Understanding Electricity: Concepts and Safety
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
STATIC ELECTRICITY
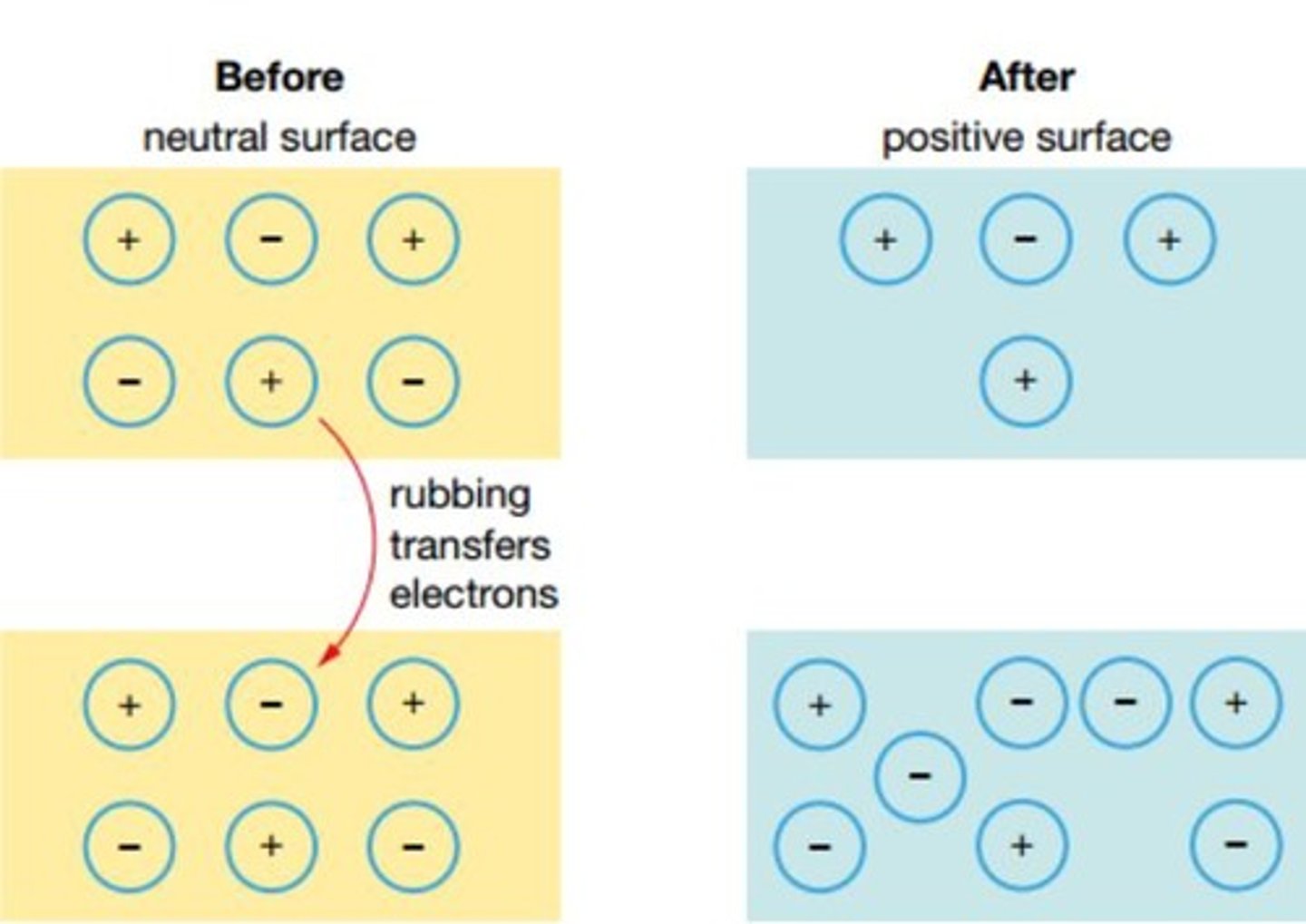
the BUILD UP of electrons on a surface
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
the FLOW of electrons along a conductor e.g. copper wire
ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT
a path along which electrons travel and deliver their energy
ENERGY SOURCE
examples include batteries and power points
Current
the RATE at which electrons are flowing in a circuit
Voltage
the DIFFERENCE in charge between two points
Resistance
