Principles of Biology Final by Lopez
1/428
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
429 Terms
What is cellular respiration?
The process by which plants and animals break down glucose and turn it into energy.
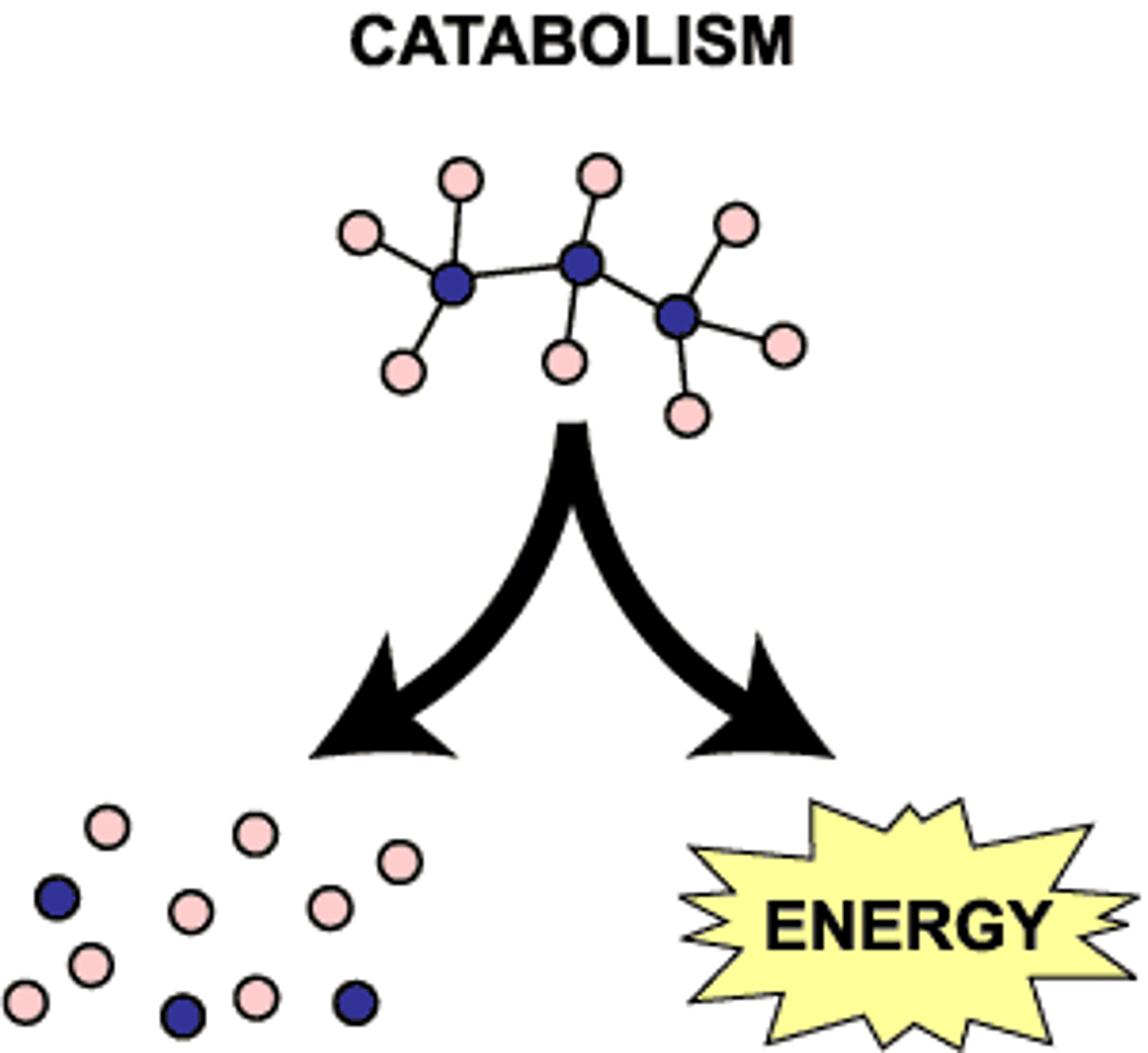
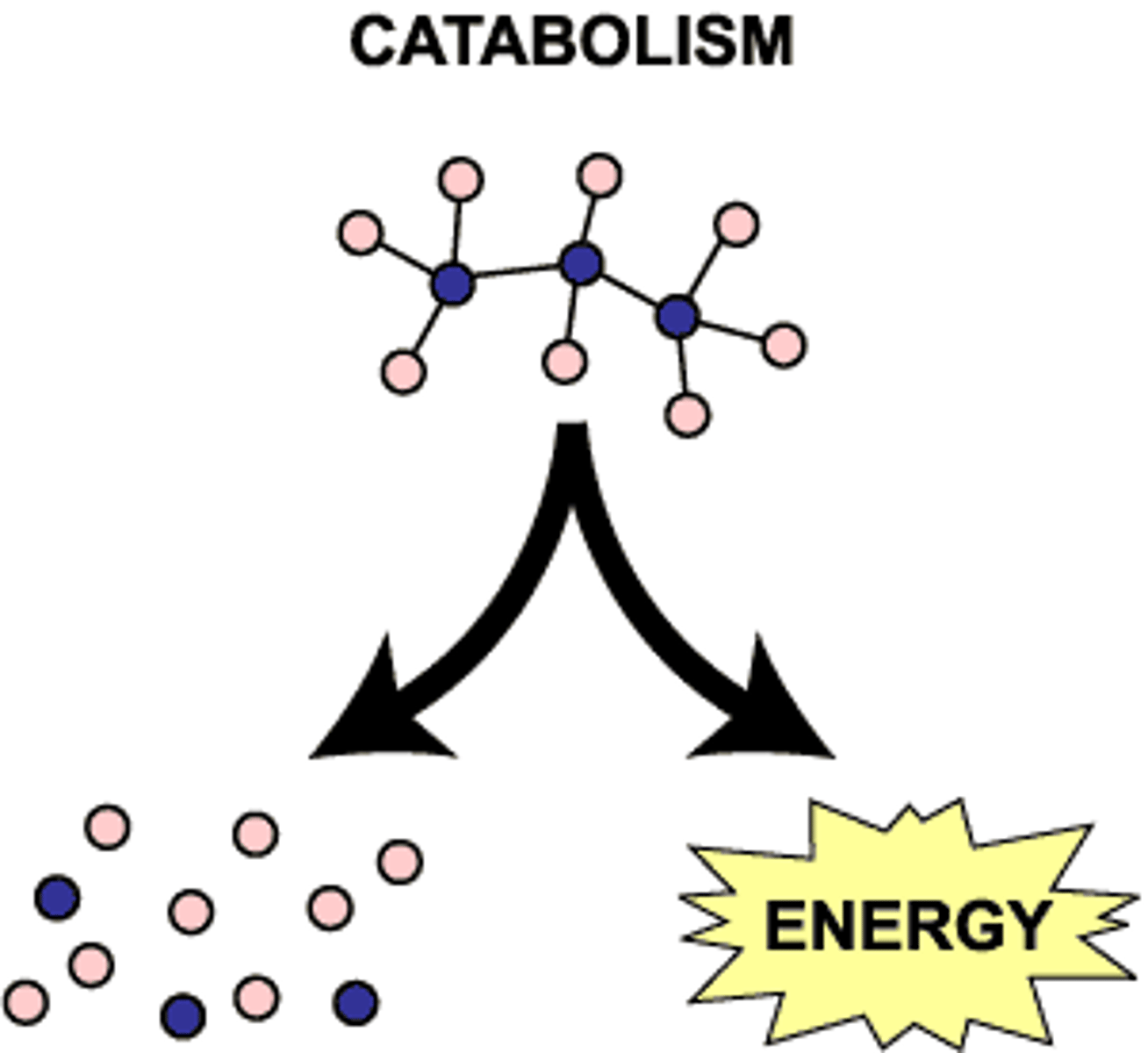
What do catabolic pathways do?
Release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules.
What two things make up oxidative phosphorylation?
-Electron transport chain
-Chemiosmosis
(generates almost 90% of the ATP)
What is potential energy?
Potential energy is stored energy that objects have because of where they are or how they're set up.

What is enzymatic activity?
Cells systematically break down complex organic molecules that are rich in potential energy into simpler waste products that have less energy.
The energy that is not used for work is lost in what way?
Heat
What is aerobic respiration?
-The process cells use to turn glucose into energy with the presence of oxygen.
-This is the most effective catabolic pathway

What is anaerobic respiration?
-Is a way cells produce energy without using oxygen.
-It involves breaking down glucose to make energy, typically producing byproducts like alcohol or lactic acid.

What is fermentation?
A partial degradation of sugars that occurs in the absence of O2.
What is cellular respiration often referred to?
Aerobic respiration
(It requires oxygen to efficiently break down glucose)
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + (ATP + heat)

Do catabolic pathways directly perform cellular work?
No
What is catabolism?
-Breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones,
together with the release of energy
-Destructive metabolism.
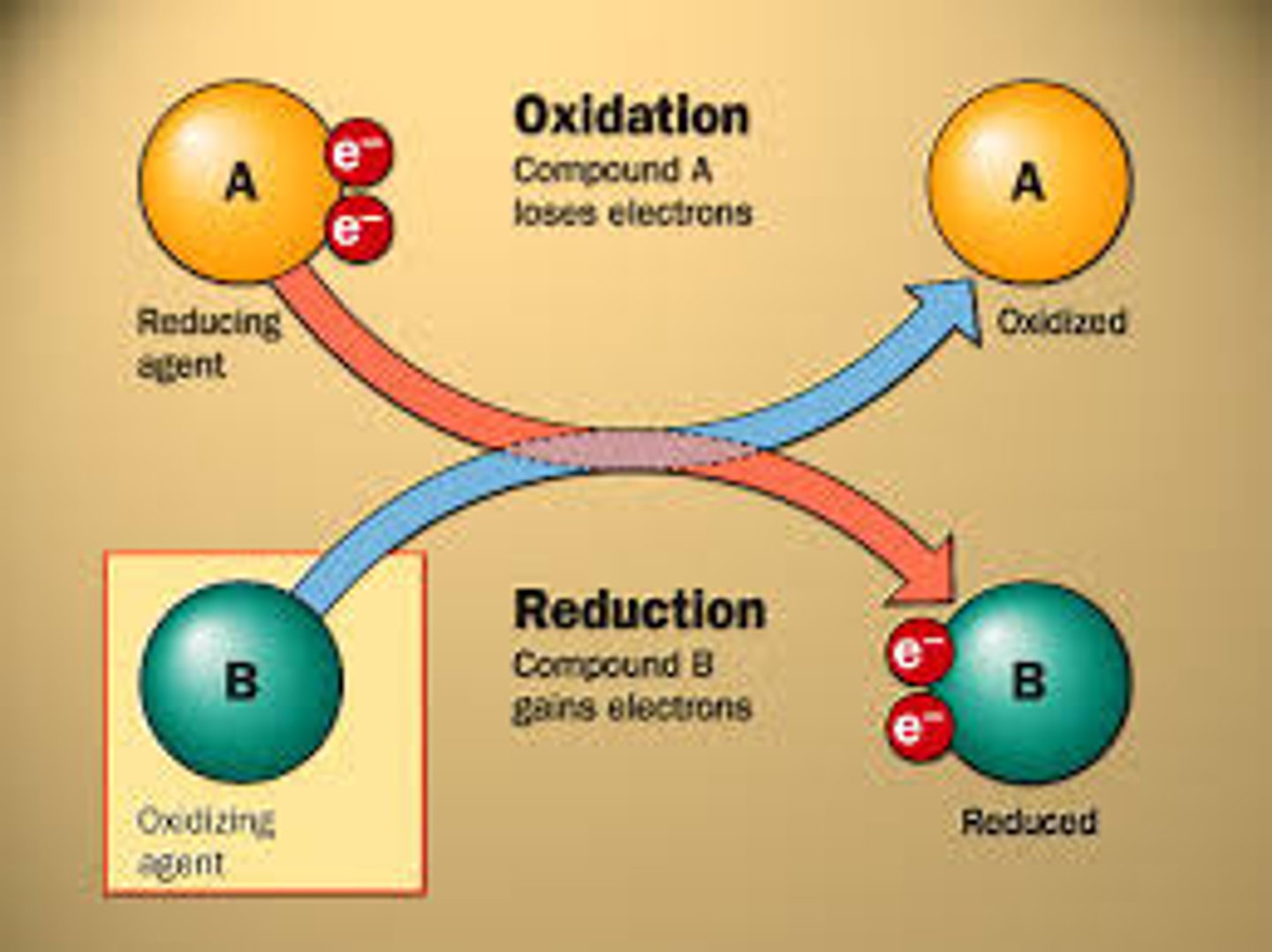
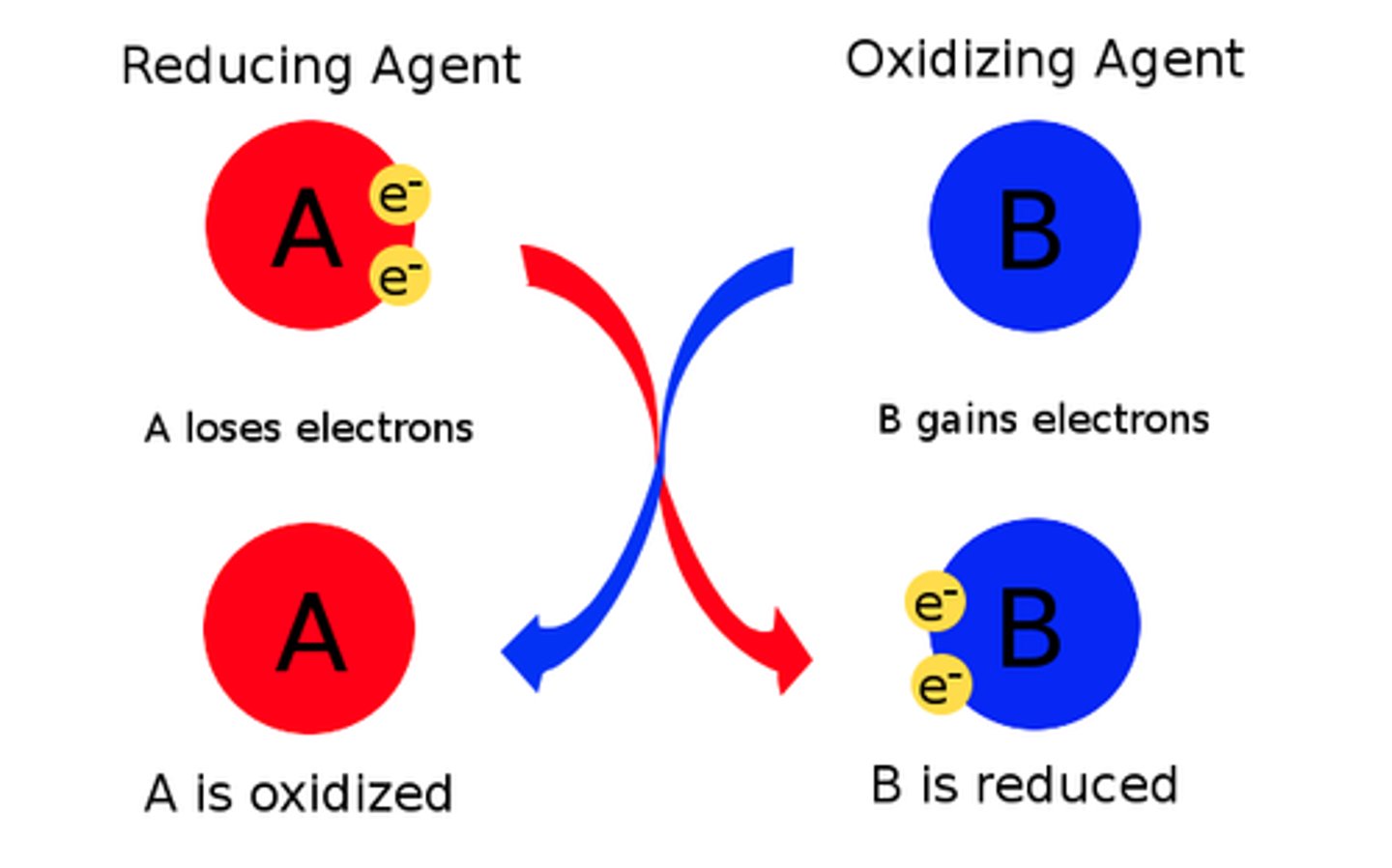
What is a redux reaction
Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants.
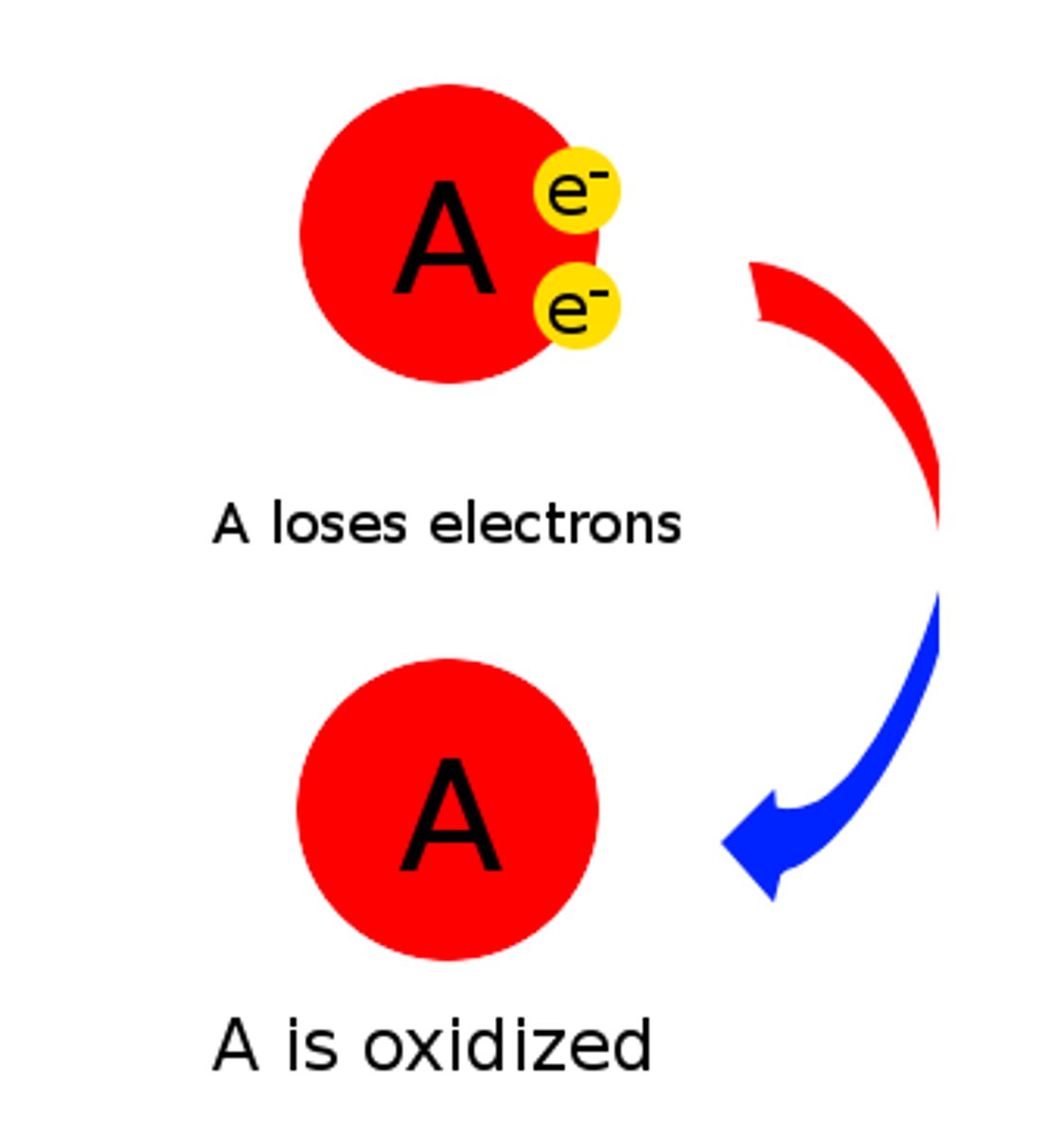
What happens in a oxidation reaction?
-Electrons are stripped from an atom in a compound
-Resulting in a decrease in the potential energy in the oxidized compound.
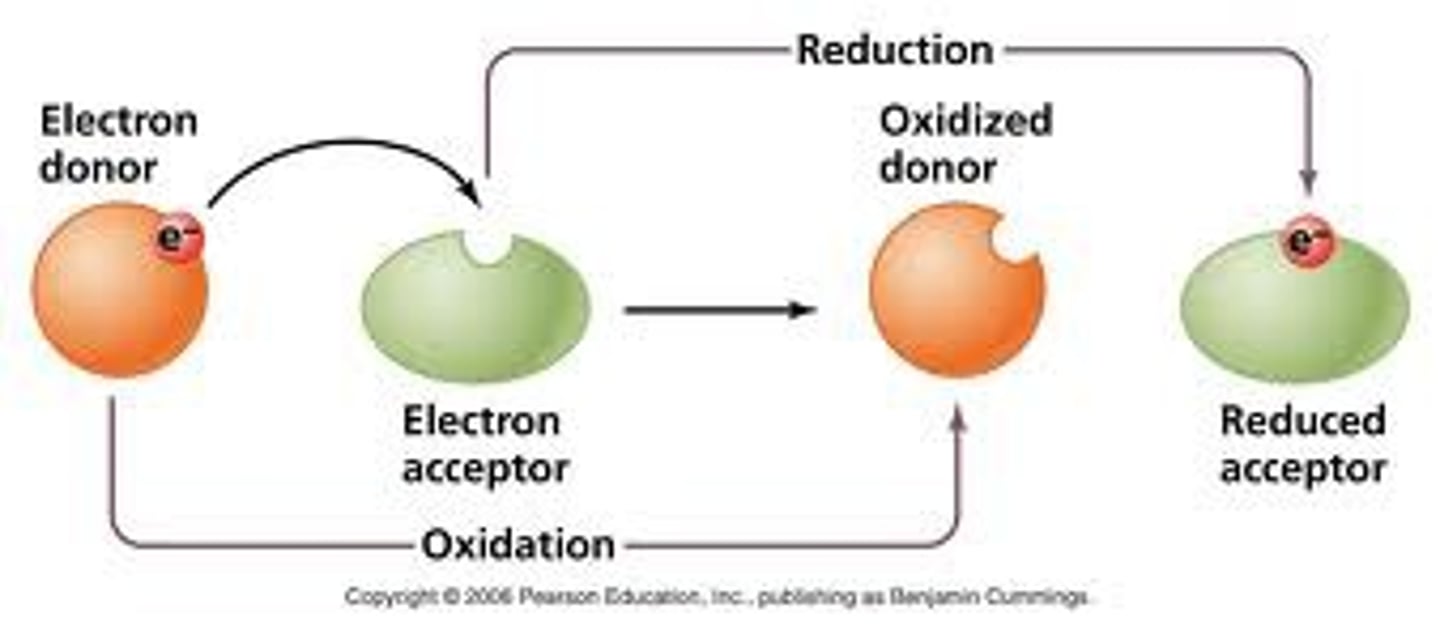
What does it mean to be oxidized?
A substance loses electrons.
What happens in a reduction reaction?
-Electrons are added to a compound.
-Increasing the potential energy of the second compound.
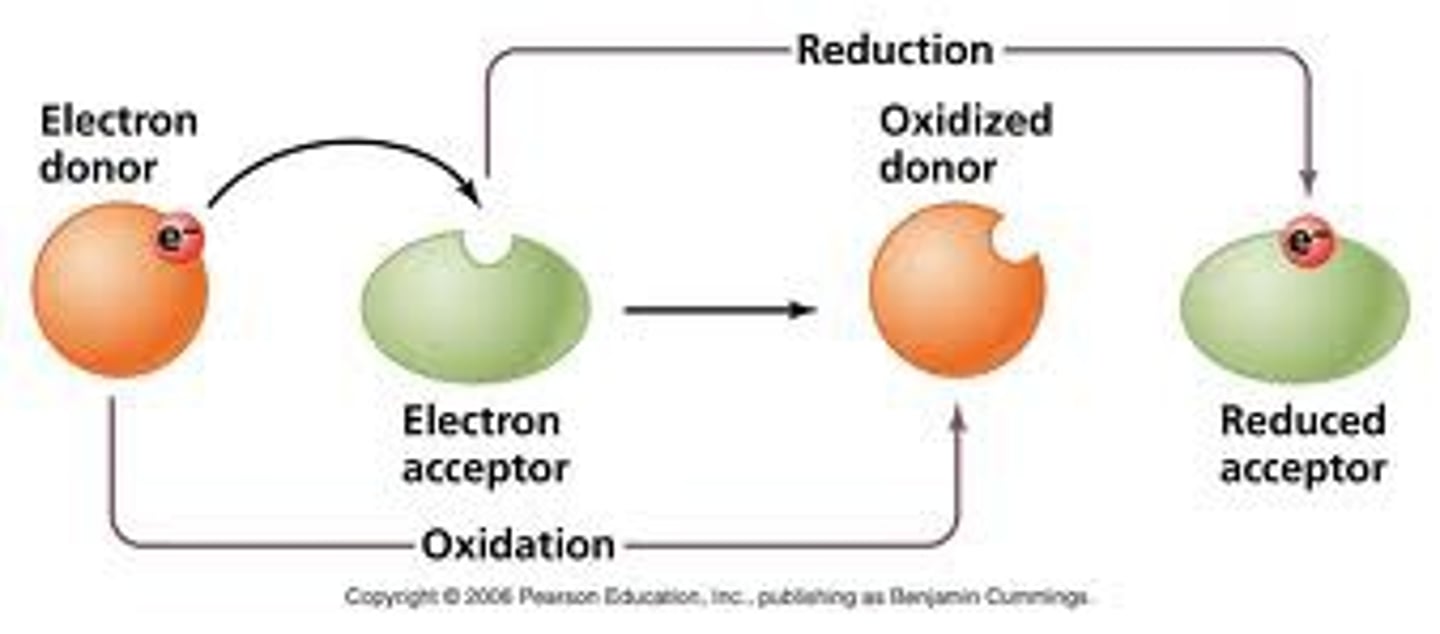
What is a reduction?
