Cartilage and Bone Tissue
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/41
Last updated 2:39 AM on 10/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
Properties of cartilage
collagen fibers
avascular
semi rigid- flexibility
avascular
semi rigid- flexibility
2
New cards
Cell of the cartilage
chondrocytes found in the lacunae
3
New cards
chondrocytes
responsible for the production of collagen and the extracellular matrix that will lead to the maintenance of cartilaginous tissues within joints.
4
New cards
Function of cartilage
support weight (discs)
protects against collapse (trachea)
increase joint mobility by reducing friction
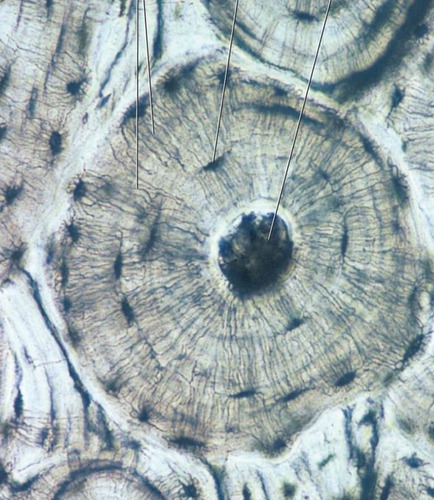
resist compression
protects against collapse (trachea)
increase joint mobility by reducing friction
resist compression
5
New cards
types of cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
fibrocartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage
elastic cartilage
6
New cards
hyaline cartilage
moderate collagen
involved in bone formation
coastal cartilage
involved in bone formation
coastal cartilage
7
New cards
fibrocartilage
lots of collagen
intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis
intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis
8
New cards
elastic cartilage
collage and elastic
Ear
Ear
9
New cards
locations of cartilage
articular
costal
nasal
intervertebral
costal
nasal
intervertebral
10
New cards
What is cartilage surrounded by ?
Dense irregular CT called perichondrium
11
New cards
Properties of bone
composed of calcium phosphate, collagen fibers, water
vascular
rigid- strong and stiff
vascular
rigid- strong and stiff
12
New cards
Cell in the bone
osteocytes found in the matrix lacunae
13
New cards
Functions of bone
Support weight
protection (cranium, thoracic cage)
lipid and mineral regulation and storage
blood cell formation
protection (cranium, thoracic cage)
lipid and mineral regulation and storage
blood cell formation
14
New cards
Types of bone cells
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
15
New cards
osteoblast
a cell from which bone develops
16
New cards
osteocyte
passes nutrients - maintain health of bone
arise from osteoblasts
arise from osteoblasts
17
New cards
osteoclast
cell that functions in the breakdown releasing calcium into blood
18
New cards
types of bone
compact and spongy
19
New cards
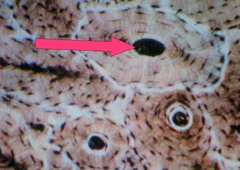
Haversian Canal
central canal
20
New cards
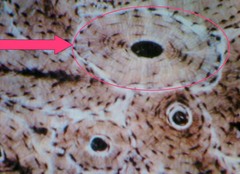
Osteon
all the concentric lamellae surrounding the Haversian canal; Haversian System
21
New cards
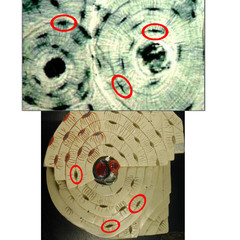
Lacunae
chambers where you find the osteocytes
22
New cards
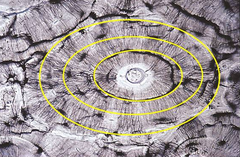
Concentric Lamellae
bone tissue is deposited into concentric layers surrounding the central canal
23
New cards
Spongy Bone
porous bone tissue that contains red bone marrow
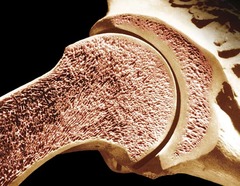
24
New cards
Compact Bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
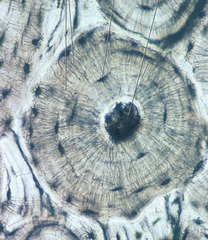
25
New cards
Periosteum
dense fibrous membrane that covers the surface on a bone
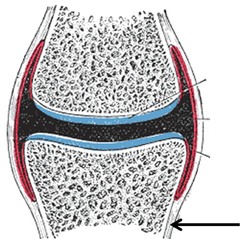
26
New cards
Osteocytes
The living cells embedded in the lacunae
27
New cards
long bones
bones of the arms, fingers and legs
28
New cards
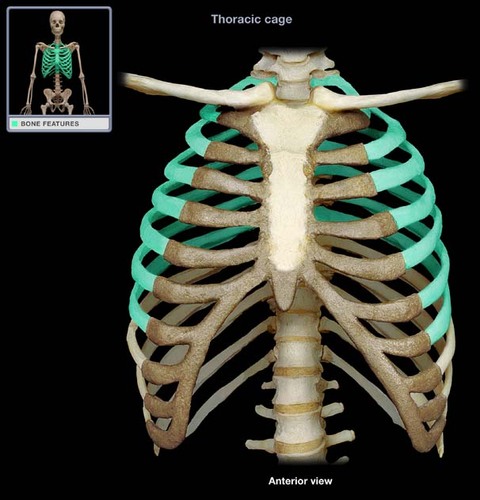
flat bones
These bones are thin, flat, and curved. They form the ribs, breastbone, and skull.