a force that OPPOSES current
High resistance
results in LOW current
Series circuits
have ONE path for current
Voltage in series circuits
is SHARED between components
Resistance in series circuits
ADDS UP to give total resistance
Parallel circuits
have MULTIPLE paths for current
Current in parallel circuits
is PROPORTIONAL to its resistance
Voltage in parallel circuits
is the FULL voltage of the battery
Resistance in parallel circuits
does NOT add up to the total resistance
Combination circuits
are made of components in both series and parallel
Household wiring
is one large parallel or combination circuit
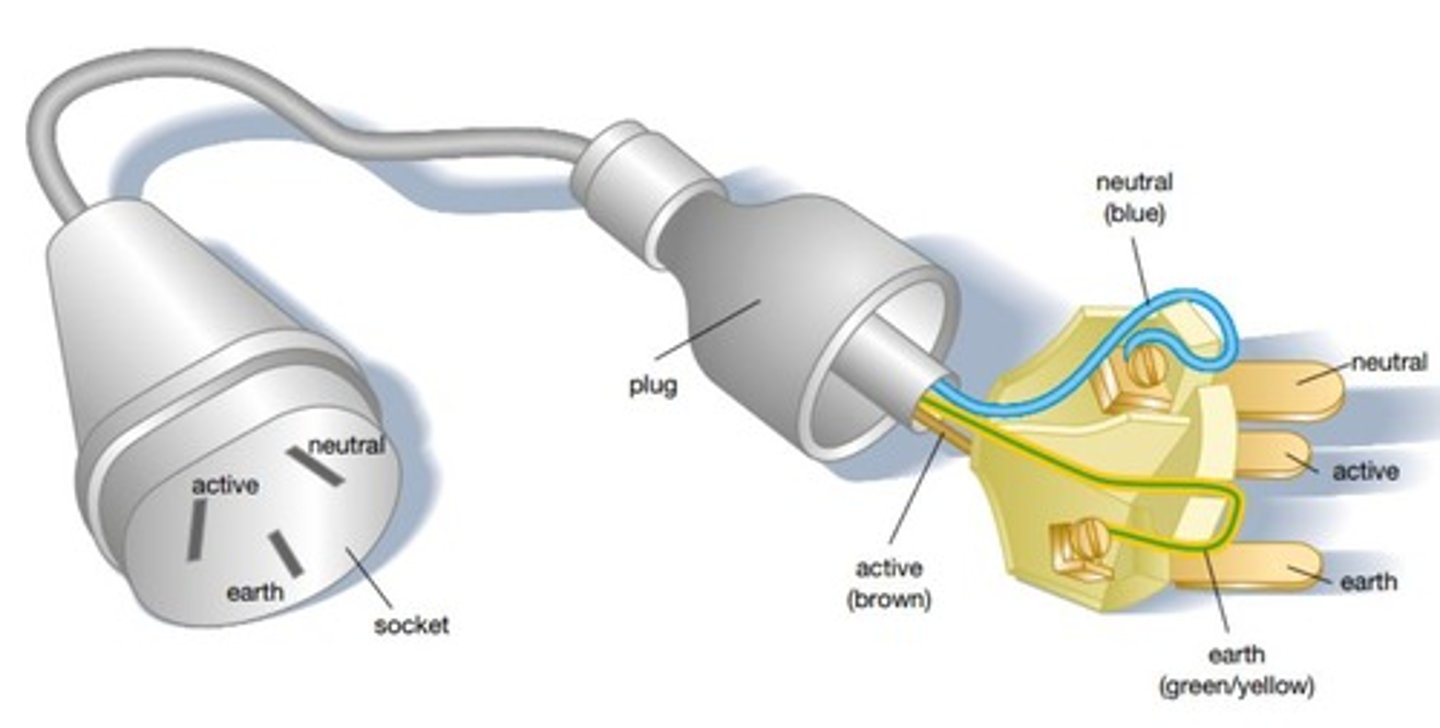
