Sociology 101 - Quiz 1
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
Sociology
The study of human society
Assumptions of Sociology
we are not independent because of the social influences
we are driven by change
we have agency because we can influence the world but constrained by social structures
Sociology Vs Psychology
Sociology: looks at society and how it affects the individual
psychology: looks at how the mind is affected
Sociological Imagination
The ability to connect the most basic, intimate aspects of an individual’s life to seemingly impersonal and remote historical forces. (6)
This is when you try to connect oneself to the grater society and connect individuals at the societal level
Example of Sociological Imagination
“im so bad at this job, im going to loose this” ← Not sociological imagination because you are just thinking about yourself
“the company is downsizing, im going to loose this job” ← Sociological imagination because you are now including the company into why you are losing the job
Sociological Imagination Way
Questioning everything
Take Notes
Identify Patter
Thinking Critically
Repeate
Society
a group of people that are bound together by similar cultures and values and they interact together to form a community
Social Institution
A complex group of interdependent positions that, together, perform a social role and reproduce themselves over time; also defined in a narrow sense as any institution in a society that works to shape the behavior of the groups or people within it. (17)
Sociologist
identify
explain patterns
how members and societies function and are organized in the present as well as how they evolve over time
develop theories
allows for them to make statements about the world
Two theories
Positivist Sociology Vs Interpretive Sociology
Positivists
The approach to sociology that emphasizes the scientific method as an approach to studying the objectively observable behavior of individuals irrespective of the meanings those actions have for the subjects themselves. (20)
General theories
they use scientific method to compare other sciences to sociology
constrained by social structures
believe that the laws constrain the individual
one objective truth
Positivist Sociology
The approach to sociology that emphasizes the scientific method as an approach to studying the objectively observable behavior of individuals irrespective of the meanings of those actions for the subjects themselves. (28)
Verstehen
German for “understanding.” The concept of Verstehen comes from Max Weber and is the basis of interpretive sociology. (27)
Interpretive Sociology
A type of sociology in which researchers imagine themselves experiencing the life positions of the social actors they want to understand rather than treating those people as objects to be examined. (28)
they do not have general rules that apply everywhere. Smaller theories that explain small phenomenon at the local level.
construct meaning of their objective reality
there is a social construct
society is made up of many ideas but these ideas are shared by many people
what you observe might be different from what you observe from someone else
anomie
A sense of aimlessness or despair that arises when we can no longer reasonably expect life to be predictable; too little social regulation; normlessness. (28)
Paradigms
Functionalism
Conflict Theory
Symbolic Interaction
Functionalistm
various institutions social institutions and processes in society exist to serve and keep necessary functions to keep society running.
they look at the world like positivists
view it as a system
they want social integration
there is no social change needed, everything is perfect
3 Functions of Functionalists
manifest function
latent
dysfunction
manifest function
intended use
ex) schools: to teach and learn
Latent
unintended use
ex) school: making friends
disfunction
negative outcomes of social actions
ex) schools: bullying
social integration
the degree to which people are tied to their social groups and untied by shared values and other social bonds
strong culture that is shared by everyone
limitations of functionalists
conservatism: functionalism is conservatively biased
social change: they see social change as negative and that society will unstable and not have any order
Conflict Theory
Believe that society is characterized by various inequalities and conflicts that arise due to differences in power, resources, and social status.
notices that there is social inequality
believe that society is working well, but not for everyone
they believe that they need a conflict to solve this problem to benefit everyone
3 types of Conflict Theory
Marxist Theory
Feminist theory
Critical Race Theory
Marxist Theory
bourgeoisie tend to hold and maintain control of the majority of resources
believes that there are 2 social classes
bourgeoisie have the money and they can control industry and proletariat while proletariat is here to work and use the means of production
Feminist Theory
Men tend to hold and maintain control over the majority of resources and power
gender factor
Critical Race Theory
White Men tend to hold and maintain control over the power
Limitations of Critical Theory
Assumes all cooperation
Rigid Dichotomies
Rigid Dichotomies
Dividing the world into ONLY two groups
lacks nuance when it comes to the theory
“saying they have to follow the group” this gives not much agency
Symbolic Interactionamism
A micro-level theory in which shared meanings, orientations, and assumptions form the basic motivations behind people’s actions. (33)
the theory that social reality is constructed in each human interaction through the use of symbols
the world is shaped by culture, social, and historical
ex) when one sees a dog, they might see it in a different meaning than another person
this theory gives more authority to the individual person
Goal: to uncover the reason why people interact the way that they do
impression management
impression management
a person influencing another person’s interpretation of a person, place or thing by controlling the information they receive
ex) the government controlling
Limitations for Symbolic Interationalism
Cannot generalize to the whole population, but only a certain group of people
lack the focus of power dynamics
WEB Du Bois
Double Conscious Theory
writes The Souls of Black Folk
The Double Conscious Theory
Black people developed a double consciousness due to their marginalization → one as a black person and one as an American
this is a theory of how racism ingrained in social structures impacts individuals’ senes of self and their interactions
Postmodernism
A condition characterized by the questioning of the notion of progress and history, the replacement of narrative with pastiche (i.e., a collage of existing ideas) or imitation of other work in the service of satire or subversion, and multiple, perhaps even conflicting, identities resulting from unconnected affiliations. (34)
Social Construct
An entity that exists because people behave as if it exists and whose existence is perpetuated as people and social institutions act in accordance with widely agreed-on formal rules or informal norms of behavior associated with that entity. (35)
midrange theory
A theory that attempts to predict how certain social institutions tend to function. (36)
microsociology
A branch of sociology that seeks to understand local interactional contexts; its methods of choice are ethnographic, generally including participant observation and in-depth interviews. (44)
macro sociology
A branch of sociology generally concerned with social dynamics at a higher level of analysis—that is, across the breadth of society. (44)
Is Sociology a Science
Yes, because they use scientific method and collect data through empirical research and analysis
Empiricism
Sociologists’ Analyses rely on empirical evidence that is gather through observations or experiments
Scientific Knowledge
A body of facts, concepts, theories, and laws derived from systematic observations, experiments, and reasonings.
