Female Reproductive System: Sexual Response, Pregnancy, Childbirth, and Contraception
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What are the phases of the female sexual response during intercourse?
Excitement, Plateau, Orgasm, and Resolution.
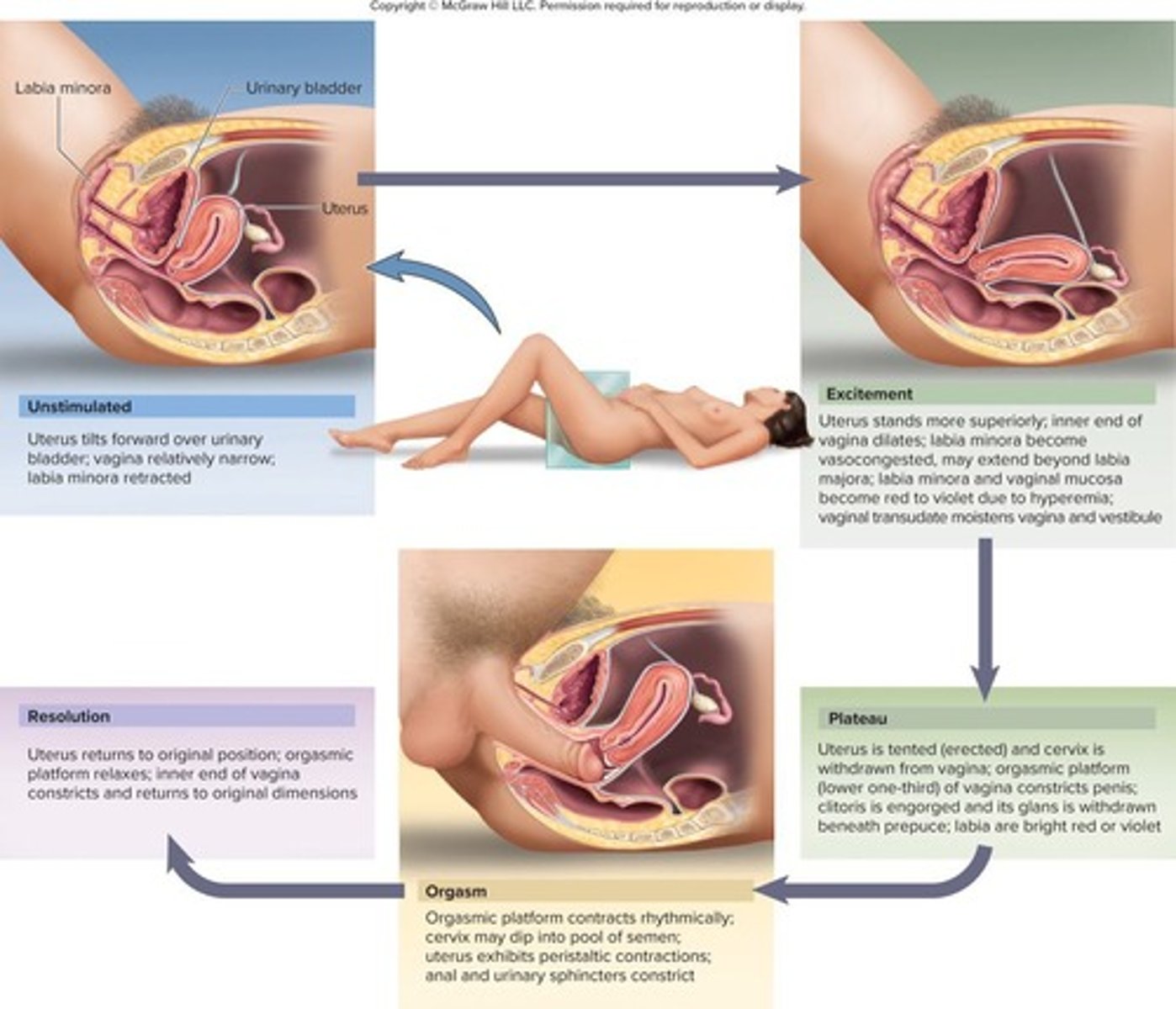
What physiological changes occur during the excitement phase of female sexual response?
Myotonia, vasocongestion, increased heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
What happens to the labia during the excitement phase?