Active wire
brings current in, typically brown
Neutral wire
takes current out, typically blue
Earth wire
is a safety device that prevents electrocution, typically green and yellow
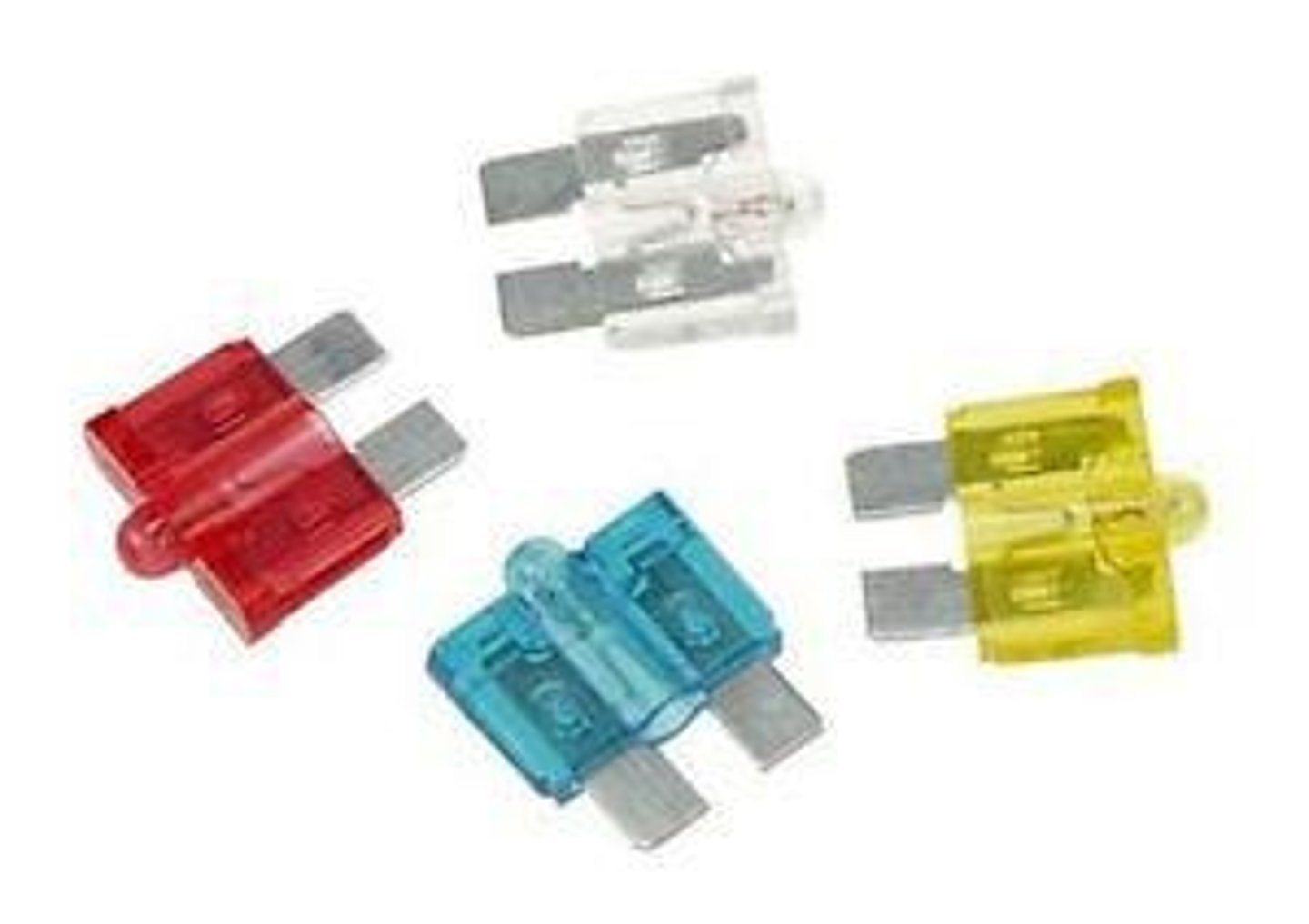
Fuses
are single-use devices that break the circuit when excessive current flows

Circuit breakers
protect electrical systems by cutting off power when detecting overloads
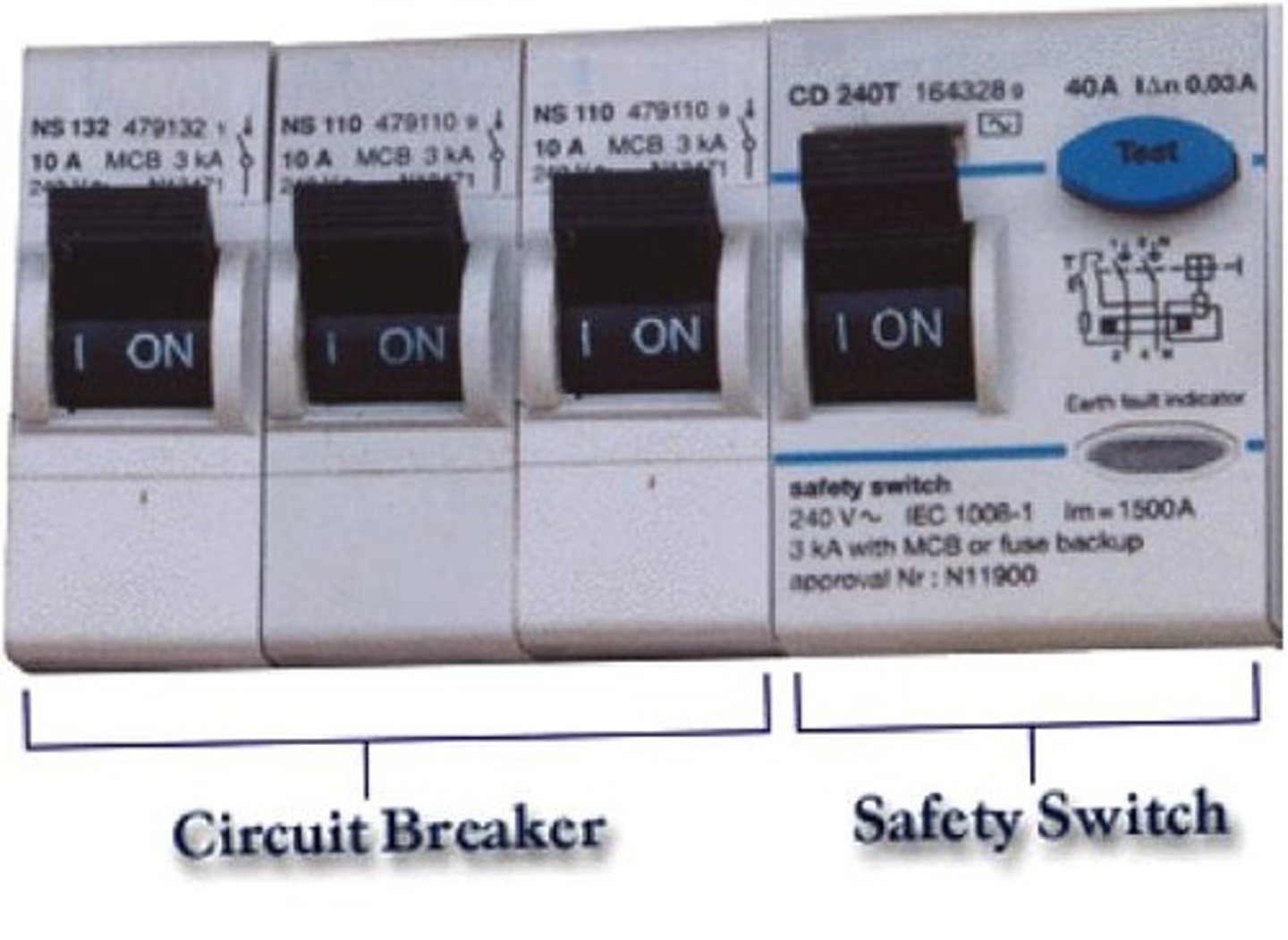
Safety switches
protect individuals from electric shock by interrupting power supply when a leak is detected
Parallel circuits
Allow individual branches to receive independent voltage and be controlled separately.
