Chap 15D - Arenes (Methylbenzene)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
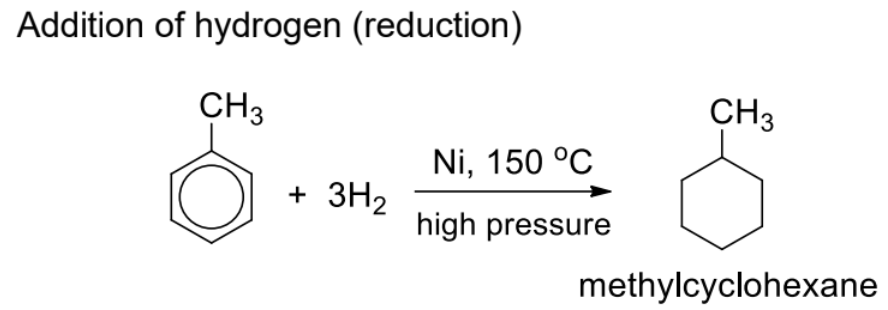
Describe addition to hydrogen (reduction)
Do not use this reaction unless specified by the question
The resonance-stabilised benzene ring is to be preserved at all times
Describe free radical substitution (reagents and conditions, excess methylbenzene VS X2)
Methylbenzene has two reactive sites
Benzene ring, which undergoes electrophilic substitution
Methyl side-chain, which can undergo free-radical substitution and oxidation to benzoic acid
