chapter 20 A&P II
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
what are the three types of blood vessels
arteries, capillaries, veins
convey blood from the heart to the capillaries
arteries
microscopic porous blood vessels
exchange substances between blood and tissues
capillaries
transports blood from capillaries to heart
veins
Walls composed of three layers called
tunics
what are the tunic walls
tunica intima, tunica media, tunica externa
space inside of vessels
lumen
innermost layer of vessel wall
endothelium of simple squamous epithelium
sub endothelial layer of areolar connective tissue
tunica intima
middle layer of vessel; circulatory arranged layers of smooth muscle cells with elastic fibers
contractions causes vasoconstriction: narrows lumen
relaxation causes vasodilation; widens lumen
tunica media
outermost layer of vessels; areolar connective tissue with elastic; and collagen fibers
helps anchor vessels to other structures
may contain vasa vasorum
tunica externa
small arteries requires to supply very large vessels
vasa vasorum
what type of vessels lie next to each other
arteries and veins serving same body region
companion vessels
Thicker tunica media and narrower lumen than veins
More elastic and collagen fibers (spring back to shape)
More resilient and resistant to changes in blood pressure
2
arteries 2
Thicker tunica externa and larger lumen than arteries
Less elastic and collagen fibers
Wall collapses if no blood in vessel
2
veins 2
•Contain only tunica intima (no subendothelial layer)
•Composed of endothelium and basement membrane
•Thin wall allows for rapid gas and nutrient exchange
2
capillaries
what do arteries branch into
smaller ventricles extending from the heart
what is decreased and increased in arteries
decrease in lumen diameter
decrease in elastic fibers
increase in relative amount of smooth muscle
what are the three basic types of arteries
elastic arteries, muscular arteries, arterioles
Largest arteries—diameters from 2.5 to 1 cm
Conduct blood from heart to muscular arteries
Have large proportion of elastic fibers allowing stretch and recoil
Helps propel blood through arteries during diastole
elastic (conducting) arteries
Medium arteries—diameters from 1 cm to 0.3 mm
Distribute blood to specific body regions
Muscle allows vasoconstriction (and dilation)
Most named arteries
E.g., brachial artery, coronary arteries
muscular (distributing) arteries
where are the elastic (conducting) arteries at
aorta, pulmonary trunk, common carotid, common iliac arteries
where are the muscular (distributing) arteries located
brachial artery, coronary arteries
Smallest arteries—diameters of 0.3 mm to 10 micrometers
Larger arterioles have three tunics
Smaller arterioles have only thin endothelium and single layer smooth muscle
Regulate systemic blood pressure and blood flow
Arterioles
Part of arterial wall thins and balloons out making it more prone to rupture
Can cause massive bleeding and death
aneurysm
what type of arteries do aneurysm have
elastic and muscular arteries
with age, less able to withstand forces from pulsating blood
where is aneurysm most common
in aorta or arteries at the base of the brain
what has the most place for blood
veins
What do capillaries connect
arterioles to venules
what is the average length of capillaries
1 mm; diameter 8-10 micrometers
what does the capillary wall consist of
consists of endothelial layer on basement membrane
thin wall and small diameter are optimal for exchange between blood and tissue fluid
what are the three types of capillaries
continuous, fenestrated, and sinusoid
groups of cappilaries functioning together
capillary beds
what do epithelial cells form
a continuous lining
tight junctions connect what
they connect cells but do not form a complete seal
gaps between endothelial cells of capillary wall
intercellular clefts
what cannot pass but can in capillaries
large particles cannot pass. However smaller molecules can pass through the wall.. where waste and nutrients go through
where are the intercellular clefts found in
muscle, skin, lungs, central nervous system
Endothelial cells form a continuous lining, but the cells have
fenestrations (pores)
what do fenestrations allow
movement of smaller plasma proteins
where are fenestrations found in
areas where much fluid transport happens
intestine capillaries absorbing nutrients
kidney capillaries filtering blood to form urine
Endothelial cells form an incomplete lining with large
gaps
what does the openings allow in sinusoids
transport of large substances
formed elements (WBC,RBS, platelets) and large proteins
where is sinusoids found
bone marrow, spleen, and some endocrine glands
•Smallest veins—diameters of 8 to 100 micrometers
•Companion vessels with arterioles
•Smallest venules are postcapillary venules
•Largest venules having all three tunics
•Merge to form veins
venules
what do small and medium size veins do
compainion vessels with muscular arteries
what do the largest veins travel with
elastic arteries
most veins have what
numerous valves
what do the veins prevent
prevent blood from pooling in the limbs; ensure flow towards the heart
valves made of tunica intima and elastic and collagen fibers
systemic veins are
blood reservoirs
what is the blood % at rest
70% of blood in systemic circulation
systemic veins
55%
systemic arteries
10%
systemic cappilaries
5%
pulmonary circulation has what % of blood
