Section 1 Questions
1/310
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
311 Terms
You obtain an expired carbon monoxide (CO) reading of 4 ppm on a COPD patient participating in a pulmonary rehabilitation program. Based on this finding, you can conclude that the patient has:
has been exposed to secondhand smoke
has abstained for more than 12 hours
has smoked within the prior 12-24 hours
has high on the job CO exposure
has abstained for more than 12 hours
Expired CO analysis is used primarily to monitor patients' smoking status. Although no universal CO cutoff exists, recent research supports using a reading in the 6 to 8 ppm range to ascertain smoking status. Lower readings indicate a nonsmoking status, with higher readings indicating that smoking has probably taken place in the preceding 12-24 hours. To confirm complete abstinence a more stringent cutoff in the range of 3-4 ppm should be applied. Working in an occupation with high CO exposure would tend to raise CO levels, while exposure to secondhand smoke has a negligible effect on expired CO levels.
The wife of a patient receiving post-operative incentive spirometry asks if this therapy will help get rid of his snoring, daytime sleepiness, and morning headaches. In communicating this information to the patient's surgeon, you would recommend which of the following diagnostic procedures?
arterial blood gas
lateral neck X-ray
diffusing capacity
polysomnography
polysomnography
The physician requests patient education for a newly diagnosed COPD patient being discharged home with continuous supplemental oxygen and inhalers. Which of the following are NOT indicated for the teaching plan?
increasing quality of life
achieving normal lung functions
recognizing signs of infection
cleaning the MDI spacer
achieving normal lung functions
A 38-year-old male patient presents to the emergency room with difficulty swallowing and double vision. He reports a history of Myasthenia Gravis at a prior time, but was never ventilator-dependent. He now has the following clinical data:
Vital Capacity Tidal volume MIP
0.9 L 350 mL -22 cm H2O
What should the respiratory therapist recommend?
NRB mask
manual ventilation
Atropine
Tensilon challenge
Tensilon challenge
A Tensilon challenge will help diagnose this patient. If positive, intubation and mechanical ventilation is indicated immediately because VC is already below 1.0 L.
Pulmonary function testing is done on a patient with a 65-pack-year history of smoking. The following pulmonary function data is recorded:
Percent of Pred Actual value
FEV1 58%
FEF200-1200 75%
FEF25-75 52%
SVC 88%
FVC 81%
DLCO 18 CO/min/mmHg
Which of the following most likely represents the patient's condition?
cystic fibrosis
chronic bronchitis
kyphosis
emphysema
emphysema
These pulmonary function results show that the patient obstructed. This is indicated because the FEV1 is less than 80% of predicted. The SVC and the FVC are normal, or about 80% of predicted. Therefore, the patient can not be restrictive. When we look at the answers we see there are three obstructive diseases to choose from. When this happens we need more information. When we return to the pulmonary function test results we further see that the DLCO is reduced and is below normal. Normal DLCO is 25 CO/min/mmHg. That means that less than 80% of predicted would be anything less than 20 CO/min/mmHg. In this case, the DLCO is 18 CO/min/mmHg. There is only one obstructive disease that is associated with the poor DLCO - pulmonary emphysema.
In reviewing a patient's chart you note a history of COPD and a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 15. Which of the following tests would you recommend?
exercise stress test
polysomnography
bronchoscopy
metabolic study
metabolic study
With a BMI of 15, this patient is severely malnourished. That alone is an indication for measurement of his metabolic parameters (VO2, VCO2, RE, REE) via indirect calorimetry. Add to that COPD--in which the O2 cost of breathing can be very high and excessive carbohydrates can increase ventilatory demand--and the need for a metabolic assessment is apparent. Other clinical situations in which IC studies may be indicated include severe sepsis, multiple trauma, burns, hyper- or hypometabolic states, mechanical ventilation weaning difficulties, and whenever a patient's response to nutritional support is inadequate.
Postoperatively, a patient suddenly develops a stabbing right-sided chest pain and dyspnea with decreased right-sided breath sounds. Which of the following is indicated?
chest X-ray
VC measurement
MVV determination
VD/VT ratio
chest X-ray
Sudden unilateral chest pain and dyspnea are classic symptoms of a pneumothorax, as is the clinical sign of decreased breath sounds on the affected side. Only a chest X-ray will determine whether a pneumothorax has occurred or if a different problem may be causing similar findings. Obtaining PFT measurements such as a VC or MVV will not help define the nature of this problem and will waste valuable time in deciding on appropriate treatment.
A 5-year old child in the emergency department is demonstrating wheezing on the right side while breath sounds are normal on the left. The respiratory therapist should FIRST do which of the following?
order a spiral CT scan
obtain a chest radiograph
perform bedside pulmonary function testing
perform and ABG
obtain a chest radiograph
When a patient is wheezing bilaterally the most likely cause is bronchoconstriction. However, when the patient is wheezing unilaterally, or on just one side, the most likely cause is foreign body aspiration (a toy or perhaps food in the main stem bronchus). To determine this a chest x-ray is most appropriate. A spiral CT scan may also see the object but is more expensive and time-consuming. The other examinations will not be helpful.
In preparing to assist a physician in the performance of cardioversion, the respiratory therapist should ensure the defibrillator is synchronized to the
R wave
T wave.
P wave.
S wave.
R wave
Cardioversion is done by synchronizing the defibrillator to the R wave (the tallest spike in the QRS complex).
To determine potential post-operative risk of a patient preparing for surgery, the respiratory therapist should recommend which of the following tests?
pulmonary diffusion studies
pulmonary stress test
cardiac stress test
basic spirometry
basic spirometry
Potential postoperative risk may be assessed preoperatively through basic spirometry.
A patient in the emergency room expectorates thick, yellow sputum. A CBC shows the following:
RBC 6.0 mill/cu mm
Hb 17 g/dL
HCT 64 %
WBC 22,000 cu mm
The patient could benefit most from which of the following?
sputum culture and sensitivity
aerosolized Nystatin
aerosolized Amphotericin B
Acetylcysteine
sputum culture and sensitivity
The presence of thick, yellow sputum, in conjunction with an elevated white blood cell count, prove that the patient has an infection in the pulmonary system. The most appropriate action is to address the infection by determining a culture and sensitivity. This will help identify the bacteria that is present and the antibiotic that is most suitable for killing that particular bacteria.
A doctor wants you to assess whether a patient with a progressive neuromuscular condition will likely need mechanical ventilation. Which of the following measures would you recommend obtaining?
Max expiratory pressure (MEP)
Vital Capacity (VC)
Max inspiratory pressure (MIP)
1 and 3
1, 2 and 3
1 and 2
2 and 3
1, 2 and 3
Neuromuscular disorders typically cause respiratory muscle weakness, which can lead to respiratory failure. You can assess respiratory muscle strength by measuring the patient's maximum inspiratory and expiratory pressures. Measurement of the patient's vital capacity also can be useful as a global measure of respiratory mechanics.
