Organic Chemistry (Reactions)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Catalytic Hydrogenation
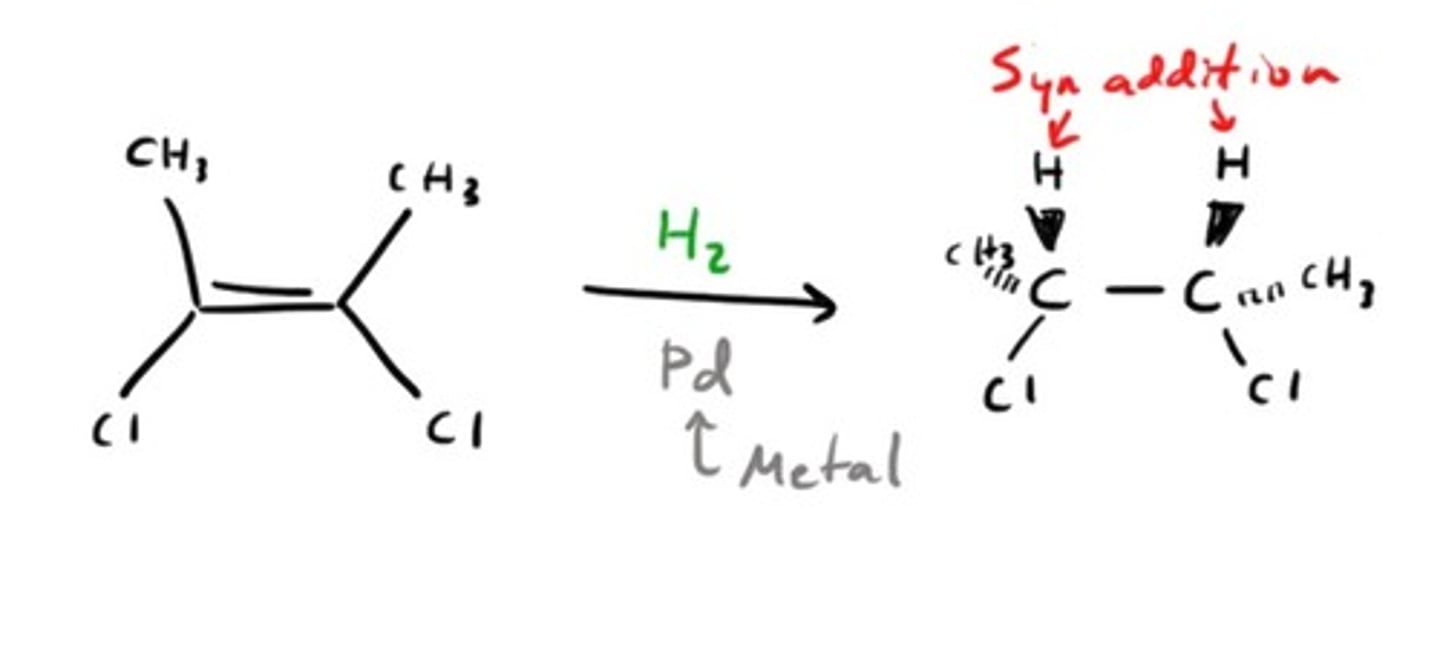
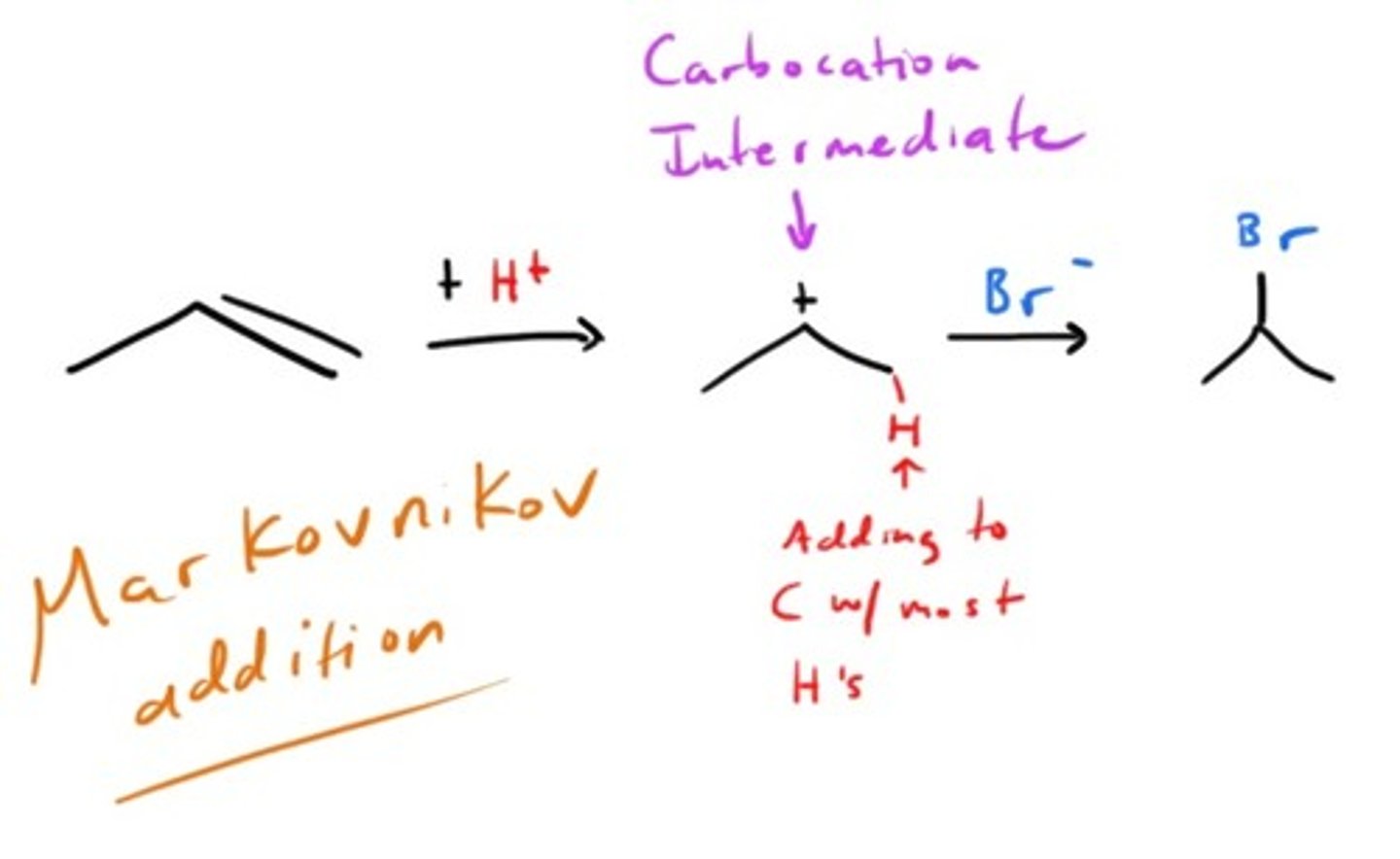
Addition of HX to an alkene
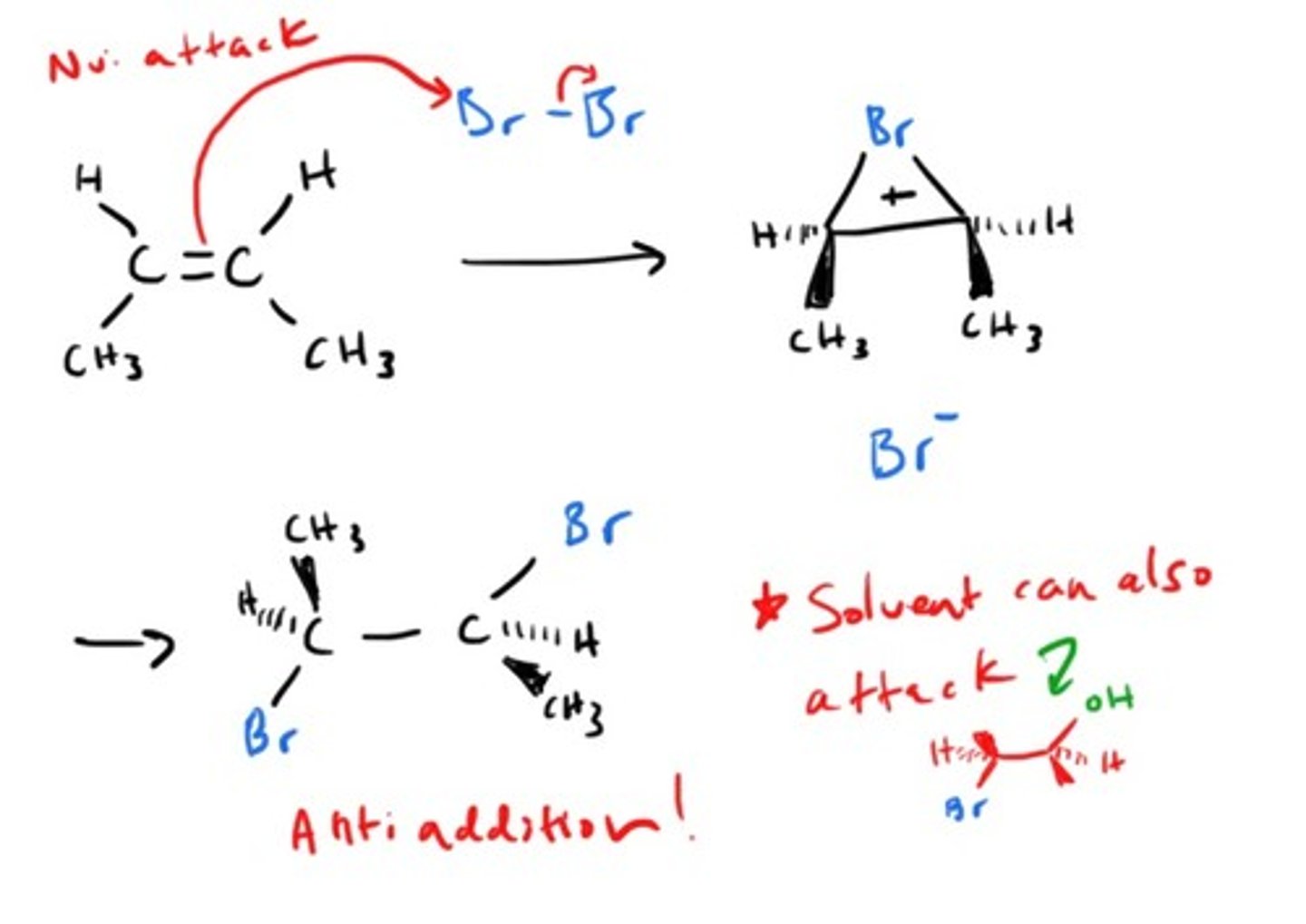
Addition of X2 to alkene
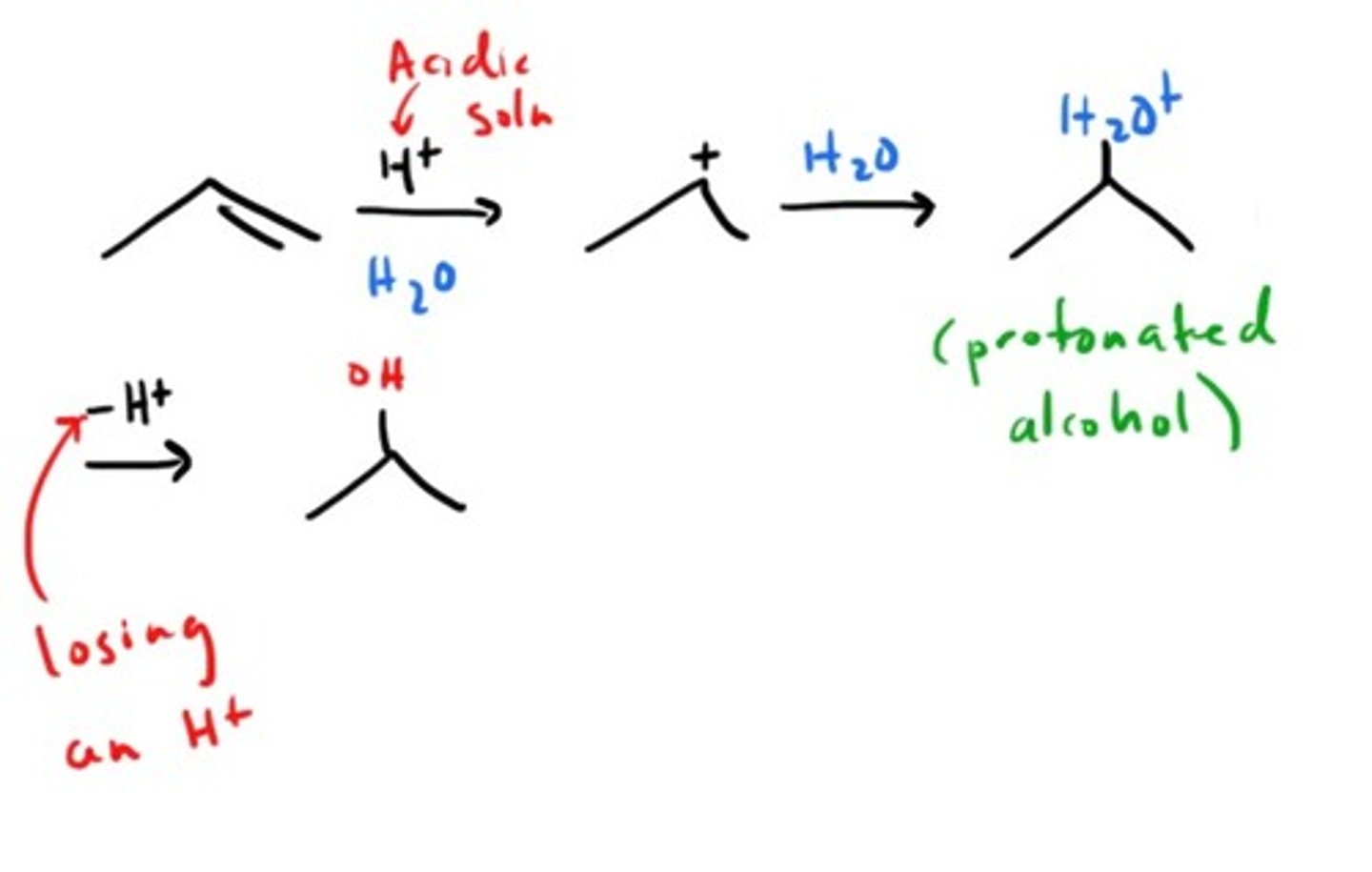
Addition of H2O to alkene
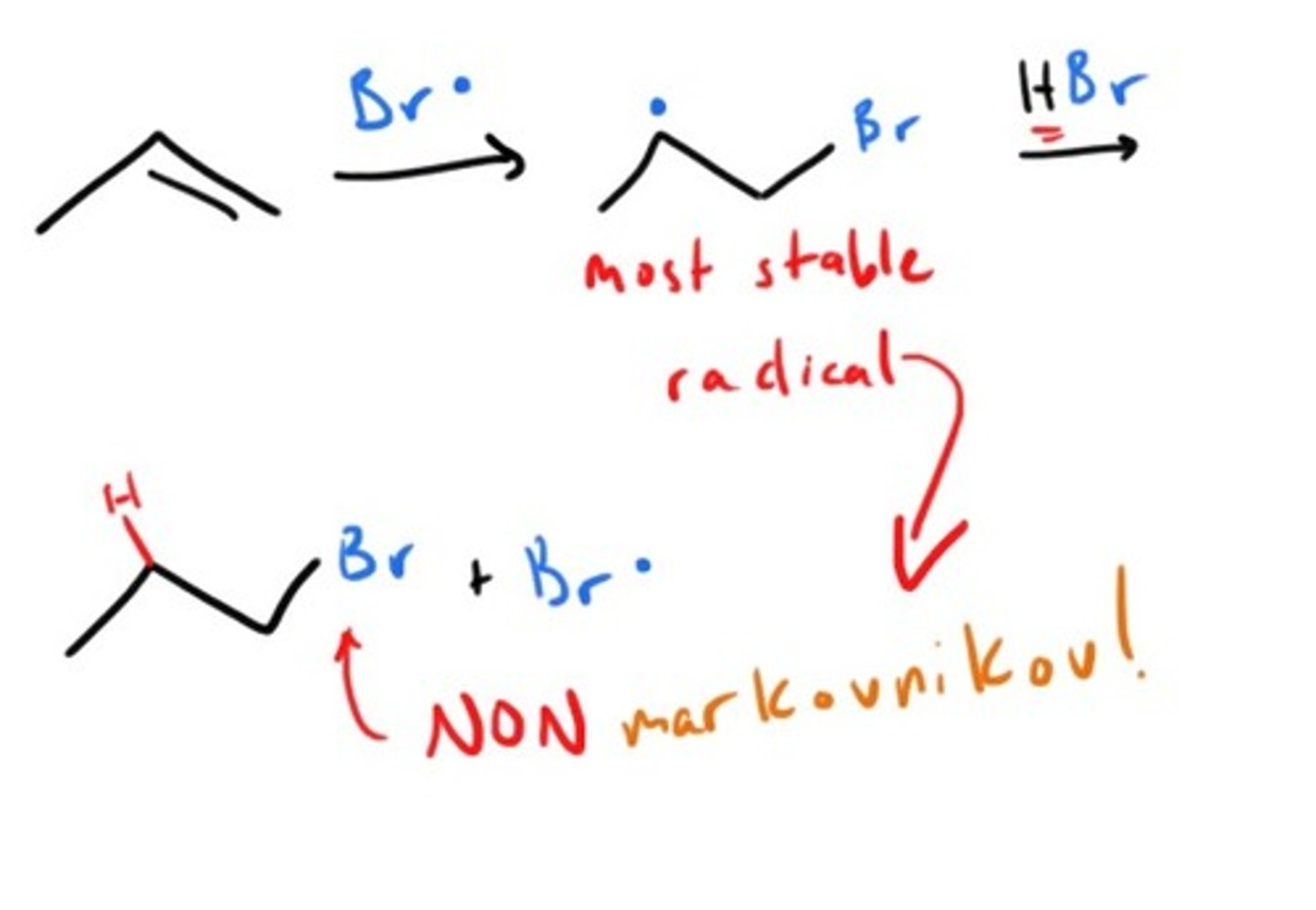
Free Radical Addtion to alkene
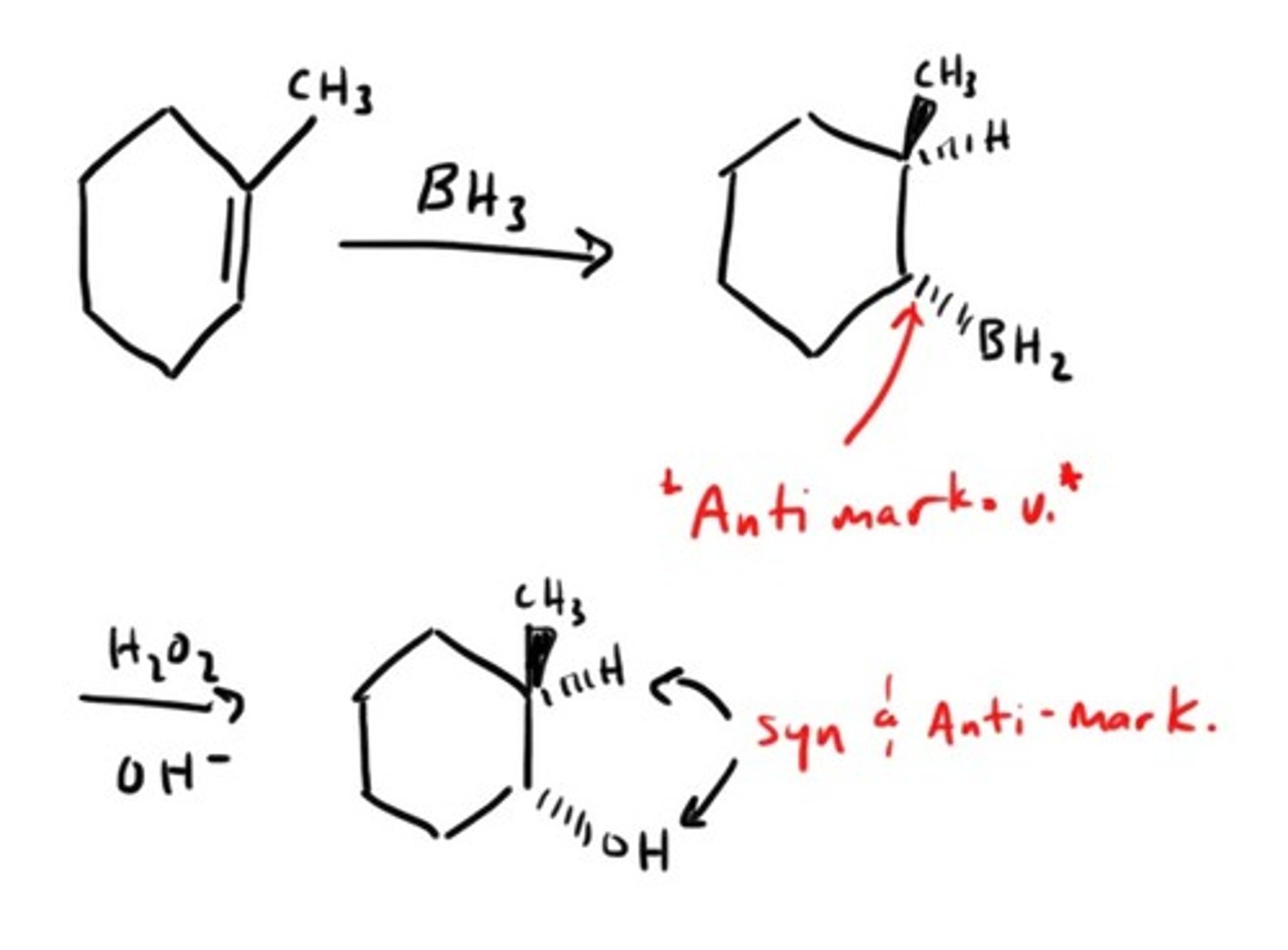
Hydroboration
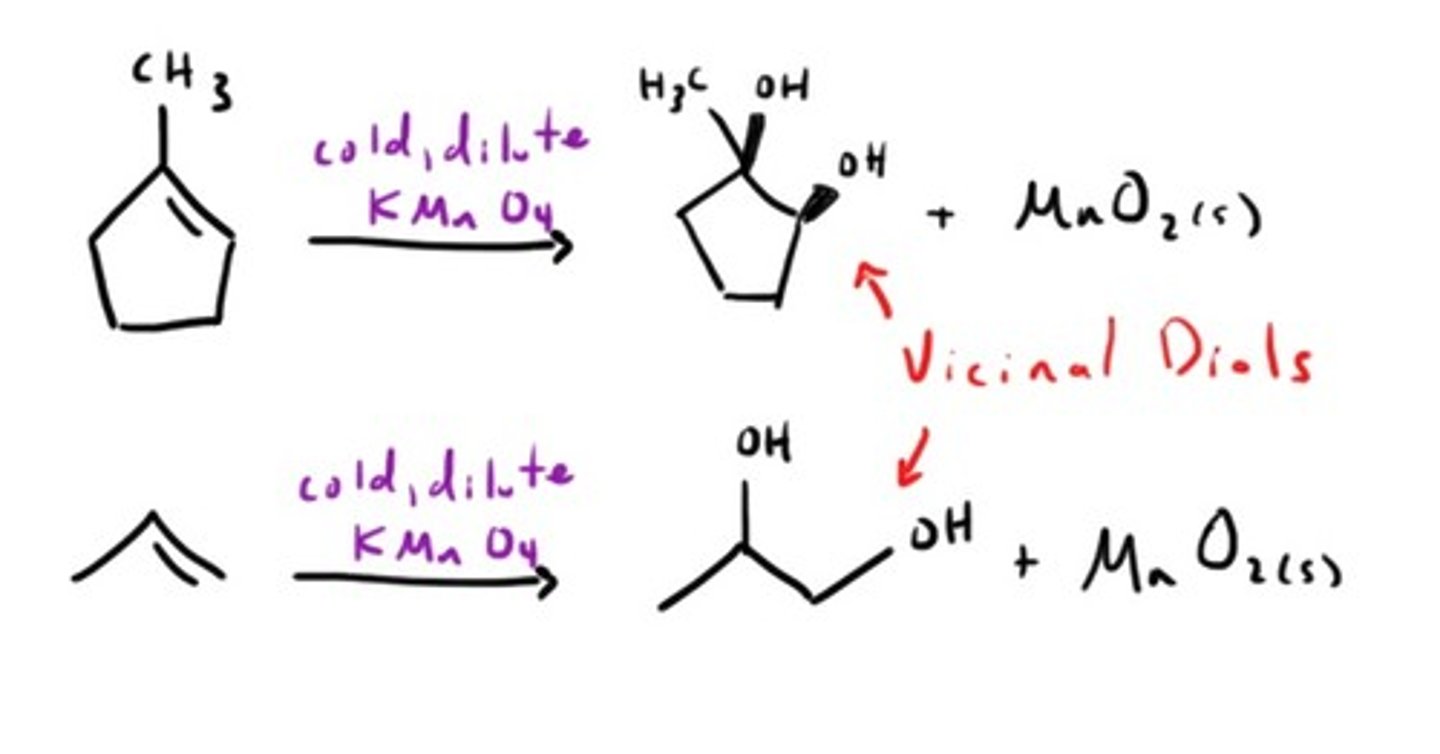