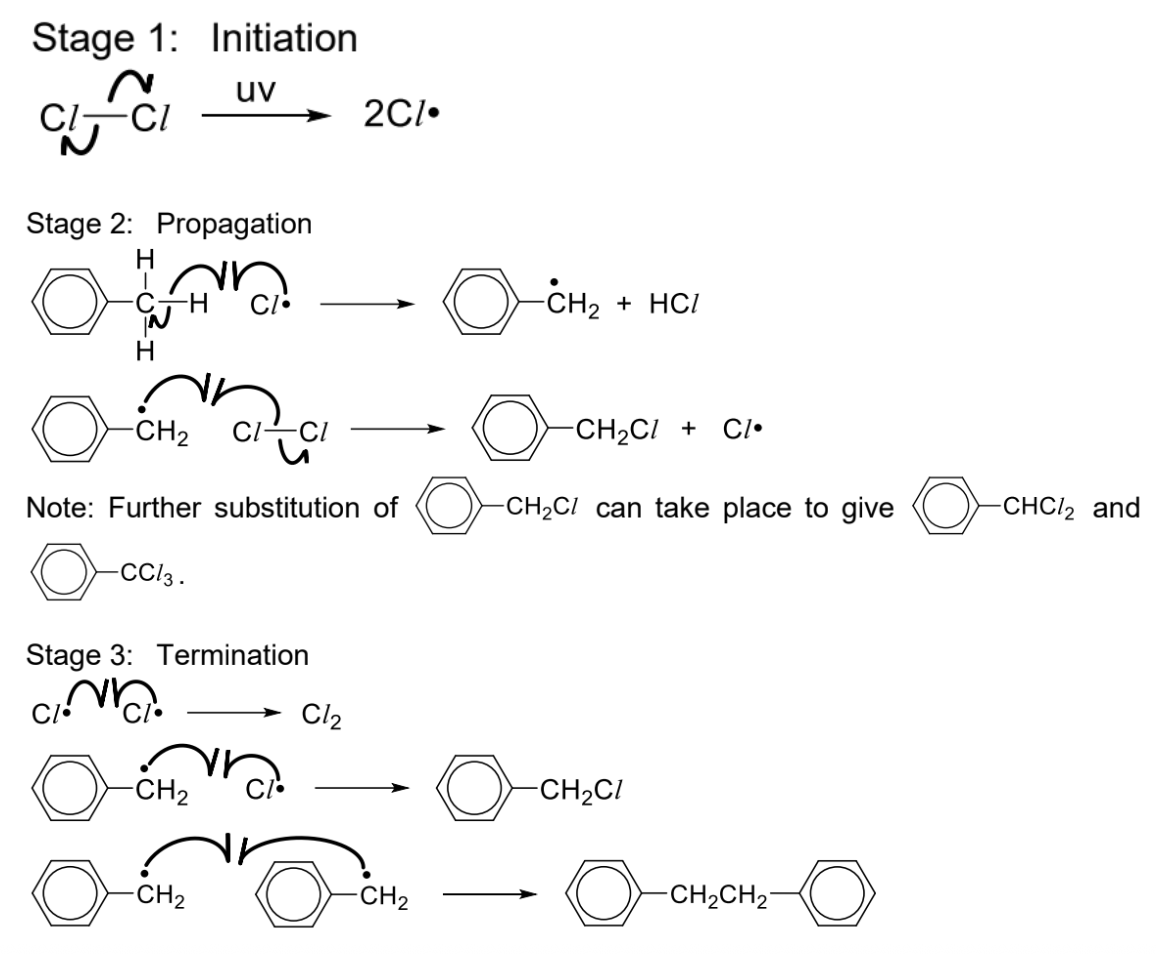
Reagents and conditions: X2 (Cl2 or Br2), UV light at room temperature
In excess methylbenzene, mono-substituted product is obtained
In excess X2, di- or tri- substituted products are obtained
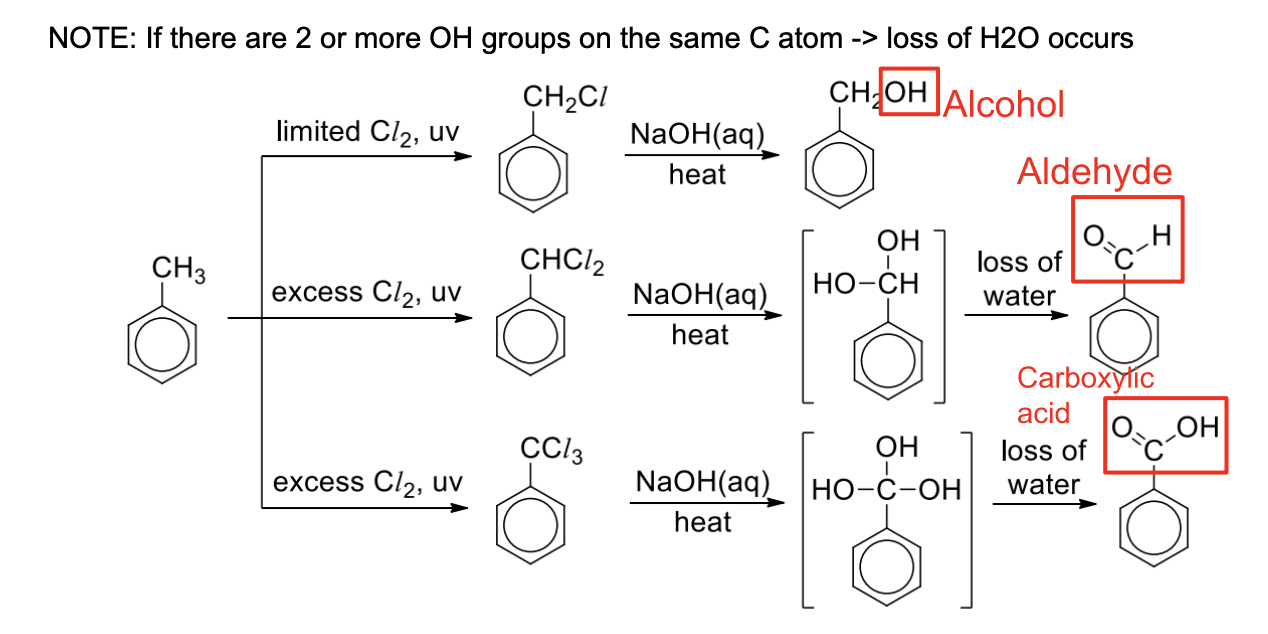
All the products formed can be hydrolysed using aqueous NaOH and heat to give alcohols, carbonyl compounds or carboxylic acids
Describe possible produces when methylbenzene reacts with limited CI2 VS excess CI2 → then NaOH + heat is added
