OPT 116: Biochemistry Lipids I
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
lipids
serve as a reserve supply of energy; organic compounds that are largely hydrophobic; mainly carbon and hydrogen, some oxygen
TAG/triacylglycerides
during periods of low food consumption, _____ can be broken down to produce energy
fatty acids
precursor of triglycerides; source of energy
triglycerides
energy storage; thermal insulation; filling space; binding organs together; cushioning organs
phospholipids
structural components of cell/organelle membranes; aid in fat digestion
sphingolipids
structural component of cell membranes (especially nerve cells); chemical messengers
cholesterol
component of cell membranes; precursor of other steroids
steroid hormones and eicosanoids
chemical messengers
bile salts
aid in digestion and nutrient absorption
fat-soluble vitamins
Vitamins A, D, E, K; involved in a variety of functions including blood clotting, wound healing, vision, calcium absorption
simple lipids
esters of fatty acid
triglycerides, triacylglycerol (TAG)
examples of simple lipids
complex lipids
esters of fatty acids + additional groups
phospholipids and sphingolipids
examples of complex lipids
derived lipids
lipids derived from the hydrolysis of simple/complex lipids
steroids, isoprenoids, eicosanoids
examples of derived lipids
bile salts, steroid hormones, sterols
examples of steroids
vitamins A, E, K
examples of isoprenoids
prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes
examples of eicosanoids
fatty acid
a hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end; typically has even number of carbons
even
A fatty acid usually has an ______ number of carbons
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid)
_____________ is the most common saturated fat in plants and animals
omega number
