clinical pathophysiology final
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
sodium
135-145mEq/L
potassium
3.5-5.0mEq/L
chloride
97-107mEq/L
bicarbonate
22-26mEq/L
calcium
9.0-10.2 mEq/L
phosphorus (phosphate)
3.0-4.5mg/dL
magnesium
1.3-2.1mg/dL
pH range
7.35 - 7.45
acidic —> basic
PaCO2 range
35 - 45
basic —> acidic
HCO3 range
22 - 26
acidic - basic
what is the normal WBC?
4,500 - 11,000
what is the normal hemoglobin level?
11 - 18 g/dL
what is the normal platelets count?
150,000 - 450,000
what are the signs and symptoms of a cervical injury?
paralysis below the neck
quadriplegia: 4 limbs paralyzed
quad = 4
diplegia: sounds like paralyzed
breathing impaired - life threatening
happens to a lot of sports figures
what are the signs and symptoms of a thoracic injury?
paralysis of the trunk of the body
paraplegic (2 legs)
legs, pelvic organs
what are the signs and symptoms of a lumbar injury?
legs and leaky bladder

what are premature atrial contractions (PACs)?
early, extra heartbeats originating in the atria
ekg characteristics: early P wave may look different from the normal P wave
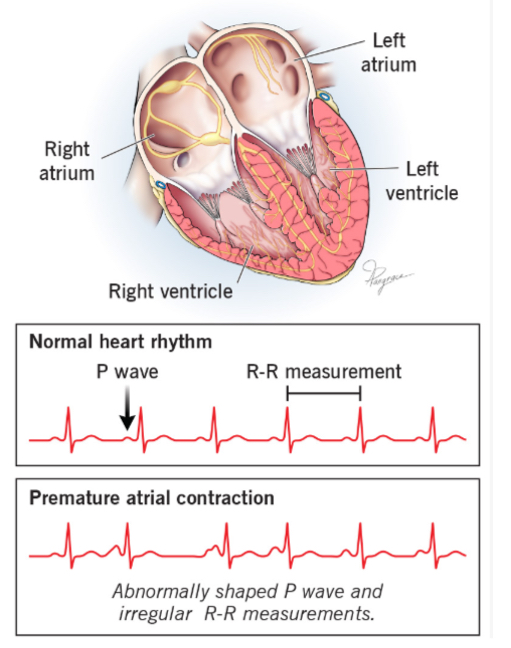
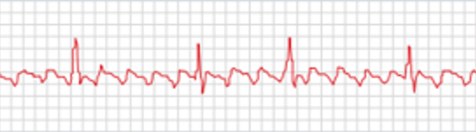
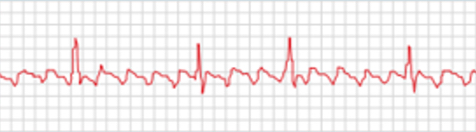
what is an atrial flutter?
atrial electrical activity becomes rapid and regular (250-350 bpm), leading to a sawtooth pattern
ekg characteristics: F waves (sawtooth pattern) instead of normal P waves
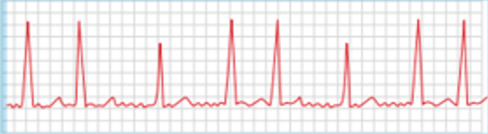
what is an atrial fibrillation (AFib)?
chaotic electrical activity in the atria, leading to an irregular and often rapid heart rate
ekg characteristics: irregularly irregular rhythm, absent P waves, fibrillatory waves

what is an ejection fraction
a key measurement used to assess how well the heart is pumping blood.
percentage of blood that is pumped out of the left ventricle w/ each contraction, compared to the total amount of blood in the ventricle before the heart pumps
EF = (stroke volume / end-diastolic volume) x 100
what is the normal EF percentage?