Adding of electrons
What is a reducing agent?
electron donor
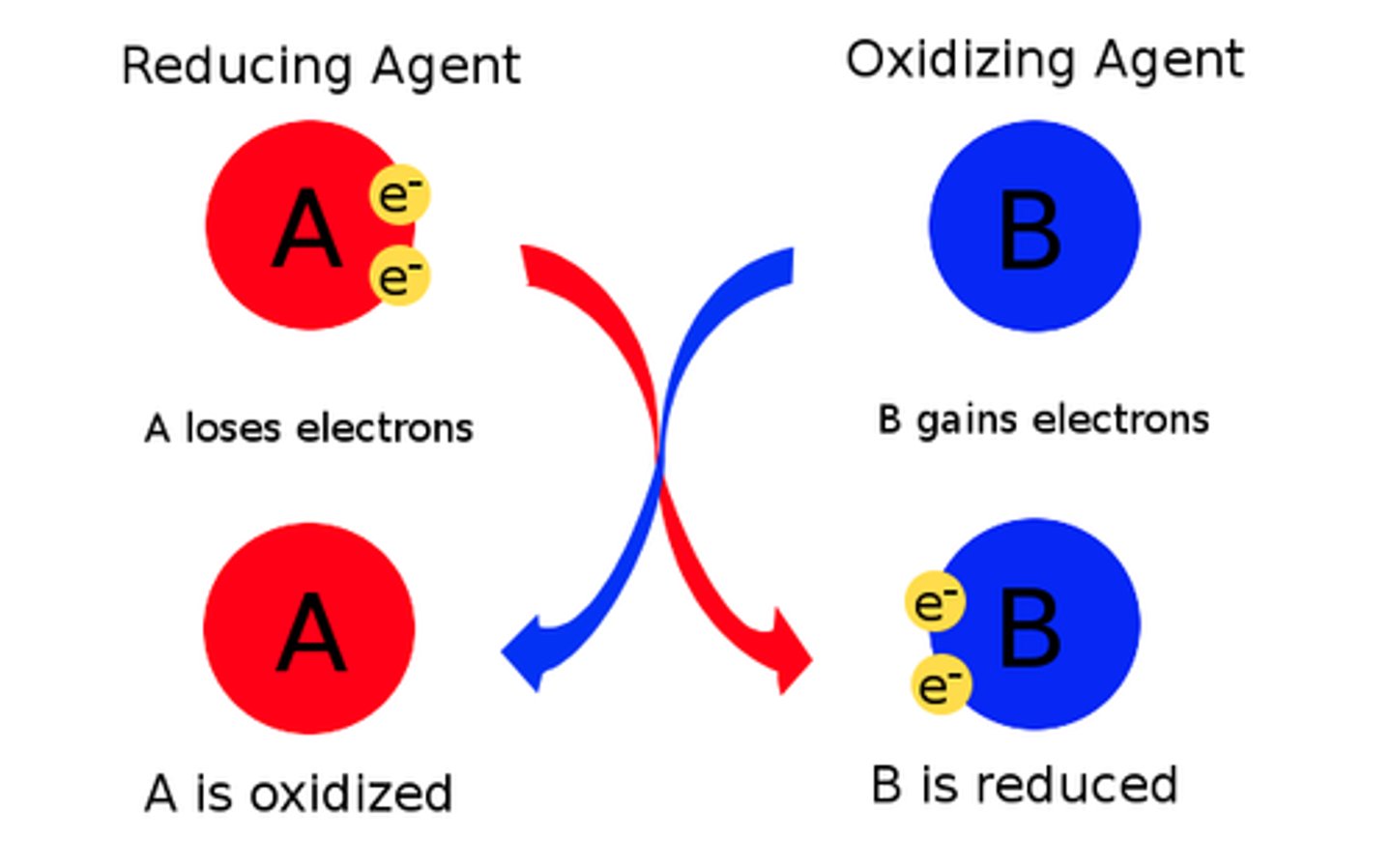
What is the oxidizing agent?
electron acceptor
What is NAD and what does it do?
(carry electrons)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
What is NAD+?
-Is the oxidized form of the molecule NAD.
-As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration.
Compared to NAD+, what is NADH?
Is the reduced form of NAD+ after it has accepted two electrons and one proton.
What are dehydrogenases?
-Enzymes that remove a pair of hydrogen atoms from the substrate (food)
-Thereby oxidizing it, then delivers the 2 electrons along with 1 proton to, NAD+, forming NADH.
What does NADH represent?
Stored energy that is used to synthesize ATP
- NADH holds onto high-energy electrons from food until they're used to make ATP.
NADH passes electrons into what?
Electron Transport Chain
What key role does O2 play in the electron transport chain?
O2 accepts the expended electrons at the end of the electron transport chain in aerobic cellular respiration.
(grabs them and helps form water)
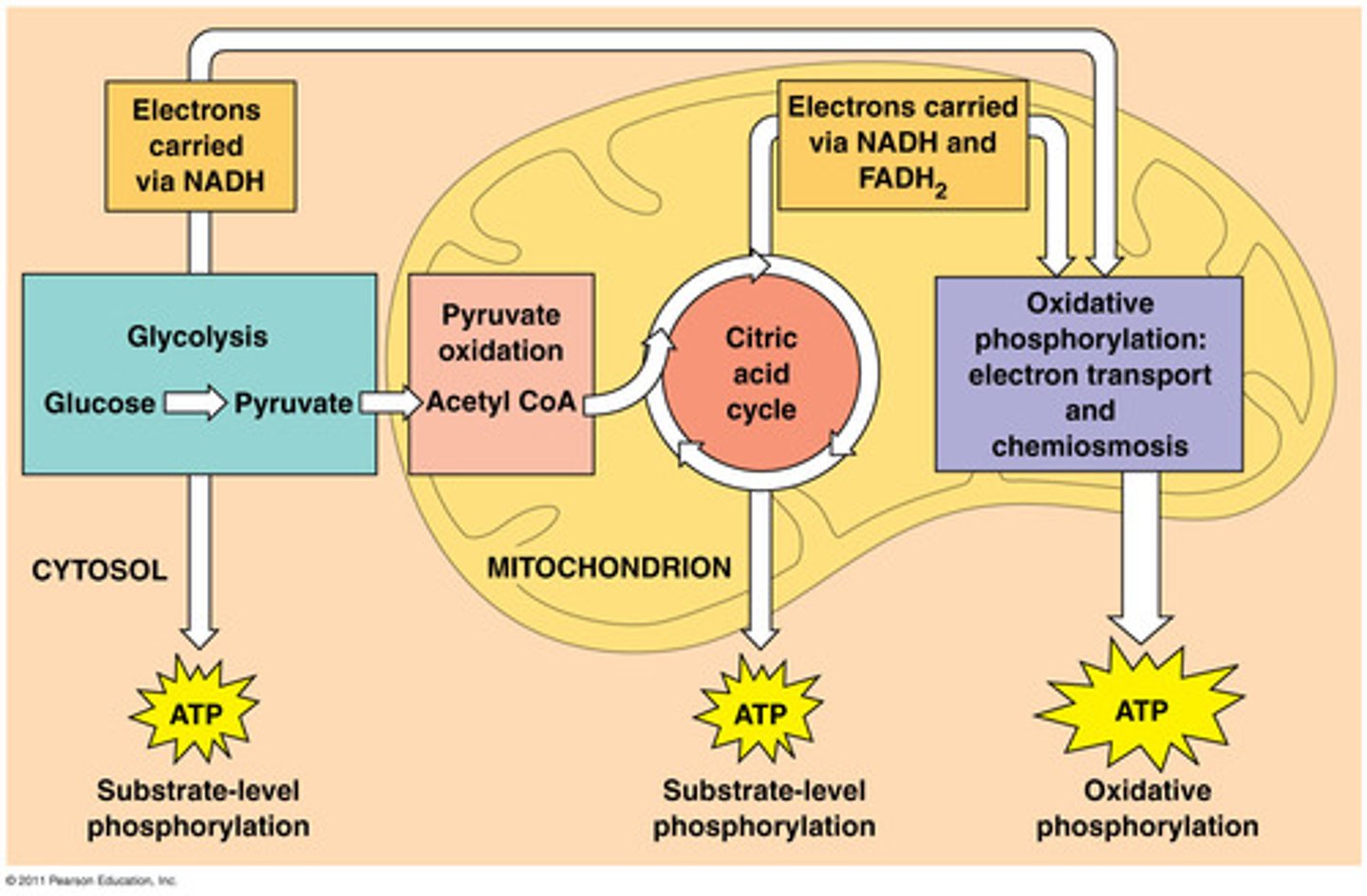
What are the 3 major steps involved in harvesting energy from glucose?
-Glycolysis
-Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb Cycle)
-Oxidative Phosphorylation
What is glycolysis?
- The breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- Generates 2 ATP and 2 NADH
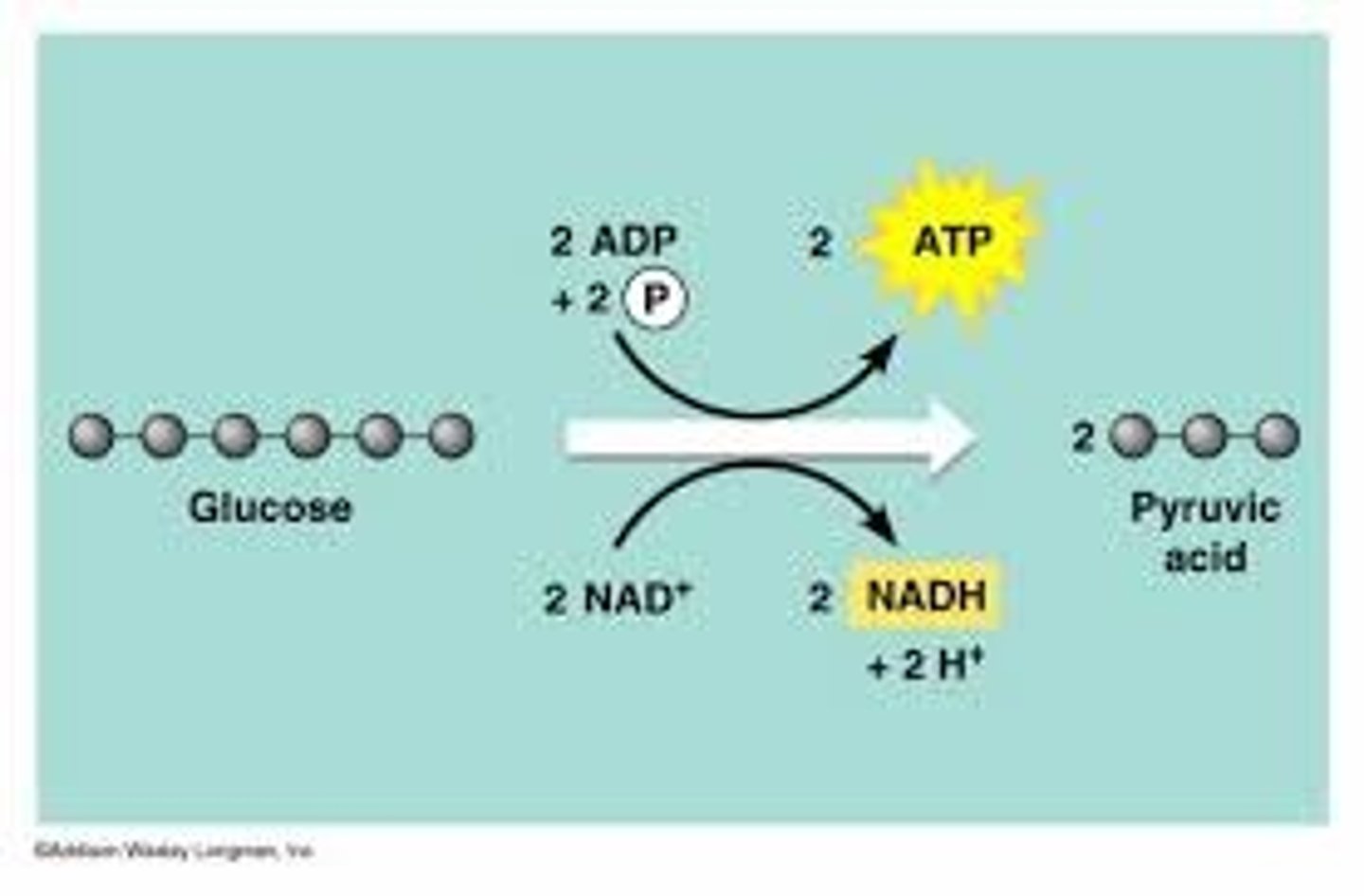
What does the citric acid cycle do?
Completes the breakdown of glucose by oxidizing a derivative of pyruvate to carbon dioxide.
- Takes place in the mitochondria matrix.
- Produces ATP, NADH, and FADH2
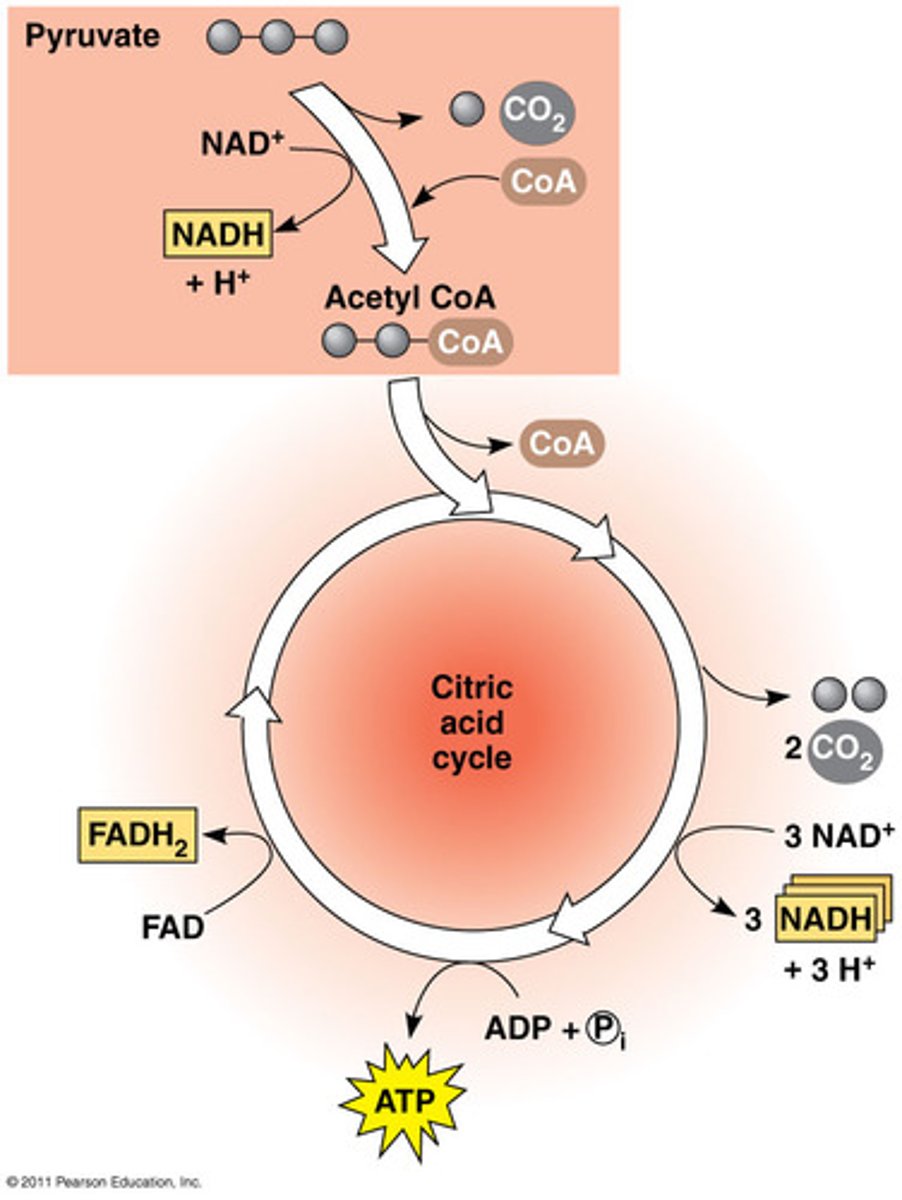
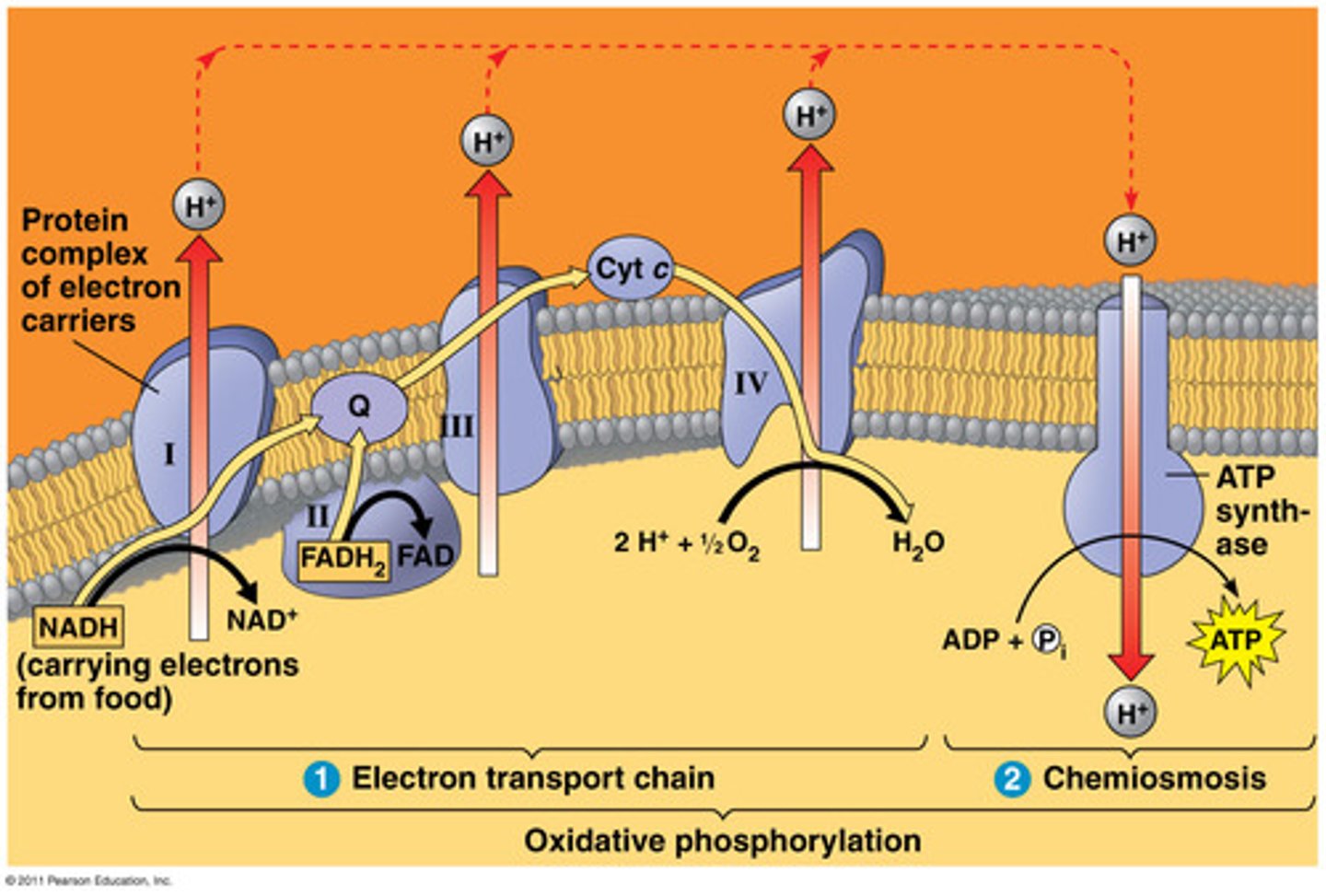
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Accounts for most of the ATP synthesis and generates almost 90% of the ATP.
- mainly involves two steps: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
- Happens in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
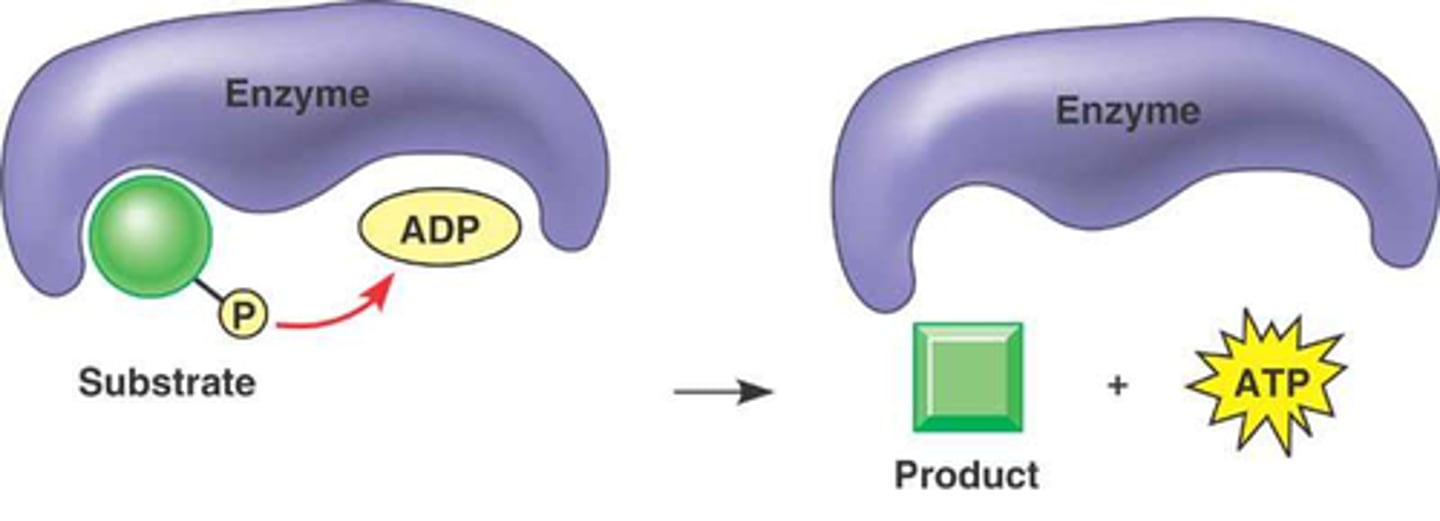
What is substrate level phosphorylation?
The formation of small amounts of ATP are formed by glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
How much ATP does the cell make from each molecule of glucose degraded to CO2 and water by cellular respiration?
32 molecules of ATP.
What are the two major phases of Glycolysis?
-Energy requiring phase
(2 molecules of ATP are used per molecule of glucose)
-Energy releasing phase
(4 molecules of ATP are produced per molecule of glucose)
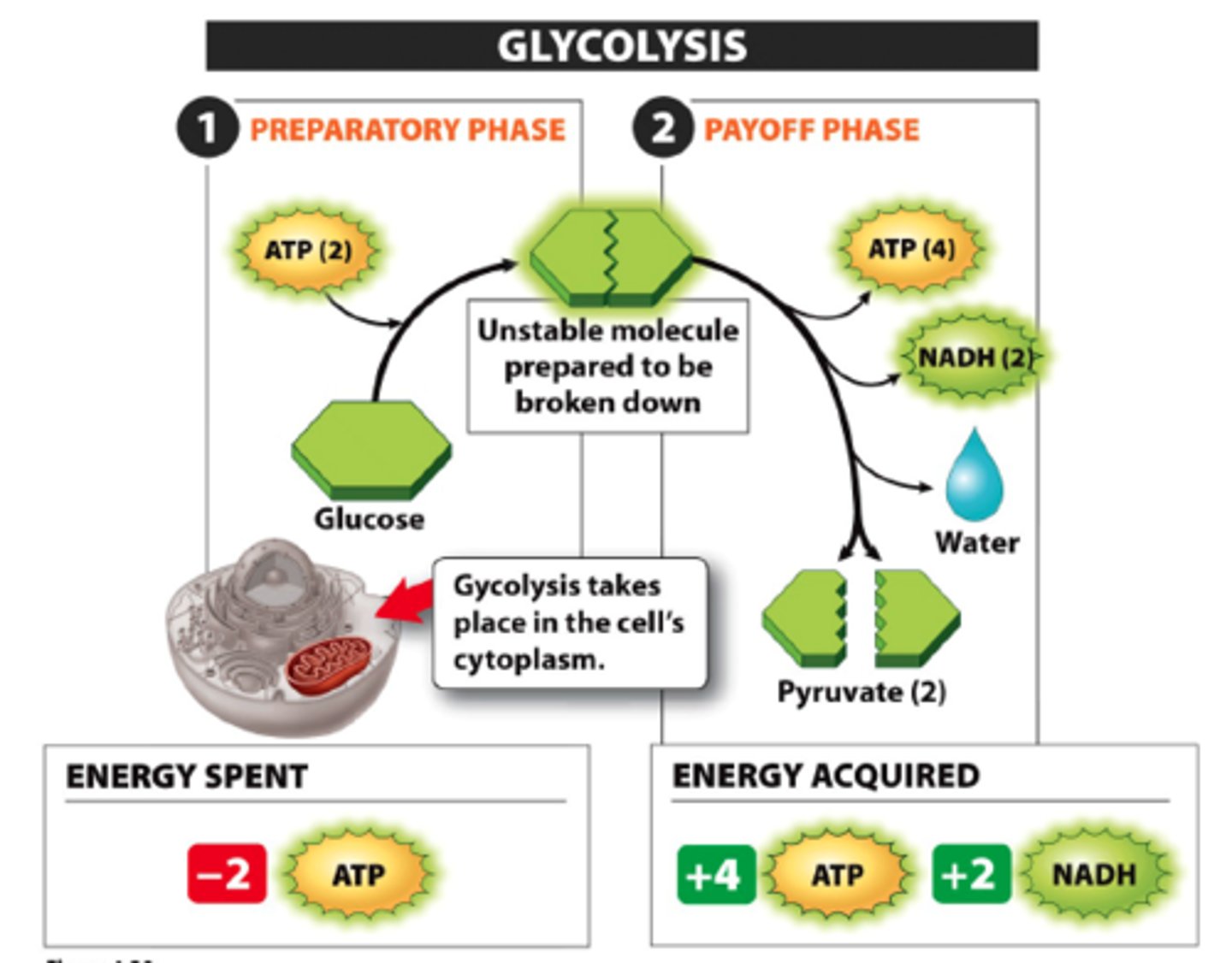
Is glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic?
