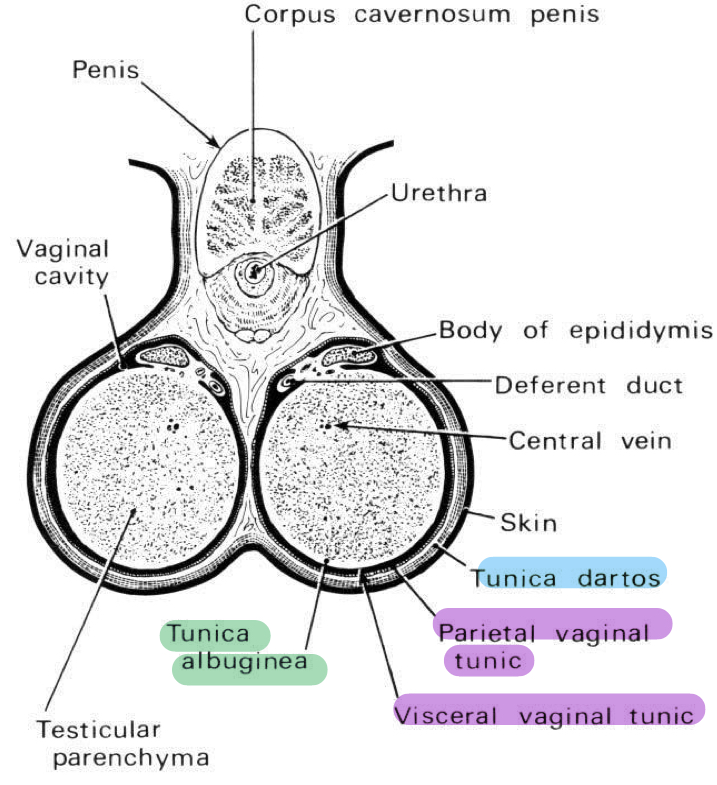
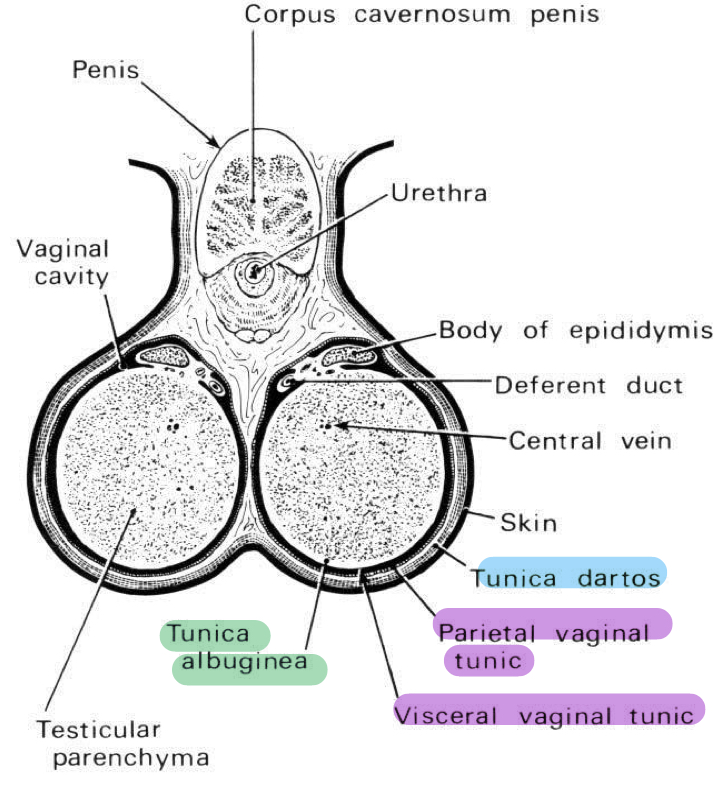
Scrotum
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Relation of scrotum and testes
Testes lie within the scrotum by tunica darto
What is tunica darto?
