Human Anatomy - Chapter 6
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:54 PM on 10/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
What is a bone?
an organ made up of bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, adipose, and nervous tissue; makes up the skeletal system
2
New cards
What are the six functions of the skeletal system?
provide support, protect internal organs, assist body movement, store and release calcium and phosphorus, blood cell production, stores triglycerides in yellow marrow
3
New cards
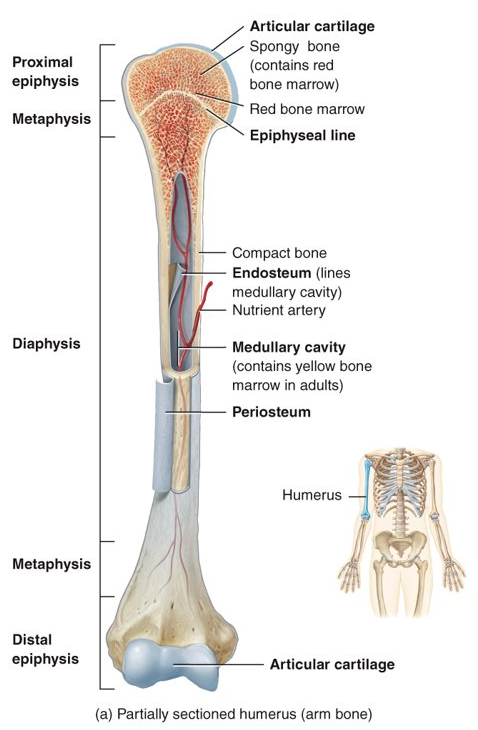
what are the seven parts of the long bone?
diaphysis (shaft), 2 epiphyses (ends of bone), 2 metaphysis (between diaphysis and epiphysis), articular cartilage (on epiphyses), periosteum (connective tissue on diaphysis), medullary cavity (in diaphysis), and endosteum (membrane on medullary cavity)
4
New cards
What is the extracellular fluid found in bones composed of?
15% water, 30% collagen, and 55% crystalized mineral salts
5
New cards
Mineral salts and collagen both contribute to the strength of our bones. What do mineral salts do compared to collagen fibres?
mineral salts confer hardness on bone while collagen fibers give bone its great tensile strength
6
New cards
What is calcification?
salts being deposited in a framework of collagen fibers
7
New cards
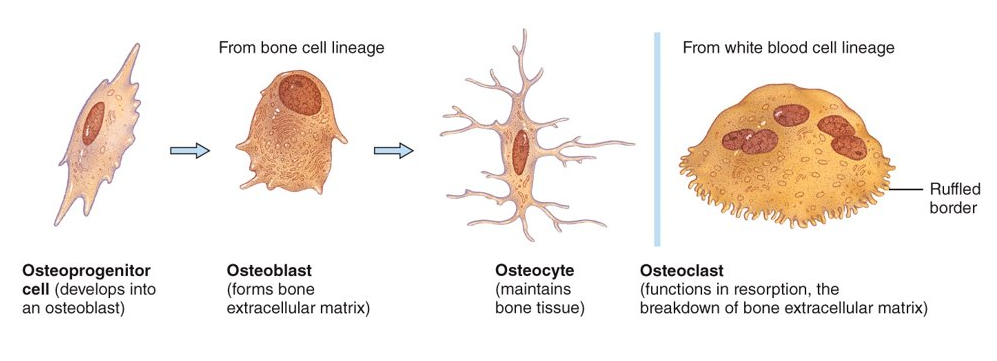
What are the four bone cells?