Oxidation with KMnO4 (Cold)
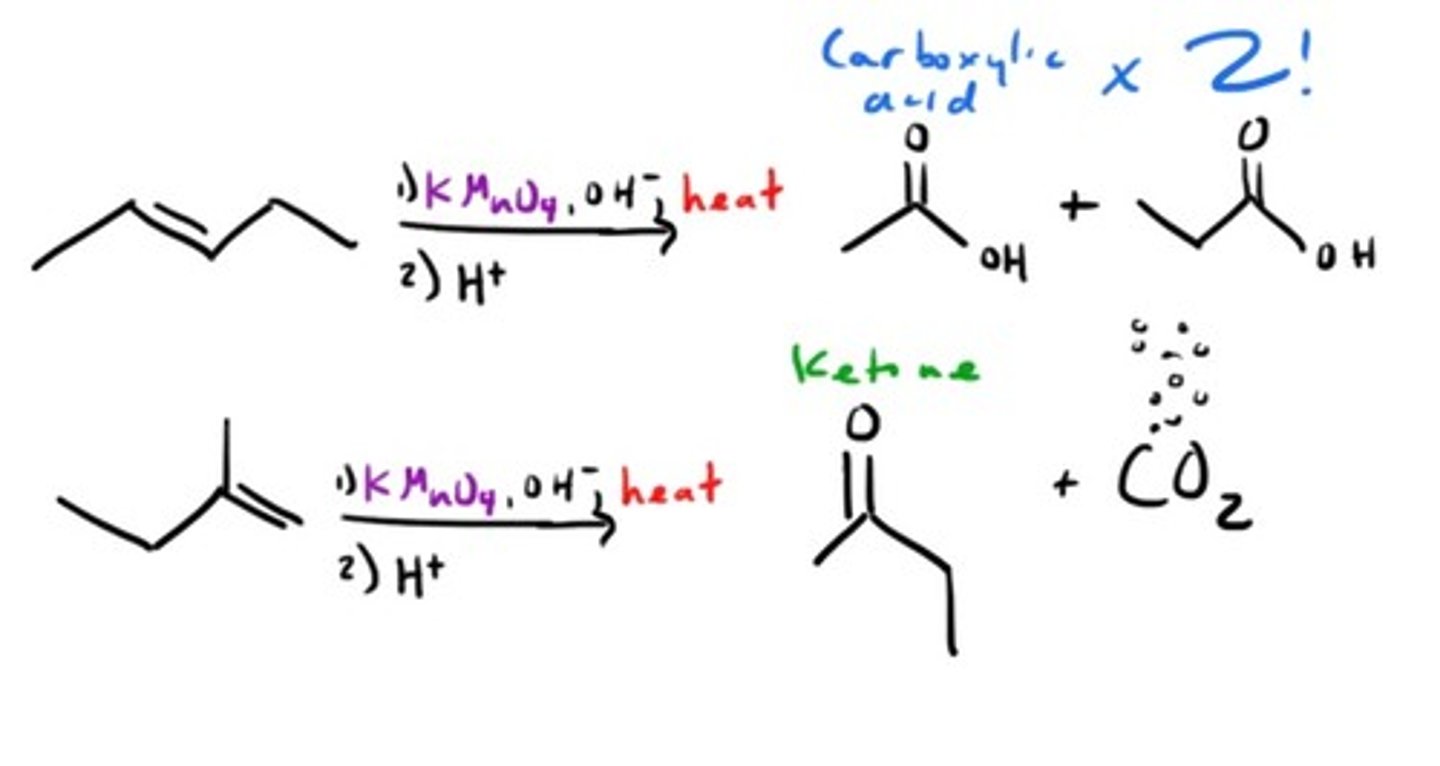
Oxidation with KMnO4 (Hot)
What do you use to add to polymers?
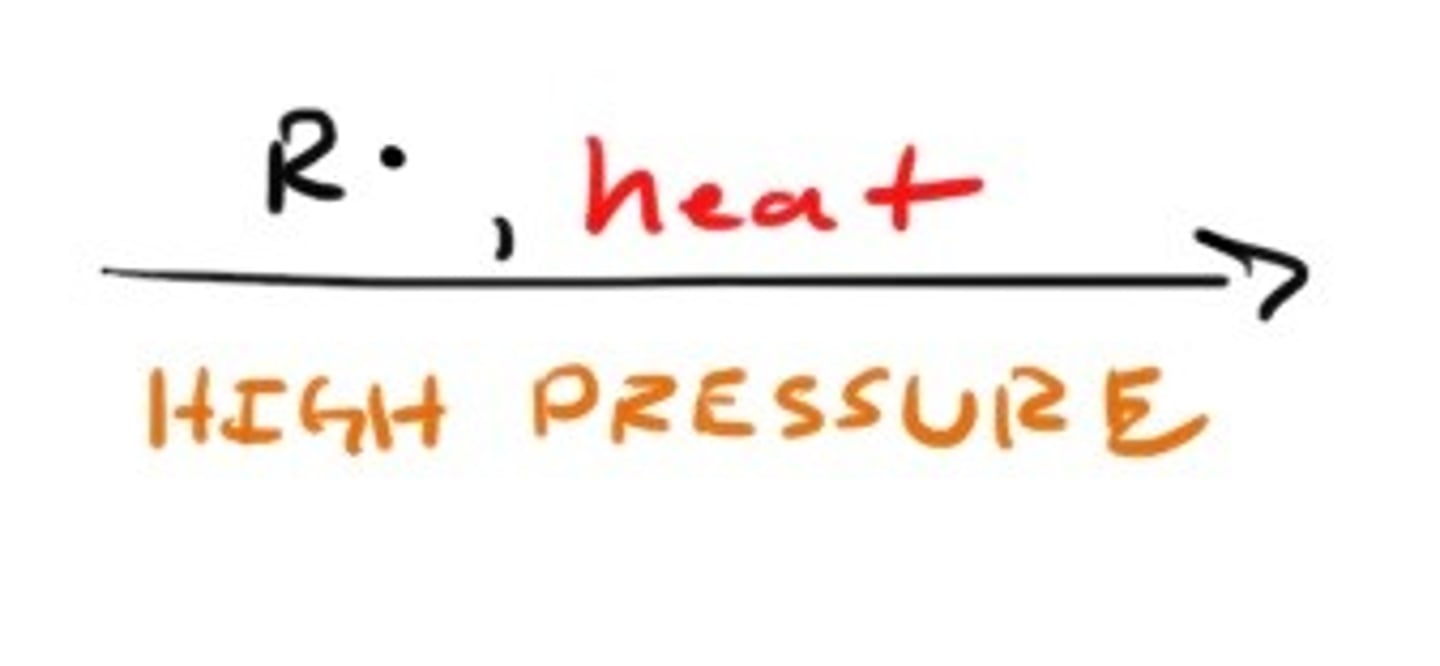
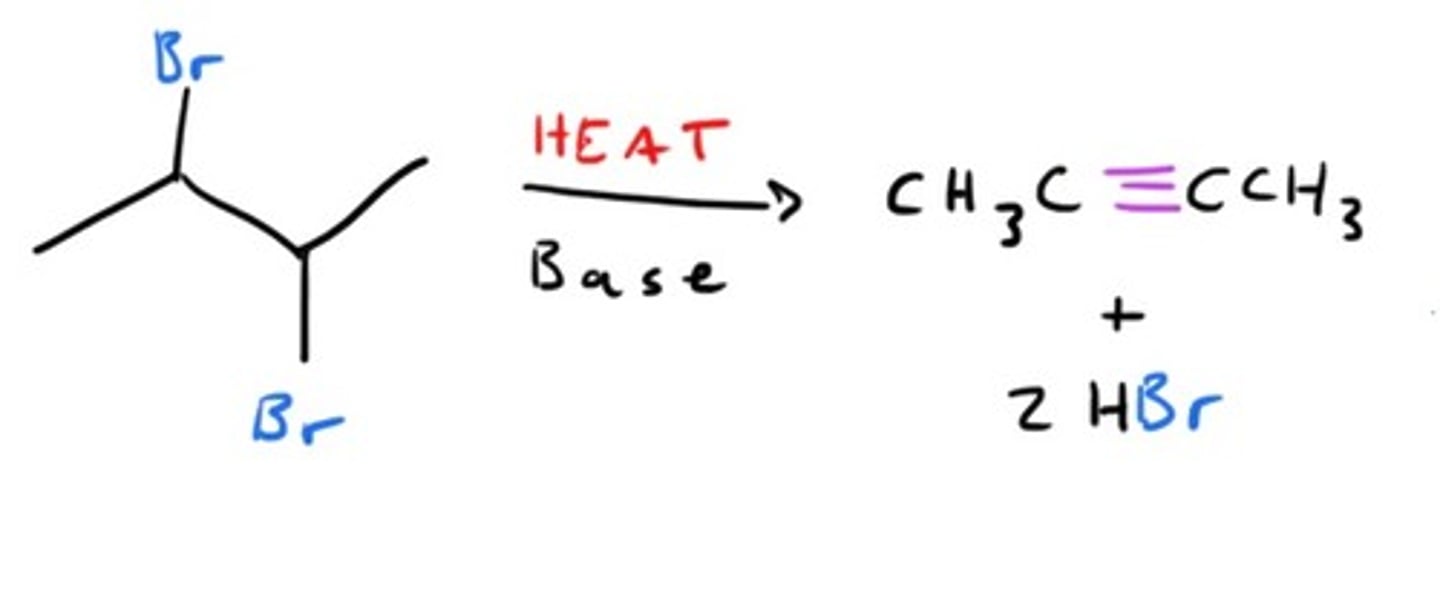
Synthesis of Alkyne starting from dihalide
Synthesis of Alkyne using acytelide ion
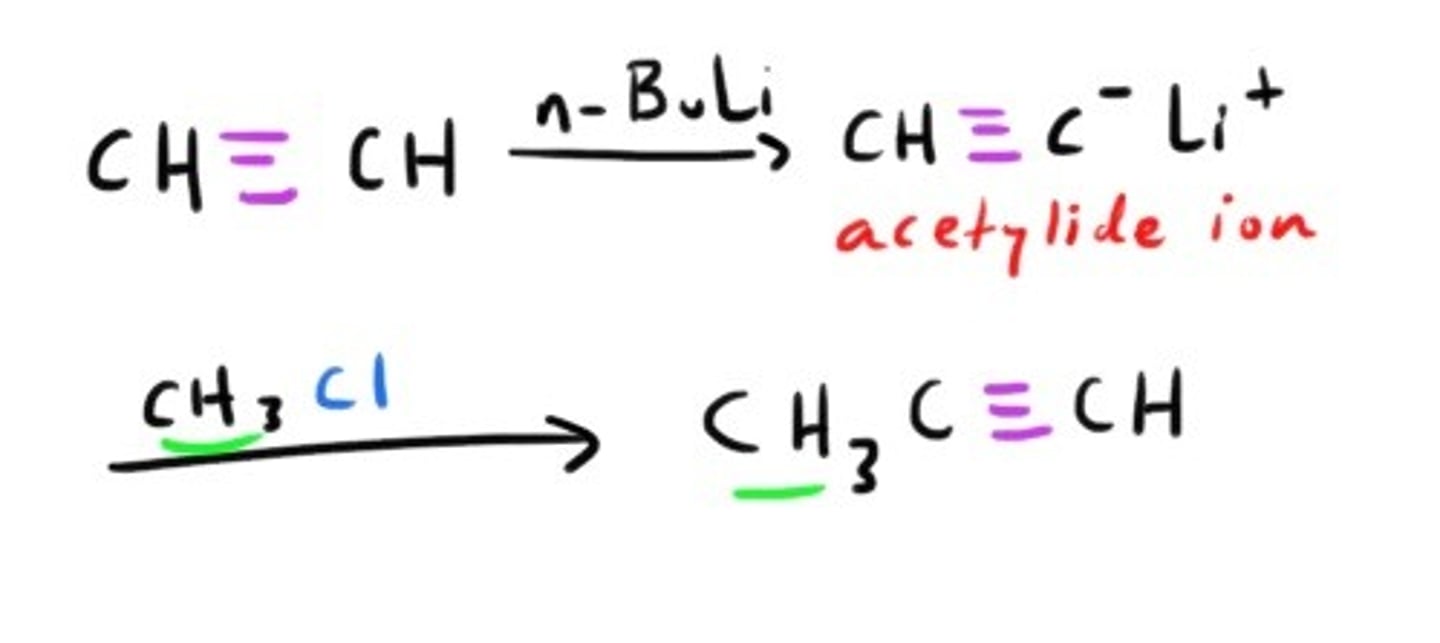
Alkyne Reduction
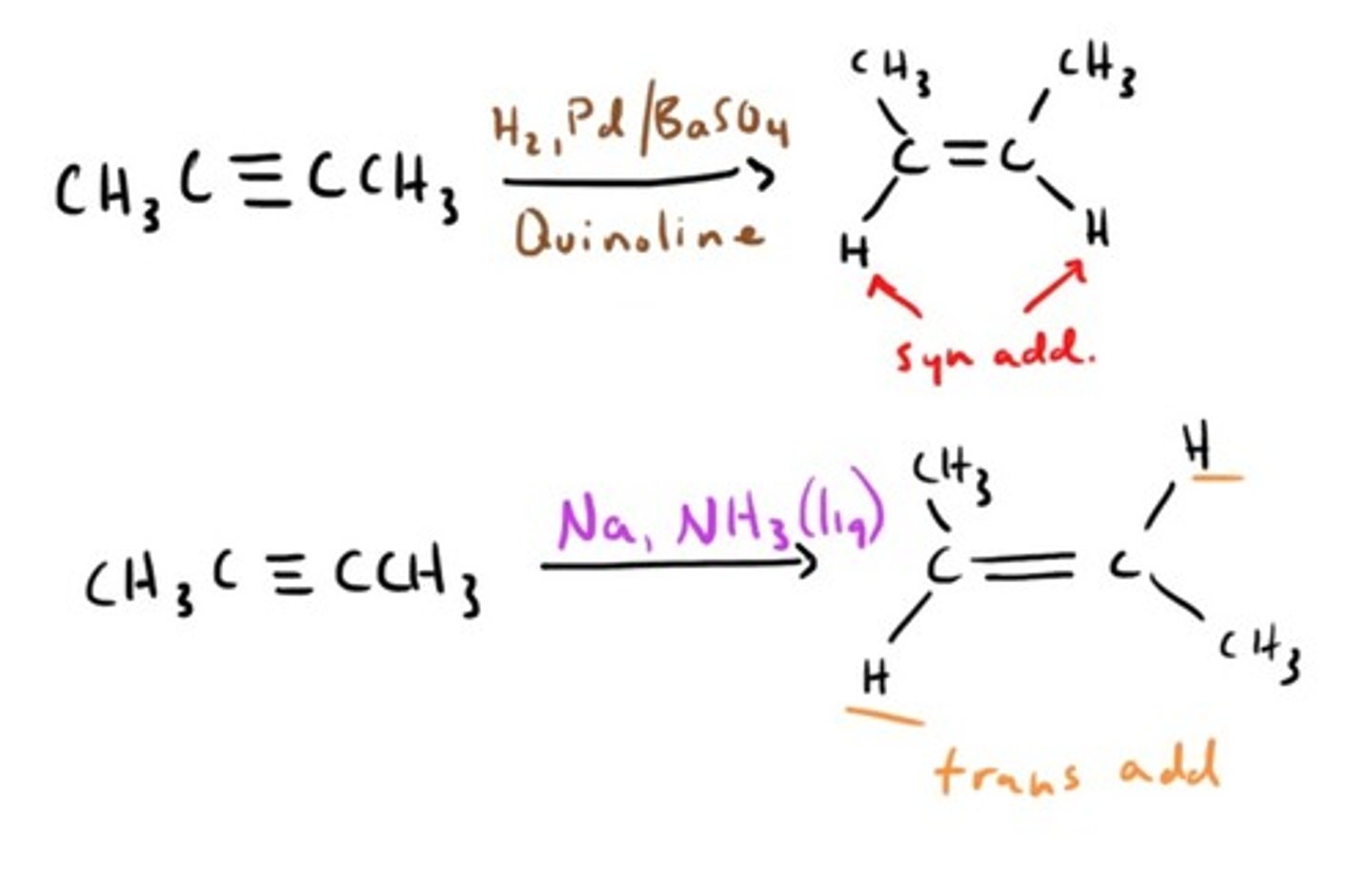
Alkyne Reduction by free radical
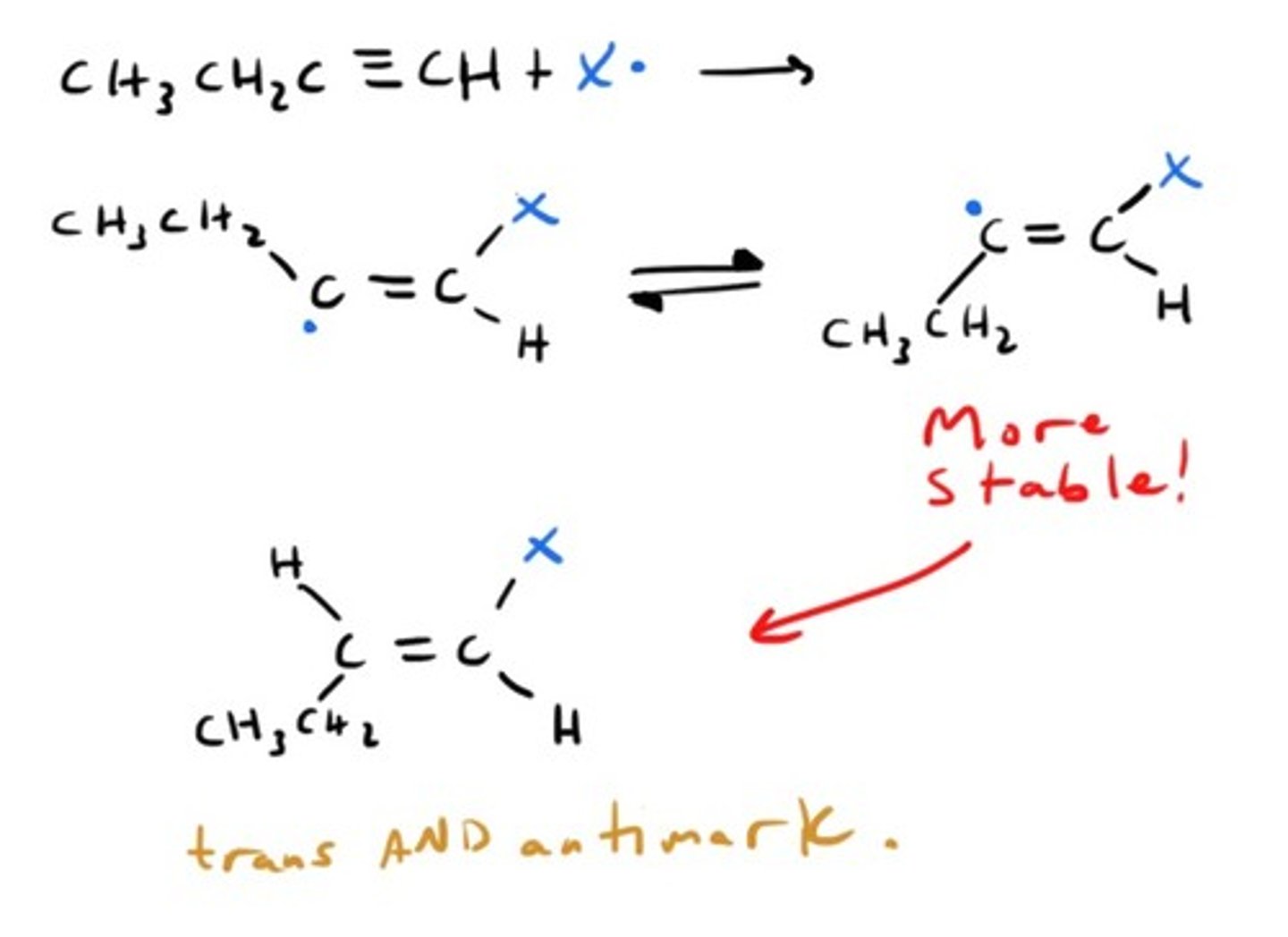
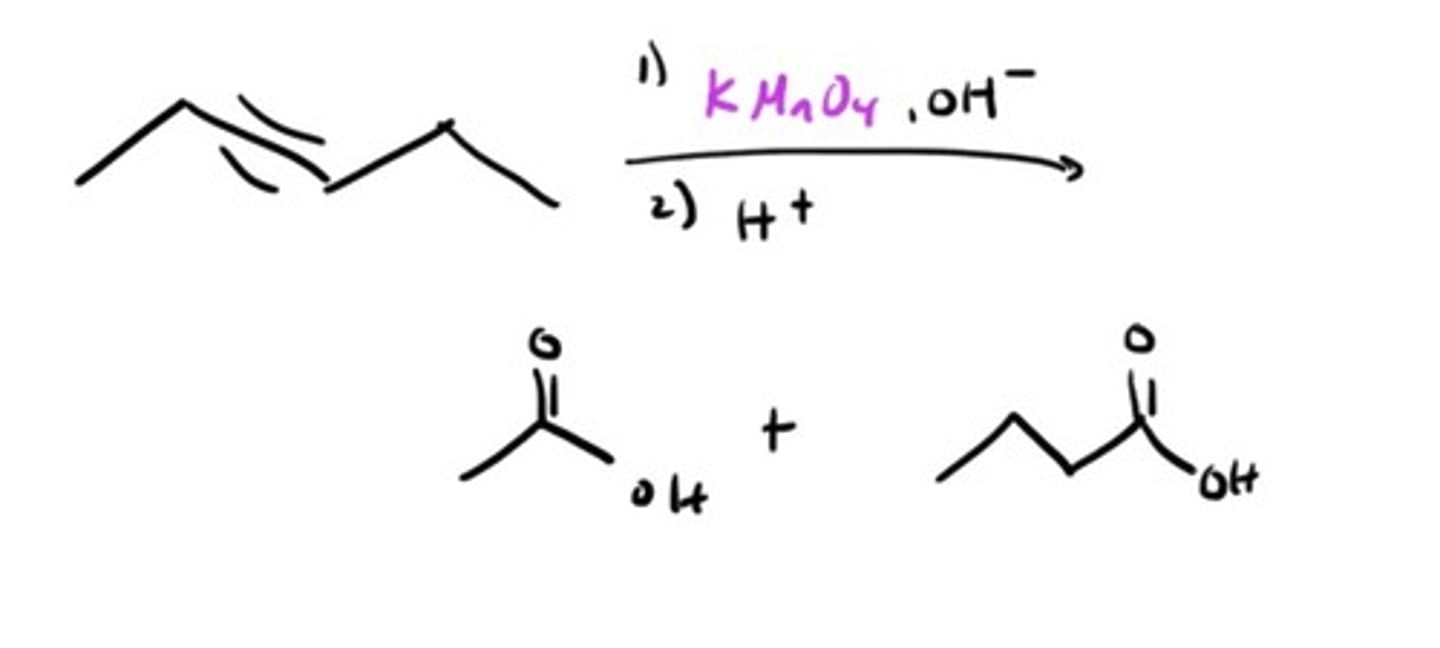