55%-70% of the blood in the left ventricle w/ each heart beat
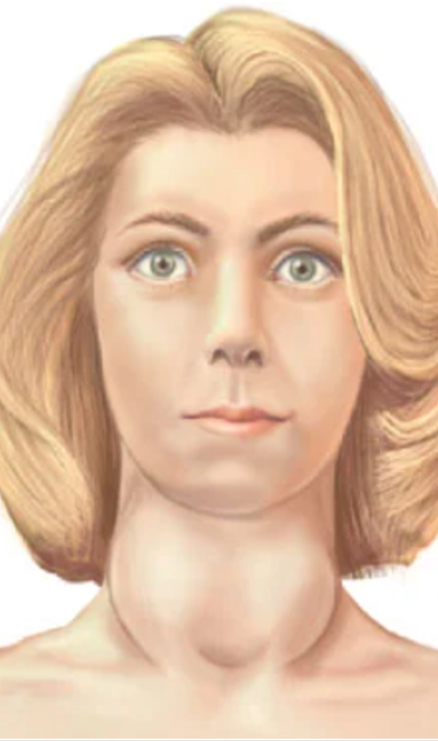
what is Graves disease?
an autoimmune disorder characterized by thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) or TSH receptor antibodies that abnormally activate the thyroid gland
Hyperthyroidism w/ goiter and ophthalmopathy
affects 0.5%-1% under 40yo
what is the etiology of graves disease?
associated w/ other autoimmune disorders like myasthenia gravis
linked to MICA genotypes: MICA A5 (risk), MICA A6/A9 (protective)
what can opthlamopathy in graves disease lead to?
diplopia, vision loss, and corneal ulceration due to exopthalmos (protruding eyeball)
what are some treatment and considerations for graves disease?
opthalmopathy usually stabilizes after treating hyperthyroidism
can worsen after radioiodine treatment; glucocorticoids may be prescribed

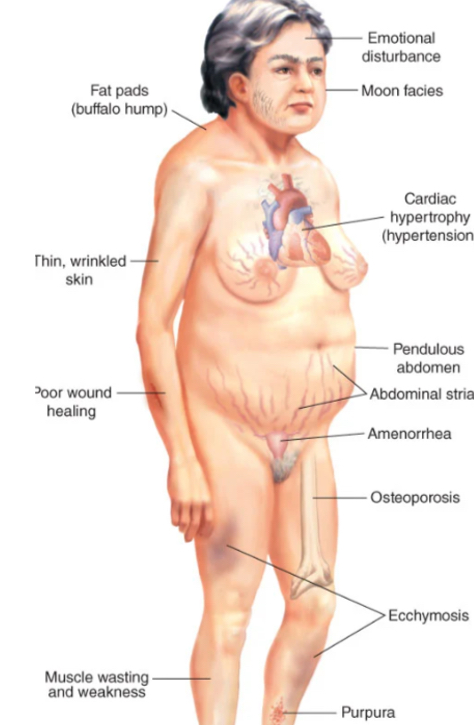
what is cushing syndrome?
hyper-cortisolism


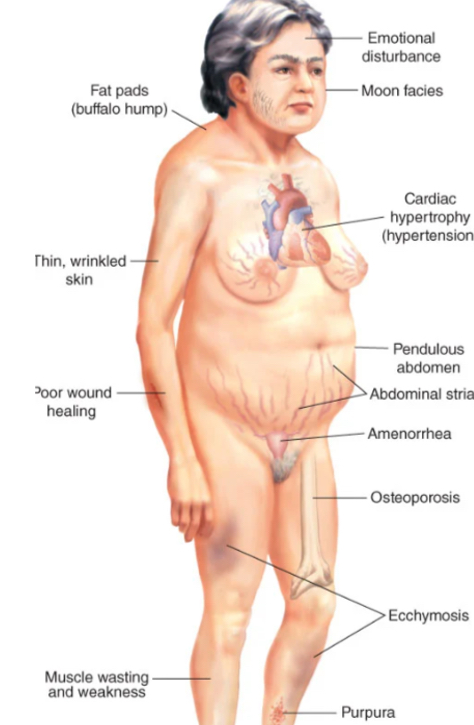
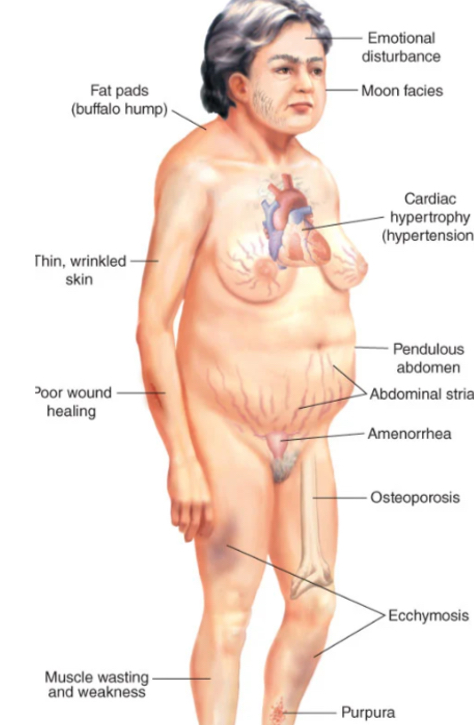
what are clinical manifestations of Cushing syndrome?