(anaerobic)
can happen in the absence of oxygen
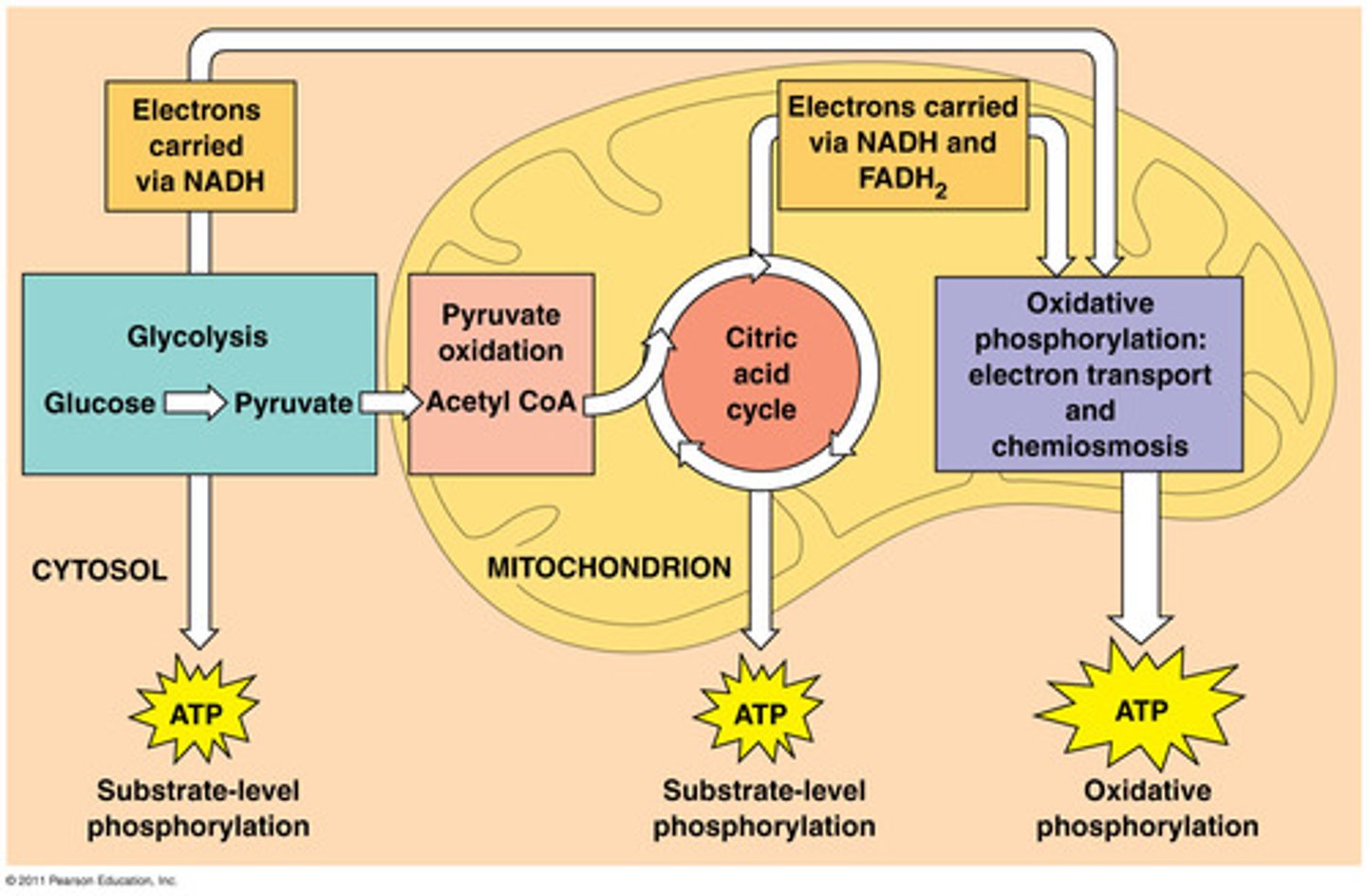
Before the citric acid cycle can begin, pyruvate must be converted to what?
Coenzyme A
(acetyl CoA)
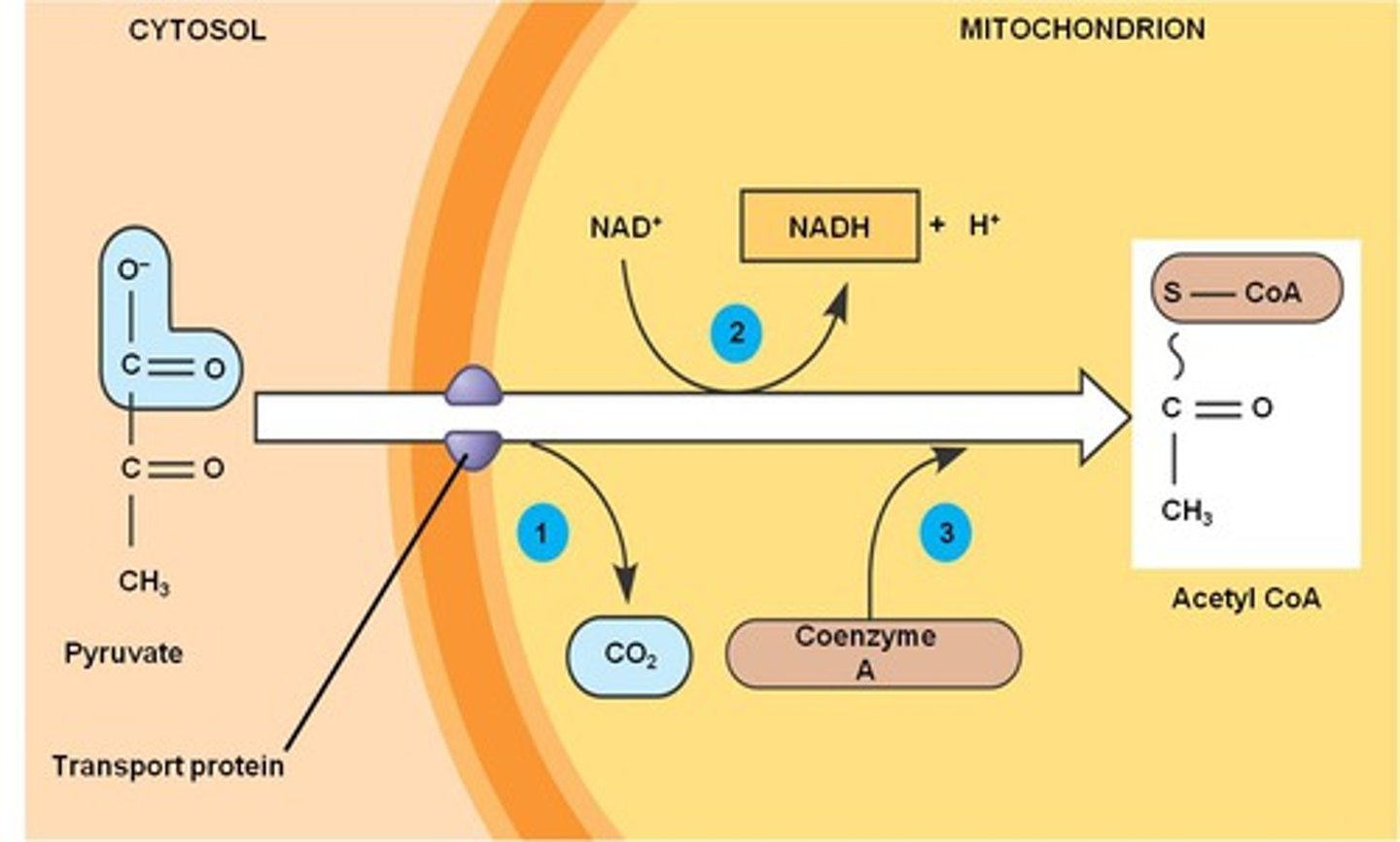
What are the steps for the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
1) Oxidation of pyruvate and release of CO2
2) Reduction of NAD+ to NADH
3) Combination of the remaining two-carbon fragment and coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA.
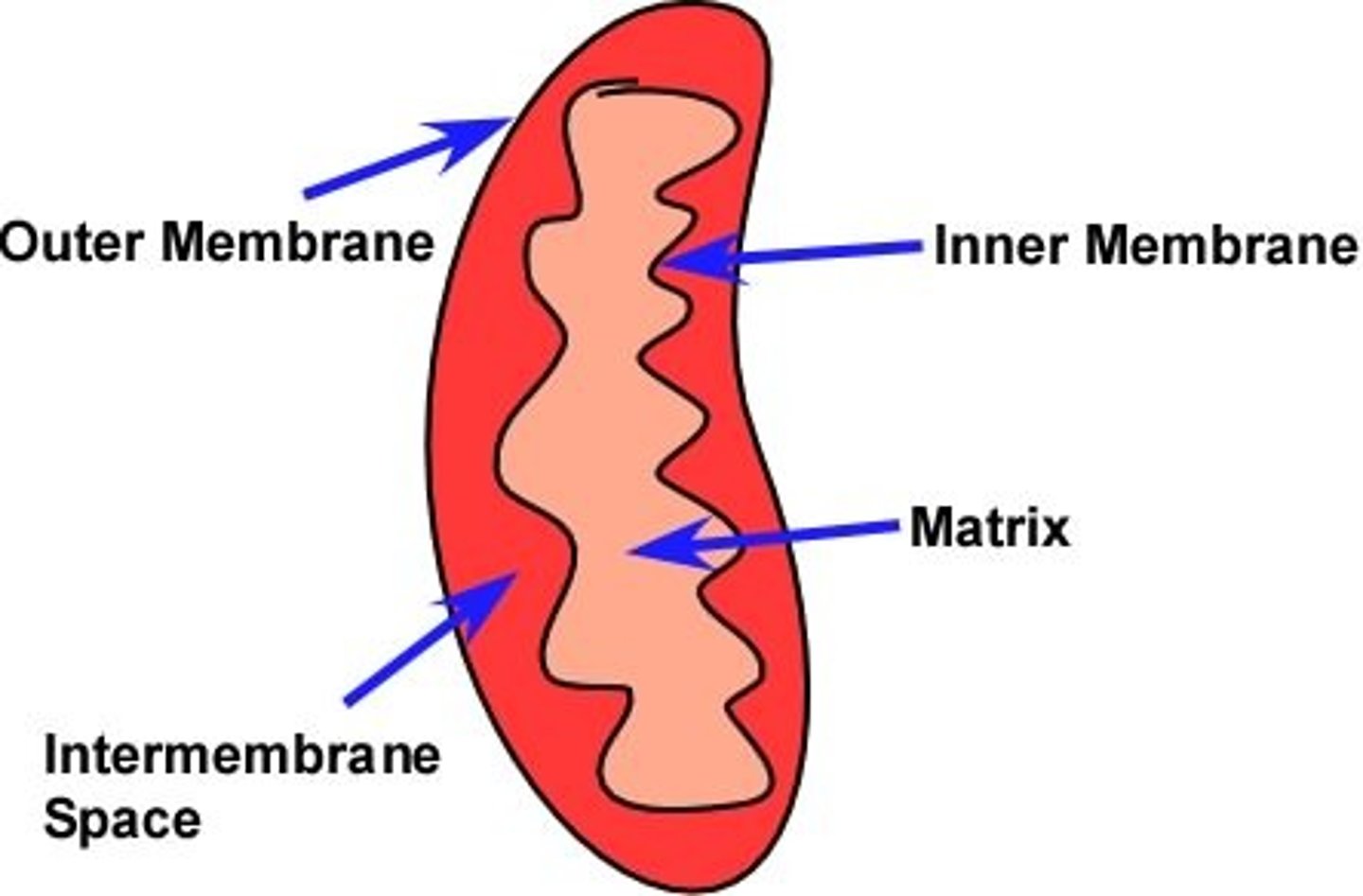
Where does the citric acid cycle occur?
matrix of the mitochondria
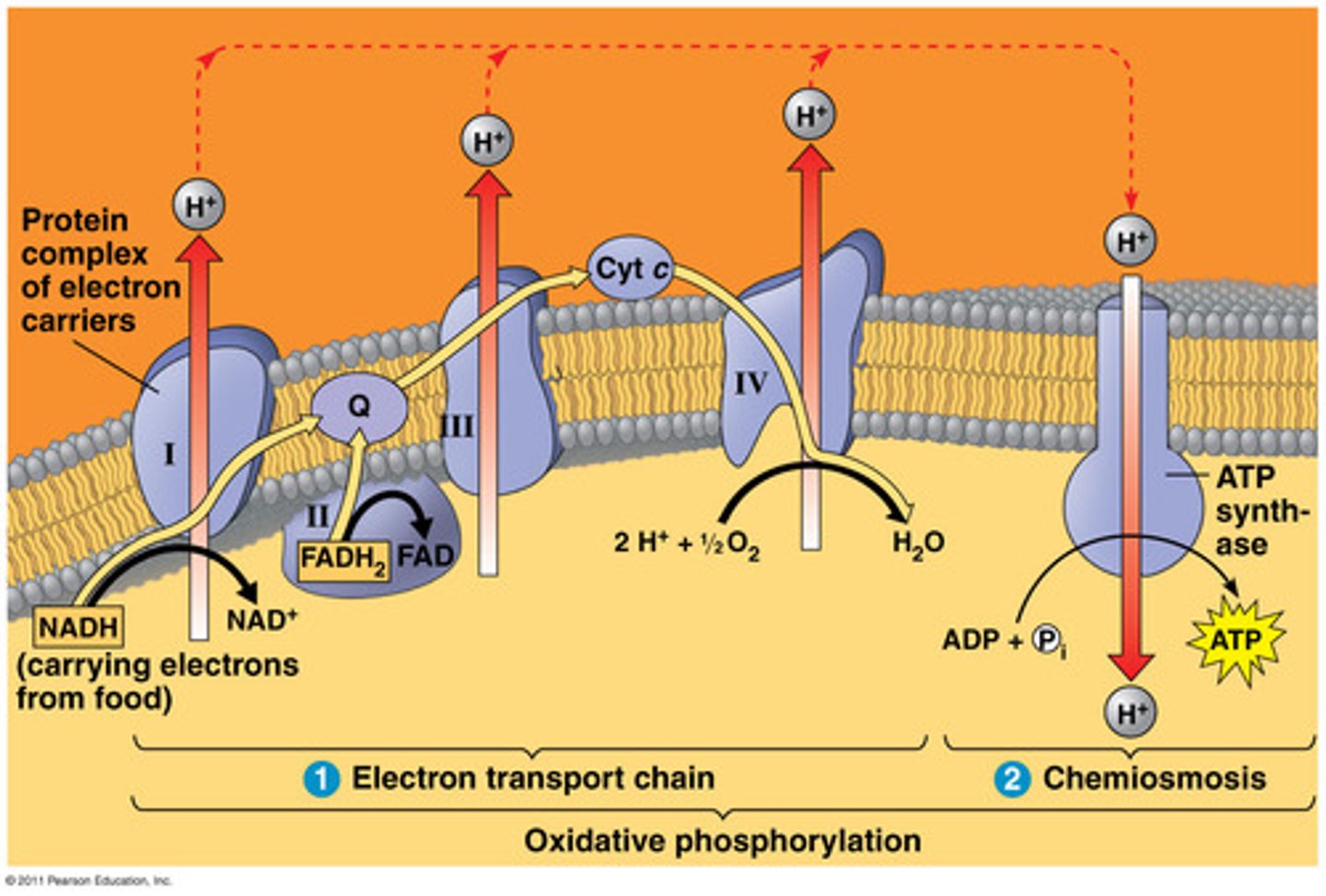
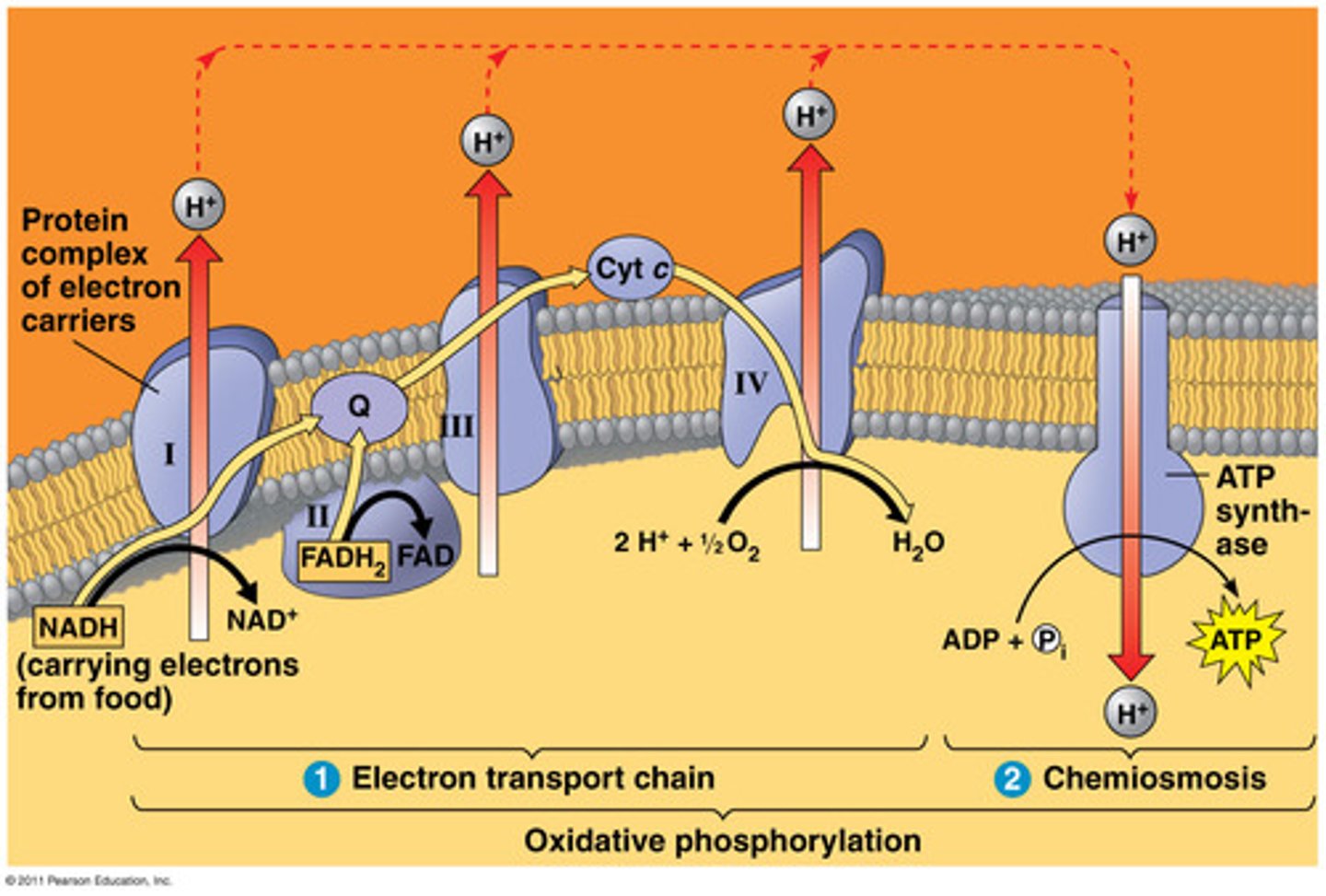
The electrons that enter the electron transport chain power ATP synthesis by what process?
oxidative phosphorylation
What is the electron transport chain?
- Is a series of electron transporters multiprotein complexes that are embedded in the inner membrane (Cristae) of the mitochondrion
- Shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular O2.
What are cytochromes?
- Special proteins that help carry electrons in cells during processes like cellular respiration.
- They're like tiny shuttles that move electrons around, helping to make energy for the cell.
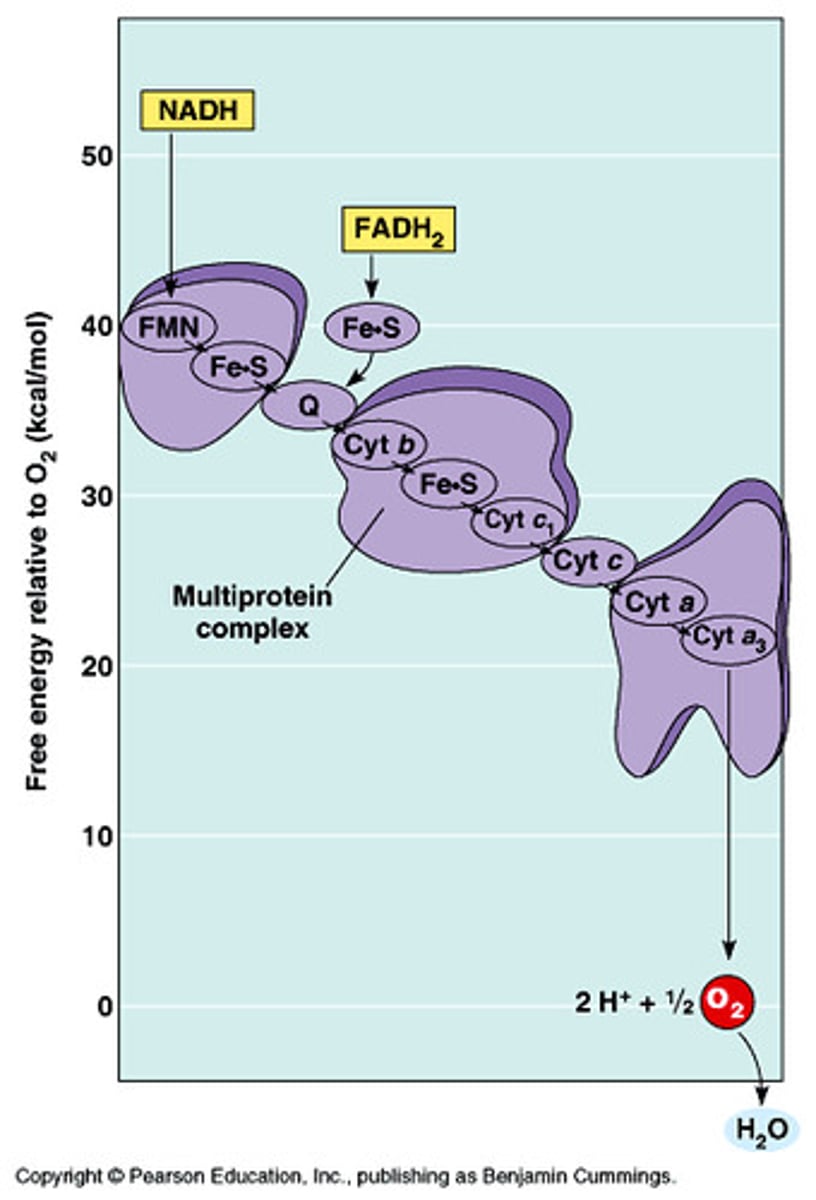
What happens with the energy released when electrons move through the electron transport chain?
Pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space.
What is ATP synthase?
- An enzyme that acts like a tiny machine in cells that makes ATP.
- It works like a turbine, using the flow of protons to produce ATP from ADP.
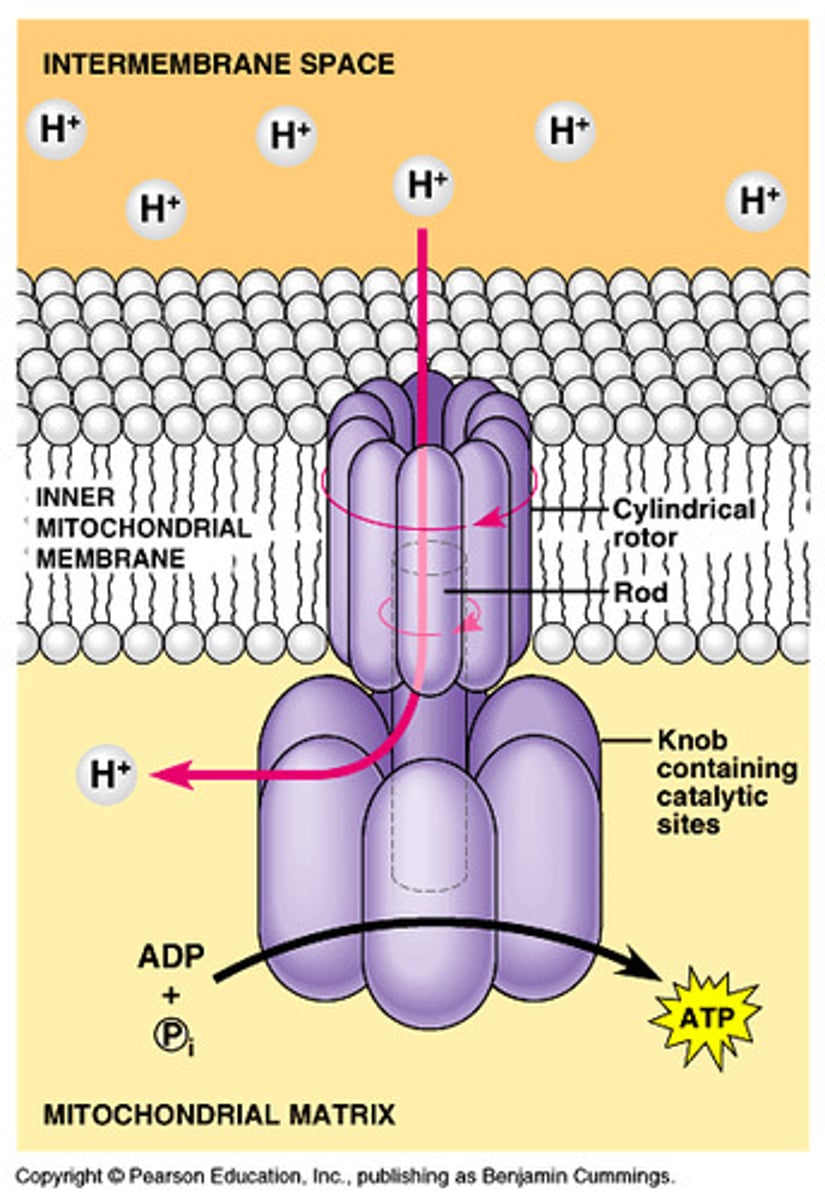
What is chemiosmosis?