Functionalist and views on the Scientific Knowledge
They believe that scientific knowledge is crucial to fix the world because scientific knowledge is based on a systematic way of doing things
Critical Theorist and views on the Scientific Knowledge
scientific knowledge is something that they would use to control their power (the bourgeoisie)
Symbolic Interactionaist
Knowledge is a social construct
All knowledge is built on social interaction and the position you hold in society
When you interact with new people, you will gain new knowledge
Objective Knowledge
Known fact that cannot be debated
Subjective Knowledge
knowledge that is bias based on your feelings
Are Social Science less objective than Natural Science
No,
Natural sciences are influenced by the social context in which scientists operate
natural sciences are also conducted by scientists who occupy specific social positions, which can influence their perspective
Researchers are studying aspects of the very societies they are part of, which can make maintaining objectivity more difficult
Reflexivity
allows for scientists to reflect on who they are and what the society influences on them
Question they might ask themselves: how am I affecting the people I am studying?
Guidelines and Ethics of Social Research
Informed consent
voluntary participation
confidentiality
anonymity
minimizing harm
Institutional Review Board
Committee that reviews research studies involving human subjects to ensure that they are ethical and comply with regulations
Different Methodological Approaches
Deductive vs Inductive
Deductive
Start with hypothesis and use data to show that hypothesis is proven
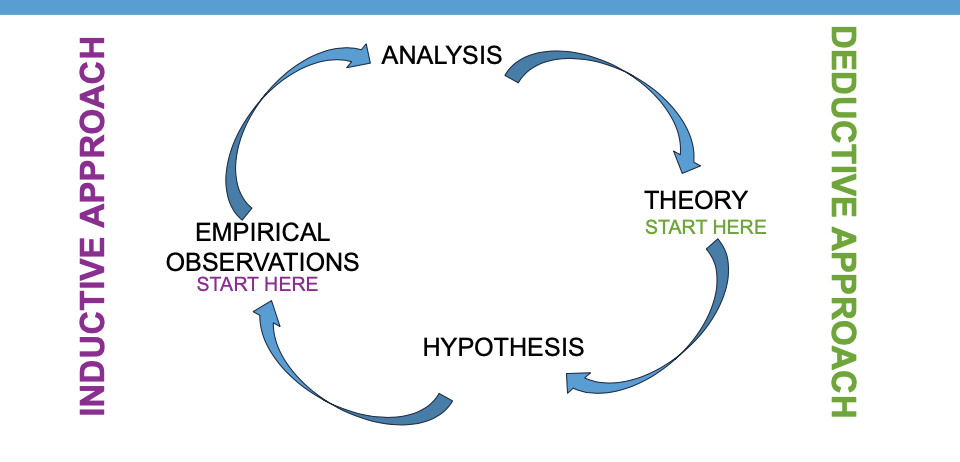
Advantage of Deductive
you can start with other people’ theories and it will guide you to proving your point
inductive
Start with observation and data sets and find surprising results
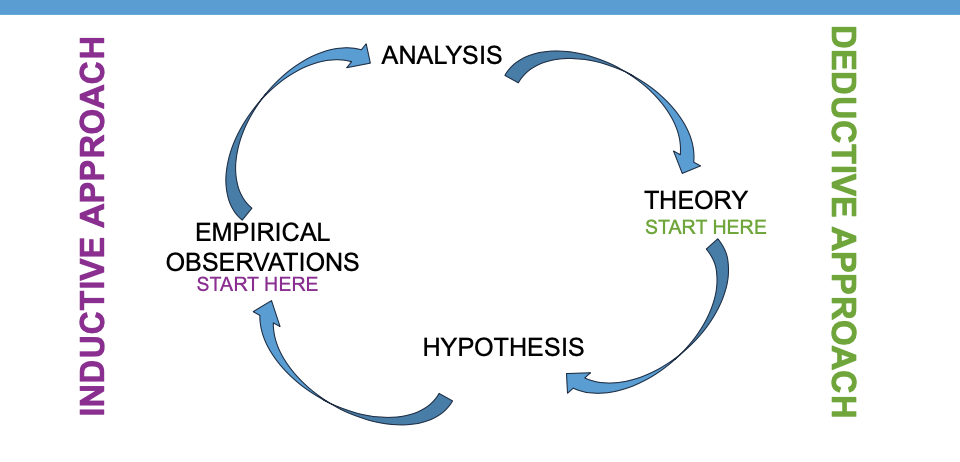
advantage to inductive
You can study something that has never been studied before
Quantitative Research
a research approach that uses numerical data
Qualitative
research methods that are used to gather information that cant be expressed numerically
Structured interviews
followed a strict set of predetermined questions
semi-structured
include predetermined questions, but can go off topic and allows for flexibility
advantage: allows for comparison of everyone’s data to be easier
unstructured interview
free flowing conversation about one topic
advantage: giving you more answers to things you weren’t thinking about before
goal of research
identify a casual relationship between 2 social elements
ethnography
A qualitative method of studying people or a social setting that uses observation, interaction, and sometimes formal interviewing to Document behaviors, customs, experiences, social ties, and so on. (50)
Scientific method
a procedure involving the formulation, testing, and modification of hypotheses based on systematic observation, measurement, and/or experiments. (51)
theory
An abstracted, systematic model of how some aspect of the world works. (51)
casual relationship
The idea that one factor influences another through a chain of events; such a dynamic is different from two factors being merely associated or correlated, in which case they may appear to vary together but that could be due to chance or a third factor causing both. (52)
natural experiment
Something that takes place in the world that affects people in a way that is unrelated to any other pre-existing factors or their characteristics, Thereby approximating random assignment to treatment or control groups. (54)
causality
The notion that a change in one factor results in a corresponding change in another. (55)
reverse causality
A situation in which the researcher believes that A results in a change in B, but B, in fact, is causing A. (56)
dependent variable
The outcome the researcher is trying to explain. (56)
independent variable
A measured factor that the researcher believes has a causal impact on the dependent variable. (56)
hypothesis