fat redistribution: buffalo hump, moon face, protruding abdomen
muscle weakness and thinning extremities due to muscle wasting
skin changes: thin, parchment-like skin, purple striae (stretch marks)
osteoporosis, back pain, compression fractures
metabolic changes: hypokalemia, hypertension, renal stones
increased susceptibility to infections due to suppressed immune response
emotional lability, mood swings, euphoria, or psychosis
gastric issues: increased acid secretion, ulcers, and bleeding
androgen excess: hirsutism, acne, menstrual irregularities in women

what are the diagnosis of cushing syndrome?
step 1: hypercortisolism diagnosis (urinary cortisol, plasma cortisol)
step 2: determine cause (CRH test, dexamethasone, suppression, imaging)
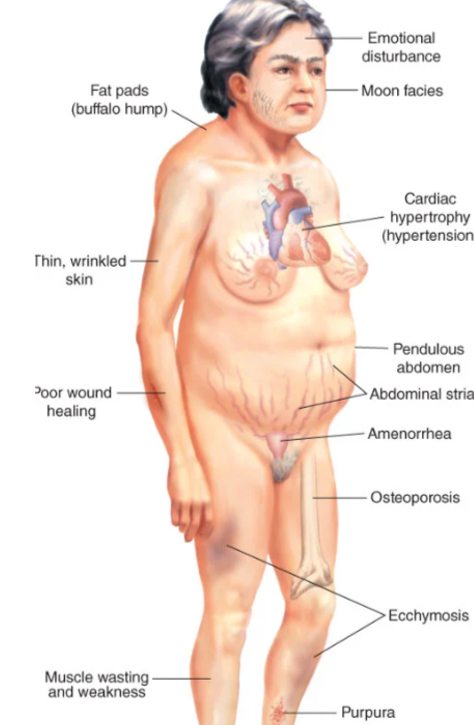
what are the treatments of cushing syndrome?
surgery: pituitary adenoma removal (transsphenoidal surgery)
radiation or pharmacologic treatments based on the cause
goal: correct the cause of hypercortisolism without damaging pituitary or adrenal glands
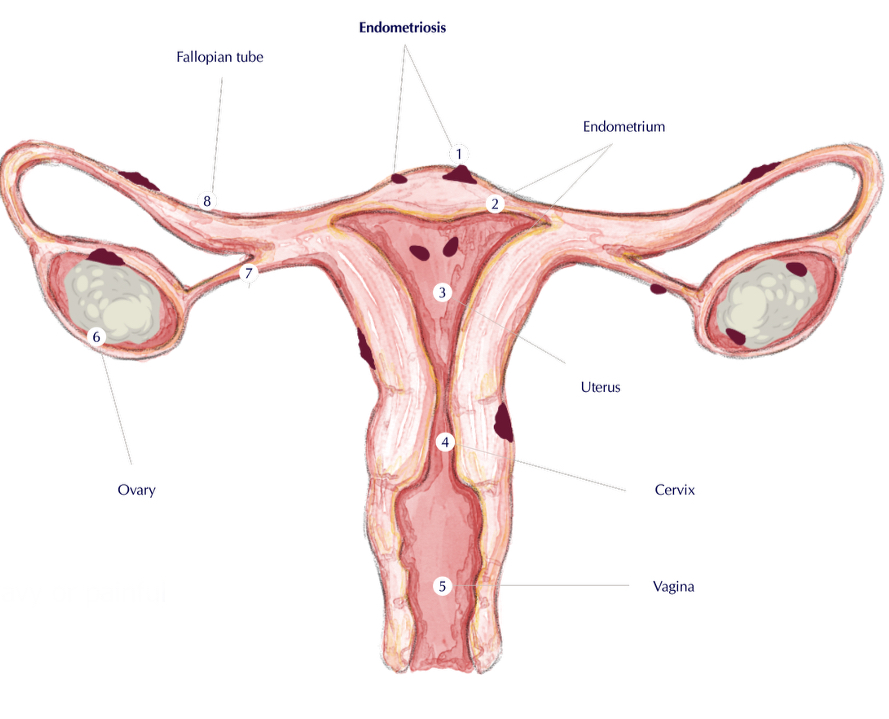
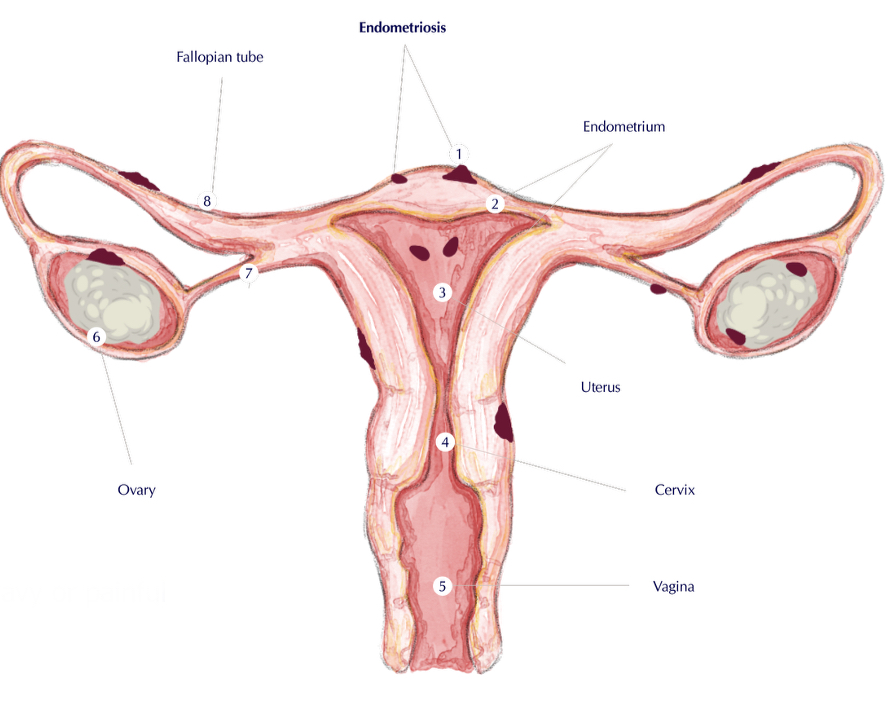
what is endometriosis?
The presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity
the endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, a muscular organ in the pelvis
can cause pelvic pain, heavy or painful periods, and infertility
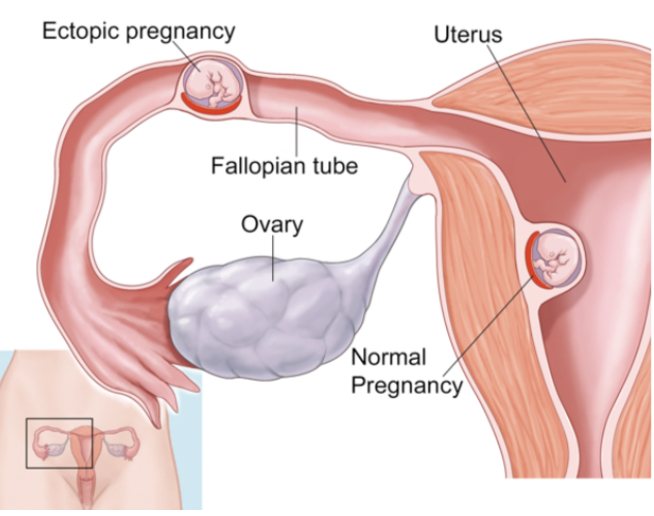
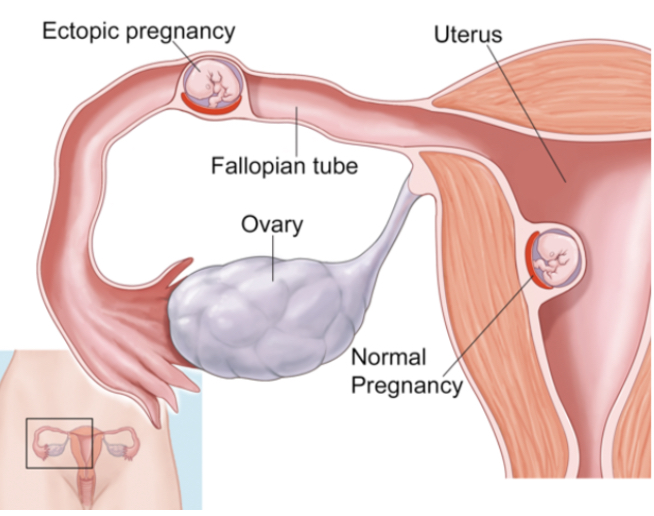
what is ectopic pregnancy?
implantation of the fertilized ovum outside of the uterine cavity, most commonly in a fallopian tube
the fetus is not viable, and salpingectomy is performed to remove both the embryo and the fallopian tube
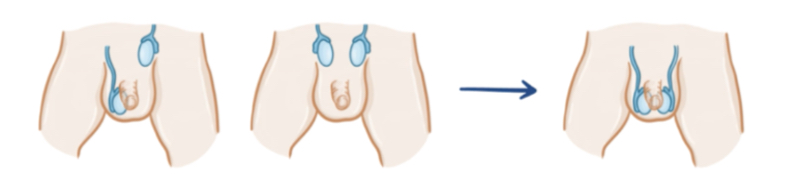
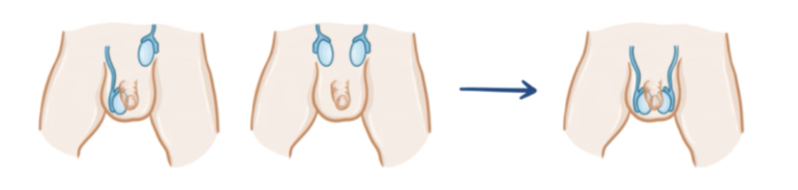
what is cryptorchidism?
PARTIAL or ABNORMAL descent of ONE or BOTH TESTICLES into the SCROTAL SAC
commonly seen in neonates
most cases —> spontaneously resolves
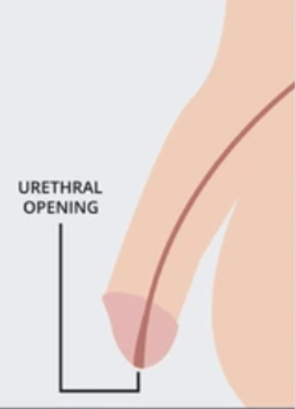
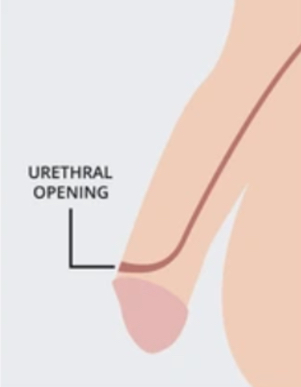
where is the normal opening of the urethral for a penis?
on the head
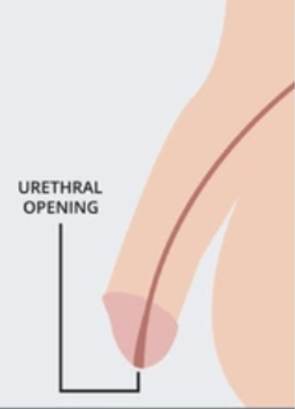
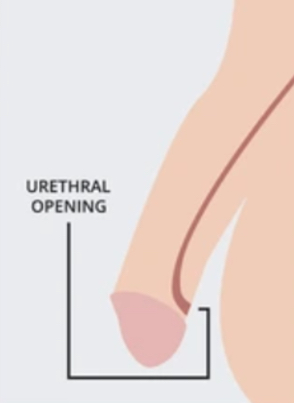
what is hypospadias?
a congenital condition where the opening of the urethra is located on the underside of the penis instead of at the tip.