Which of the following tests should you recommend for a patient with suspected hepatitis and history of alcohol and drug abuse?
partial prothrombin time
liver enzymes
cardiac enzymes
complete blood count
liver enzymes
Liver enzymes are indicated to assess suspected liver damage due to infections, alcohol and drug abuse, among others. Cardiac enzymes are indicated when myocardial damage is suspected due to an MI or ischemia. Complete blood count and partial prothrombin time are indicated to evaluate red and white blood cell counts and coagulation status of the blood.
A high-volume, low pressure cuff should be
actively deflated prior to extubation
passively deflated during extubation
kept at a pressure that minimizes tracheal wall pressure
kept at a pressure that maximizes tracheal wall pressure
2 and 3 only
1 and 3 only
2 and 4 only
1 and 4 only
1 and 3 only
High-volume, low-pressure endotracheal tube cuffs must be actively deflated prior to extubation. When sealing the cuff, minimum pressure should be placed upon the tracheal wall by use of a minimum seal technique or minimum occluding volume technique. Additionally, cuff pressure should be monitored.
Which of the following would result in an increase in CVP?
hypokalemia
hypervolemia
increased SVR
decreased PVR
hypervolemia
A chest radiograph of an orally intubated patient shows the end of the radio-opaque line on the 8.0-mm ET tube to be 1 inch above he carina. Breaths sounds are clear and diminished bilaterally. The respiratory therapists should
maintain tube position
advance the tube by 1 cm
withdraw the tube by 2 inches
replace the tube with a 7.0-mm size ET tube
maintain tube position
Normally, the end of an endotracheal tube should be positioned approximately 2 cm above the Carina. However, in some cases, that distance may be expressed as approximate inches. 1 inch is approximately 2.54 cm and therefore one-inch is considered acceptable, and tube position should be maintained.
You normally should recommend AGAINST performing a diagnostic bronchoscopy procedure on a patient with
fresh blood in the sputum
a ventricular tachyarrhythmia
unexplained infiltrates on X-ray
suspected inhalation injury
a ventricular tachyarrhythmia
You should recommend against performing diagnostic bronchoscopy in patients who (1) cannot be adequately oxygenated during the procedure (severe refractory hypoxemia); (2) have a bleeding disorder that cannot be corrected; or 3) are hemodynamically unstable (including those with pre-existing major arrhythmias). Abnormal X-ray findings of unknown etiology (e.g., suspected atelectasis, infiltrates, presence of mass or nodules); unexplained cough, dyspnea, wheezing or stridor; hemoptysis; suspected inhalation injuries (e.g., burns, toxic gases, etc.); and suspicious or positive sputum cytology results are all potential indications for diagnostic bronchoscopy.
A patient has the following arterial blood gas results and ventilatory parameters:
pH 7.12
PaCO2 30 mm Hg
PaO2 80 mm Hg
HCO3- 9 mEq/L
BE +15 mEq/L
RR 34
VT (spont) 600 mL
Which of the following would provide helpful diagnostic information?
blood glucose level
venous level of HCO3-
creatinine
BUN
blood glucose level
The blood glucose level should be evaluated in his case in order to determine the cause of the severe metabolic acidosis, which is likely to be diabetic ketoacidosis.
Which of the following tests would you recommend for a patient suspected of having methemoglobinemia due to excessive nitrate exposure?
pulse oximetry
blood gas analysis
hemoximetry
serum electrolytes
hemoximetry
Methemoglobin (metHb) is an abnormal hemoglobin most commonly cause by environmental exposure to oxidizing drugs and their metabolites (such as benzocaine, dapsone and nitrates). Only hemoximetry (CO-oximetry) can accurately metHb and other common abnormal hemoglobins (HbCO, sulfhemoglobin) and determine actual blood O2 saturation (as opposed to that computed via standard blood gas analysis). Standard 2-wavelength pulse oximetry cannot detect metHb.
Which of the following is a contraindication against performing CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA)?
right bundle branch block
bleeding abnormalities
allergy to contrast media
pulmonary embolism
allergy to contrast media
CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is the preferred imaging test for diagnosing pulmonary embolism. The primary contraindications against CTPA are 1) known or suspected allergy to the contrast media and 2) renal insufficiency (where contrast media could further impair renal function). Bleeding disorders, right bundle branch block, phlebitis and thrombosis represent contraindications against the older more invasive angiography procedure, which required insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter. CTPA simply requires regular peripheral venous access to inject the contrast media.
An infrared PetCO2 detector is attached to the end of an ET tube on a patient who was just intubated after being discovered apneic for at least several minutes. What initial end-tidal CO2 reading would the respiratory therapist expect to observe once manual resuscitation begins?
normal PetCO2 followed by a slight reduction
low PetCO2 followed by a gradual rise
plateau PetCO2 followed by a steady decrease
high PetCO2 followed by a gradual decrease
low PetCO2 followed by a gradual rise
For a patient who was apneic, initial end-tidal CO2 readings will likely be low at first because CO2 has not been perfused across the alveolar capillary membrane into the alveoli. Therefore, initial readings will be low but will then slowly rise as the patient is ventilated. Eventually, exhaled CO2 will demonstrate a plateau and then gradually decrease.
A patient in the cardiac intensive care unit has a Swan-Ganz pulmonary artery catheter in place. The following data is available:
CVP 6 torr
mPAP 19 torr
PCWP 12 torr
C.I. 1.7 L/min/m2
Which of the following is the most likely cause of these data?
affects of high PEEP
fluid overload
pulmonary hypertension
right side heart failure
affects of high PEEP
CVP is essentially normal and mPAP is elevated. This does not indicate a problem with the right heart but rather a problem downstream. mPAP is elevated and PCWP is also elevated, indicating no problem within the vasculature of the lungs. PCWP is elevated but cardiac output is low. Remember, cardiac output is determined by doubling cardiac index. That would give a cardiac output of 3.4 L which is low. The problem, therefore, is in the left heart. The answer that can explain this most closely is the affects of high PEEP.
A bedside PFT is completed on a patient who is being evaluated for effects and progress of Myasthenia Gravis. Reproducible results are:
FVC FEV1 SVC
Trial 1: 2.0 1.1 2.1
Trial 2: 2.1 1.0 2.2
Trial 3: 2.1 1.2 2.2
Trial 4: 2.1 1.0 2.2
Which is best trial?
2
4
1
3
3
To determine the best test, multiple FVC maneuvers should be done. Attempts should not differ by more than 5%. The highest sum of FEV1 + FVC is considered the "best test". In this case FVC 2.1 + FEV1 1.2 = 3.3
A patient is being evaluated for obstructive lung disease as the following pulmonary function data:
Pre-bronchodilator Post-bronchodilator
FEV1 2.8 L 2.8 L
FVC 3.3 L 3.4 L
The patient's medical record indicates a 4-month history of episodic dyspnea with mild exercise. Chest radiograph and ECG are normal. Echocardiography shows an ejection fraction of 65% and normal stroke volume. Which of the following should the therapist recommend NEXT?
methacholine challenge
Tensilon challenge
CT scan of the chest
lung volume determination
lung volume determination
The pulmonary function data shown in this case demonstrates very little response to bronchodilators, decreasing the ability for the practitioner to speculate on causative factors. Thus, additional information is required. The determination of lung volumes, which includes more comprehensive testing such as FRC determination, would be the next step in determining a possible cause.
