attack?
When a person is having a heart attack, the pain fibers in the heart and hand go to the spinal cord and they converge (cross-talk). The pain fibers from the heart can induce action potentials in the pain fiber coming from the arm.
What are the five different types of special senses?
Taste (gustation), smell (olfaction), sight (vision), hearing (audition) and balance/equilibrium (equilibrioception).
Based on your list, would you expect these senses to enter the nervous system at the level of the spinal cord or brain?
These senses enter the nervous system at the level of the brain
How many cells are involved in the peripheral processing of olfactory information?
There are 2 cells involved in the peripheral processing of olfactory information
In what cell are action potentials generated?
An action potential is generated in the primary bipolar sensory neuron and the secondary sensory neuron.
Thinking anatomically, can you explain why smell is the only special sense that does not enter the brain by relaying through the thalamus?
The primary neurons enter the brain through tiny holes in the floor of the cranium and synapse with the secondary neurons in the olfactory bulbs at the base of the brain
What are the five different tastes we can perceive and what is/are the tastant(s) for each of these different tastes?
For bitter, the tastants are coffee, beer, unsweetened cocoa, earwax, etc.; for sweet, the tastants are monosaccharides; for umami, the tastant is glutamate; for sour, the tastant is proton; for salty, the tastant is sodium
Is "spicy" one of the basic tastes? Why or why not?
Our bodies detect spice using a completely different system than the one for taste. The nerve that sends touch, pain, and temperature feelings from your face to your brain, interprets it
Many individuals who have experienced COVID-19 symptoms have been said to have "lost their sense of taste". Is this a true statement?
Technically, no. Many patients notice a loss of their sense of smell. However, because smell is necessary to taste flavor, these individuals are no longer able to discern flavors.
How many cells are involved in the peripheral processing of gustatory information?
2 cells are involved in the peripheral processing of gustatory information. These are the taste receptor cell and the bipolar sensory neuron.
In what cell are action potentials generated?
Action potentials are generated in the bipolar sensory neuron
What are the three layers of the eyeball, and what composes each layer?
The sclera is composed of thick connective tissue and forms the "white" of the eye, as well as the cornea of the eye. The choroid is composed of vascular tissue and forms the ciliary body and iris. The retina is composed of photoreceptors, also known as rods and cones, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells
What is the relationship between the lens, the ciliary body, and suspensory ligaments?
The lens is attached to the ciliary body via the suspensory ligaments.
Where is aqueous humor located?
The aqueous humor is located in the anterior chamber of the eye.
Where is the vitreous humor located?
The vitreous humor is located in the posterior chamber of the eye
What are the functions of the aqueous and vitreous humors?
The aqueous humor plays an essential role in nourishing the cornea and the lens by supplying nutrition such as amino acids and glucose. It also maintains intraocular pressure. The vitreous humor (or body) allows the light to pass through the lens to the retina and helps to keep the eye in its round shape
What is glaucoma?
Glaucoma is the term applied to a group of eye diseases that gradually result in loss of vision by permanently damaging the optic nerve.This disease can occur due to high pressure in the eye due to an over accumulation of fluid (aqueous humor)
If you were to stand straight and look straight ahead, where would most light entering your pupil light fall on your retina?
If you were to stand straight and look straight ahead, where would most light entering your pupil light fall on the fovea centralis
What is the visual axis (i.e., principal optical axis)?
The visual axis is an imaginary straight line that passes through the center of the pupil and lands on the center of the fovea centralis
What is the optic disc, why is it also known as the blind spot?
The optic disc optic is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. There are no photoreceptors in this area. Therefore, it is known as the blind spot
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light rays as they pass through different refractive media
What is a refractive index?
A refractive index is the number that reflects the degree to which a particular medium bends light rays. Larger numbers bend light more than smaller numbers
What is the refractive index of air, water, the cornea, and the lens?
Refractive index of air is 1.00, water is 1.33, cornea is 1.38, and lens is 1.41
If light passes from a medium with a refractive index of 2.0 into a medium with a refractive index of 1.0, what will happen to the light rays?
They will diverge. If light comes from a medium with a lower refractive index and enters a medium with a higher refractive index, then the light rays will converge
The human lens is concave or convex?
The human lens is convex
Does the human lens converge or diverge light rays?
The lens converges light rays
What does converging and diverging mean in reference to the visual axis?
To converge means to bend light towards the visual axis and to diverge means to bend light away from the visual axis.
What is the focal length?
The focal length is the distance between the center of the lens and the focal point
What is the focal point?
The focal point is where the light rays converge after passing through the lens
A diopter is a unit of converging or diverging power?
A diopter is a unit of converging power
Which structure of the eye plays the most important role in focusing light on the retina?
The cornea plays the most important role in focusing light on the retina because it has the highest converging power
The refractive index of the cornea is 1.38 while that of water is 1.33. If the two indices are so similar, why don't humans have clear vision underwater?
