Study for test on Tuesday
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is Diffusion
Movement of a salute (particles) from a region of high concentration to low concentration.
how many factored determine the rate of the fusion
There are four types of factors that determine the rate of the diffusion
Viscosity
Temperature
Molecular rate
Permeability/molecular size
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion
Temperature increase molecules move fast
How does molecular size affect the rate of diffusion?
It will not let large molecules pass through a semi permeable membrane
How does molecular weight affect the rate of diffusion?
weight and diffusion rates are inversely proportional
How does viscosity effects the weight of diffusion
an increase in viscosity( thickness) will decrease the rate of diffusion
What is osmosis?
Movement of water through is semi permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration.
What happened when you place the cell into it isotonic solution
Will be no net flow into or out of the cell in the cell volume will remain stable
What happened when you play a cell into a hypotonic solution
Water move into the cell/cell swell or burst/laces
What happen when you place a cell into a hypertonic solution?
Water moves out of the cell/cell shrink/cremates
What is filtration?
Solve(and its dissolved substance) will move from region of high-pressure to original of low pressure.
Epithelial tissue
Simple squamous
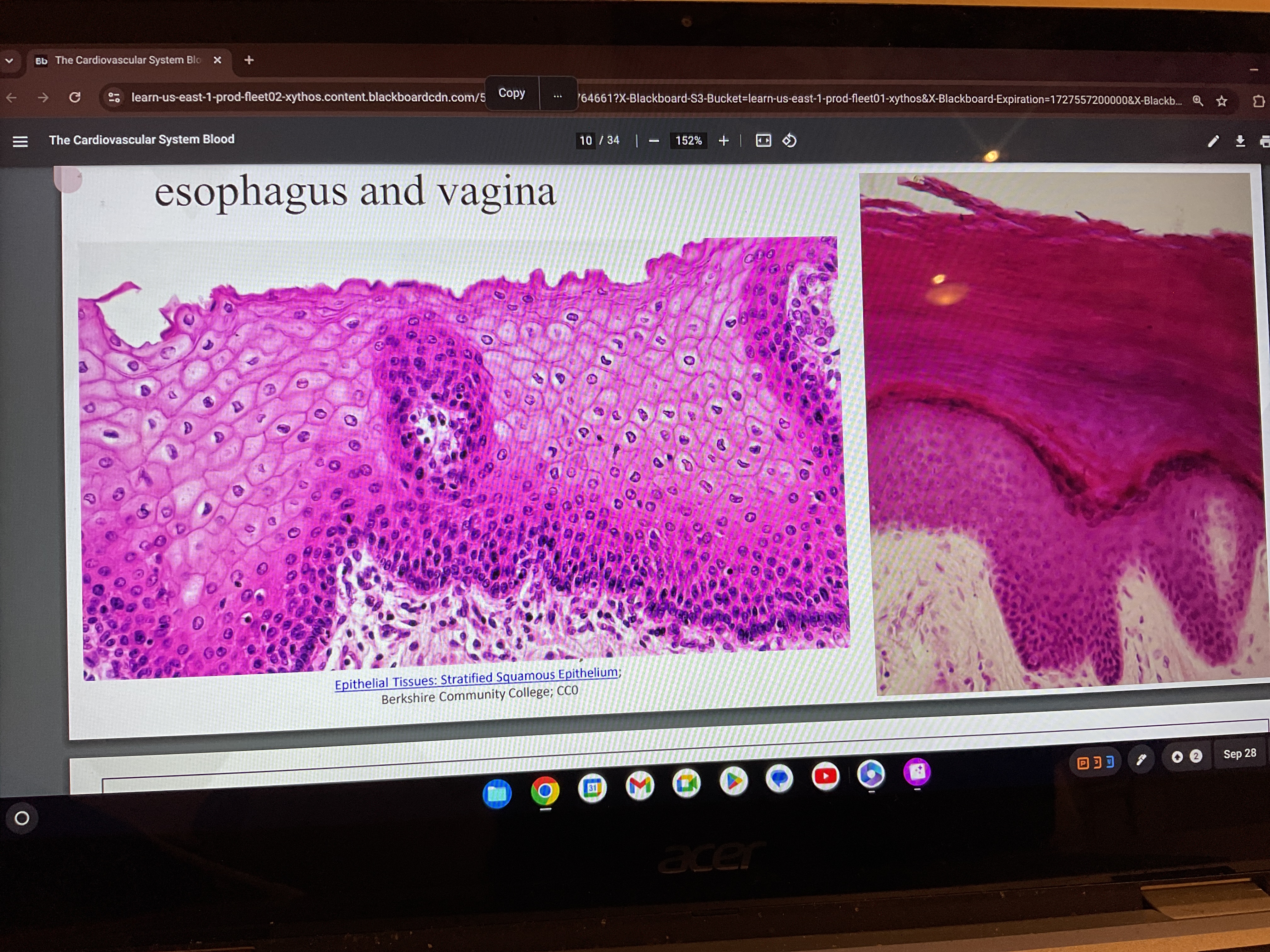
Stratified squamous
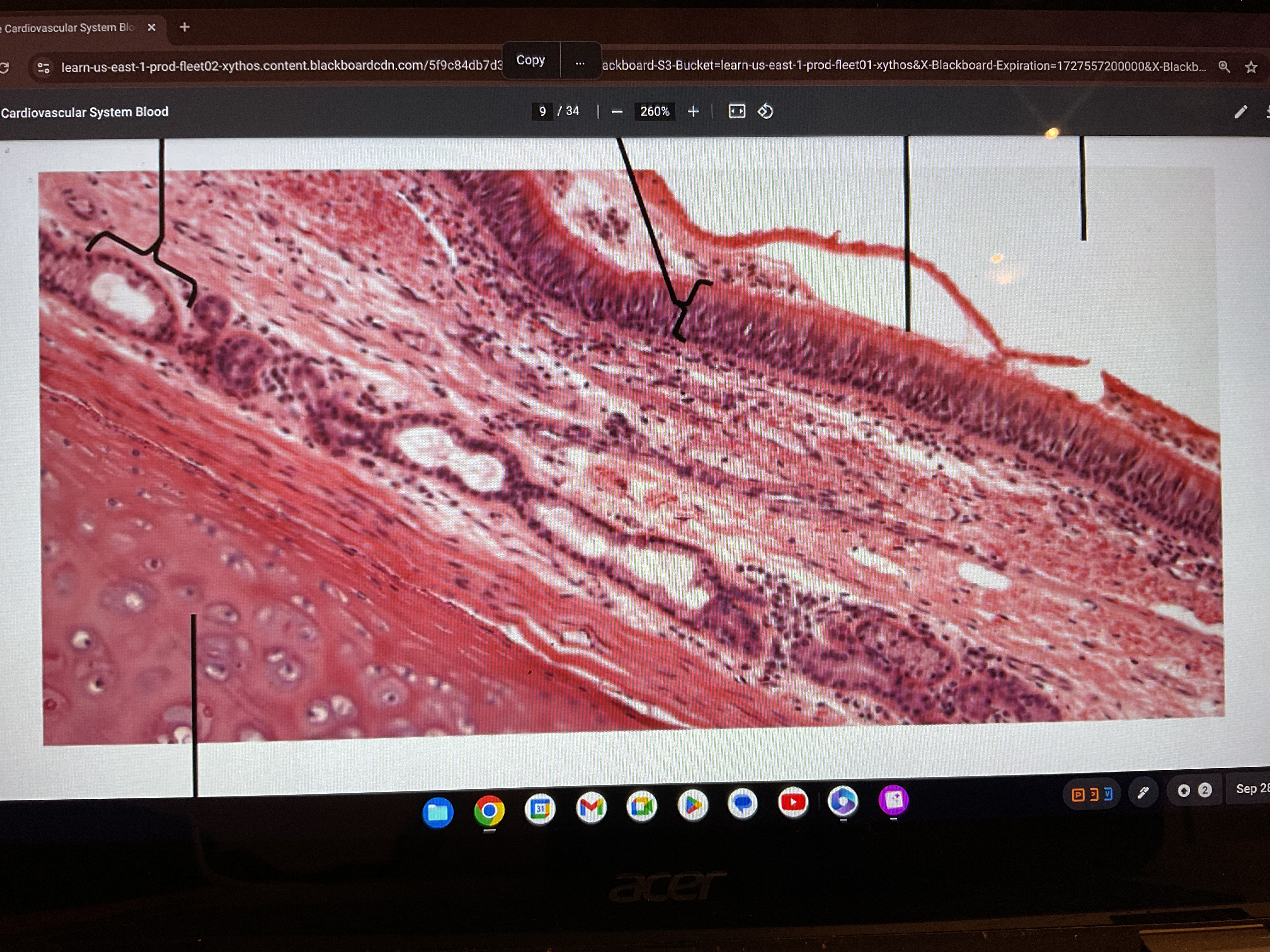
Pseudo stratified ciliated columnar
Simple columnar
Simple squamous

Simple Columnar
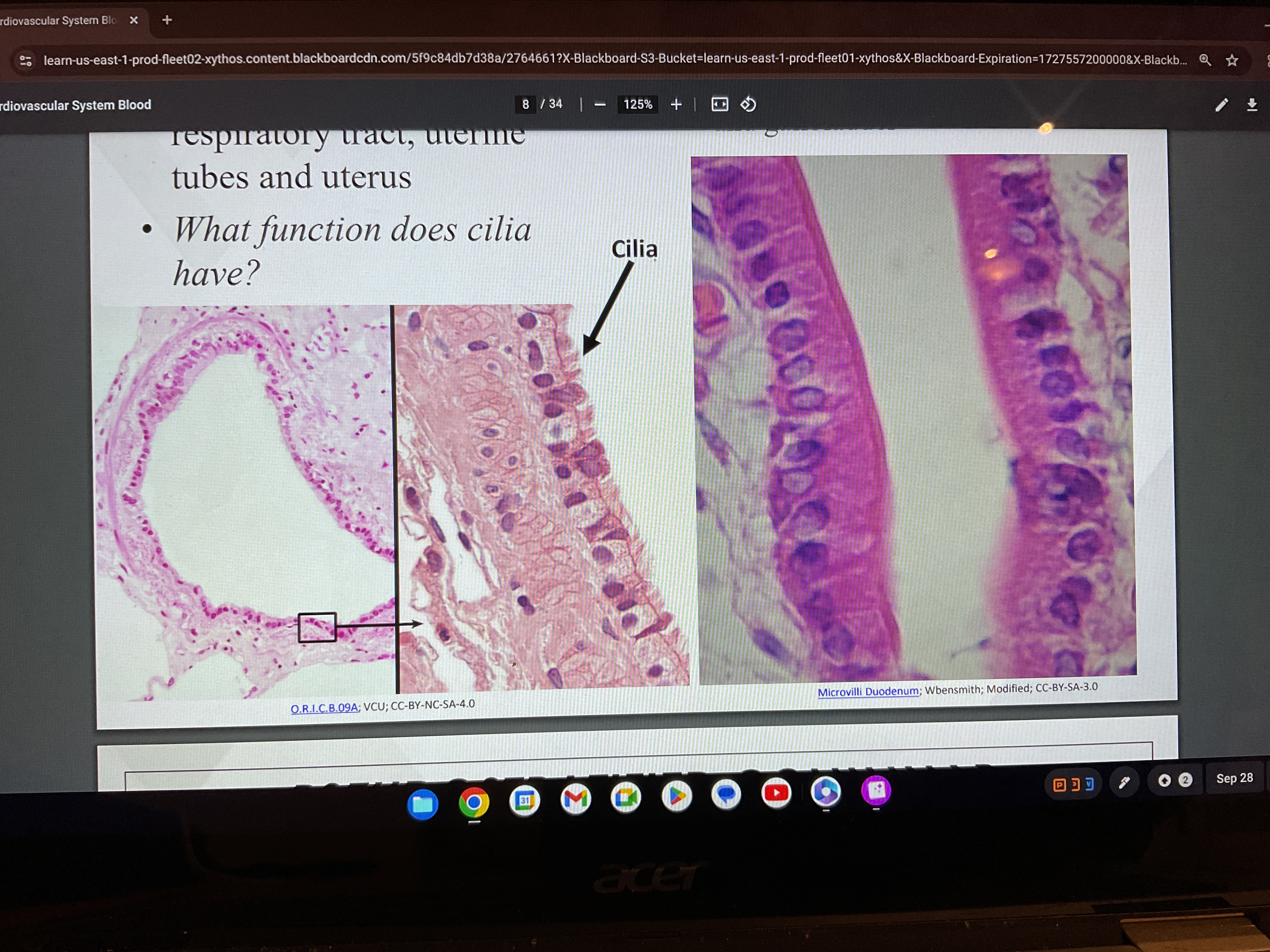
Pseudo stratified columnar
Stratified squamous
Connective tissue
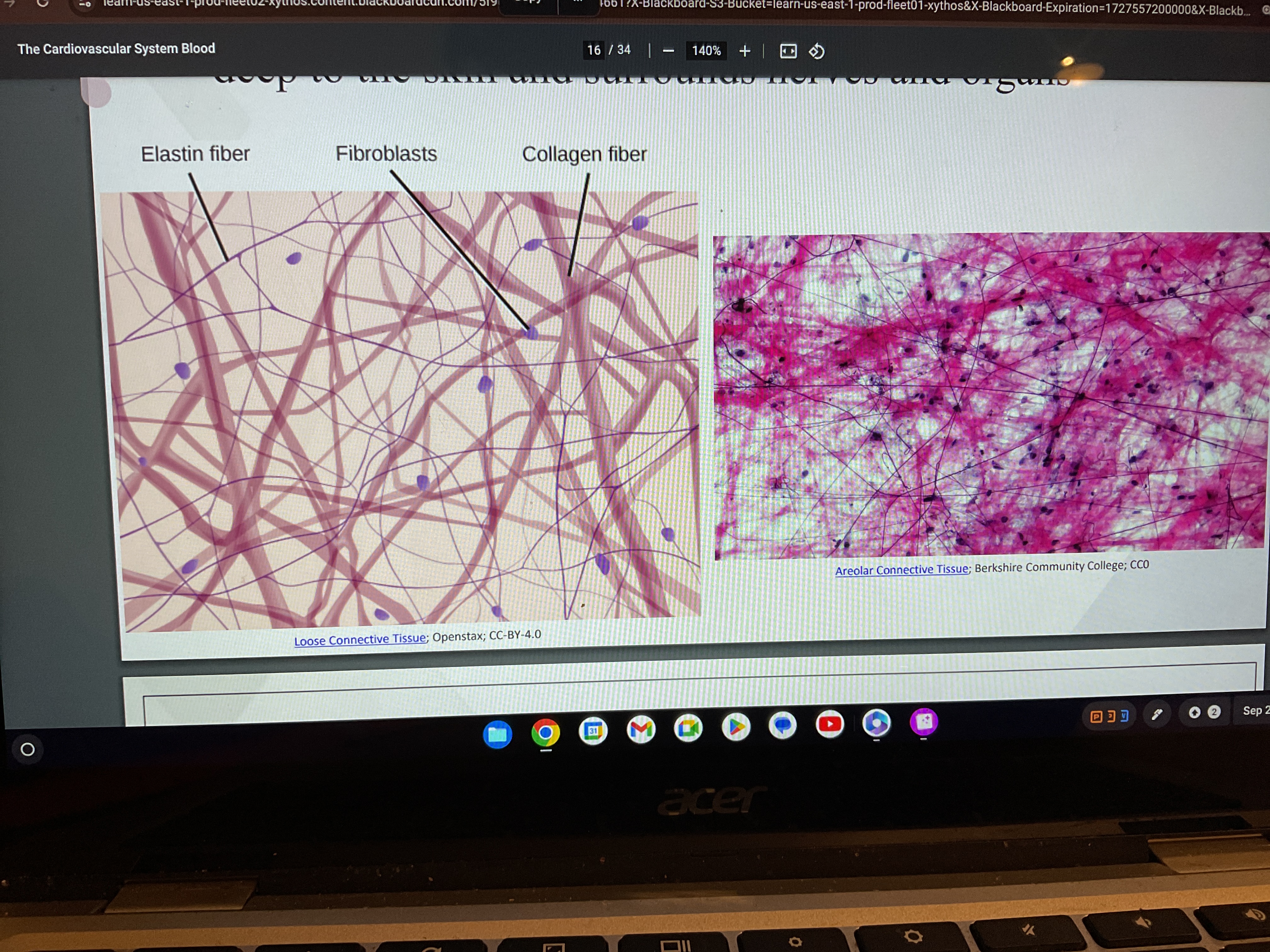
Areolar
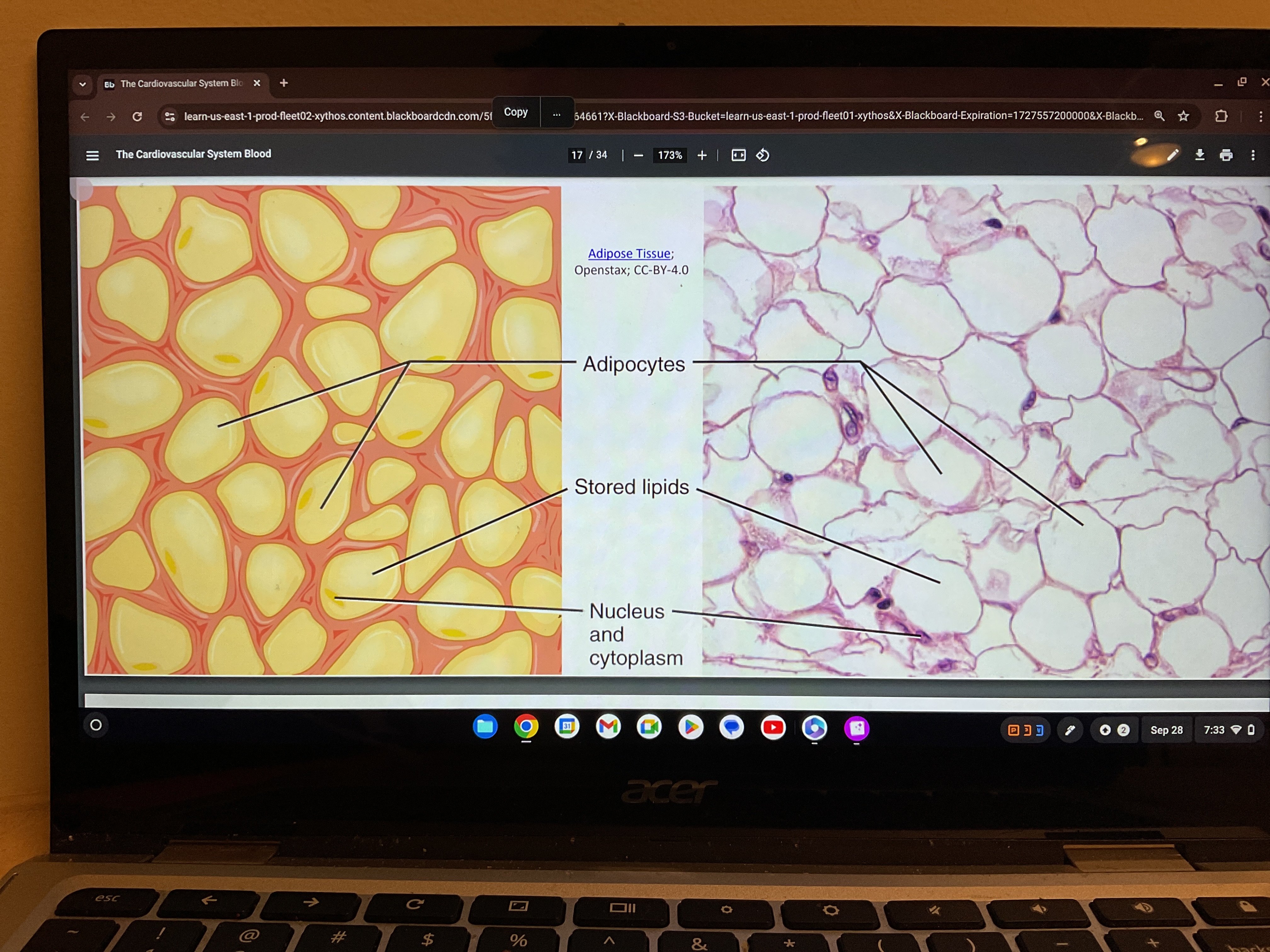
Adipose
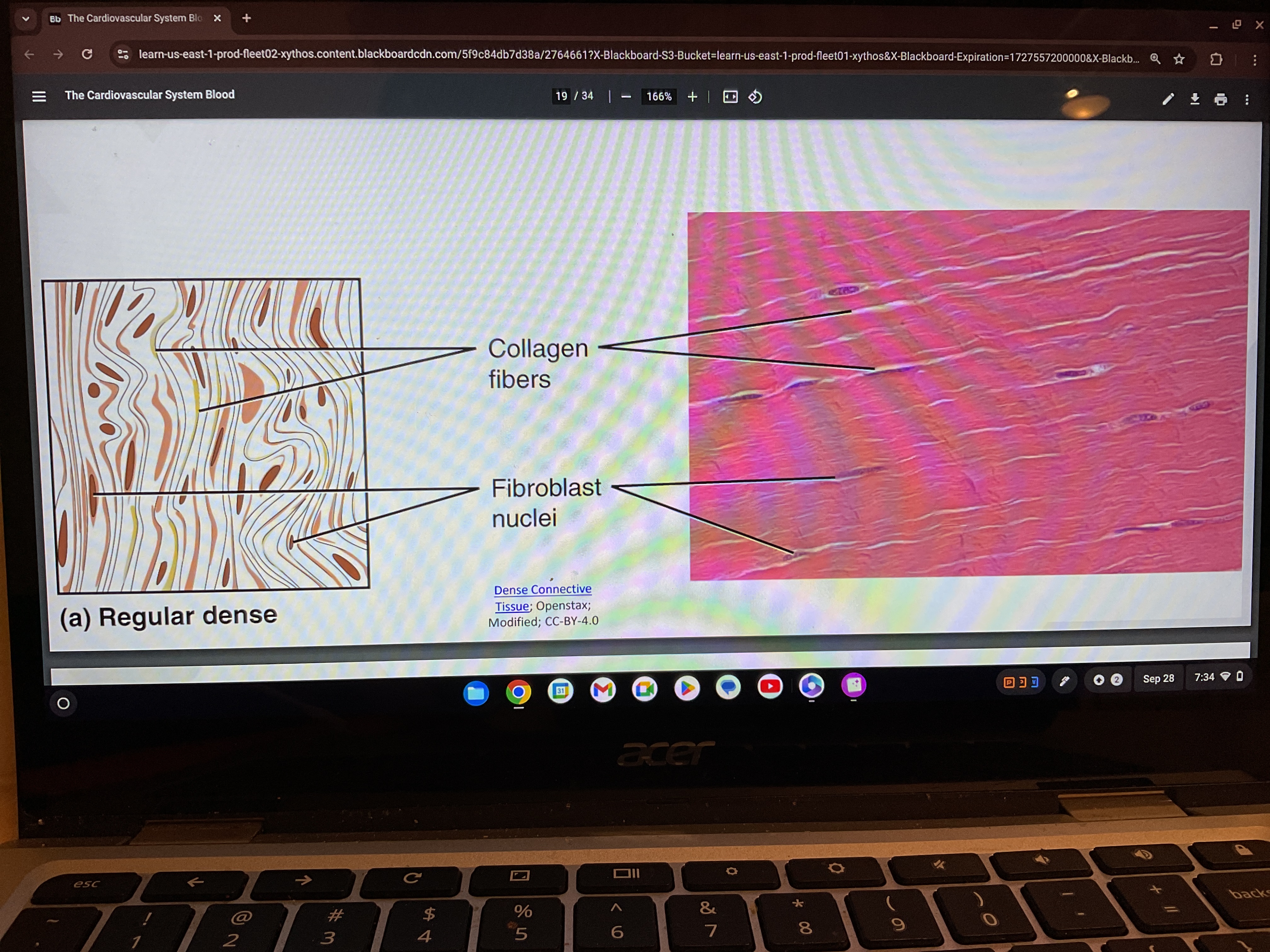
Dense regular