At patient in pulseless ventricular tachycardia is receiving chest compressions while being orally intubated. Immediately after ET tube insertion, the respiratory therapist checks breath sounds and notices vesicular sounds bilaterally. The therapist should next do which of the following:
recommend a chest radiograph
withdraw the ET tube by 2 cm, observe chest rise
advance the ET tube and auscultate the chest
remove the ET tube and attempt nasal intubation
recommend a chest radiograph
To determine potential post-operative risk of a patient preparing for surgery, the respiratory therapist should recommend which of the following tests?
cardiac stress test
pulmonary diffusion studies
basic spirometry
pulmonary stress test
basic spirometry
A 64 year old male admitted to the ED with severe chest pain has an ECG suggesting myocardial infarction or ischemia. Which of the following lab tests would you recommend to help confirm the diagnosis?
alkaline phosphatase
serum troponin
total cholesterol
blood urea nitrogen
serum troponin
You should recommend arterial blood gas analysis with co-oximetry for which of the following patients?
38-year-old female with pulmonary embolism
40-year-old male with acute myocardial infarction
10-year-old patient in status asthmaticus
23-year-old firefighter with smoke inhalation
23-year-old firefighter with smoke inhalation
The one patient whose blood gases would indicate normal values in the presence of an abnormal condition is smoke inhalation. Therefore it is vital to do co-oximetry on these patients.
A sputum gram stain report indicates the presence of a gram-positive organism (diplococcus) in the sputum. The following data is available:
WBC 28,000 cu mm
Hb 14.5 g/dL
RBC 4.6 g/dL
HCT 42%
Which of the following medication would be most appropriate?
gentamycin
amoxicillin
vancomycin
budesonide
amoxicillin
Gram positive organisms, such as diplococcus, staphylococcus, etc) are treated using penicillin class antimicrobials. These include penicillin, amoxicillin, carbenicillin, and others.
For which of the following is the respiratory therapist evaluating if examining phase IV of a single-breath nitrogen test (SBN2)?
Closing volume
Mixed deadspace and alveolar gases
Pure deadspace gases
Evenness of gas distribution
Closing volume
A single-breath nitrogen elimination test (SBN2) is used to determine the adequacy of distribution of gases and the evenness of that distribution. A patient breathes out a single breath and the nitrogen is analyzed in four phases. The first phase is pure dead space. The second phase is a mixture of dead space and alveolar gas. The third phase represents pure alveolar gas and is the stage where gas distribution is truly assessed. Phase 4 is called closing volume.
Which of the following imaging procedures is used to evaluate the arteries for abnormalities such as aneurysm, atherosclerosis, embolism, occlusion, stenosis, thrombosis, trauma, or vasculitis?
standard radiography
PET scanning
angiography
V/Q scanning
angiography
Angiography involves visualization of the arteries by injection of contrast medium. It is used to evaluate the arteries for abnormalities such as aneurysm, atherosclerosis, embolism, fistula, hemorrhage, neoplasm, occlusion, arteriovenous shunting, stenosis, thrombosis, trauma, vasculitis. In pulmonary medicine, the most common application of pulmonary angiography is to confirm the diagnosis and location of pulmonary embolism.
A Bronchogram would be most helpful in evaluating and diagnosing which of the following?
bronchiectasis
ARDS
mycoplasma pneumonia
chronic bronchitis
bronchiectasis
A bronchogram is a procedure used to diagnose bronchiectasis - not helpful for Mycoplasma pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, or adult respiratory distress syndrome.
You obtain a sputum sample from a patient using hypertonic saline aerosol. Soon after receipt, the laboratory rejects it, indicating that it contains primarily squamous epithelial cells. Which of the following is the most likely reason for rejecting the sample?
the collection container was not sterile
the sample is contaminated with saliva
the saline concentration was too high
the sample is contaminated with gastric fluid
the sample is contaminated with saliva
Squamous epithelial cells line the oral cavity. A 'good' sample from the lungs typically will contain few squamous cells. When large numbers of these cells are observed during microscopic examination the sputum, it indicates serious contamination of the sample with the patient's saliva. To avoid contamination with saliva and/or oral flora, the patient should expectorate any saliva before coughing sputum into the sterile collection cup. Alternatively, some protocols minimize oropharyngeal contamination by having the patient gargle, orally 'swish' and expectorate saline solution before the procedure.
Arterial blood gases on a patient in the cardiac intensive care unit are as follows:
pH 7.19
PaCO2 30 mmHg
PaO2 90 mmHg
HCO3- 17 mEq/L
BE -8 mEq/L
Which of the following represents an accurate interpretation of these results?
compensated respiratory alkalosis
respiratory acidosis
respiratory compensated metabolic alkalosis
metabolic acidosis
metabolic acidosis
A 14-year-old patient with no history of lung disease is comatose and in the emergency department. ABG results on room air are below:
pH = 7.18
PaCO2 = 14 torr
PaO2 = 120 torr
HCO3 = 5 mEq/L
SaO2 = 99%
BE = -18 mEq/L
You can conclude from these data that the patient:
is hyperventilating and hypoxemic
is hyperventilating due to an acid-base disturbance
has compensated for hyperventilation
must be breathing supplemental oxygen
is hyperventilating due to an acid-base disturbance
The pH indicates a severe acidemia. Because the pH is below normal, the primary cause must be the low HCO3/BE, making this a metabolic acidosis. The low PaCO2 (hyperventilation) likely represents a compensatory response to the metabolic acidosis, which is not sufficient to bring the pH fully back to normal (partially compensated metabolic acidosis). The rise in PO2 above normal is consistent with the fall in PCO2 (breathing room air, sum of PaO2 + PaCO2 ~ 130-140), so it is unlikely that the patient is receiving supplemental oxygen.
A patient in shock exhibits the following cardiovascular responses: an INCREASED pulmonary artery pressure, an INCREASED systemic vascular resistance, and a DECREASED cardiac output. Given these data, the most likely type of shock is:
neurogenic shock
cardiogenic shock
anaphylactic shock
septic shock
cardiogenic shock
In combination, an INCREASE in pulmonary artery pressure, an INCREASE in systemic vascular resistance, and a DECREASE in cardiac output are all consistent with cardiogenic shock. In this case, the key distinguishing feature is the increase in pulmonary artery pressure, which occurs only in cardiogenic shock.