Draw free radical substitution mechanism (between methylbenzene + limited CI2)
Describe methylbenzene reacting with weak oxidation agents + reagents
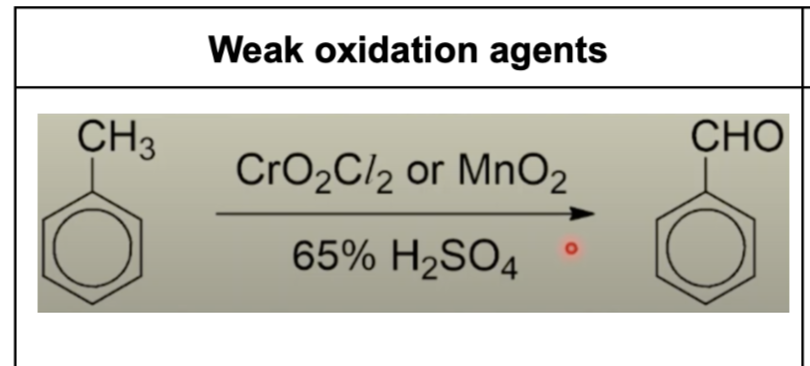
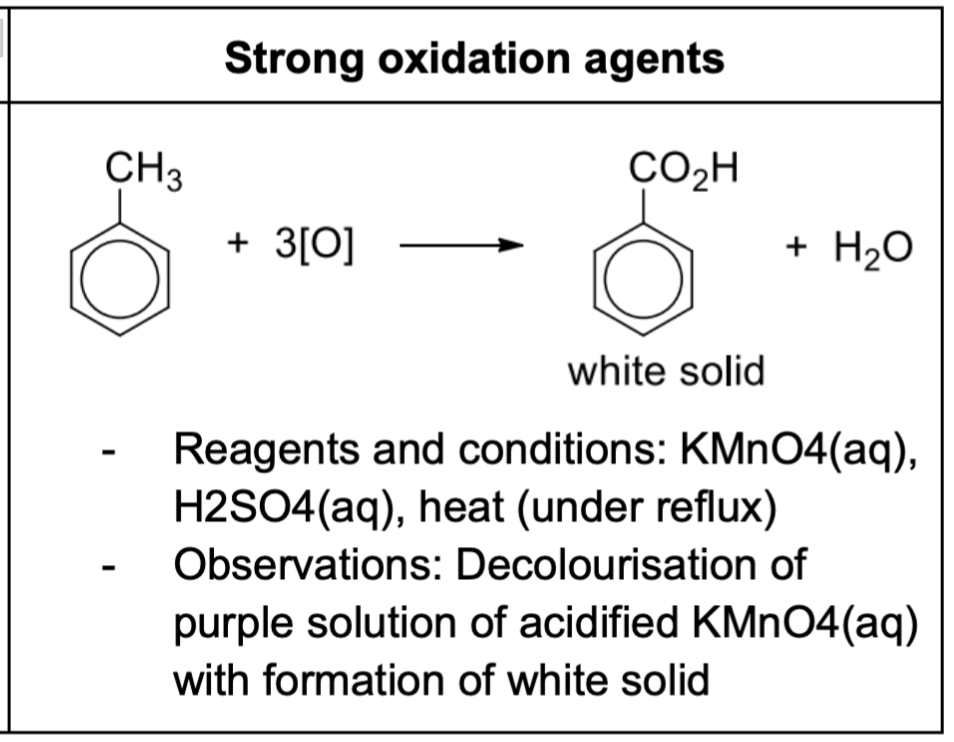
Describe methylbenzene reacting with strong oxidation agents + reagents + observations
Acidic conditions: benzoic acid produced
Alkaline conditions: benzoate ions obtained
This is a chemical test to distinguish between benzene and methylbenzene
Potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, is unable to oxidise the side chain of benzene