Household wiring colors
Brown = Active, blue = Neutral, green and yellow = Earth.
Fuses
Devices in modern appliances with wires that melt at high temperatures, breaking the circuit to reduce the likelihood of house fires and electrocution.
Safety switches
Work to prevent electrocution in people.
Circuit breakers
Work to prevent appliances from overheating, which reduces the risk of fire.
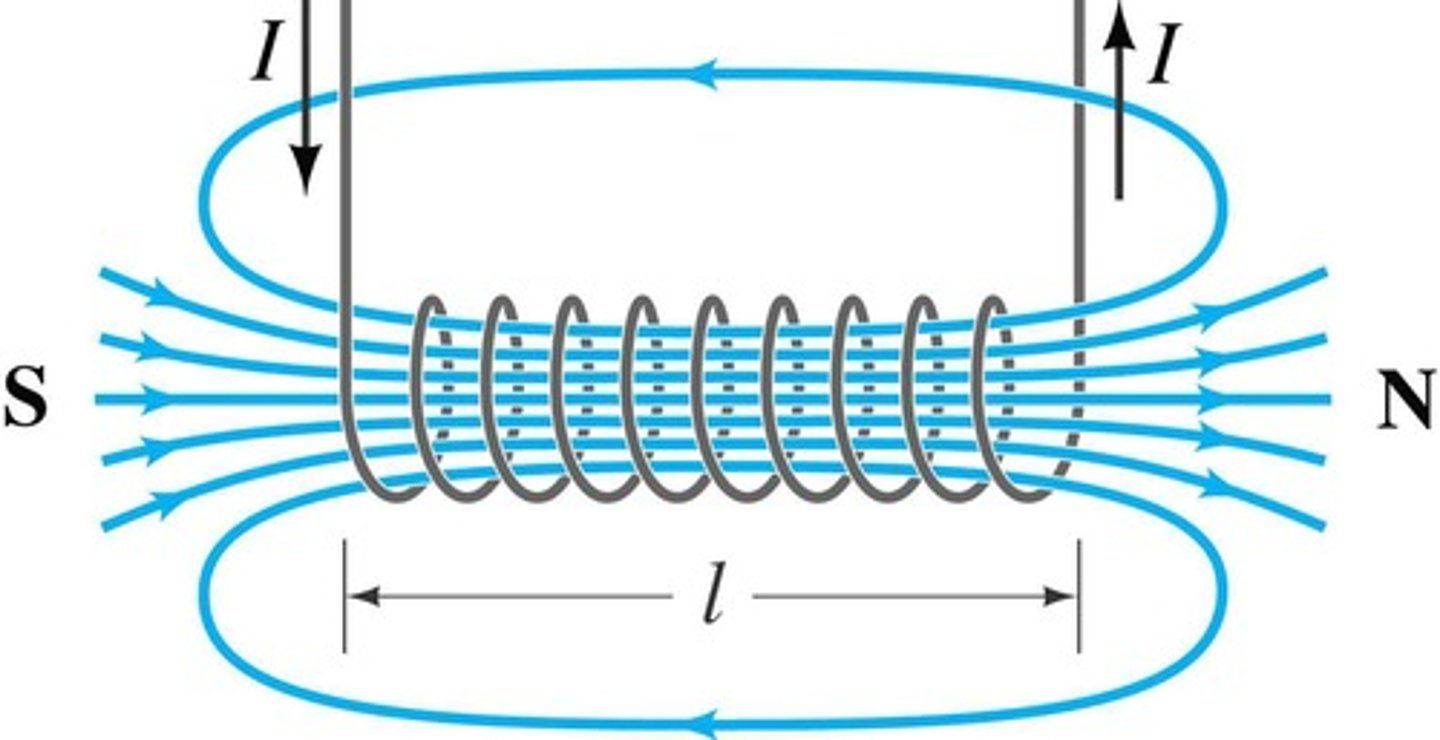
Electromagnetism
An electric current produces a magnetic field; when current moves along a wire, it generates a circular magnetic force around it.