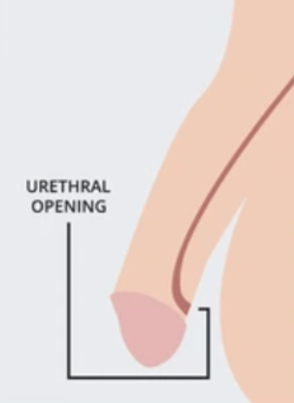
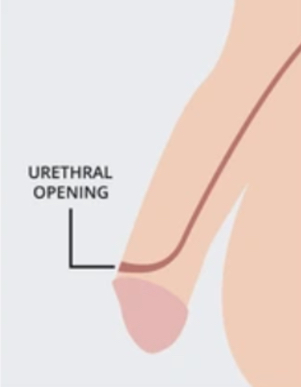
what is epispadias?
a congenital condition where the urethra ends on the upper side of the penis.
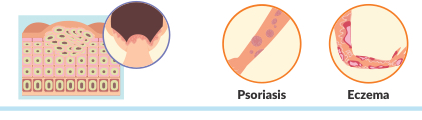
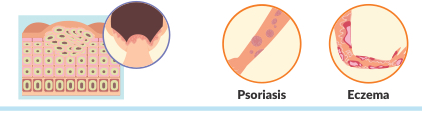
what is plaque?
Fast growth of skin cells that appear in a few small spots looking similar to dandruff.
(Psoriasis & eczema)
what is urticaria?
hives wheal, weal
Superficial skin coloring or pale skin swelling, usually surrounded by erythema that lasts anywhere from a few minutes to 24 hours (Heat hives)
what are the types of fractures?
Closed Fracture
Does not break skin
Open Fracture “Compound”
skin surface broken
tetanus
bone protrudes through —> osteomyelitis
Complete Fracture
bone is broken into pieces
Incomplete Fracture “Greenstick”
partially through bone
Spiral Fracture
common in child abuse
Oblique Fracture
bone breaks at an angle
common in ankle
Compression Fracture “Impact”
collapsed bone in front area of vertebrae
after high fall or jump
Crush “Compression” Fracture
entire collapse of vertebrae
under heavy objects
DEADLY FAT EMBOLISM
what is a hip fracture?
shortening of leg on the affected area
muscle spasms around the affected area
ecchymosis on thigh and hip
groin & hip pain w/ weight bearing
what is compartment syndrome?
extremely painful condition that happens when pressure within the muscles builds to dangerous levels - cutting off blood flow & O2, resulting in a dead limb
decreased perfusion
PAIN
Unrelieved with morphine
Not resolving with medication
Extreme pain with passive movement
PARESTHESIA
“Tingling” “burning” “numbness”
Problems moving or extending fingers or toes.
“Great difficulty”
what are PMSC used in intervention for cast & care?
Pulses: pulses - NOT pulseless
Movement: grips
Sensation: NO tingling, numbness
Capillary refill & Color:
NOT over 3 secs
NOT pale “pallor”
temperature — NOT cold or cool
what are the 6 Care P’s
Pallor, Pulse, Pain, Paresthesia, Paralysis, Pressure
what do you do for itching under cast?
Use cool air from a hair dryer to alleviate itching, but avoid inserting objects into the cast
how do you assess for circulation?
Check capillary refill, pulse, and skin temperature.
what are cast care complications?
*Hot Spots: Infection
*Compartment syndrome: decreased tissue perfusion
Pain:
unrelieved with morphine
Unresolved with medication
Extreme pain with passive movements
Paresthesia:
Tingling, burning numbness
Problems moving/extending fingers
how do you use crutches?
1. Weight on hands & arms NCLEX TIP
NOT armpits! = injury to the brachial plexus nerves
DO NOT use someone else’s crutches
2. Technique Gait
Step 1: both crutches forward WITH injured leg
Step 2: move unaffected leg forward
3 types of gaits
2 point
3 point
4 point gait: most advanced gait
“Most closely resembles normal walking”
how do we document for pressure injuries?