_________ _________ refers to the position of the 1st double bond relative to the methyl end (omega end)
single bonds
saturated, linear, solid
double bonds
unsaturated, bent, liquid
cis or trans
unsaturated fatty acids have either ______ or ______ configuration
cis
2 hydrogens attached to the carbon double bond are on the same side; most commonly occurring unsaturated fatty acids
trans
2 hydrogens attached to the carbon double bond are on the opposite side; hydrocarbon chain is straight
unsaturated trans; unsaturated cis
What's "1" and "2"?
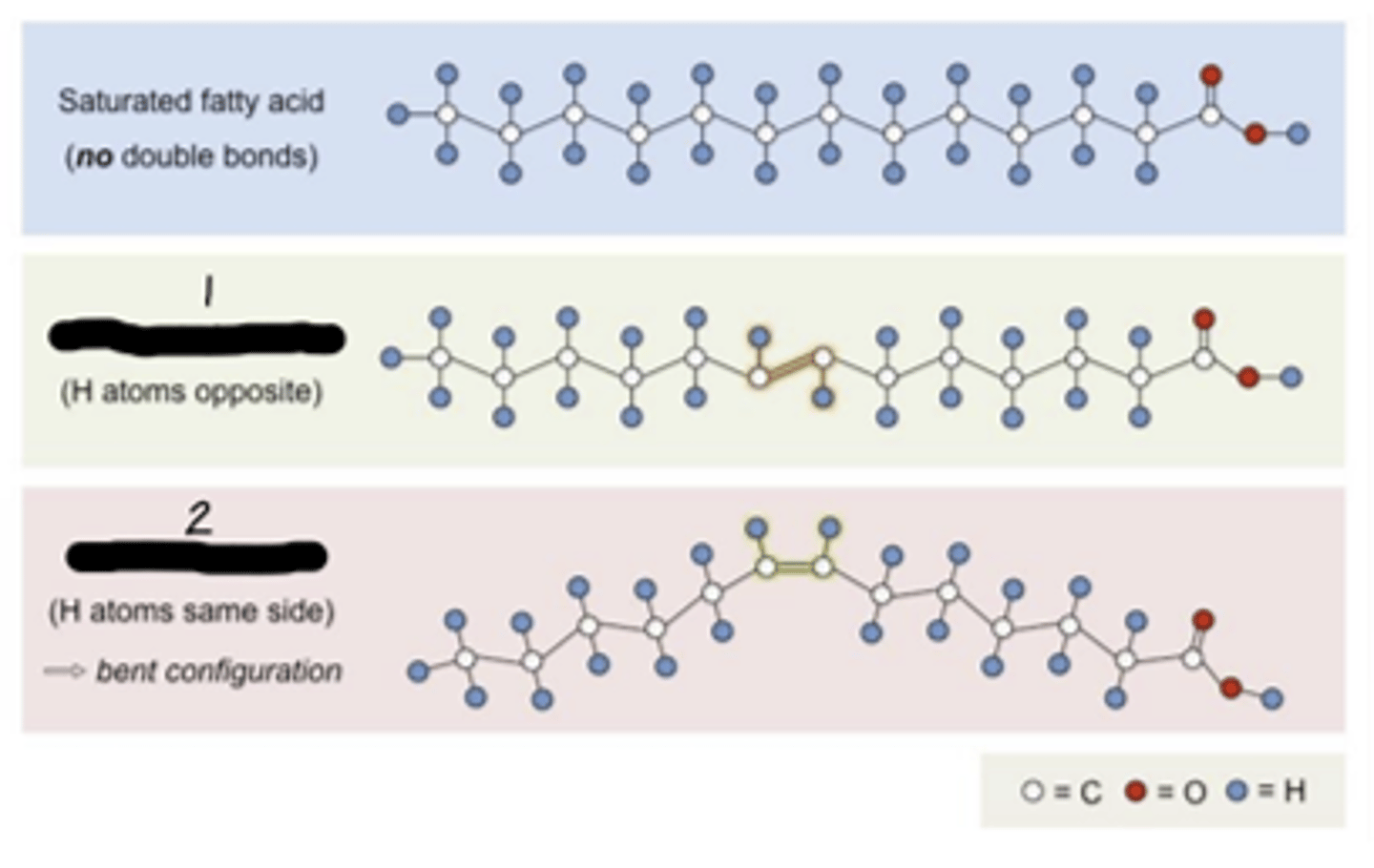
trans fatty acids
Most ______ ______ ______ are created in an industrial process that adds hydrogen to liquid vegetable oils to make them more solid
ester of a fatty acid
alcohol + fatty acid
alcohol
compound that contains hydroxyl groups attached to carbon
glycerol and sphingosine
examples of alcohols
triglycerides (AKA triacylglycerol, TAG, fats, oils)
3 fatty acids + glycerol; hydrocarbon chain length varies; degree of unsaturation varies; storage form of fatty acids
phospholipids
2 fatty acids + glycerol + phosphate + 1 polar group
phosphate; polar head group; glycerol backbone; fatty acids chains
This is a phospholipid. What's "1","2","3", and "4"?
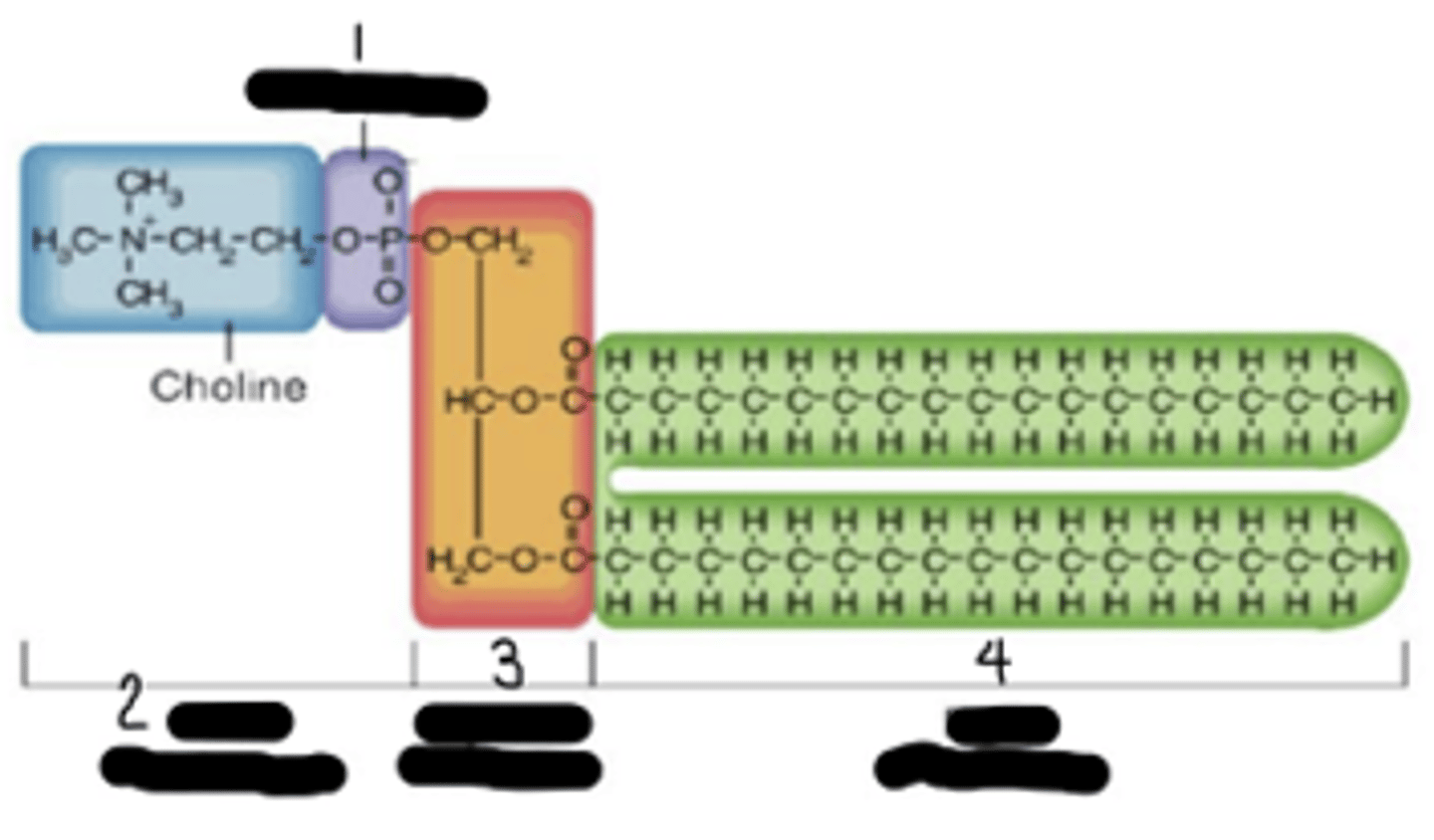
possible polar groups of phospholipids
ethanolamine, serine, inositol, choline
ethanolamine
found in cell membranes and pharmaceuticals
serine
metabolism and immune system
inositol
signal transduction
choline
cell membrane maintenance
sphingolipids
fatty acid + sphingosine + 1 head group
possible head groups of sphingolipids
hydrogen (ceramides), phosphocholine (sphingomyelin), and sugar (glycolipid)
sphingosine; fatty acid; head group (sugar in this case)
This is a sphingolipids. What's "1","2", and "3"?