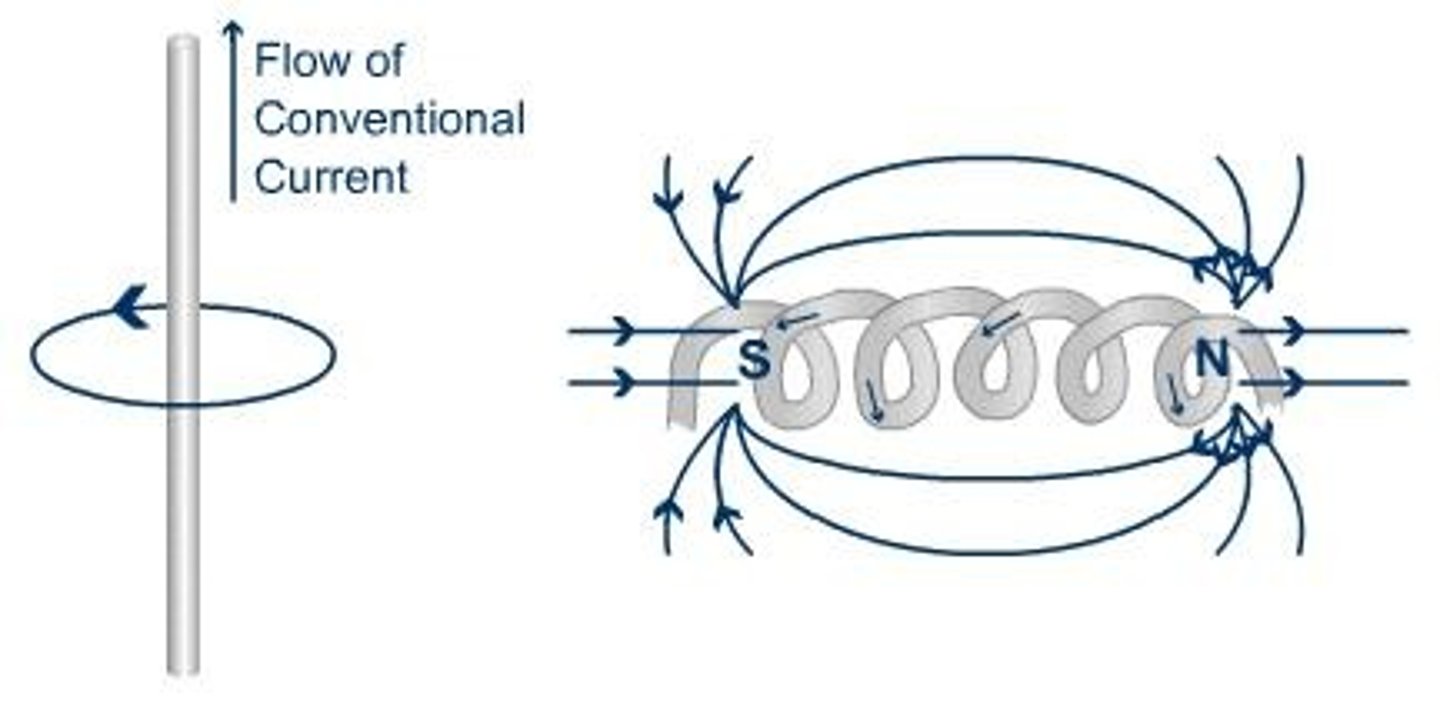
Solenoid
A coil of wire with electricity flowing through it.