Oxidation of Alkyne by KMnO4
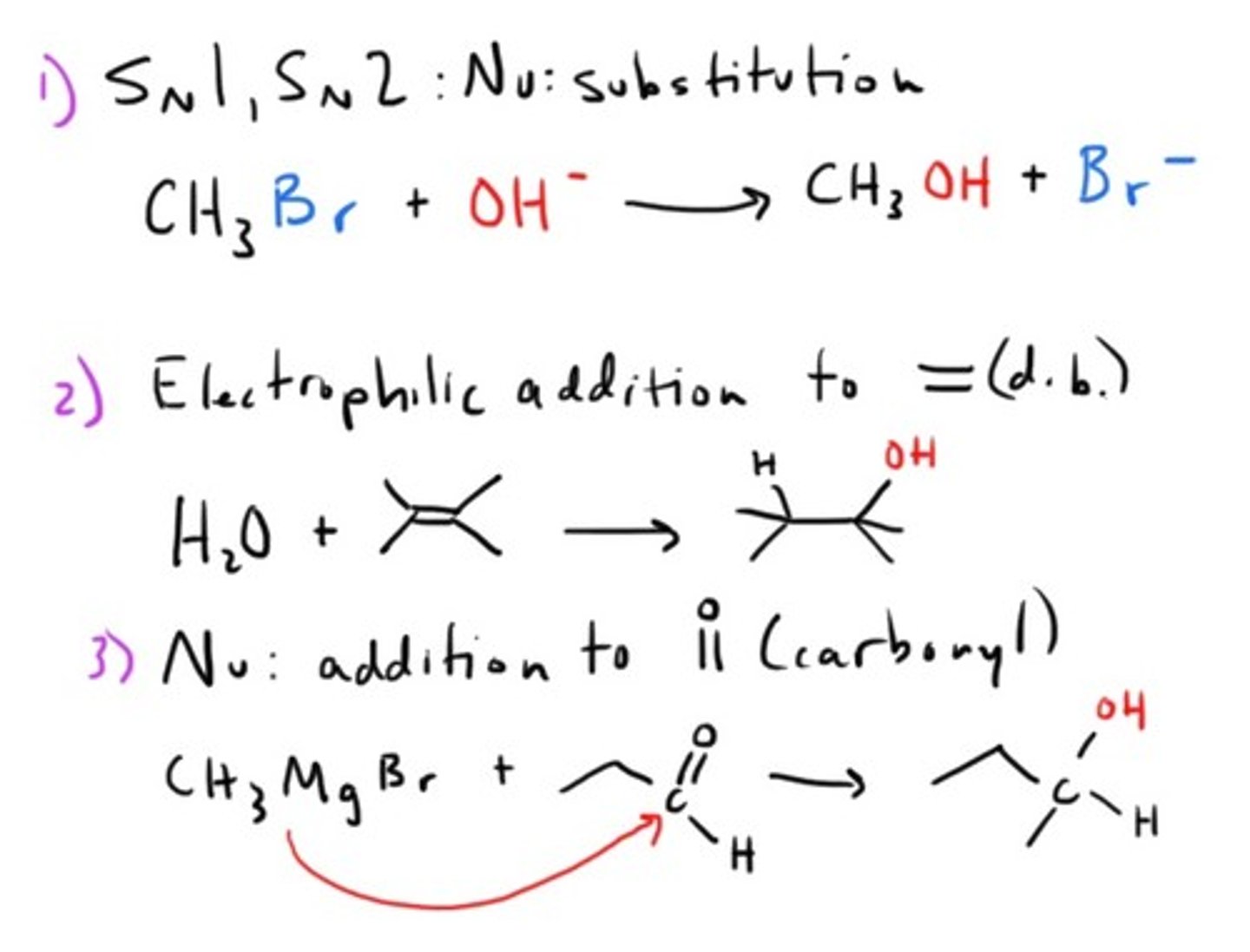
Key reaction mechanisms for Alcohols and Ethers
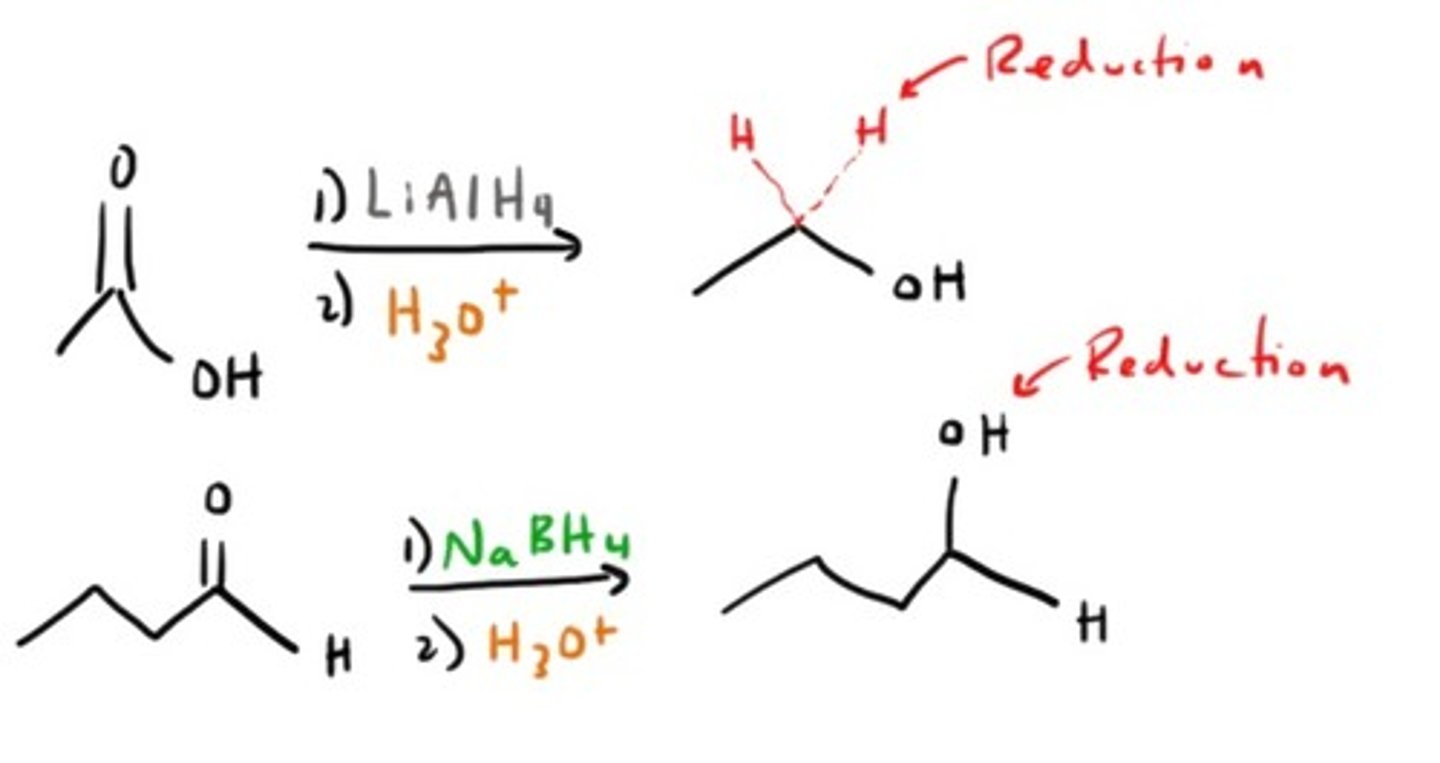
Reduction to make Alcohol
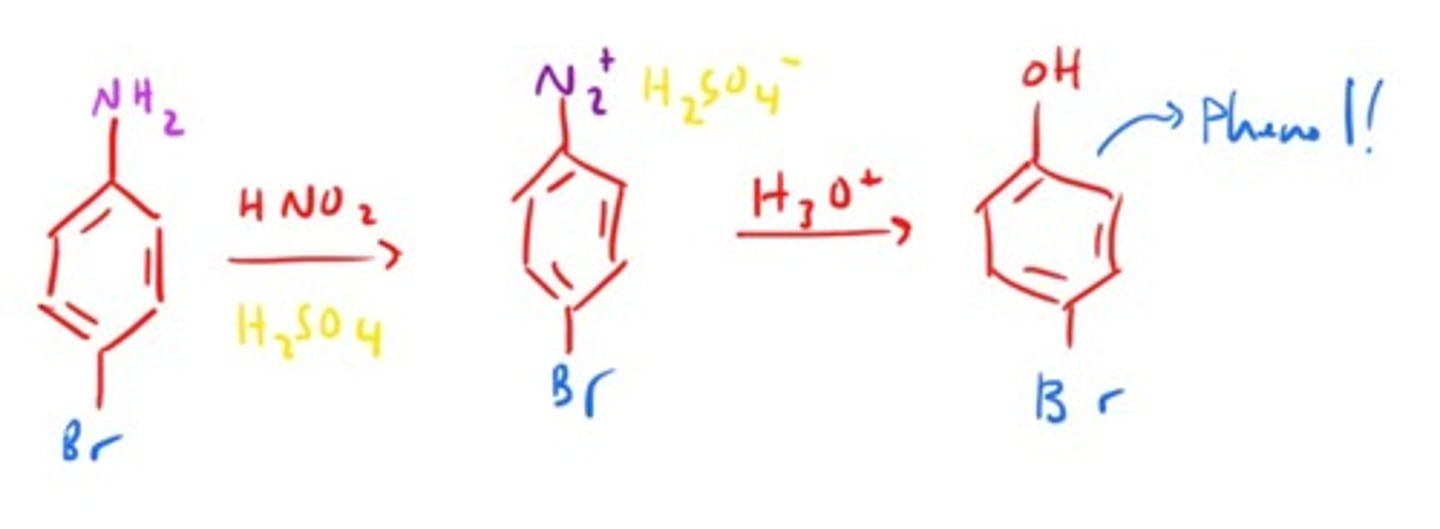
Phenol Synthesis
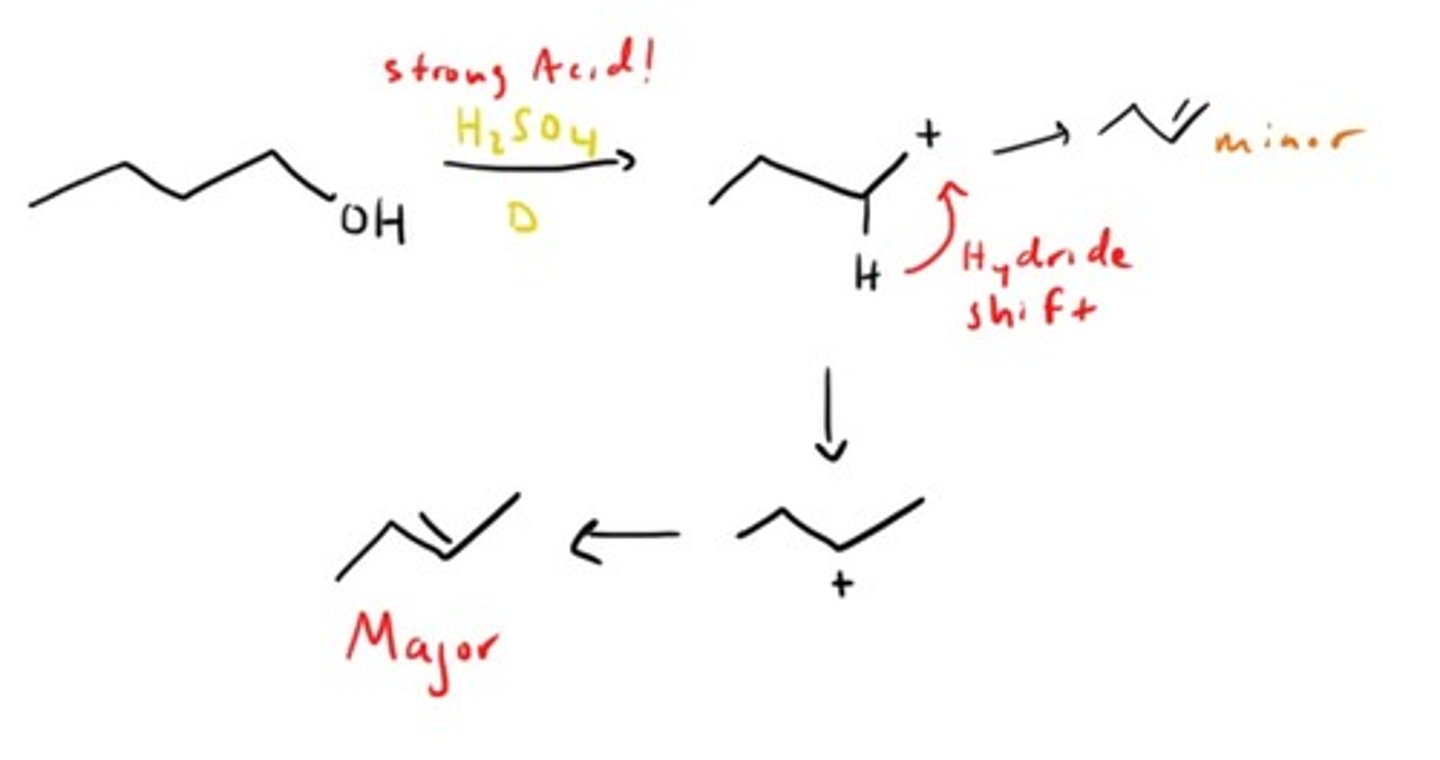
Alcohol dehydration (elimination)
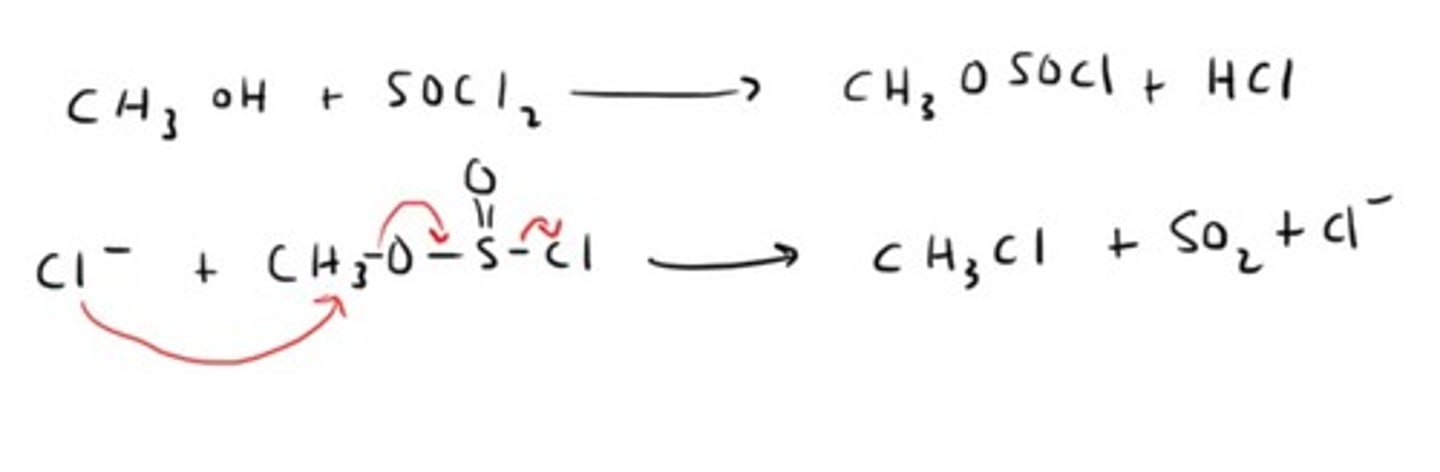
How do you convert an alcohol into an alkyl halide with an ester as an intermediate?
Do ethers boil at high or low temperatures?
Low...no H-bonding.