- It is the movement of protons (H+ ions) across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a build-up of energy.
-When these protons flow back through a enzyme called ATP synthase, it spins like a turbine, making ATP,
(which is like storing that energy in a battery for the cell to use later)
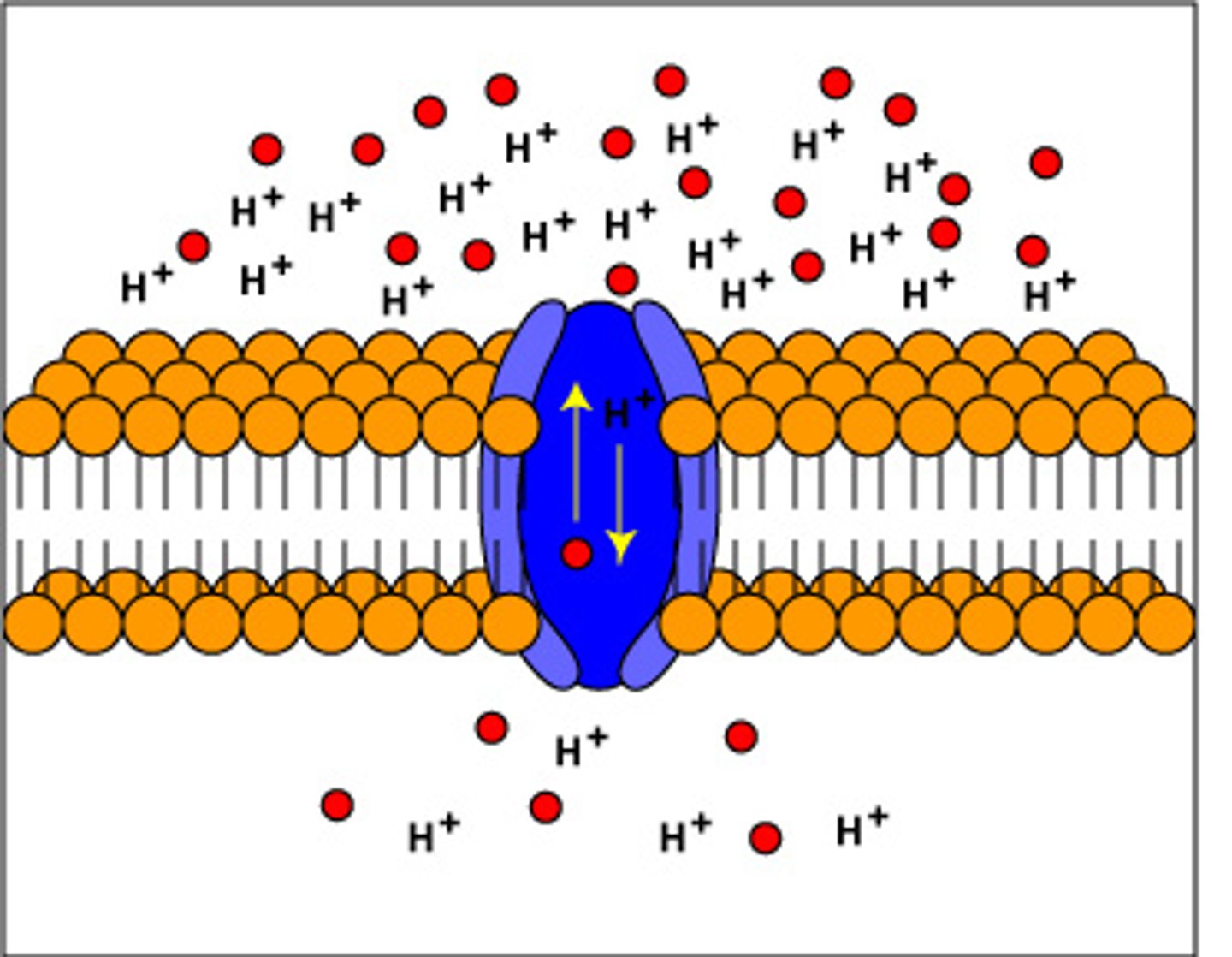
What is the proton motive force?
A cell's way of storing energy by building up protons on one side of a membrane.
-This stored energy can then be used for important cellular tasks, like making ATP.
What % of the energy in glucose molecules is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration?
About 34%
What are the 3 reasons why the number of ATP is not known exactly?
- Photophosphorylation and redox reactions aren't directly linked; the ratio of NADH to ATP isn't a whole number.
- ATP production changes based on whether electrons go to NAD+ or FAD in the mitochondria.
- The proton-motive force powers additional types of tasks too.
Why is O2 the final electron acceptor?
Most cellular respiration depends on the electronegativity of oxygen to pull electrons down the transport chain.
What are the two common types of fermentation?
-Alcohol fermentation
-Lactic acid fermentation
Instead of an electron transport chain to generate ATP, Fermentation uses what?
Substrate-level phosphorylation
What does fermentation consist of?
- Glycolysis +
- (reactions that regenerate NAD+)
which can be reused by glycolysis
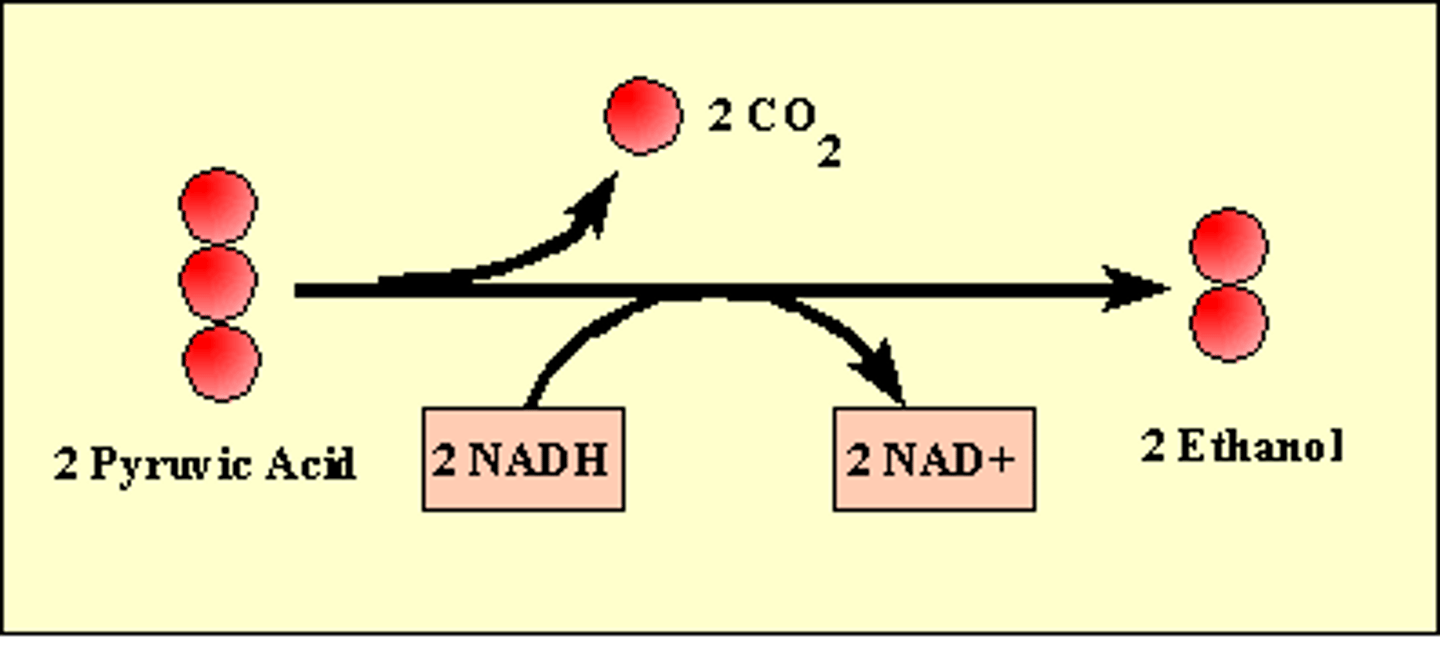
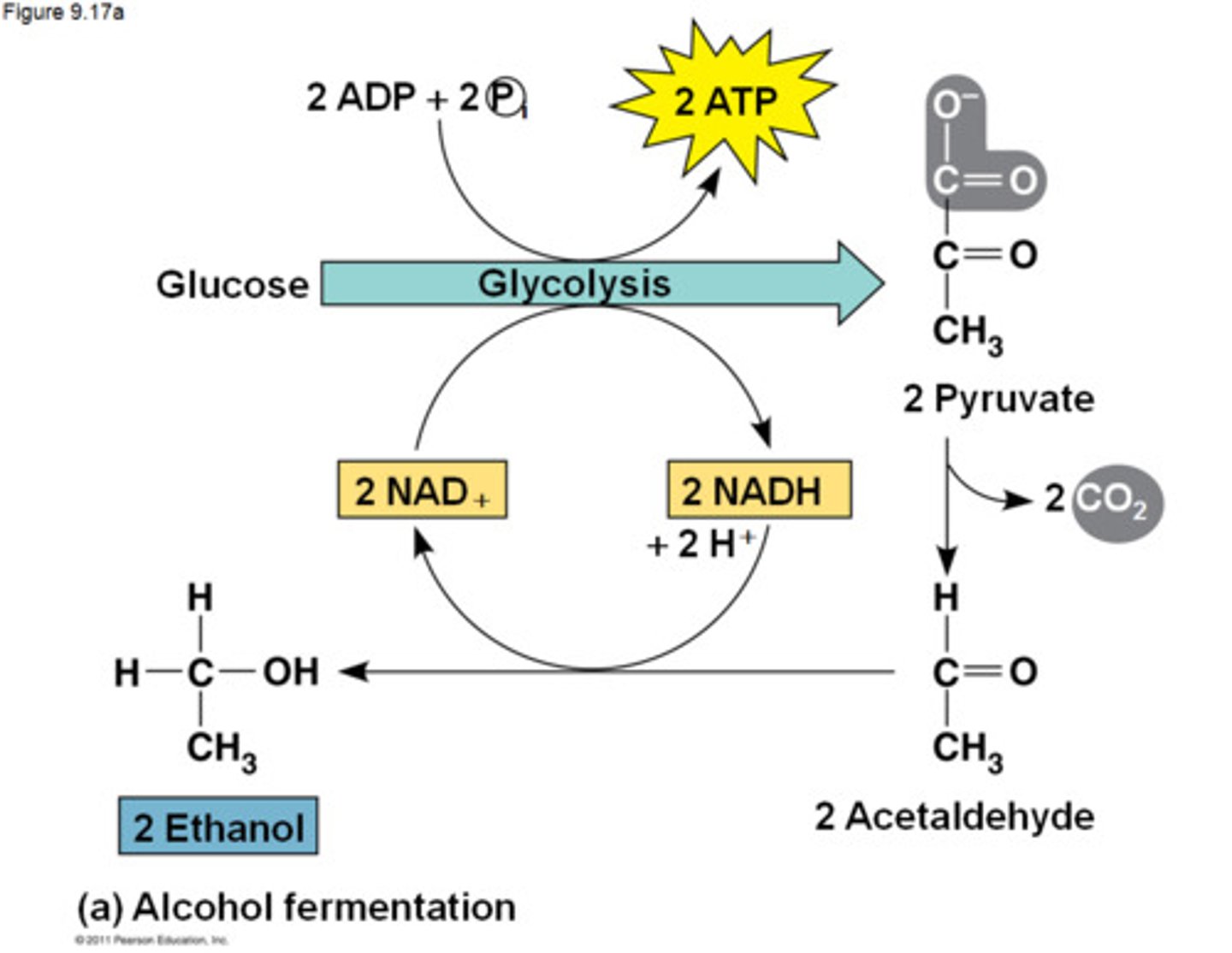
What happens in alcohol fermentation?
Pyruvate is converted to ethanol and CO2.
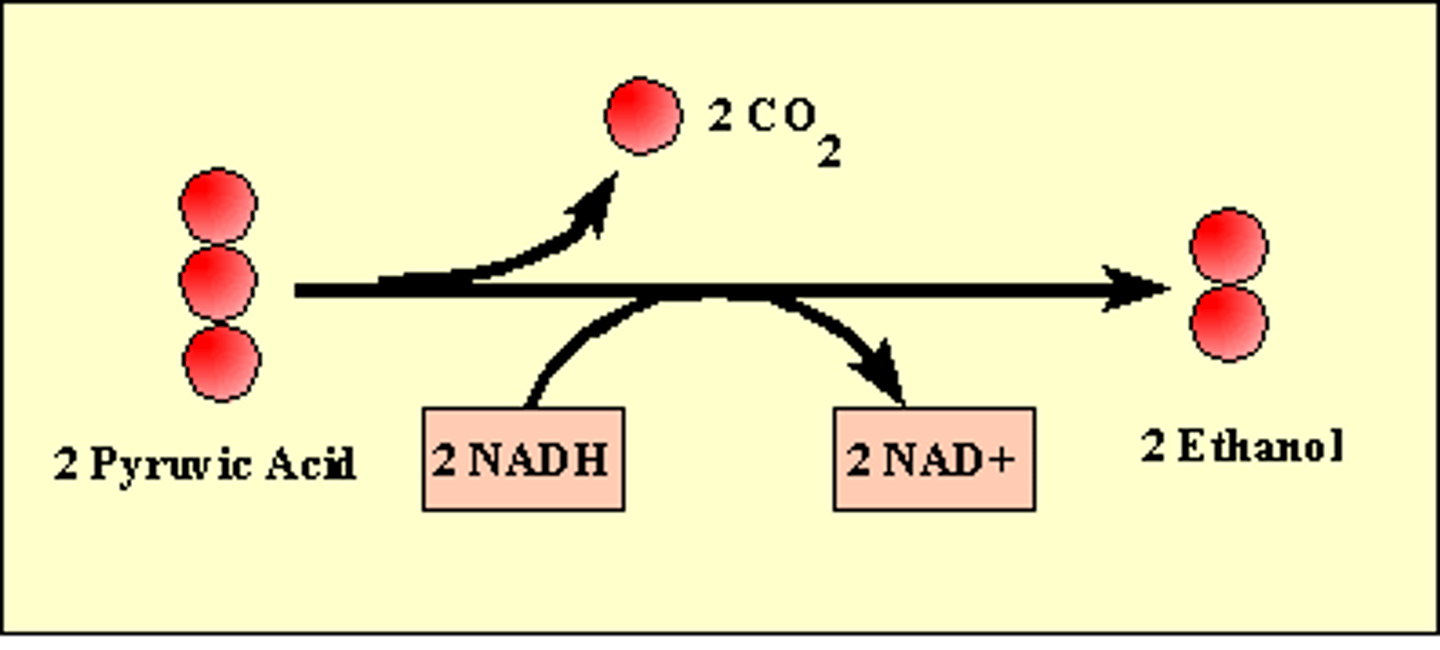
What are the two steps of alcohol fermentation?
1) CO2 is released from pyruvate
2) NAD+ and ethanol are produced
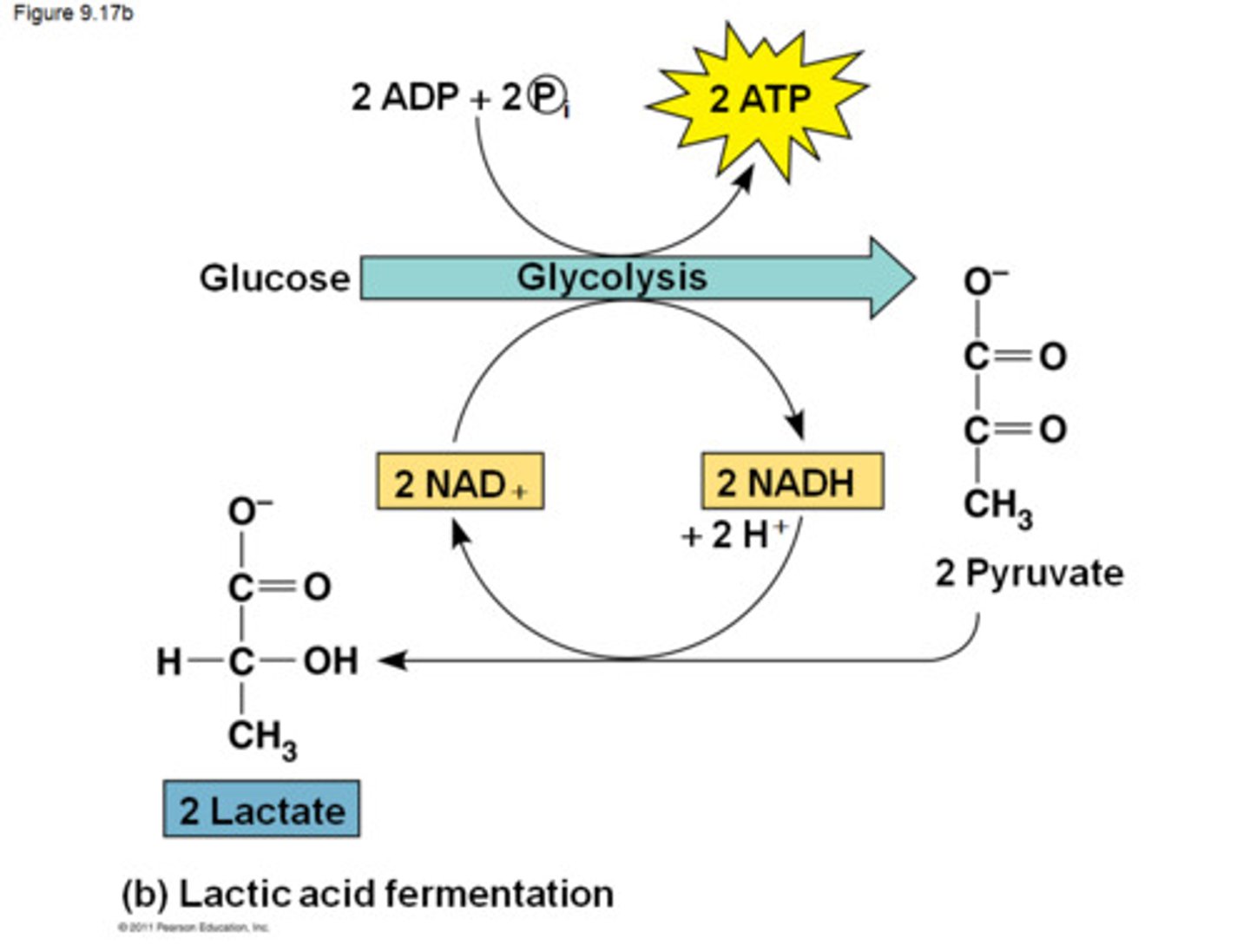
What happens in lactic acid fermentation?
Pyruvate is reduced by NADH, forming NAD+ and lactate as end products, with no release of CO2.
What do fermentation, anaerobic, and aerobic respiration have in common?
- Glycolysis is the initial step in all three processes, where glucose is oxidized, and a small amount of ATP is produced (net ATP = 2).
- NAD+ is used as the oxidizing agent during glycolysis in all three processes, accepting electrons to form NADH. This is crucial for transferring energy from glucose to ATP.
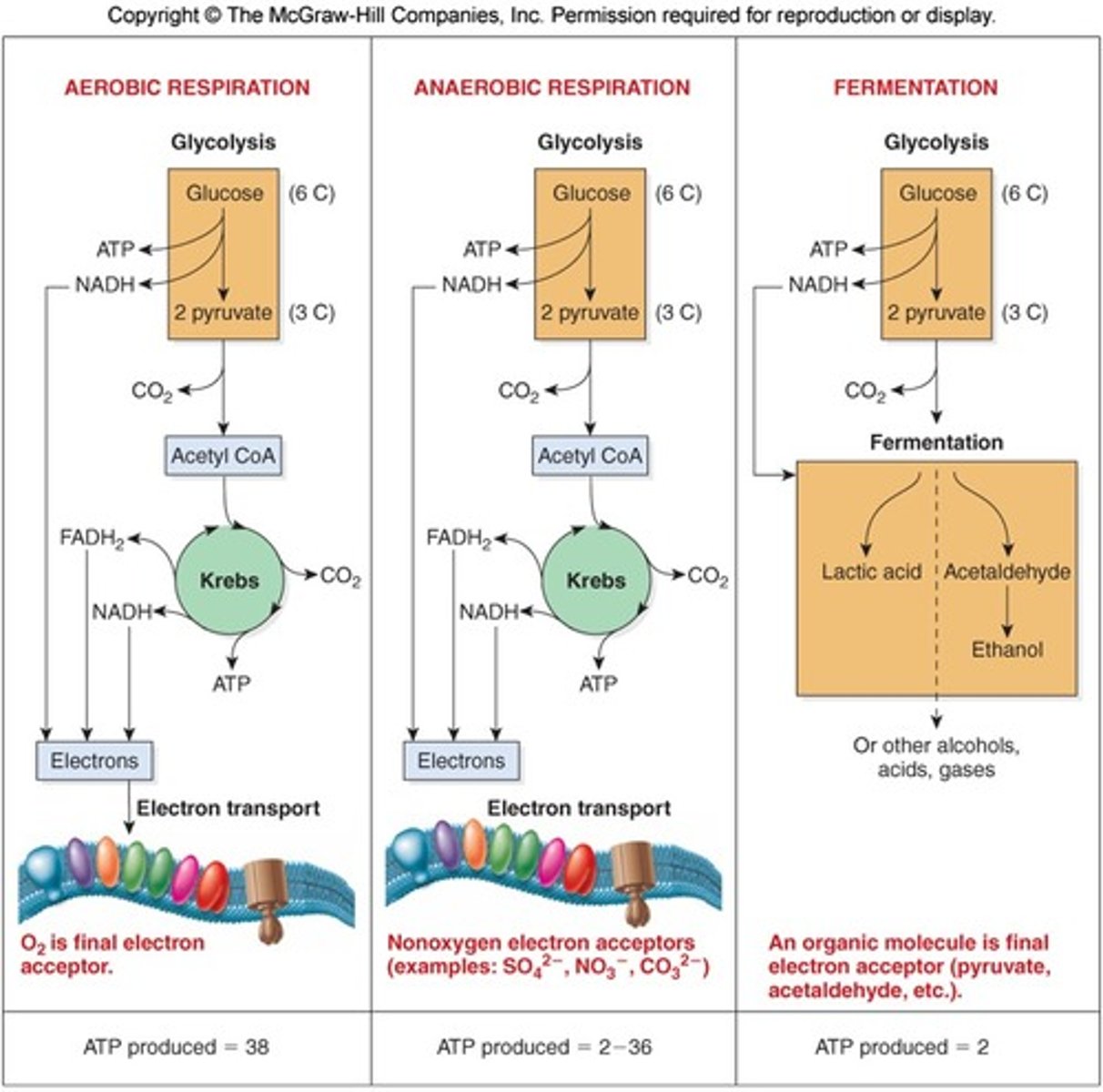
How do fermentation, anaerobic and aerobic respiration differ in oxidizing NADH to NAD+?
- In fermentation, an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) acts as a final electron acceptor and only generates 2 ATP per glucose molecule.
- In cellular respiration, electrons are transferred to the electron transport chain and generate 32 ATP per glucose molecule.
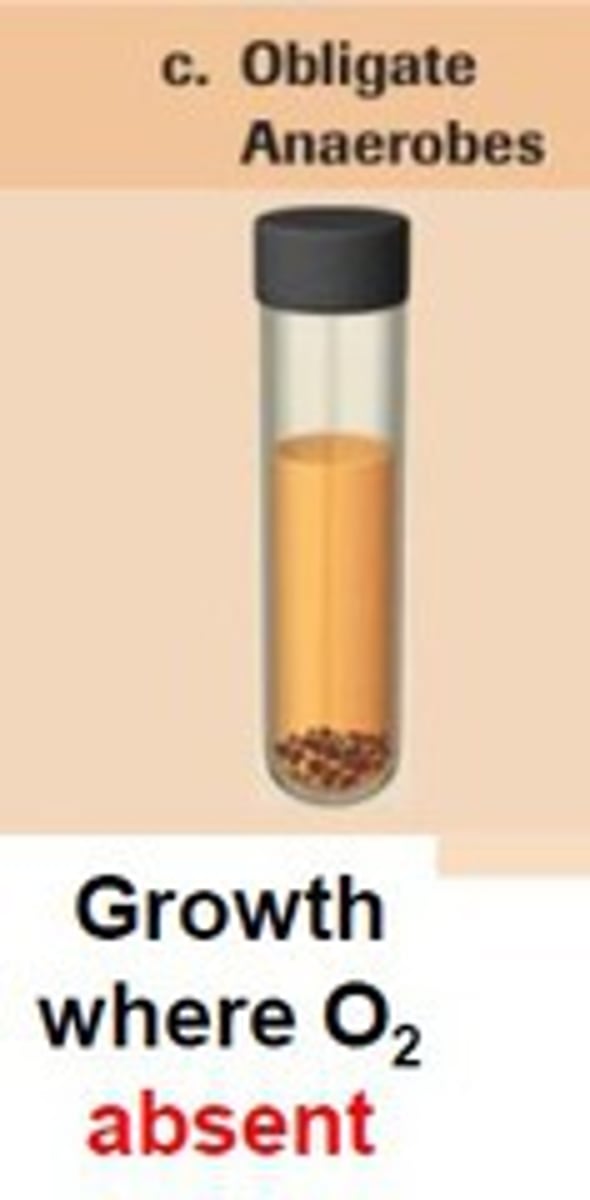
What do obligate anaerobes do?
- Carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration
- Cannot survive with oxygen.

What is a facultative anaerobe?
organism that can live with or without oxygen
(fac oxygen they don't need it)
Ex: bacteria, yeast, fungi

What is beta oxidation?