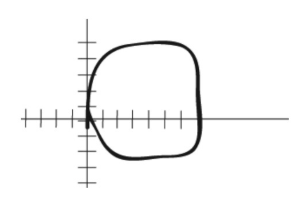
The following flow-volume loop is obtained from a 45-year-old male with vocal cord cancer. Which of the following interpretations is most accurate?
foreign body aspiration
COPD
asthma
fixed airway obstruction
fixed airway obstruction
A patient's bedside spirometry results (as compared to normal) are as follows:
FVC decreased
FEV1 normal
FEV1% increased
What is the most likely problem?
poor patient effort
a restrictive disorder
an obstructive disorder
within normal limits
a restrictive disorder
A patient with a decreased FVC, normal FEV1 and increased FEV1% is exhibiting the classic pattern of a restrictive pulmonary disorder, i.e., decreased volumes and normal (or increased) flows.
A forced expiratory measurement obtained after the administration of a bronchodilator shows an increase in FEV1 from 60% to 80% of predicted. This indicates a
fixed airway obstruction
normal diffusion capacity
reversible airway obstruction
restrictive process
reversible airway obstruction
To achieve clinical significance, the post-bronchodilator FVC, FEV1 and/or FEV1/FVC% should be at least 12-15% greater than the pre-bronchodilator value. This indicates reversible airway obstruction.
Which of the following lung volume measurements is normally the largest?
Residual capacity
Vital Capacity
Functional residual capacity
Inspiratory reserve volume
Vital Capacity
Of the volumes offered, vital capacity would be the largest.
An apnea monitor on a premature infant indicates an abnormal decrease in respiratory rate and an abnormal increase in heart rate. What is the most likely cause of this problem?
apnea of prematurity
hypoxemia
periodic breathing
motion/activity artifact
hypoxemia
A decreased respiratory rate in combination with an increased heart rate in a neonate most likely indicates hypoxemia, which should be confirmed by pulse oximetry or an ABG.
A patient has an FEV1/FVC of 55% of predicted before bronchodilator therapy. After bronchodilator therapy, the FEV1/FVC is 75% of the predicted norm. These findings indicate which of the following?
reversible restrictive disease
reversible obstructive disease
obstructive and restrictive disease
fixed obstructive disease
reversible obstructive disease
The low FEV1/FVC indicates expiratory airway obstruction. The %change inFEV1/FVC that occurred before and after bronchodilator therapy is significant (> 12-15%), indicating reversible obstructive disease.
Which of following calculations will determine vital capacity?
TLC - IRV - ERV
ERV + VT - IRV
FRC + IRV
IC + FRC - RV
IC + FRC - RV
For which of the following responses to therapy should a respiratory therapist discontinue aerosolized albuterol?
heart rate increases by 10 beats per minute
poor cooperation by a 2-year-old patient
bleeding gums
patient reports no change in dyspnea
bleeding gums
Bleeding from the mouth, nose, or gums is a rare but serious symptom of an allergic response to albuterol.
Immediately after oral intubation, the respiratory therapist notes the endotracheal tube marking are at 28 cm at the lips. Additionally, chest movement is asymmetrical. The first recommendation of the therapist should be to
withdraw the endotracheal tube by several centimeters
advance the endotracheal tube until chest movement is symmetrical
perform diagnostic chest percussion bilaterally
obtain a chest radiogram
withdraw the endotracheal tube by several centimeters
A patient who is orally intubated should have endotracheal tube markings at the lip line that are in the low 20s. In this case, chest movement is asymmetrical, further evidence that the endotracheal tube is inserted too far. To correct this, the endotracheal tube should be withdrawn by several centimeters and an x-ray should be obtained to observe the exact location of the tube.
Upon a return visit to a home care COPD patient on a inspiratory resistive breathing exercise program, you note no increase in MIP (maximum inspiratory pressure) since the last measure taken two weeks ago. No other changes are noted in the patient. What is the most likely cause of the observed lack of improvement in respiratory muscle strength?
development of an upper airway infection
noncompliance with the exercise regimen
a faulty inspiratory resistive device
rapid progression of the disease process
noncompliance with the exercise regimen
As compared to predicted normals, a patient has a normal FEV1%, but a reduced FEF25-75. Test results are repeatable. Which of the following is the most likely underlying problem?
a restrictive disorder of the chest wall
peripheral (small) airway obstruction
severe central (large) airway obstruction
combined restrictive and obstructive disease
peripheral (small) airway obstruction
A normal FEV1/FVC (FEV1%) does not rule out either an early or mild airway obstruction. The FEF25-75 is specific to the peripheral airways. Therefore a reduced FEF25-75 in the presence of a normal FEV1/FVC signifies peripheral airway obstruction.
During initial assessment of a patient with a closed-head injury, the patient opens his eyes in response to pain only. On a follow-up exam, the patient opens his eyes to verbal commands. These observations indicate which of the following?
there is increased seizure activity
intracranial pressure has increased
cerebral perfusion has decreased
the level of consciousness is improving
the level of consciousness is improving
According to the Glasgow coma scale, a neurologic patient who at first only responds to deep pain stimuli and then progresses to following verbal commands is improving.
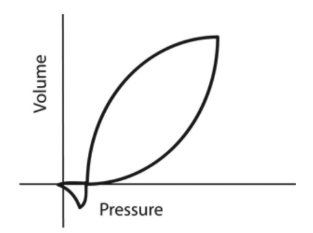
A 24-year-old patient is receiving mechanical ventilation. The following pressure - volume graph is available. What can accurately be stated about this information?
inspiratory flow is set too high
sensitivity is set too high
this breathing was machine-initiated
this breathing was machine-initiated
this breathing was machine-initiated
The presence of a "fishtail" on a pressure-volume ventilator graphic indicates the patient initiated a negative pressure prior to the machine administering the breath. This means the breath was patient-triggered.
Which of the following ventilatory patterns would result in the MOST wasted ventilation per minute (assume constant physiologic dead space)?
VT = 160 mL; RR = 30/min
VT = 24 mL; RR = 24/min
VT = 400 mL; RR = 12/min
VT = 220 mL; RR = 18/min
VT = 160 mL; RR = 30/min
Alveolar ventilation depends on the relationship between the frequency of breathing and tidal volume. Ventilatory patterns characterized by high frequencies and low tidal volumes result in the most wasted ventilation per minute.
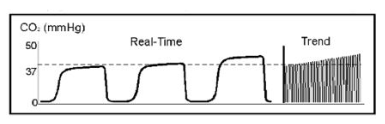
You observe the following on the bedside capnograph display of a patient receiving ventilatory support. What is your interpretation of this display data?
the capnogram indicates a leak around the ET tube
the capnogram indicates hypoventilation
the capnogram indicates hyperventilation
the capnogram indicates rebreathing
the capnogram indicates hypoventilation
This capnogram shows an increase in PetCO2. An incremental rise in plateau and end-tidal PCO2 usually indicates hypoventilation, increased metabolism/CO2 production or a rapid rise in body temperature.