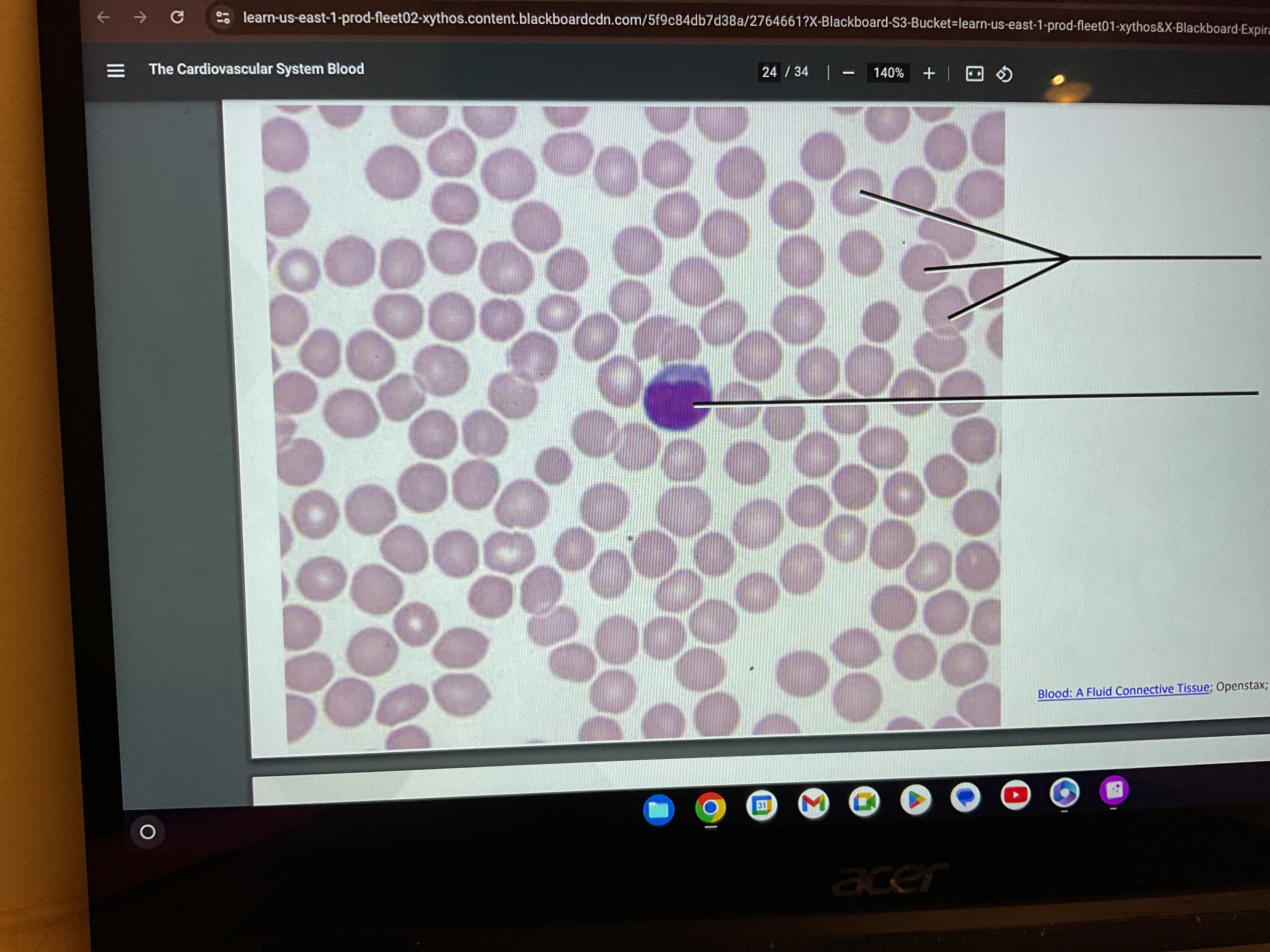
Blood
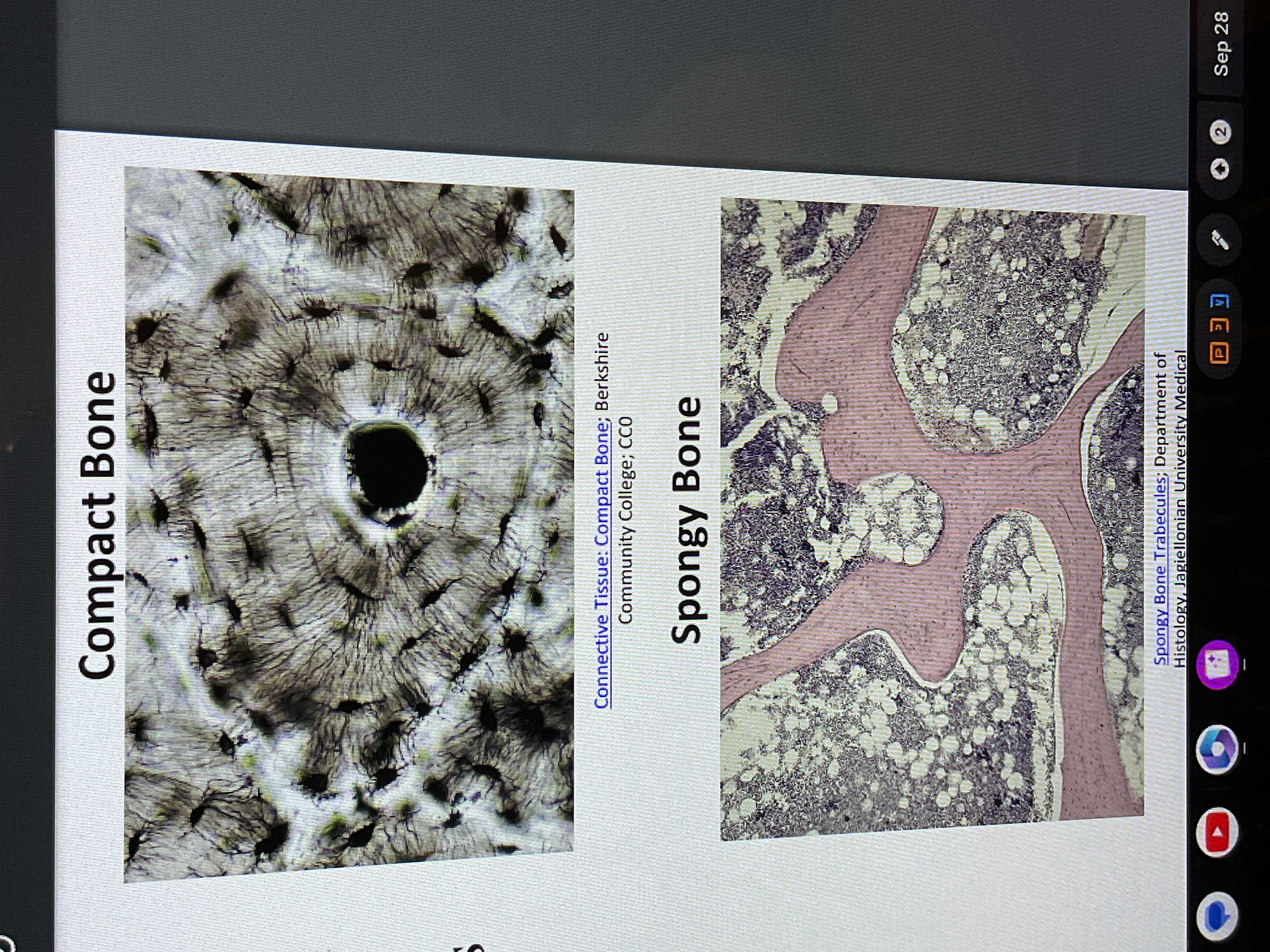
Bone
Areolar connective tissue
Adipose connective tissue
Dense, regular connective tissue
Blood connective tissue
Bone connective tissue
Muscle tissues
Skeleton, cardiac, and smooth
skeletal
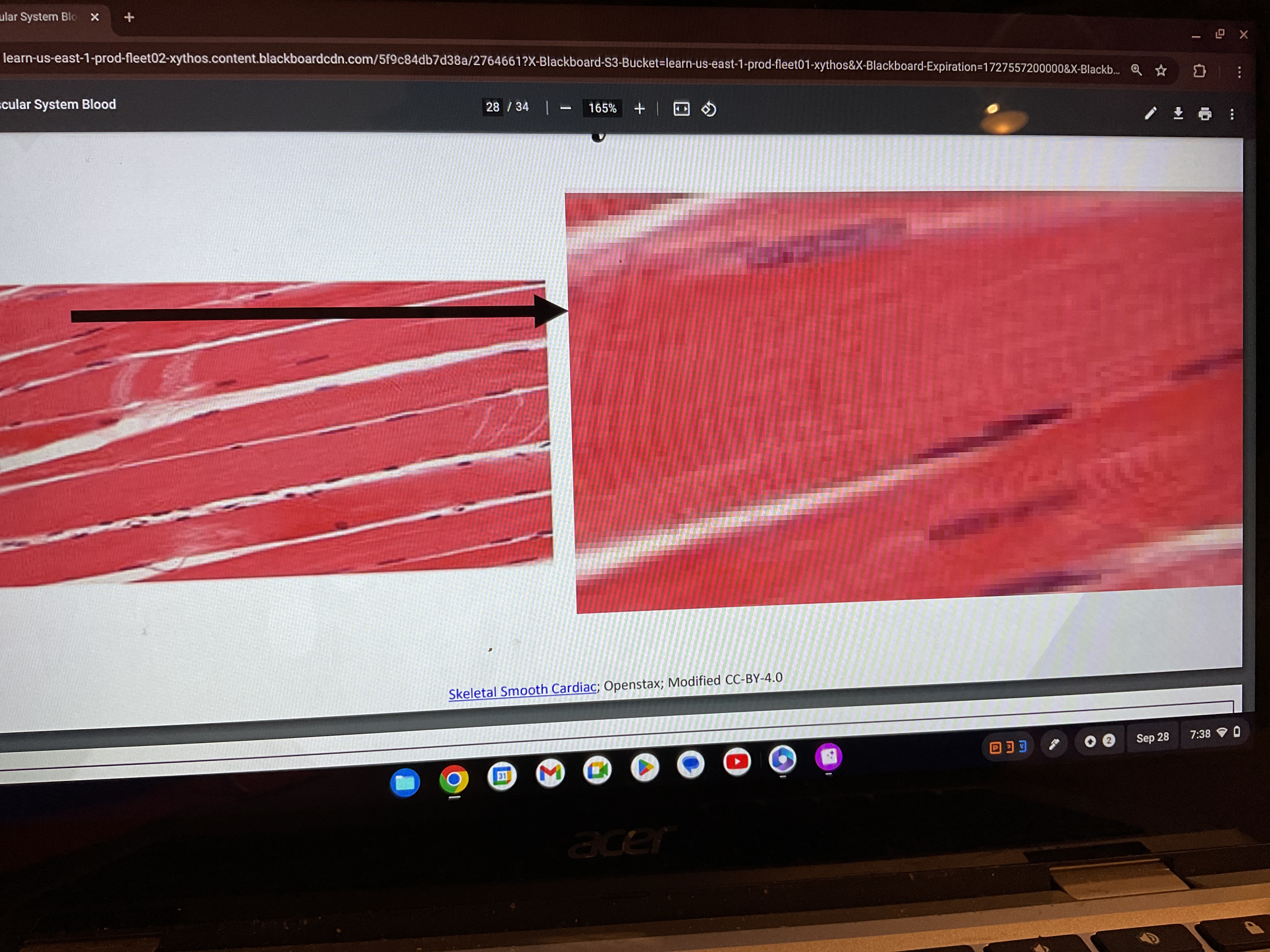
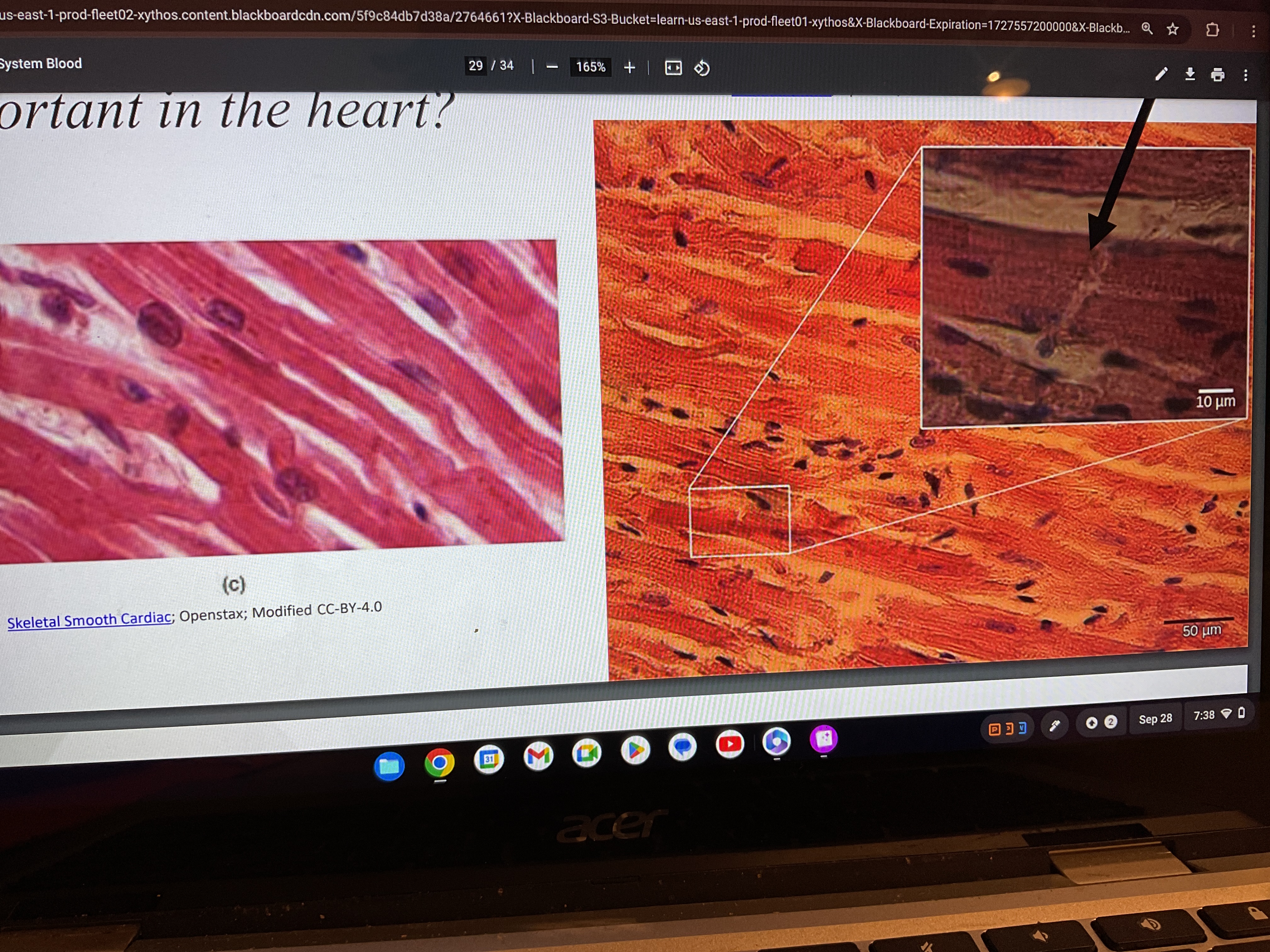
Cardiac muscle
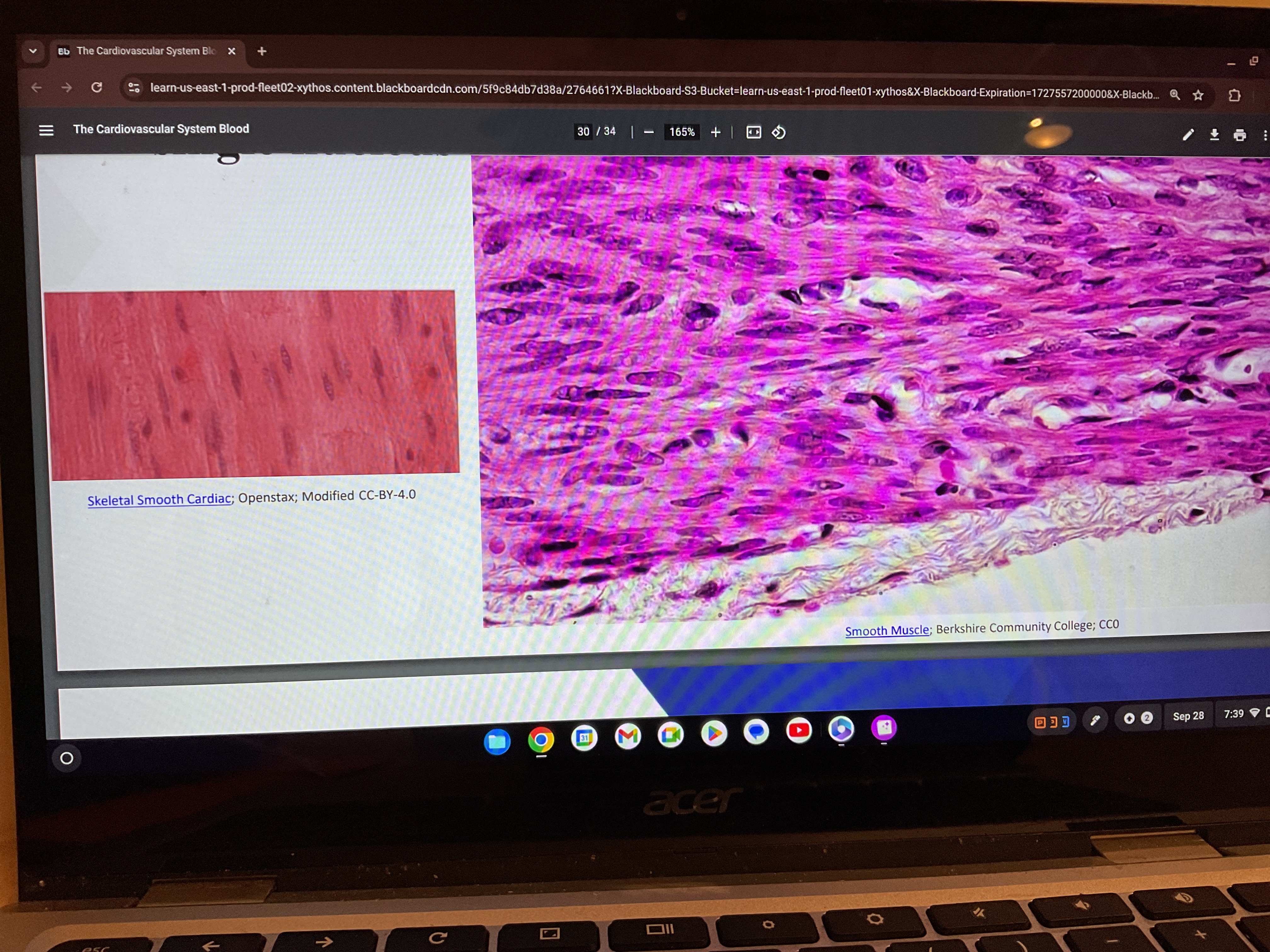
Smooth muscle
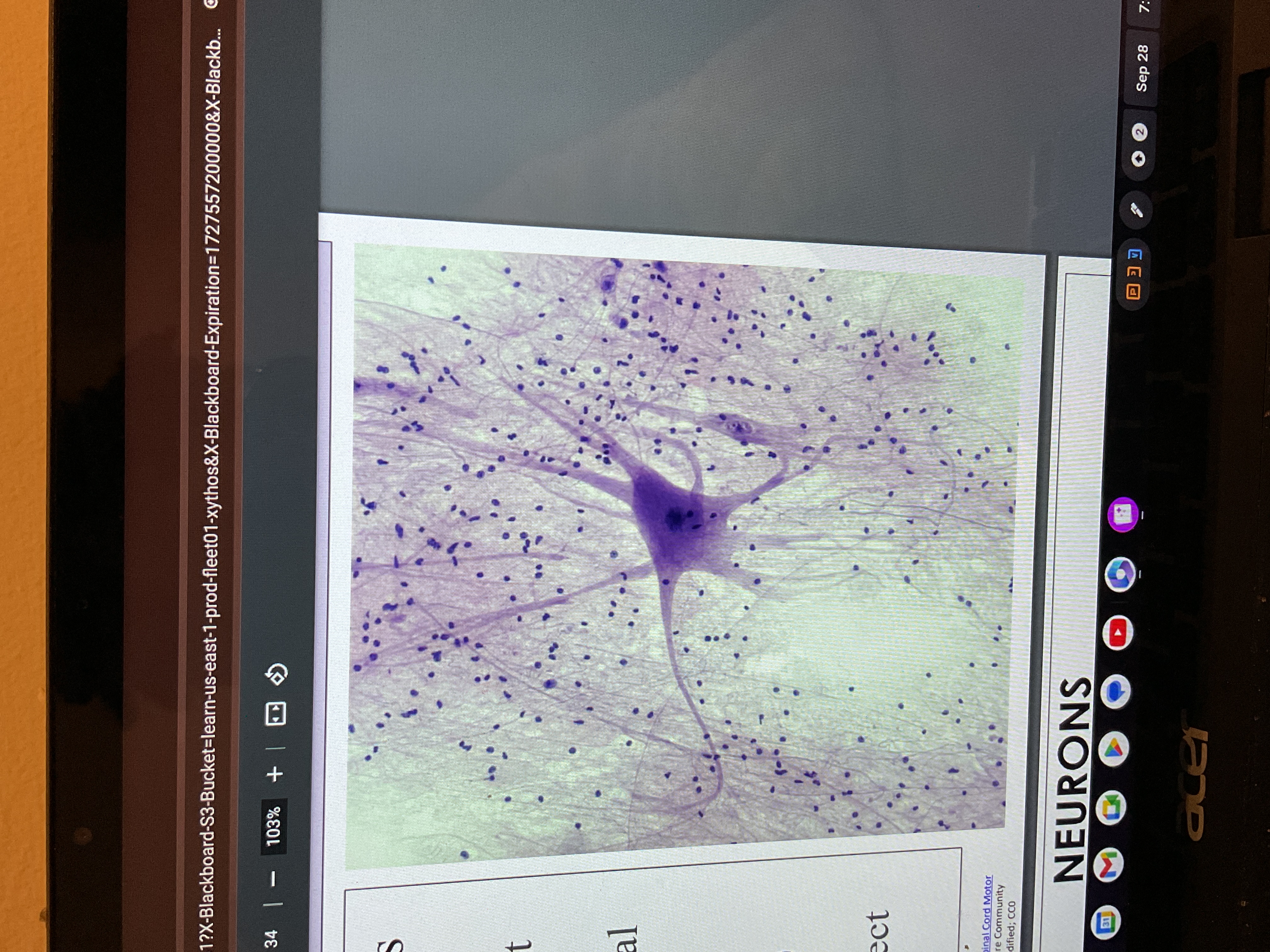
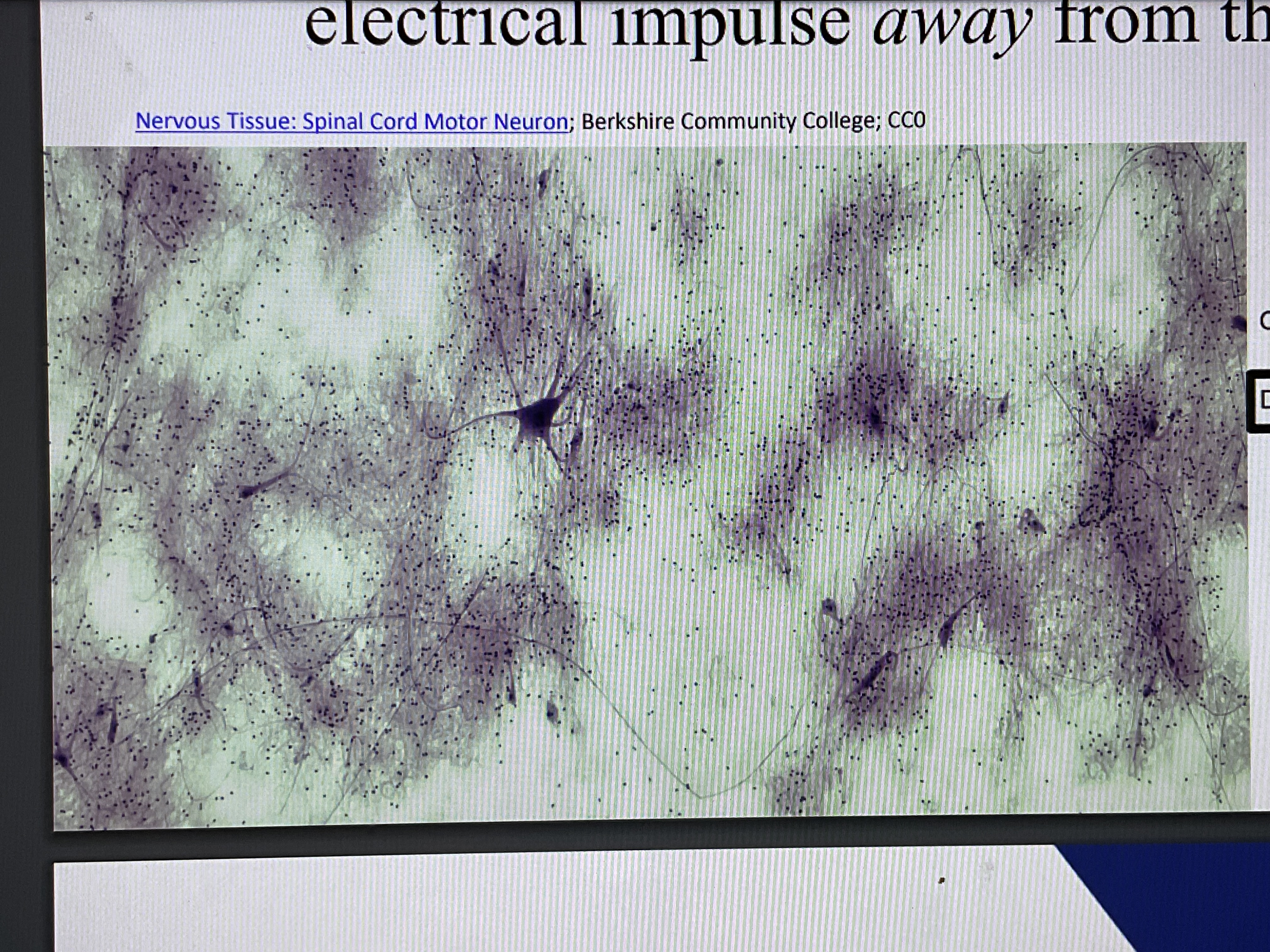
Nervous tissues
Made up of two type of cells neurons, and Neuroglia
Neurons
Where is simple squamous tissue found?
