Thermodynamic Systems and describing the First Law of thermodynamics
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Define Heat
-Heat is energy that is transferred due to a difference in temperature.
Define work
-Work is done as a result of motion against an opposing force.
Define a system
System refers to the part of the universe that is of interest where the sample of matter is being studied within a specific boundary. The rest is referred to as surroundings
-When referring to systems we can label them as one of three types dependant on whether matter or energy can be transferred to or from the surroundings.
State and describe the three types of system
-Isolated systems, is one where there is no exchange of matter nor an exchange of energy
-Closed systems, contain a fixed amount of matter but allow for the exchange of energy
-Open systems, allow for both matter and energy too be exchanged with the surroundings.
Describe what isothermal change is
-Isothermal change, takes place at a constant temperature, so despite the volume if the system changing the temperature does not, this may be due to exchange of heat with surroundings stabilising it.
Describe what adiabatic change is
-Adiabatic change, no heat exchange with surroundings due to insolation meaning it can have change in temperature, for example takes place when gas expands and temperature falls.
What does enthalpy change refer to
Refers to the energy transferred as heat due to a chemical change at constant pressure. This energy may also be a result of work.
What does work refer to
Work refers too when force is applied to an object causing it to move
Why doe we often only account for work in volume changes with gases
In reactions involving gases, volume changes can be large so that a significant amount of work is done.
Whereas, often times with liquid and solids this change is small enough to usually be ignored.
State 2 equations for work and how we can derive them
-In order to derive an expression for expansion work, consider a quantity of gas trapped in a cylinder by a piston. When the gas expands the piston moves upwards to a new position against the external pressure and changes the volume from V initial to V final.
Work = force x distance moved
-You can work out that the energy transferred as work is given by the product of pressure and the change in volume
Work = -External Pressure (Final volume – Initial volume)
Describe internal energy
-Internal energy ,u, sum of all kinetic and potential energies in a system.
In practice why cant we sum all of the kinetic and potential energies in a system
In practice we cannot do this as we would have to add all the various contributions so absolute values are not possible, we can however measure the change in the same way we do enthalpy but not absolute values enthalpy.
Describe the First Law of thermodynamics
-energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only interconverted between forms
-In a closed system, change in internal energy is the sum of the energy changes due to transfer of heat ,q, and work ,w.
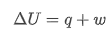
What is the value for change in internal energy for an isothermal energy
its 0 as q = w