Thin layer of smooth muscle that extends as septum dividing scrotum into left and right
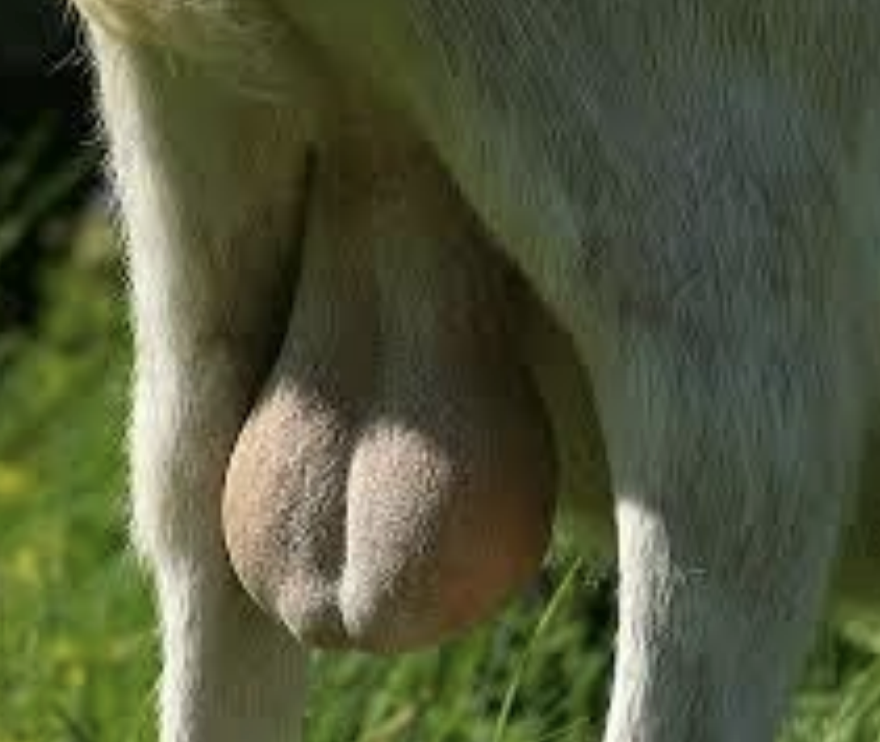
What is the scrotum?
Pouch of skin that is between the groin and perineum
What does the scrotum contain?
Sweat and sebaceous glands
What divides the scrotum into left and right?
Median groove
What is the function of scrotum?
For protection and thermoregulation
What are the layers of the scrotum?
Tunica dartos
Tunica vaginalis
Tunica albuginea
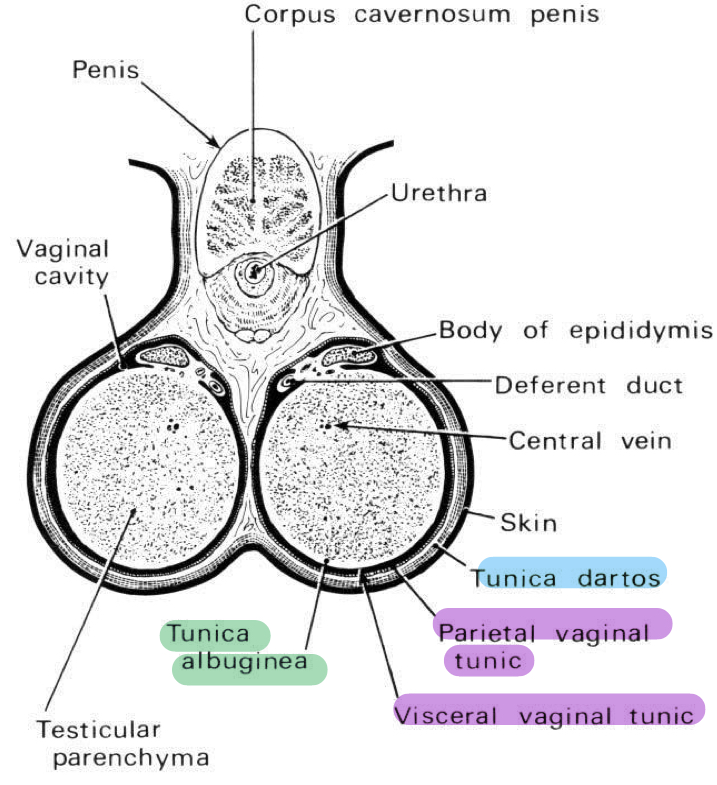
Tunica Vaginalis
What
Function
Continuation of
Visceral part attaches to
Parietal part attaches to
Cavity contains
What: Peritoneal process
Function: Envelope the testes
Continuation from: Invagination of the abdominal lining through inguinal ring
Visceral part attaches to: Testes
Parietal part attaches to: Tunica daros or scrotum
Cavity contains: Serous fluid
Tunica Albuginea
Location
Forming
Has
Location: Invaginate into parenchyma
Forming: A septa converge at the mediastinum
Has:
Capsule (aka tunica vasculosa)
Blood vessels
Testes also suspended by
Spermatic cord that attaches to epididymis
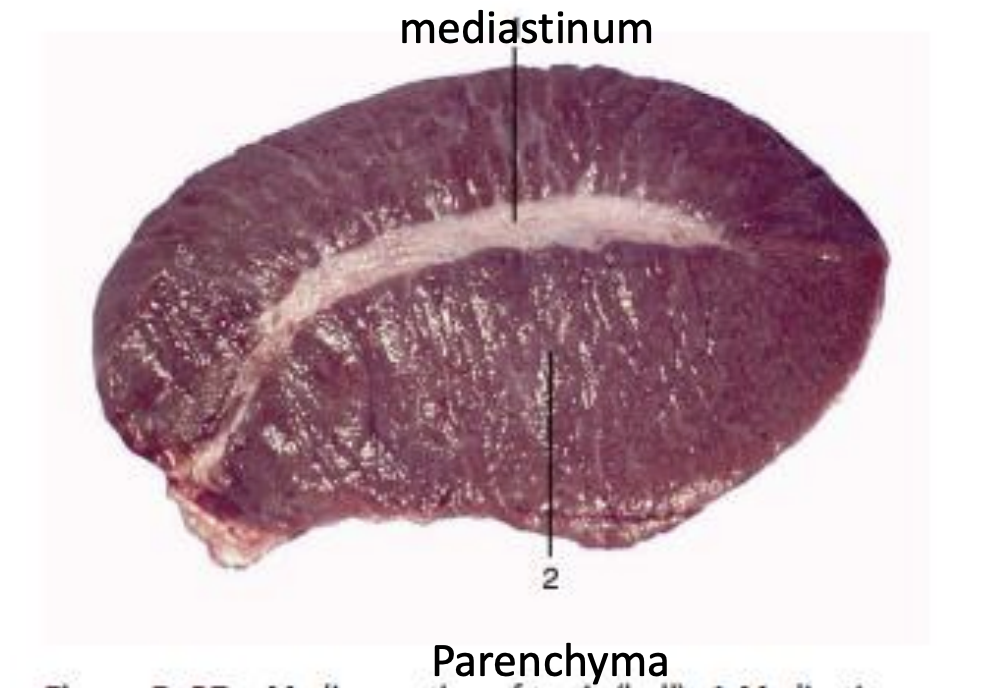
General Structure
What is the parenchyma like
What is the mediastinum testis
Location
Contains
What are the main components of interstitial compartment
What do Leydig cells produce
What is the parenchyma like: Soft, brownish tissue that forms main body of testis
What is the mediastinum testis:
Location: Connective tissue structure located at the center
Contains: Rete testis and blood vessels
What are the main components of interstitial compartment: Leydig cells, blood vessels and lymph vessels
What do Leydig cells produce: Androgens and testosterone
Seminiferous Tubules
Main components
Function of Sertoli cells
What are the two compartments
Main components:
Basement membrane
Sertoli cells
Spermatogenic cells
Function of Sertoli cells: Nourish germ cells and produce hormones and growth factors
What are the two compartments:
Basal compartment (before tight junction, compose mainly spermatogonia)
Abluminal compartment (after tight junction, consist of differeniating germ cells
Blood Testis Barrier
What forms it
Function
Formed by: Tight junctions between adjacent Sertoli cells
Function: Prevent haploid post meiotic germ cells from immune attach
How does seminiferous tubule connect to epididymis?
Seminiferous tubules →
Straight tubules →
Rete testis (in the mediastinum) →
Efferent ducts →
Epididymis
What happens to seminiferous tubules as they approach the mediastinum?