- Beta-oxidation is how cells break down fats to make energy.
- Makes acetyl CoA, NADH, and FADH2 as by-products.
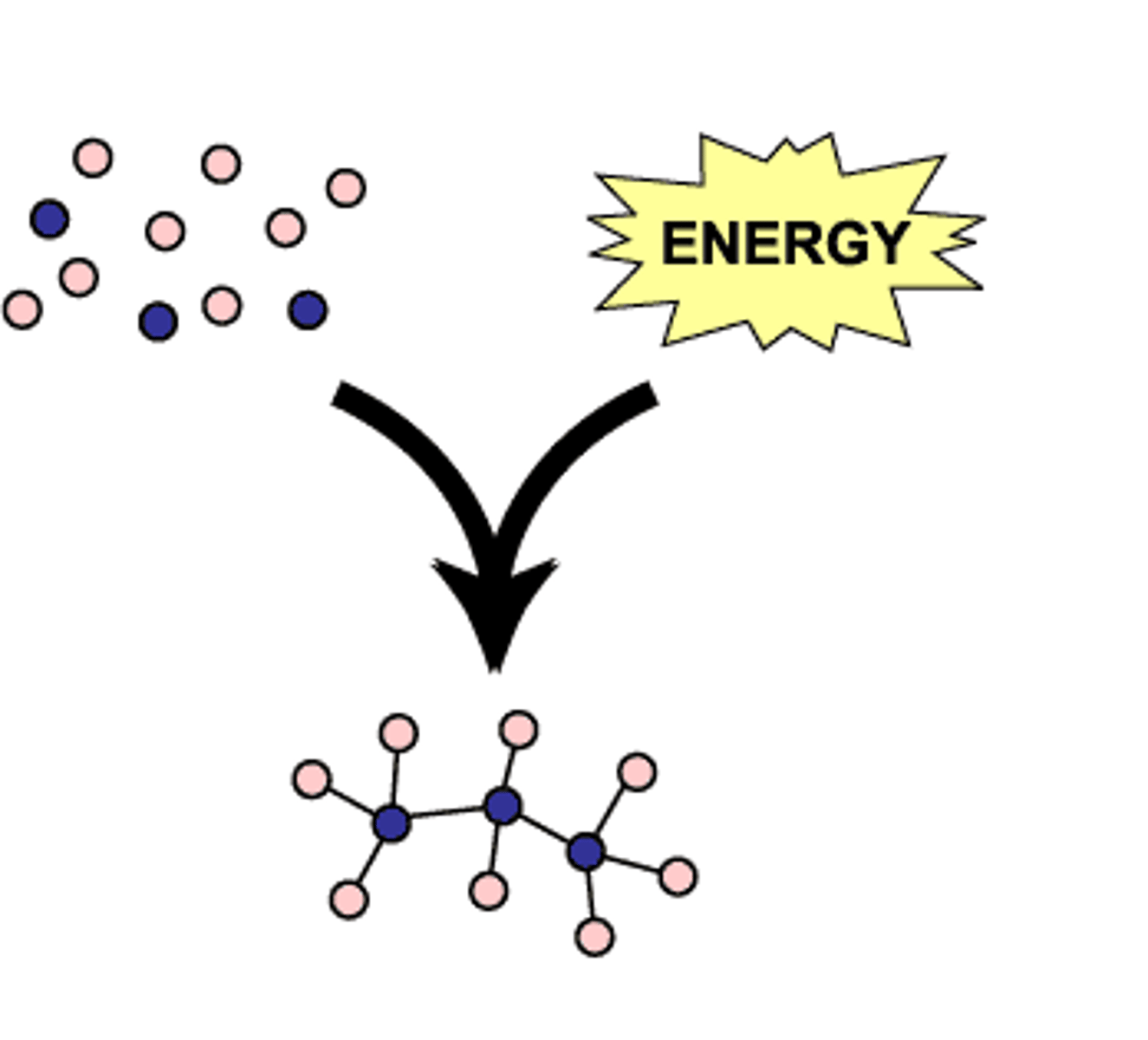
What is biosynthesis?
How living things make complex molecules they need for growth and functioning, using simpler building blocks.
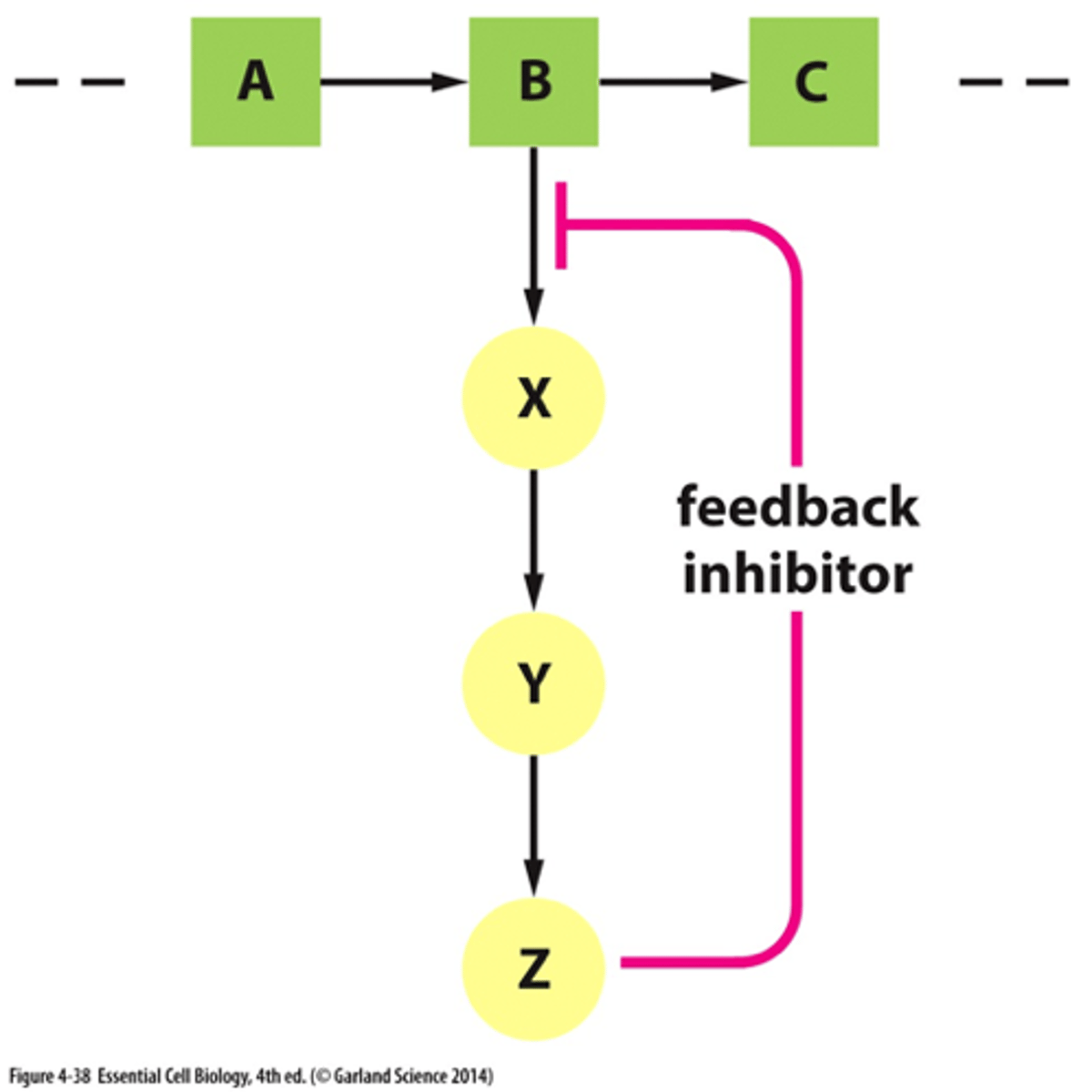
What regulates feedback inhibition?
Enzyme activity at strategic points within the catabolic pathway.
Ture or false, Fermentation and anaerobic respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen.
True
(Fermentation and anaerobic respiration let cells make ATP without needing oxygen.)
What are the outputs of one glucose molecule after pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle occurs?
6 molecules of Carbon dioxide (CO2)
8 molecules of NADH
2 molecules of FADH2
2 molecules of ATP
(Can Never F### Around)
What gets generated by one turn in the citric acid cycle?
- 3 molecules of NADH
- 1 molecule of FADH2
- 1 molecule of ATP
(Never Fart Again)
and release two molecules of carbon dioxide as byproducts
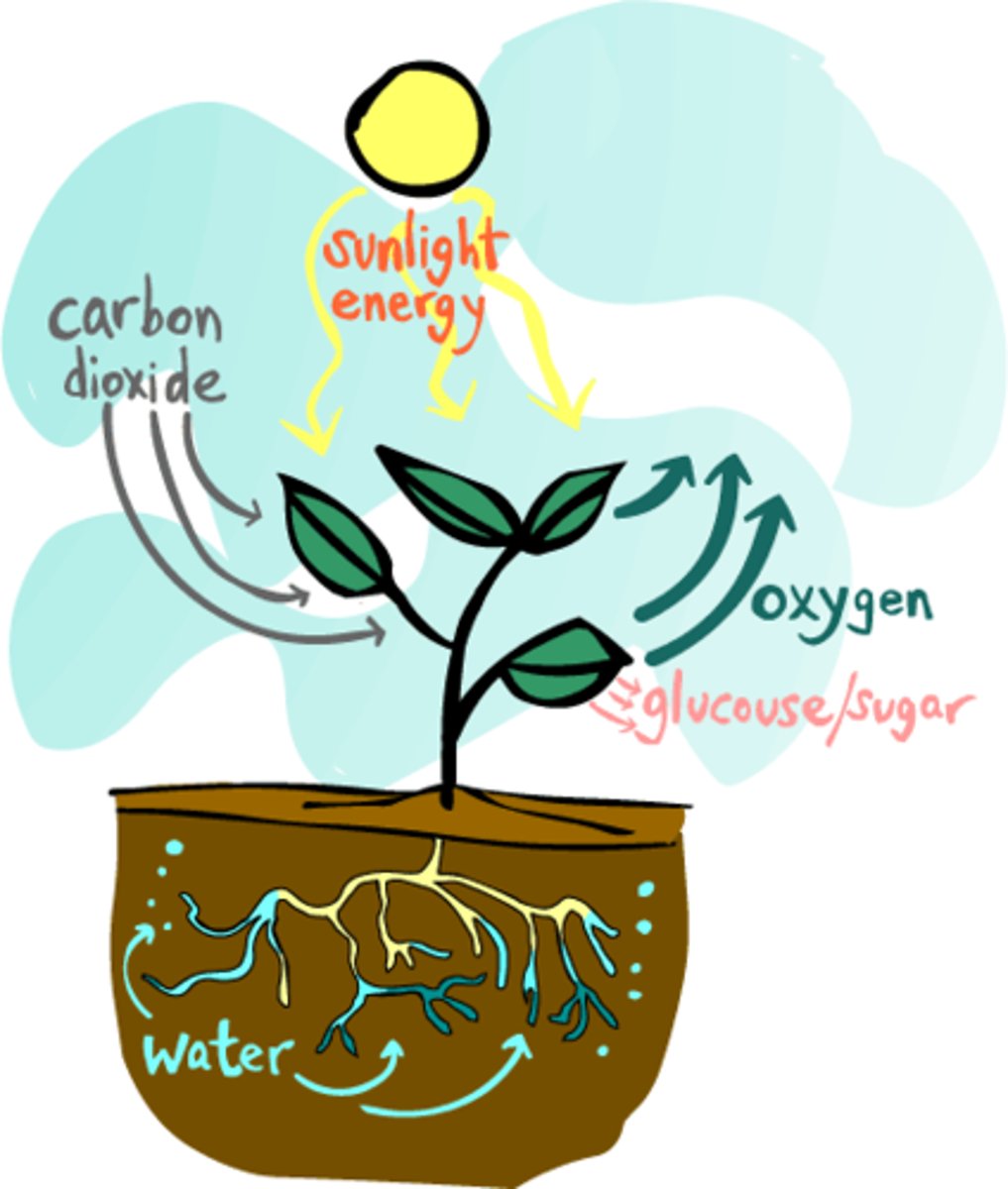
Define Photosynthesis.
- Is how plants make food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
- They turn these ingredients into sugar and release oxygen into the air with the chloroplast.
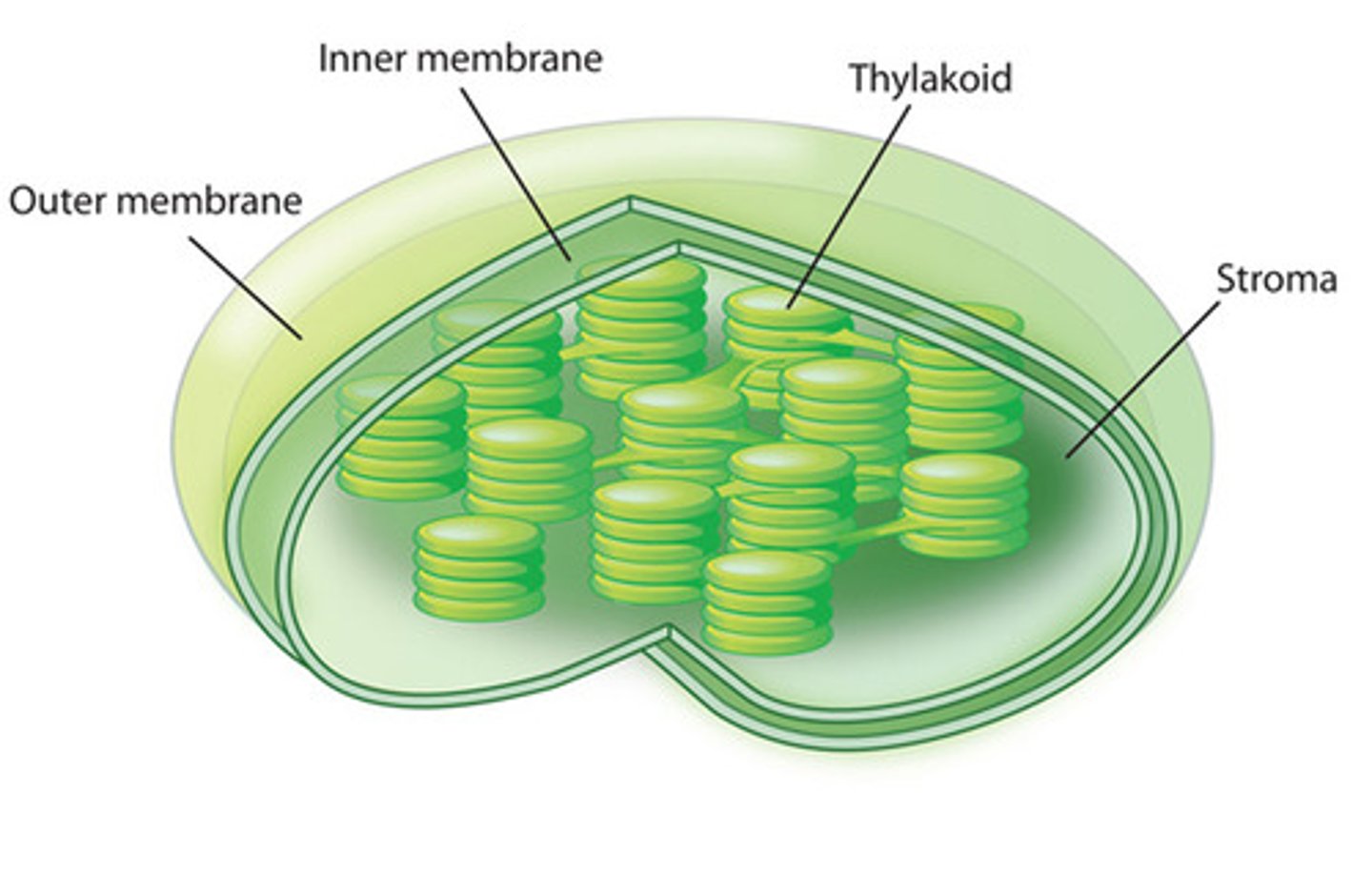
What are chloroplasts?
Membrane-bound organelles where photosynthesis takes place in plants
What are autotrophs?
(Photoautotrophs)
"Self-feeders" that sustain themselves without eating anything derived from other organisms.

What are heterotrophs?
"Other Eaters"- because they obtain organic material from other organisms

What is mesophyll?
- the interior tissue of the leaf
- where chloroplasts are found
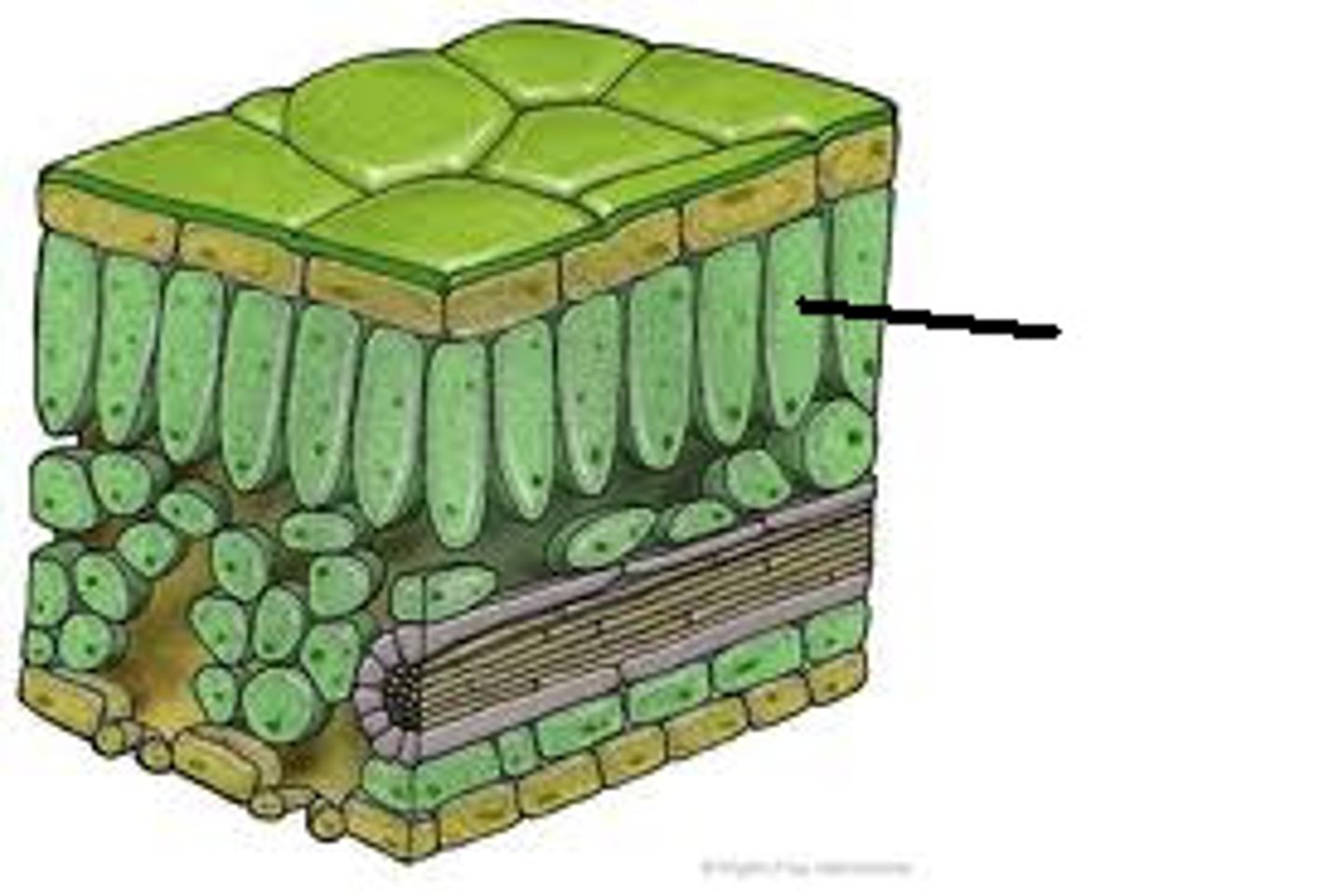
What is the stomata?
- Pores where a gas exchange occurs.
- such as CO2 enters and O2 exits the leaf
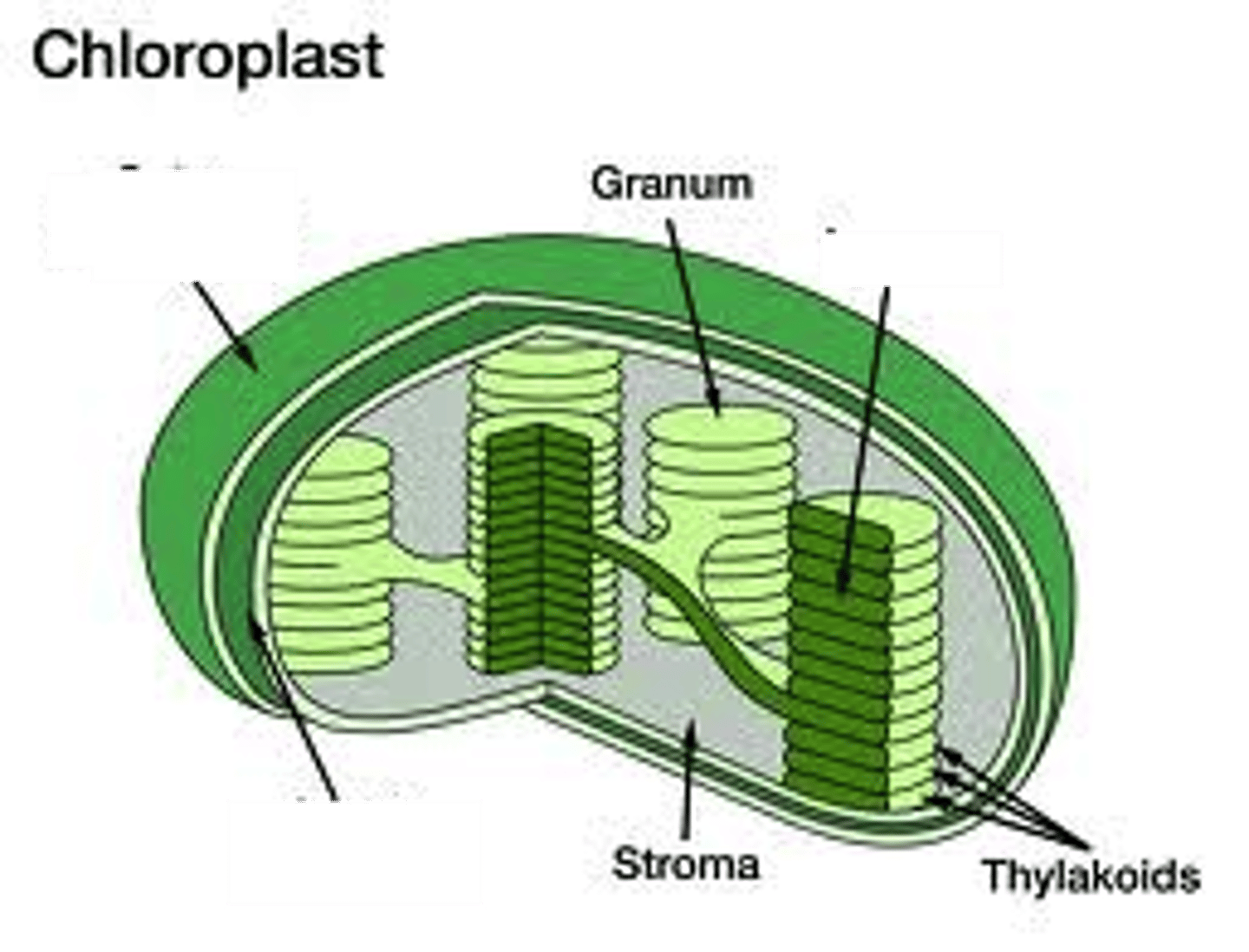
What is the fluid-filled space inside the chloroplast called?
- Stroma
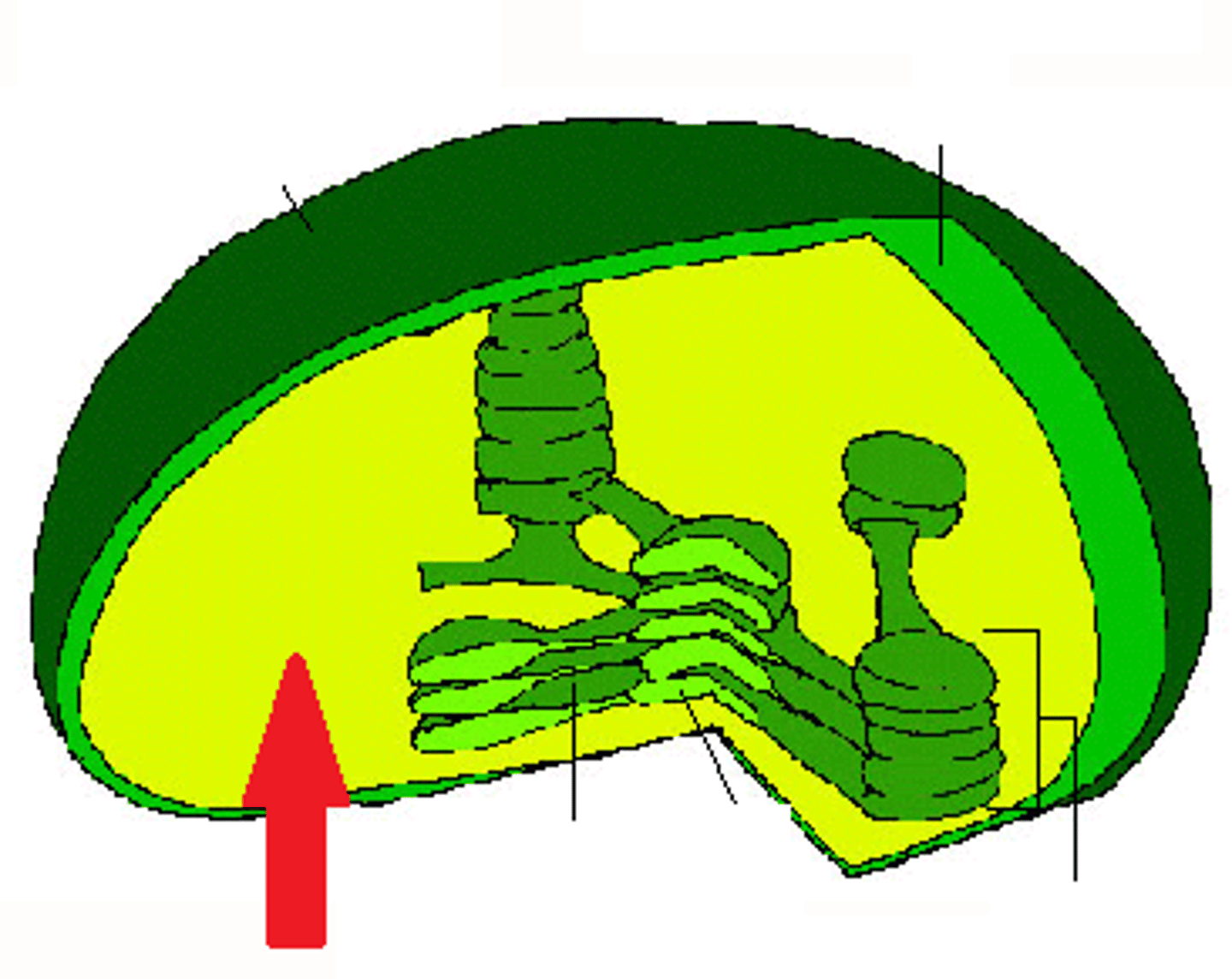
What are thylakoids?
