IB biology HL - classification and cladistics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
terminal branch
endpoint of a cladogram which represents one group - AKA individual species within a clade
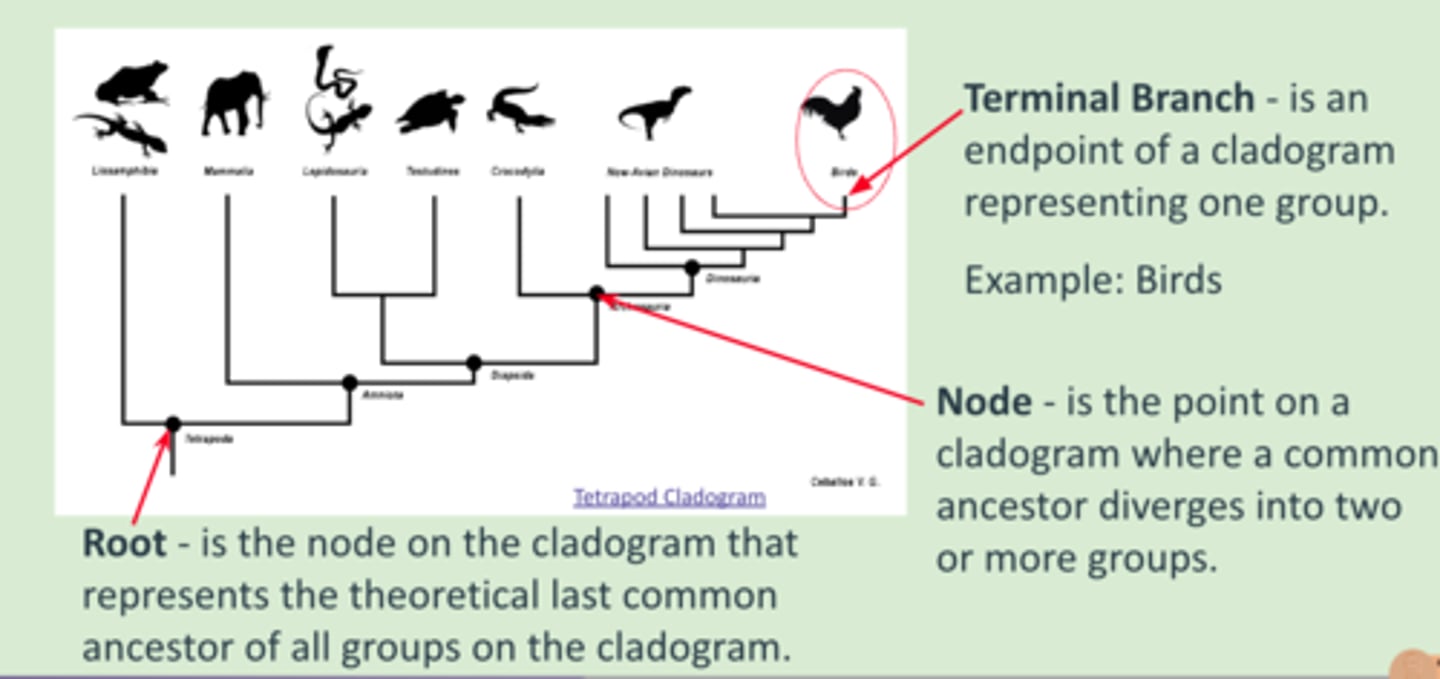
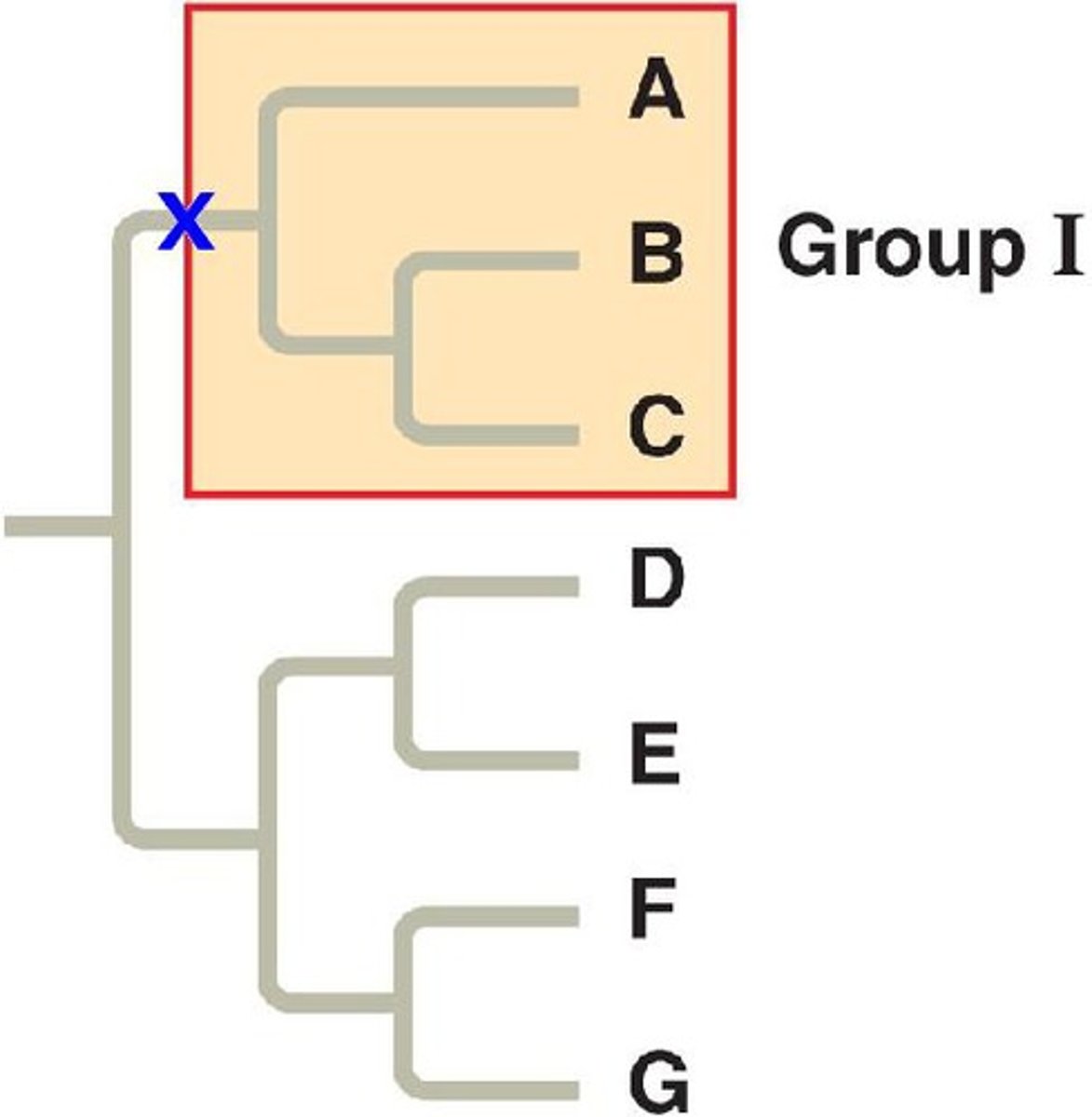
clade
A group of organisms and their common ancestor
nodes cladogram
the branching points on a cladogram (T). This represents the point at which the ancestral species split to form two or more clades
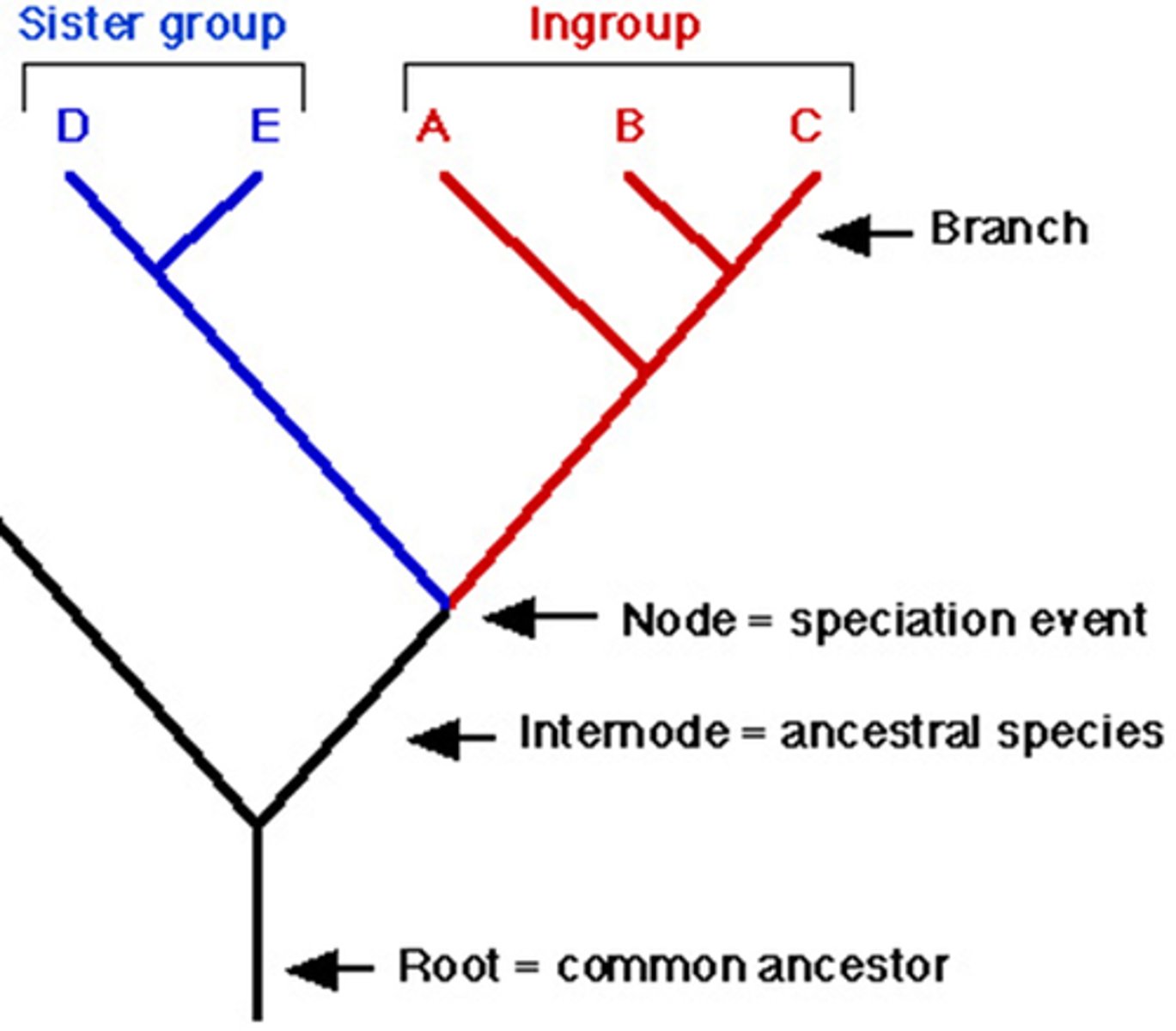
root
base of cladogram - This represents the common ancestor of all the clades
Why were species in the Figwort family first grouped together?
Due to their physical characteristics
What led to the reclassification of over 5000 species in the Figwort family?
Genome sequences revealing they did not share a common ancestor
what causes gradual divergence
the accumulation of mutations
what are the 3 domains
Eukaryota (plants, animals, fungi) , Bacteria (cyanobacteria, heterotrophic bacteria) , and Archaea (thermophiles and halophiles)