Osteoprogenitor cells (bone stem cells), osteoblasts (bone-building cells), osteocytes (mature bone cells), and osteoclasts (bone remodel)
8
New cards
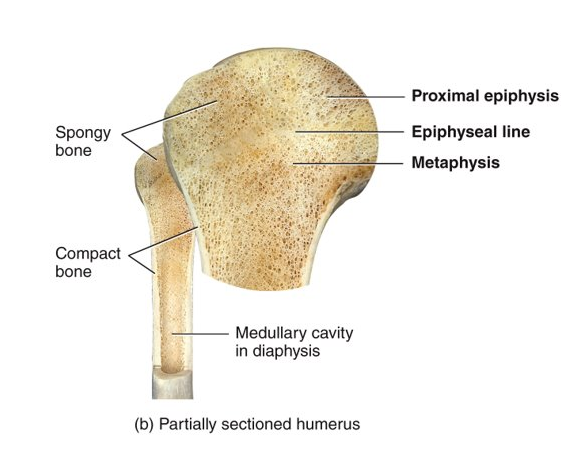
What is compact bone?
it is the strongest bone; provides protection and support; few spaces; found beneath periosteum of all bones
9
New cards
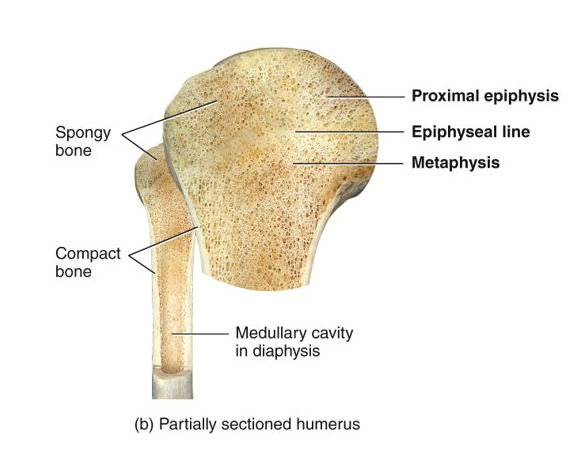
What is spongy/cancellous/trabecular bone?
provides tissue support; interior of bone; red bone marrow in bones, yellow in others
10
New cards
Just a complex picture of bone.
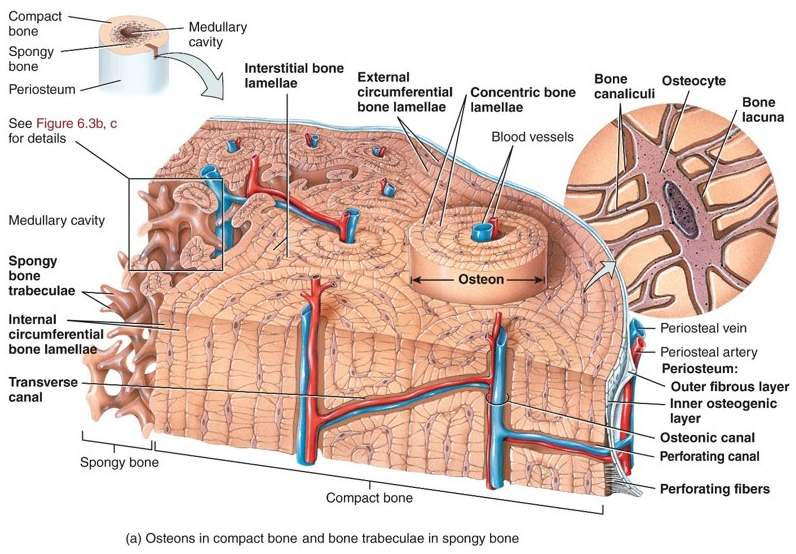
11
New cards
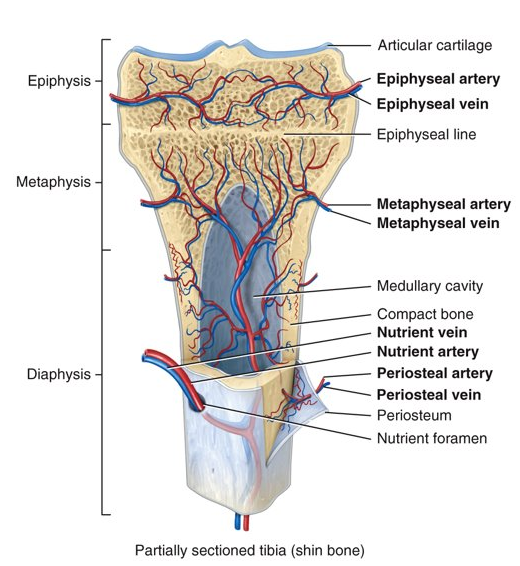
How do blood vessels pass through bone?