Are connected disk-like structures within the chloroplast that compose a third membrane system.
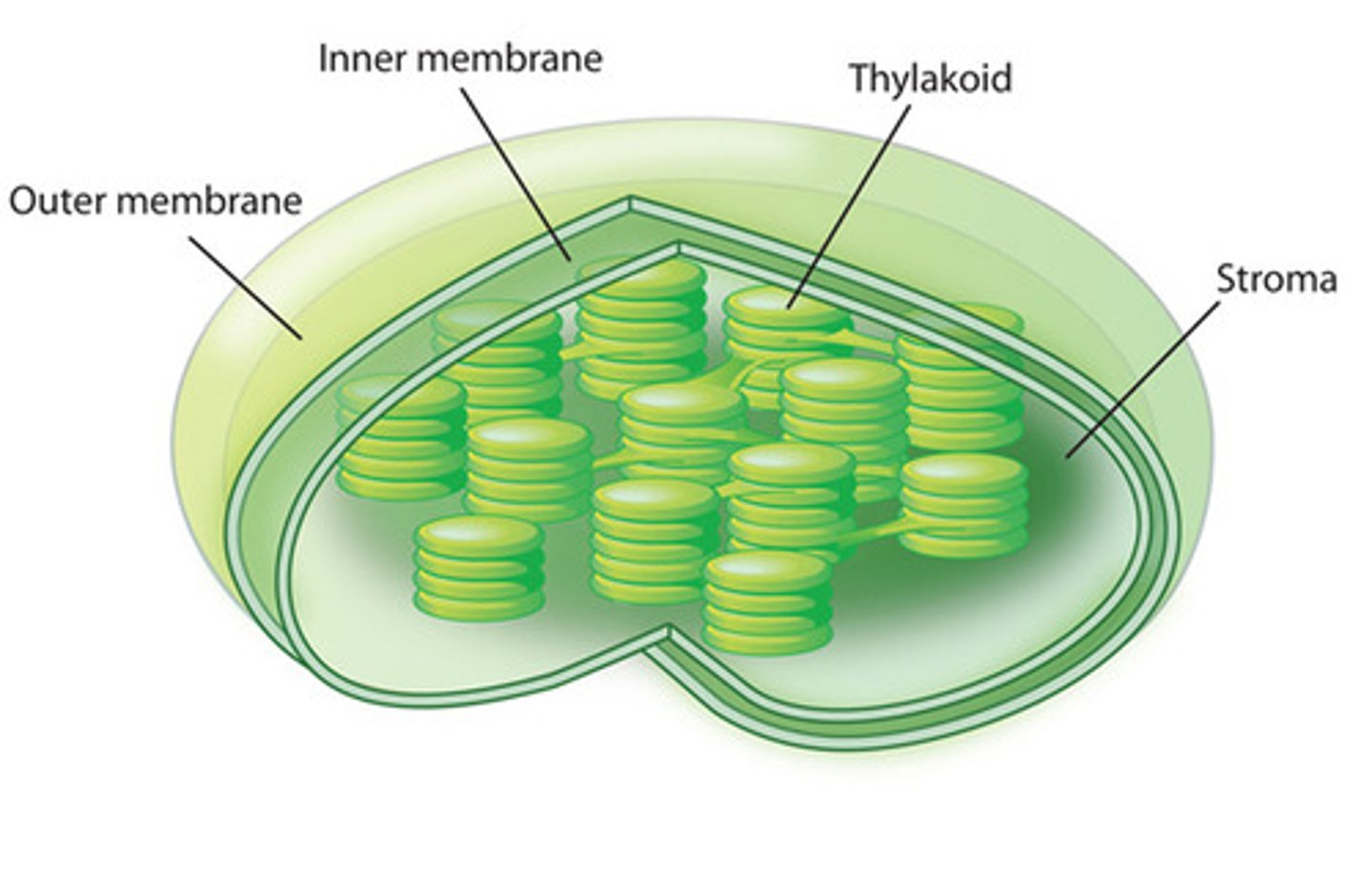
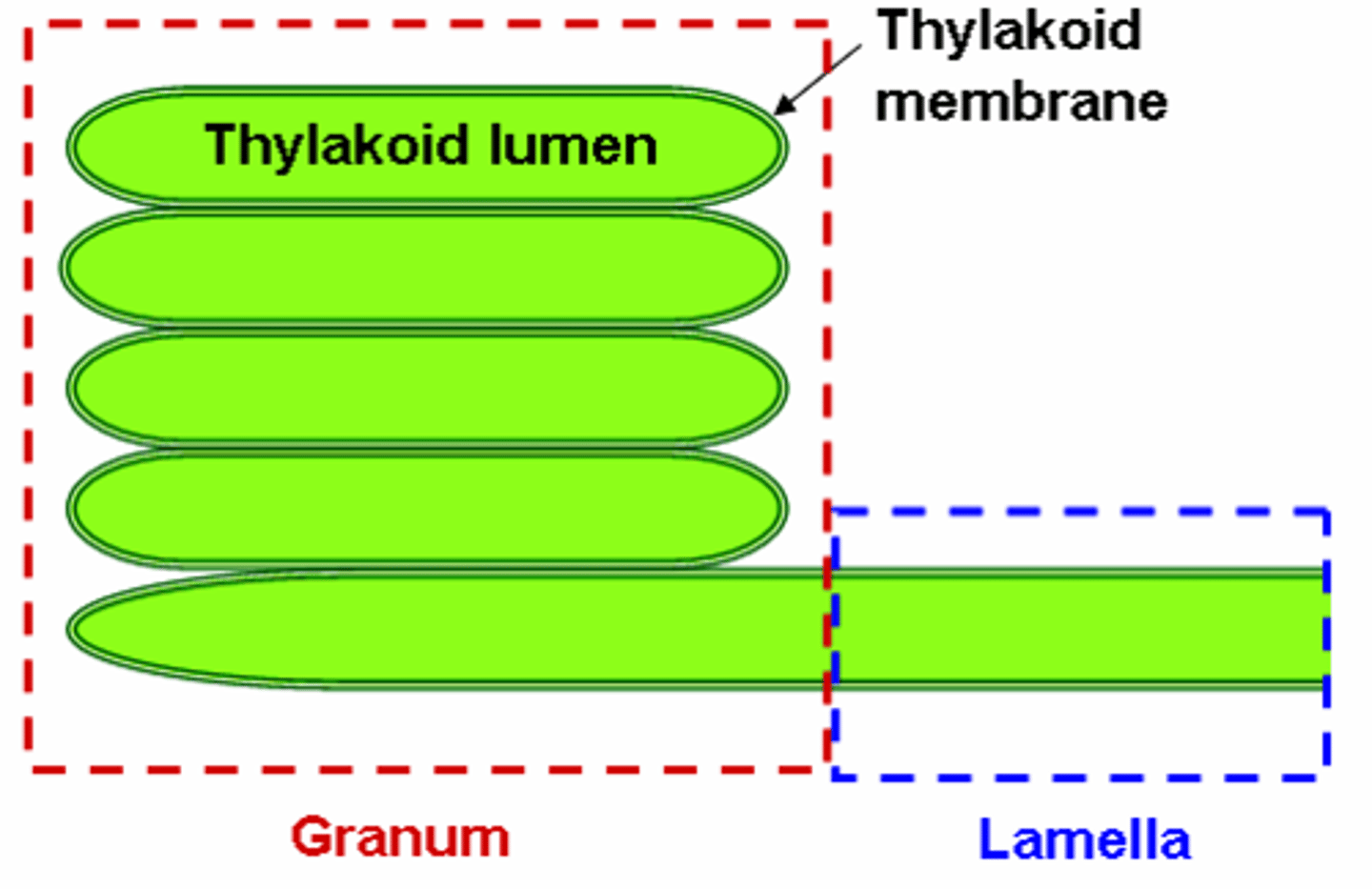
What is granum?
A stack of thylakoids.
What is thylakoid lumen?
Space inside the thylakoid
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy -----> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What kind of process is photosynthesis?
Redox Process
What are the two types of reactions in photosynthesis?
-light-dependent reaction
-light-independent reaction
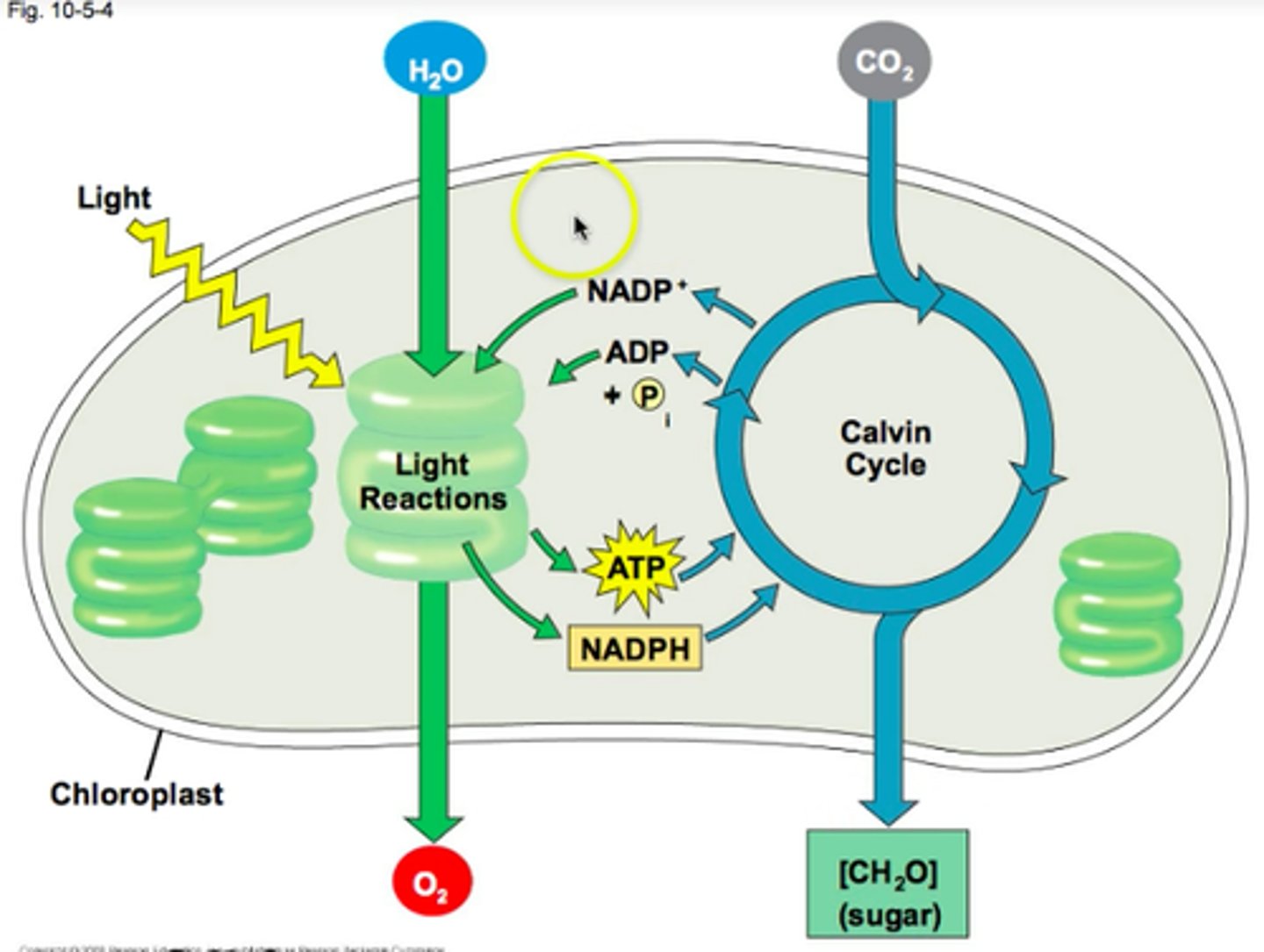
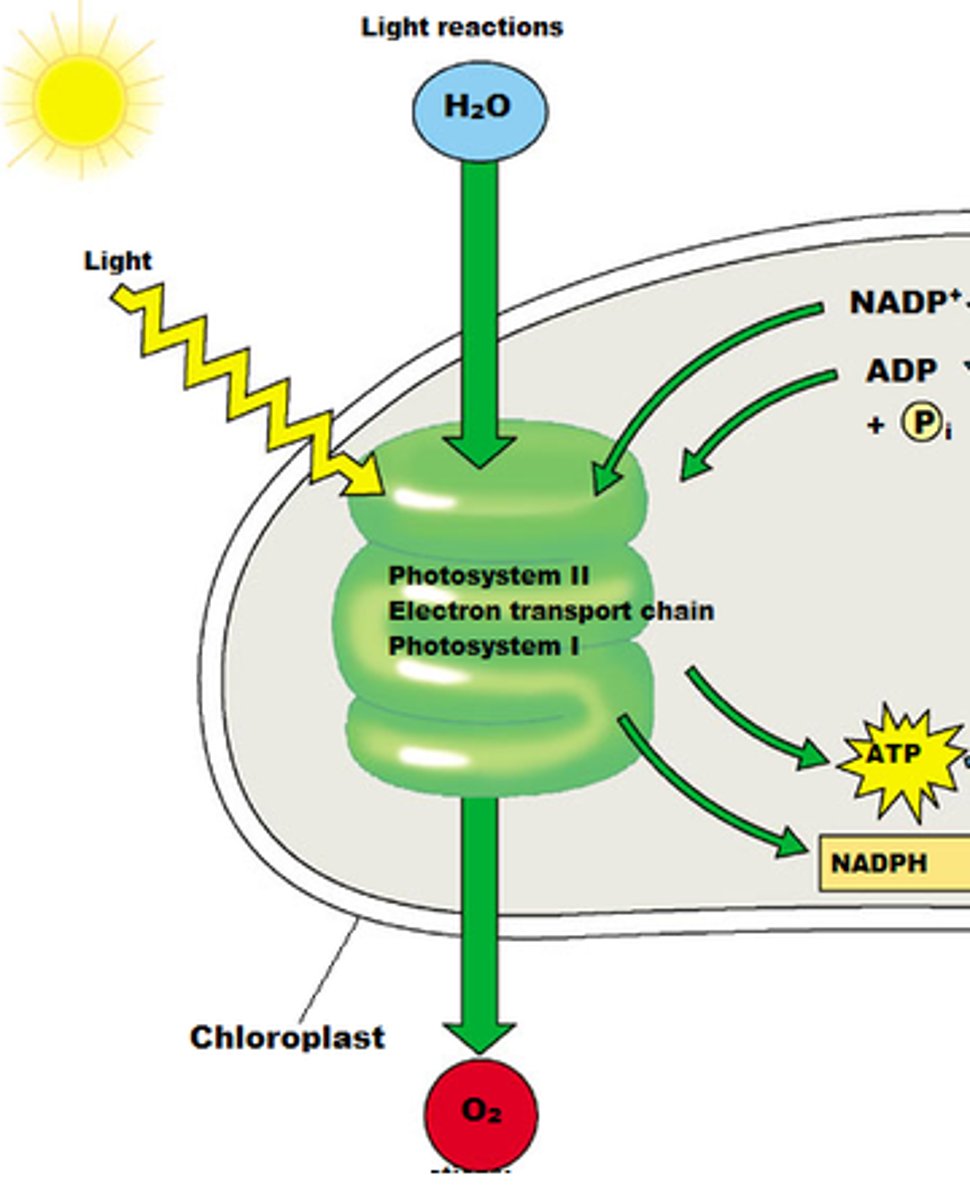
What happens in a Light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis?
- Sunlight is used to split water molecules, releasing oxygen and creating energy molecules ATP and NADPH.
- which are used in the next stage of photosynthesis
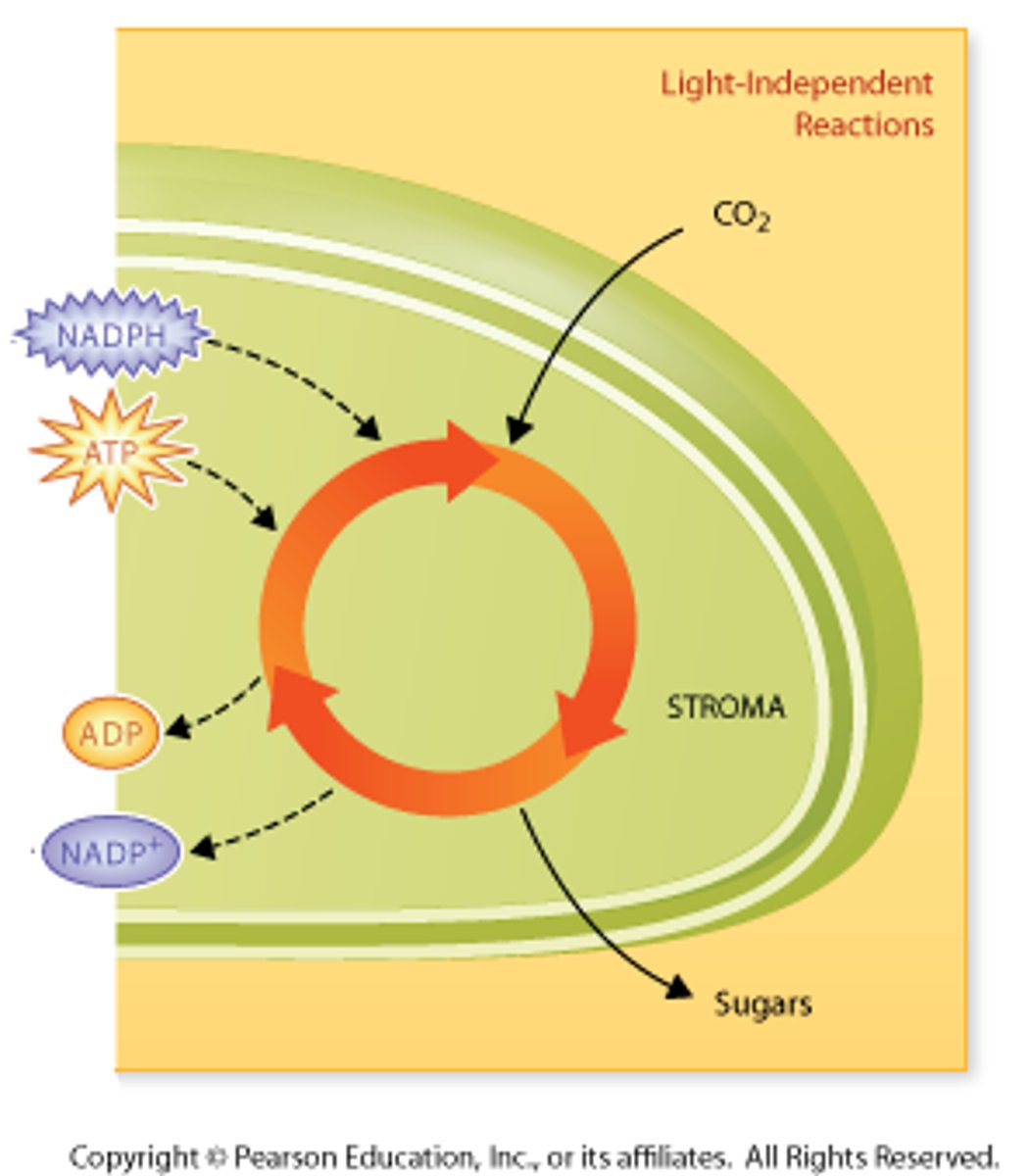
What happens in a light-independent reaction
(Calvin cycle) and where does it take place?
-Carbon dioxide is turned into glucose using energy from ATP and NADPH, which happens in the stroma of the chloroplast.
-It doesn't need direct light but uses products from light-dependent reactions.
Where do light reactions take place?
Thylakoids
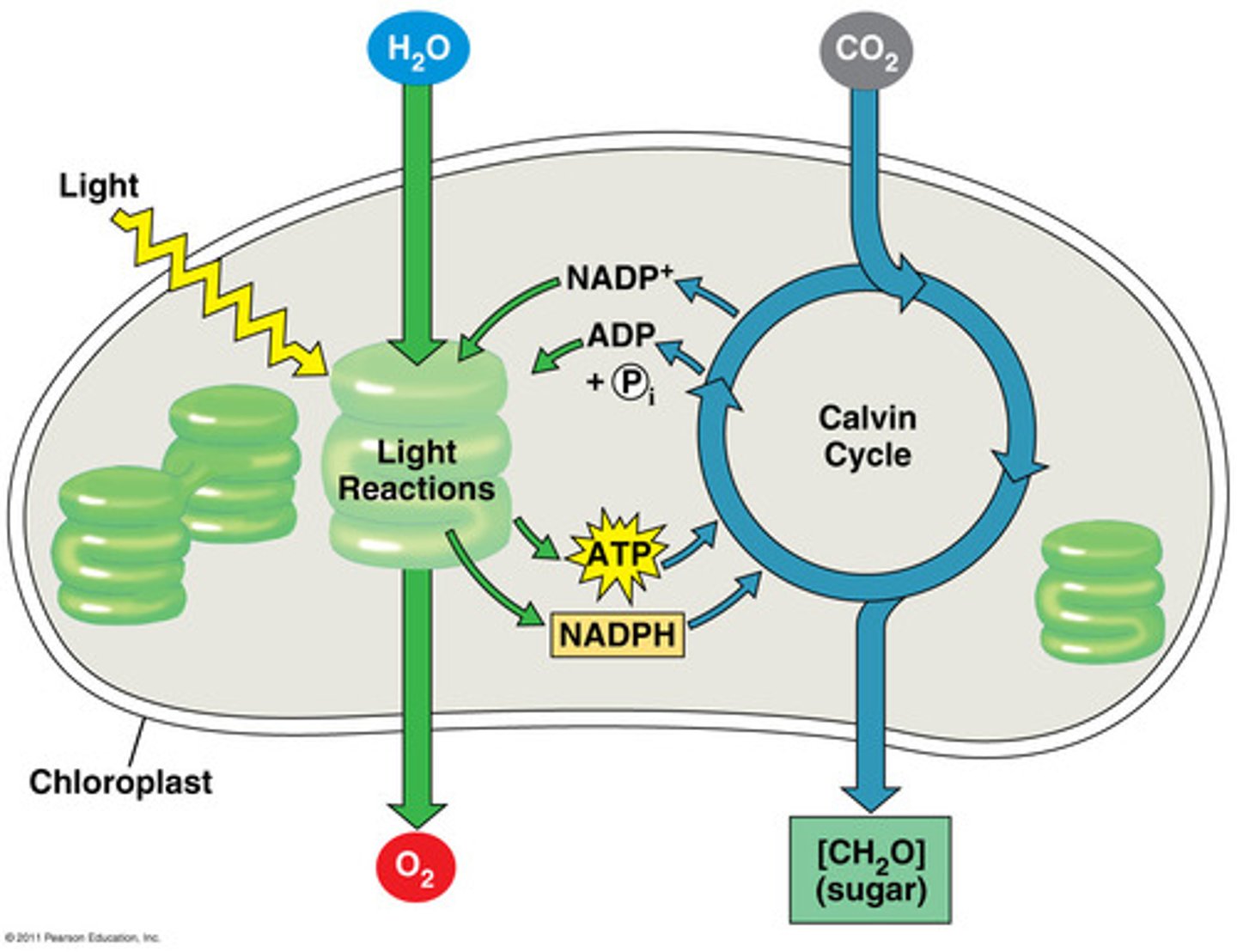
Where does the Calvin Cycle take place?