William Ether Synthesis
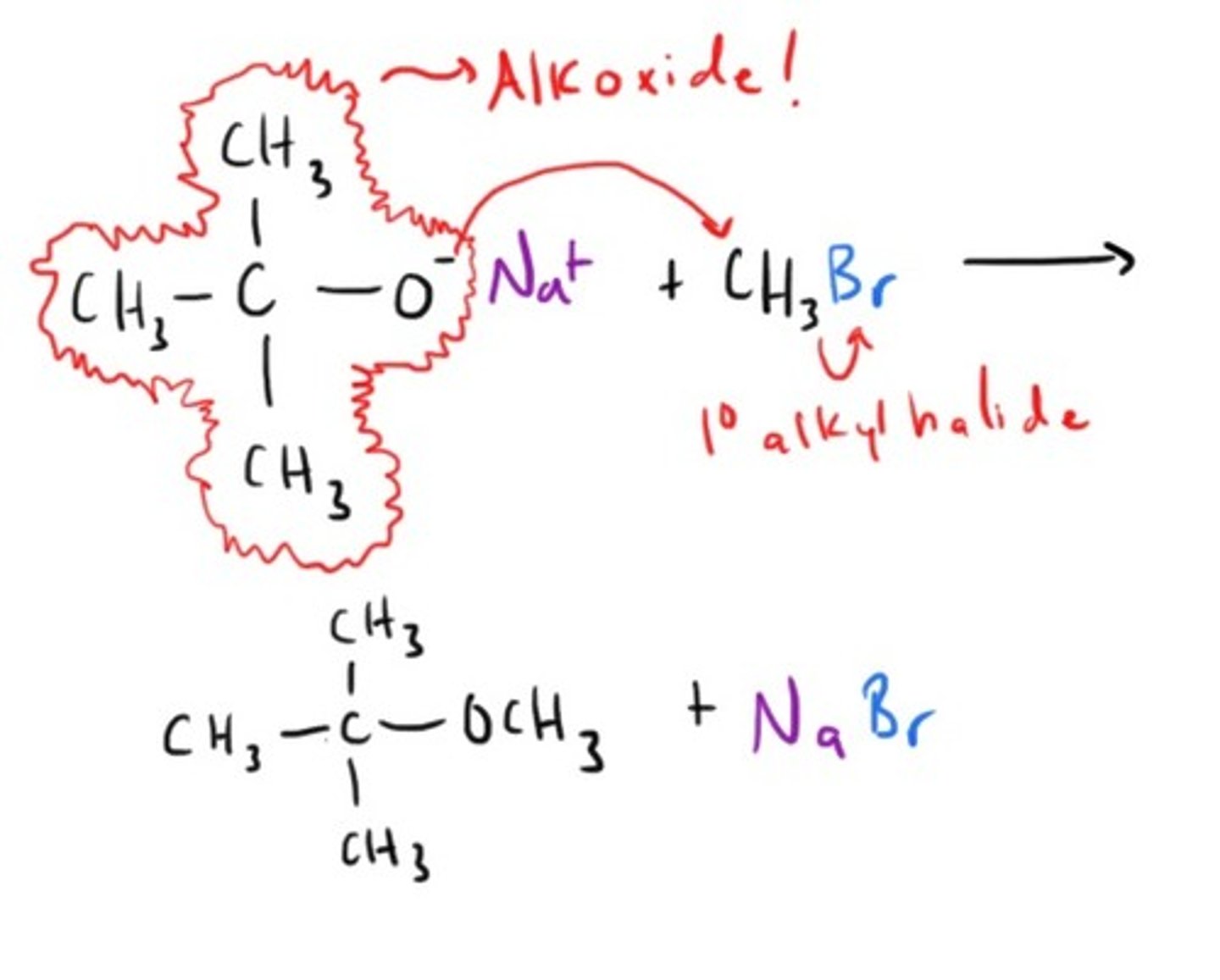
How to Cleave an Ether!
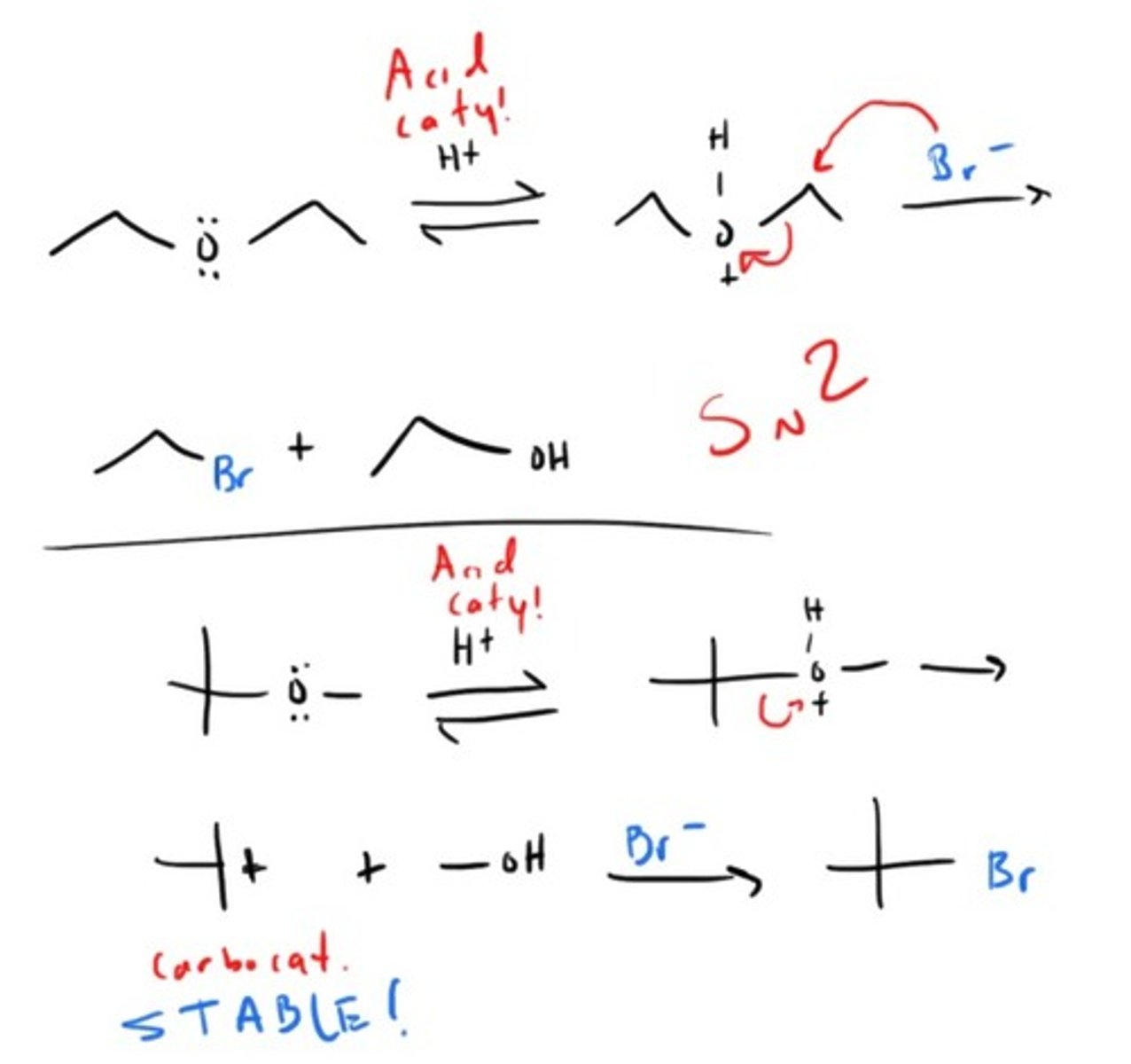
How can you get ketones or aldehydes?
Oxidation of primary or secondary alcohols. Or ozonolysis of alkenes.
What oxidizes an aldehyde and what do you get?
KMnO₄, CrO₃, Ag₂O, H₂O₂ and you get a carboxylic acid.
What reduces aldehydes and ketones?
LAH or NaBH₄
Electron withdrawing vs donating...what do each do to a negative charge and acidity?
Withdrawing delocalize/stabillize the negative charge (spread it over the molecule) which increase acidity. Donating do the opposite.
Only primary alcohols can be oxidized to carboxylic acids. T/F?
True!
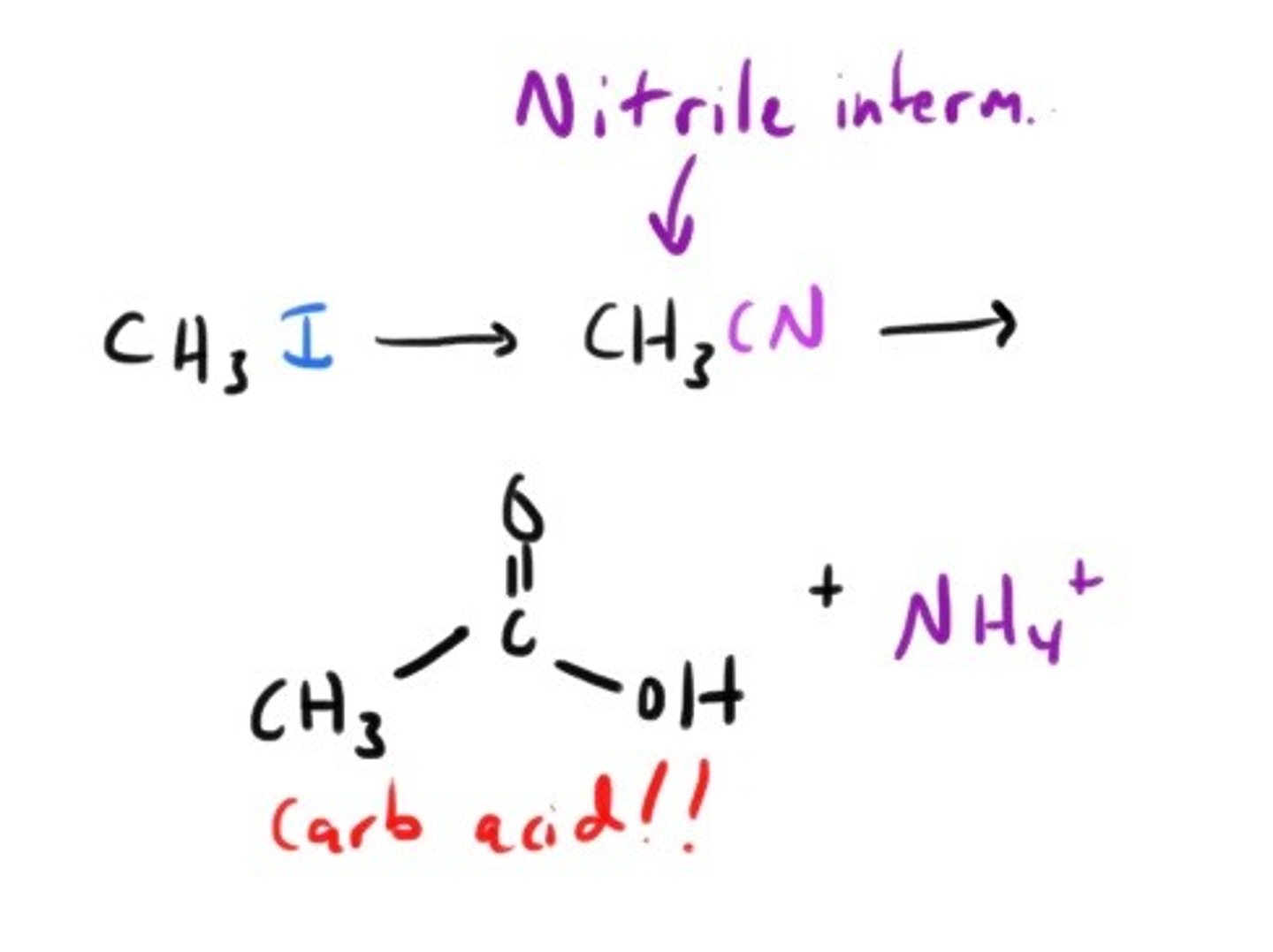
Is there a way to convert primary and secondary alkyl halides into carboxylic acids? Sure!!
nitrile formation followed by acid or base catalyzed hydrolysis.
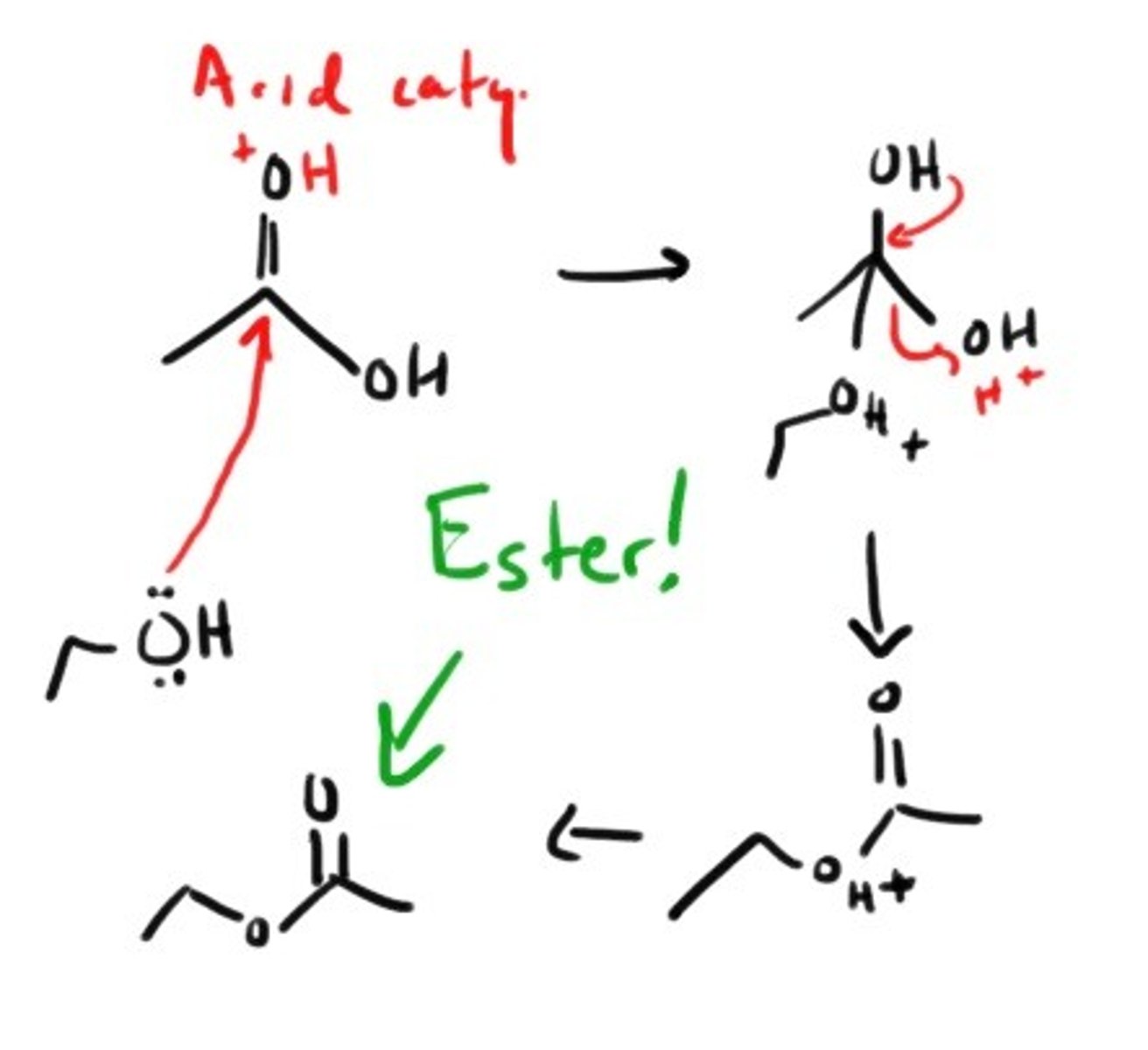
How do you form an ester with a carboxylic acid?
Addition of a primary alcohol under ACIDIC conditions.
How can one make an anhydride?
React a carboxylic acid with a carboxylate salt or heat! to stabilize the carboxylic acid.
The conversion of a carboxylic acid into ANYTHING depends on what?
The nucleophile!!
Can nitrogen containing compounds form hydrogen bonds?
Yes, but the are not as strong as the hydrogen bond between H and oxygen! (Therefore lower boiling point).
Amine from Nitro compound
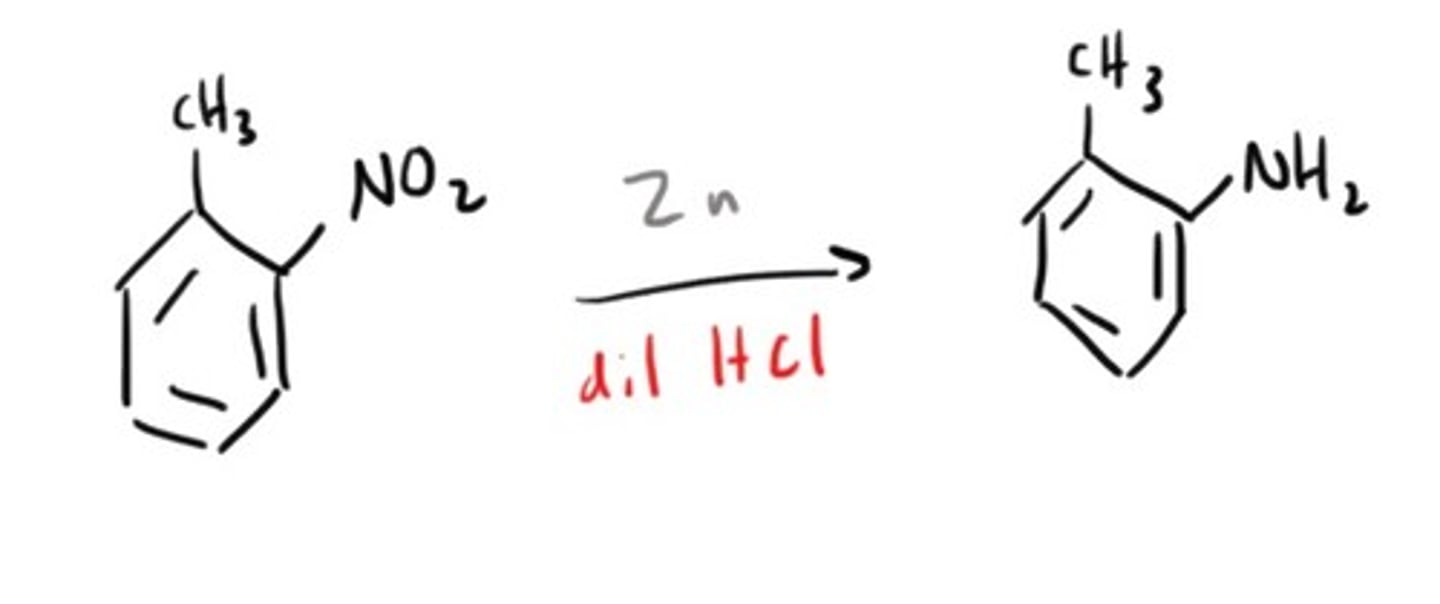
Amine from a Nitrile/Cyanide
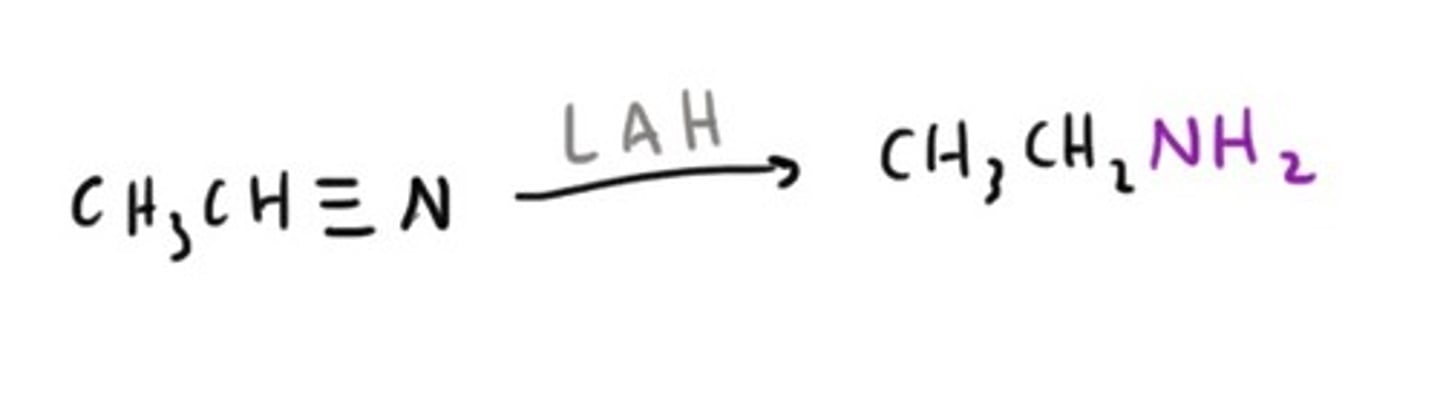
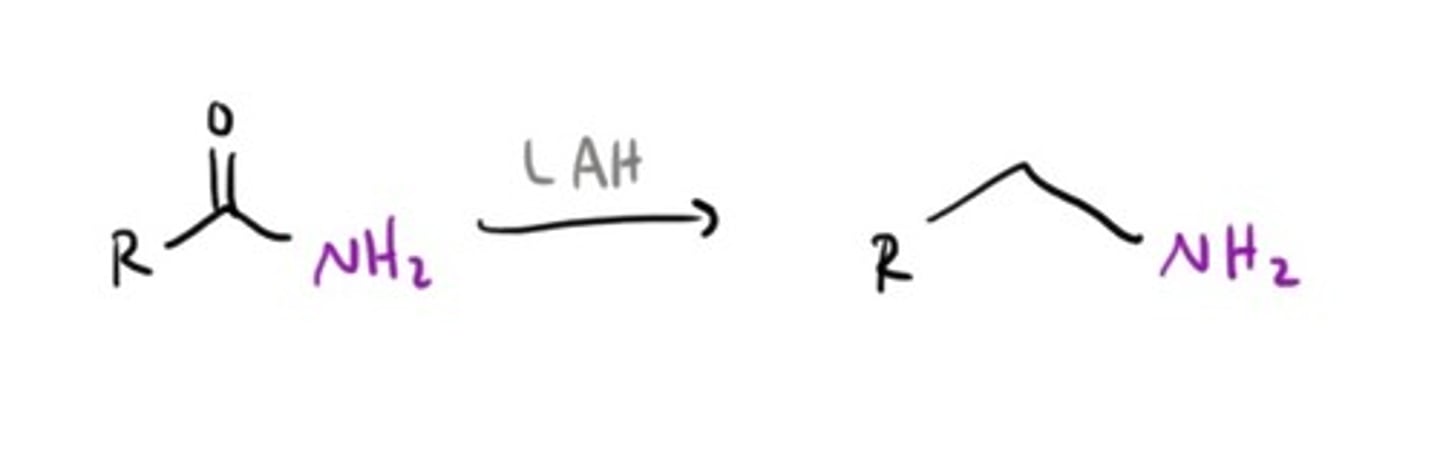
Amine from an Amide
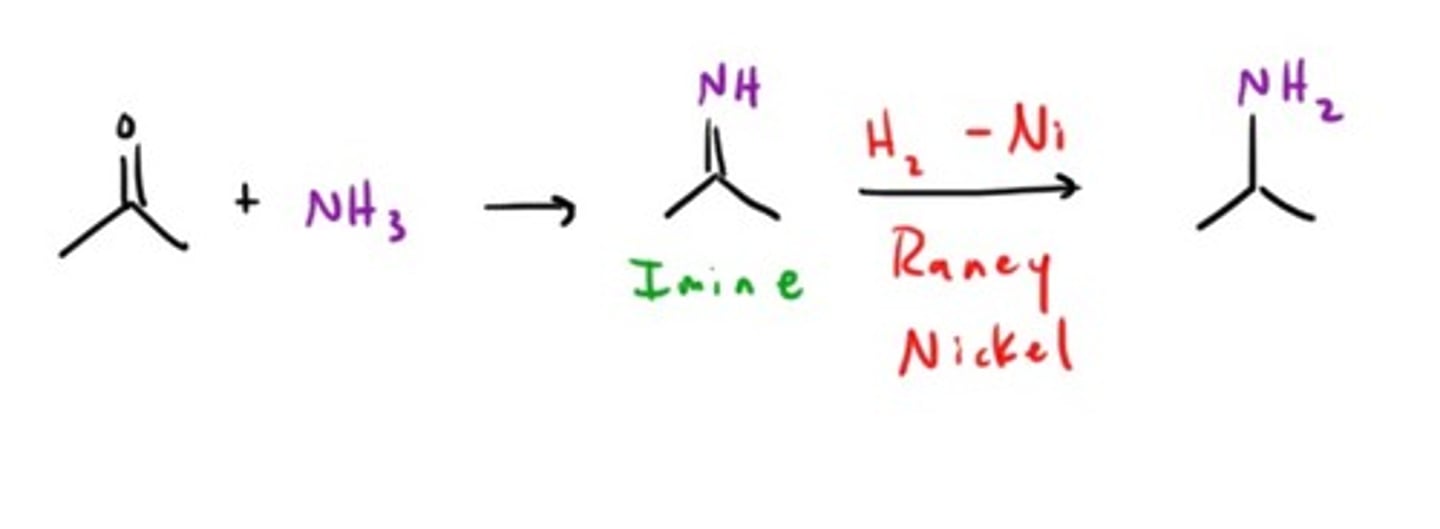
Amine from an Imine
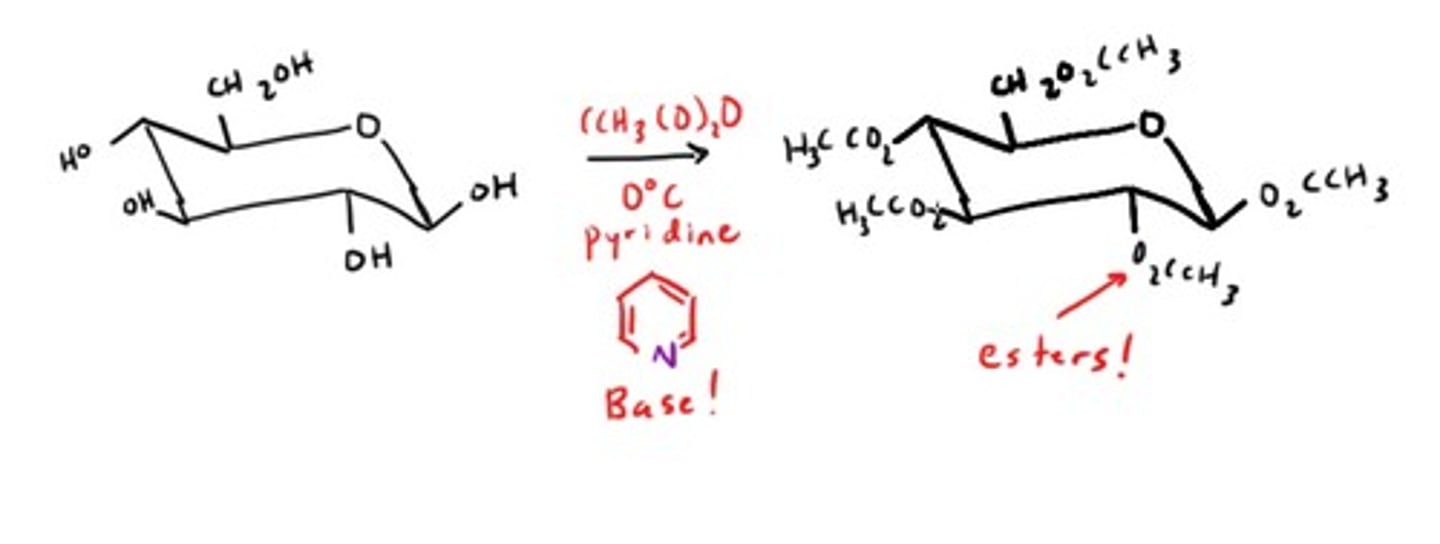
Monosaccharide ester formation
All hydroxyl groups will be esterified!