Become straightened and form rete testis
What do rete testis continue as
Efferent ducts that enter the epididymis
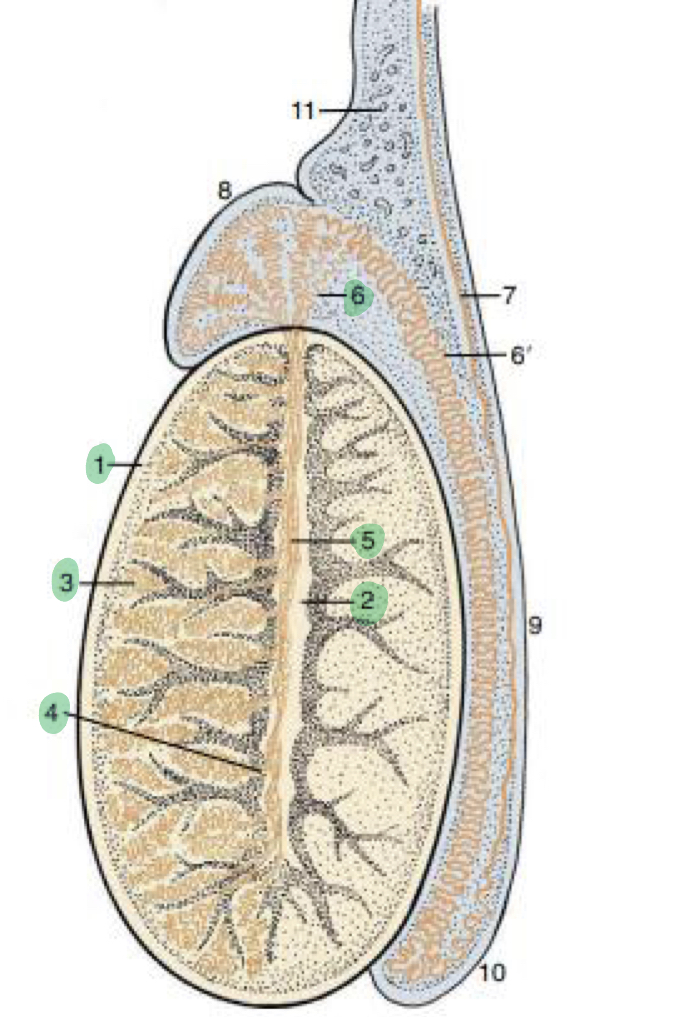
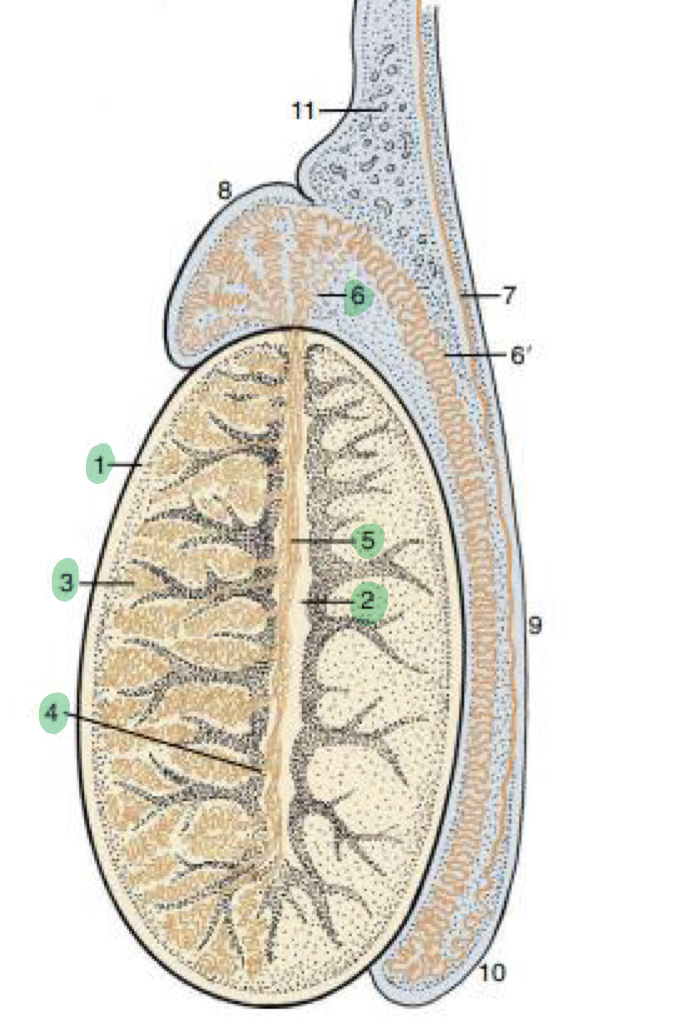
Label 1-6
Tunica albuginea
Mediastinum
Seminiferous tubules
Straight tubules
Rete testis
Ductus efferent