To determine the evenness of distribution of inhaled gases in an obstructive patient, the therapist should observe which of the following results?
closing volume
phase III of a nitrogen elimination test (SBN2)
thoracic gas volume by body box
phase I and II of an SBN2 test
phase III of a nitrogen elimination test (SBN2)
A single breath nitrogen elimination test (SBN2) I is useful in determining the evenness of gas distribution in the lungs. The results come in four phases as the patient exhales a single breath. Phase I is the exhalation of pure deadspace gas. Phase II consists of some deadspace and some alveolar gas. Phase III consists of pure alveolar gas and is the phase that indicates the evenness of distribution. Phase IV is called "closing volume".
Upon a return visit to a home care COPD patient on a inspiratory resistive breathing exercise program, you note no increase in MIP (maximum inspiratory pressure) since the last measure taken two weeks ago. No other changes are noted in the patient. What is the most likely cause of the observed lack of improvement in respiratory muscle strength?
a faulty inspiratory resistive device
noncompliance with the exercise regimen
development of an upper airway infection
rapid progression of the disease process
noncompliance with the exercise regimen
A 38-week gestational age infant is receiving supplemental oxygen by oxyhood. An air/oxygen blender is set at 40% and the heated large volume aerosol is set at 100%. A capillary blood sample reveals the following values:
pH 7.45
PcCO2 35 torr
PcO2 47 torr
HCO3- 22 mEq/L
BE -2 mEq/L
SpO2 is reading 97% and the patient appears to have good color. The therapist should conclude which of the following?
the air/oxygen blender should be set to 100%
these are normal findings
nasal CPAP of 4 cmH2O should be implemented
FIO2 should be increased
these are normal findings
Infants have the same blood gas values as adults except for the PaO2. Close examination of the data provided shows that arterial CO2 and arterial oxygen is not what is being reported. The small "c" noted before the CO2 and O2 level indicate the blood was taken from the capillaries. When this is the case it must be remembered that capillary CO2 and the corresponding pH may be trusted but capillary oxygen levels are not accurate and may not be used. Therefore, this capillary blood gas reveals normal levels in term so ventilation. But the capillary oxygen data must be ignored entirely.
Within 2 hours of abdominal surgery, a patient has a blood pressure of 70/45 mmHg while receiving 10 mcg/kg/min Dopamine HCL, IV. The patient has not awakened from anesthetics and is ashen in color. The respiratory therapist should suspect the patient
is in a state of shock
is hemorrhaging
has cor Pulmonale
has left heart failure
is hemorrhaging
A patient is receiving VC AC ventilation with the following data:
3 PM 5 PM
Plateau pressure (cm H2O) 33 33
Peak pressure (cm H2O) 39 46
VT (mL) 500 500
This data indicates
pulmonary overdistension
increase airway resistance
decreased static compliance
development of autoPEEP
increase airway resistance
The C(a-v)O2 on a patient in the cardiac intensive care unit has decreased from 9.1 vol% to 4.3 vol%. What other change has also likely occurred?
increase in PaO2
decrease in cardiac stroke volume
increase in tissue oxygen consumption
increase in cardiac output
increase in cardiac output
When the C(a-v)O2 is changing in one direction, cardiac output is changing in the opposite direction. In this case the C(a-v)O2 has fallen from 9.1 vol% to 4.3 vol%. This decrease indicates cardiac output must be increasing. It also indicates tissue oxygen consumption is decreasing. This is true because when cardiac output decreases the blood flowing past the tissue perfusion beds slows, allowing more time for the tissues to extract and consume more oxygen. However, when cardiac output is high the opportunity to consume more oxygen from the blood is decreased because the blood is moving more quickly.
Which of the following changes will cause a patient's peak inspiratory pressure delivered during volume controlled ventilation to increase?
Increased set VT
Increased patient compliance
Increased set inspiratory flow
Increased set PEEP
1, 2, 3 and 4
2 and 4
1, 3 and 4
1 and 3
1, 3 and 4
During volume controlled ventilation (VC), the peak inspiratory pressure increases if 1) set VT increases, 2) set inspiratory flow increases, 3) set PEEP increases, 4) patient compliance decreases, or 5) patient airway resistance increases. Peak pressure also increases during VC if the airway is occluded by secretions or obstructed by compression due to biting or tube misplacement.
A 39-week gestational age infant is receiving supplemental oxygen by oxyhood. An air/oxygen blender is set at 30% and the heated large volume aerosol is set at 100%. A capillary blood sample reveals the following values:
pH 7.30
PcCO2 49 torr
PcO2 48 torr
HCO3- 23 mEq/L
BE -1 mEq/L
SpO2 97%
Which of the following is an accurate interpretation of this data?
metabolic alkalosis with mild hypoxemia
hypoxemia and respiratory acidosis
hypoventilation and respiratory acidosis
acute-on-chronic metabolic acidosis
hypoventilation and respiratory acidosis
The results of a V/Q scan shows poor perfusion with adequate ventilation. A chest radiograph shows a wedge-shaped infiltrate over the right lung field. The patient most likely has
pneumonia
fluid overload
ARDS
a pulmonary embolism
a pulmonary embolism
A VQ scan that shows poor perfusion but adequate ventilation is most closely associated with a pulmonary embolism. Supportive data is found in the radiological report of wedge shaped infiltrates.
A respiratory therapist is doing pulmonary function studies on a patient. The upper inflection point of a flow-volume loop is considered which of the following pulmonary function values?
inspiratory capacity
peak expiratory flow rate
functional residual capacity
expiratory reserve volume
peak expiratory flow rate
The very top (inflection point) of a flow volume loop reveals peak expiratory flow rate.
An FEV1/FVC (FEV1%) of 25% would indicate which of the following?
mild obstructive defect
normal ventilation
severe restrictive defect
severe obstructive defect
severe obstructive defect
Since a normal person should be able to forcibly exhale over 70% of their vital capacity in one second, an FEV1/FVC of 25% indicates severe obstruction to flow.
Which of the following best represents the normal range for adult patients' minute volume?
12 - 20 L/min
8 - 12 L/min
10 -15 L/min
5 - 10 L/min
5 - 10 L/min
Which of the following pre/post bronchodilator pulmonary function test results is the most meaningful in suggesting that a bronchodilator is indicated?
FEV1 increases by 150 mL
FEV1/FVC % increases by 10%.
FVC increases from 2.5 L to 2.6 L
FEF200-1200 increases by 17%
FEF200-1200 increases by 17%
The two primary considerations in pre-and post-bronchodilator studies are (1) whether flows increased by at least 12% or more and (2) whether the FEV1 increases by at least 200 mL. The FEF200-1200, indicating the condition of the large airways, increases by well over 12%, and is therefore the correct choice.
Which of the following would result in an increase in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure?
decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR)
cor pulmonale
mitral valve stenosis
dehydration
mitral valve stenosis
If mitral valve stenosis is present, blood would have difficulty transitioning the left ventricle. This would result in a backup pressure occurring and an elevation of the PCWP.