Basic structure of an Amino Acid
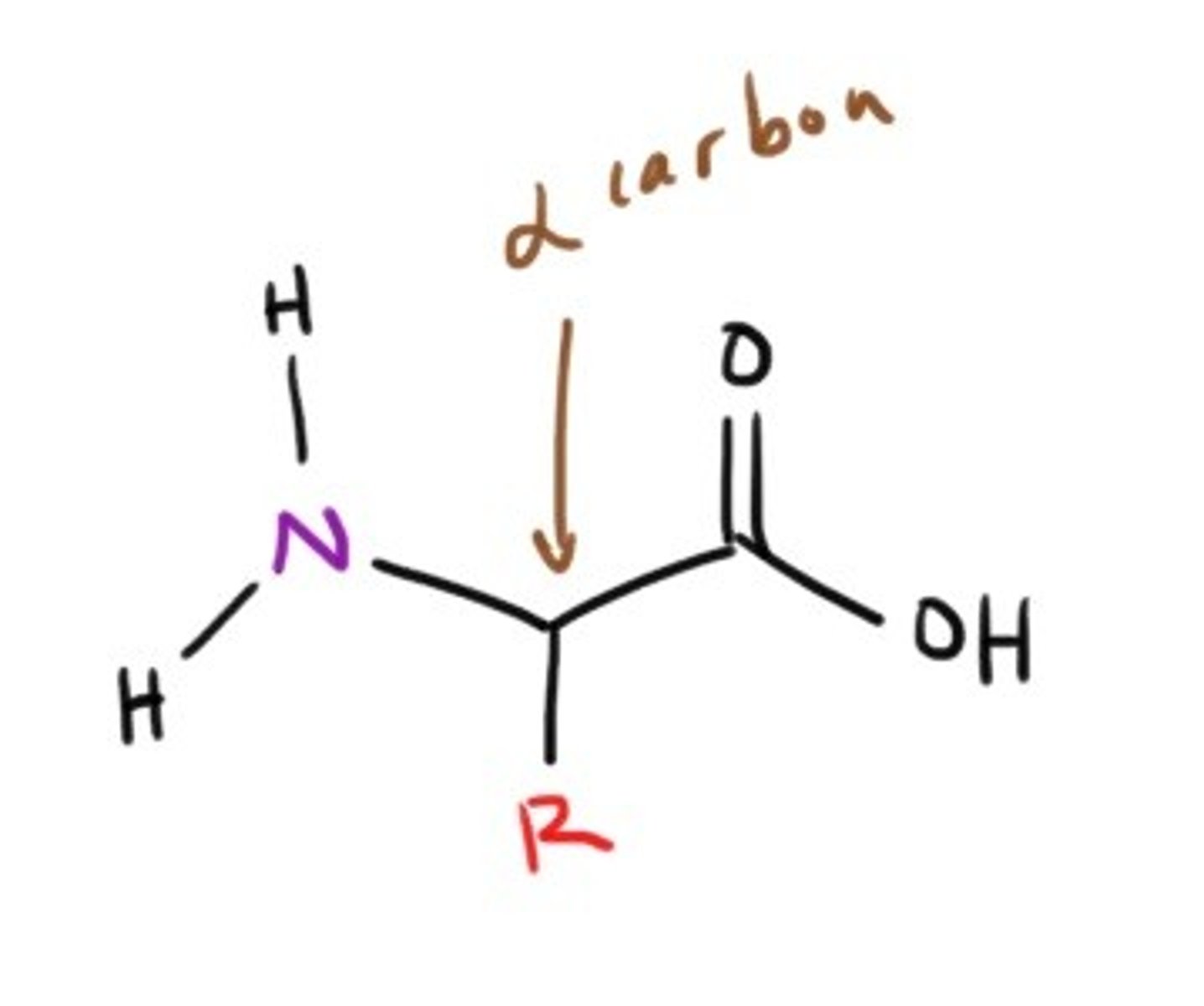
What looses an H first in basic titration, the amino or carboxyl group?
The carboxyl group duh!
Things to know about titration of amino acids...
1.Buffering capacity is greatest at the Ka's
2. Two moles of base need to be added in order to deprotonate one mole of most a.a.
3. When adding base, the carboxyl group looses the H first.
4. Titrations can be done in reverse starting with a basic solution and adding acid.
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
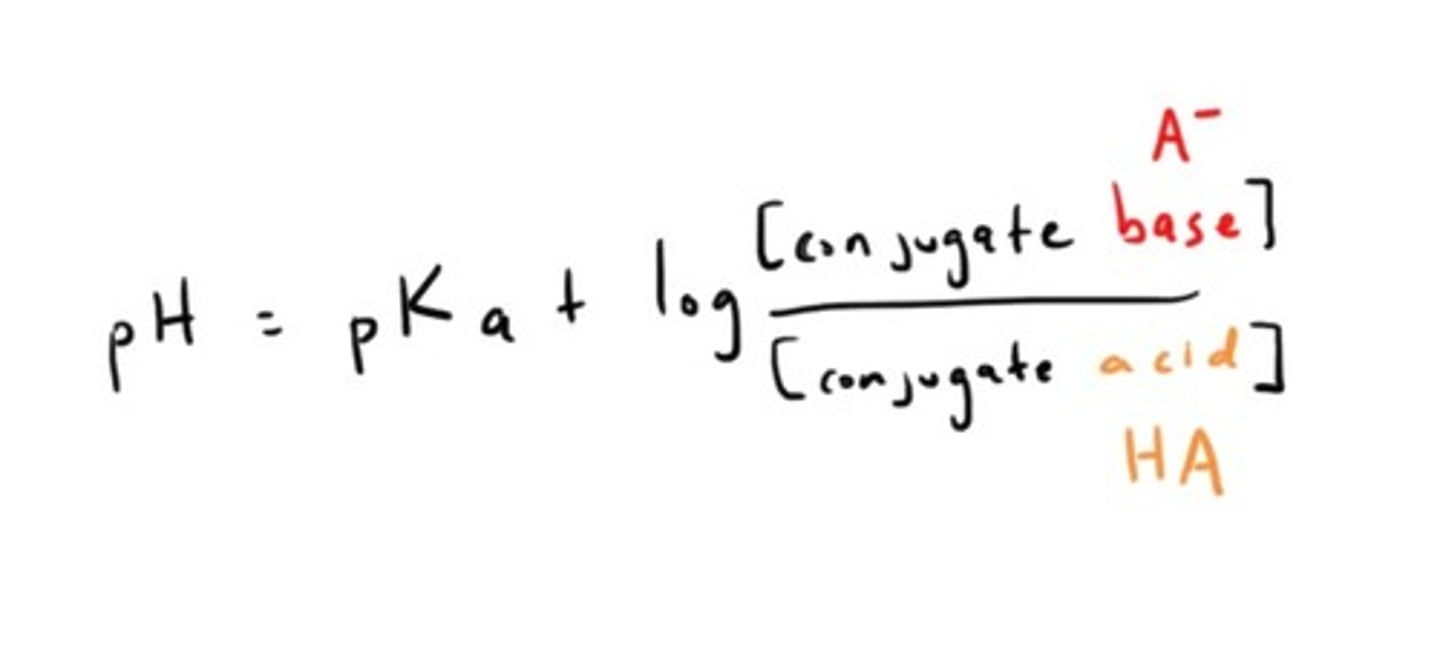
Alanine
Valine
Leucine
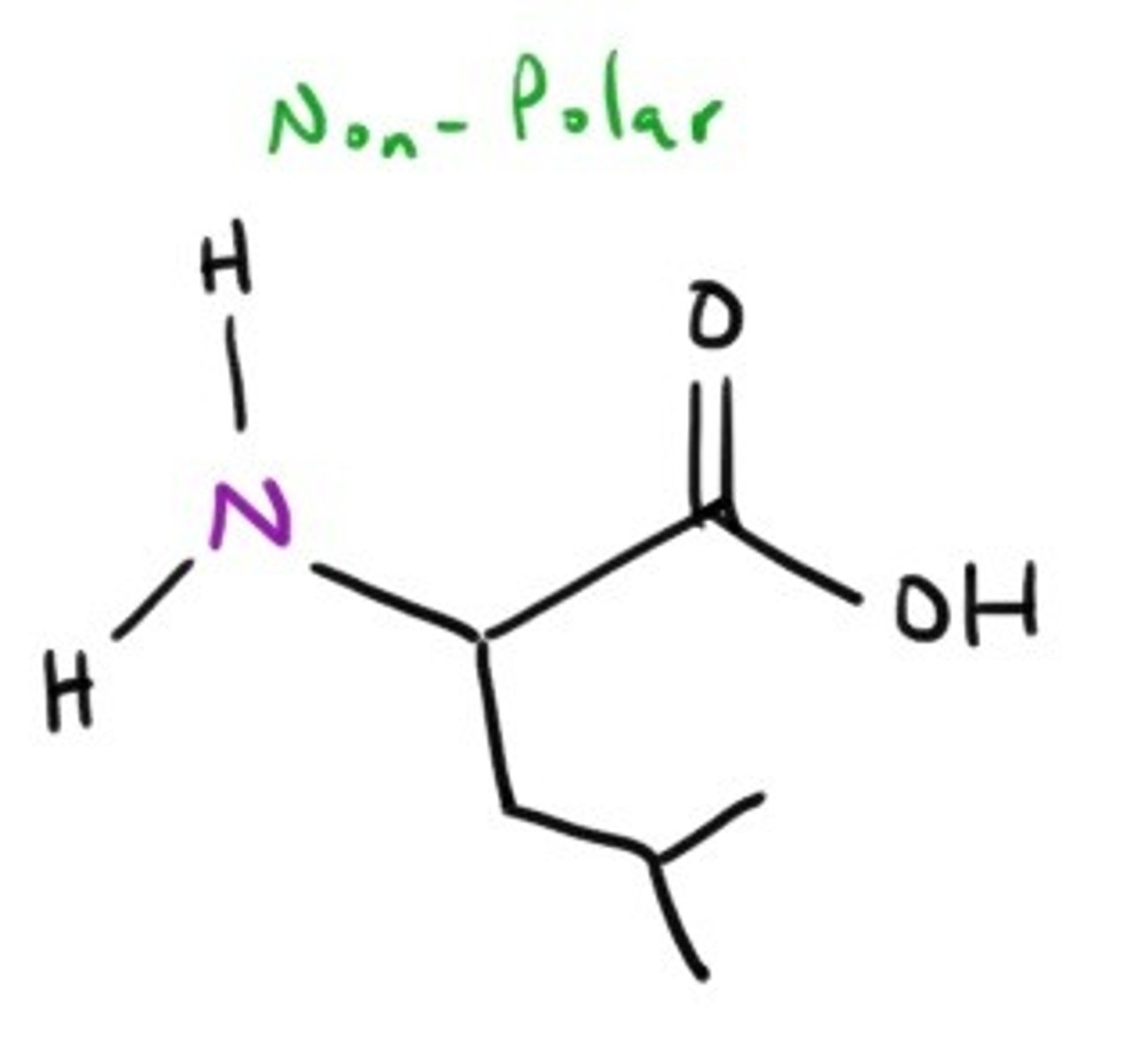
