hi im gonna kms
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
a cell that completed the cell cycle without undergoing cytokinesis would:
have two nuclei
a correct comparison between a benign and a malignant tumour is that:
benign tumours do not metastasise; malignant tumours fo
a duplicated chromosome consists of two:
sister chromatids
a karyotype (a display of the chromosomes in a cell) is often used to look for genetic disorders. karyotype results would not be useful to determine:
eye colour
a promising new type of cancer treatment, immunotherapy, may involve all but one of these treatments
injecting molecules harvested from other cured cancer patients into the patient with cancer
a(n) ____ is an example of an organism that can sometimes reproduce asexually by parthenogenesis
zebra shark
anaphase II is essentially the same as mitotic anaphase except that in anaphase II ____ and in mitotic anaphase ____
the cells are haploid and sister chromatids separate; the cells have the same number of chromosomes as the original cell and sister chromatids separatea
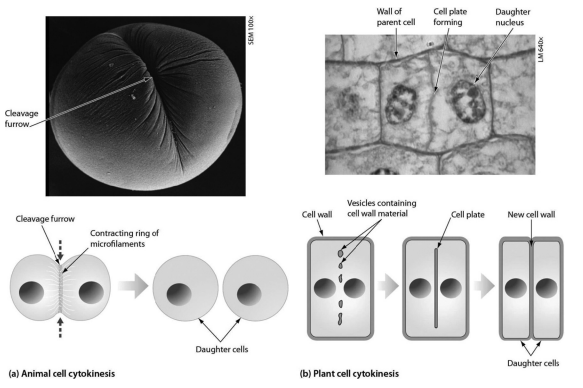
as shown in the accompanying figure, plant cell cytokinesis differs from animal cell cytokinesis because:
plant cells form a cell plate and animal cells do not
Bdelloid rotifiers appear to reproduce only asexually. which outcome, if found in this group, would demonstrate that sexual reproduction may occur?
cells in which meiosis occurs
chromatin consists of
DNA and protein
chromosomes that do NOT determine the sex of an individual are called
autosomes
consider an organism that usually reproduces sexually. if it produces haploid offspring through the development of unfertilised eggs, what would be the genetic similarity of those offspring to one another¡
if the eggs were products of meiosis, the offspring would NOT be genetically just alike
crossing over during prophase I results in
genetic recombination
cytokinesis typically begins during the ____ stage of mitosis
telophase
during anaphase I:
homologous chromosomes randomly separate and migrate to opposite poles
during metaphase I:
homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
during metaphse:
chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
during telophase:
the events of prophase are reversed
eukaryotic cells have their chromosomes packaged in the:
nucleus
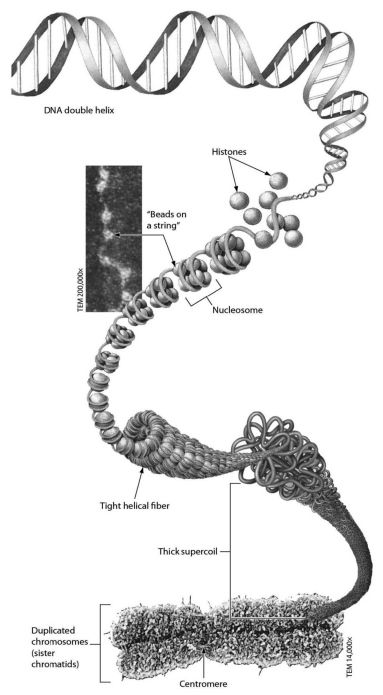
examine the figure below. nucleosomes are made of:
DNA and histone proteins
for a species with four pairs of chromosomes, ____ chromosomes combinations are possible
16
genetic variation is accomplished by all but one of the following:
the events of meisosis II
homologous chromosomes
carry genes controlling the same inherited characteristics
homologous chromosomes (pt2)
separate at meiosis I
how many chromosomes does an individual with turner syndrome have?