The following arterial blood gases are obtained on four patients. Which of these patients is most in need of ventilatory support?
pH 7.34; PaCO2 = 62; HCO3 = 32
pH 7.35; PaCO2 = 51; HCO3 = 27
pH 7.39; PaCO2 = 58; HCO3 = 34
pH 7.14; PaCO2 = 67; HCO3 = 22
pH 7.14; PaCO2 = 67; HCO3 = 22
A patient in shock exhibits the following cardiovascular measures: a DECREASE in pulmonary artery pressure, an INCREASE in systemic vascular resistance, and a DECREASE in cardiac output. Given these data, the most likely type of shock is:
cardiogenic shock
neurogenic shock
septic shock
hypovolemic shock
hypovolemic shock
In combination, a DECREASE in pulmonary artery pressure, an INCREASE in systemic vascular resistance, and a DECREASE in cardiac output are all consistent with hypovolemic shock. These findings are also consistent with hypodynamic septic shock.
You obtain an SpO2 reading of 90% using an oximeter with an accuracy of ±5%. This could indicate a PO2 as low as:
50 torr
70 torr
80 torr
60 torr
50 torr
With some oximeters' accuracy being only ±5%, an SpO2 reading of 90% could mean an actual SaO2 of as low as 85%, corresponding to a PO2 of about 50 torr.
Capnographic waveforms associated with a sudden pulmonary embolism in the right lung would
be the same as normal lung capnography.
double that of normal lung capnography.
be slightly higher than normal lung capnography.
result in a gradually decreasing end-tidal CO2.
result in a gradually decreasing end-tidal CO2.
A pulmonary embolism would result in hyperventilation for a patient experiencing hypoxemia. This hyperventilation would likely result in a gradually declining exhaled CO2 level.
What is the primary purpose for a nitrogen washout test?
evaluate evenness of pulmonary gas distribution
directly measure TLC
determine FRC
determine closing volume
determine FRC
A nitrogen washout test is used to determine three different lung volumes: TLC, RV, and FRC. For the NBCR exam the most important of those volumes is the FRC. Thus, when asked what a nitrogen washout test is for (or helium dilution test), the correct answer is FRC.
A patient is receiving hyperinflation therapy by IPPB with an inflatable mask. The respiratory therapist notices prolonged inspiratory time and unpredictable cycling into the exhalation phase. The respiratory therapist should evaluate which of the following?
1. circuit connections
2. end-tidal CO2
3. mask-face seal
4. sensitivity control
1 and 4 only
1 and 3 only
1, 2 and 4 only
2 and 3 only
1 and 3 only
When an IPPB machine fails to cycle into exhalation, the most likely cause is a leak. Of the options offered, a leak between the mask and the patient's face is most likely. Sensitivity affects the start of inhalation not exhalation.
A patient in shock exhibits the following cardiovascular measures: a DECREASE in pulmonary artery pressure, an INCREASE in systemic vascular resistance, and a DECREASE in cardiac output. Given these data, the most likely type of shock is:
septic shock
neurogenic shock
hypovolemic shock
cardiogenic shock
hypovolemic shock
In combination, a DECREASE in pulmonary artery pressure, an INCREASE in systemic vascular resistance, and a DECREASE in cardiac output are all consistent with hypovolemic shock. These findings are also consistent with hypodynamic septic shock.
A patient in shock exhibits the following cardiovascular responses: an INCREASED pulmonary artery pressure, an INCREASED systemic vascular resistance, and a DECREASED cardiac output. Given these data, the most likely type of shock is:
neurogenic shock
cardiogenic shock
septic shock
anaphylactic shock
cardiogenic shock
In combination, an INCREASE in pulmonary artery pressure, an INCREASE in systemic vascular resistance, and a DECREASE in cardiac output are all consistent with cardiogenic shock. In this case, the key distinguishing feature is the increase in pulmonary artery pressure, which occurs only in cardiogenic shock.
You obtain an SpO2 reading of 100% on a patient receiving oxygen via a nonrebreathing mask. What range of arterial PO2s is possible in this patient?
60 - 90 mm Hg
90 - 100 mm Hg
100 - 200 mm Hg
100 - 600 mm Hg
100 - 600 mm Hg
At the high end, pulse oximetry data can be meaningless. Due to the characteristics of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve, a patient with a SpO2 of 100% could have a PaO2 anywhere between about 100 and 600 mm Hg! Obviously, pulse oximeters should not be use to monitor for hyperoxia (as may be important in neonates).
Prior to obtaining an MEP value with a pressure manometer, the respiratory therapist notes the needle is pointing at a positive pressure of -4 cmH2O prior to the maneuver. During the MEP maneuver, the needle reaches 32 cmH2O. The therapist should
report the problem to the medical director
record an MEP of 36 cmH2O
record an MEP of 28 cmH2O
record and MEP of -28 cmH2O
record an MEP of 36 cmH2O
Although 32 cmH2O is observed on the pressure manometer the real pressure being produced is 36 cmH2O. This is because the manometer is not properly calibrated to zero. Therefore the adjustment must be accounted for when taking a measurement. You must account for the 4 cm H2O negative baseline defection of the needle and add that to the final observed positive number. In this case you must add the observed 32 to the amount of negative deflection of the needle (4). This means the needle is moved by a total of 36 cmH2O, which is the real, corrected MEP.
According to Fick principle, if the oxygen consumption remains constant, a DECREASE in cardiac output will manifest itself as:
a decrease in the C(a-v)O2
an increase in the CvO2
an increase in the CaO2
an increase in the C(a-v)O2
an increase in the C(a-v)O2
According to the Fick equation, the C(a-v)O2 (indicating oxygen extraction in proportion to blood flow), together with the total body oxygen consumption (VO2) may be used to calculate cardiac output: QT = VO2/[C(a-v)O2 x 10]. Based on this formula, if the O2 consump- tion remains constant, a decrease in cardiac output will manifest itself by an increase in the C(a-v)O2.
A mixed venous sample obtained from a pulmonary artery catheter has a PO2 of 84 torr and an HbO2 saturation of 96%. Which of the following best explains these results?
the sample was drawn from the proximal, not distal port
the PO2 and HbO2 sat are within normal limits
the patient has a high cardiac output
the sample was withdrawn too quickly
the sample was withdrawn too quickly
When obtaining a mixed venous sample from a pulmonary artery catheter, if the balloon is not deflated or the sample is withdrawn too quickly, you may contaminate the venous blood with blood from the pulmonary capillaries (oxygenated blood). The result is always a falsely high oxygen level. A sample drawn from the proximal port of a PA catheter (CVP port) also is venous blood, but that primarily coming from the upper body (abbreviated as 'ScvO2'). On average (except in patients with sepsis) ScvO2 values run about 5% higher than true mixed venous saturations. This is likely due to the contribution of deoxygenated blood from the heart (via the coronary sinus) in a true mixed venous sample.
