Physics - Electricity and magnetism
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
Describe the forces between magnetic poles
Explain that magnetic forces are due to interactions between magnetic fields
2
New cards
Describe the forces between magnets and magnetic materials
3
New cards
Describe induced magnetism
Induced magnetism is the temporary magnetism that occurs in a material when it is brought near a magnet or when a magnetic field is applied to it. This magnetism is not inherent to the material and disappears once the external magnetic field is removed.
It is caused by the alignment of the material's atomic or molecular magnetic moments in response to the external magnetic field.
It is caused by the alignment of the material's atomic or molecular magnetic moments in response to the external magnetic field.
4
New cards
Describe methods of magnetization
* By stroking
* Placing solenoid inside a coil of wire with d.c
* Placing solenoid inside a coil of wire with d.c
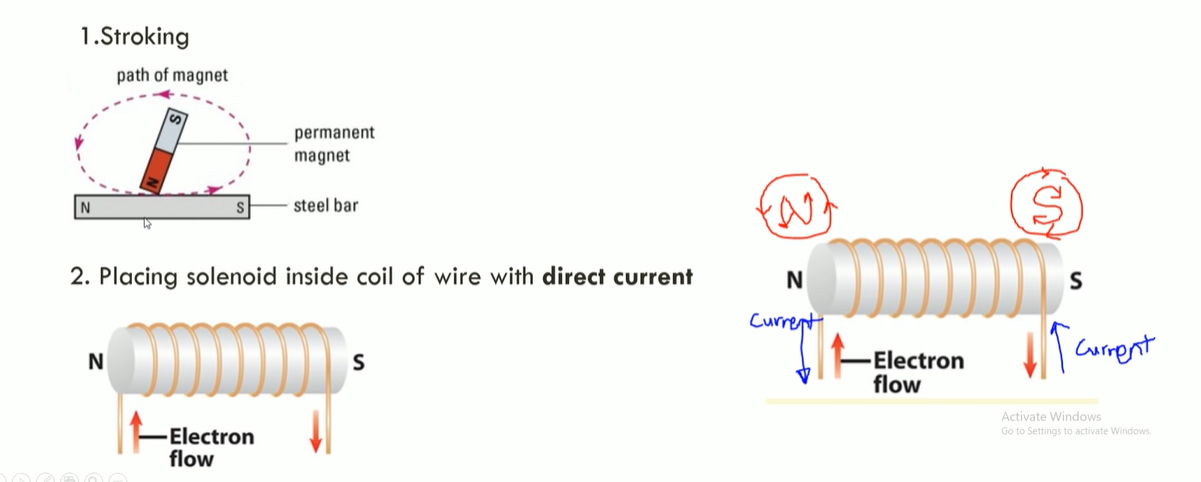
5
New cards
State the difference between magnetic and nonmagnetic materials
6
New cards
State the differences between the properties of temporary magnets and permanent magnets
Temporary magnets and permanent magnets have distinct properties:
1. **Magnetization:** Temporary magnets can be magnetized and demagnetized easily, while permanent magnets retain their magnetization over a long period.
2. **Source of Magnetism:** Temporary magnets are usually made from soft magnetic materials, such as iron or steel, which can be easily magnetized. Permanent magnets are made from hard magnetic materials, like neodymium or ferrite, which have strong intrinsic magnetism.
3. **Strength of Magnetism:** Permanent magnets have a stronger magnetic field compared to temporary magnets. This allows them to attract or repel other magnets with greater force.
4. **Durability:** Temporary magnets can lose their magnetism quickly when the external magnetic field is removed. Permanent magnets, on the other hand, retain their magnetism for a longer time, making them more durable.
5. **Applications:** Temporary magnets are commonly used in applications where magnetism is required temporarily, such as electromagnets in electric bells or relays. Permanent magnets find applications in various devices like speakers, motors, and generators.
It's important to note that these are general differences, and specific types of magnets may have additional or unique properties.
1. **Magnetization:** Temporary magnets can be magnetized and demagnetized easily, while permanent magnets retain their magnetization over a long period.