2n - 1
how much genetic material is present in a cell during prophase I compared to a cell that has completed meiosis II?
four times as much
if organisms reproduced sexually but without meiosis, what would the result?
the chromosome number would double each generation
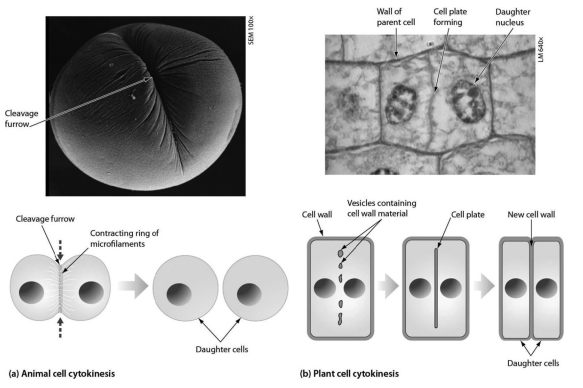
if the cleavage furrow or cell plate shown in the figure formed nearer one pole of the dividing cell rather than at the midline, what would be the predicted result??
the resulting cells would be very different in size
in meiosis how does prophase I differ from prophase II?
during prophase I there is one diploid cell, during prophase II there are two haploid cells
in sexual reproduction in humans:
haploid sperm fertilises a haploid egg
nondisjunction might result in gametes with the chromosome number:
n + 1 or n - 1
one difference between mistosis and meiosis is that mitosis:
produces cells genetically identical to the parent cell, but meiosis does not
amanda’s parents realised that her body was not developing properly about the time she was 12 years old. she was shorter than most of her friends and was not going through changes normally associated with female puberty. they took her to a doctor who initially diagnosed amanda with turner syndrome because of her physical features. the doctor ordered a karyotype that confirmed his diagnosis. amanda was born with only one X chromosome. although there is no specific cure, the doctor was able to treat her and correct some of the problems associated with the condition. for example, she received growth hormone to improve her growth and estrogen to help her develop the physical changes of puberty.
amanda’s abnormal number of sex chromosomes resulted from:
nondisjunction
amanda’s parents realised that her body was not developing properly about the time she was 12 years old. she was shorter than most of her friends and was not going through changes normally associated with female puberty. they took her to a doctor who initially diagnosed amanda with turner syndrome because of her physical features. the doctor ordered a karyotype that confirmed his diagnosis. amanda was born with only one X chromosome. although there is no specific cure, the doctor was able to treat her and correct some of the problems associated with the condition. for example, she received growth hormone to improve her growth and estrogen to help her develop the physical changes of puberty.
amanda would be designated as:
XO
amanda’s parents realised that her body was not developing properly about the time she was 12 years old. she was shorter than most of her friends and was not going through changes normally associated with female puberty. they took her to a doctor who initially diagnosed amanda with turner syndrome because of her physical features. the doctor ordered a karyotype that confirmed his diagnosis. amanda was born with only one X chromosome. although there is no specific cure, the doctor was able to treat her and correct some of the problems associated with the condition. for example, she received growth hormone to improve her growth and estrogen to help her develop the physical changes of puberty.
what percentage of amanda’s gametes would likely have the total number of chromosomes?
50%
amanda’s parents realised that her body was not developing properly about the time she was 12 years old. she was shorter than most of her friends and was not going through changes normally associated with female puberty. they took her to a doctor who initially diagnosed amanda with turner syndrome because of her physical features. the doctor ordered a karyotype that confirmed his diagnosis. amanda was born with only one X chromosome. although there is no specific cure, the doctor was able to treat her and correct some of the problems associated with the condition. for example, she received growth hormone to improve her growth and estrogen to help her develop the physical changes of puberty.
if the diagnosis had discovered that some, but not all, of amanda’s somatic (body, not gamete) cells had only one X chromosome, this could indicate that an error occurred:
during mitosis, which occurred at a multicellular stage of amanda’s development
the CORRECT sequence of stages of mitosis is
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
the cells that result from the mitotic cell cycle can be described as:
two cells, each with the same amount of genetic material and the same genetic information
the structure where sister chromatids are joined is called the:
centromere
the type of cell division that produces two genetically identical daughter cells is important for all the following functions except:
production of sperm and eggs
there is evidence of a phenomenon called quorum sensing in rotifers. under certain conditions, a chemical released by females who usually reproduce asexually results in males being produced. The presence of these males allows sexual reproduction. what conditions would most likely lead to a switch to sexual reproduction?
a change in the environment
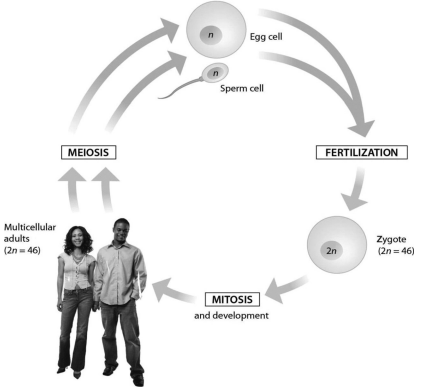
this diagram of the human life cycle shows that:
meiosis produces haploid sperm and egg cells
what best explains the chromosome number of the resulting cell if a cell that had completed only meiosis I were fertilised by a normal sperm?
both cells would be haploid, so the chromosome number of the resulted cell would be diploid
what happens during interpahse
chromosome duplication occursw
what happens during prophase?
the mitotic spindle begins to form
what is the chromosome composition of a normal human female?
