Cornea Disease
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
OD2 Winter
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Functions of the tear film
Refractive qualities
Comfort and lubrication
Oxygen supply
Immunity
Disposal
What’s the difference between DEWS I (2007) and DEWS II (2017) ?
DEWS I: Initial report describing dry eye as a disease
DEWS II:
Newest definition of dry eye
Multifactorial nature of dry eye with a loss of homeostasis of tear film
Neurosensory abnormalities
Patient-centered approach
Most patients have a mix of aqueous deficient DED and evaporative DED
What are the different types of Dry Eye Disease?
Aqueous tear deficient
Evaporative
Exposure
Neurosenseory
Neurotrophic
Neuropathic
What’s the difference between neurotrophic vs. neuropathic?
Neurotrophic: Stain with no pain
Neuropathic: Pain with no stain
Psychopathic, why are you feeling pain with no stain?
If a patient has a true aqueous issue, what else should you ask about?
Sjrogren’s Syndrome
Symptoms: Dry eyes, dry mouth
Generally associated with rheumatologic disorder
Difficult to treat since glands are already destroyed
Known as lymphoma proliferative disease (likely to develop lymphoma - cancer of lymph nodes)
Commonly associated conditions with gland not producing tears?
Dry surfaces, problems with glands:
Medications (beta blockers, antihistamines - designed to dry surfaces)
Sjogren’s Syndrome
Rheumatologic/connective tissue disorder
Sarcoidosis - causes issues within gland tissues
HIV (+)
Graft vs. host disease
Familial dystautonomia
Xerophthalmia
Commonly associated conditions with ducts not transporting tears?
Problems with mucous membranes:
Mucous membrane pemphigoid - adhesions blocking flow
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Commonly associated conditions with insufficient hormonal stimulation
Tends to affect women more:
Menopause
Oral BC
Pregnancy
Androgen deficiency
Commonly associated conditions with insufficient neural stimulation
Problems with corneal sensitivity:
Neurotrophic keratitis: HZO, HS, Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Stroke
Radiation
Ocular surgery: LASIK, cataract extraction
What is the significance of Matric Metalloproteinases (MMP) in dry eye disease?
MMP are proteolytic enzymes produced by stressed epithelial cells on the ocular surface
In Tears:
Non specific inflammatory markers
Normal ranges (3-41 ng/ml)
High levels of MMP in ocular surface diseases like dry eyes
Corneal ulcers, erosions, keratitis, MGD, ocular rosacea, Sjogren’s syndrome
What is the first, second, & third line treatment of dry eyes? ( A Midterm Q)
First:
Artificial tears
Second:
Seborrheic blepharitis
Eyelid margin scrubs
Culture, than antibiotics
MGD
Warm compress
Mmega 3 supplements
oral low dose doxycycline
Third (for all types of dry eyes):
Topical Steroids (short tern) short-term
Immunomodulating medications (Cequea, Restasis)
What is the difference between the Fluorescein Dye Appearance Jones 1 and the Lacrimal Dilation and Irrigation Jones 2 Test?
Jones 1: Have the patient blow their nose onto a tissue and look at it with cobalt blue filter. To check if there is drainage of tears or is it blocked?
Jones 2: Irrigate with saline and ask if they can taste it. We’re trying to push out the blockage before testing for dye appearance again
Main differences between episcleritis and scleritis
Episcleritis: Doesn’t hurt
Blanches with 10% of 2.5% Neosynephrine or Phenylephrine
Scleritis: Painful
Blue Sclera
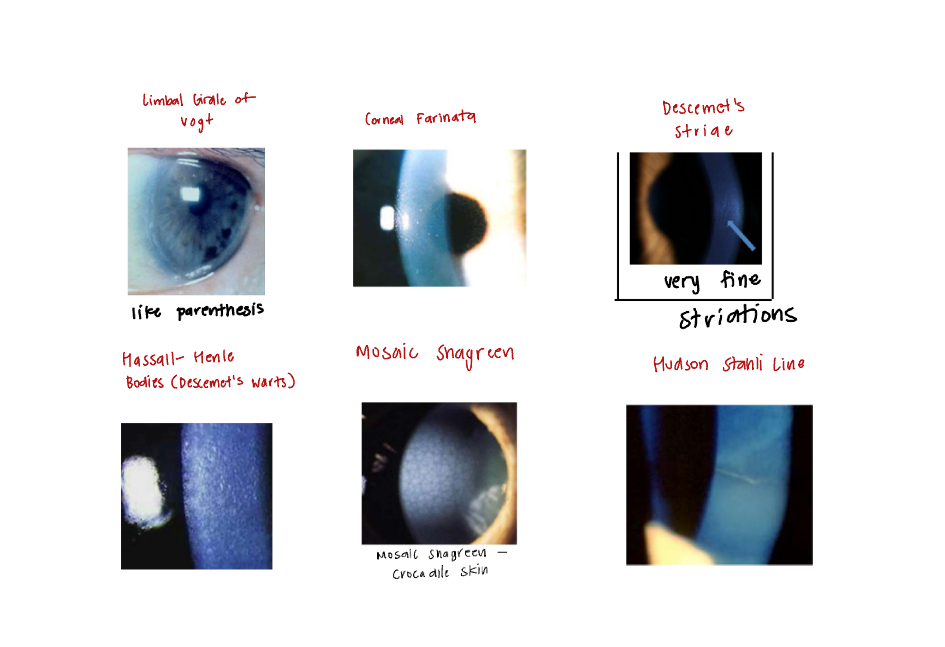
Corneal Involutional Degenerations (Due to Age):
Limbal Girdle of Vogt
Corneal Farinata
Descemet’s Striae
Hassal-Henle Bodies (Descemet’s “Warts”)
Mosaic Shagreen (crocodile skin)
Hudson Stahli Line
Generally asymptomatic and not visually significant
Limbal Girdle of Vogt:
Below epithelium at Bowman’s level
Looks like parenthesis
4th year said you have this
Corneal Farinata:
Flour dust deposits deep in the corneal stroma
Almost exclusively at the central interpalpebrel limba region
Normal endothelial “mosaic” underneath
Descemet’s Striae:
DDX: Vogt’s striae (vertical), Hobbes striae (horizontal)
Hassal-Henle Bodies (Descemet’s “Warts”):
Buildup of hyaline material on the endothelium
Mosaic Shagreen (crocodile skin):
Anterior: b/w Basal Epithelium and Bowman’s
Posterior: b/w Stroma and Descemet’s
Hudson Stahli Line:
Iron deposits on the lower 1/3 of the cornea
Corneal Degenerations (Related to something)
Corneal Arcus
Calcific Band Keratopathy
Dellen
Terriens Marginal Degeneration (Gutter Degeneration)
Salzmann’s Nodular Degeneration
Mooren’s Ulcer
Corneal Arcus:
Lipid deposit in stroma
Calcific Band Keratopathy
Calcific degeneration in Bowman’s layer
Dellen:
Near an elecation
Terriens Marginal Degeneration (Gutter Degeneration):
Superior peripheral corneal thinning, sub-epithelial degen
Salzmann’s Nodular Degeneration:
Hyaline plaques b/w Epithelium and Bowman’s membrane
Mooren’s Ulcer:
Marginal ulcer, autoimmune