Labia minora become congested and protrude beyond labia majora; labia majora redden and enlarge.
What is vaginal transudate?
Serous fluid that seeps through the vaginal walls, providing lubrication.
What is the orgasmic platform?
The constricted lower one-third of the vagina that enhances stimulation and helps induce orgasm.
What is the tenting effect in female sexual response?
The uterus stands nearly vertical during the excitement phase.
What are the major hormones regulating pregnancy?
Estrogens, progesterone, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), and human chorionic somatomammotropin (HCS).
What is the conceptus?
All products of conception, including the embryo or fetus, placenta, and associated membranes.
What are the stages of prenatal development?
Blastocyst (first 2 weeks), Embryo (Day 16 to Week 8), Fetus (Week 9 to birth).
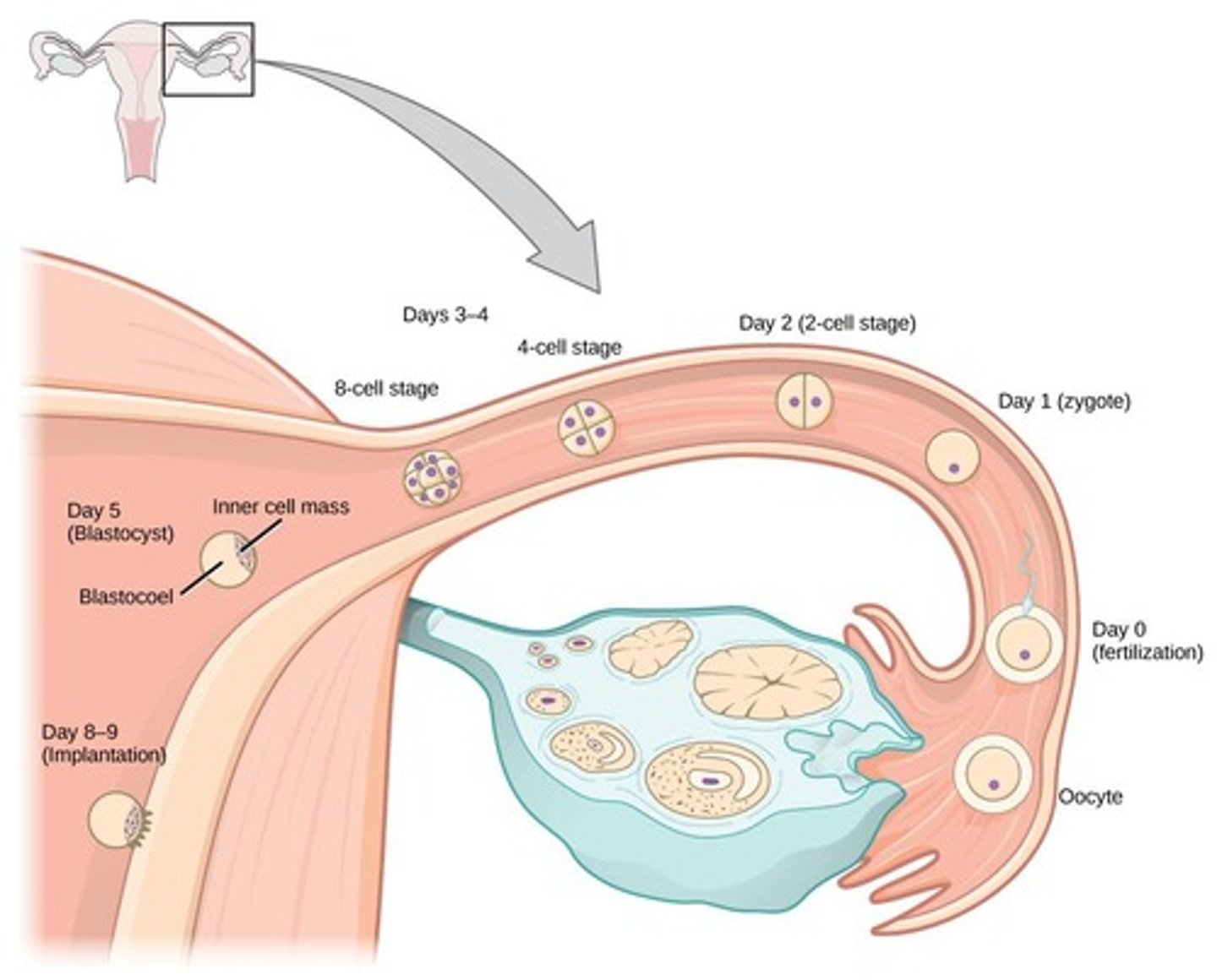
What role does the placenta play during pregnancy?