from the periosteum
12
New cards
How do nerves pass through bone?
follow vessels into bone tissue and the periosteum where they sense damage and transmit pain messages
13
New cards
What is the process of bone formation?
ossification/osteogenesis
14
New cards
What are the two forms of ossification?
intramembranous and endochondral
15
New cards
What is intramembranous?
occurs in flat bones when a connective tissue membrane is replaced by bone
16
New cards
What is endochondral?
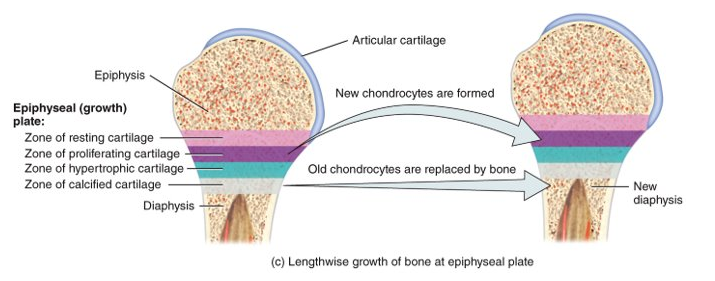
replaces cartilage with bone in the developing embryo and fetus; also occurs in epiphyseal plates of long bones as they grow in length
17
New cards
When does the diaphysis increase in length?
during the activity of the epiphyseal plate
18
New cards
How do you know when a bone is done growing?
the epiphyseal line appears
19
New cards
When can bone grow in thickness?
appositional growth at the periosteum
20
New cards
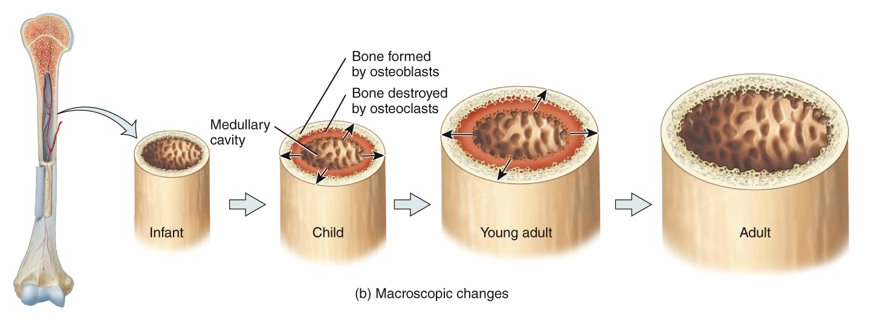
What is appositional growth?
the addition of new bone tissue by osteoblasts around the outer surface of the bone and to a lesser extent internal bone dissolution by osteoclasts in the bone cavity
21
New cards
What is bone remodeling?
the ongoing replacement of old bone tissue by new bone tissue
22
New cards
What kind of vitamins and minerals are need for bone growth?
calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, fluoride, manganese, and vitamins C, D, K, B-12, and A
23
New cards
What is the most important hormone for bone growth?
insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) stimulated by human growth hormone (hGH)
24
New cards
What stimulates the modification of the skeleton at puberty?
estrogen and testosterone
25
New cards
What are three phase (four steps) to bone repair?
