UNIT 7: BREAST, THORAX, LUNGS (ABNORALITIES)
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
NOTES AND BOOK
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
a recent increase in the size of one breast may indicate inflammation or an abnormal growth
(breast)
abnormal findings for inspection of size and symmetry of breast
redness (is associated with breast inflammation)
peau d’orange
(breast)
abnormal findings for inspection of color and texture of breast
peau d’orange
(breast)
pigskin-like or orange peel appearance results from edema, which is seen in metastatic breast disease.
the edema is caused by blockage lymphatic disease
resulting from edema
an orange peel appearance of the breast
associated with cancer
(breast)
peau d’orange
paget's disease
(breast)
redness, mild scaling, and flaking nipple of the may be seen early in Paget's disease of the nipple and then disappear.
however, this does not mean that the disease is gone, thus further assessment is needed.
tingling, itching, increased sensitivity, burning, discharge and pain in the nipple are late signs of this.
nipple can occur in both breasts, but is rare.
in approximately half of patients with this of the nipple, a lump or mass in the breast can be felt
retracted nipple
dimpling
retracted breast tissue
(breast)
(3) suggests malignancy
peau d’orange
(breast)
breast is edematous (pitting edema)
commo with patients that have breast cancer
paget’s disease
(breast)
crusty, red, scaly nipples
assess in the nipples
gynecomastia
(breast)
enlargement of breast for male patients
hormonal problem
possible abuse of steroids
retracted breast
(breast): nipple
normal to px with malignant tumors
supernumerary nipples
(breast): nipple
normal variation of the nipples
additional nipple
found at your embryonic milk line
dimpling or retraction
(breast): retraction and dumpling
usually caused by a malignant tumor that has fibrous strands attached to the breast tissue and the fascia of the muscles.
as the muscle contracts, it draws the breast tissue and skin with it, causing dimpling or retraction.
restricted movement of breast or retraction of the skin or nipple indicates fibrosis and fixation of the underlying tissues.
this is usually due to an underlying malignant tumor.
malignant tumors
(breast): masses
most often found in the upper outer quadrant of the breast.
they are usually unilateral, with irregular, poorly delineated borders.
they are hard and nontender and fixed to underlying tissues.
fibroadenomas
(breast): masses
are usually 1-5 cm, round or oval, mobile, firm, solid, elastic, nontender, single or multiple benign masses found in one or both breasts.
milk cysts (sacs filled with milk) and infections (mastitis),
(breast): masses
these may turn into an abscess and occur if breastfeeding or recently given birth.
lipomas
(breast): masses
are a collection of fatty tissue that may also appear as a lump
intraductal papilloma
(breast): masses
is a small growth inside a milk duct of the breast, often near the areola. It is harmless and occurs in women ages 35 to 50.
discharge
(breast): nipples
may be seen in endocrine disorders and with certain medications (i.e., antihypertensives, tricyclic antidepressants, and estrogen).
from one breast may indicate benign intraductal papilloma, fibrocystic disease, or cancer of the breast.
watery, pink discharge
(breast): nipples
sometimes there is only a _____________ from the nipple. This should be referred to a primary care provider
barrel chest
(chest & lungs): configuration
when the diameter in anteroposterior is equal to the transverse diameter
pectus excavatum
(chest & lungs): configuration
depressed sternum
funnel because of shape
congenital
pectus carinatum
(chest & lungs): configuration
pigeon because of beak
barrel chest
(chest & lungs): configuration
ribs appearing horizontal at an angle greater than 45 degrees with the spinal column are frequently the result of an increased ratio between the anteroposterior-transverse diameter
barrel chest
(chest & lungs): configuration
this condition is commonly the result of emphysema due to hyperinflation of the lungs.
tripod position
(chest & lungs): accessory muscles
client leans forward and uses arms to support weight and lift chest to increase breathing capacity
this is often seen in COPD.
kyphosis
(chest & lungs)
normal finding for inspection of configuration:
an increased curve of the thoracic spine
common in older clients
it results from a loss of lung resiliency and a loss of skeletal muscle
it may be a normal finding
crepitus
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for crepitus
can be palpated if air escapes from the lung or other airways into the subcutaneous tissue, as occurs after an open thoracic injury, around a chest tube, or tracheostomy.
also may be palpated in areas of extreme congestion or consolidation.
in such situations, mark margins and monitor to note any decrease or increase in the crepitant area.
unequal fremitus
(chest & lungs)
abnormality fremitus
is usually the result of consolidation (which increases fremitus) or bronchial obstruction, air trapping in emphysema, pleural effusion, or pneumothorax (which all decreases this).
diminished fremitus
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for fremitus
even with a loud spoken voice may indicate obstruction of the an tracheobronchial tree.
apnea
apeustic
tachypnea
bradypnea
hyperventilation
hypoventilation
cheyne-stokes respiration,
biot's respiration.
(chest & lungs)
abnormal breathing patterns includes:
apnea
(chest & lungs)
abnormal breathing patterns
no breathing/none
apneustic
(chest & lungs)
abnormal breathing patterns
abnormal breathing pattern
biot’s respiration
(chest & lungs)
abnormal breathing patterns
regular breathing followed by apnea
cheyne-stokes
(chest & lungs)
abnormal breathing patterns
irregular–none
kussmaul’s breathing
(chest & lungs)
abnormal breathing patterns
rapid, deep, labored breathing
tenderness over thoracic muscles can result from exercising (e.g., pushups) especially in a previously sedentary client
(chest & lungs)
abnormal finding for tenderness, sensation, and surface masses
unequal chest expansion
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for chest expansion
can occur with severe atelectasis (collapse or incomplete expansion), pneumonia, chest trauma, or pneumothorax (air in the pleural space).
decreased chest excursion
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for chest expansion
at the base of the lungs is characteristic of COPD.
this is due to decreased diaphragmatic function.
hyperresonance
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for tone
is elicited in cases of trapped air such as in emphysema or pneumothorax.
dullness
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for diaphragmatic excursion
tone that is present when fluid or solid tissue replaces air in the lung or occupies the pleural space, such as in lobar pneumonia, pleural effusion, or tumor.
diaphragmatic descent
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for diaphragmatic excursion
may be limited by atelectasis of the lower lobes or by emphysema, in which diaphragmatic movement and air trapping are minimal.
uneven excursion
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for diaphragmatic excursion
may be seen with inflammation from unilateral pneumonia, damage. to the phrenic nerve, or splenomegaly.
diminished or absent breath sounds
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
often indicate that little or no air is moving in or out of the lung area being auscultated.
this may indicate obstruction within the lungs as a result of secretions, mucus plug, or a foreign object.
it may also indicate abnormalities of the pleural space such as pleural thickening, pleural effusion, or pneumothorax.
hyperinflated nature of the lungs; loss of elasticity of lung tissue
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
in cases of emphysema, the _____________, together with a _____________, may result in diminished inspiratory breath sounds.
increased (louder) breath sounds
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
often occur when consolidation or compression results in a denser lung area that enhances the transmission of sound.
crackles (rales)
wheezes (rhonchi)
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for adventitious sounds
adventitious lung sounds, such as ______and ______ are evident.
fine crackles
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
characteristics:
high-pitched, short, popping sounds heard during inspiration
not cleared with coughing
sounds are discontinuous and can be simulated by rolling a strand of hair between your fingers near your ear.
source:
inhaled air suddenly opens the small, deflated air passages that are coated and sticky with exudate.
associated conditions:
crackles occurring late in inspiration are associated with restrictive diseases such as pneumonia and congestive heart failure.
crackles occurring early in inspiration are associated with obstructive disorders such as bronchitis, asthma, Or emphysema.
coarse crackles
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
characteristics:
low-pitched, bubbling, moist sounds that may persist from early inspiration to early expiration
also described as softly separating Velcro
source:
inhaled air comes into contact with secretions in the large bronchi and trachea.
associated conditions:
may indicate pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and pulmonary fibrosis.
"Velcro rales" of pulmonary fibrosis are heard louder and closer to stethoscope, usually do not change location, and are more common in clients with long-term COPD.
pleural friction rub
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
characteristics:
coarse, dry, grating sound
sound is much like crackles, only more superficial and occurring during both inspiration and expiration.
source:
sound is the result of rubbing of two inflamed pleural surfaces.
associated conditions:
pleuritis
sibilant wheeze
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
characteristics:
high-pitched, musical sounds
heard primarily during expiration but may also be heard on inspiration.
source:
air passes through constricted passages (caused by swelling, secretions, or tumor).
associated conditions:
often heard in cases of acute asthma or chronic emphysema.
sonorous wheeze
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
characteristics:
low-pitched snoring moaning sounds heard primarily during expiration but may be heard throughout the respiratory cycle.
source:
same as sibilant wheeze.
the pitch of the wheeze cannot be correlated to the size of the passageway that generates it.
associated conditions:
are often heard in cases of bronchitis or single obstructions and snoring before an episode of sleep apnea.
stridor
(chest & lungs)
abnormality for breath sounds
is a harsh, honking wheeze with severe broncholaryngospasm, such as occurs with croup
normal (eupnea)
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: 12-20 breaths/min and regular
clinical indication: normal breathing pattern