Stroma of the chloroplast
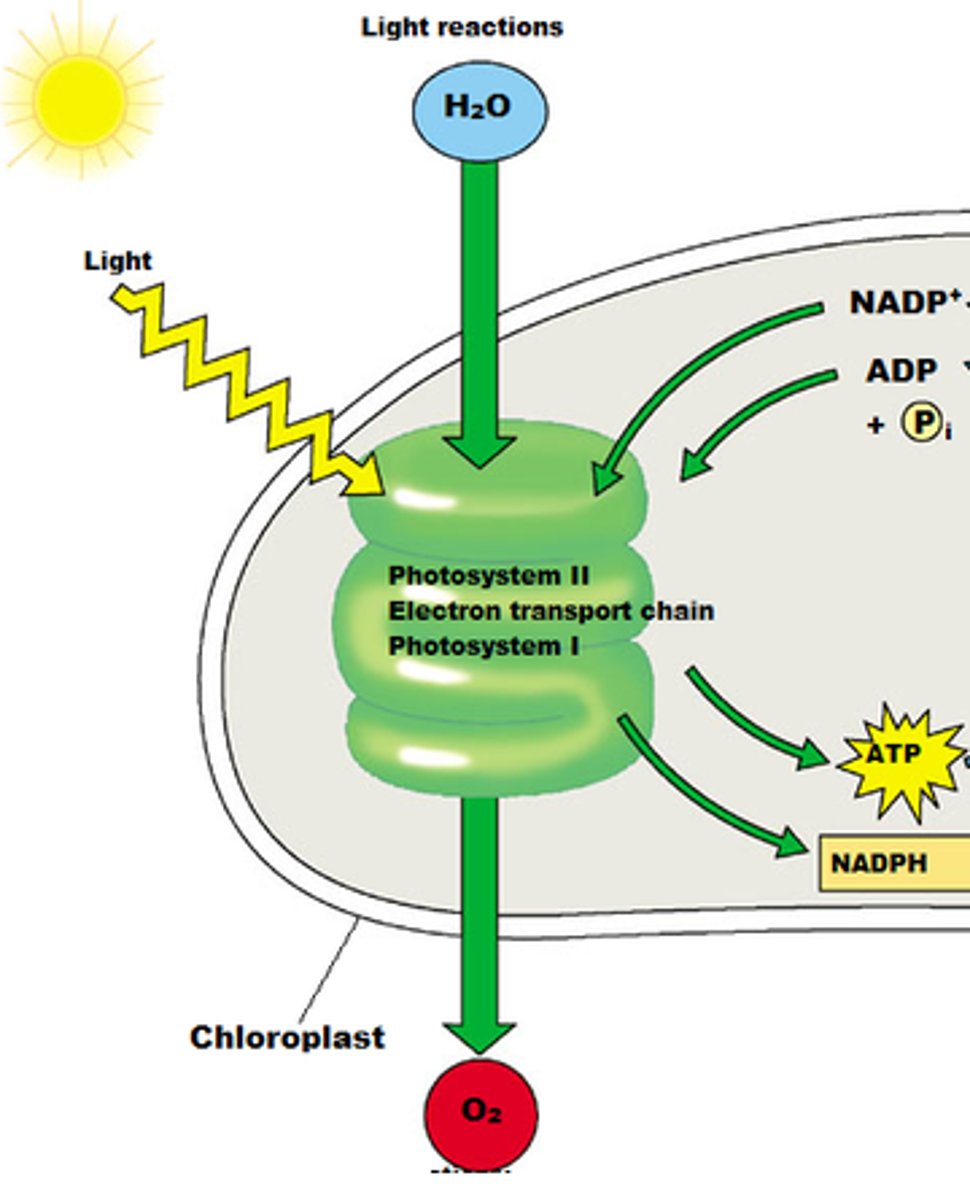
What are the steps to a light dependent reaction?
1) H2O is split
2) O2 is released
3) NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
4) ATP is generated from ADP by photophosphorylation
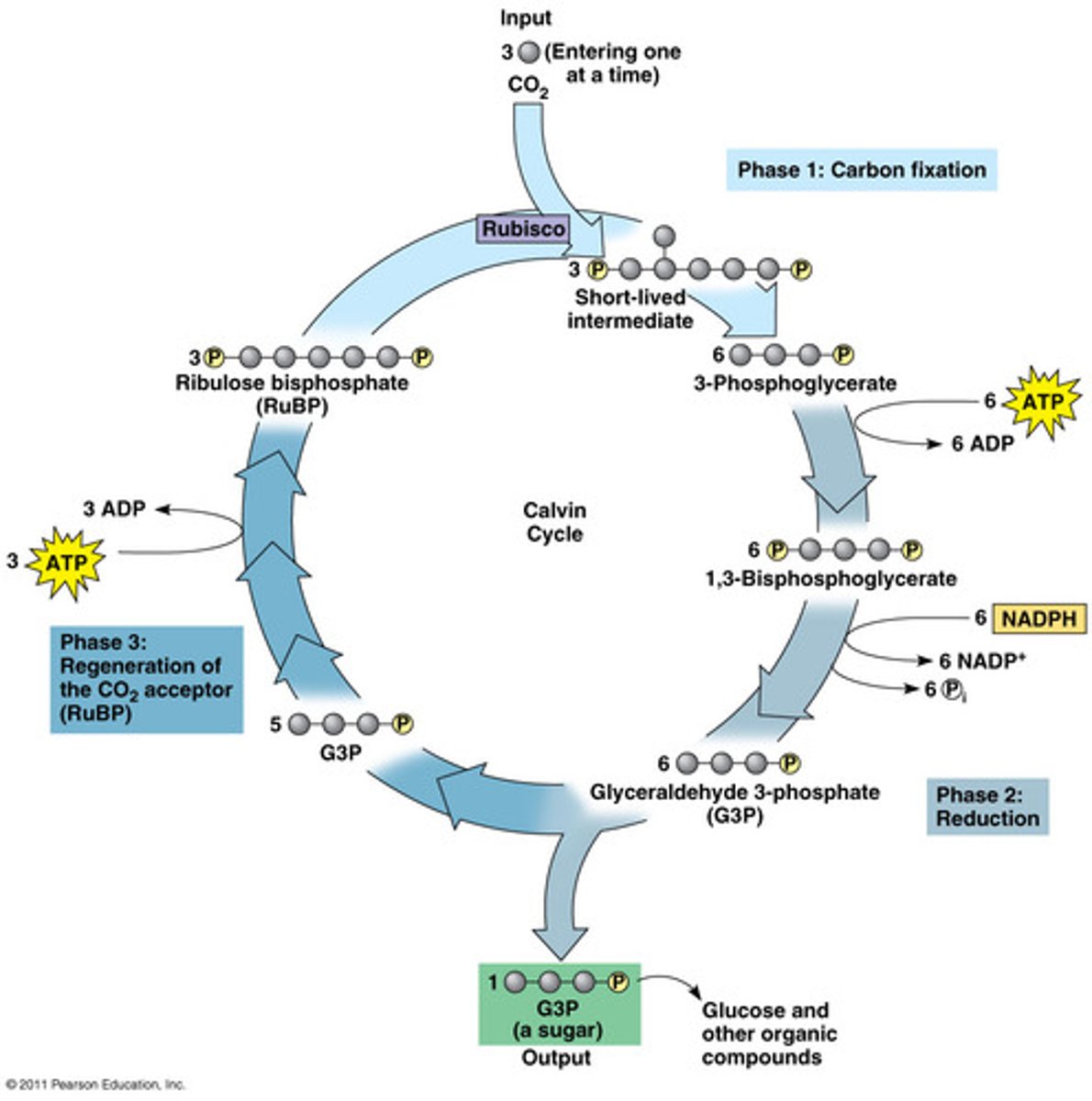
What are the steps to the Calvin Cycle?
1) CO2 enters
2) ATP is used
3) The electron carry NADPH is oxidized to NADP+
4) The organic molecule sugar is generated (CH2O)
What gets converted in light reactions?
Solar energy ----> chemical energy of ATP and NADPH
What are photosynthetic pigments?
Molecules in plant cells that soak up sunlight, turning it into energy for photosynthesis.
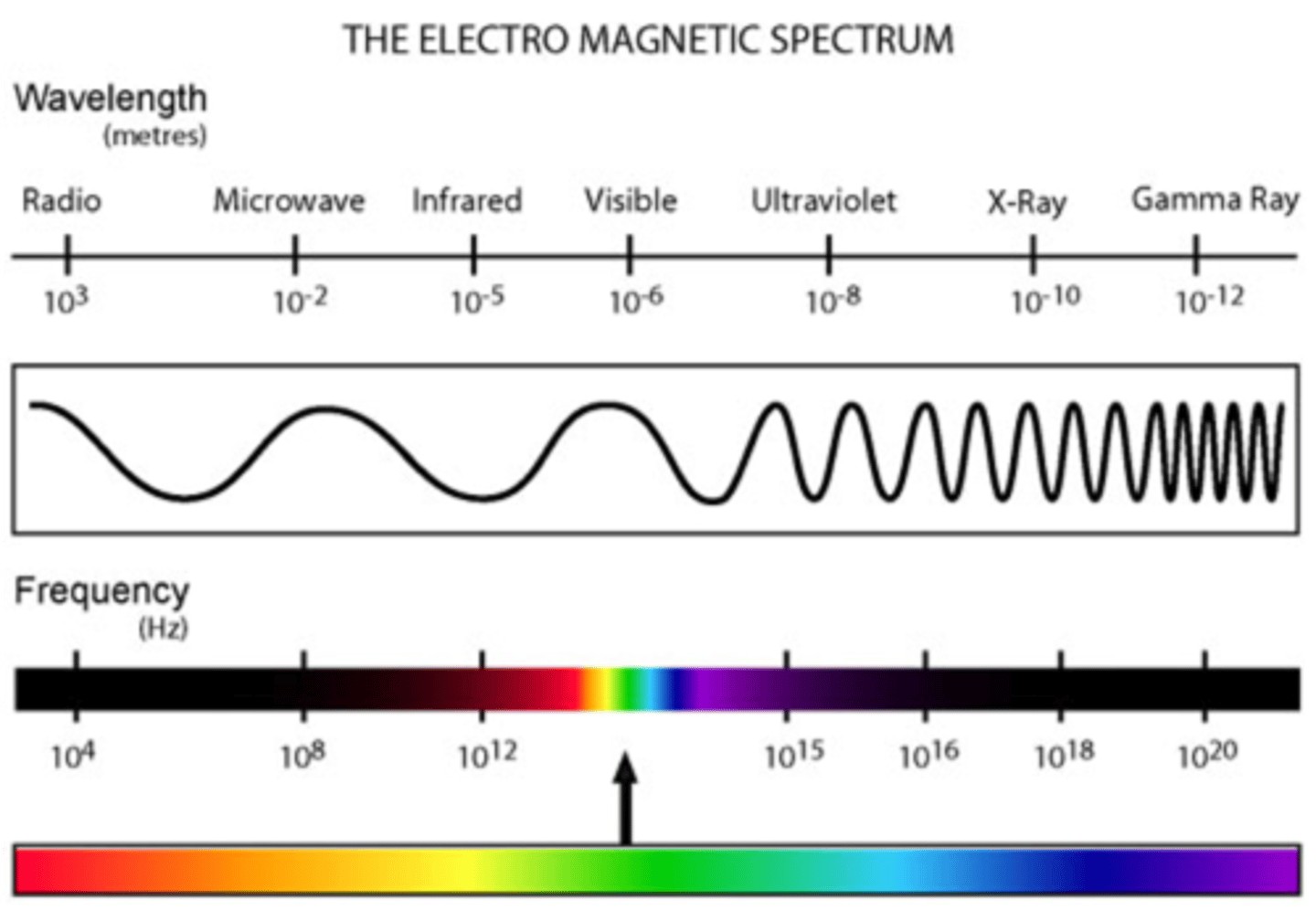
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
Is the entire range of all electromagnetic energy or radiation
What happens to wavelengths that are not absorbed?
Reflected or transmitted.
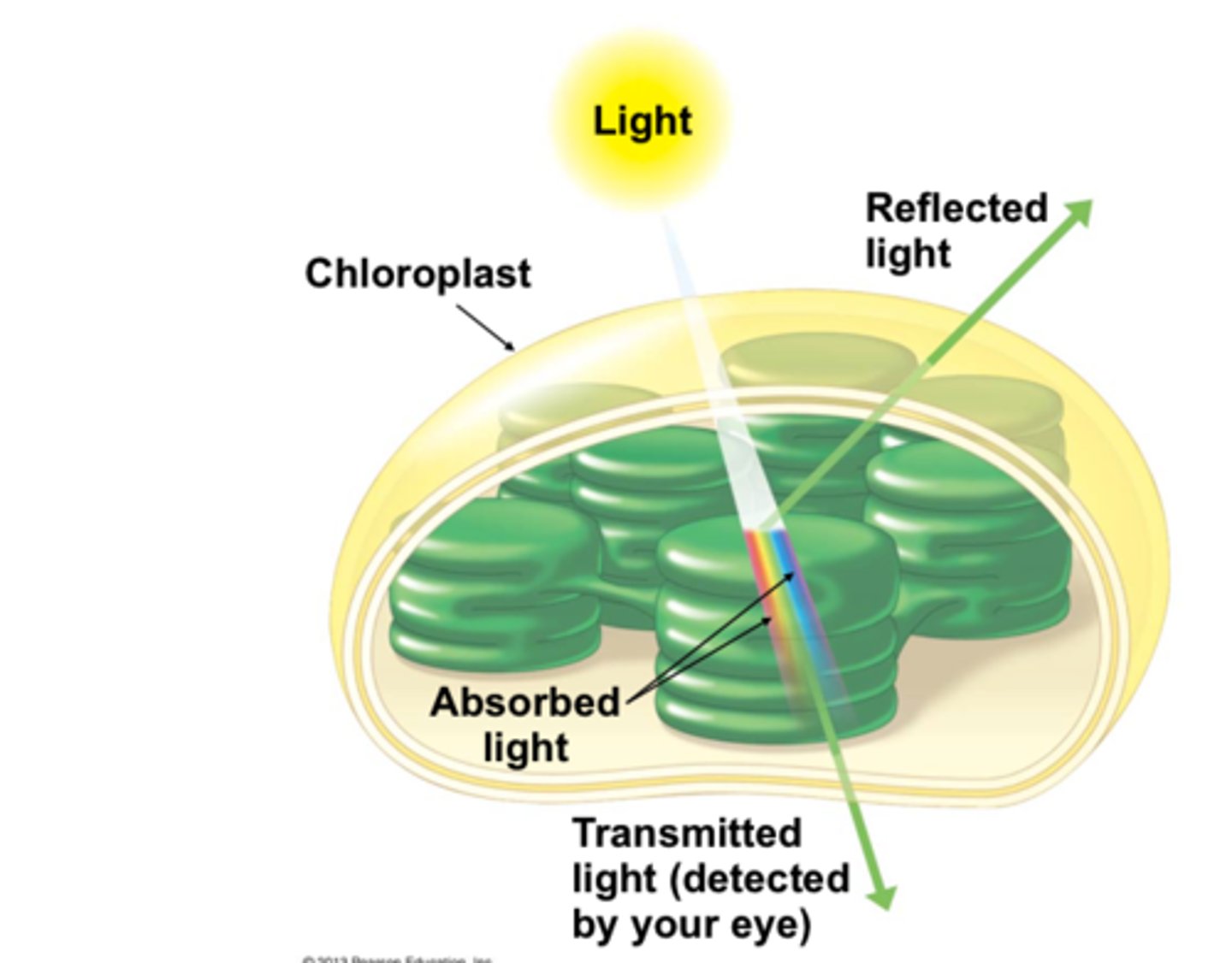
Why do leaves appear green?
Chlorophyll reflects green light rather than absorbing it.
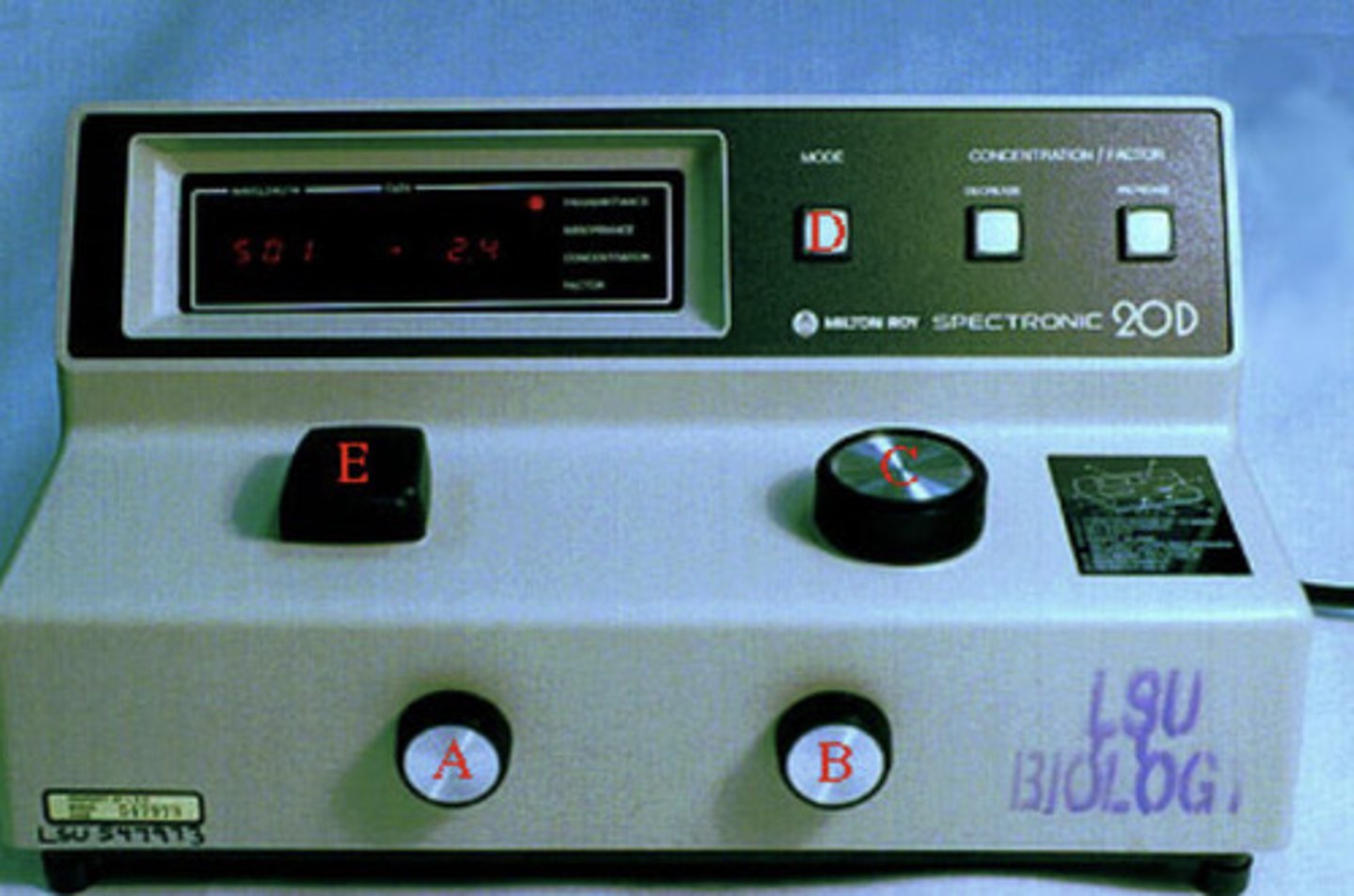
What is a spectrophotometer used for?
-Measures a pigment's ability to absorb various wavelengths
- Sends light through pigments and measures the fraction of light transmitted at each wavelength.

What is a absorption spectrum?
Is a graph that plots a pigment's light absorption vs. wavelength.
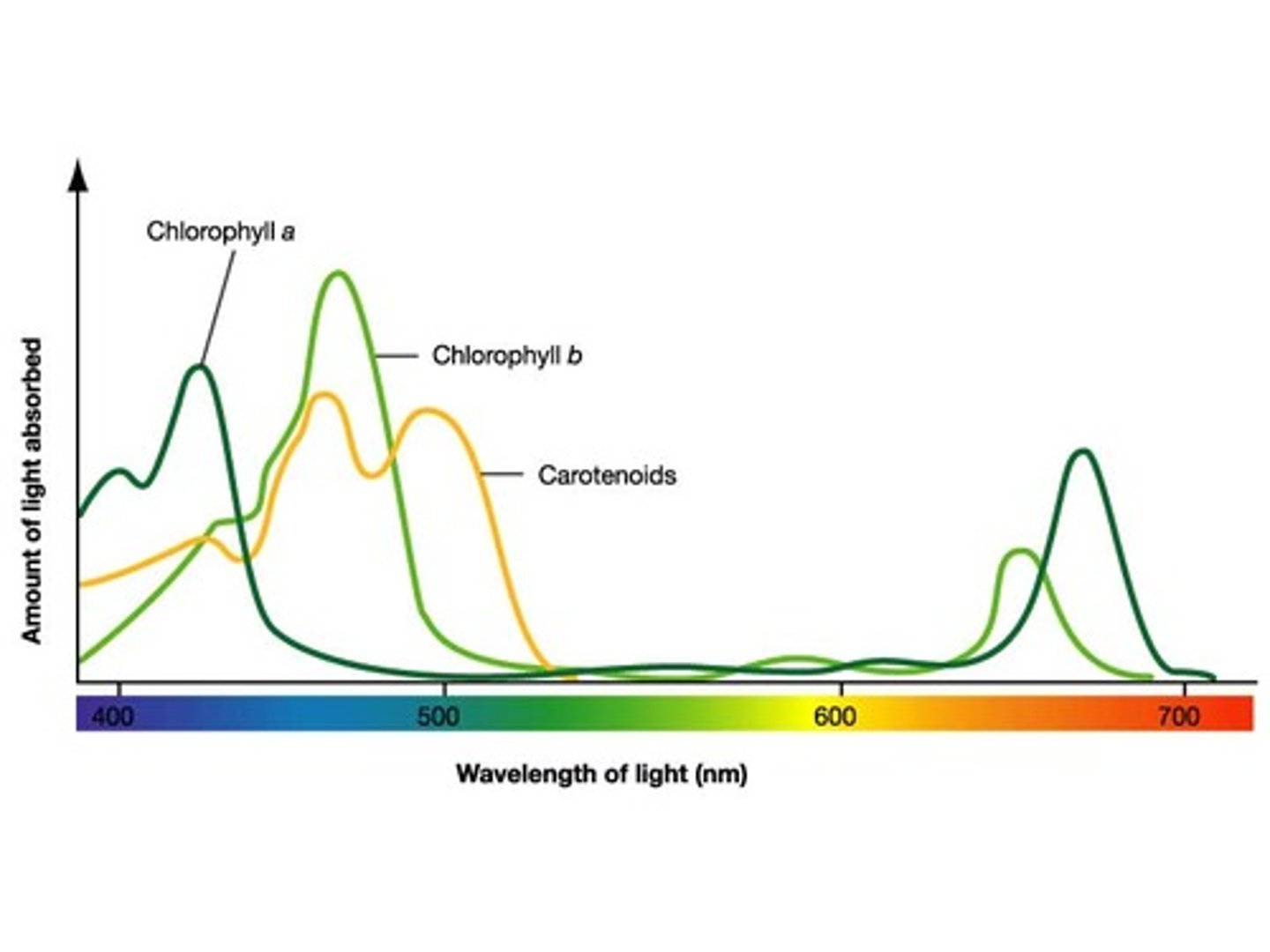
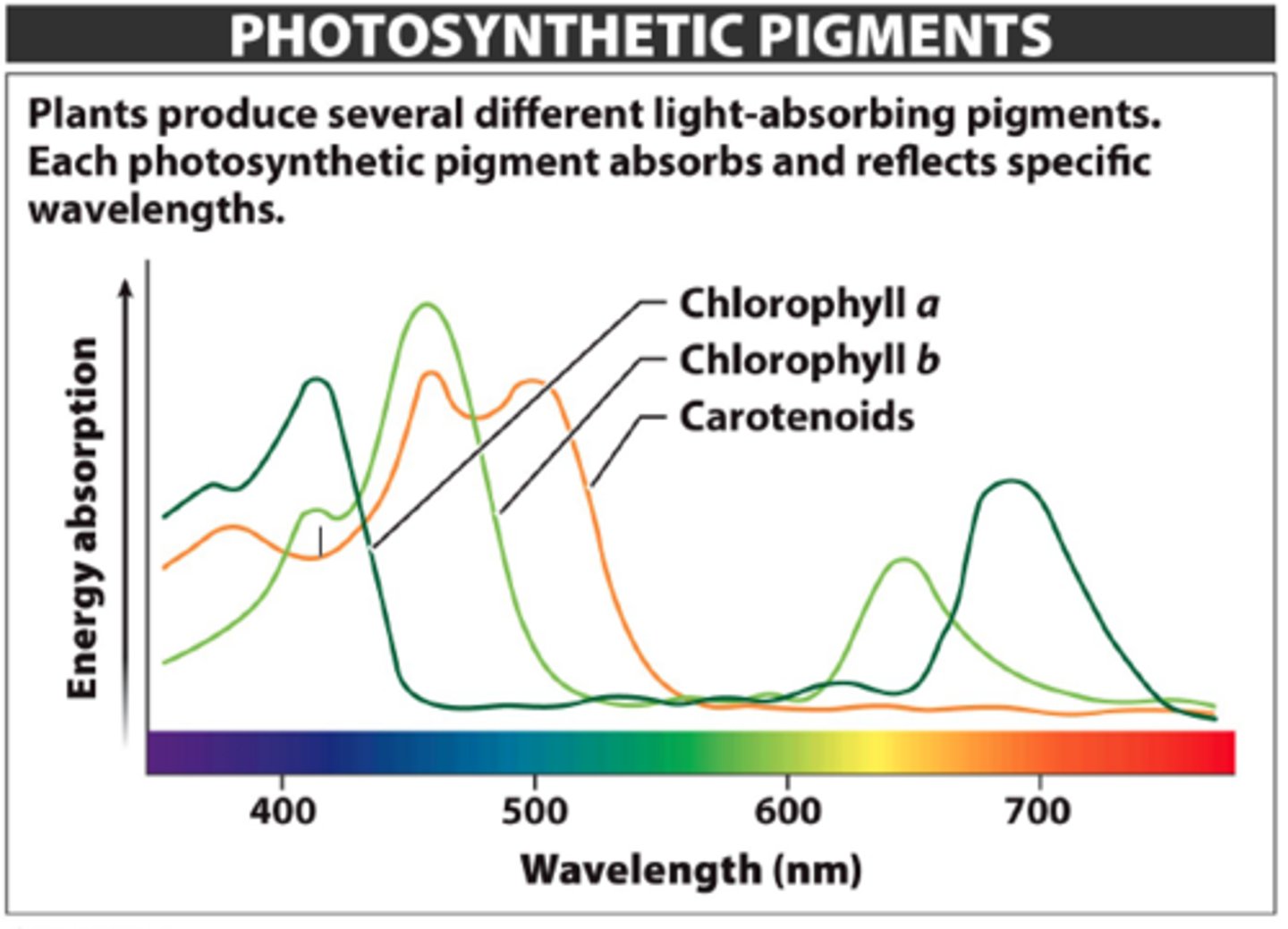
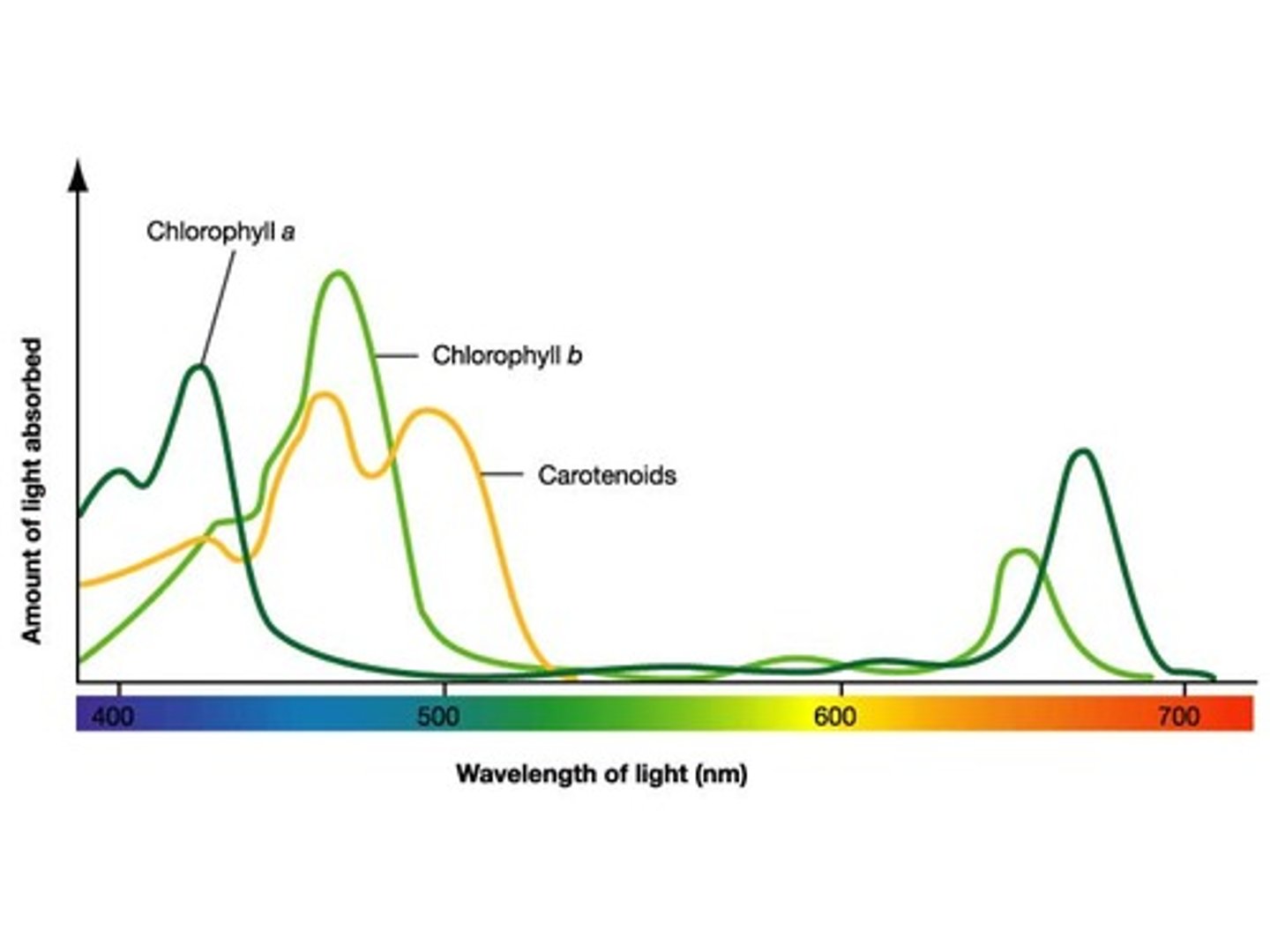
What are the 3 types of pigments in chloroplasts?