Document full head to toe skin assessment upon injury within 24 hours
Why do we turn patients q1-2h for pressure injuries?
To prevent tissue breakdown and promote circulation, turning patients regularly redistributes pressure on the skin and underlying tissues.
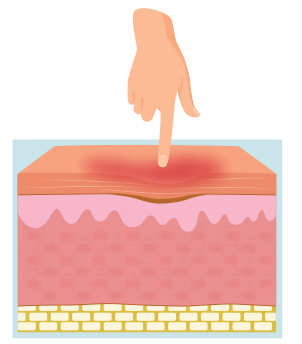
what is a stage 1 pressure injury?
1 layer damage (epidermis)
red skin is NONblanchable & NOT broken
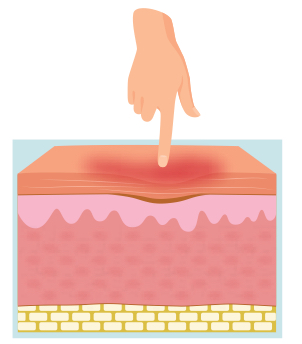
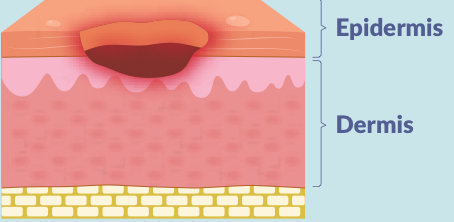
what is a stage 2 pressure injury?
2 layers of skin damage
open wound: affecting both the epidermis & dermis
wound bed is red/pink & shiny
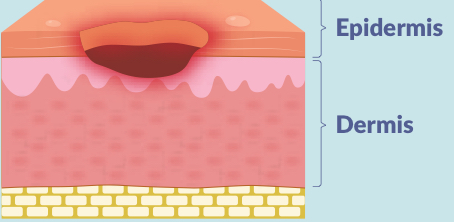
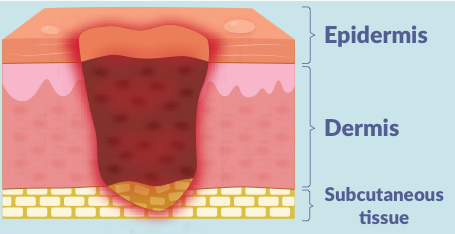
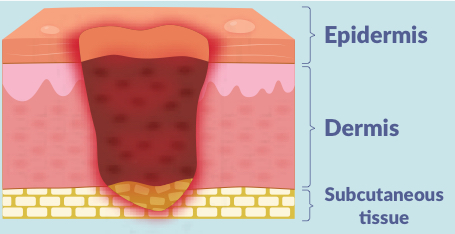
what is a stage 3 pressure injury?
3 layers of skin damage (epidermis, dermis & subcutaneous)
full thickness skin loss into the subcutaneous fat; wound may tunnel under the edges of the wound bed
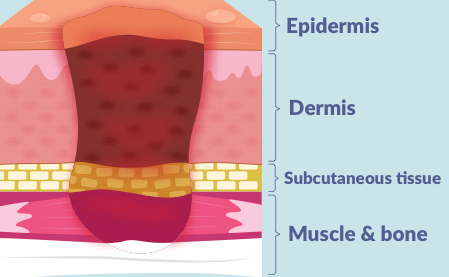
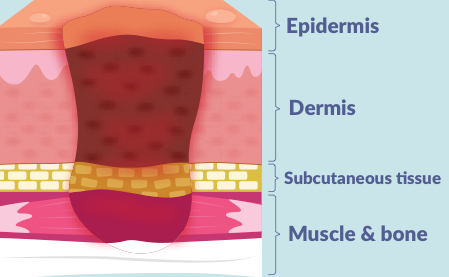
what is a stage 4 pressure injury?