Provides fetal nutrition, waste disposal, and secretes hormones regulating pregnancy.
What is the function of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)?
Stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete progesterone and estrogen; detectable in urine 8-9 days after conception.
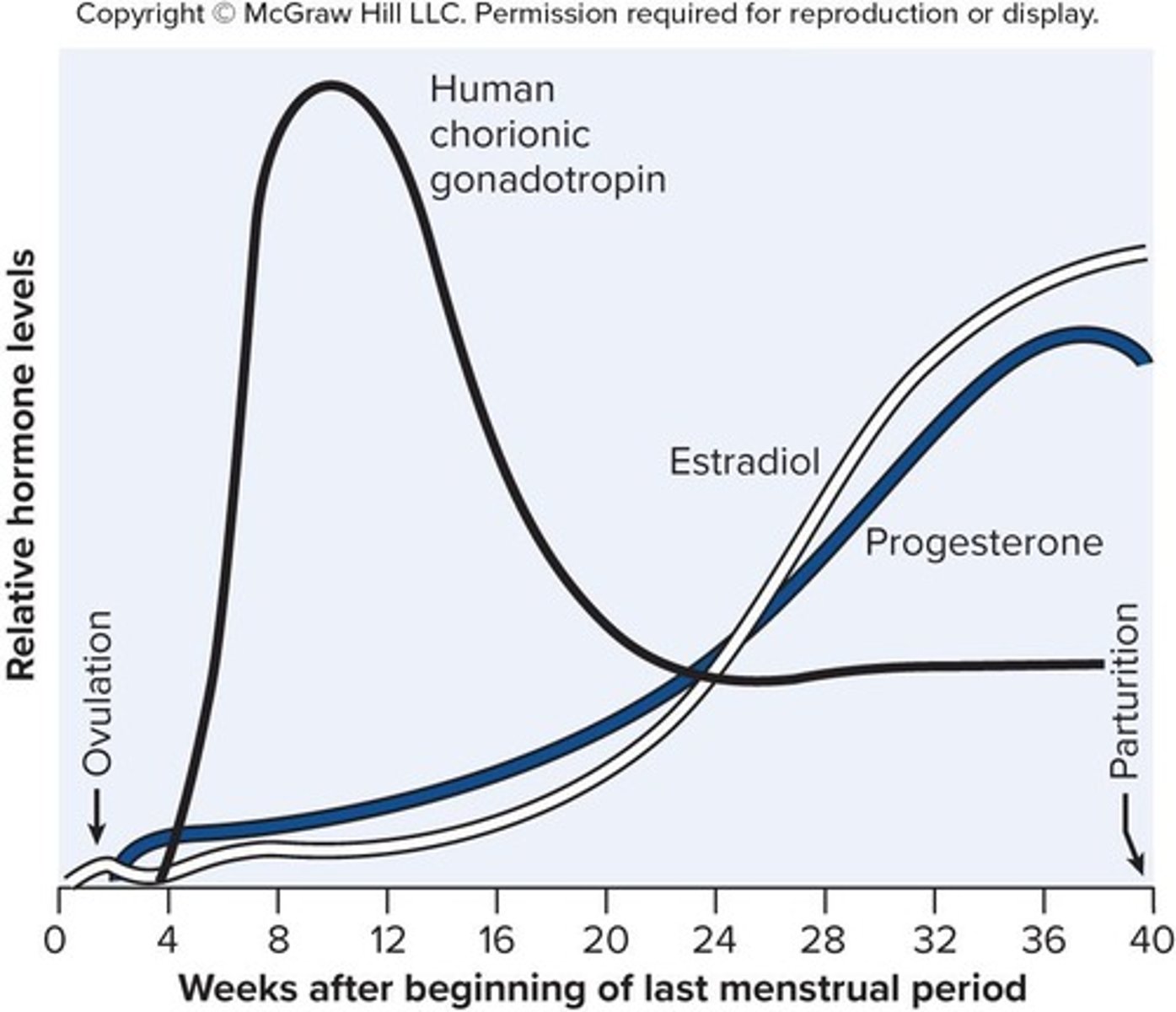
How do estrogens affect the body during pregnancy?