Isoleucine
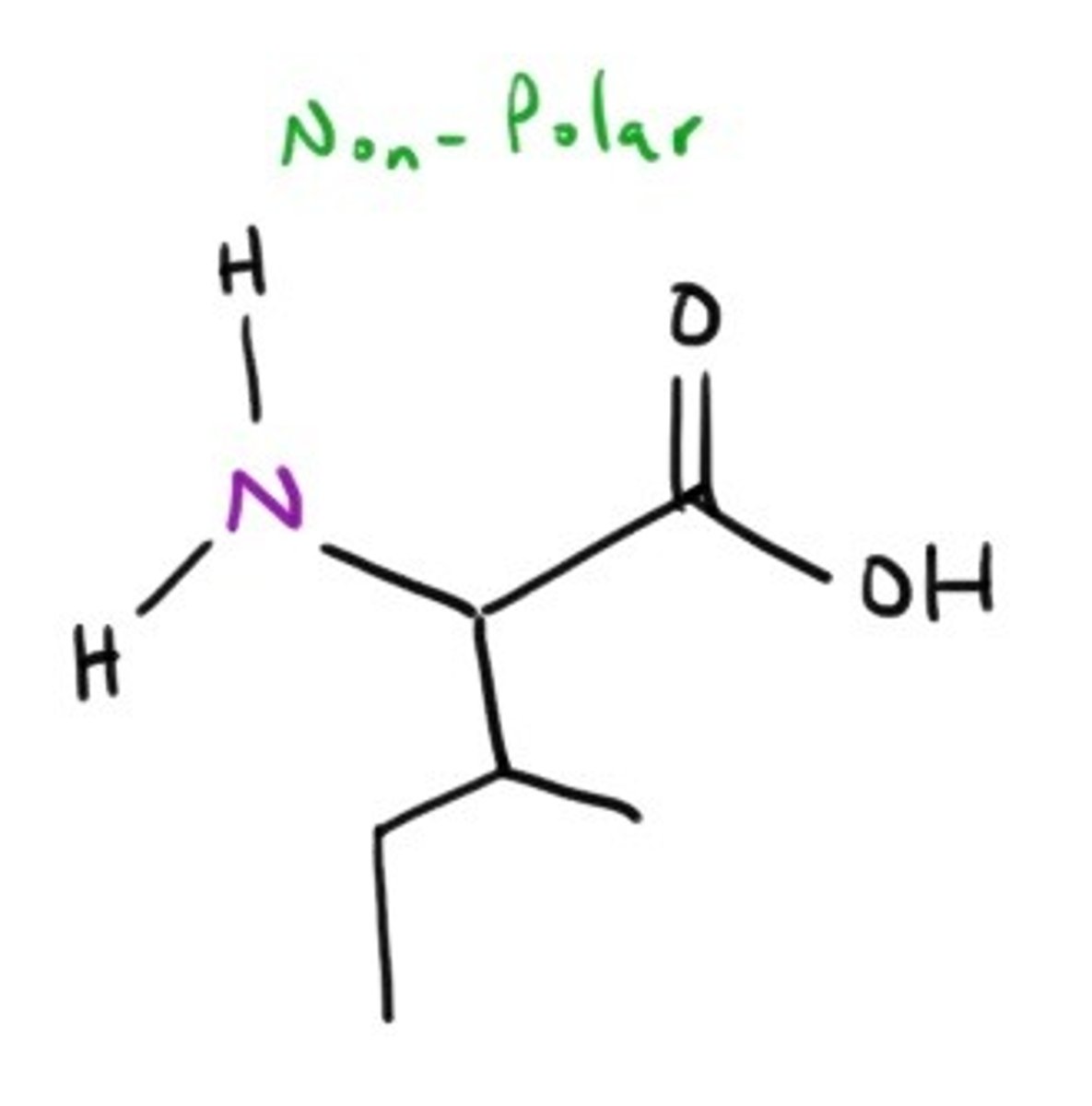
Methionine
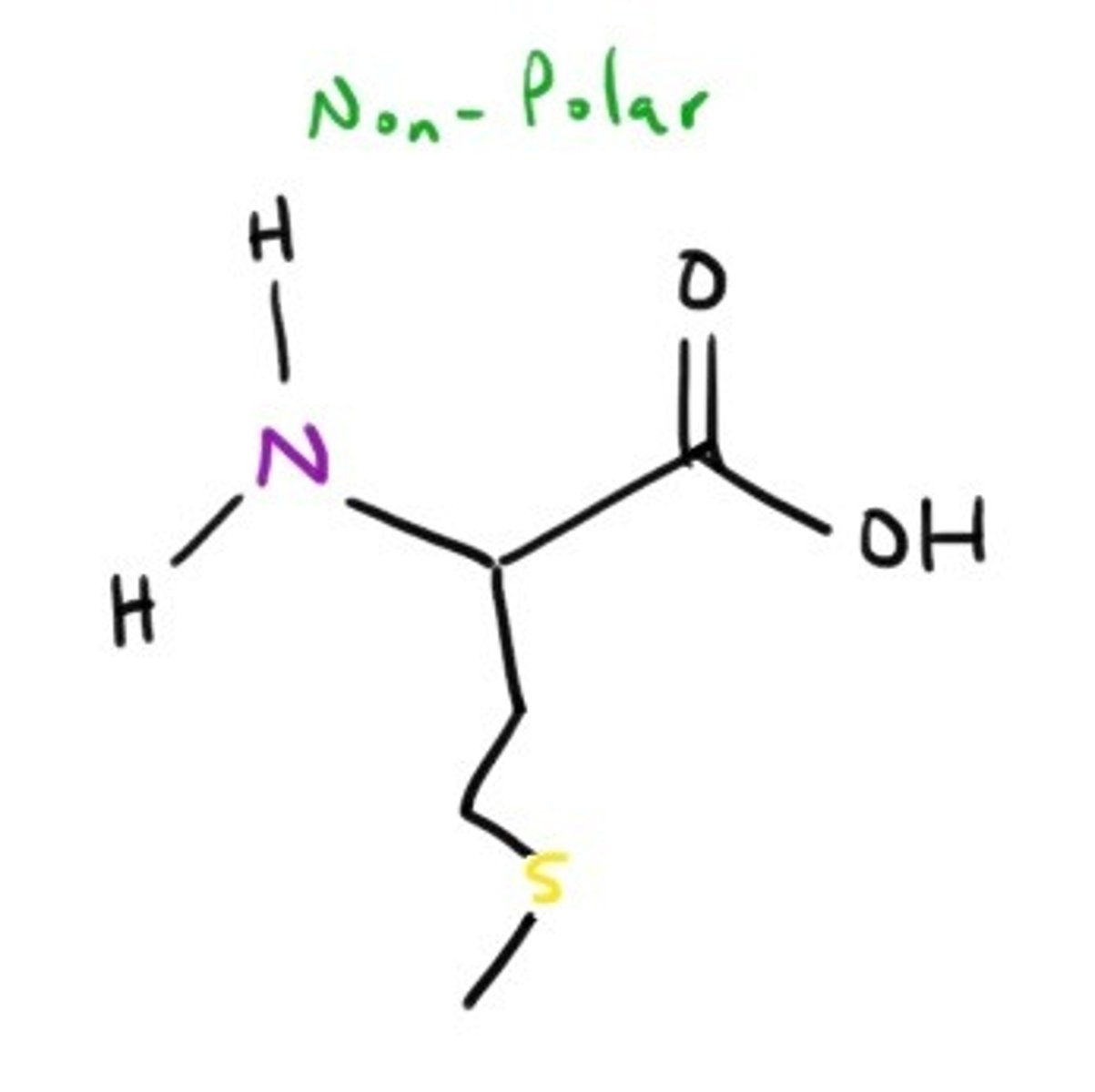
Proline
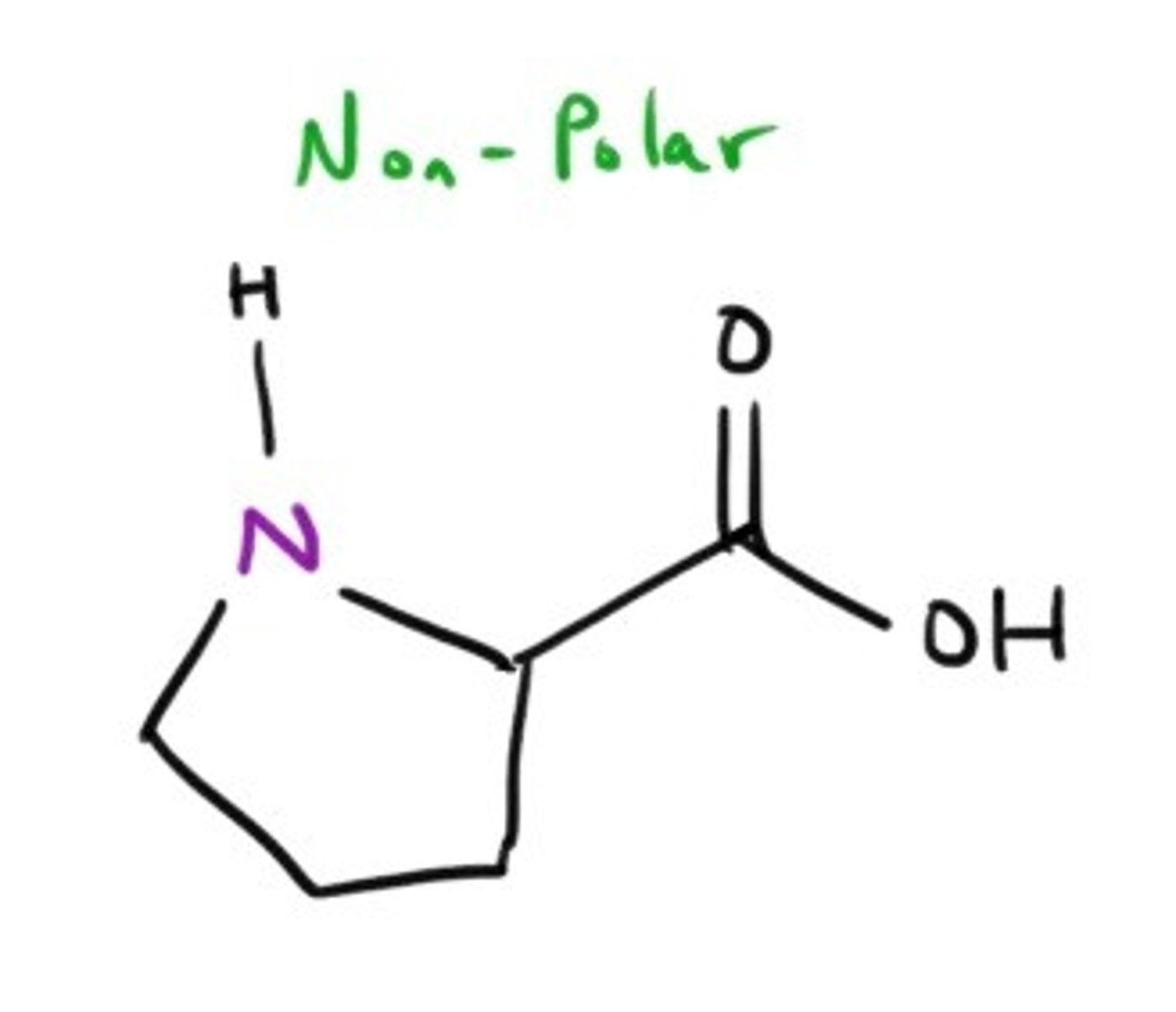
Phenylalanine
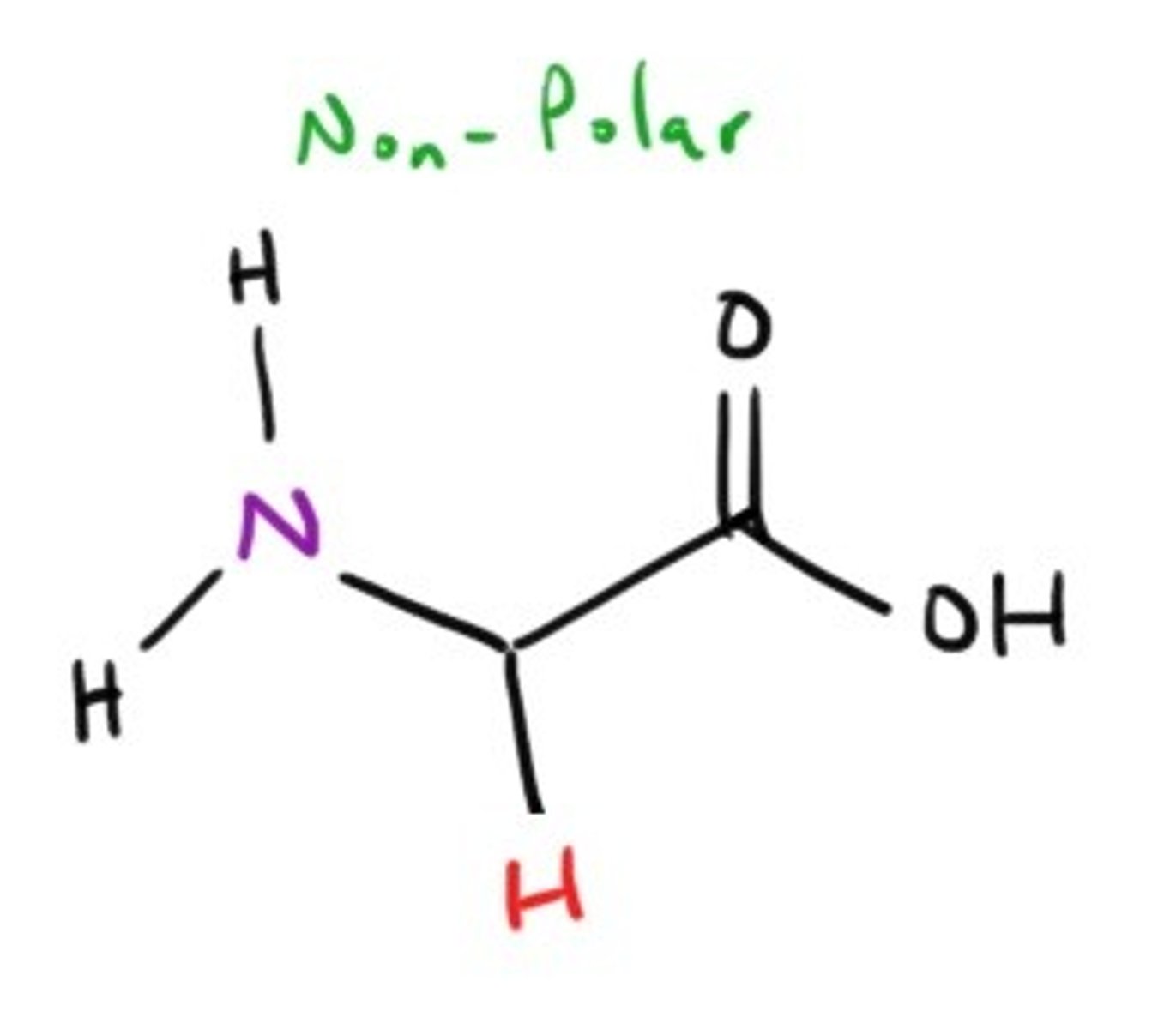
Glycine
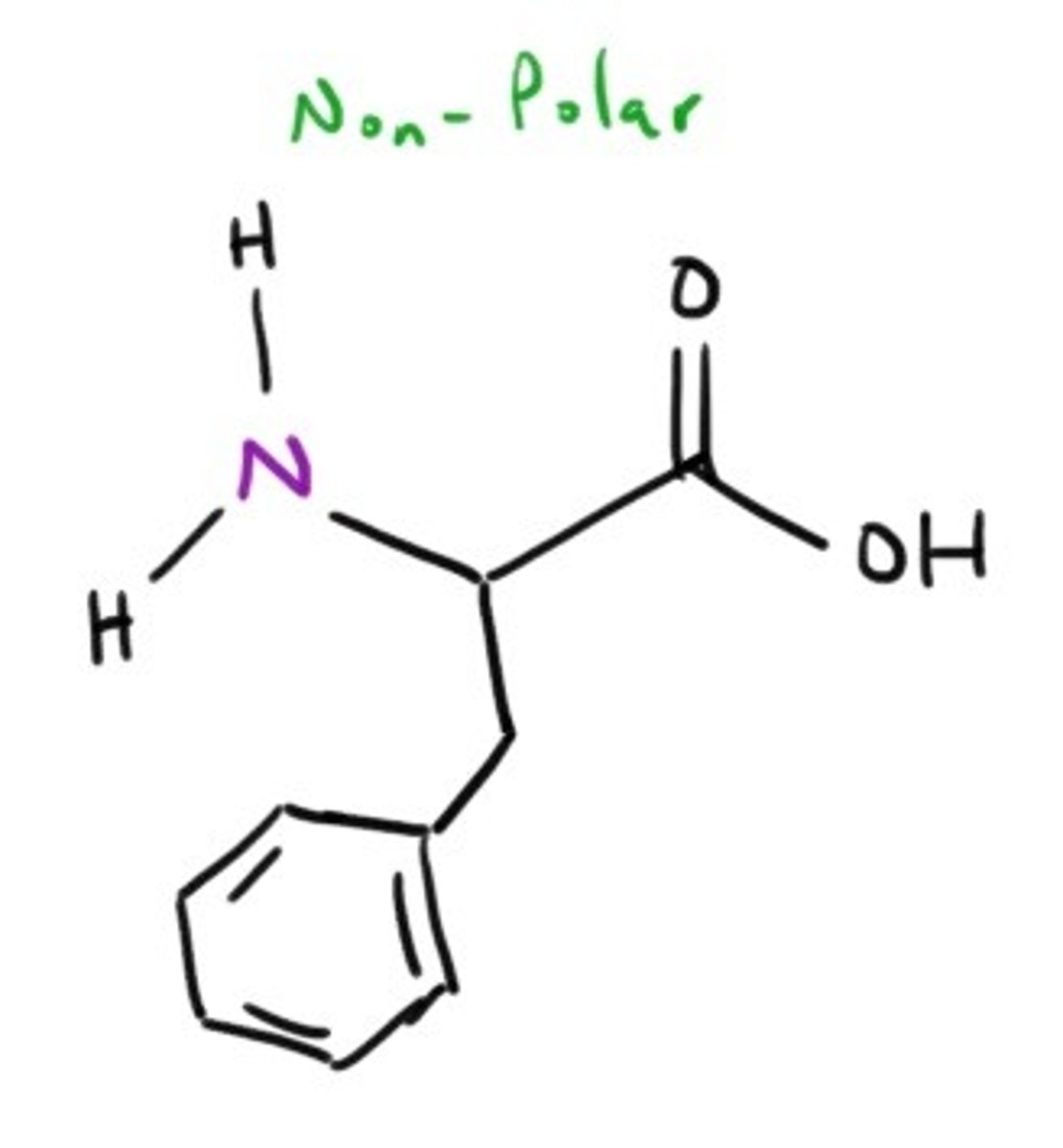
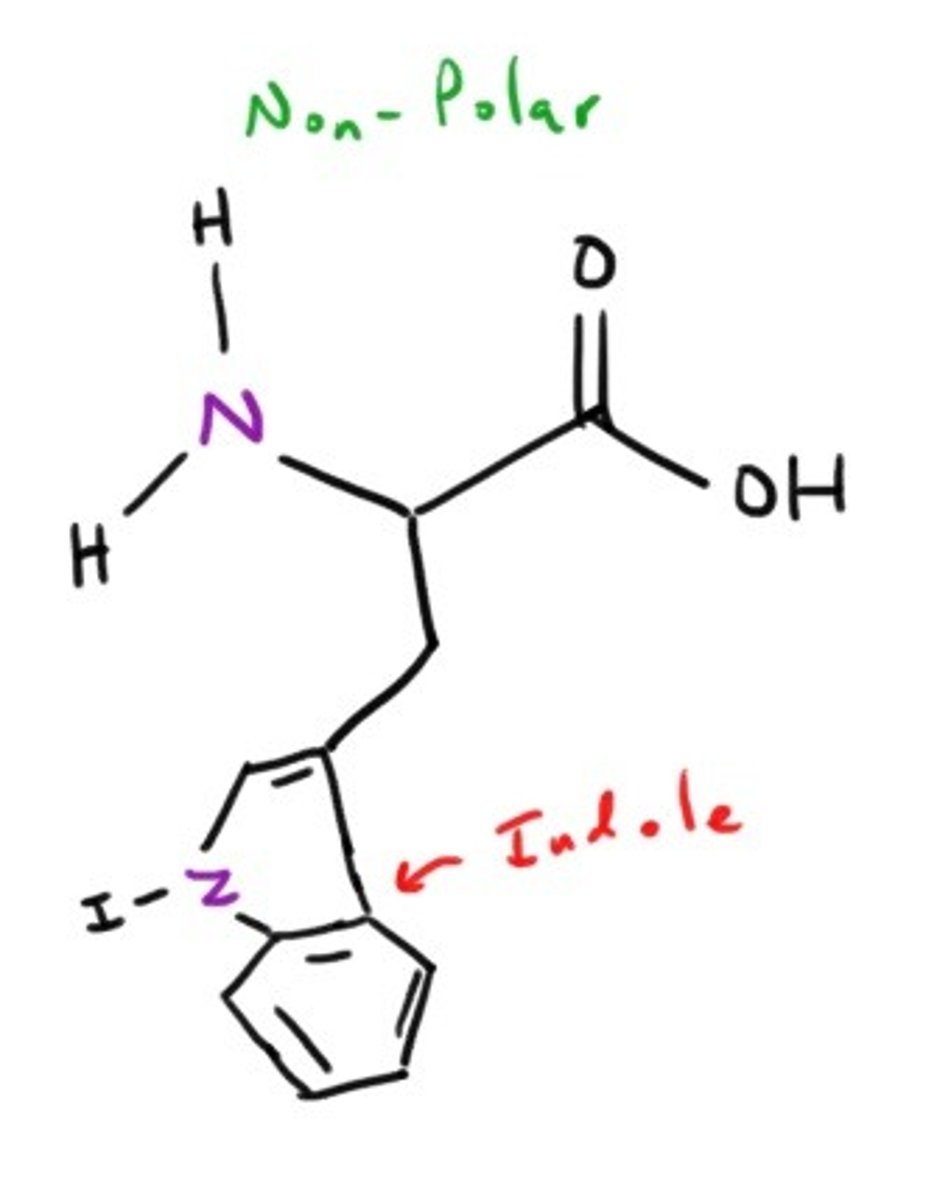
Tryptophan
Serine
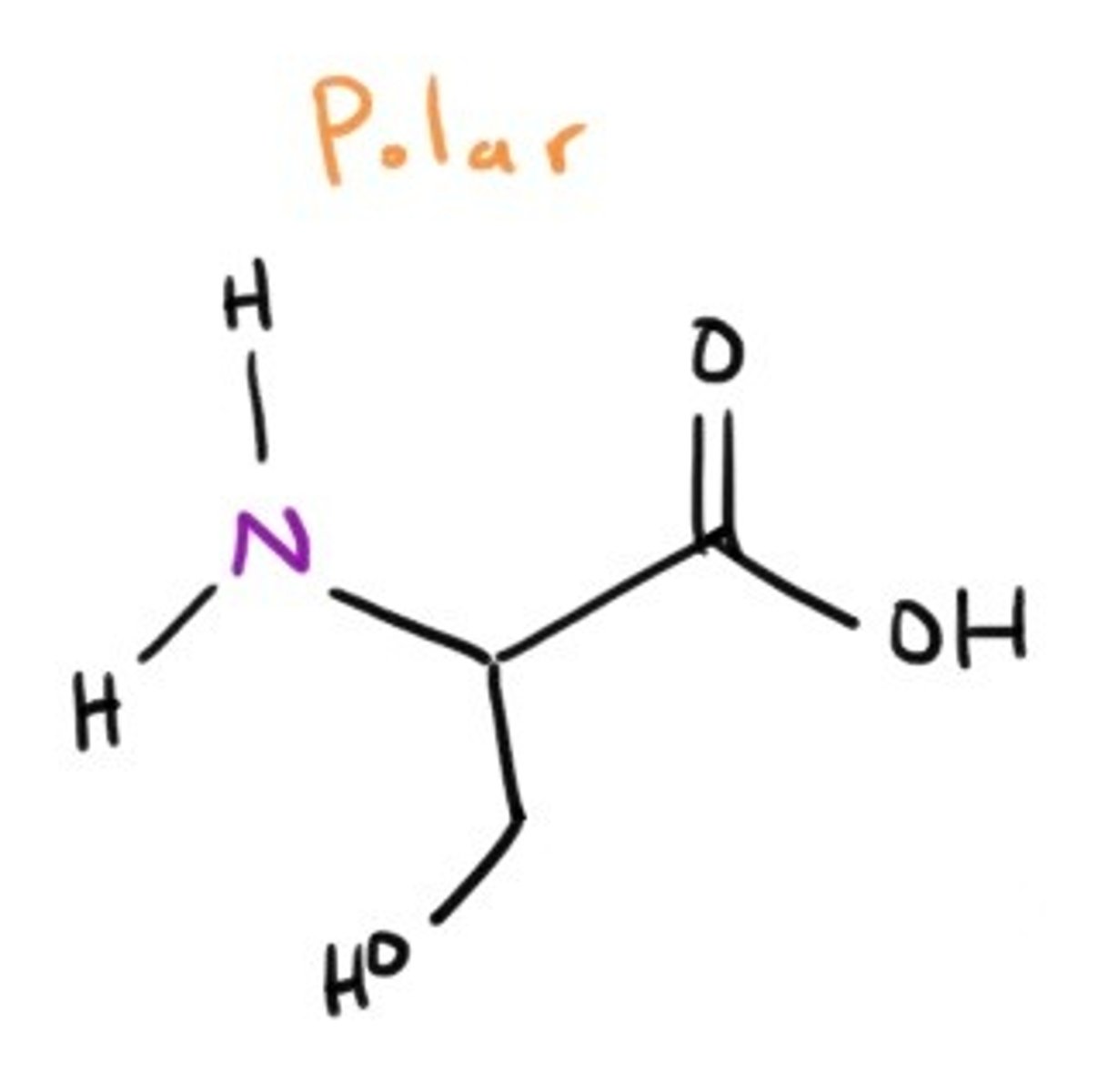
Threonine
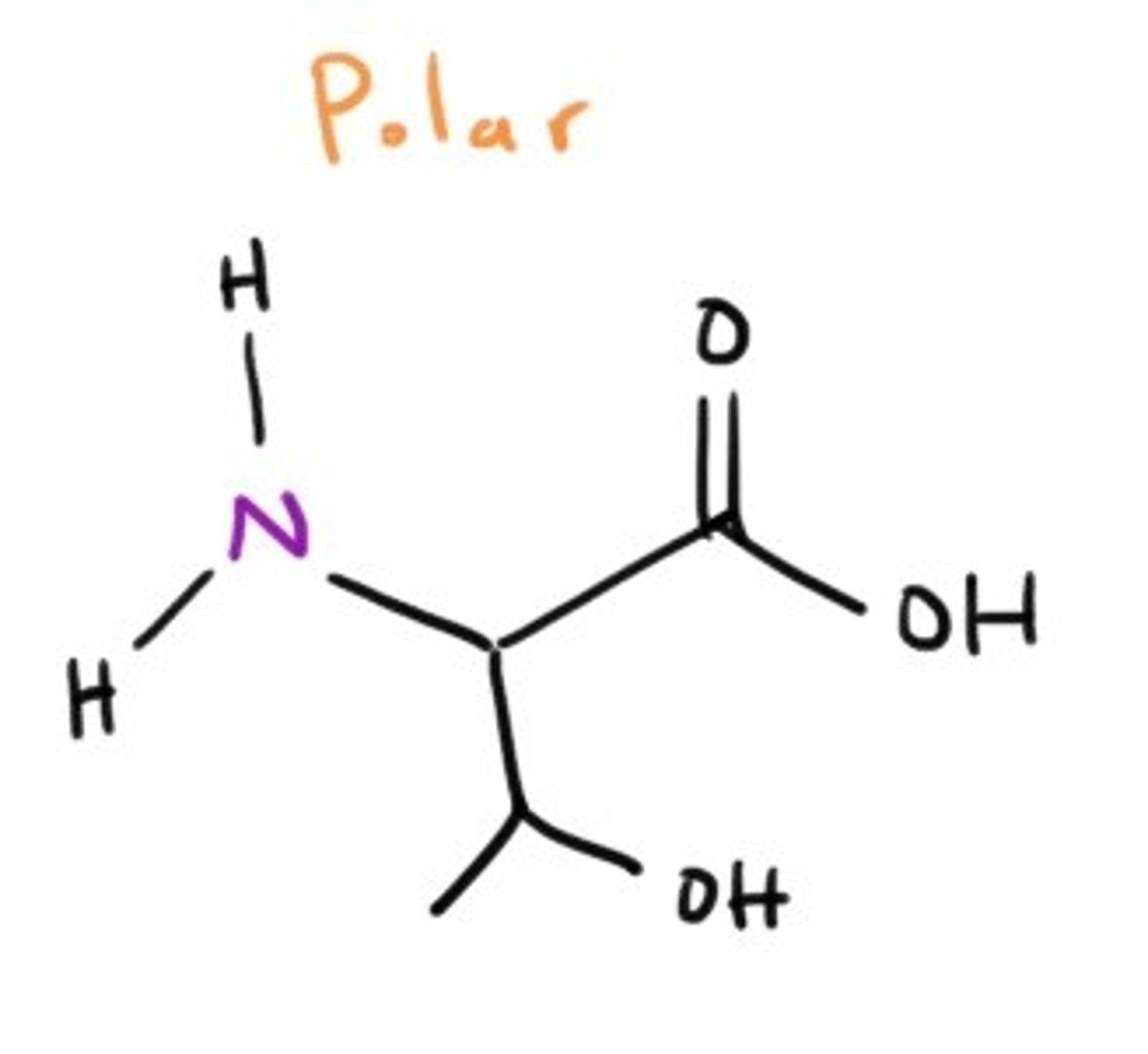
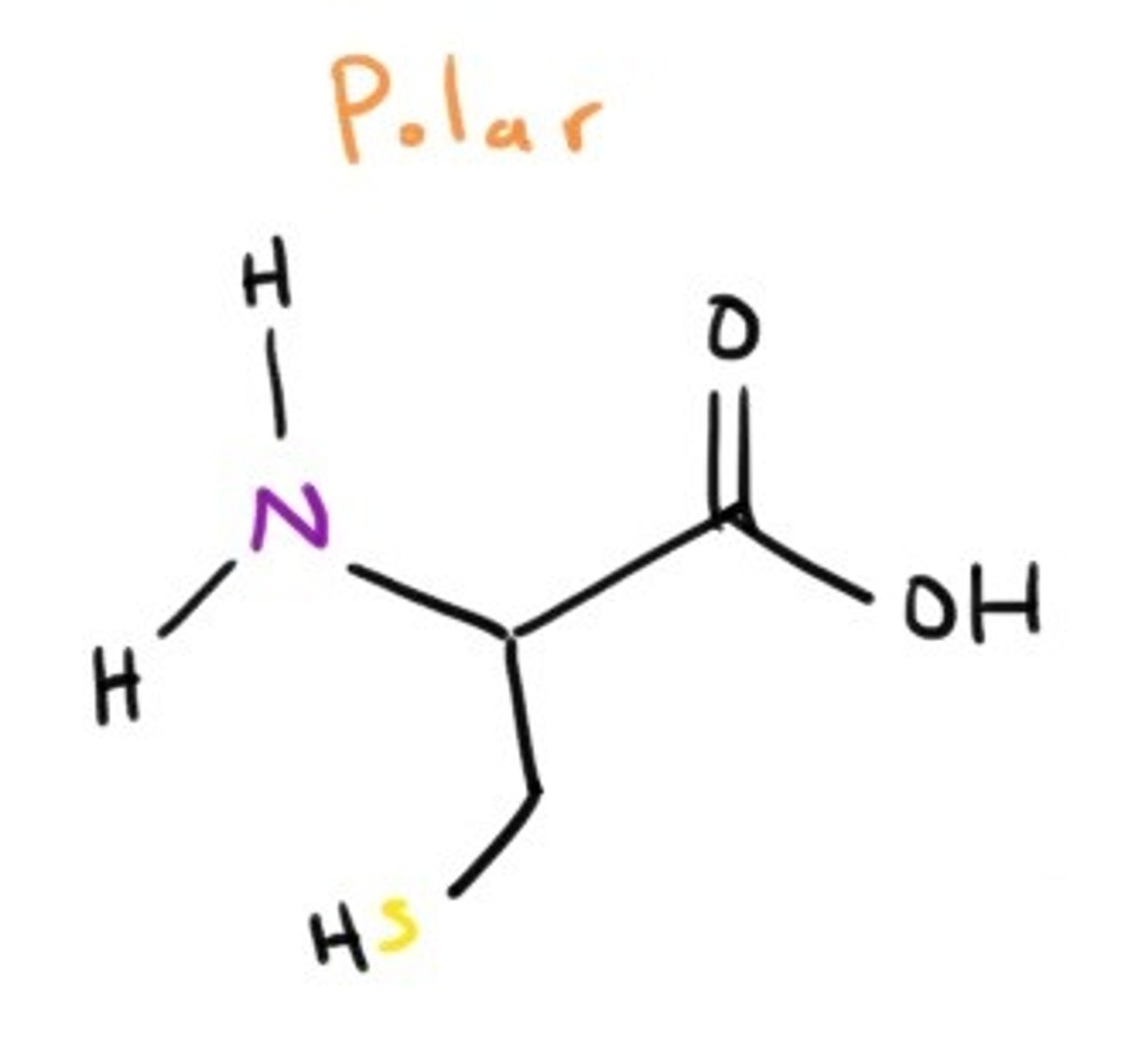
Cysteine
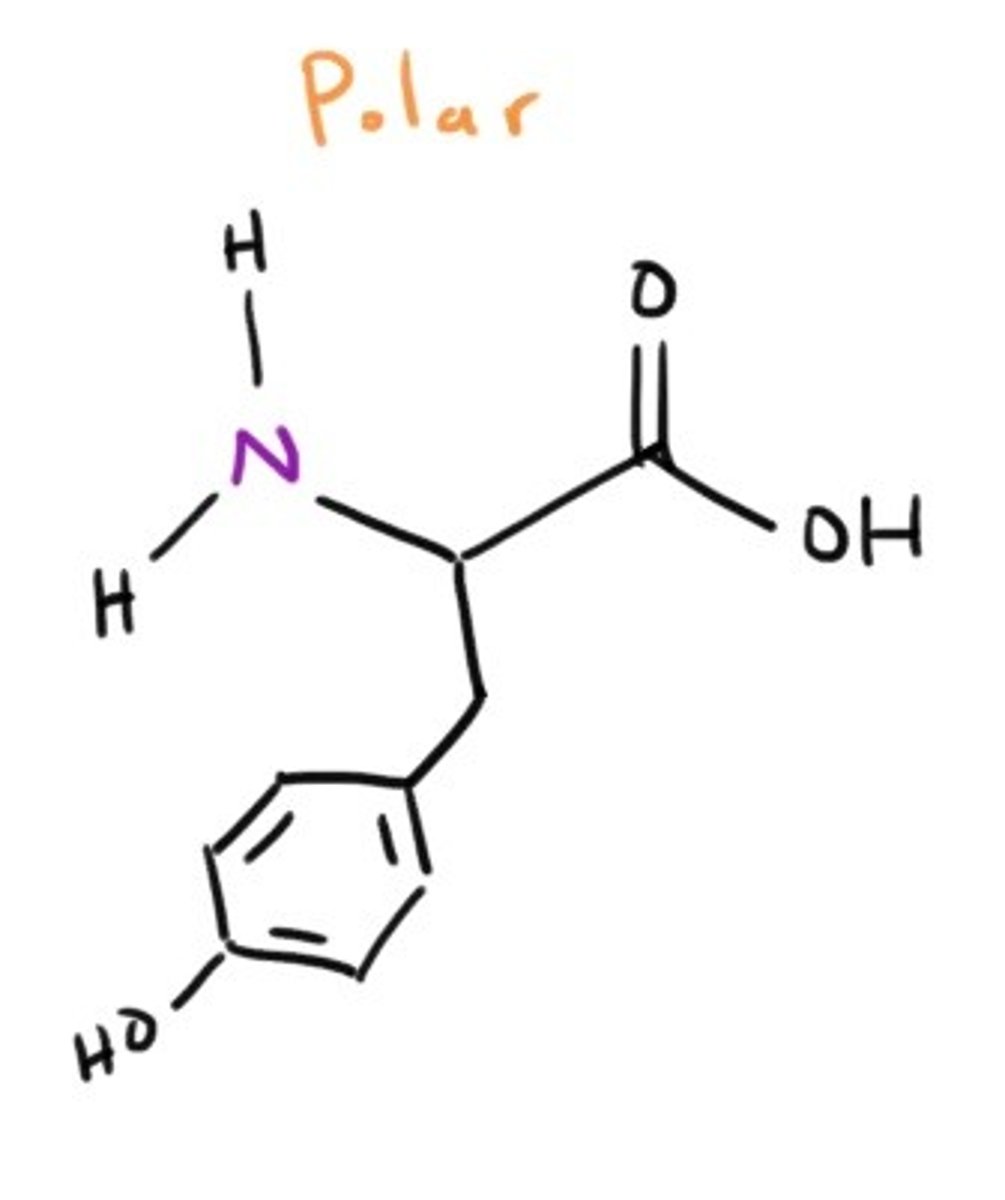
Tyrosine
Asparagine
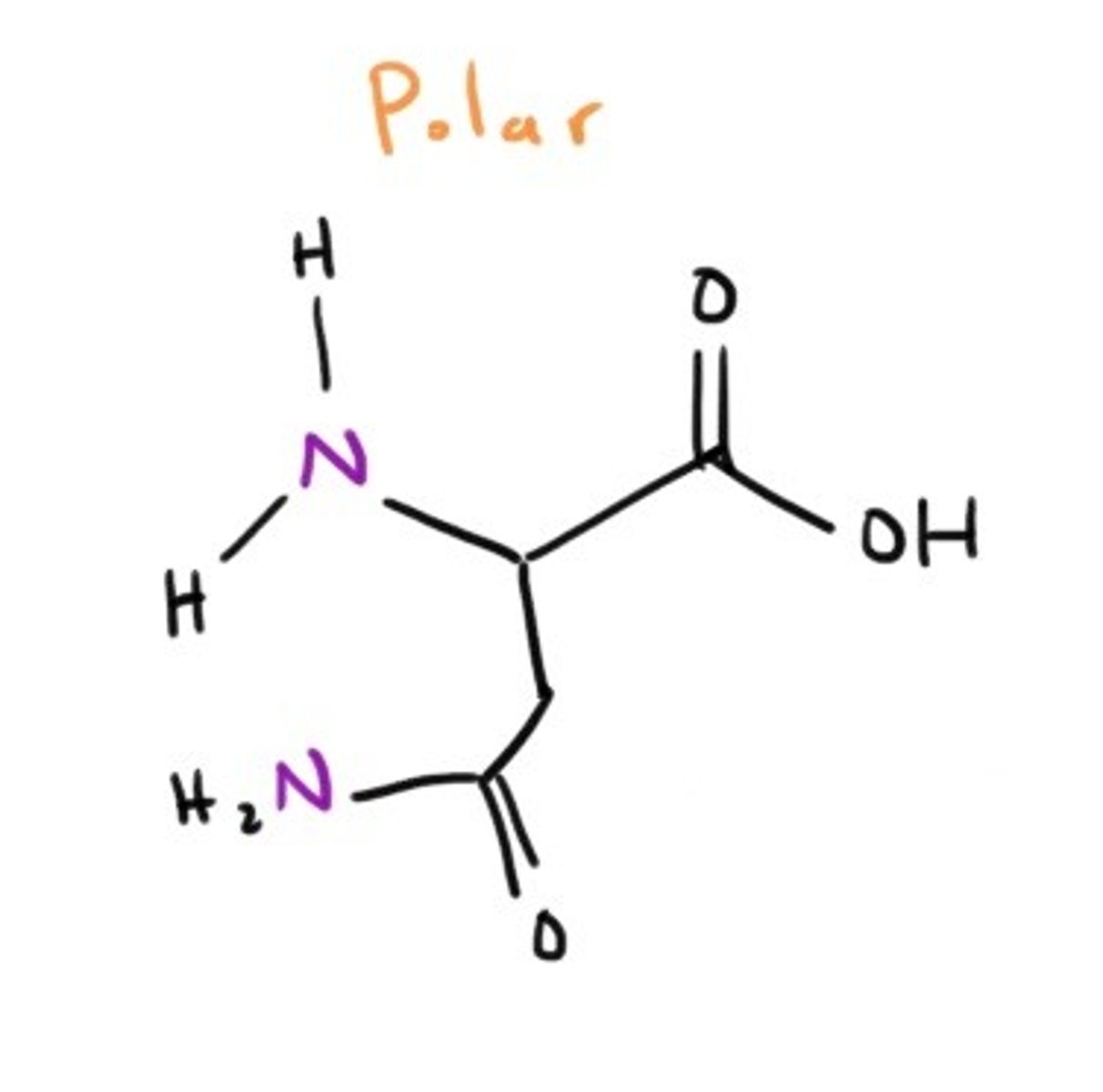
Glutamine
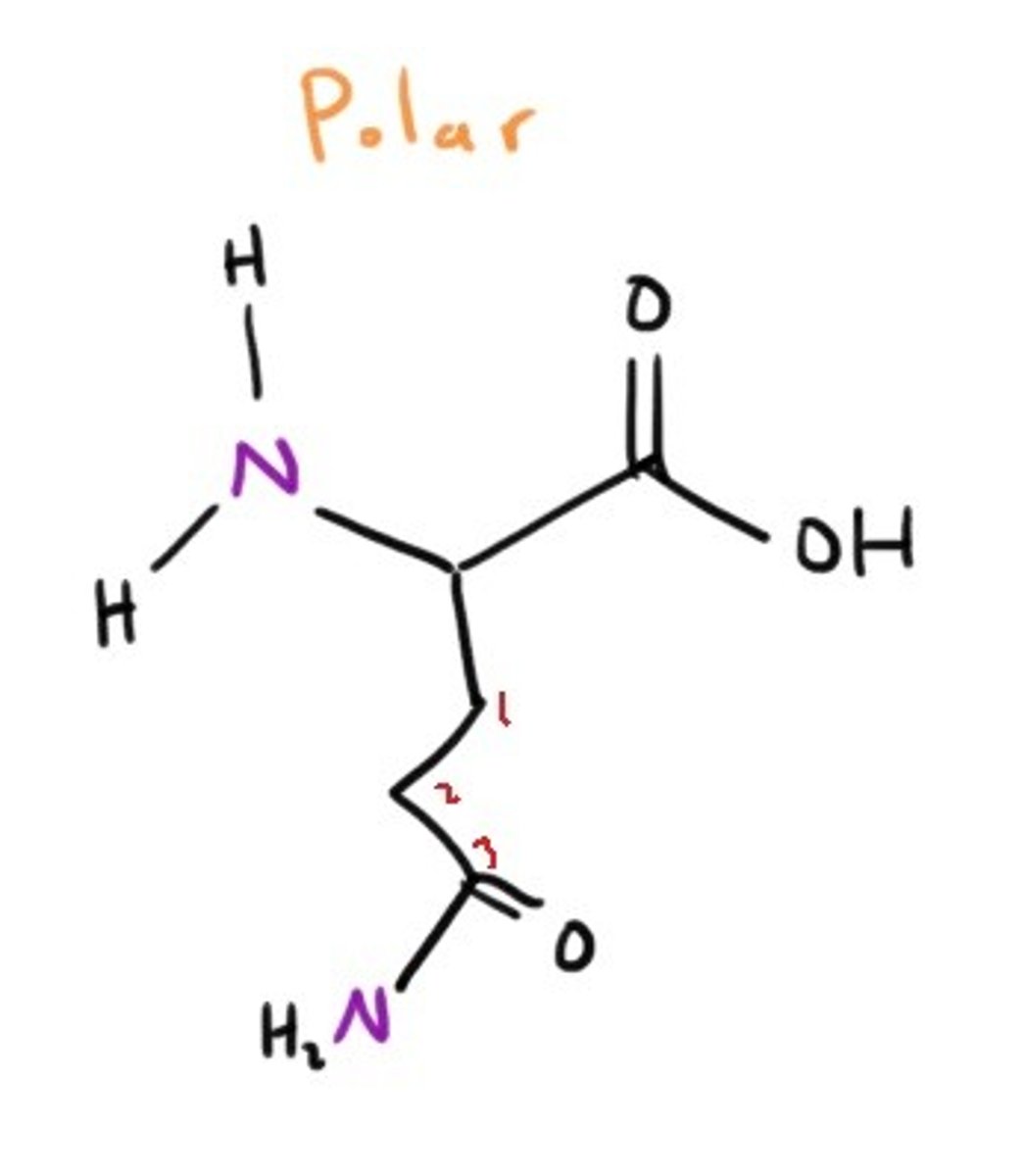
Aspartic Acid
