Bandura Case Study
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
background
children known for mimicking adu→ imitative learning may lead to observing aggression/non-agression by children → believed in 1950s that watching aggressive behaviors would decrease aggression in youth
aims/hypothesis
(1) to investigate whether a child would learn aggression by observing a model / (2) investigate whether a child would reproduce this aggressive behavior in the absence of a model / (3) investigate whether the gender of the role model was important to the learning of aggression by children
research methodology
laboratory experiment (controlled setting) / IMD
participant sample
72 children, aged 4-6y/o, 36 M 36 F, Stanford University nursery school, opportunity sample
psychology being investigated
social learning theory: proposes people observe & imitate the behavior of others, esp w/ whom they identify / aggression: both physical & verbal, behavior where there is intention to harm another personor object & is usually forceful or hostile
IV’s and DV’s
IV 1: aggressive or non-aggressive role model / IV 2: same sex or opposite sex role model / IV 3: whether child was a boy or girl / DV: the learning the child displayed (aggression or non-aggression)
procedures
info: 2 adult role models (1 F & 1 M), 1 female experimenter, 6 boys saw non-aggressive male, 6 boys saw aggressive male, (same for 6 girls each), each group contained equally aggressive children (rated on aggression before experiment — rated on physical aggression, verbal aggression, aggression to inanimate objects, self control) / experimental condition: all P brought to a roomfull of toys & seated by table by experimenter → showed them how to make pics w/ potato prints & had colored stickers, experimenter took model to another corner of room w/ table, chair, tinker toy set, mallet, inflatable bobo doll before leaving room / non-aggressive condition: model played w tinker toys in a quiet manner & ignored bobo dol, → aggression condition: after a min of playing w/ tinker toys, model focused on bobo doll & agressive towards it for 9 min → after 10 mins, experimenter returned to room & P taken to game room / aggression arousal: P taken to game room to induce mild aggression arousal → ensured all P primed to initiate aggressive acts equally → P told toys were taken for them to play w/ & that the best toys are reserved for better children → P taken to experimental room frustrated / test for delayed imitation: experimenal room contained variety of aggressive & non-aggressive toys, P spent 20 min in this room while behavior was recorded w/ behavioral checklist in one-way mirror (recorded every 5 sec) / 3 categories of imitation: physical aggression (hitting/sitting/punching/kicking bobo doll), verbal aggression (“kick him”), non aggressive verbal (he sure is a tough fella) / some children only partially imitated aggressive behavior → 2 categories: mallet aggression, sit on bobo doll / non initiative aggressive behavior → punches bobo doll, non-initiative physical & verbal aggression (words but not performed), aggressive gun play (shooting darts/firing imaginary gun shots) / # of times a P playing non-aggressively or sat quietly recorded
equipment/material used
attractive toys in game room: fire truck, baby crib → experimental room: potato prints, tinker toys, sticker pictures, mallet,peg boards, dart guns, tether ball, tea set, plastic animals, color paper, balls, dolls, stuffed bears
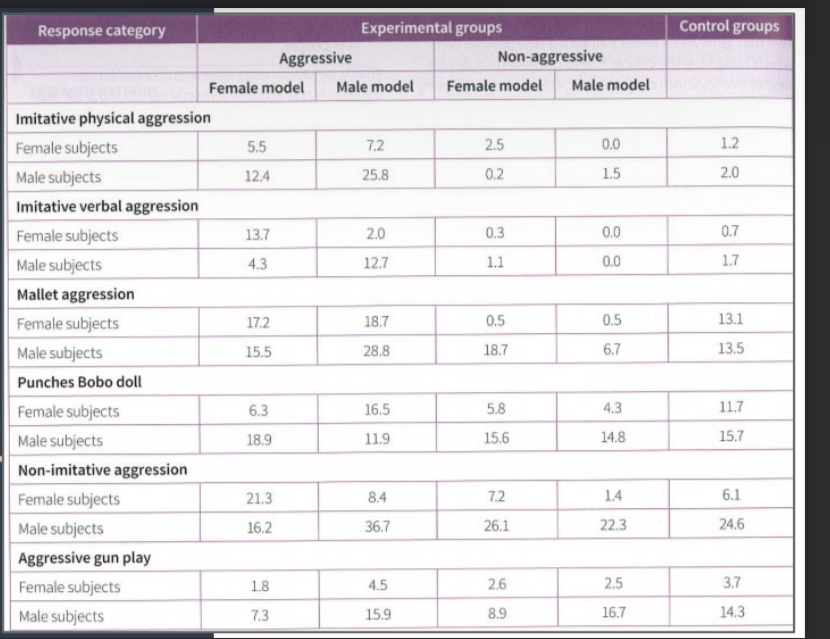
results (quantitative data)
results (qualitative data)
words children used: sock him, hit him down, throw him in the air, pow, boom, he keeps coming back for more, he sure is a tough fella / children actions: striking bobo w/mallet, striking bobo w/ other objects, sitting/kicking/laying on bobo doll, shooting darts
conclusions
(1) observed aggressive behaviors ar e imitated: children who see aggressive models more likely to be aggressive than those seeing no or non-aggressive model / (2) observed non-aggression behaviors are imitated: children seeing non-aggression models will be less aggressive than those seeing no model / (3) children more likely to copy a same-gender model / (4) boys more likely to copy aggression than girls / (5) boys more likely to engage in physical aggression / (6) girls more likely to engage in verbal aggression
strengths
controlled laboratory observation → controled extraneous variables / standardized procedures → increases reliability / high inter observer reliability
weaknesses
small sample → only 6 children used in each experimental condition / children may be similar bc they all come from stanford university nursery school → weakens validity / no interviews or self reports so understanding ‘why’ for qualitative data may be difficult / snapshot study → no long-term follow up of how children developed when it came to aggressive behaviors
situational & individual explanations
situational: children observing & copying behaviors or actions that they witnessed from adult
nature vs nurture
nurture: children watching & imitating adult behavior & then replicating what they witness
generalizability
(weakness) not generalizable to P from lower socioeconomic backgrounds → children all from nursery of prestigious university → learning experiences may differ from other children / (weakness) lacks mundane realism → unusual set-up since very rare for adult to be seen attacking toy & children → bobo dolls designed to hit & bounce back → not possible to show aggressive behavior towards toys extends to violence towards real ppl
reliability
(strength) standardized procedures & instructions → same steps for each child observed, recoorded, & processed, same behavioral checklist / (strength) high inter-observer reliability → 2 observers independently recorded P behavior using behavioral checklist in 5 sec intervals → results correlated (+0.90) → ensured consistency in scoring behaviors / (strength) inter-rater reliability → raters scores had a correlation at +0.89 → high lvl consistency in how children rated across aggression levels
validity
(strength) P matched on aggression levels → reduces individual differences in prior aggression levels / (strength) utilizing multiple inter-observers checking for reliability increased validity of qualitative data / (weakness) possible confounding variable of only one stooge being used in each male & female condition → may have imitated model due to some individual feature rather than sex
applications
important for TV networks to consider censoring content or providing warnings / parents can actively expose children to friendly role models / working w/ children can positively model 7 reinforce behaviors deemed socially acceptable
ethics
(weakness) risk of psychological harm → 1/3 of P witnessed aggressive behavior, possible that they continued to show delayed imitation of aggressive behavior / (weakness) use of children → concerning due to testing imitation of aggressive behaviors / (weakness) teacher consented, NOT guardian/parent