The problem is that the reflective indices are too similar, so light rays don't converge much. This causes the focal point to form behind the retina, similar to hyperopia.
How do swimming goggles help improve your underwater vision?
Swimming goggles help to improve your vision underwater because they restore the air-corneal interface
What are the ways in which the image formed on your retina is different from the object itself?
Inverted, backwards, and a fraction of the actual size of the object.
When is the near reflex triad employed?
The near reflex triad is employed in response to focusing on an ear object, meaning that the object is closer than 20 ft from the eye
What is lens accommodation?
Lens accommodation is the process by which the eye increases its converging power by making the lens more convex.
What is the state of the ciliary body, suspensory ligaments, and lens when an object is more than 20 feet away?
Ciliary muscles are relaxed, suspensory ligaments are taut, and the lens is flattened out.
What is the state of the ciliary body, suspensory ligaments, and lens whenan object is less than 20 feet away?
Ciliary muscles are contracted, suspensory ligaments are loose, and the lens is bulged (or very convex).
If the ciliary muscles of the eye are relaxed, which receptor must be activated?
The β2 receptors must be activated if the ciliary muscles of the eye are relaxed.
What neurotransmitter binds to the β2 receptor?
Norepinephrine
If the suspensory ligaments are loose, which receptor must be activated in the ciliary muscle?
Ciliary muscle contraction causes loosened suspensory ligaments. The M3 receptors must be activated in the ciliary muscles of the eye if contracted
Which neurotransmitter binds to the M3 receptor?
Acetylcholine
What is miosis?
Miosis is pupillary constriction
What is mydriasis?
Mydriasis is pupillary dilation
What are the muscles of the iris that control the diameter of the pupil?
Pupillary constrictor (sphincter) muscles and pupillary dilator (radial) muscles control the diameter of the pupil.
The pupil is not an anatomical structure. How can it be likened to a blackhole of the universe?
All light enters the pupil, but none exits it. That is why it appears black
Can you list a few drugs that would cause miosis?
Opiates, such as heroin or morphine, and other central nervous system depressants, such as benzodiazepines and barbiturates, will cause miosis while under the influence of the drug
What receptors and neurotransmitters are responsible for miosis?
M3 receptors are responsible for miosis and acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter.
Can you list a few drugs that would cause mydriasis?
Stimulant drugs like cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamines, and ecstasy will cause mydriasis, along with cannabis and hallucinogenic drugs like LSD and ketamine.
What receptors and neurotransmitters are responsible for mydriasis?
α1 receptors are responsible for mydriasis and norepinephrine is the neurotransmitter
If you were being chased by a bear in the woods, would your eyes undergo miosis or mydriasis?
Mydriasis
Which part of the ANS is elicited?
Mydriasis is elicited by the sympathetic system of the ANS
If an individual has an eyeball that is longer than normal, which refractive defect would they likely have?
If an individual has an eyeball that is longer than normal, they would have myopia
Where does the focal point form in this condition?
The focal point in this condition forms in front of the retina
Which type of lenses are used to correct for this refractive defect?
Concave, or diverging lenses, are used to correct for myopia
If an individual has an eyeball that is shorter than normal, which refractive defect would they likely have?
If an individual has an eyeball that is shorter than normal, they would have hyperopia
Where does the focal point form in this condition?
The focal point in this condition forms behind the retina.
Which type of lenses are used to correct for this refractive defect?
Convex, or converging lenses, are used to correct for hyperopia.
What is presbyopia and how does the amplitude of accommodation of the lens change over time?
Presbyopia is a disease caused by loss of elasticity of the lens. The amplitude of accommodation decreases with age due to this, and as a result, the lens cannot bulge as much during lens accommodation. Thus, an individual with presbyopia is essentially farsighted
What is astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a defect in the eye or in a lens caused by a deviation from the spherical curvature
What is a cataract?
A cataract occurs when the lens of the eye accumulates pigments and becomes progressively opaque
What is LASIK?
LASIK is laser eye surgery or laser vision correction. Essentially, it is a procedure where the cornea is reshaped with a laser to change the way light rays bend
What is a Snellen chart?
A Snellen chart is an eye chart that can be used to measure visual acuity
What does 20/20 vision literally mean?
20/20 vision is considered "normal" vision. From 20 feet away, the smallest you can read are the letters on the 20/20 line of the Snellen chart. Most humans should theoretically be able to read that line from 20 feet away.
What does it mean to have 20/40 vision?
If your visual acuity is 20/40, you are myopic. From 20 feet away, the smallest you can read are the letters on the 20/40 line of the Snellen chart. However, someone with 20/20 vision can read that same line from 40 feet away.
If the Snellen chart reveals that your visual acuity is 20/20, does this mean you have perfect vision?
No, it just means you perfect visual acuity.
A person's eyeglass prescription is -2.5. What are the units of this prescription?
The units are in diopters