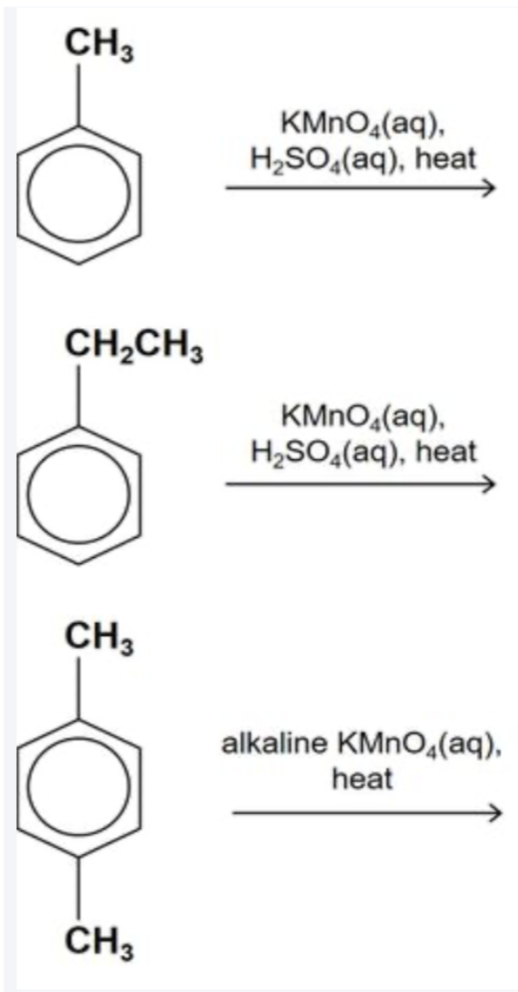
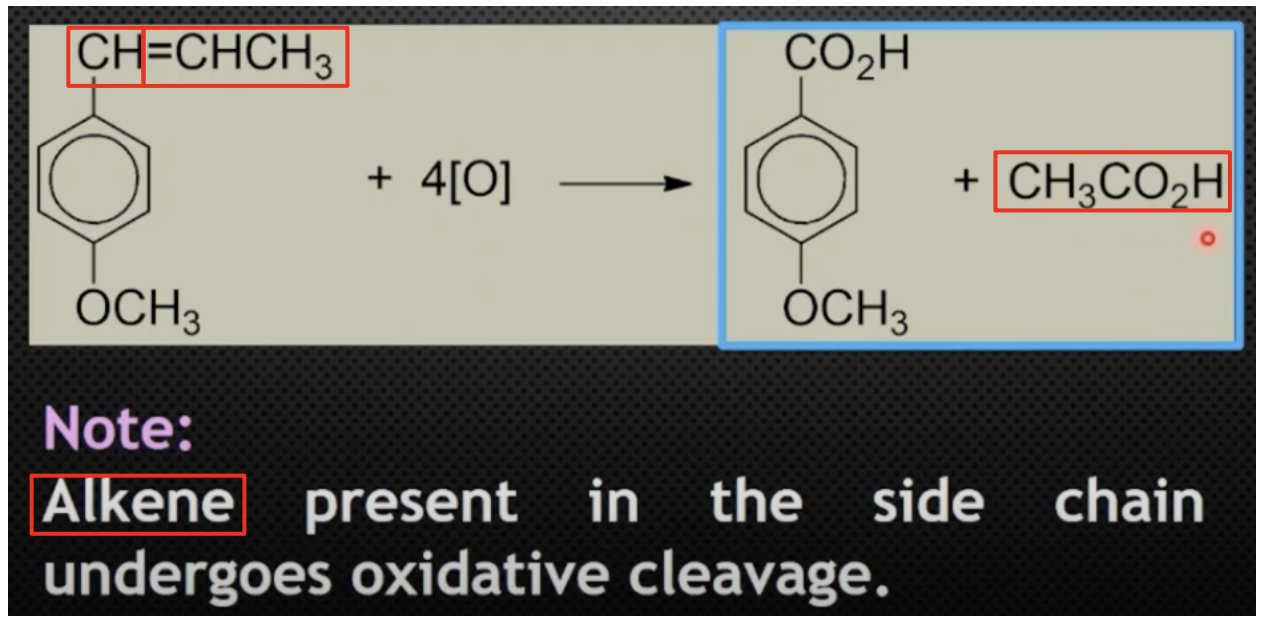
Describe these reactions
Position of the carboxylic acid group gives information on the location of the original alkyl side-chain
Eg. Benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid = alkyl groups were originally at the 1st and 4th carbons of the benzene ring
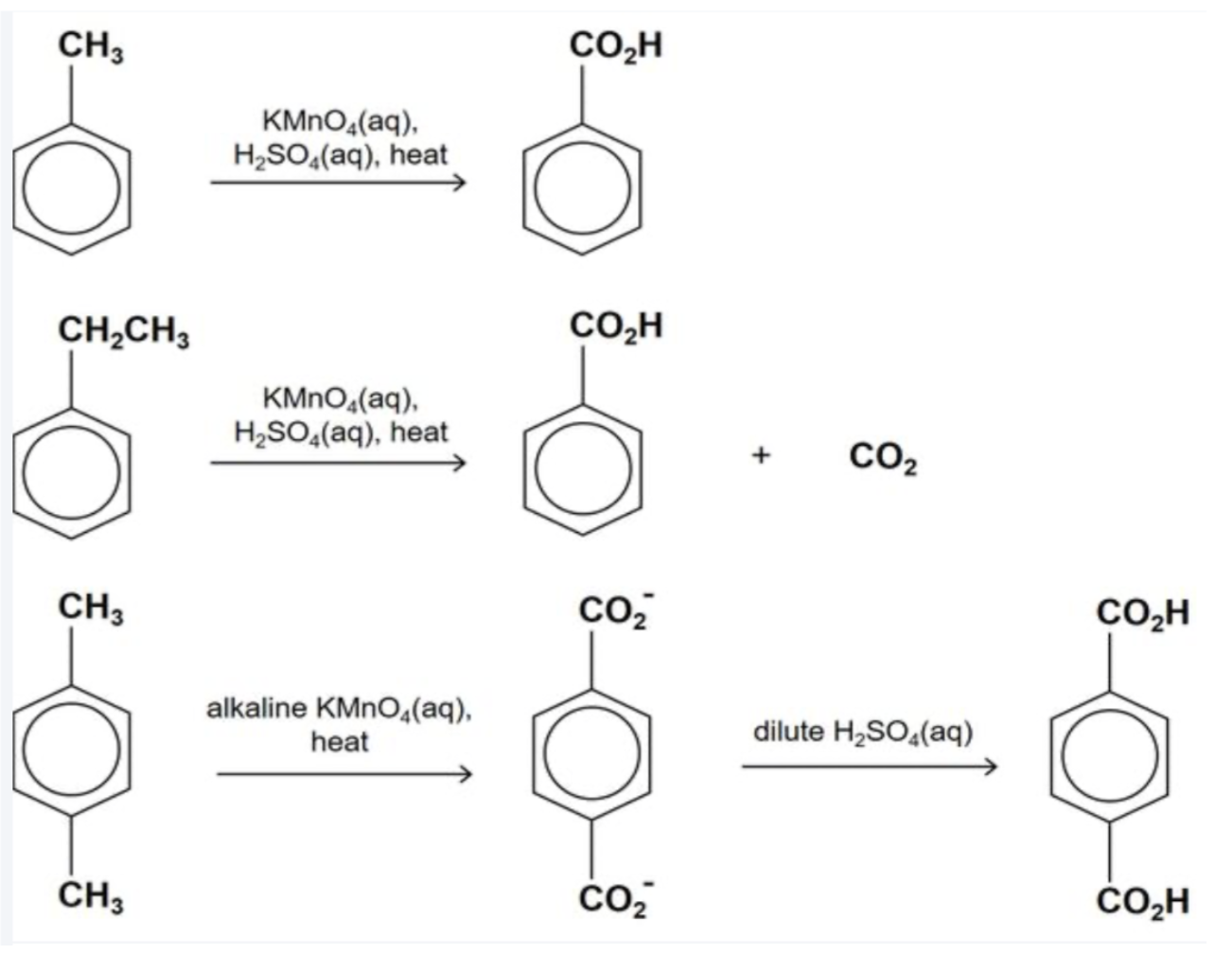
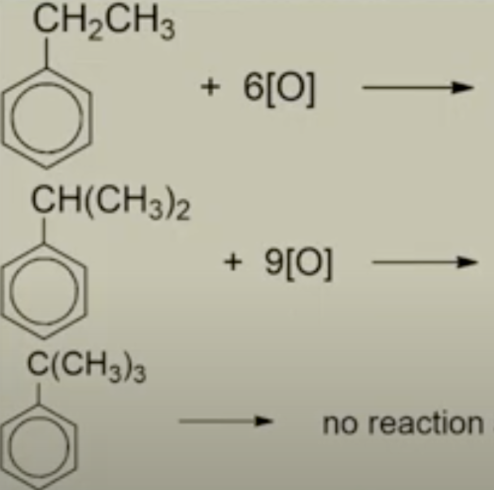
Describe these reactions + products
