exam 3- advanced covalent bonding
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
valence bond theory
covalent bonding is the overlap of half-filled atomic orbitals that yield a pair of electrons shared between two bonded atoms.
whats creates stronger bonds
The better/greater the overlap or alignment of atomic orbitals, the stronger the covalent bond.
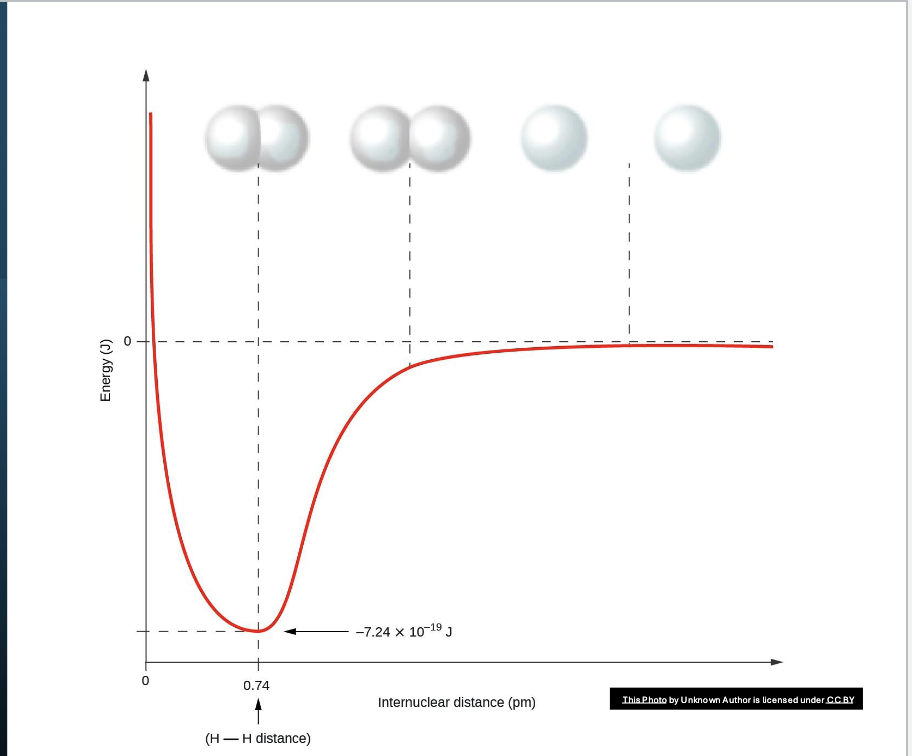
The lowest possible energy is called the ideal internuclear distance; this will be the bond length for a given molecule. The decrease in energy is because the electrons are interacting with the protons in both atoms, stabilizing the bond.
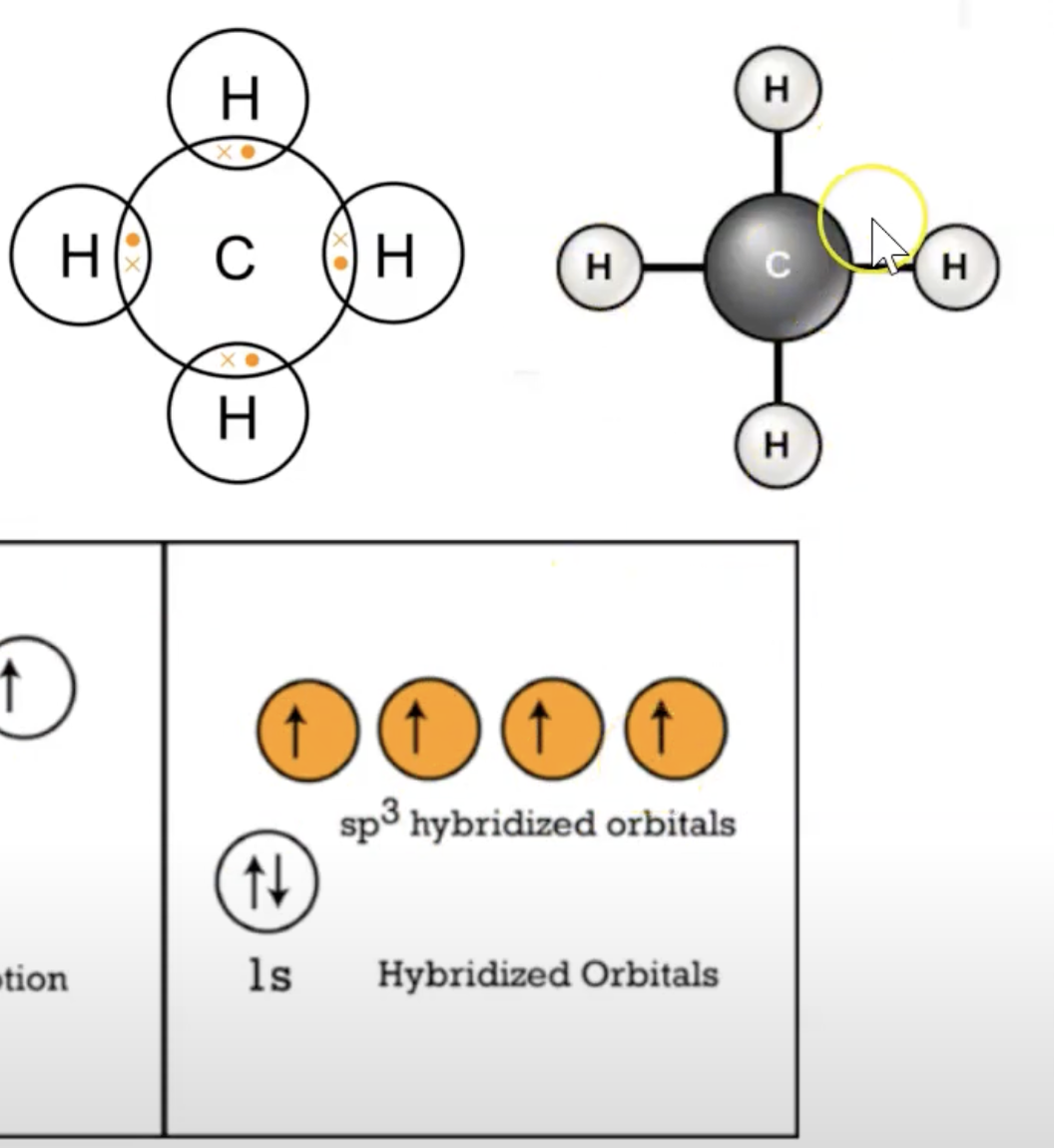
sp3 hybridized orbital blending
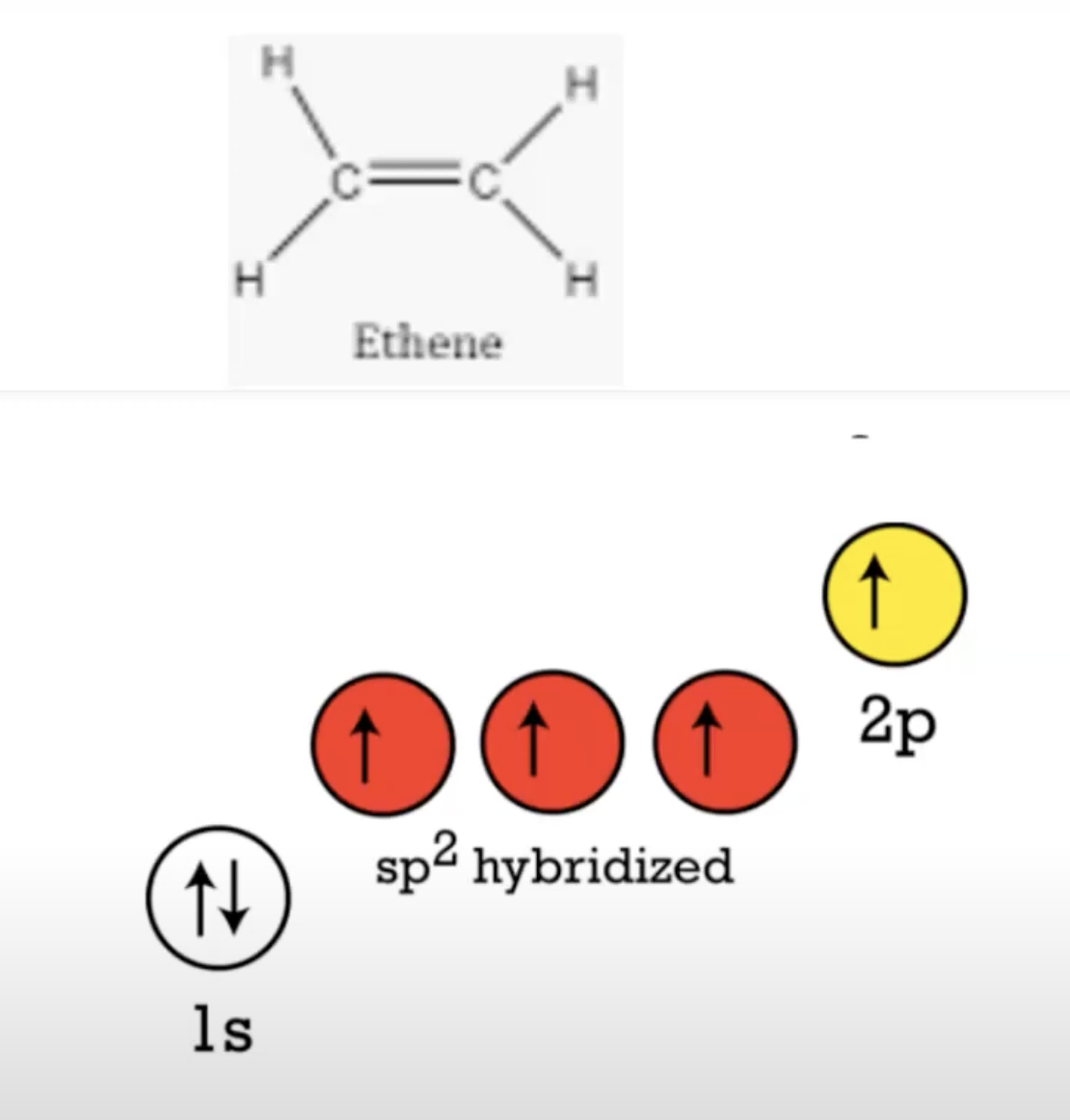
sp2 hybridized orbital blending

sp hybridized orbital blending
how i can decide the hybridized levels based on looking at a lewis structure
count sigma bonds, those belong in sp(2/3) orbtal, then put the left over pi bonds in the 2p orbital
paramagnetic
substance that is attracted to an inducing magnetic field due to unpaired electrons.
diamagnetic
substance that is repelled by an inducing magnetic field due to all electrons being paired.
bond order from a molecular orbital
Bonding electrons - antibonding electrons / 2.
atomic orbitals mix to form…
molecular orbitals
orbitals that have constructive interference of waves are…
bonding (lower on diagram)
orbitals that have destructive interference of waves are…
antibonding (higher on diagram)
As bond order increases
stability increases, energy decreases, bond length decreases
Whats the relationship between energy and stability?
inversely proportional