44 autosomes and 2 X chromosomes
what is the chromosome composition of a normal human male?
44 autosomes, 1 X chromosome and 1 Y chromosome
what is the chromosome number found in human cells if meiosis I is completed normally?
22 autosomes and a sex chromosome
when in mitosis are there twice as many chromatids compared to the original cell’s chromosomes?
prophase
which activity will help prevent cancer and increase survival?
seek early detection of tumours
which characteristic seen in prophase I does NOT occur in prohpase II
crossing over occurs
which event occurs during anaphase?
sister chromatids become separate chromosomes
which type of reproduction is most adaptive in a rapidly changing environment with many different parasitic diseases present?
sexual reproduction, because the diversity of genotypes increases the likelihood that there is one which can survive in a new environment
____ is a stage of mitosis
telophase
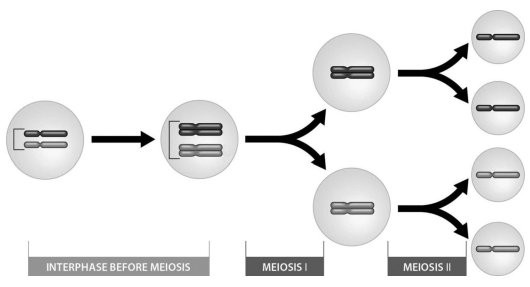
the 2n number for the cell depicted here is ____
two
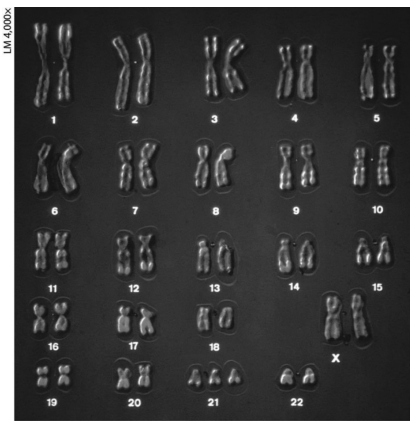
the karyotype above shows:
trisomy 21, a cause of down syndrome
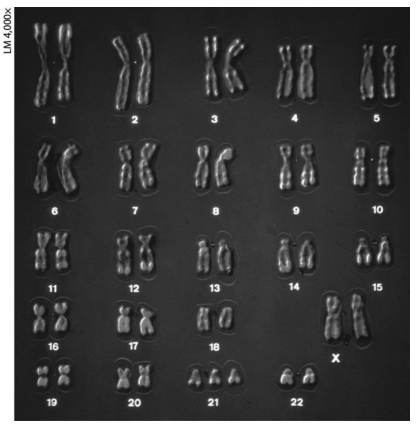
which of these mistakes would be evident in the karyotype shown?
a nondisjunction in meiosis II in gamete formation
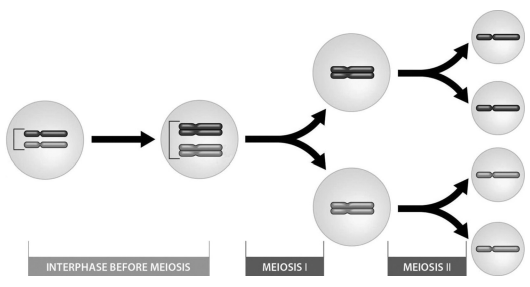
the above figure shows that:
meiosis results in the formation of four haploid daughter cells
a mutation within a gene that will insert a premature stop codon in mRNA would:
result in a shortened polypeptide chain
a(n) ___ is to bacteria as a ____ is to animal cells
prophage; provirus
after replication:
each new DNA double helix consists of one old strand and one new strand
all of the following are examples of potential emerging viruses except one. choose the exception
a virus that is harmful to humans mutates very slowly over long periods of time
all of the following are ways that viruses may give rise to new diseases except one. choose the exception
viruses that are made of DNA that cannot be used to make vaccines
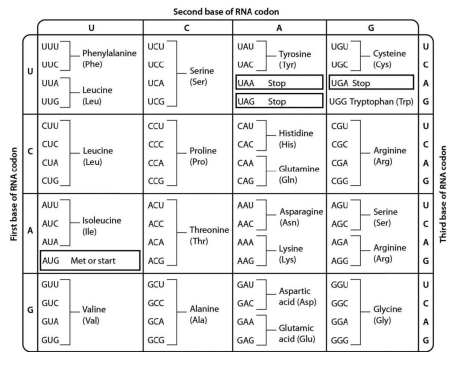
an mRNA is expressed that begins with the sequence AUGGGGCGAAUU. using the genetic code below, determine what peptide will be translated from this mRNA:
Met Gly Arg Ile
as an experiment, you infect bacteria with an unknown virus to see how the virus affects the bacteria. after a few days, you notice that the bacterial population is growing normally and that the cells appear healthy. assuming that the infection occurred successfully, what can you conclude from your observations
the virus is a bacteriophage that is reproducing via the lysogenic cycle
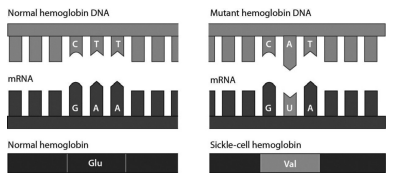
consider the following figure. it illustrates that a single amino acid substitution in the haemoglobin gene:
changes an amino acid in the haemoglobin protein
DNA and RNA are polymers composed of ____ monomers
nucleotide
DNA contains the nitrogenous base ____ instead of ____ which is found only in RNA
thyme; uracil
DNA replication:
requires the cooperation of over a dozen enzymes and other proteins
during translation, what is the CORRECT order of events that occur as an amino acid is added to a growing polypeptide chain?
