AP Physics 2 Formula Test
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Mass-Energy Equivalence
E = mc2
Absolute Pressure
Pobs = Patm + Pguage
Buoyant Force
Fg = PfVfg
Density
ρ = m/V
Bernoulli’s Equation
P1 = pgh1 + 1/2pv12 = P2 + pgh2 + 1/2pv22
Formula definition of Work
W = Fd = |F||d|cos(ø)
Frictional Force
Ff = Fnμ
Frictional Force on an incline
Ff = mgcos(ø)μ
Acceleration
a = ∆V/t = (V-Vo)/t
Average Speed
S = dT/tT
Velocity
V = ∆x/t
Acceleration of a mass sliding UP an incline, with friction
a = gsin(ø) + gcos(ø)μ
Acceleration of a mass sliding DOWN an incline, with friction
a = gcos(ø)μ - gsin(ø) or gsin(ø) - gcos(ø)μ
Forgotten Power Equation
P = FV
Newton’s Second Law of motion
∑F = ma
Torque
𝜏 = rF = |r||F|sin(ø)
Kinetic Energy
K = 1/2mv2
Hooke’s Law
Fs = -kx
Gravitational Potential Energy (on Earth)
Ug = mgh
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
Fg = G(mM/r2)
Centripetal Acceleration
ac = v2/r
Acceleration due to gravity at the surface of a planet mass M and radius R
g = G(M/r2)
Momentum
p = mv
Impulse (two formulas)
J = Ft = mv - mvo
Weight
W = Fg = mg
First Kinematic
V = Vo + at
Second Kinematic
∆x = Vot + ½ at2
Third Kinematic
V2 = Vo2 + 2a∆x
Spring Potential Energy
Us = ½ kx2
Speed
S = d/t
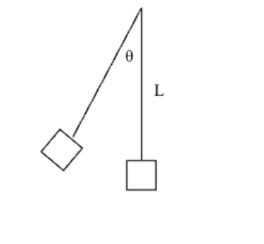
Height of the block in terms of ø and L
h = L - Lcos(ø)
Three formulate for Power Definition of Power
P = W/t
Gravitational Potential Energy (in general)
Ug = -G(mM/r)
Units of Momentum
kg m/s
Units of Energy (both)
J = kg m2/s2
Units of the spring constant k
N/m
Units of Power (both)
W = J/s
Units of Force (both)
N = kg m/s2