Species Interactions (2)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Population
a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time, and are capable of interbreeding
Ecosystem
A community of interdependent organisms and the physical environment with which they interact.
Biotic factors
all the living components of an ecosystem such as plants, animals, fungi, bacteria and viruses, and all the interactions between the living components.
Producers
Plants that produce eat their own food
Consumers
animals that eat plants and other animals
Decomposers
organisms that break down the waste of other organisms
Abiotic factors
non-living factors that affect organisms (temperature, sunlight, water, salinity)
Niche
the particular set of abiotic and biotic conditions and resources on which an organism or a population depend
the ecological role of a species in an ecosystem.
Niches cannot overlap —> competition
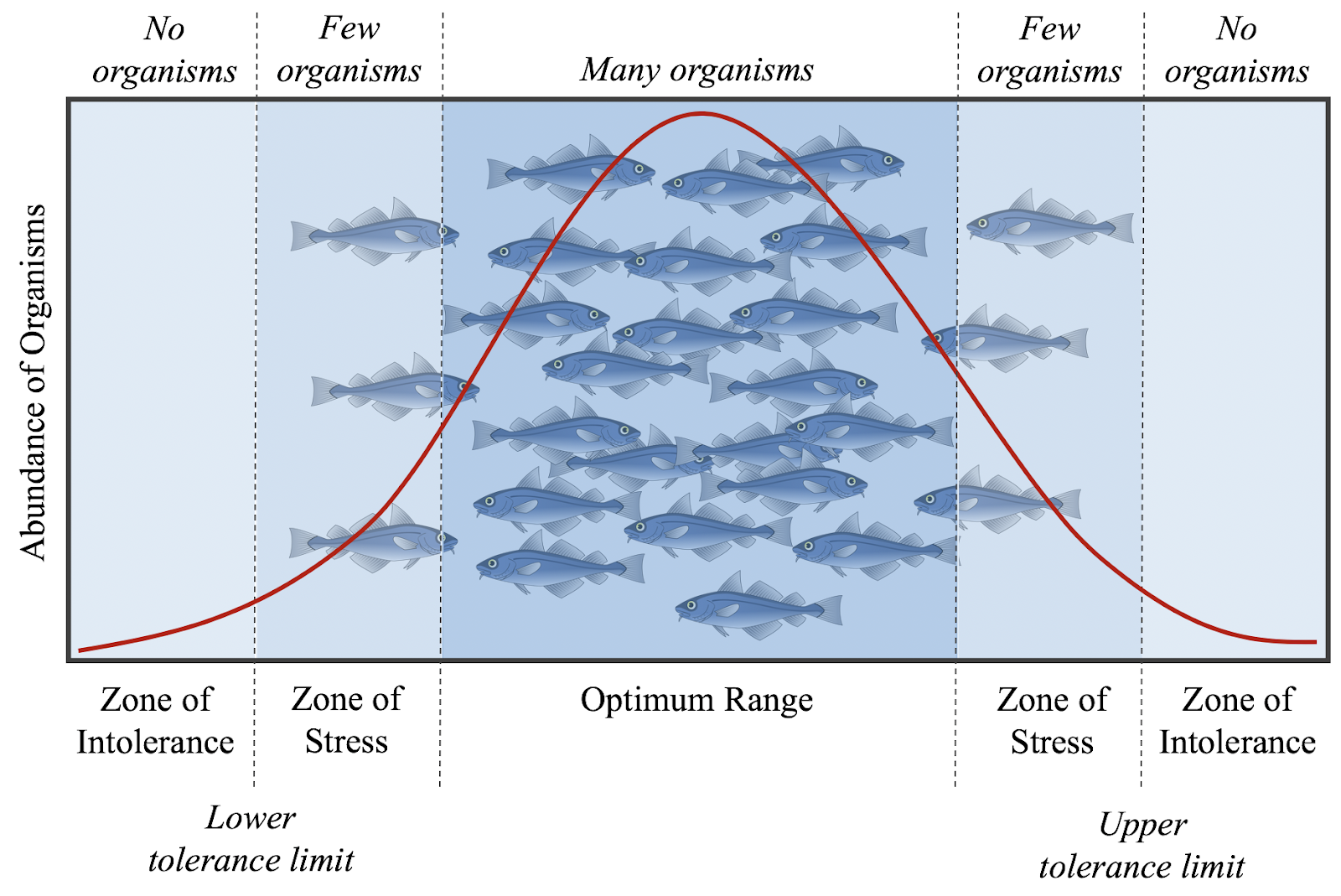
Graph of environmental gradient
optimal range —> where organisms are abundant
tolerance range (range of physiological stress) —> less organisms
range of intolerance —> organisms absent
Types of species interactions (6) -
Predation
Herbivory
Parasitism
Mutualism
Disease
Competition
Predation (3 points)
When an organism acts as the predator and feeds on another organism, called the prey
The predator depends on the prey for its own survival.
The population size of the prey is controlled by the predators (negative feedback)
Herbivory
An interaction between species, where organisms, often animals, feed on plants.
Parasitism
a one-way relationship between two species where one, the parasite, takes resources from the host within giving anything in return. —> the parasite does not want the host to die
Mutualism
an interaction where both species benefit from one another and neither suffers. Mutualism is needed for ecosystems functioning and regeneration
Disease
a departure from the normal state of functioning of any living organism and is marked by symptoms of illness
Can be caused by other organisms: pathogens: An organism or substance that causes disease in another organism.
Competition
where organisms compete for a resource that is in limited supply
Intraspecific competition
occurs when members of the same species compete for limited resources
Interspecific competition
occurs when members of different species compete for limited resources
Symbiotic relationships
relationships between organisms that live together
Ectoparasites
parasites living on the outside of the host (tick)
Endoparasites
parasites living on the inside of the host (tapeworm)
Competitive exclusion
interspecific competition can result in one species outcompeting the other
Selective pressure
an evolutionary force that causes a particular phenotype to be more favorable in certain environmental conditions
Community
A group of interacting populations of different species living within an ecosystem

Ecosystems obtaining energy
Producers supply energy to consumers in ecosystems
Energy is neither created nor destroyed —> producers get energy get, CO2, create glucose, consumed by consumers, then produce out CO2.