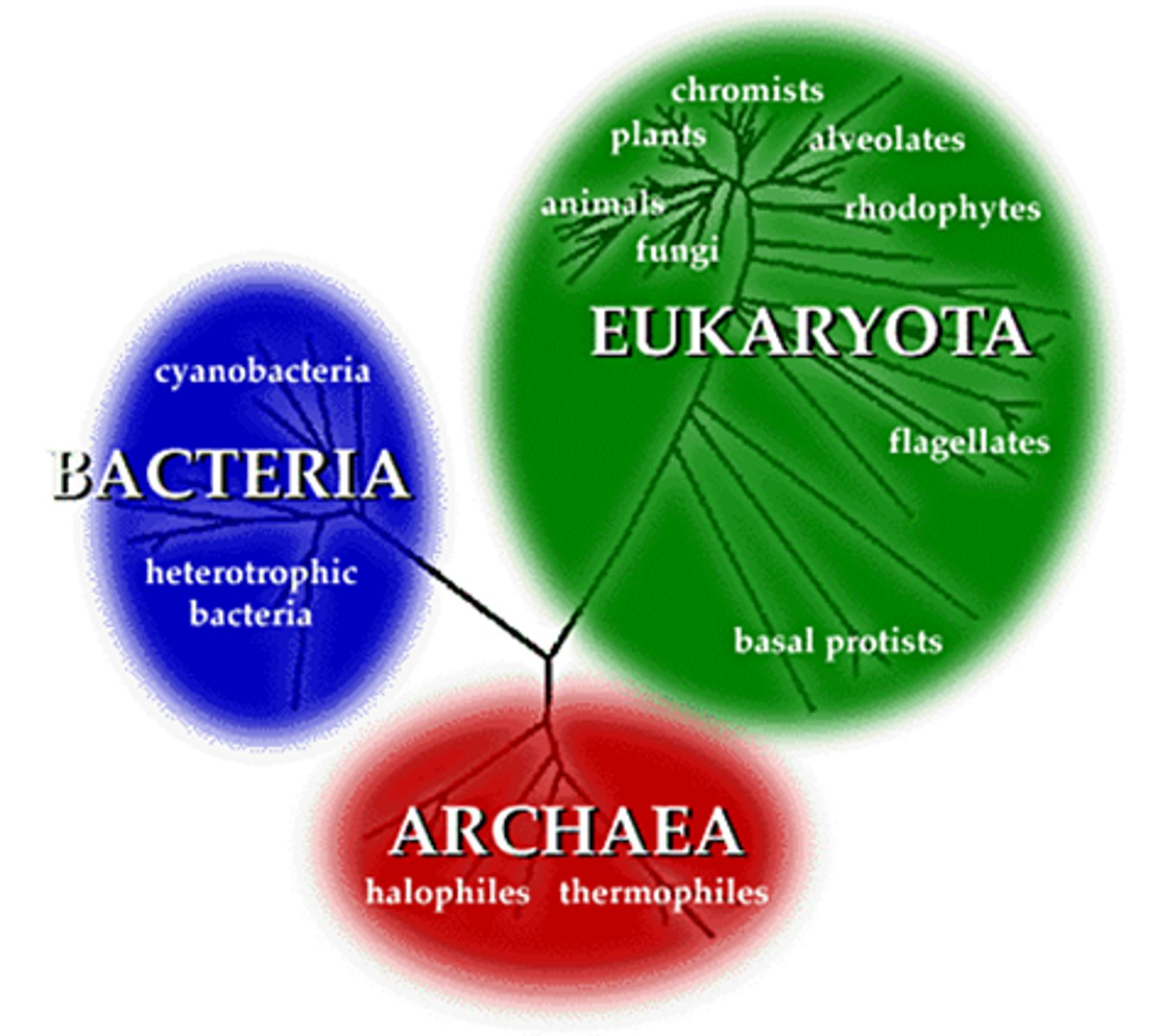
what made the 3 domains, eubacteria, archaebacteria, and eukaryote
Even though eubacteria and archaebacteria are both prokaryotes (lack a nucleus), scientists discovered there were actually more similarities between archaebacteria and eukaryotes than there was to the other prokaryote (eubacteria)
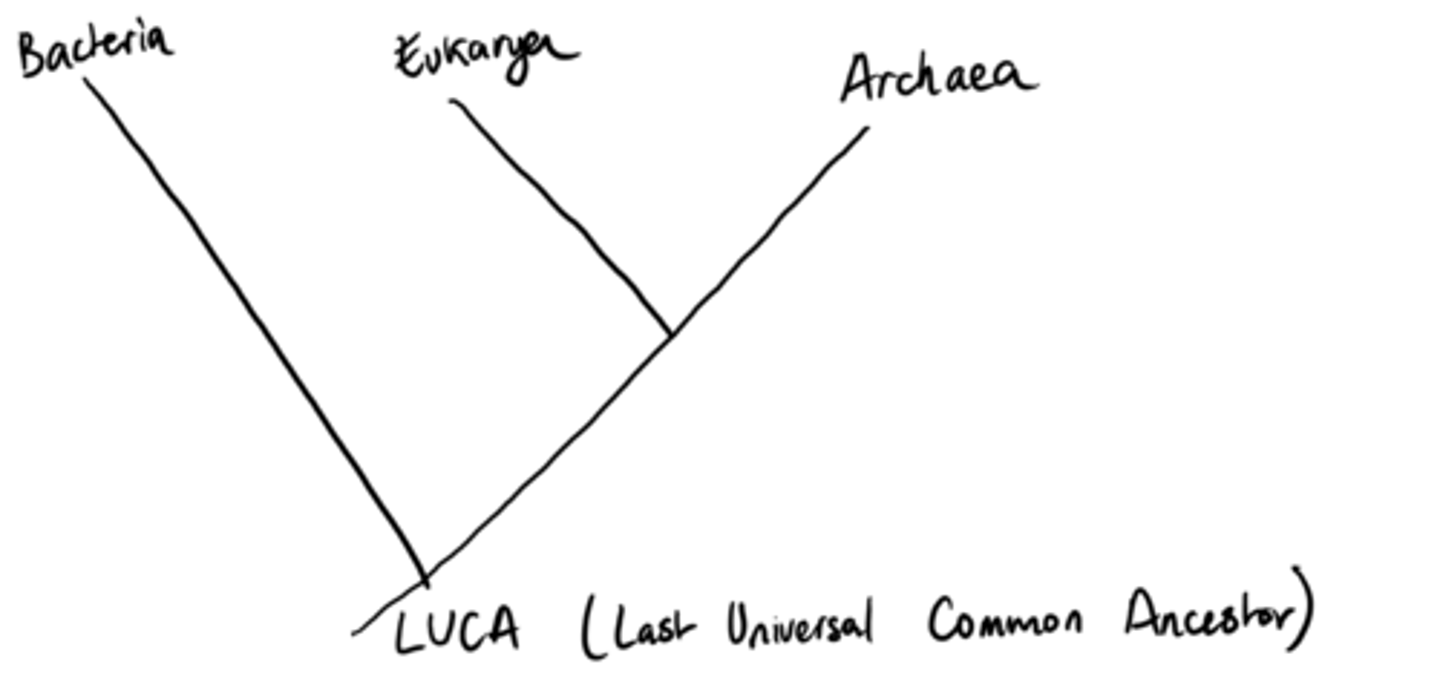
What is a molecular clock?
method used by researchers that uses mutation rates in DNA to estimate the length of time that species have been evolving from their common ancestor using number of differences in the base sequences
why is the molecular clock flawed
because mutation rates can vary due to other factors like mutagens whihc may cause mutation rate to accelerate
what causes mutations / can accelerate them
Mutagens (Radiation and Chemicals), and Errors as a gene is being copied
what is introgression
when fertile offspring of a cross between species then goes on to breed only with members of one of its parents species
