Nuclear Energy
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Nuclear energy
Energy released by nuclear fission or fusion
Example of Radioactive Isotope
Uranium (U-235) decays over time to lead (Pb-207)
5 steps of Nuclear Fuel Cycle
Neutron bombardment
Nucleus splits into atomic fragment
And free neutrons
Free neutrons bombard-235 nuclei
More free neutrons released
How Electricity is Produced
Nuclear fission → Heat → Steam → Turbine → Generator → Electricity → Cooling → Recycle
A type of nuclear fission in which non-fissionable U-238 is converted into
fissionable Pu-239
Promising for energy, but
safety concerns
Mixed Oxide Fuel
Combination of uranium and plutonium oxides, can reprocess spent fuel from other reactors
Common in Europe
Pros of Nuclear Energy
Less of an immediate environmental impact compared to fossil fuels
Carbon-free source of electricity
May be able to generate H-fuel
Cons of Nuclear Energy
No insurance that an accident will not happen
Generates radioactive waste
Many steps require fossil fuels (mining and disposal)
Expensive
Cost of Electricity from Nuclear Energy
is very high
Electricity from Nuclear Energy
Affordable due to government subsidies
US: 20 %, France: 75 %, Taiwan: 8 %
Three Mile Island (USA)
Chernobyl (Ukraine)
Fukushima Daiichi (Japan)
Three-Mile Island accident
1979: most serious reactor accident in US
50% meltdown of reactor core
Containment building kept radiation from escaping
No substantial environmental damage
No human casualties
12 years and 1 billion dollars to repair
Elevated public apprehension of nuclear energy: Led to cancellation of many new plants in US
Chernobyl (1986) accident
Worst accident in history
1 or 2 explosions destroyed the nuclear reactor => Large amounts of radiation escaped into atmosphere
Spread across large portions of Europe
Radiation spread was unpredictable and uneven
4,000 deaths attributed to plant explosion => Mostly due to cancer
Death toll is 10,000 – 100,000
Fukushima Daiichi (2011) accident
March 11, 2011 - caused by magnitude 9.0 earthquake and ensuing tsunami
Disrupted power systems that pump cooling water to reactor cores and spent fuel rods
Increased radiation in local water and food supplies => May limit seafood catches for decades
2nd worst accident in history
Earthquake & Tsunami combined with human negligence
Poor management by TEPCO
Several partial meltdowns
Japan: 3rd World rank
54 reactors in 17 plants
Interactions Nuclear Plants and Climate change
Cooling requires huge quantity of water
Installation along large rivers and oceans
Increase vulnerability of nuclear plants
Threatens electricity supply
Droughts
Sea rise
Jellyfish
31 countries use nuclear energy to
create electricity
These countries have access to spent fuel needed to
make nuclear weapons
Safe storage and handling of these weapons
is a concern
Low-level radioactive waste
Radioactive solids, liquids, or gases that give off small amounts of ionizing radiation
Produced by power plants, research labs, hospitals and industry
States responsible for all waste they generate
High-level radioactive waste
Radioactive solids, liquids, or gases that give off large amounts of ionizing radiation
Temporary storage solutions - In nuclear plant facility (require high security)
Under water storage
Above ground concrete and steel casks
Radioactive Wastes
Low-level radioactive waste
Radioactive solids, liquids, or gases that give off small amounts of ionizing radiation
Produced by power plants, research labs, hospitals and industry
States responsible for all waste they generate
High-level radioactive waste: Radioactive solids, liquids, or gases that give off large amounts of ionizing radiation
Temporary storage solutions - In nuclear plant facility (require high security)
Under water storage
Above ground concrete and steel casks
Need approved permanent options soon.
Map of radioactive matters and wastes in France
Old uranium mine
Nuclear plant (electricity)
Radioactive matter and waste storage
1.54 million tons of radioactive matters and wastes
Case-In-Point Yucca Mountain
70,000 tons of high-level radioactive waste
Tectonic issues have been identified
Abandoned in 2012
Decommissioning Nuclear Power Plants
Licensed to operate for 40 years: Several have received 20-year extensions
Power plants cannot be abandoned when they are shut down
Licensed to operate for 40 years
Several have received 20-year extensions
Power plants cannot be
abandoned when they are shut down
Three solutions of Decommissioning Nuclear Power Plants
Storage
Entombment
Decommissioning (dismantling) costs billions, 10 years
Taiwan Nuclear power
Import 99 % of its energy
14 % of electricity comes from nuclear power
6 reactors
1 plant currently in construction
2 reactors in a 30 km radius from Taipei
Nuclear Waste Storage on Orchid island
High seismic activity
Most dangerous nuclear plants in the world
Attitudes Towards Nuclear Power
Generally a major case of mistrust on the part of the public towards pro-nuclear power scientists and politicians
NIMBY - Not In My BackYard: Citizens to not want a nuclear facility or waste disposal site near their home
Dad- Decide, Announce, Defend
Pronuclear advocates
Based on the science, not fears
NIMBY - Not In My BackYard
Citizens to not want a nuclear facility or waste disposal site near their home
Fuel
isotopes of hydrogen
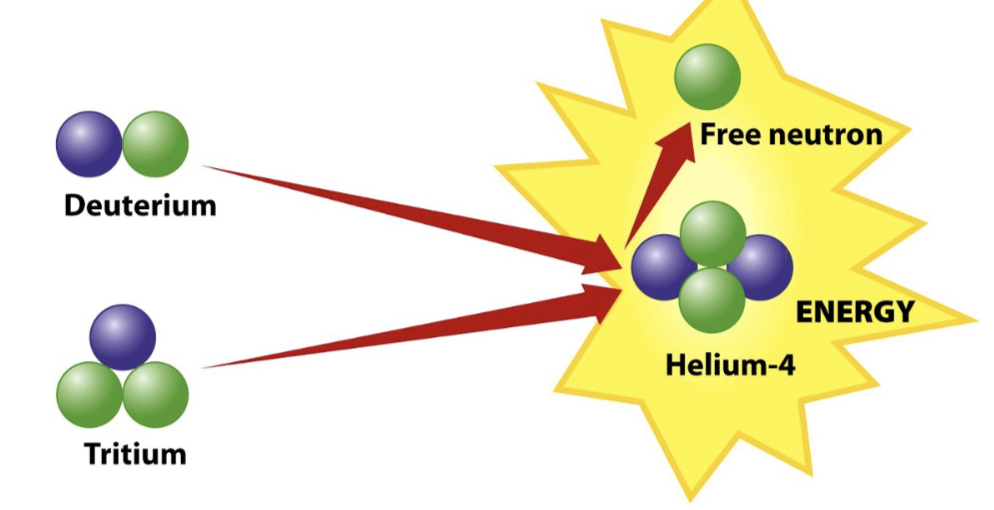
Way of the Fusion future
Produces no high-level waste
Fuel is hydrogen
Still in research phase
Problems of Fusion
It takes very high temperatures (millions of degrees) to make atoms fuse
Confining the plasma after it is formed
Scientists have yet to be able to
create energy from fusion