A comatose patient breathing room air has an a/A ratio of 0.85 but is hypoxemic. What is the likely cause of the hypoxemia?
hypoventilation
V/Q imbalance
laboratory error
pulmonary shunting
hypoventilation
A normal a/A ratio (0.80 or higher) rules out V/Q imbalances or shunting as the cause of hypoxemia. Breathing room air, a patient can develop hypoxemia with severe hypoventilation and still have a normal a/A ratio. Typically this would occur when the PCO2 rises above 60-70 torr, which also could explain the patient’s comatose state.
After a bout of violent coughing, the respiratory therapist notices that patient who is intubated with 7.5 mm oral endotracheal tube is difficult to ventilate with a bag-valve. Additionally, the right chest appears to be rising more than the left chest. Which of the following is most likely the cause?
Right sided pneumothorax
Kinked endotracheal tube
Inadvertent advancement of the ET tube
Pleural effusion
Inadvertent advancement of the ET tube
The decrease in dynamic compliance (difficulty squeezing the resuscitator bag) and the asymmetrical chest rise indicates the endotracheal tube has been inadvertently advanced into the main stem bronchus and is ventilating one lung side more than the other.
A patient with a normal PaO2 and cardiac output is exhibiting signs and symptoms of tissue hypoxia. What is the most likely cause of her hypoxia?
a hemoglobin deficiency
a low ambient PO2
a R-L physiologic shunt
hypoventilation
a hemoglobin deficiency
Of and by itself, a normal PaO2 does not guarantee adequate arterial O2 content or delivery. For the arterial O2 content to be adequate there must also be sufficient quantities of saturated hemoglobin in the blood. Thus, even in the presence of a normal PaO2, a deficiency in Hb can result in hypoxia
As measured by the single breath DLco method, the diffusing capacity of the lungs would be decreased in which one of the following cases?
pulmonary emphysema
secondary polycythemia
strenuous exercise
pulmonary hypertension
pulmonary emphysema
The DLco is low in conditions that actually impair membrane diffusion (as in pulmonary fibrosis) or decrease surface area (as in emphysema). The DLco can also be less than normal with reduced Hb (as in anemia), decreased pulmonary capillary blood flow, or decreased alveolar volume. Increases in DLco occur with increased Hb (as in secondary polycythemia), increased pulmonary blood flow, increased alveolar volume, and during exercise.
A patient receiving 30% O2 has a PaO2 of 66 torr and PaCO2 of 32 torr. Which of the following best describes this patient’s oxygenation status?
A mild disturbance of oxygenation consistent with a V/Q imbalance
A severe disturbance of oxygenation consistent with ARDS
A mild disturbance of oxygenation consistent with hypoventilation
A moderate disturbance of oxygenation consistent with acute lung injury
A mild disturbance of oxygenation consistent with a V/Q imbalance
Over a 2 hour period, you note that a patient's peak and plateau pressures have both been steadily increasing, but the difference between the two remains about the same. Which of the following is the best explanation for this observation?
the patient has increased secretions
the patient's airway resistance has increased
the patient is developing bronchospasm
the patient's compliance has decreased
the patient's compliance has decreased
Repeated comparisons of a patient's peak pressure and plateau pressure help identify the cause of changes in mechanics. If the peak pressure and plateau pressures both increase equally (without a significant change in the difference between them) lung and/or thoracic compliance has decreased. A rapid decrease in lung compliance, as here, would likely be due to factors such as atelectasis, pulmonary edema, tension pneumothorax or bronchial intubation.
A patient is receiving volume control A/C ventilation. The patient has become increasingly agitated and the end-tidal CO2 has decreased from 39 to 28 torr over the last 2 hours. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
increased cardiac output
high body temperature
mainstem intubation
increased ventilation
increased cardiac output
The most likely cause of this patient’s low end-tidal CO2 is hyperventilation caused by the patient’s agitation. Treating the cause of the agitation may restore normal ventilation and thus normalize end-tidal CO2. High body temperature (fever) increases metabolism and would tend to increase, not decrease expired CO2 levels. Mainstem intubation normally does not affect capnographic readings.
A respiratory therapist is reviewing the medical record of a patient receiving PC, A/C ventilation. The ventilator flow sheet shows both a gradual decrease in plateau pressures and a recent increase in peak airway pressures. What conclusions can be made?
increased static compliance, decreased dynamic compliance
increased pulmonary compliance, increased airway resistance
deceased pulmonary compliance, increased dynamic compliance
decreased static compliance, decreased airway resistance
increased pulmonary compliance, increased airway resistance
Which of the following would NOT be an indication for implementing mechanical ventilatory support?
acute ventilatory failure
VT of 6 mL/kg
VC of 8 mL/kg
impending ventilatory failure
VT of 6 mL/kg
A patient with a tidal volume of less than 5 mL per kilogram or a vital capacity of less than 10 mL per kilogram requires mechanical ventilatory support. Additionally, if blood gases are consistent with acute ventilatory failure or impending ventilatory failure, mechanical ventilation is indicated. This question is asking which of the following is NOT an indication for mechanical ventilation. Because the patient's tidal volume is 5 mL per kilogram and this is sufficient, this is the correct answer.
Which of the following would most adversely affect the accuracy of pulse oximetry measurement?
coma
fever
tachycardia
shock
shock
Accurate SpO2 readings depend on the adequacy of circulation to the monitored area. For this reason, vasoconstrictor drugs, shock, and placement over areas with poor perfusion (e.g., a bony area) may adversely affect the accuracy of pulse oximetry.
A known COPD patient presents to the emergency room with increasing shortness of breath and large amounts of yellow sputum. ABGs on 2 L/min nasal cannula are:
pH 7.46
PaCO2 48 torr
PaO2 48 torr
HCO3- 34 mEq/L
The proper interpretation for the arterial blood gas is:
compensated respiratory acidosis
compensated respiratory alkalosis
compensated metabolic alkalosis
the blood gas analysis is in error
compensated respiratory acidosis
At first glance, the respiratory therapist may believe that the patient had alkalosis because the pH is on the high-end of the normal range. However, with a closer review you will see that the patient has a very high HCO3-, is known to have COPD, and is likely experiencing an acute on chronic episode. This is further confirmed with a very low PaO2 while receiving supplemental oxygen. The low hypoxemia is causing a much higher then normal minute ventilation due to air hunger. This is the cause of the pH being in the high-end of the range. When the patient does not have an infection, the normal blood gas values probably show a pH on the low side of the usual range, a very high PaCO2, with a very high HCO3-.
Which of the following is a KEY indicator of hypovolemia?
reduced PAP
reduced PCWP
reduced right atrial filling pressure
increased CVP
reduced right atrial filling pressure
Hypovolemia is indicated by a reduction in all hemodynamic values including CVP, PAP, PCWP, and cardiac output. However, of these four values CVP by itself is a primary indicator of the body's fluid status. CVP is known by many names, including right atrial filling pressure, right side preload, right ventricular end-diastolic pressure, and right atrial pressure. All of these terms are interchangeable with CVP. Dehydration or hypovolemia is indicated when these values are reduced. If CVP is increased, hypervolemia is present.