a observation that is testable
A proposed relationship between two variables, usually with a stated direction. (57)
operationalization
How a concept gets defined and measured in a given study. (57)
white coat effect
The phenomenon wherein a researcher’s presence affects her subjects’ behavior or response, thereby disrupting the study. (59)
feminist methodology
A set of systems or methods that treat women’s experiences as legitimate Empirical and theoretical resources, that promote social science for women (think public sociology, but for a specific half of the public), and that take into account the researcher as much as the overt subject matter. (62)
participant observation
A qualitative research method that seeks to uncover the meanings people give their social actions by observing their behavior in practice. (65)
population within a experiment
An entire group of individual persons, objects, or items from which samples may be drawn. (68)
historical methods
Research that collects data written from reports, newspaper articles, journals, transcripts, television programs, diaries, artwork, and other artifacts that date back to the period under study. (70)
comparative research
A methodology by which two or more entities (such as countries), which are similar in many dimensions but differ on one in question, are compared to learn about the dimension that differs between them. (71)
content analysis
A systematic analysis of the content rather than the structure of a communication, such as a written work, speech, or film. (71)
Stereotypes
exaggerated idea of a culture
Culture
The sum of the social categories and concepts we embrace in addition to beliefs, behaviors (except institutional ones), and Practices; everything but the natural environment around us. (84); Entirety of a society’s way of life
culture is hard to recognize
Two Types of Cultural Norms
Nonmaterial Culture vs Material Culture
these concepts can overlap
ex) a table can carry meaning that is only used to study
Nonmaterial
everything that is not tangible
material culture
anything that is tangible
Values
Moral Beliefs. (96); culture‘s standards for discerning what is good and just in society
these are generally accepted ideas
Norms
How values tell us to behave. (96); general accepted behavior
values effect norms
two types of norms
formal vs informal
formal norm
one that is written down like a piece of legislation
informal norm
unspoken rules
culture shock
feeling of confusion and shock in a culture
Culture Relativism
Taking into account the differences across cultures without passing judgment or value. (92); invites another culture without comparing what you observe to your own cultural less judgmental way
as sociologist we should not assume
Limitation to Culture Relativism
no sociologist can turn their brain off and they always bring their beliefs wherever they observe something
Ethnocentrism
The belief that one’s own culture or group is superior to others, and the tendency to view all other cultures from the perspective of one’s own. (86); when you look at things only through your own lens
judging culture based on what you think is right because of the culture that you were used to growing up
Cultural Imperialism
the practice that powerful culture and society will impose its values and practices and beliefs onto less powerful societies
Franchises - in the sense of cultural imperialism
Franchises can be considered cultural imperialism because the companies originate from one culture that is being implanted on other cultures
Media - in the eyes of cultural imperialism
Specific US shows contribute to specific values which can change and control the cultures that are in the other countries
Two theories in Cultural Imperialism
Reflection Theory vs Media Effect Theory
they are both soft power
Reflection Theory
The idea that culture is a projection of social structures and relationships into the public sphere, a screen onto which the film of the underlying reality of social structures of a society is projected. (97); culture reflects the social life and reality