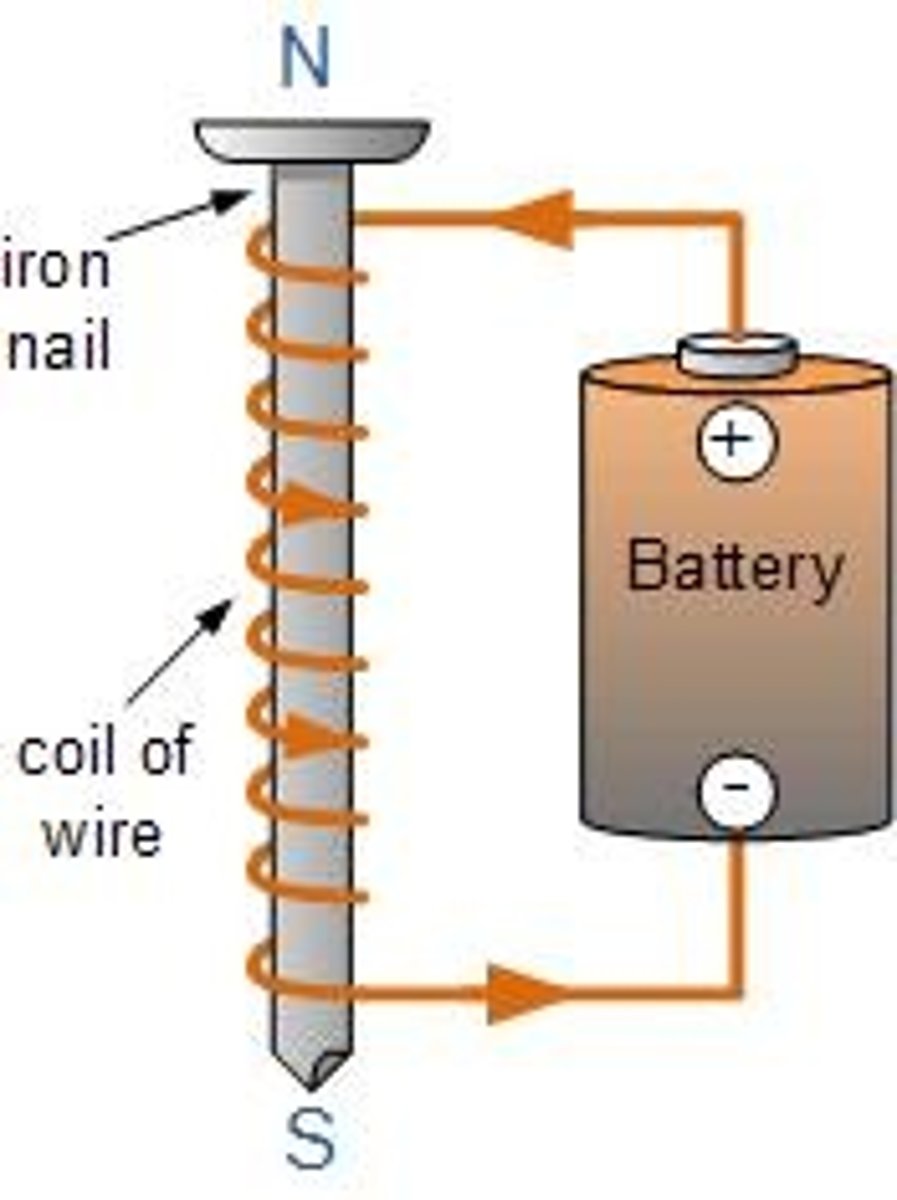
Electromagnets
Created by placing an iron rod or a magnetic material in the center of a coil, strengthening the magnetic field.
Electric motors
Convert electrical energy to kinetic energy by placing a solenoid on a swivel between a permanent magnet.
Generators
Use kinetic energy to produce electrical energy by manually spinning either the magnet or solenoid.
Turbines
Need to be spun at high speeds; larger generators spin their magnets while keeping their solenoids fixed.
Hydro-electricity
Water flowing down spins the turbine.
Steam power plants
Act like large gas kettles where water is heated and turned into high-pressure steam that turns the turbine.
Dynamos
Small magnets spun around a solenoid, often used to power lights of bicycles.
AC/DC
Batteries and solar cells produce direct current (DC), while generators, dynamos, and turbines produce alternating current (AC).
Electricity in AC
Changes direction 50 times every second.
Power plants
Produce electricity at 20,000V.
Electricity Transmission
Electricity must be transmitted from the power plants to homes/businesses.
Resistance in Wires
Wires that transport electricity have resistance, resulting in 'wasted' energy, especially over long distances.
Electric Current
An electric current produces a magnetic field.
Solenoid
A coil of wire with electricity flowing in it is called a solenoid.
Electric Motors
Electric motors convert electrical energy into kinetic energy.