codon recognition, peptide bond formation, translocation
evidence for the spiral nature of DNA came from:
x-ray crystallography studies
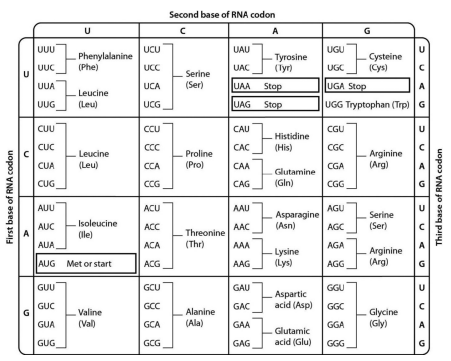
examine the genetic code table shown below. the codon CAU codes for the amino acid:
histidine
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) must use its own ____ to reproduce
reverse transcriptase
how can bacteriophage DNA be spread from cell to cell without causing cell death?
via a lysogenic cycle
how is the zika virus most commonly transmitted?
through a single species of mosquito
how many amino acids are common to all living systems?
20
how many nucleotides make up a codon?
three
if a strand of DNA has the sequence GACTTA, transcription will result in an(n):
single RNA strand with the sequence CUGAAU
if guanine makes up 60% of the bases in a DNA double helix, what percent of the bases is adedine?
40%
if one strand of a DNA double helix has the sequence ATCCGA. what is the sequence of the other strand?
TAGGCT
in a DNA double helix, adenine pairs with ____ and guanine pairs with ____
thymine; cytosine
mad cow disease is caused by:
infectious proteins called prions
peptide bonds form between:
amino acids
plant viruses:
often use RNA, rather than DNA, as their genetic material
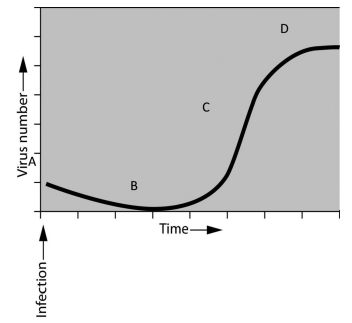
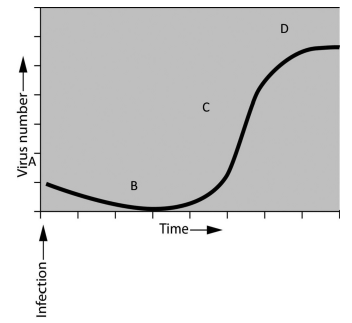
if you were asked to study the pattern of bacterial growth (increase in numbers over time) during an infection, you would find that numbers of bacteria increase exponentially up to a certain point, assume that you have been asked to interpret the growth of bacteriophages. you infect the host bacteria and measure the increase of phages over a defined period of time. you plot the results and observe the graph shown here.
the first thing you notice is that there is no immediate increase in viruses following infection.
this is because:
although the virus has infected the host, it takes time to complete the lytic cycle
if you were asked to study the pattern of bacterial growth (increase in numbers over time) during an infection, you would find that numbers of bacteria increase exponentially up to a certain point, assume that you have been asked to interpret the growth of bacteriophages. you infect the host bacteria and measure the increase of phages over a defined period of time. you plot the results and observe the graph shown here.
once viruses are detected, the number of viruses increases rapidly.
