Lesson 91 - Parasitic and Dietary Diarrhea
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What are types of protozoa associated with diarrhea?
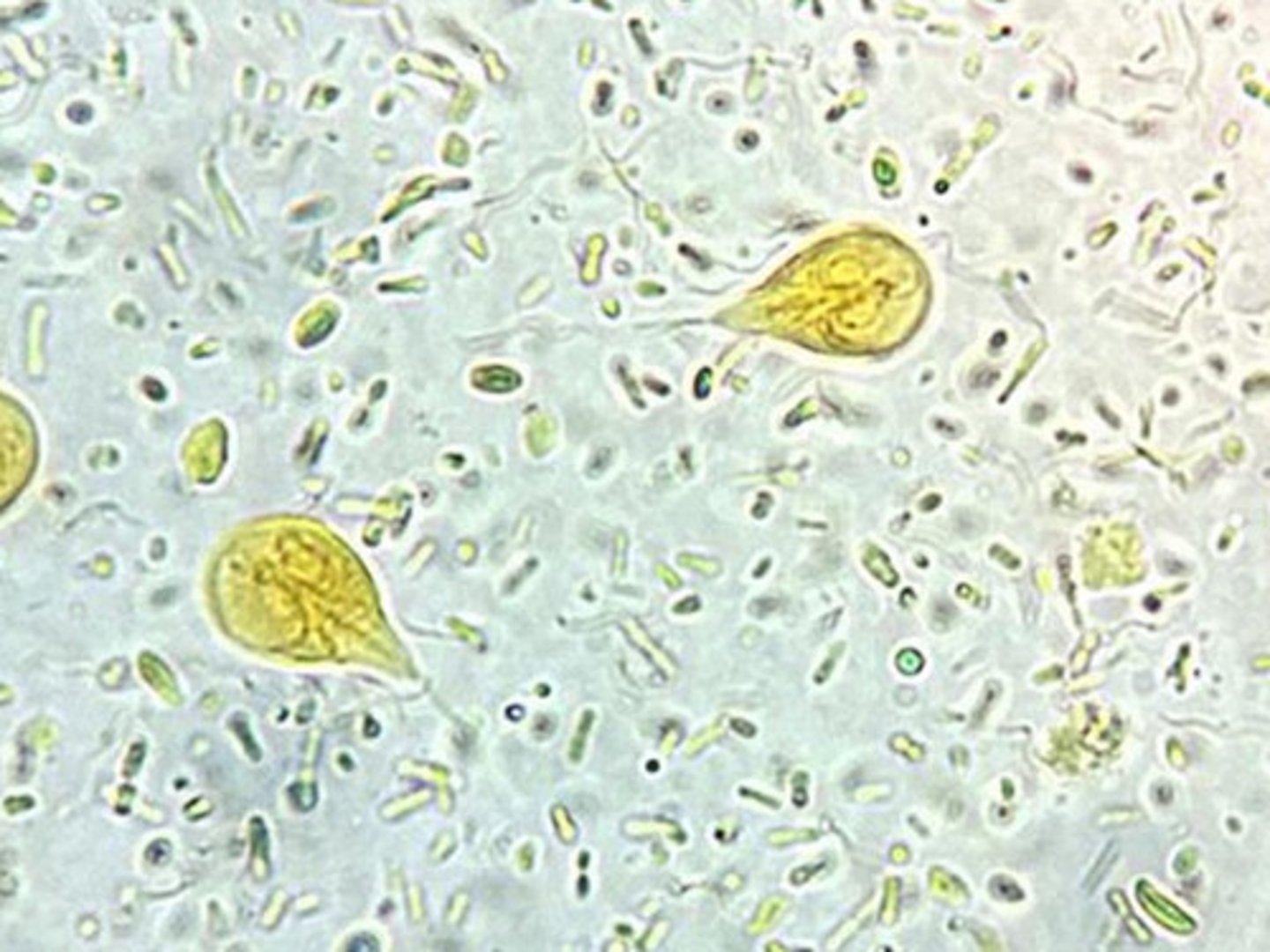
coccidia, giardia, tritrichomonas, cryptosporidium
What are types of nematodes associated with diarrhea?
hookworms, trichuris, strongyloides, trichostrongyles, strongyles
Where is coccidia found?
small and large intestine
Where is giardia found?
small intestine
Where is cryptosporidium found?
small intestine
Where are hookworms found?
small intestine
Where are strongyloides found?
small intestine
Where are trichostrongyles found?
small intestine
Where are tritrichomonas found?