29
New cards
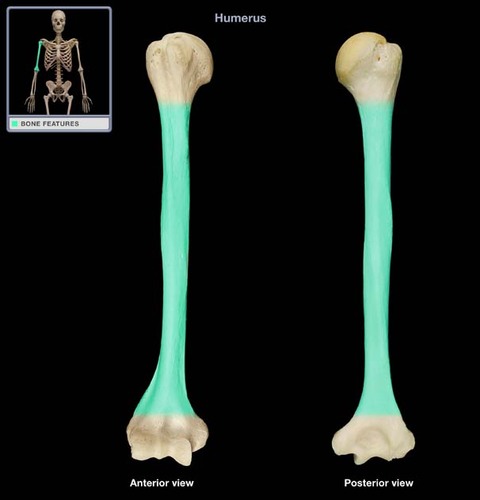
diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
30
New cards
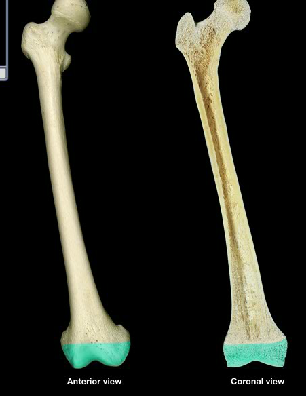
epiphysis
End of a long bone
31
New cards
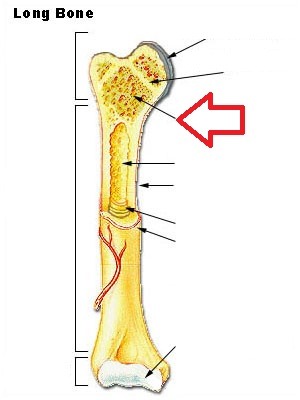
spongy bones
part of bone with many small pores or spaces
32
New cards
compact bone
Hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
33
New cards
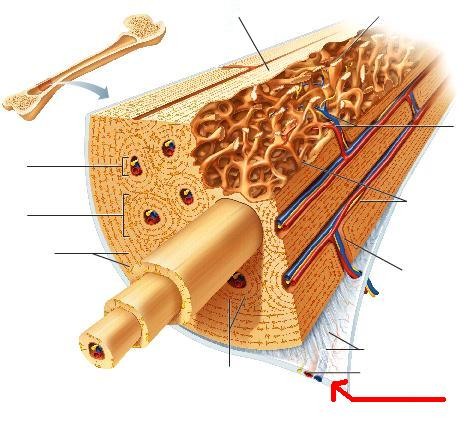
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
34
New cards
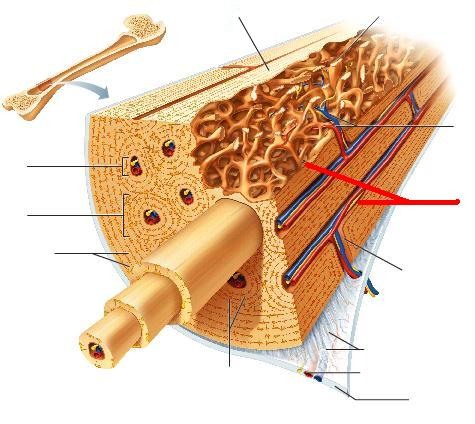
Endosteum
membranous lining of the hollow cavity of the bone
35
New cards
Calcification
process that hardens bones by adding calcium phosphate and collagen
36
New cards
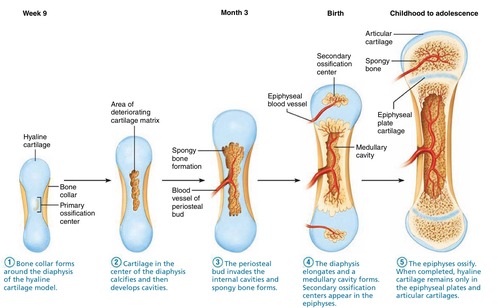
endochondral ossification
growth plates- new cartilage is added
primary ossification
calcification
vascular invasion
cancellous bone diaphysis compacted
epiphyses ossify
primary ossification
calcification
vascular invasion
cancellous bone diaphysis compacted
epiphyses ossify
37
New cards
bone development
Primary bone form
secondary bone form
secondary bone form
38
New cards
primary bone formation (from new)
endochondral - long bones cartilage replaced with bone
intramembranous- Flat bone forms within a membrane of CT
intramembranous- Flat bone forms within a membrane of CT
39
New cards
secondary bone formation (after og bone absorbed)
intramembranous new bone deposited in periosteum
bone remodeling - old bone repaired and replaced
bone remodeling - old bone repaired and replaced
40
New cards
intramembranous ossification
mesenchyme cells cluster into osteoblasts
osteocytes trapped in matrix
trabecular and periosteum form
collar of compact bone form
osteocytes trapped in matrix
trabecular and periosteum form
collar of compact bone form
41
New cards
Bone remodel
osteoclasts : bone resorption (dig pits)
osteoblasts: bone deposition (lay down calcifcation)
osteoblasts: bone deposition (lay down calcifcation)
42
New cards
fracture repair
1. hematoma formation
2. fibrocart callus form
3. bony callus form
4. done
2. fibrocart callus form
3. bony callus form
4. done