Generators
Generators convert kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Ohm's Law
Ohm's law can be used to find the current, voltage or resistance in a circuit if the other two variables are known.
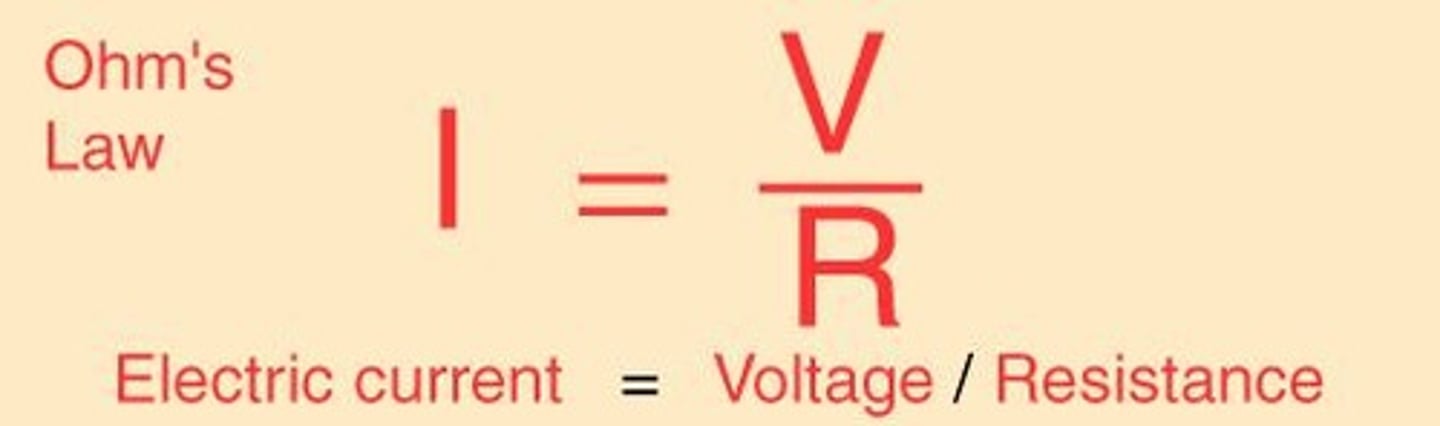
Series Circuits - Current
In a series circuit, the current flowing through the whole circuit is the same.
Series Circuits - Voltage
In a series circuit, the voltage supplied by the battery is shared by all components.
Series Circuits - Resistance
In a series circuit, the resistance of each component adds up to give the total resistance.
Parallel Circuits - Voltage
In parallel circuits, each branch gets the full voltage of the battery.
Parallel Circuits - Current
In parallel circuits, each branch draws a current proportional to its resistance.
Parallel Circuits - Resistance
In parallel circuits, you do NOT add the resistance of different branches together.
Combination Circuits
Combination circuits are made of components in both series and parallel.
Voltage in Combination Circuits
The circuit is powered by a 9V battery.
Resistance of Bulbs
Assuming each bulb has a resistance of 2Ω.
Total Current Calculation
Calculate the current in each branch and deduce the total current flowing through the circuit.
Voltage Received by Bulbs
Find the voltage received by each globe in this circuit.
Current Flowing Through Bulbs
Find the current flowing through each branch.
Household wiring
A household is one large parallel or combination circuit.
Active wire
Brings electricity in, colored brown.
Neutral wire
Takes current out, colored blue.
Earth wire
Prevents electrocution, colored green and yellow.
Fuses
Devices with wires that melt at high temperatures, breaking the circuit.
Safety switches
Designed to protect you from electrocution by detecting leaking current in 0.03 seconds.
Circuit breakers
Designed to protect the wiring and circuitry of your house by cutting the power when too much current is present.
Direct Current (DC)
Electrons flow in the same direction, e.g., battery.
Alternating Current (AC)
Electrons shuffle back and forth, e.g., power points.
Ammeter
Measures the amount of charge (electrons) flowing through it per second.
Voltmeter
Measures voltage, the difference in charge between two points.
Energy source
Supply voltage from which electrons gain their energy.
Transformer
Used to reduce voltage for an appliance.
Multiple cells/Batteries
Connecting multiple batteries next to each other makes their voltage add up.
Wet cells
Conducting electrodes submerged in liquid electrolyte.
Dry cells
One electrode wrapped in another, small and don't leak.
Photovoltaic cells
Convert solar energy into electrical energy.
Resistance
A force that opposes current, measured in ohms (Ω).
Ohmmeter
Measures resistance.
Resistance: wires
Connecting wires also have resistance.
Resistance
A force that reduces current in a circuit.
Current
The rate at which electrons flow in a circuit.
Resistors
Circuit components used to reduce the current flowing in a circuit.
Variable resistors
Resistors that allow you to change their resistance to control current.
Conductors
Materials that allow electrons to flow easily, such as metals.
