Cross Sectional Anatomy
1/332
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
333 Terms
List the 9 Addison’s regions. Which one are sonographers most likely to use as a reference in imaging the abdomen?
Right and Left Hypochondrium
Epigastric
Right and Left Lumbar
Umbilical
Right and Left Iliac Fossa
Hypogastrium
The most common region to use would be the epigastrium. The majority of organs we scan (liver, pancreas, GB, major vessels) are contained in the epigastrium. Can be more useful to use Addison’s 9 instead of 4 quadrants bc these organs do not remain in just one quadrant.
When you are looking at a CT scan, it is as if you are looking
from the feet up to the head
On a CT, you will see a “hat” on top of each kidney. This is called the
adrenal gland
Which organ is NOT an organ found in the pelvic cavity?
kidneys
A gallbladder stone will appear echogenic on ultrasound but will not be echogenic on CT.
false
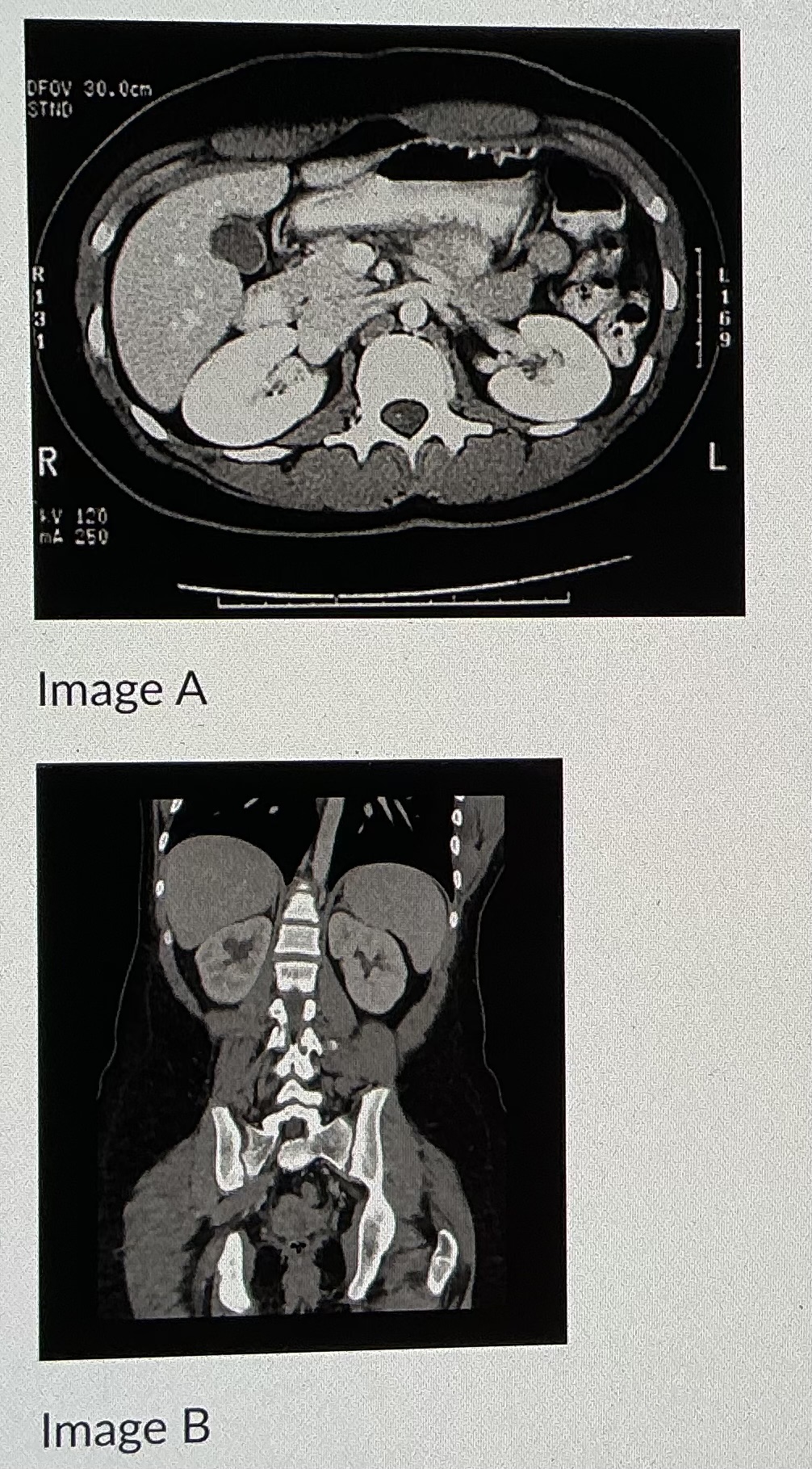
Image B shows an image taken in what plane
coronal
List the 3 layers of the arterial wall, what type of cells/tissue they are composed of, and describe the difference when compared to a vein wall.