large intestine
Where are trichuris found?
large intestine
Where are strongyles found?
large intestine
What are the species of coccidia?
cystoisospora and eimeria
What type of coccidia is in dogs and cats?
cystoisospora
What type of coccidia is in cattle, sheep, goats?
eimeria
What is the transmission of coccidia?
direct, fecal-oral ingestion of sporulated oocysts, tissue of paratenic hosts with encysted sporozoites
What do sporozoites of Cystoisospora and Eimeria do?
invade the epithelial cells of the small and large intestine, replicate, and eventually rupture cells
What are clinical signs of cystoisospora?
asymptomatic, water diarrhea, weight loss, dehydration
How is eimeria transmitted?
direct, fecal-oral ingestion of sporulated oocysts
What are the clinical signs of Eimeria?
reduced feed consumption and body weight, soft diarrhea, CNS signs in cattle, lower wool quality
What is the species of Giardia?
giardia duodenalis
What are the hosts for giardia duodenalis?
dogs, cats, ruminants
What parasites are zoonotic?
giardia, cryptosporidium, hookworms, strongyloides,
What is the transmission of giardia?
direct, fecal-oral ingestion of infective cysts
What do the trophozoites of giardia do in the small intestine?
attach to enterocytes surface
What are clinical signs of giardia?
maldigestion, malabsorption, malodorous diarrhea, weight loss, growth retardation