this is because:
the viruses lyse the hosts to release mature viruses quickly in a short amount of time
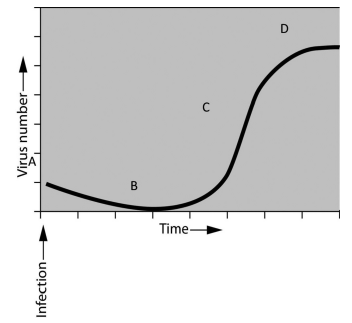
if you were asked to study the pattern of bacterial growth (increase in numbers over time) during an infection, you would find that numbers of bacteria increase exponentially up to a certain point, assume that you have been asked to interpret the growth of bacteriophages. you infect the host bacteria and measure the increase of phages over a defined period of time. you plot the results and observe the graph shown here.
at what point on the graph are the viruses increasing in number the fastest?
C
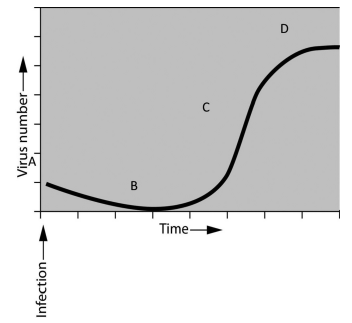
if you were asked to study the pattern of bacterial growth (increase in numbers over time) during an infection, you would find that numbers of bacteria increase exponentially up to a certain point, assume that you have been asked to interpret the growth of bacteriophages. you infect the host bacteria and measure the increase of phages over a defined period of time. you plot the results and observe the graph shown here.
assume that you want to take a sample of viruses so that you could use them to infect the most bacteria. at what point on the graph should you take your sample from if you want to achieve this goal?
D
while working with cultured mouse cells, a researched unknowingly treated the cells with a mutagen that causes the deletion or insertion of individual nucleotides in DNA. subsequently, the researcher isolated and cultured a single cell from this group and noticed that the progeny of this cell were not producing a certain protein, and that this affected their survival.
the mutation that resulted from the accident was probably:
one that changed the triplet grouping of the genetic message
while working with cultured mouse cells, a researched unknowingly treated the cells with a mutagen that causes the deletion or insertion of individual nucleotides in DNA. subsequently, the researcher isolated and cultured a single cell from this group and noticed that the progeny of this cell were not producing a certain protein, and that this affected their survival.
the mutation would be most harmful to the cells if it resulted in:
a single nucleotide insertion near the start of the coding sequence
while working with cultured mouse cells, a researched unknowingly treated the cells with a mutagen that causes the deletion or insertion of individual nucleotides in DNA. subsequently, the researcher isolated and cultured a single cell from this group and noticed that the progeny of this cell were not producing a certain protein, and that this affected their survival.
the researched isolated a different single cell and determined that it was producing a certain protein. however, the protein was much shorter than it should have been.
what kind of mutation likely occurred in this protein?
one that introduced a premature stop codon
prions are infectious molecules that can cause brain diseases in several animals. what type of molecule is a prion?
protein
RNA vaccines have shown promise but have yet to be tested in humans. however, further evidence needs to be collected before human clinical trials can begin. which would be the best experiment to perform to test the efficacy of an RNA vaccine against zika virus in mice?
give one group of healthy mice the vaccine and another healthy group a placebo. then infect both groups with the zika virus and test their blood for the presence of the zilka virus
researchers are currently investigating different forms of anti-HIV drugs. which could be an effective drug to prevent HIV from being incorporated into human chromosomes?
a drug that blocks DNA transport through the nuclear envelope
researchers have tested RNA vaccines against the west nile virus in dogs and cats. the study design for this experiment is shown in the figure. what group(s) was(were) the experimental groups?
low dose and high does of vaccine for cats and low dose of vaccine for dogs only
scientific research companies sell kits that allow researchers to produce proteins in test tubes via a process known as “in vitro translation.” all of the following components are needed except one:
DNA
the CORRECT sequence of events that occurs during transcription is:
initiation, elongation, termination
the RNA that is translated into a polypeptide is _____ RNA
messenger
the absence of a terminator in transcription will result in:
the production of a longer RNA molecule
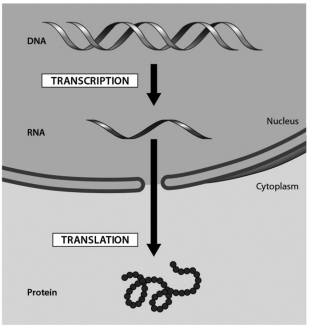
the accompanying figure shows the flow of genetic information in a eukaryotic cell. the transfer of information from RNA into a protein is known as:
translation