why is it inaccurate to only look at the physical characteristics of an organism when classifying it
because physical similarities don't mean that the organisms share a common ancestor which is why scientists have developed the method to look at genome sequences and amino acid sequences
What is binomial nomenclature?
two word naming system (Genus species)
why do we classify organisms
- To identify species
- accurately determine # of known species
- Predict characteristics
- Find evolutionary links
- identify and treat new diseases quicker
taxonomic levels in order
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (did king Phil come over for great sex)
what is classfication
placing organisms in groups based on common ancestry and/or shared traits
what is the boundary paradox?
since divergence is gradual, it is hard to tell when things are different enough to be placed in separate groups
why is their difficulty classifying organisms into the traditional hierarchy of taxa
Some taxonomists might feel that two organisms are similar enough to be part of the same family while another might feel there is enough evidence to be the same genus
what is taxonomy
the science of classifying, describing and naming organisms
what is a taxa
group or level of organization into which organisms are classified
what are advantages of corresponding classification to evolutionary relationships
allows to make predictions on new species characteristics based off the characteristics of the ancestor E.G. mammal warm blooded, produces milk
what are the 2 conditions that classification must satisfy
1) every organism sharing the same common ancestor has to be in the same taxonomic group
2) in each group, all of the species evolved from the sa,e common ancestor
why do common ancestors often not exist anymore
Common ancestors often do not exist bc they have
evolved into modern species or have become extinct
which mutations occur at a predictable rate
Mutations in DNA that persist and are inherited
If the DNA base sequences or two species are similar, what does it mean?
that few mutations have occurred, and therefore the species only diverged relatively recently
what do the length of the lines separating species on cladograms often represent?
often used to represent the estimated time since they diverged
The molecular clock assumes that the mutations are not accelerated by selection pressures in the environment, population size amongst others
what are morphological traits
physical characteristics of an organism
What is wrong with a fixed ranking of taxa?
its arbitrary- doesn't show gradation of variation
What does cladistics determine?
evolutionary relationships by looking at nucleic acids and amino acid sequences
What are the rules regarding binomial nomenclature?
1. the genus name starts with a capital letter
2. species name starts with a lowercase
3. Is always in italics, but when handwritten its underlined
4. After already being used once in a text, the Genus can be abbreviated to the first letter