What are the hosts for cryptosporidium?
cattle, small ruminants, dogs, cats
What is the transmission for cryptosporidium?
direct, fecal-oral ingestion of sporulated oocysts
What does cryptosporidium do in the small intestine?
invasion and development in the microvillus brush border
What are the clinical signs of cryptosporidium?
watery diarrhea with yellowish color, dehydration, life-threatening in immunocompromised hosts
What are hosts for hookworms?
cats, dogs, ruminants
What is the zoonotic importance of hookworms?
cutaneous larva migrans
What is the transmission of hookworms?
ingestion, skin penetration, paratenic hosts, transmammary of L3
What are the clinical signs of hookworms?
anemia, weight loss, melena, dermatitis, pruritis, papules, respiratory signs
What hookworms have 3 pairs of teeth?
Ancylostoma caninum, Ancylostoma tubaeforme
What hookworms have 1 pair of teeth?
Ancylostoma braziliense
What hookworms have cutting plates?
Uncinaria stenocephala and Bunostomum spp.
What are the hosts for strongyloides?
dogs, cats, ruminants, horses
How is strongyloides transmitted?
ingestion of infective filariform larvae, skin penetration, transmammary, autoinfection
What are the clinical signs of strongyloides?
diarrhea with blood, malabsorption, lesser extent verminous pneumonia
What is the zoonotic importance for strongyloides?
S. stercoralis can penetrate the skin like CLM