2. **Source of Magnetism:** Temporary magnets are usually made from soft magnetic materials, such as iron or steel, which can be easily magnetized. Permanent magnets are made from hard magnetic materials, like neodymium or ferrite, which have strong intrinsic magnetism.
3. **Strength of Magnetism:** Permanent magnets have a stronger magnetic field compared to temporary magnets. This allows them to attract or repel other magnets with greater force.
4. **Durability:** Temporary magnets can lose their magnetism quickly when the external magnetic field is removed. Permanent magnets, on the other hand, retain their magnetism for a longer time, making them more durable.
5. **Applications:** Temporary magnets are commonly used in applications where magnetism is required temporarily, such as electromagnets in electric bells or relays. Permanent magnets find applications in various devices like speakers, motors, and generators.
It's important to note that these are general differences, and specific types of magnets may have additional or unique properties.
7
New cards
magnetic field
region in which a magnetic pole experiences a force
the direction of a magnetic field at a point is the direction of the force on the N pole of a magnet at that point
the direction of a magnetic field at a point is the direction of the force on the N pole of a magnet at that point
8
New cards
Draw the pattern and direction of magnetic field lines around a bar magnet
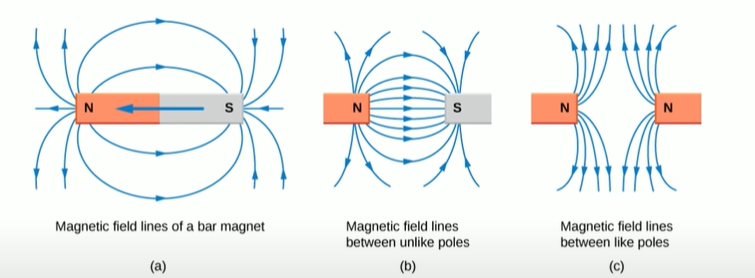
9
New cards
Describe the uses of permanent magnets and electromagnets
10
New cards
Charge
* positive and negative charges
* positive charges attract negative charges
* measured in coulombs
* electric field as a region in which an electric charge experiences a force
* positive charges attract negative charges
* measured in coulombs
* electric field as a region in which an electric charge experiences a force
11
New cards
Describe simple experiments to show the production of electrostatic charges
by friction and to show the detection of electrostatic charges
12
New cards
Explain that charging of solids by friction…….
involves only a transfer of negative charge (electrons)
13
New cards
Describe an experiment to distinguish between electrical conductors and insulators
14
New cards
Recall and use a simple electron model to explain the difference between electrical conductors and insulators and give typical examples
15
New cards
electric current
the charge passing a point per unit time; recall and use the equation
I = Q / t
I = Q / t
16
New cards
Describe the use of ammeters (analogue and digital) with different ranges
17
New cards
Know the difference between direct current (d.c.) and alternating current (a.c.)
18
New cards
Define electromotive force
the electrical work done by a source in moving a unit charge around a complete circuit
measured in volts (V)
E = W/Q
measured in volts (V)
E = W/Q
19
New cards
Define potential difference (p.d.)
* the work done by a unit charge passing through a component
* p.d. between two points is measured in volts (V)
* V = W/Q
* p.d. between two points is measured in volts (V)
* V = W/Q
20
New cards
Describe the use of voltmeters (analogue and digital) with different ranges
21
New cards
Resistance
R = V/I
a) resistance is directly proportional to length
(b) resistance is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area
a) resistance is directly proportional to length
(b) resistance is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area
22
New cards
Recall and use the equation for electrical power
P = IV
23
New cards
Recall and use the equation for electrical energy
E = IVt
24
New cards
Define the kilowatt-hour (kWh) and calculate the cost of using electrical appliances where the energy unit is the kWh
25
New cards
Series vs Parallel

26
New cards
State the advantages of connecting lamps in parallel in a lighting circuit
27
New cards
Explain that the sum of the currents into a junction is the…….
same as the sum of the currents out of the junction
28
New cards
Describe the action of a variable potential divider