Lines heart, blood and lymphatic vessels, alveoli of the lungs
Where does stratified squamous tissue found?
skin, lines oral cavity, esophagus and vagina
Where does areolar tissue found
deep to the skin and surrounds nerves and organs
PSEUDOSTRATIFIED Found in the what
Lines airways of respiratory tract, lines glands and ducts
Dense regular tissue found in what
tendons and ligaments inner layer of the skin an sclera( the white outer layer of the eyes)
Cardiac muscle tissue found in what
Found in the walls of the heart only
What is the function of the adipocyte
Provide energy storage, insulation from extreme temperatures and cushioning around soft organs
What tissue are a vascular?
Tissues that like blood vessels in lymphatic system like knee, trachea, nose, and ear.
What are the three types of cartilage in? Where are they found?
Hyaline cartilage (found in the ends of bones at joint nose, and respiratory passages)
Elastic cartilage (found in the outer ear and epiglottis), and fibrocartilage( found in the outer ear and epiglottis)
Fibrocartilage( found in the intervertebral discs of the spine and the menisci)
What are the types of loose connective tissues
Areolar, recticular, and adipose tissues
What are the types of fluid connective tissues
Blood and lymph
What are cardiac muscle
A striated and involuntary
What are skeletal muscles
It is striated, multinucleated and voluntary
What are smooth muscle
It is nonstrated and involuntary
Dendrites
Short extensions of the cell body that receive the electrical impulse from the previous neuron.
Axon
Largest singular extension that transmit the electrical impulses away from the cell body.
What is the the function of simple, stratified, and transitional epithelium
Transitional ( allow tissue to expand and contract)
Simple( to regulate the passages of substances into underlying tissue
Stratified ( is to protect)
Why did we get the result of the effect of viscosity and the diffusion rate?
Because smaller molecules tends to diffuse faster than larger molecules
Why did we get the result of the effect of molecular size on the fusion rate?
Because smallest size of molecules, the higher is the rate of diffusion
Why did we get the result of the effect of particle size and diffusion rate?
Because smaller particle diffuse faster in large particles
Why did we get the result that we did on osmosis?
Because it maintain the turgidity of cell
Why did we get the result that we did on tonicity
Because if you place a cell in a hypotonic solution, water will leave the cell in the cell will shrink