4 layers of skin damage
extends all the way down into muscle, bone, or tendon
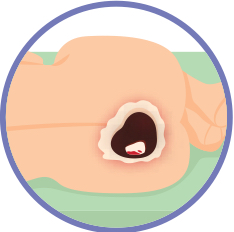
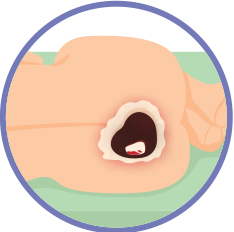
what is an unstageable pressure injury?
eschar (black/brown)
dead necrotic tissue
esCHARCOAL
slough (yellow stringy)
slough = skin of a chicken
*these wounds needs to be debrided before a stage is made
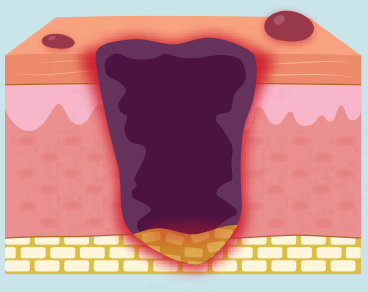
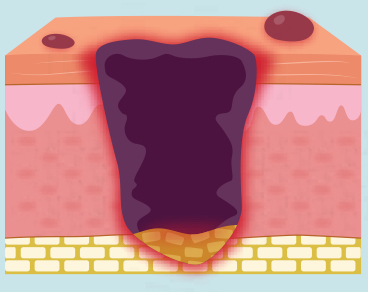
what is a deep tissue pressure injury?
the fatty tissue is injured below the skin (dark purple, & sometimes open wound)
what are characteristics for burns?
first-degree (superficial)
dry w/ blanchable redness
second-degree (partial thickness)
painful blisters
*red, moist, shiny fluid vesicles”
third-degree (full-thickness)
dry waxy white, leathery, or charred black color, non-blanchable
fourth-degree (full-thickness)
Second, you feel the MOST pain.
Third and fourth are the most deadly
what is a pre-hospital care for burns?
cool injury w/ water is the primary intervention
briefly soak area
NO ice, creams, antibiotic ointment to open skin
cover area “clean dry cloth”
clothing & jewelry removal
not adhered
for burns, do no remove…
clothing/jewerly adhering to burn prior to provider care
what is the top intervention for major burns?
IV fluids Lactated Ringers/Normal Saline only
which lab (electrolyte) is elevated after burns?
K+ potassium
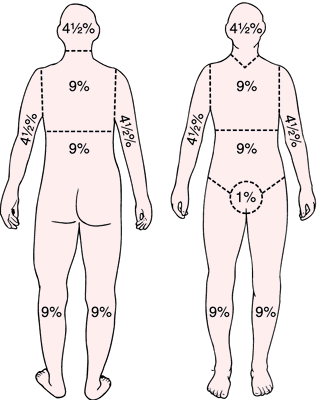
What are the rule of 9’s used for?
Total Body Surface Area: used to calculate exact amount of fluid resuscitation needed
Head and neck: 9% total (4.5% front and back)
Arms: 9% total each arm (4.5% front and back)
Legs: 18% total each leg (9% front and back)
Upper and lower back: 9% each → together 18%
Perineum: 1%
when do you worry about the urine output and when is the volume concerning?
It indicates potential kidney injury or dehydration when it falls below 30 mL/hour.
what is best indicator of effective fluid resuscitation?
Urine output reflects renal perfusion and hydration status
how do you use crutches up and down the stairs?
UPstairs
UP with Strong leg
Cane moves next
Weak leg last
DOWNstairs
Descend with cane
Weaker leg down
Strong leg
how do you use a cane?
Stronger side HOLDS the cane
Move cane 1st, weak leg 2nd
2 points of support on the floor
how do you care for minor burns?
CCC
Cool water, cover the area, clothing removal
C - Cool water
Briefly soak area
NO ice, creams, antibiotic ointment to open skin
C - Cover the area - “Clean dry cloth” → to prevent infection and more damage
C - Clothing & jewelry removal
Not adhered
HCP remove anything sticking to the skin
what are major burns treatment?
Assessment of Fluid Resuscitation
Urine output
30 mL/hr or MORE
Blood pressure
(90/systolic or MORE)
Heart rate less than 120/min
what is the average hematocrit in women?
36%-44%
what is the average hematocrit in men?
41%-50%