Insulators
Materials with high enough resistance to block the flow of electrons.
Electric charge
The property of electrons that allows them to move and create electricity.
Static Electricity
The build-up of electrons that have been displaced on a surface.
Current Electricity
The flow of electrons along a conductor, such as copper wire.
Simple Electric circuits
A path along which electrons travel and deliver their energy.
Closed circuit
A complete circuit that allows electrons to flow.
Open circuit
A circuit with a break that prevents electrons from flowing.
Energy source
Components like batteries or power points that provide energy in a circuit.
Energy user
Devices like light bulbs or motors that use energy in a circuit.
Electrons
Small, negatively-charged particles that are part of atoms.
Atoms
The basic units of matter, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
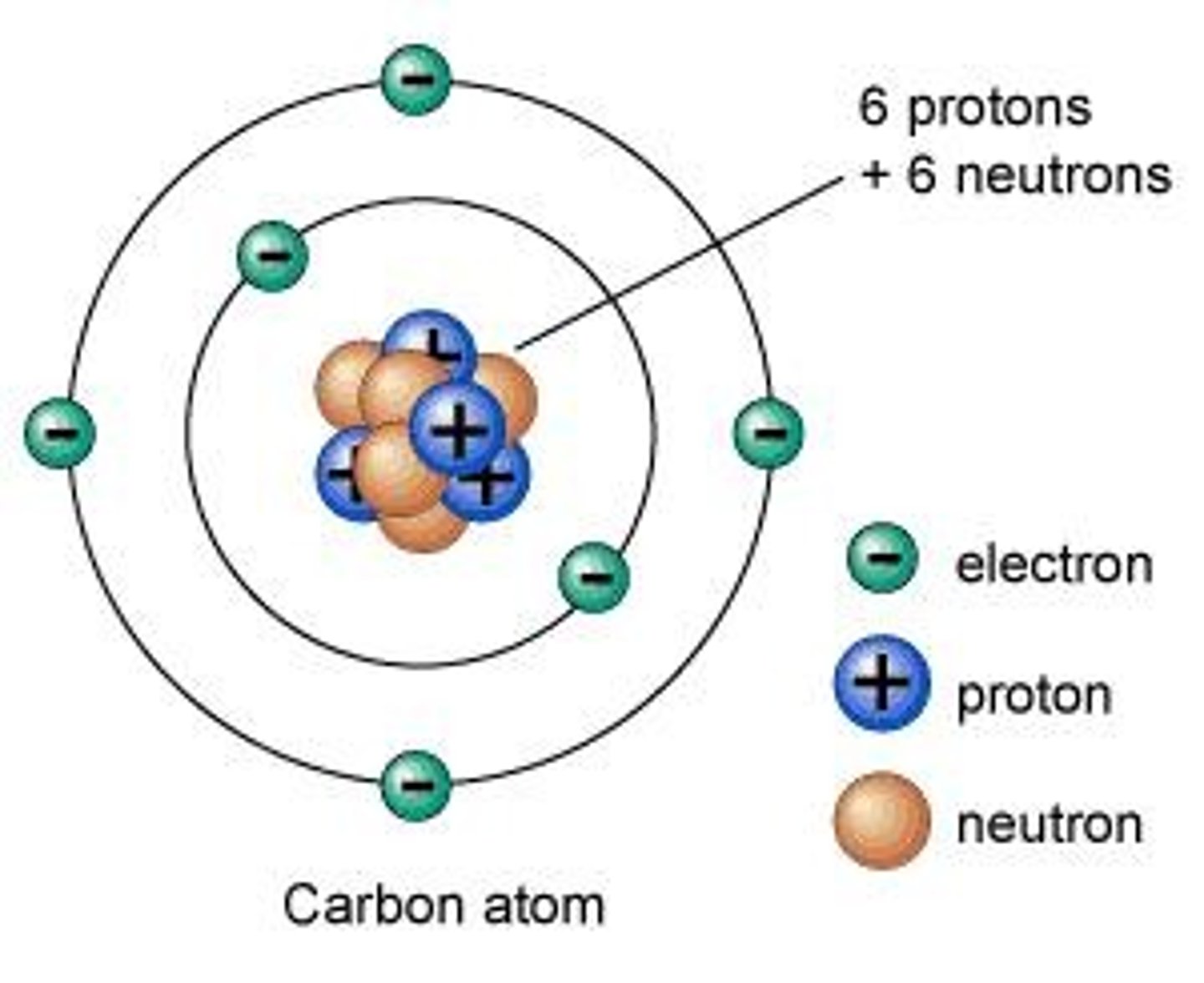
Protons
Sub-atomic particles with a positive charge located in the center of the atom.
Neutrons
Sub-atomic particles with no charge located in the center of the atom.
Copper
A good conductor of electricity, commonly used in circuits.