tachypnea
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: more than 24 breaths/min and shallow
clinical indication: may be a normal response to; can fever, anxiety, or exercise occur insufficiency, with respiratory alkalosis, pneumonia, or pleurisy

bradypnea
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: less than 10 breaths/min and regular
clinical indication: may be normal in well-conditioned athletes; can occur with medication-induced depression of the respiratory center, diabetic coma, neurologic damage

hyperventilation
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: increased rate and increased depth
clinical indication: usually occurs with extreme exercise, fear, or anxiety; causes of hyperventilation include disorders of the central nervous system, an overdose of the drug salicylate, or severe anxiety
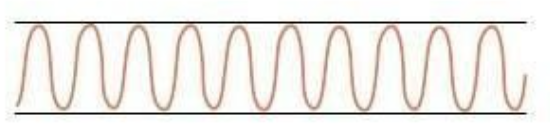
kussmaul breathing
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: rapid, deep, labored
clinical indication: a type of hyperventilation associated with diabetic ketoacidosis

hypoventilation
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: decreased rate, decreased depth, irregular pattern
clinical indication: usually associated with overdose of narcotics or anesthetics

cheyne-stokes respiration
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: regular pattern characterized by alternating periods of deep, rapid breathing followed by periods of apnea
clinical indication: may result from severe congestive heart failure, drug overdose, increased intracranial pressure, or renal failure; may be noted in elderly persons during sleep, not related to any disease process

biot’s pattern
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: irregular pattern characterized by varying depth and rate of respirations followed by periods of apnea
clinical indication: may be seen with meningitis or severe brain damage

ataxic
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: significant disorganization with irregular and varying depths of respiration
clinical indication: more extreme expression of biot's respirations indicating respiratory compromise

air tapping
(chest & lungs)
respiration patterns:
description: increasing difficulty in getting breath out
clinical indication: in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, air is trapped in the lungs during forced expiration