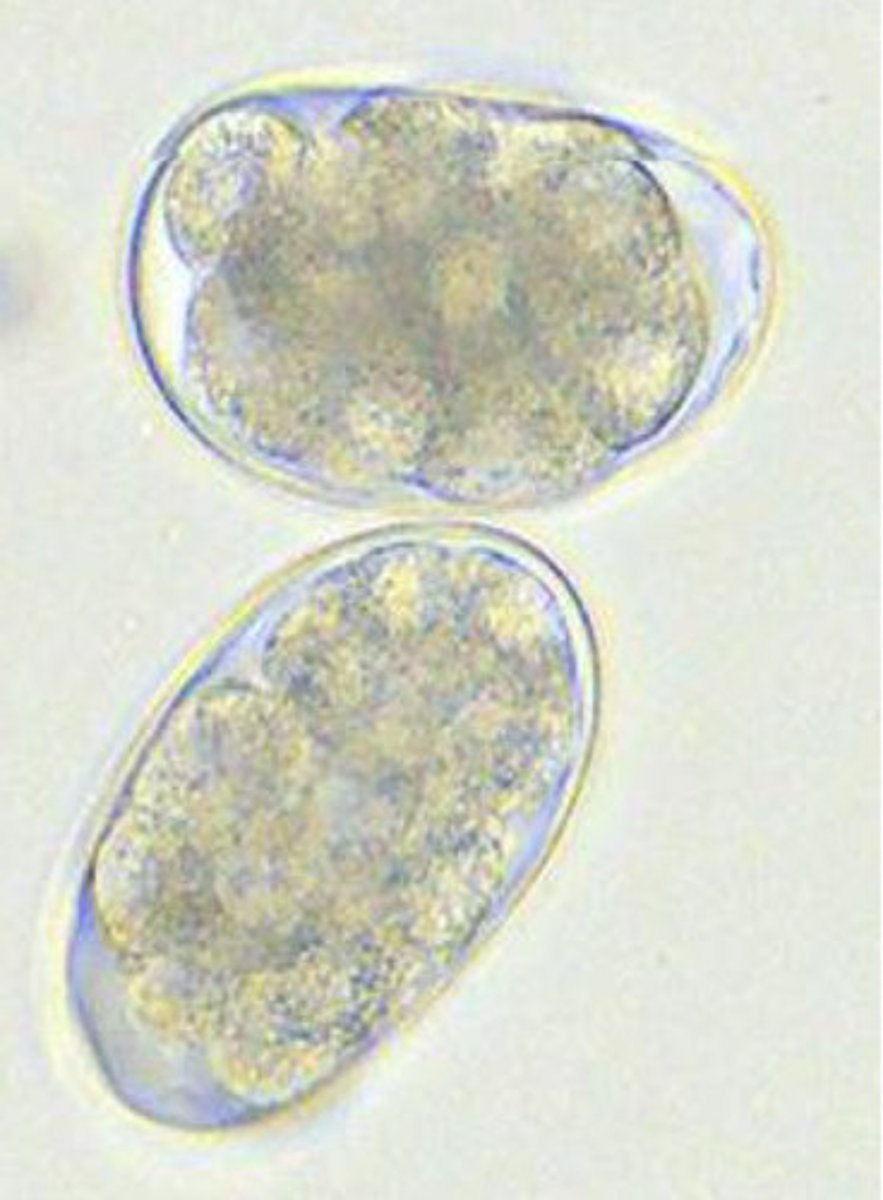
What are the hosts for trichostrongyles?
sheep, goats, cattle
Where are trichostrongyles located?
abomasum and small intestine
What are the clinical signs of trichostrongyles?
anorexia, weight loss, diarrhea, dehydration, abomasal lesions
What are the hosts for tritrichomonas?
cats
How is tritrichomonas transmitted?
direct, fecal-oral ingestion of trichomonads
Where are tritrichomonas mostly located?
cecum
What are the clinical signs of tritrichomonas?
chronic water diarrhea, fecal incontinence, flatulence, relapse of diarrhea, rectal prolapse may occur
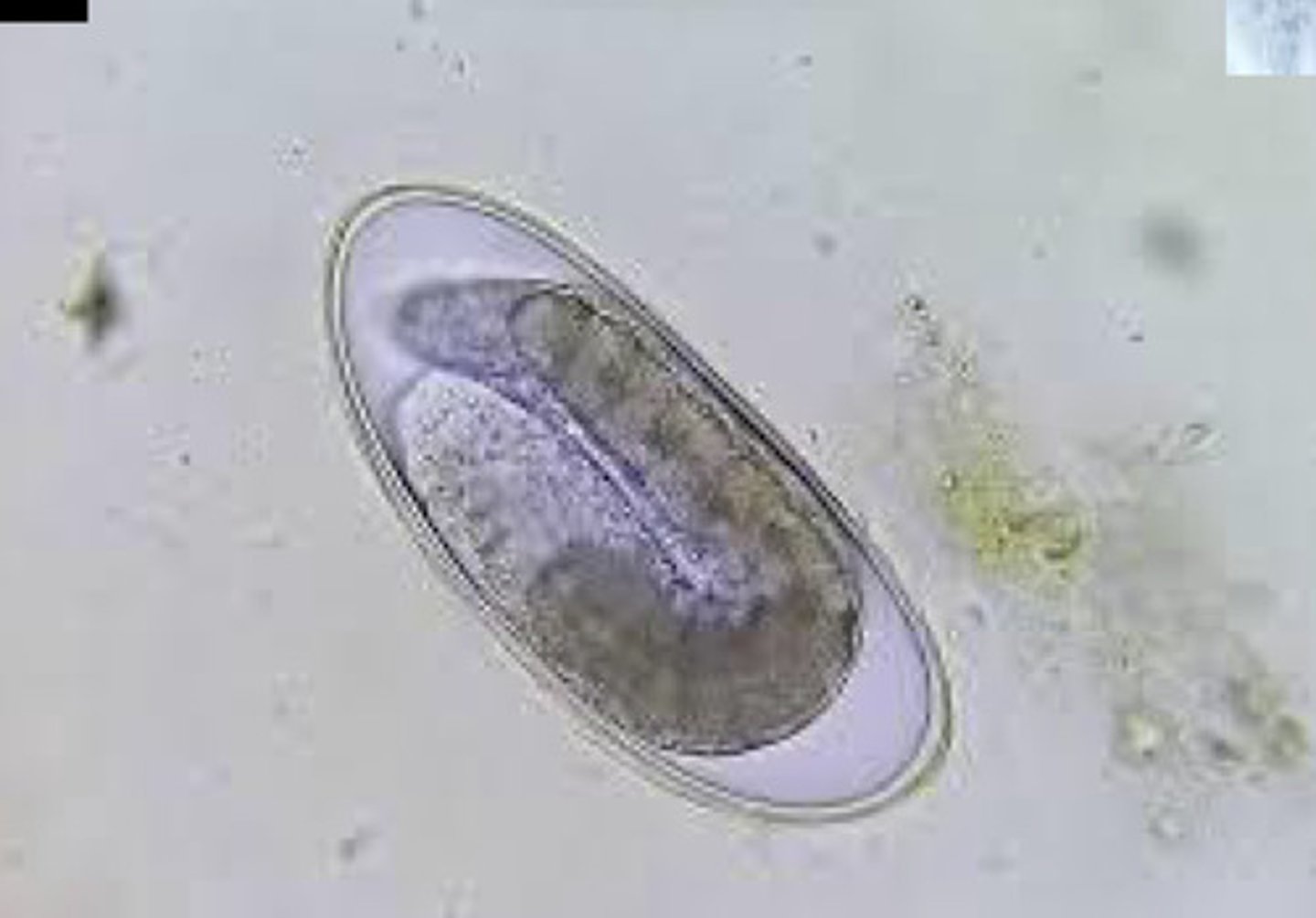
What are the hosts for trichuris?
dogs and cats
How is trichuris transmitted?