A patient who weighs 70 kg (154 lb) has a minute ventilation requirement of 15 L/min to maintain a PaCO2 of 43 torr. Which of the following can explain the ventilatory requirements?
febrile conditions
decreased dead space ventilation
decreased PVR
pulmonary emphysema
febrile conditions
The patient is febrile and likely has an infection, which can cause an increase in minute ventilation. Intrapulmonary shunting will also cause the patient to increase minute ventilatory requirements.
A 58-year old adult complains of a non-productive cough for the past 2 months. Auscultation reveals a slight inspiratory and expiratory wheeze over the left lobe. Which of the following most likely represents the patient's condition?
left-sided bronchoconstriction
development of a mass in the bronchials of the left lung
foreign body in the left mainstem bronchus
ALS (acute lung injury)
development of a mass in the bronchials of the left lung
When a patient is wheezing bilaterally the most likely cause is bronchoconstriction. However, when the patient is wheezing unilaterally, the cause is either foreign body aspiration, or a cancerous mass in the upper airway. In this case, the nonproductive cough has persisted for two months, indicating a greater likelihood of it being a mass in the lungs. If a foreign body is apirated the affect is acute the patient usually seeks medical treatment right away.
Which of the following conditions could produce a central venous pressure of 9 torr, and a pulmonary artery pressure of 11 torr?
hypervolemia
Cor pulmonale
mitral valve stenosis
excessive airway pressure
Cor pulmonale
Normal CVP is approximately 4 or 5 mm Hg. Normal PAP is 14 mm Hg. Since the CVP is high and PAP is low, it tells us that the right heart is not functioning properly and blood cannot flow correctly through it. CVP is the pressure entering the right heart and PAP is the pressure leaving the right heart. Cor pulmonale is a right heart condition.
A patient is undergoing a maximal exercise tolerance test. During the exam, as workload is increased, an increase in heart rate from 90 to 120 bpm while blood pressure remained steady at 110/88 mmHg is noted. Which of the following can be correctly stated about the exam results?
abnormal cardiac response, normal blood pressure response
normal cardiac response, abnormal blood pressure response
abnormal cardiac response, abnormal blood pressure response
normal cardiac response, normal blood pressure response
normal cardiac response, abnormal blood pressure response
During an exercise tolerance test, also known as a stress test, blood pressure and heart rate should rise as workload is increased. If this does not occur, the patient is said to have an abnormal blood pressure and/or abnormal cardiac response. In this case the patient's heart rate did increase but the blood pressure did not. The best interpretation is "normal cardiac response with an abnormal response in blood pressure".
A patient's radiological image is reported to have hyperlucency with diffuse dry crackles auscultated throughout the chest. These findings are most closely associated with
pulmonary edema
Atelectasis
subcutaneous emphysema
Pneumonia
subcutaneous emphysema
Auscultated dry crackles is the main sign of subcutaneous emphysema in the scenario. Increased radiolucency in the lung is also an indication that extra air exists in the chest, even though it is on the outside of the lung. Pulmonary edema would show fluffy infiltrates. Pneumonia is more localized and is associated with a reduced radiolucency.
The difference between actual aortic pressure and that measured noninvasively at a peripheral artery can be as much as:
30 to 40 cm H2O
30 to 40 mm Hg
5 to 10 cm H2O
5 to 10 mm Hg
30 to 40 mm Hg
Peripheral vasoconstriction can cause variations of as much as 30 to 40 mm Hg between the pressure in the aorta and cuff pressures measured at the peripheral arteries. This is why invasive monitoring of arterial pressures is preferred in critical care settings.
A 68-year-old male patient has the following pulmonary function values:
FEV1/FVC% 79%
FVC 62% of predicted
FEF25-75 81% of predicted
FEF200-1200 84% of predicted
Which of the following could represent the patient's diagnosis?
chronic bronchitis
chronic asthma
bronchiectasis
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
When looking at pulmonary function data, the primary purpose is to differentiate between an obstructive defect and a restrictive effect. To determine if the patient is obstructive, we must look at flows. To determine if they are restrictive we must look at volumes. In this case the Fev1/FVC% is 79%. Most pulmonary function data requires 80% of predicted or higher to be considered normal. With Fev1/FVC%, 75% is considered normal. This is because it is not a predicted value but the actual value of the ratio. In other words, a person should be able to blow out 75% of their forced vital capacity in one second. This data indicates that the patient is not obstructive. Further examination shows a forced vital capacity of 62% of predicted. This is consistent with a restrictive pulmonary defect. Examining the options reveals three diseases that are obstructive in nature and only one that is restrictive - idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
When performing bedside spirometry on a 46-year-old man who is 6 feet tall, you obtain a peak flow measurement of 3.3 L/sec. The best interpretation of this test result is:
the patient has poor gas distribution
the patient is not exerting full effort
the patient has low compliance
the patient's peak flow is normal
the patient is not exerting full effort
Normal adult male peak flows range between 8-12 L/sec, while adult female normal peak flows range between 6-9 L/sec. This patient's peak flow is considerably below normal which generally indicates an expiratory flow obstruction. However, the peak flow test is highly effort-dependent. For this reasons, poor effort should always be considered when peak flow results are below predicted norms.
A patient has a FRC via helium dilution of 2400 mL and a FRC via body plethysmography (body box) of 3400 mL. Which of the following statements could help explain this difference?
airway obstruction causes low results via helium dilution
the helium dilution test was obviously in error
the body box measures the entire thoracic gas
the body box tends to overestimates actual FRC
the body box measures the entire thoracic gas
Because the body plethysmography method of FRC determination actually measures the total amount of gas in the thorax, the values obtained may be substantially larger than those resulting from either helium dilution or nitrogen washout techniques. Such a difference would occur whenever there is gas in the thorax that is not in communication with the airways, as might be the case in air trapping, pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum.
A 65-year-old female patient experiencing progressive shortness of breath is diagnosed with COPD. Her pulmonary function test shows a slow vital capacity that is 95% of predicted. Which of the following would most likely be her residual volume compared to predicted?
115%
80%
95%
100%
115%
COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, is a condition which results in air-trapping, which increases one's residual volume. Therefore the actual residual volume would be higher than the predicted residual volume.
When performing spirometry on an adult patient, which of the following would indicate invalid/unacceptable test results?
forced expiratory time > 6.0 sec
time to peak flow 500 msec
back extrapolated volume 100 mL
repeat FVCs match within 150 mL
time to peak flow 500 msec
valid patient effort include: (1) a back extrapolated volume < 150 mL; (2) a time to peak expiratory flow < 120 msec; (3) a forced expiratory time > 6.0 seconds with the change in exhaled volume during the last 0.5 sec of the maneuver < 100 mL; and (4) all repeat FEV6 values matching within 150 mL.