-chlorophyll a
-chlorophyll b
-carotenoids
What is chlorophyll a?
the key light-capturing pigment
What is chlorophyll b?
an accessory pigment
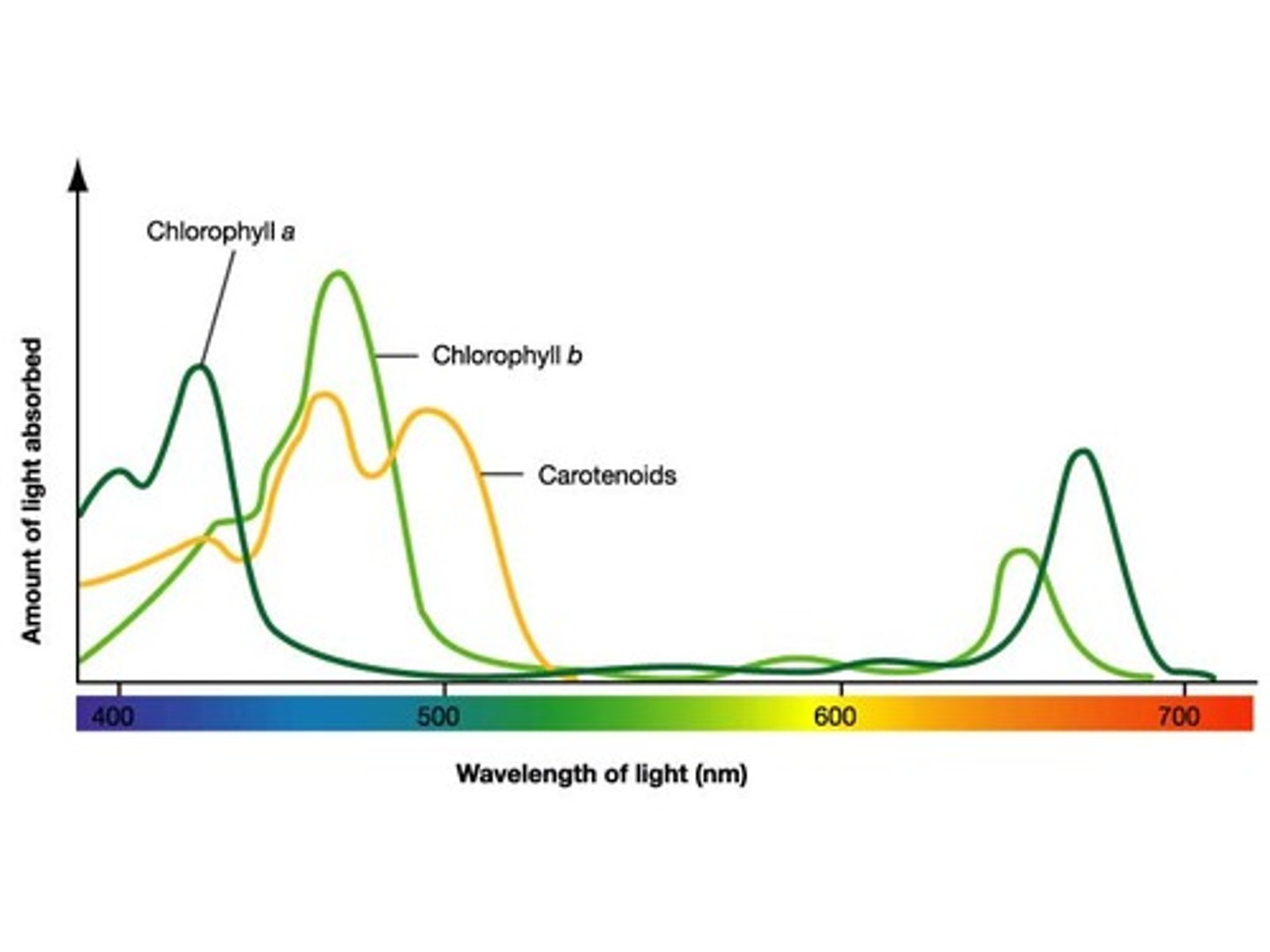
What are carotenoids?
- A separate group of accessory pigments
- May broaden the spectrum of colors that drive photosynthesis and gives plants their color
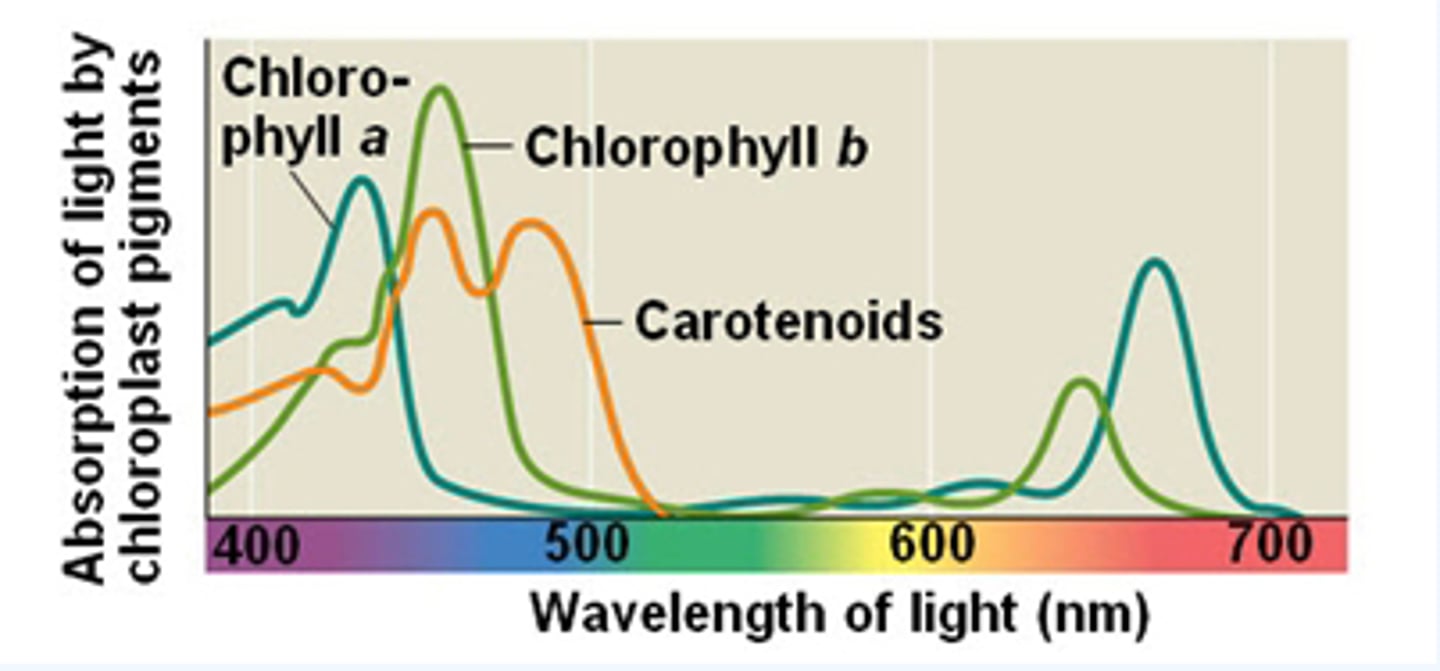
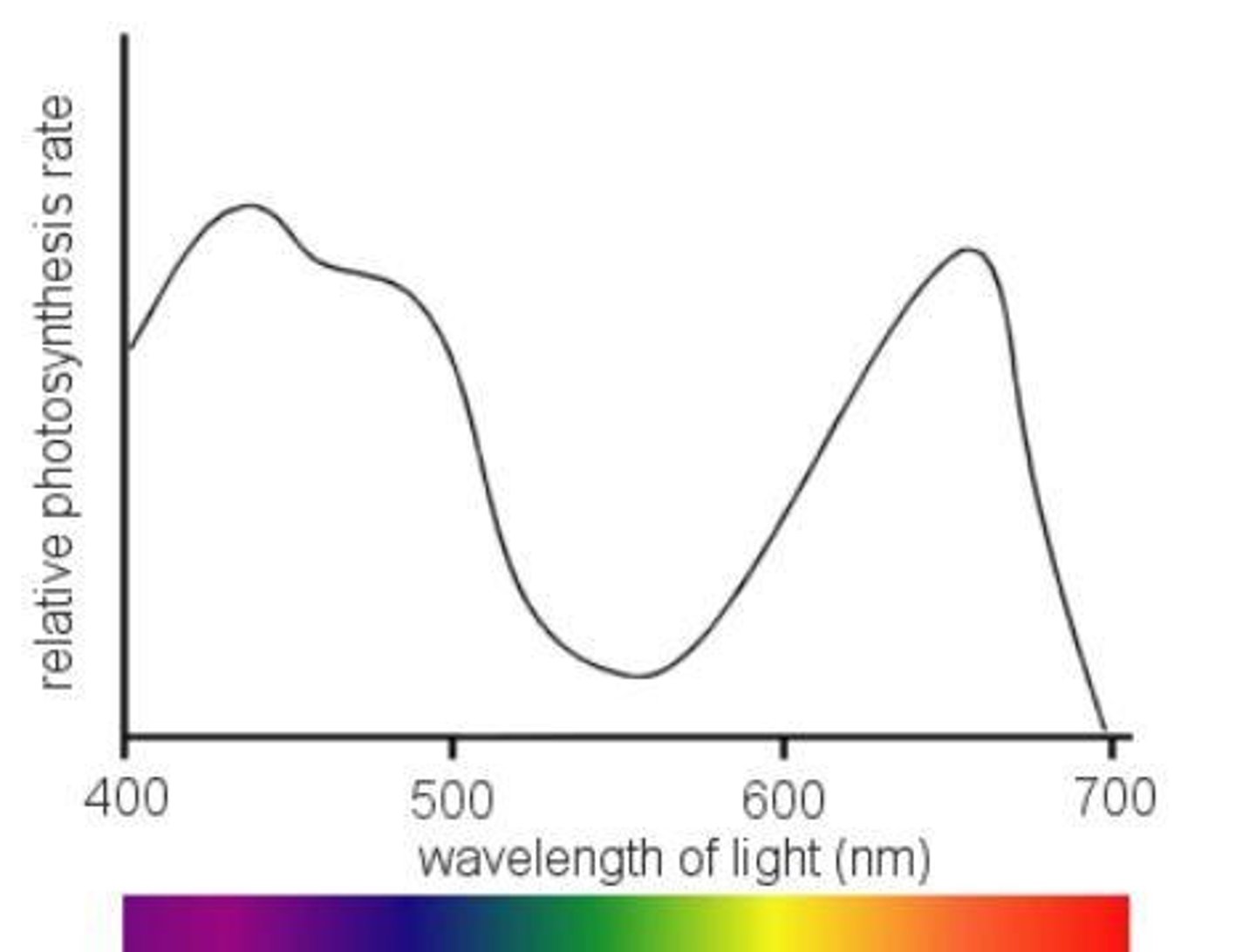
What does the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll A suggest?
Violet- blue and red light works best for photosynthesis.
What is the action spectrum?
The action spectrum is a chart showing which colors of light plants use best for making food through photosynthesis.
What is a photosystem?
consists of a reaction-center complex surrounded by light-harvesting complexes
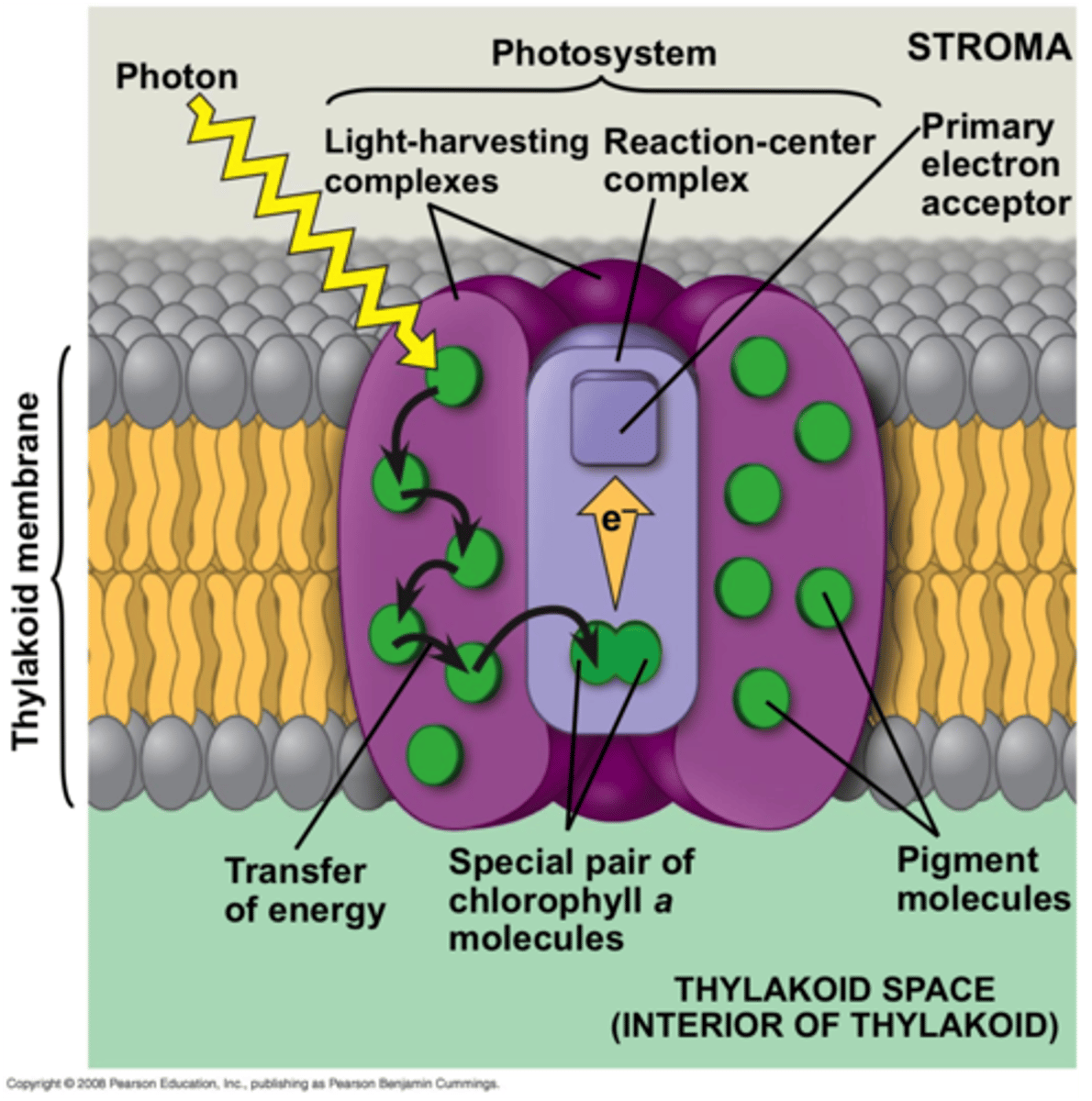
What is the reaction-center complex?
An association of proteins holding a special pair of chlorophyll A molecules and a primary electron acceptor (acceptor of excited electrons)
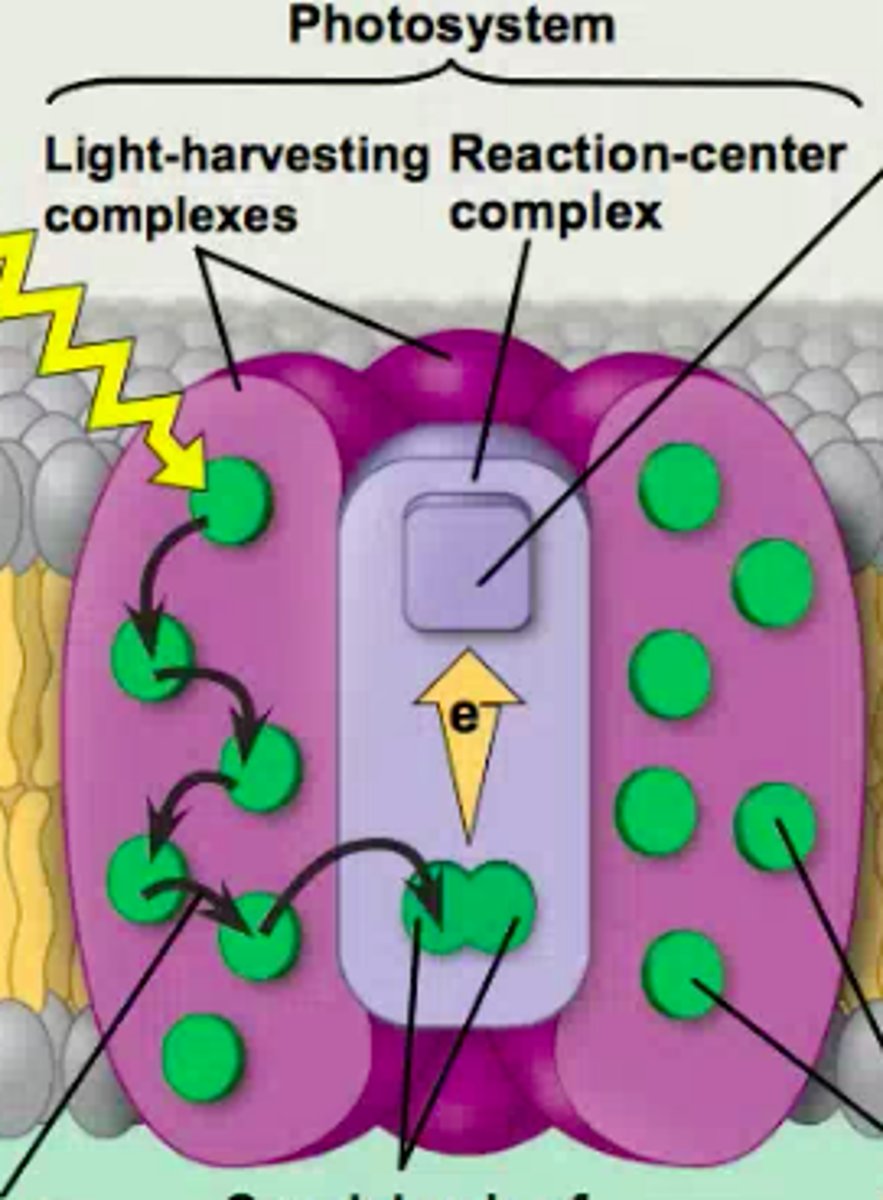
What is a light harvesting complex?
-Consists of pigment molecules bound to proteins
-transfer the energy of photons to the chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction-center complex
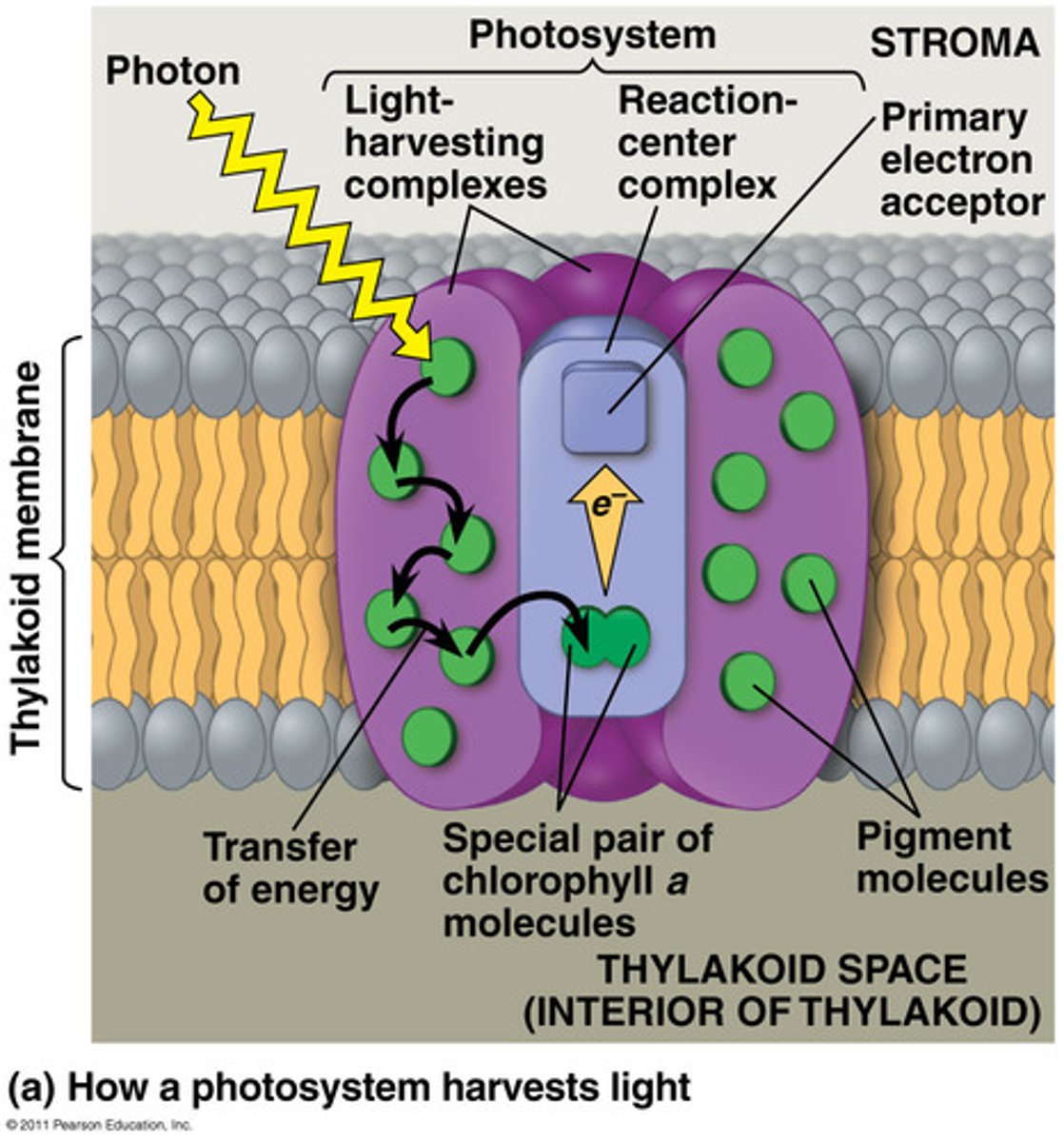
What does a primary electron acceptor do?
Accepts excited electrons and is reduced as a result