Strong oxidising agents like hot acidified KMnO4(aq) is capable of oxidising the longer side chains with a benzylic hydrogen (H atom bonded to C atom adjacent to the benzene ring) to form benzoic acid (white solid) with effervescence of CO2
The rest of the side chain is destroyed, forming carbon dioxide and water
Describe reaction between methylbenzene + hot alkaline KMnO4
Hot alkaline KMnO4 gives the salt of carboxylic acid which must be acidified before solid benzoic acid can be obtained
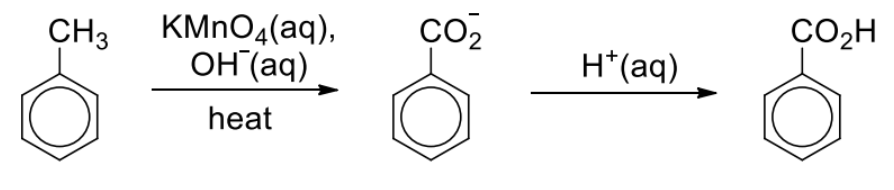
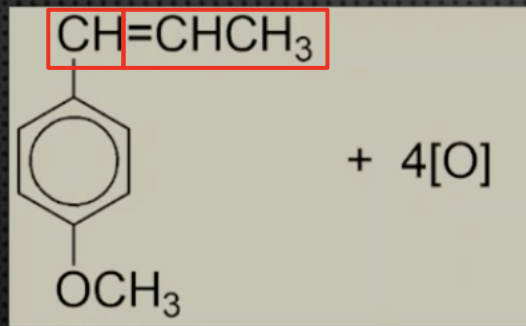
Describe this reaction