18%
heart has what % of blood
12%
blood can be moved from what
can be moved from veins into circulation via vasoconstriction of veins
ex: when more blood needed during exercise
blood can be shifted back where
into reservoirs via vasodilation
when less blood needed during rest
capillaries function to
exchange substances
gases, nutrients, wastes, hormones between blood and surrounding tissues
when capillaries exchange, where does the exchange partake
diffusion
vesicular transport
bulk flow
substances leave or enter blood according to their concentration gradient (high to low concentration)
•Oxygen, hormones, nutrients move from blood to interstitial fluid
diffusion
_________ and wastes diffuse from tissue to blood
carbon dioxide
what depends on diffusion’s route
particle size
in diffusion, where do small solutes go
diffuse through endothelial cells or intercellular clefts
in diffusion, where do large solutes go
pass through fenestrations or gaps in sinusoid
what do epithelial cells use
pinocytosis and exocytosis
(cellular drinking, bringing substances inside the cell)
pinocytosis
when epithelial cells use pinocytosis and exocytosis what happens
Take substances in by pinocytosis
Form fluid-filled vesicles at plasma membrane
Transport vesicle across cell
Secrete substance from other side by exocytosis
This process used in both directions (both to and from blood)
Certain hormones and fatty acids transported by this method
fluid flow down pressure gradient
bulk flow
what is the movement of bulk flow
it depends on net pressure of opposing forces
hydrostatic pressure vs colloid pressure
fluid moves out of blood
Fluid and small solutes flow easily through capillary’s openings
Large solutes blocked
Occurs on arterial end of capillary
filtration
fluid moves back into blood
Occurs on venous end
reabsorption
force exerted by a fluid
hydrostatic pressure (HP)
Force exerted per unit area by blood on vessel wall
Promotes filtration from capillary
blood hydrostatic pressure (HPb)
Force of interstitial fluid on outside of blood vessel
Close to zero in most tissues
interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure (HBif)
the “pull” on water due to the presence of proteins (colloid)
collid osmotic pressure (COP)
Draws fluid into blood due to blood proteins (e.g., albumins)
Promotes reabsorption (opposes the dominant hydrostatic pressure)
Clinically called oncotic pressure
blood colloid osmotic pressure (COPb)
Draws fluid into interstitial fluid
Since few proteins present in interstitial fluid, this is relatively low (0 to 5 mm Hg)
interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure (COPif)
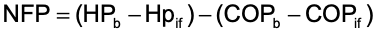
NFP is the difference between net hydrostatic pressure and net colloid osmotic pressure
net filtration pressure
•Difference between blood and interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressures
net hydrostatic pressure
•Difference between blood and interstitial fluid osmotic pressures
net colloid osmotic pressure
NFP changes along length of capillary..
it is higher at the arterial end than at the venous end
at the arterial end, NFP favors filtration
at the venous end, NFP reabsorption
•Picks up excess fluid not reabsorbed at venous capillary end
15% of fluid not reabsorbed by capillary
Filters fluid and returns it to venous circulation
Changes in capillary exchange or absorption by the lymphatic system can result in edema—excess fluid remaining in tissues
lymphatic systemm
what is important for delivery of nutrients and oxygen, and removal of metabolic wastes
flow of blood
•Physical principles of blood flow based on pressure and resistance
hemodynamics
•The greater the pressure difference between two points…
the greater the flow; the greater the resistance, the less the flow
force of blood against vessel wall
blood pressure
change in pressure from one end of vessel to other
Propels blood through vessels
Pressure is highest in arteries and lowest in veins
blood pressure gradient
•Blood flow in arteries pulses with cardiac cycle
arterial blood pressure
DEF: occurs when ventricle contracts (systole)
Highest pressure generated in arteries (they are stretched)
Recorded as the upper number of the blood pressure ratio
E.g., systolic pressure is 120 mm Hg, if blood pressure is 120/80
systolic pressure
DEF: occurs when ventricles relax (diastole)
Lowest pressure generated in arteries (they recoil)
Recorded as the lower number of blood pressure ratio
E.g., diastolic pressure is 80 mm Hg, if blood pressure is 120/80
Diastolic pressure
average arterial blood pressure across entire cardiac cycle
Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
what does it mean that diastole lasts longer than systole
the mean is weighted to be closer to diastolic pressure
if blood pressure is 120/80
MAP = 80 + 40/3 = 93
what does MAP provide
provides index of perfusion
<60
what assists venous return from limbs
skeletal muscle pump
as muscle contracts
veins are squeezed
during muscle pump, blood is pushed and what are valves doing
valves prevent backflow
during muscle pump, blood is moved to where
moved more quickly during exercise and it pools in leg veins with prolonged inactivity
assists venous return in the thorax
•Both inspiration and expiration cause pressure gradient changes that help
respiratory pump
what is deep vein thrombosis
clot (thrombus) in a vein