Biology 207 Introductory 1.1-1.5
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:44 PM on 2/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
5 fundamental characteristics of living organisms
1. contains cells
2. replication
3. information processing
4. energy
5. evolution
2
New cards
explain replication characteristic
capable of reproduction, cell division
3
New cards
explain information processing characteristic
process genes and information from environment
4
New cards
explain energy
acquire and use energy to live
5
New cards
is a virus a cell?
* no
* cannot reproduce by itself
* cannot reproduce by itself
6
New cards
what makes something a cell
ability to reproduce by itself
7
New cards
evolution
genetic variation resulting in change in characteristic of a population over time
8
New cards
define theory
explanation or observation supported by wide body of evidence
9
New cards
what are 3 theories that form framework for biological science
* cell theory
* theory of evolution by natural selection
* chromosome theory of inheritance
* theory of evolution by natural selection
* chromosome theory of inheritance
10
New cards
who first discovered cells
* 1660s
* Robert Hooke and Anton van Leeuwenhoek
* Robert Hooke and Anton van Leeuwenhoek
11
New cards
explain cells
* Highly organized compartments
* Separated from their environment by membrane barrier
* Separated from their environment by membrane barrier
12
New cards
explain cell theory
* cell is the fundamental structural unit in all organisms.
* All species are related by common ancestry and have changed over time in response to natural selection.
* All species are related by common ancestry and have changed over time in response to natural selection.
13
New cards
explain relationship between cell theory and spontaenous generation
* Cell theory challenged spontaneous generation
* All-cells-from-cells vs spontaneous generation
* All-cells-from-cells vs spontaneous generation
14
New cards
what is All-cells-from-cells
cells are produced when pre-existing cells grow and divide
15
New cards
what is spontaneous generation
belief that organisms could arise spontaneously under certain conditions
16
New cards
louis pasteur’s experiment hypothesis
* concluded all cells theory was correct, cells come from cells
* hypothesis: microbes (bacteria) come from cells of organisms on dust particles in the air, **not the air**
* hypothesis: microbes (bacteria) come from cells of organisms on dust particles in the air, **not the air**
17
New cards
Chromosomal theory of inheritance
* proposed by Sutton and Boveri:
* Hereditary or genetic information is encoded in genes
* Genes are units located on chromosomes
* Hereditary or genetic information is encoded in genes
* Genes are units located on chromosomes
18
New cards
Explain Louis Pasteur’s Classical Experiment
* 2 flasks, straight neck and swan neck flask
* both flasks boiled
* cells appeared in straight flask from ==air== and not in swan neck because air lack of air
* both flasks boiled
* cells appeared in straight flask from ==air== and not in swan neck because air lack of air
19
New cards
Explain chromosomes
* 1950s
* molecules of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
* molecules of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
20
New cards
explain DNA
* contains info for growth and reproduction
* hereditary material
* genes are segments of DNA, code for cell products
* double helix
* hereditary material
* genes are segments of DNA, code for cell products
* double helix
21
New cards
what are the 4 building blocks of DNA
* A
* T
* C
* G
* T
* C
* G
22
New cards
Explain RNA
* molecules that perform specialized functions in cells
Ex: mRNA (messenger RNA) is read to make proteins
Ex: mRNA (messenger RNA) is read to make proteins
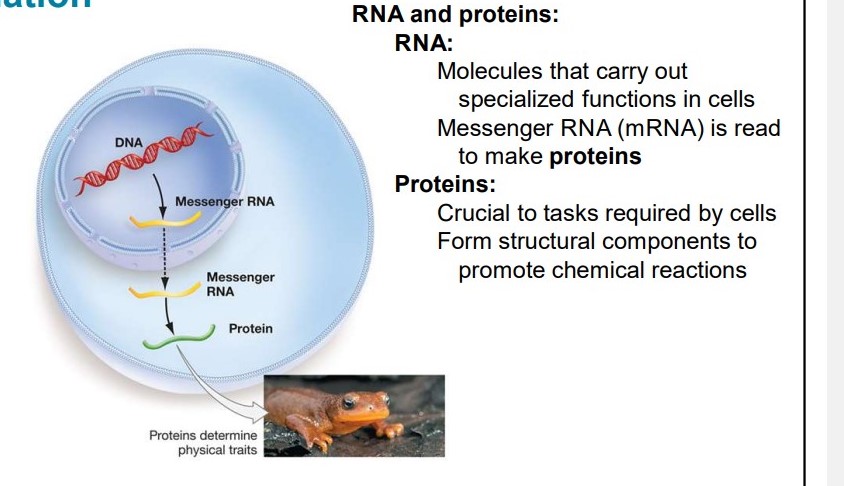
23
New cards
Explain proteins
* required for cells to function
* determine physical traits
* determine physical traits
24
New cards
Tree of life
* depicts evolutionary history
* family tree of organisms
* describes genealogical relationships between species
* family tree of organisms
* describes genealogical relationships between species
25
New cards
phylogeny
genealogical relationship among all organism
26
New cards
3 domains of life
* Eukaryotes
* archaea
* bacteria
* archaea
* bacteria
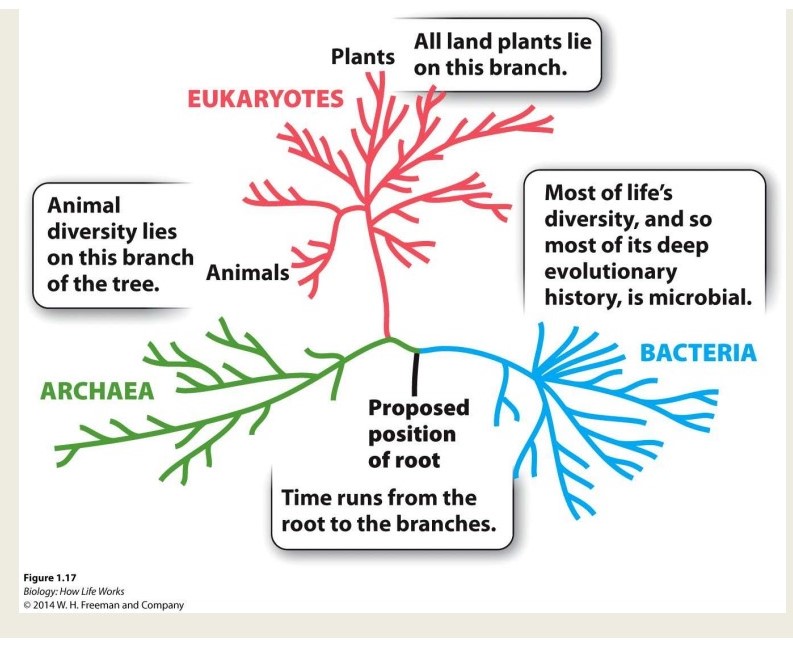
27
New cards
Eukaryotes
* 4 kingdoms
* membrane-bound nucleous
* membrane-bound nucleous
28
New cards
4 kingdoms of eukaroytes
* protists
* fungi
* plants
* animals
* fungi
* plants
* animals
29
New cards
2 types of prokaryotes
* archaea
* bacteria
* no membrane-bound nucleous
* bacteria
* no membrane-bound nucleous
30
New cards
How are species grouped?
taxonomy based on common ancestry