direct, fecal-oral ingestion of embryonated L1 eggs
What are the clinical signs of trichuris?
weight loss, dehydration, diarrhea with bright blood
What are the hosts for strongyles?
sheep, goats, cattle
How are strongyles transmitted?
ingestion of infective L3 larvae
What are the clinical signs of strongyles?
nodules formation due to larvae, diarrhea
What is a species of strongyles?
esophagostomum
What do the eggs of strongyles look similar to?
trichostrongyles
What can you see on direct wet mount/smear?
protozoa motility
What can you see on flotation?
eggs, larvae, cysts
What can you see with Baermann technique?
larval stages of strongyloides
What can you see on histology?
oocysts and nematodes
What is modified acid-fast staining good for?
Cryptosporidium
What are clinical signs of dietary indiscretion?
acute diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, flatulence, possible lethargy and dehydration
What type of diarrhea is seen with dietary indiscretion?
osmotic diarrhea
What types of foods alter gut microbiota?
spoiled food or high-fat diets
Toxocara canis

Trichuris
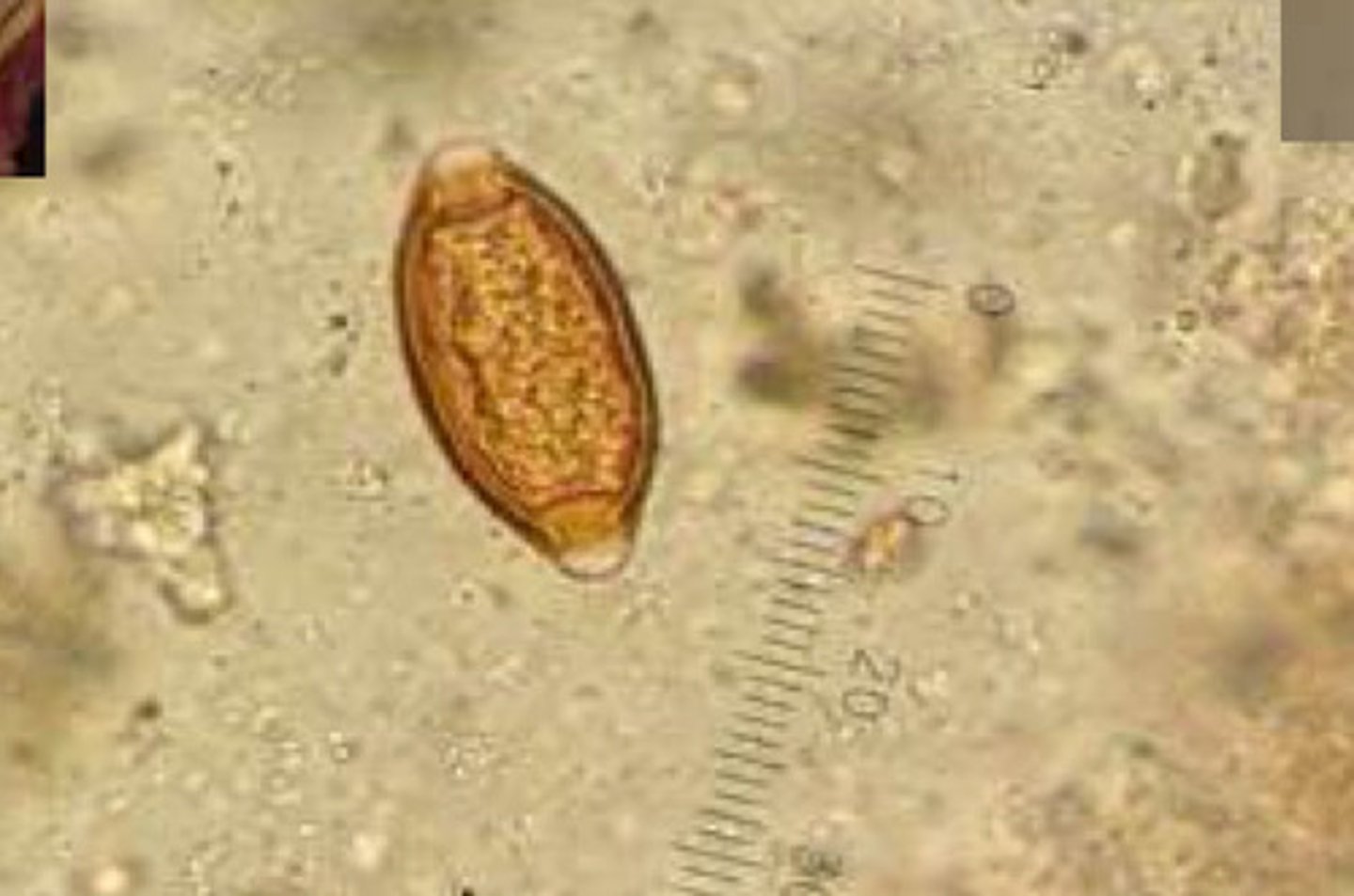

Strongyloides
Trichostrongyloides
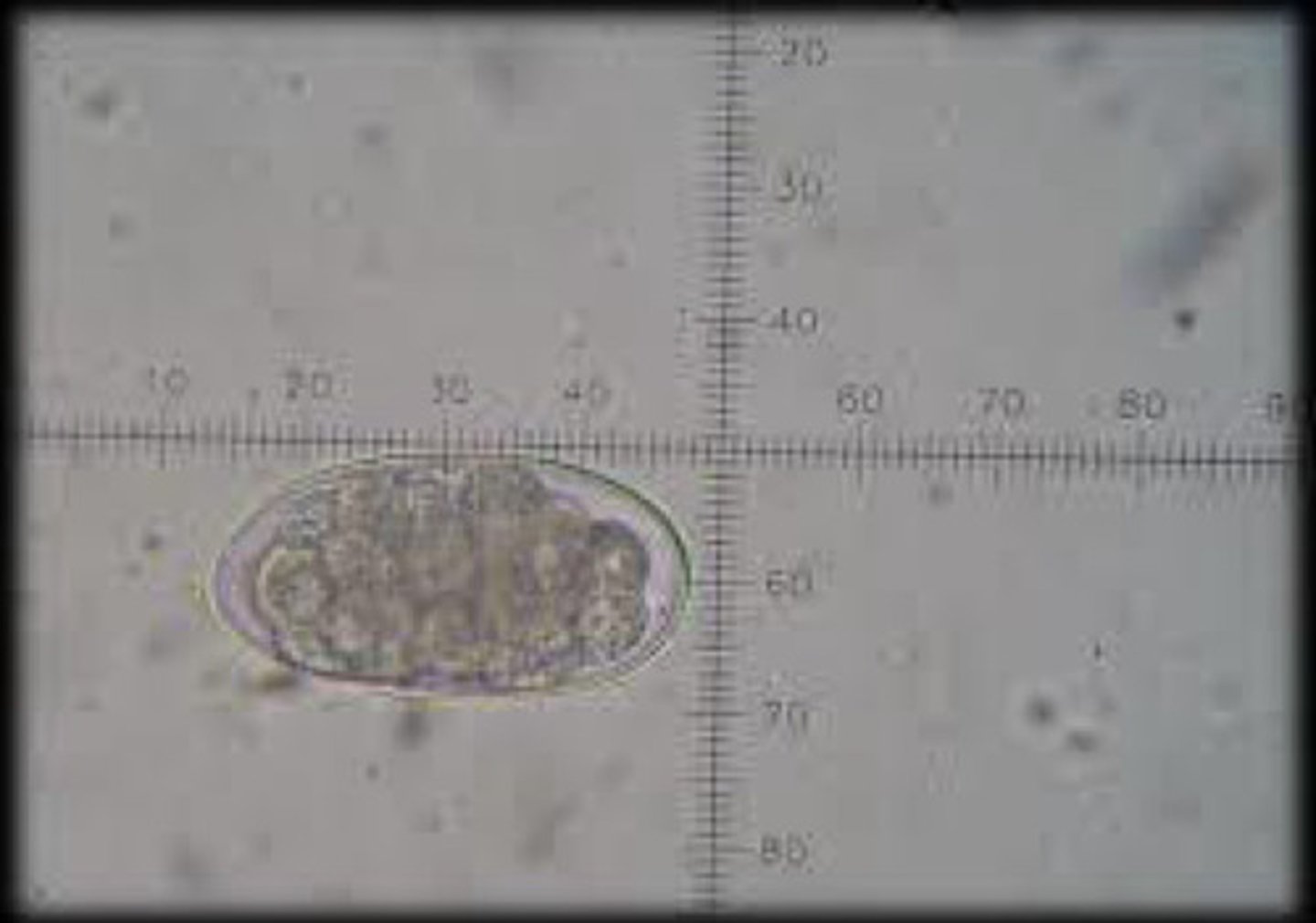
Hookworms
Trichuris
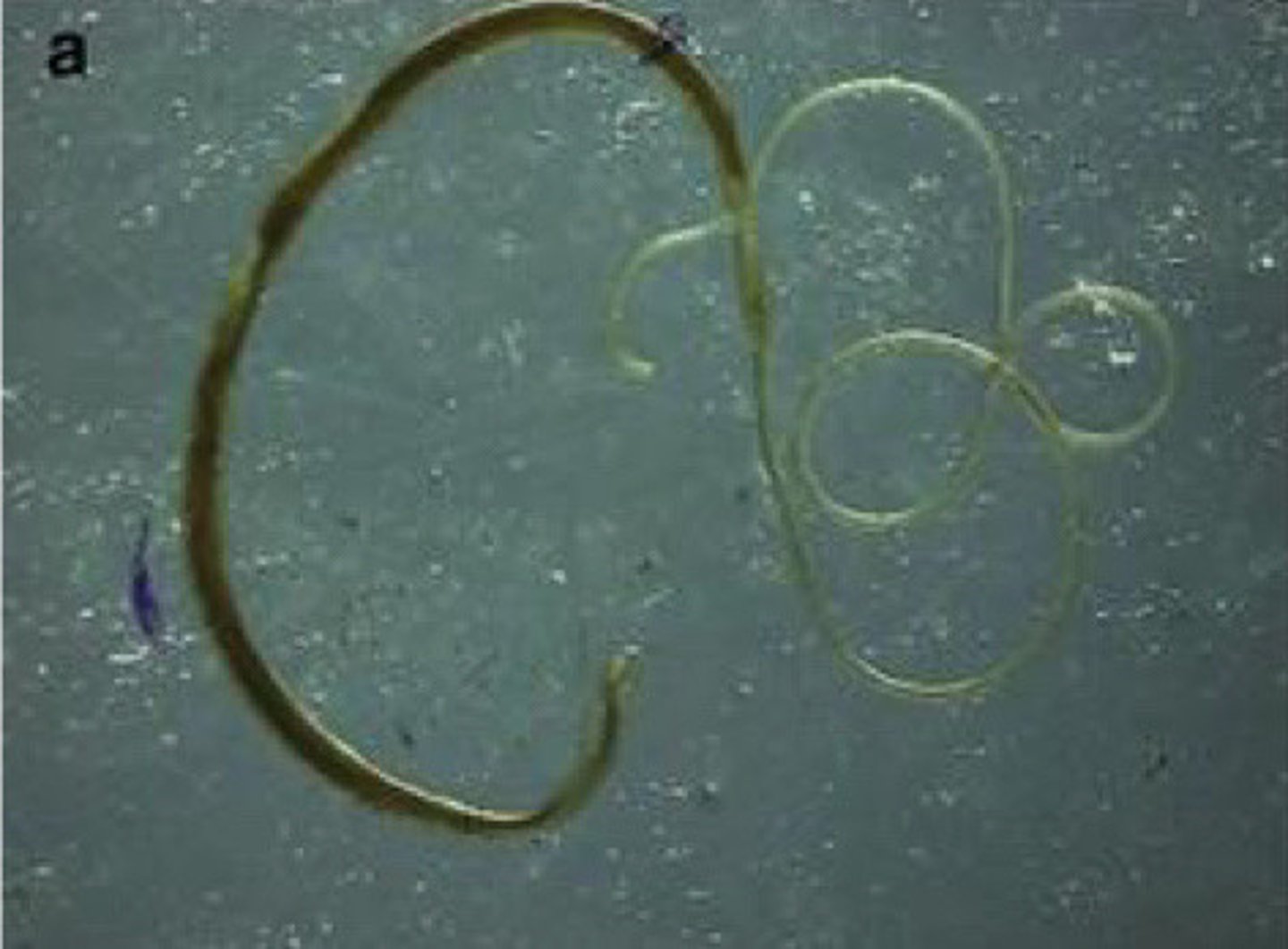

Strongyloides
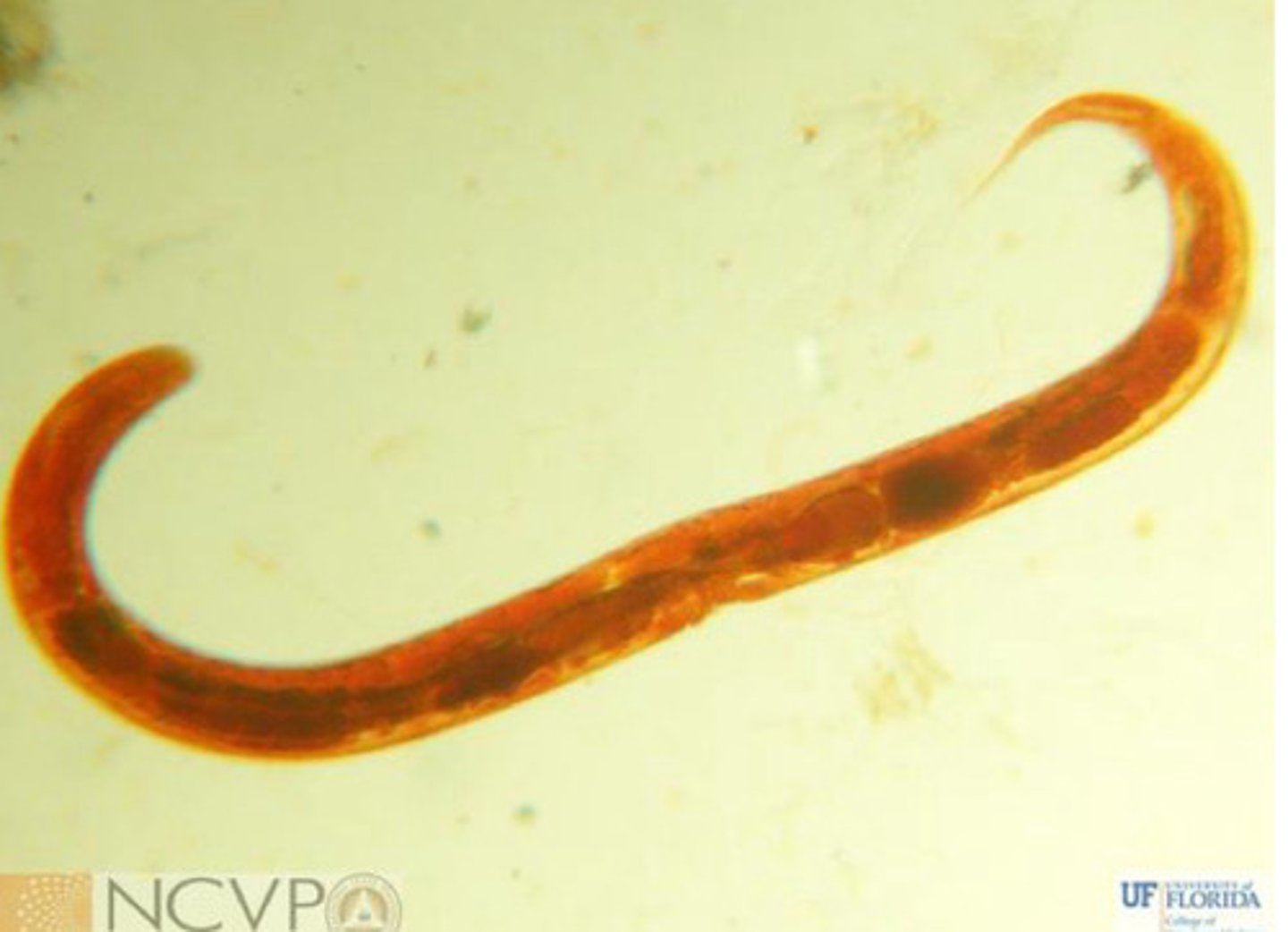
Trichostrongyles
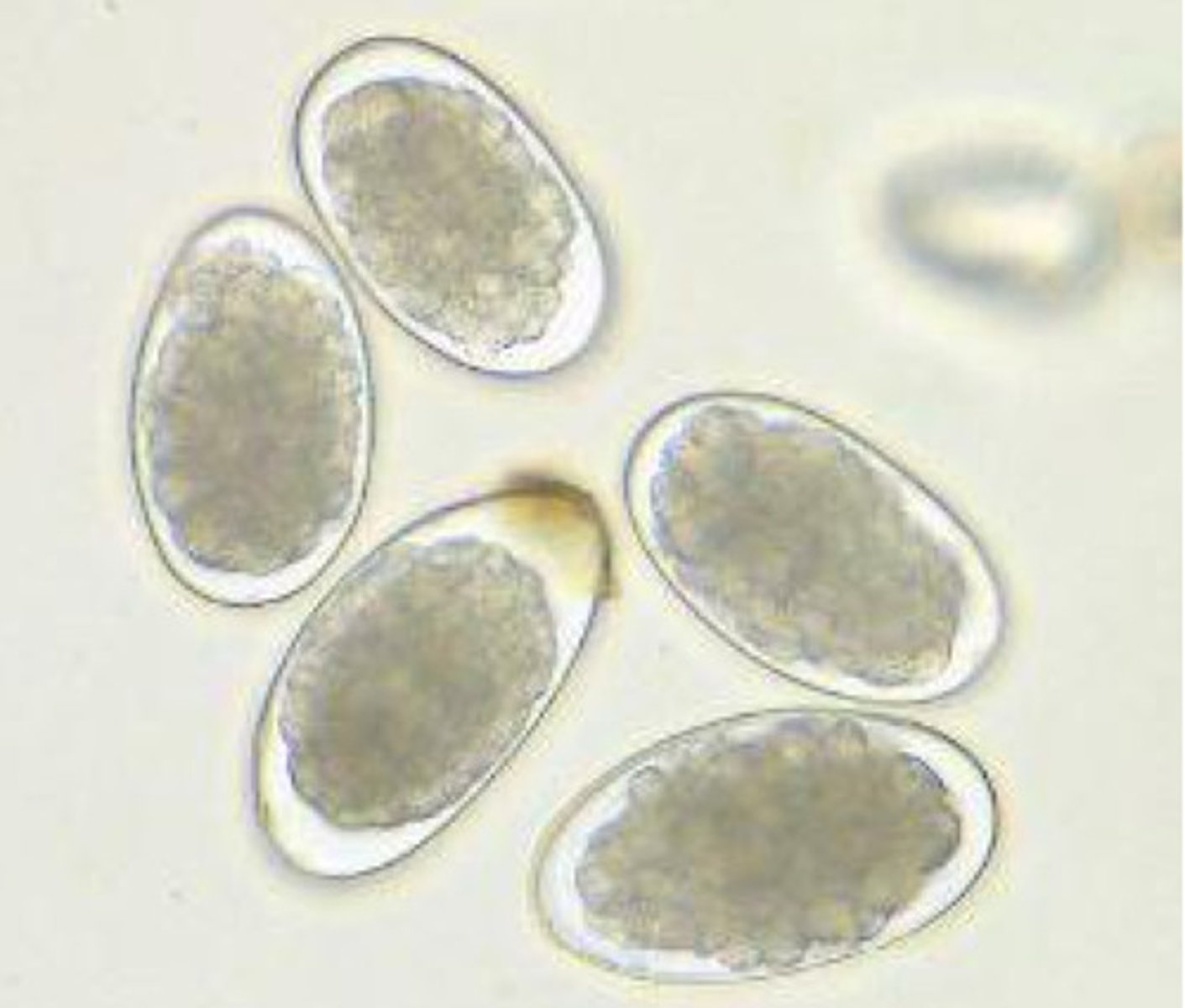
Giardia