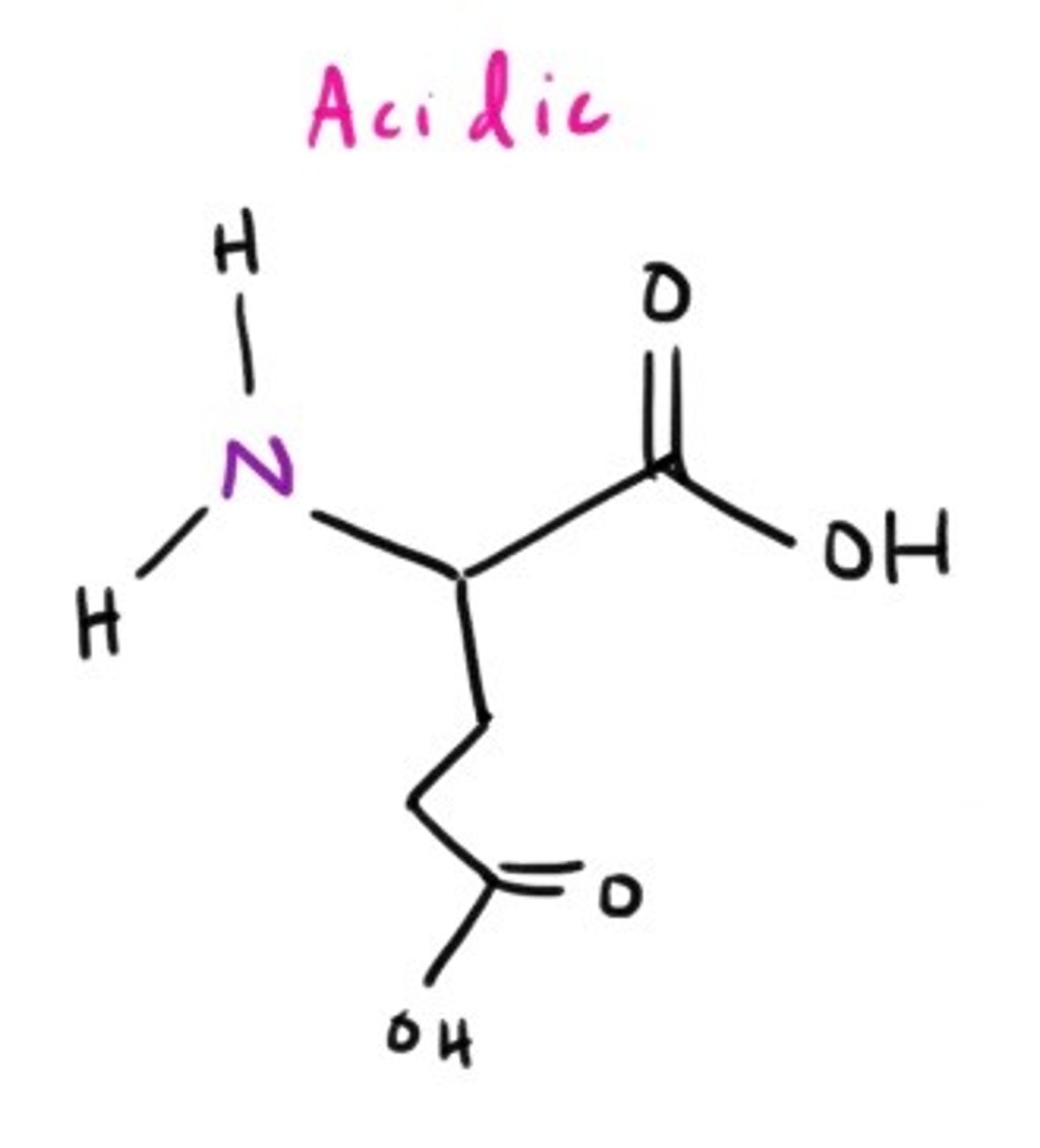
Aspartate Salt
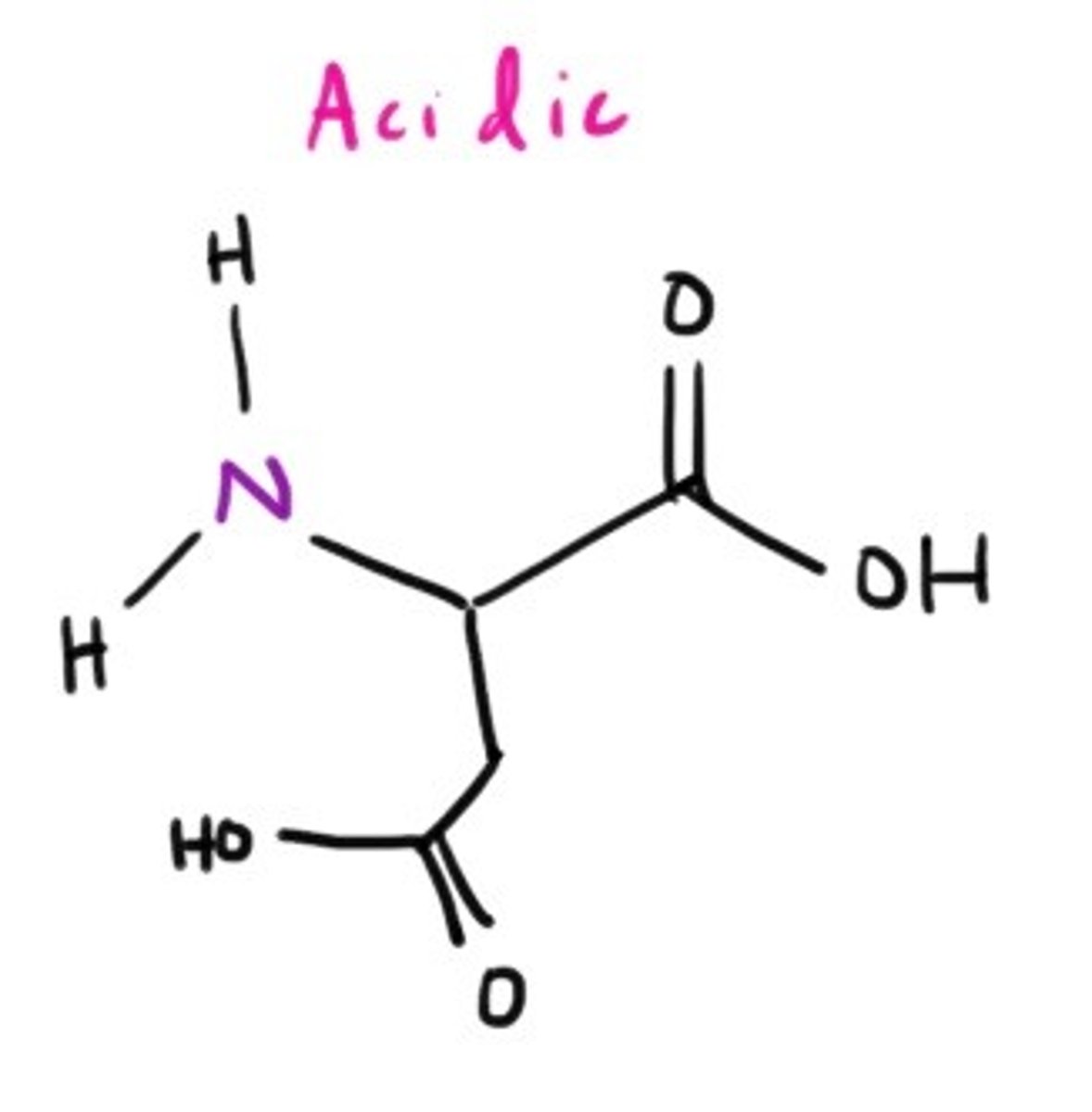
Glutamic Acid
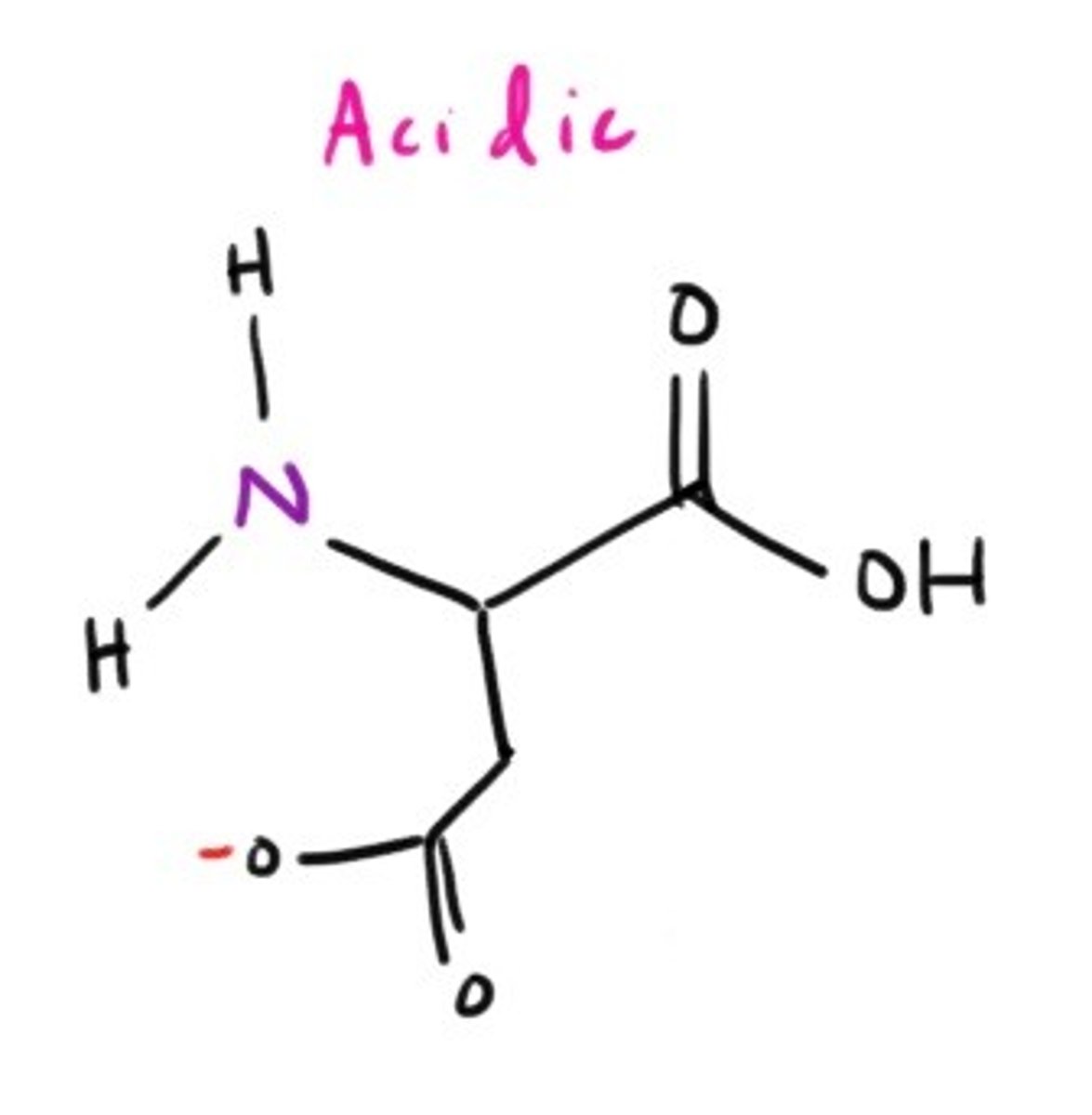
Glutamate Salt
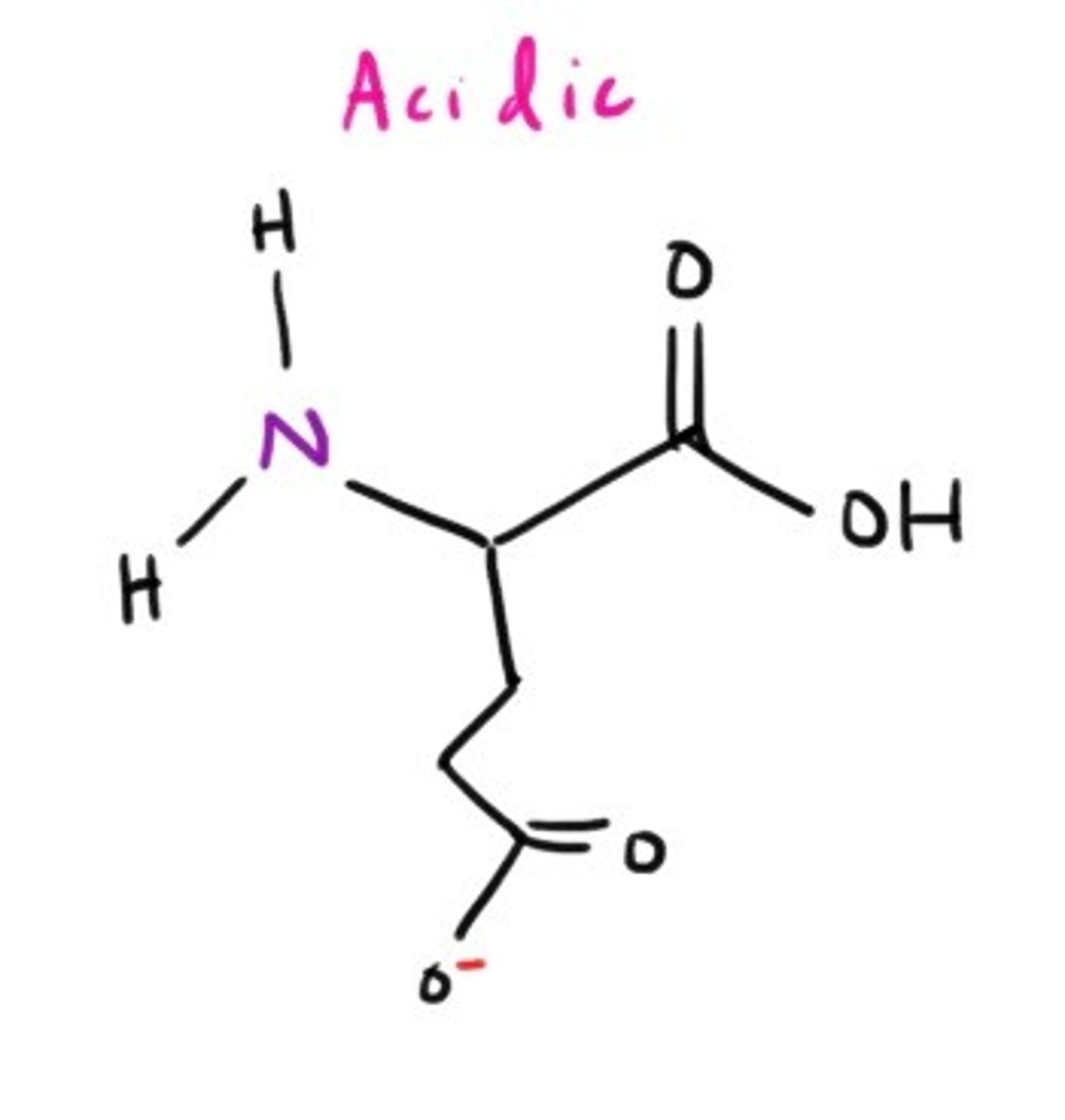
Arginine
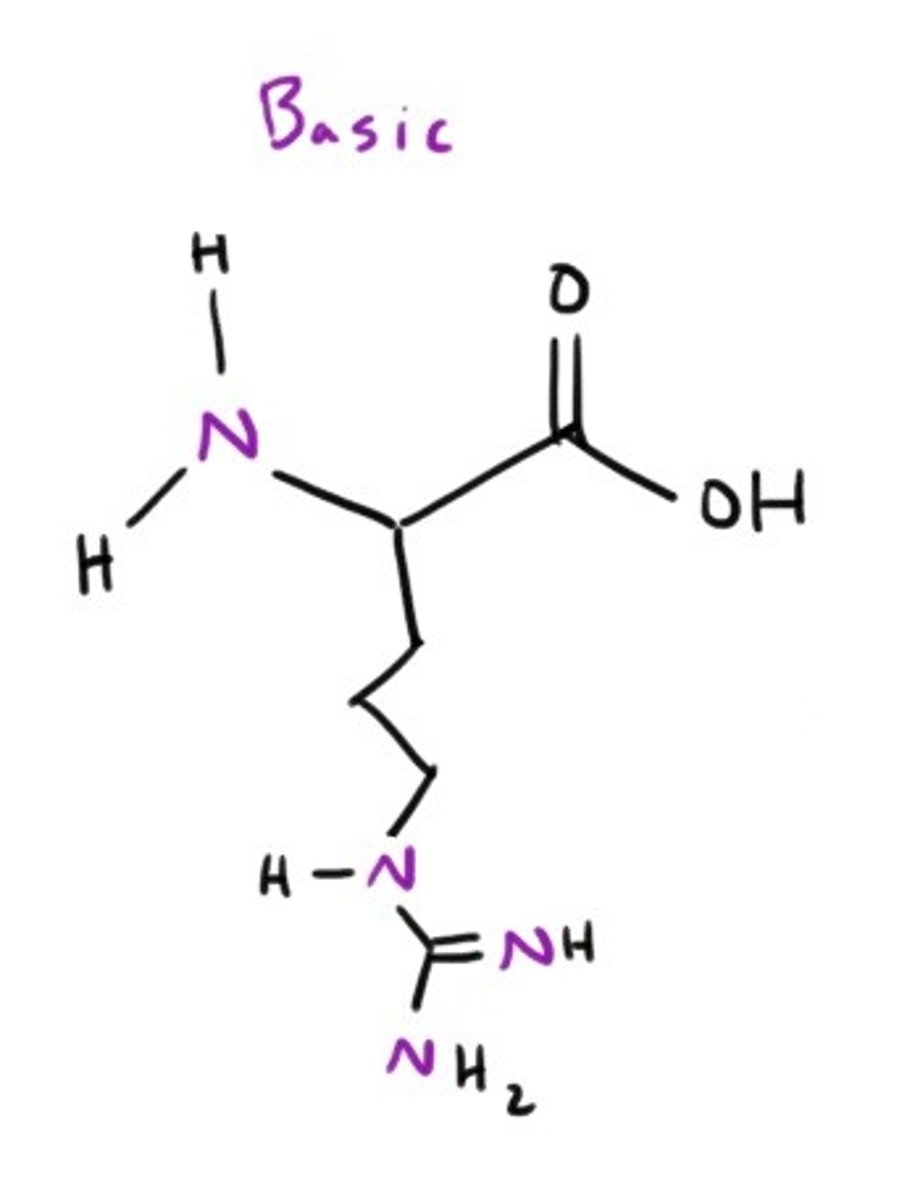
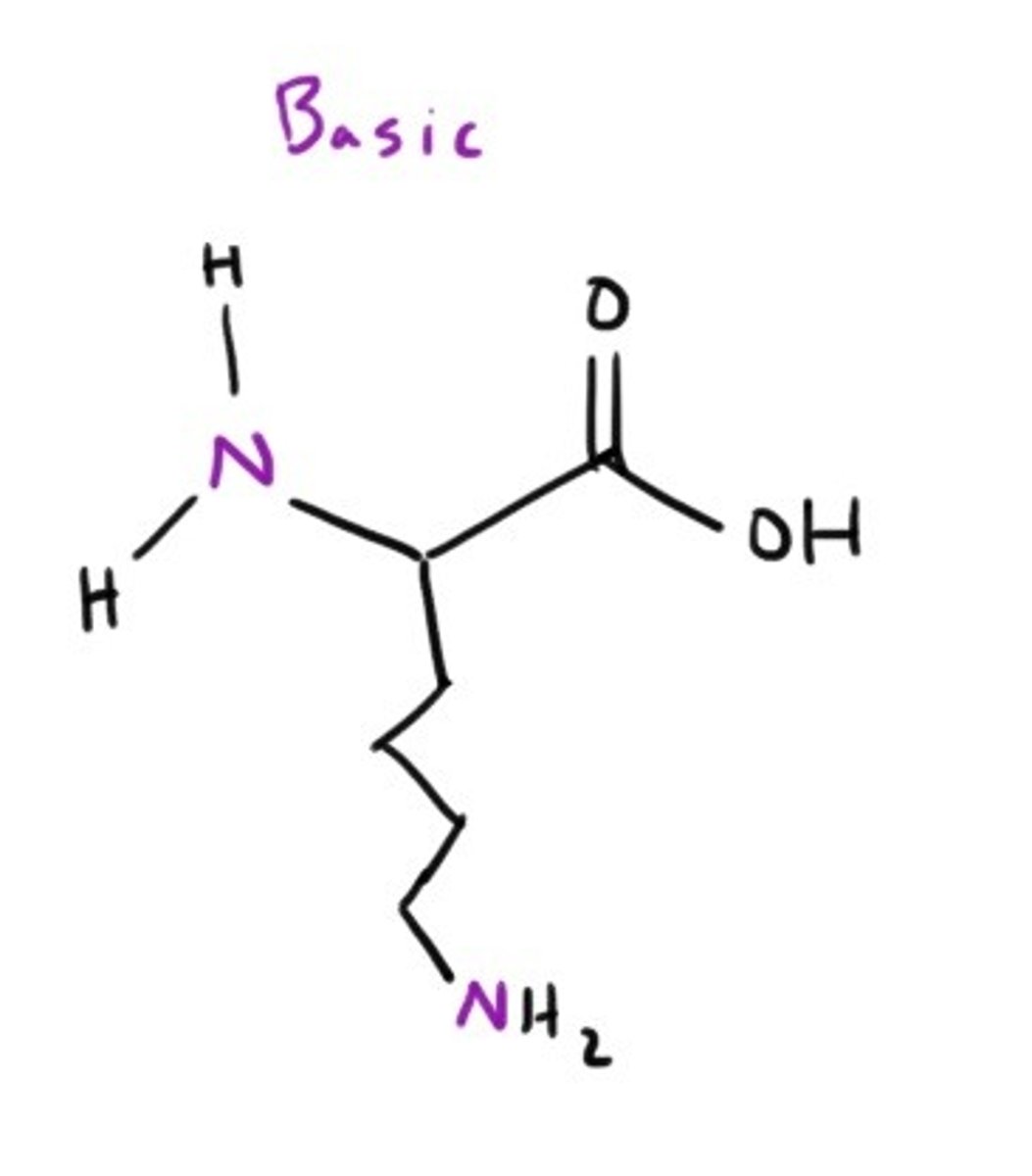
Lysine
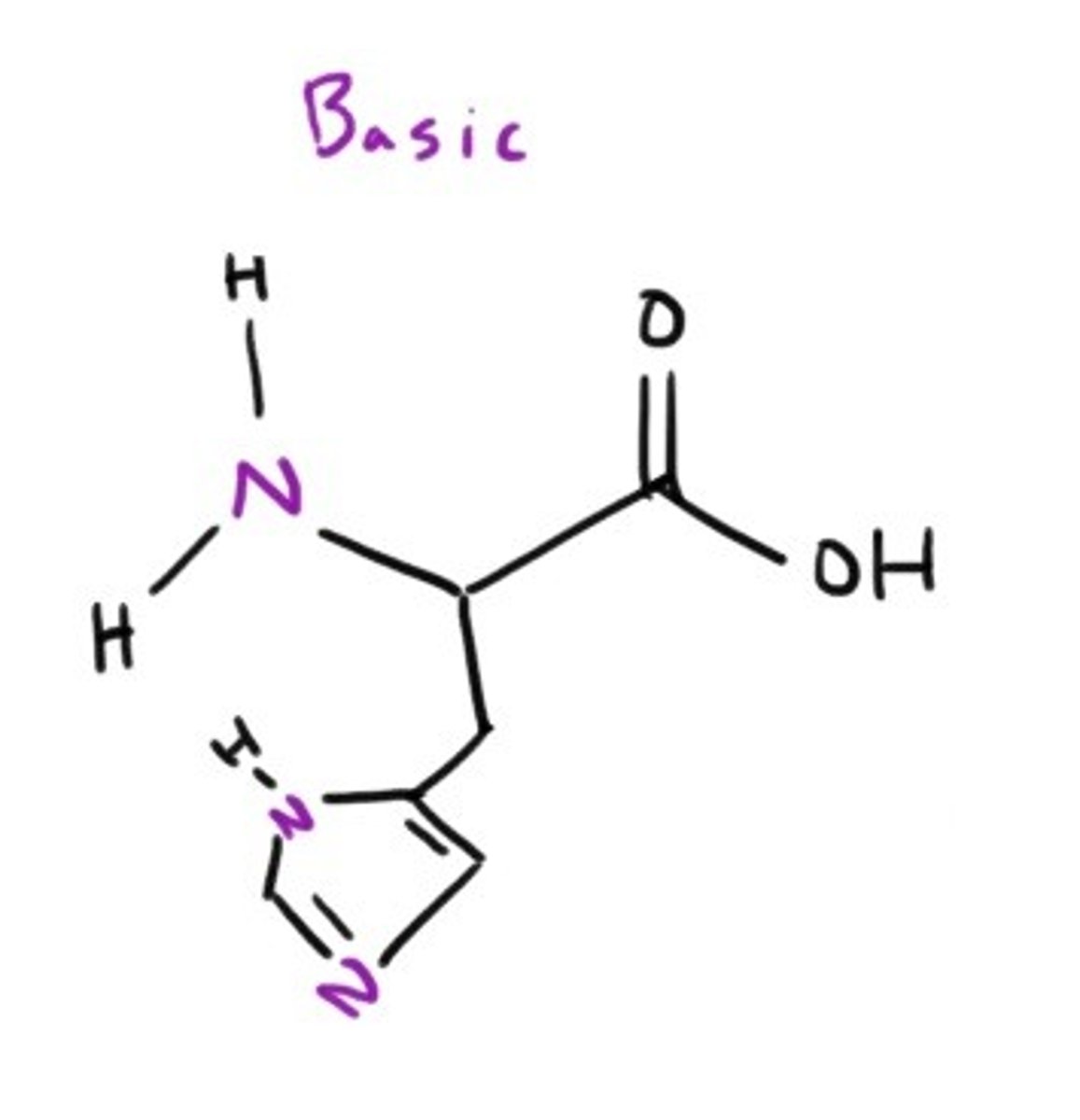
Histidine
How many moles of acid are needed to neutralize 1 mole of a basic amino acid?
3 moles because of the extra R amino group.
What is an amino acid called after it becomes a part of a peptide?
A residue.
Why is rotation of the peptide bond limited?
There is resonance about the C-N bond giving it some double bond character.
What level of structure is guided by hydrogen bonds for proteins?
Secondary structure resulting in α-helix and β-pleated sheets.
What level of structure determines whether you have collagen or myoglobin?
Tertiary structure in that at this level you have the determination of fibrous vs globular proteins.
What is a conjugated protein?
One that gets part of their function from a prosthetic group.
What is zaitsev's rule?
When producing alkenes (usually from elimination reactions) there will be a major and minor product, the major one being the more subsituted and stable form.
What is a Diels-Alder Reaction?
...