reactive phase (early inflammation), fibrocartilaginous callus reparative phase and bony callus reparative phase, and bone remodeling phase
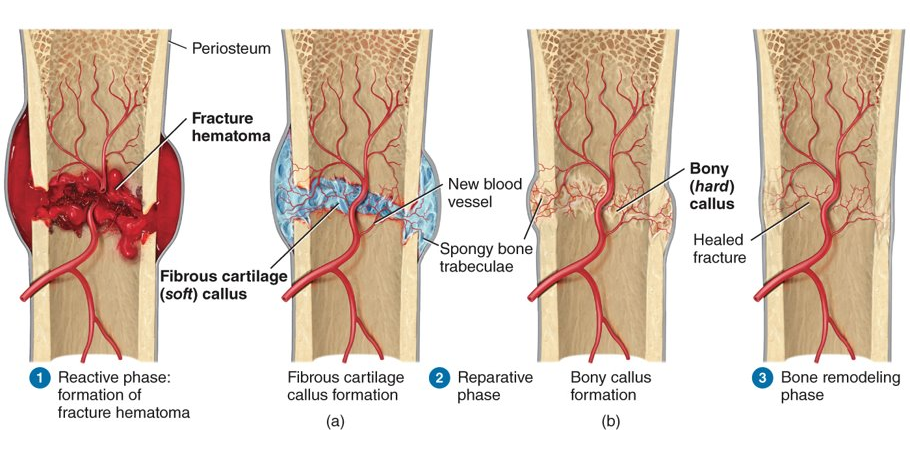
26
New cards
What are the seven types of bone fractures and what are they?
open/compound: broken end of bone sticks from skin
comminuted: crushed pieces at site of impact, small bone fragments
greenstick: partial fracture, bone bends while other side is broken (occurs only in children)
impacted: one end of fractured bone is driven into interior of other
pott: fracture at the distal end of fibula and injury to the distal tibial articulation
colles: fracture at the distal end of radius displaced posteriorly
vertebral compression fracture: one or more vertebrae fractures and become compressed into a wedge-shaped
comminuted: crushed pieces at site of impact, small bone fragments
greenstick: partial fracture, bone bends while other side is broken (occurs only in children)
impacted: one end of fractured bone is driven into interior of other
pott: fracture at the distal end of fibula and injury to the distal tibial articulation
colles: fracture at the distal end of radius displaced posteriorly
vertebral compression fracture: one or more vertebrae fractures and become compressed into a wedge-shaped
27
New cards
What hormones regulate the calcium ion exchange between bone and blood?
parathyroid hormone (raises blood calcium ion levels) and calcitonin (lowers blood calcium ion levels)
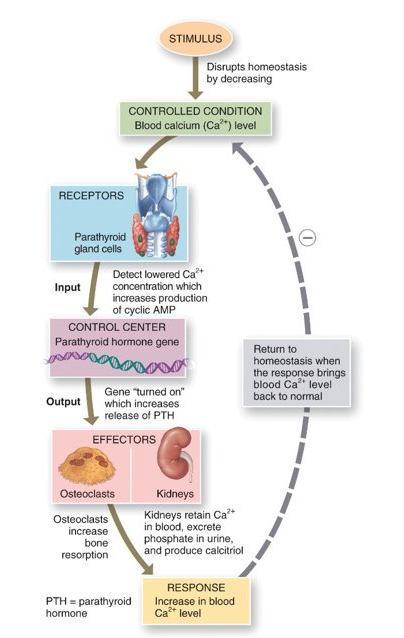
28
New cards
Why does bone get stronger when under stress?
increased deposition of mineral salts and production of collagen fibers
29
New cards
What helps build/retain bone mass?
weight-bearing activities
30
New cards
What are the two principal effects of aging on bone?
demineralization and decreased rate of protein synthesis, resulting in decreased production of matrix components (mostly collagen) and increased susceptibility to bone fracture
31
New cards
What is a bone scan?
a nuclear medicine imaging test; looks at the bones to see if there fractures, tumours or infections
32
New cards
What is osteoporosis?
porous bones with low bone mass; bone resorption is faster then bone deposition
33
New cards
What is ricketts and osteomalacia?
Inadequate calcification of the extracellular bone matrix, usually caused by a vitamin D deficiency (bowed legs)