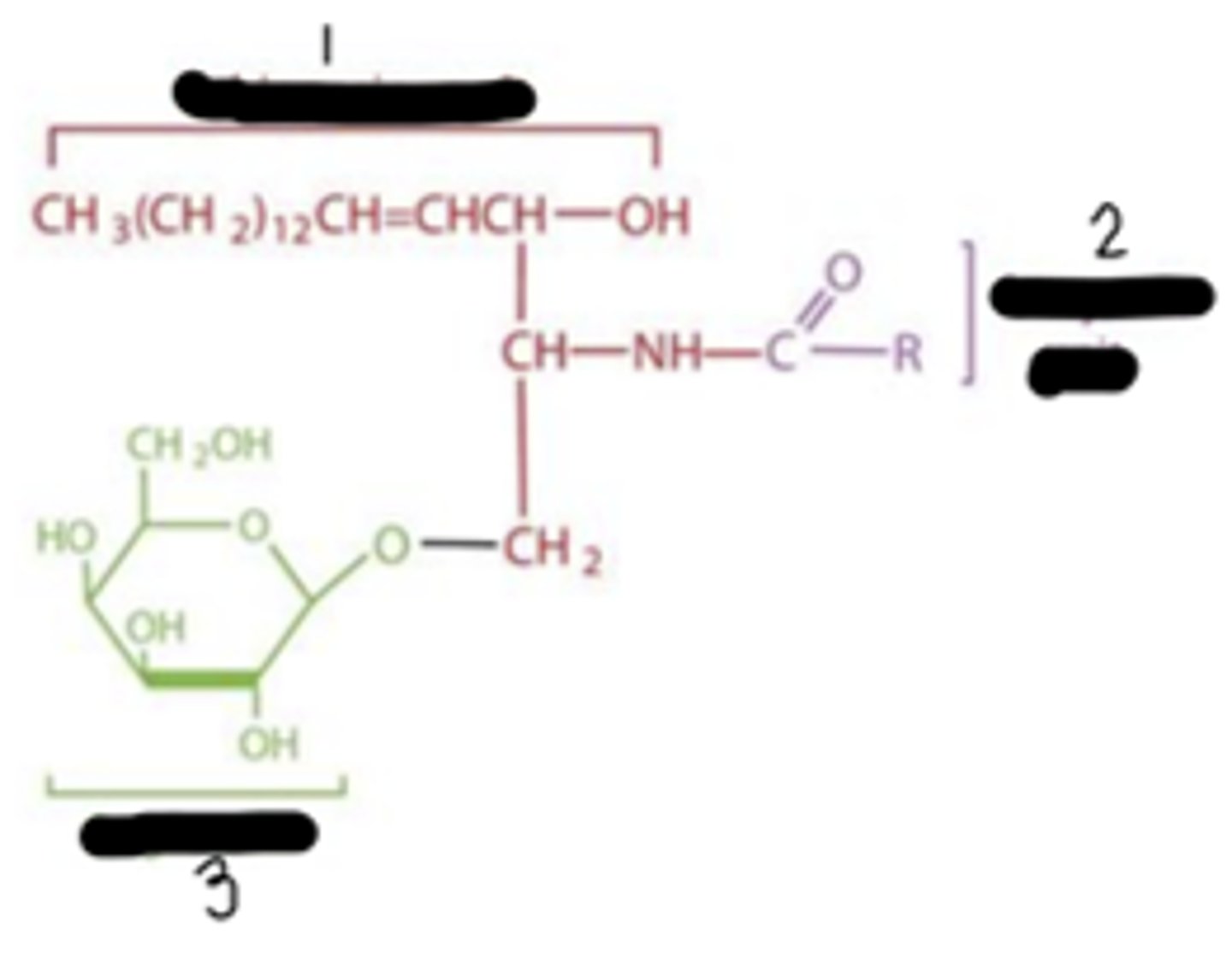
1 sugar
cerebroside
>1 sugar
ganglioside
rhodopsin
the pigment in rod cells that causes light sensitivity