Increase tissue growth in both the fetus and mother, causing enlargement of the uterus and external genitalia.
What is the function of progesterone during pregnancy?
Suppresses FSH and LH secretion, prevents premature childbirth, and promotes proliferation of decidual cells.
What is the role of human chorionic somatomammotropin (HCS)?
Function is not well understood but may reduce maternal insulin sensitivity, leaving more glucose for the fetus.
What are the adjustments to the circulatory system during pregnancy?
Mother's blood volume rises by about 30%, and cardiac output increases by 30% to 40%.
What respiratory changes occur during pregnancy?
Tidal volume and minute ventilation increase by about 40% to meet oxygen demands.
How does pregnancy affect the urinary system?
Glomerular filtration rate increases by 50%, and the bladder's capacity is reduced, leading to frequent urination.
What integumentary changes can occur during pregnancy?
Skin growth, added fat deposition, striae (stretch marks), and darkening of certain skin areas.
What is the weight of the uterus at the end of pregnancy?
About 900 grams, compared to 50 grams when not pregnant.
What is the significance of vitamin K during late pregnancy?
Promotes prothrombin synthesis to minimize the risk of neonatal hemorrhage.
What is the importance of folic acid before and during pregnancy?
Reduces the risk of neurological fetal disorders such as spina bifida and anencephaly.
What hormone is released by the posterior pituitary to promote labor?
Oxytocin (OT)
How does oxytocin contribute to labor?
It directly stimulates the muscles of the myometrium and stimulates fetal membranes to produce prostaglandins, which aid in labor contractions.
What initiates the neuroendocrine reflex during labor?
Cervical stretching induces a reflex through the spinal cord, hypothalamus, and posterior pituitary.
What is the primary cause of pain during the early stages of labor?
Ischemia of the myometrium due to restricted blood circulation during contractions.
What is the purpose of an episiotomy?
To widen the vaginal orifice and prevent random tearing during childbirth.
What are the three stages of labor?
1. Dilation (first stage), 2. Expulsion (second stage), 3. Placental (third stage).
What occurs during the dilation stage of labor?
The cervical canal widens to 10 cm, and the fetal membranes may rupture, leading to loss of amniotic fluid.
What happens during the expulsion stage of labor?
The baby is delivered from the entry of the head into the vagina until the baby is expelled.
What is the role of uterine contractions during the placental stage?
They cause placental separation and ensure that all membranes are expelled.
How does breast-feeding affect uterine involution?
It promotes involution by suppressing estrogen secretion and stimulating oxytocin secretion, which helps the uterus contract.
What is lactation?
The synthesis and ejection of milk from the mammary glands.
What is colostrum?
A secretion similar to breast milk that provides nutrition for the first 1 to 3 days after birth and contains antibodies.
What hormone promotes milk synthesis?
Prolactin, secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
What triggers the release of oxytocin during milk ejection?
The infant's suckling stimulates sensory receptors in the nipple, signaling the hypothalamus and posterior pituitary.
What are some differences between breast milk and cow's milk?
Breast milk has a laxative effect, supplies antibodies, and is easier to digest compared to cow's milk, which has more protein and is harder to digest.
What is the effect of nursing on prolactin levels?
Prolactin levels surge every time an infant nurses, stimulating milk synthesis for the next feeding.
What are behavioral methods of contraception?
Methods include abstinence, fertility awareness, and withdrawal (coitus interruptus).
What are barrier methods of contraception?
Methods include male and female condoms, diaphragms, and sponges.
What are hormonal methods of contraception?
Methods that prevent ovulation, such as birth-control pills, patches, injections, and vaginal rings.
What is the purpose of emergency contraceptive pills?
To induce menstruation if implantation has not occurred and inhibit ovulation.
What is an intrauterine device (IUD)?
A springy device left in the uterus to prevent pregnancy by irritating the uterine lining.
What is surgical sterilization in terms of contraception?
Clamping or cutting the genital ducts, such as vasectomy for males and tubal ligation for females.