tunica intima: endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells
tunica media: thickest layer, thicker in arteries than veins; smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts
tunica adventitia: thickest layer in veins; fibroblasts, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, nerve cells, and immune cells
List the three sections of the entire aorta (not just the abdominal aorta)
ascending aorta
aortic arch
descending aorta / thoracic aorta
(abdominal aorta)
List the anterior branches of the aorta
celiac artery/axis/trunk
superior mesentary artery
inferior mesentary artery
median sacral iliac artery
Normal range for the aorta measurements
Should not exceed 3 cm at any section
Proximal: 2-2.6 cm
Mid: 1.6-2.4 cm
Distal: 1.1-2.0 cm
What is the most common cause of portal hypertension?
cirrhosis
What are varices?
Dilated vessels in venous circulation.
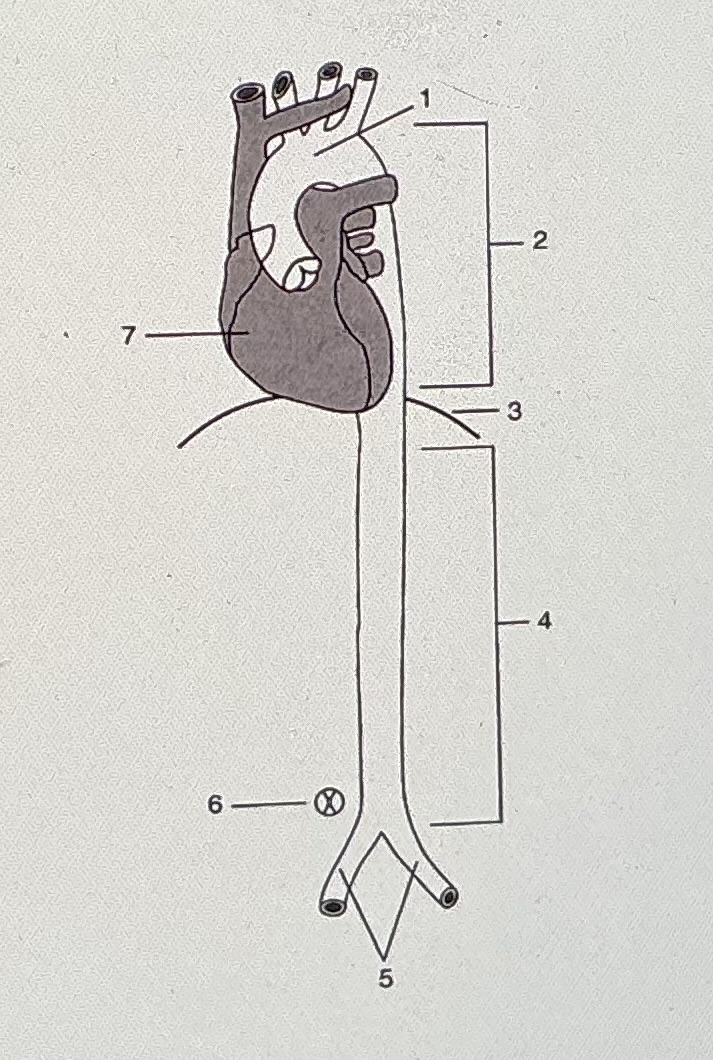
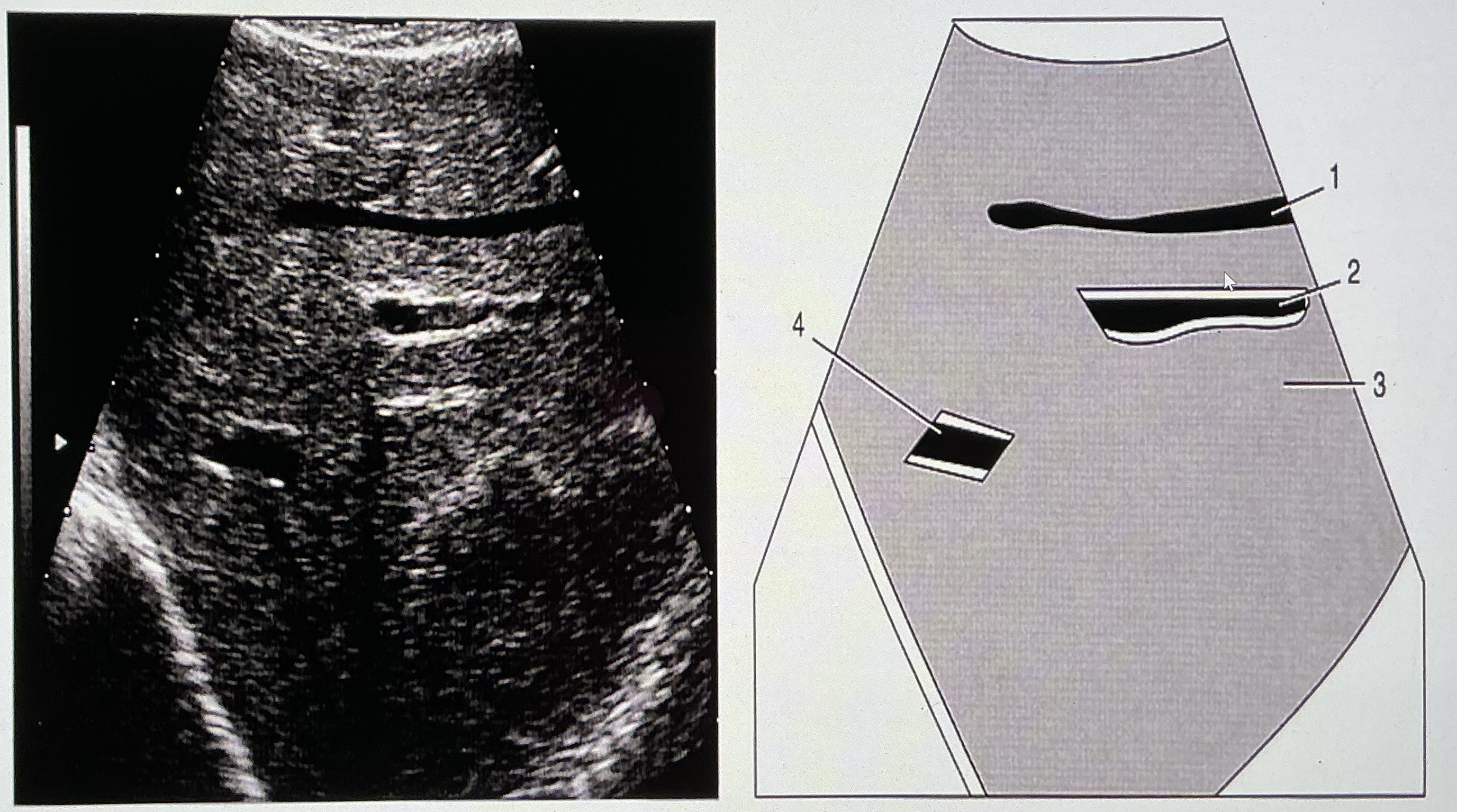
#1 Indicates
none of the above
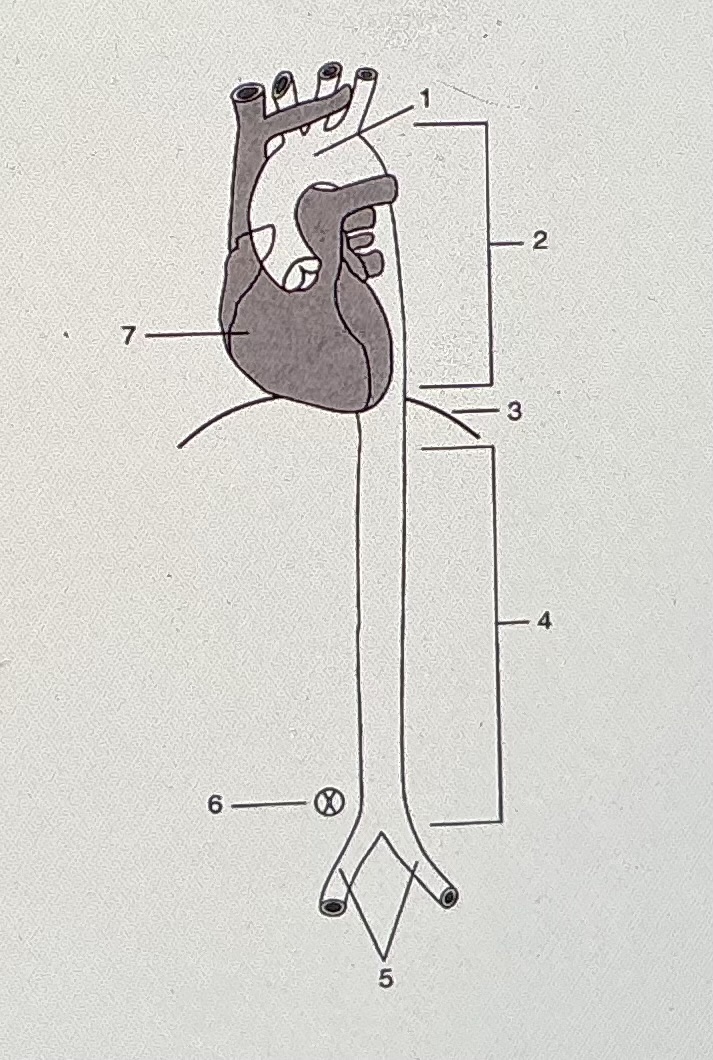
#2 indicates
thoracic aorta
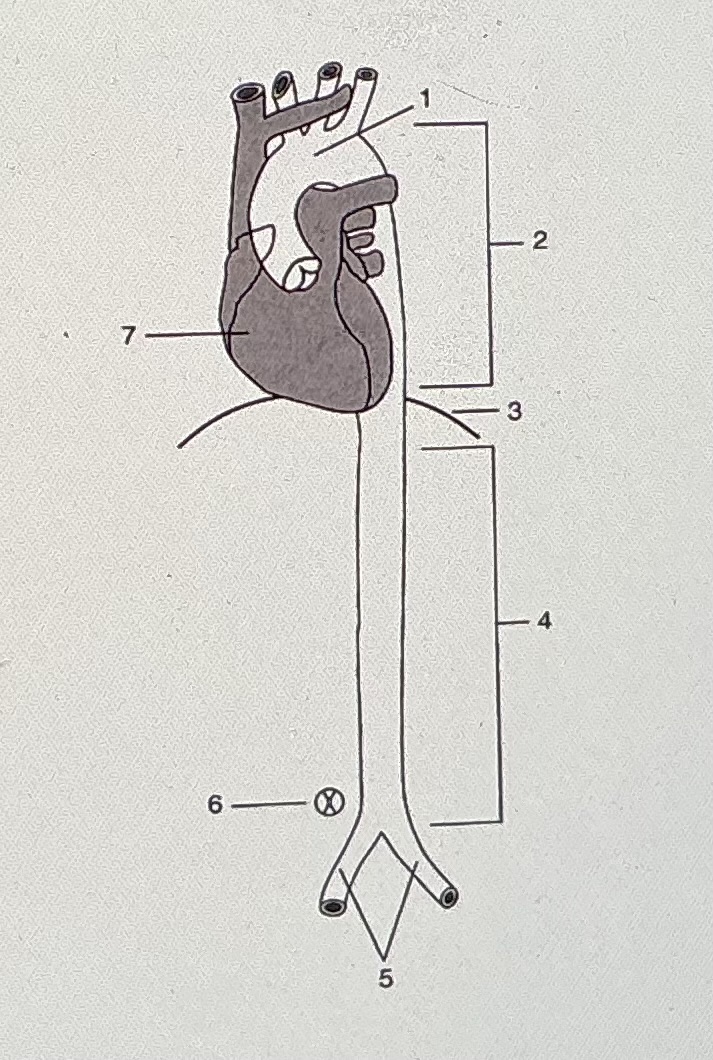
#3 refers to the rectus abdominus muscle
false
The aorta bifurcates into _______ at the level of the _________
Lt and Rt Common Iliac arteries; umbilicus
All of the following are anterior branches of the aorta, EXCEPT:
renal arteries
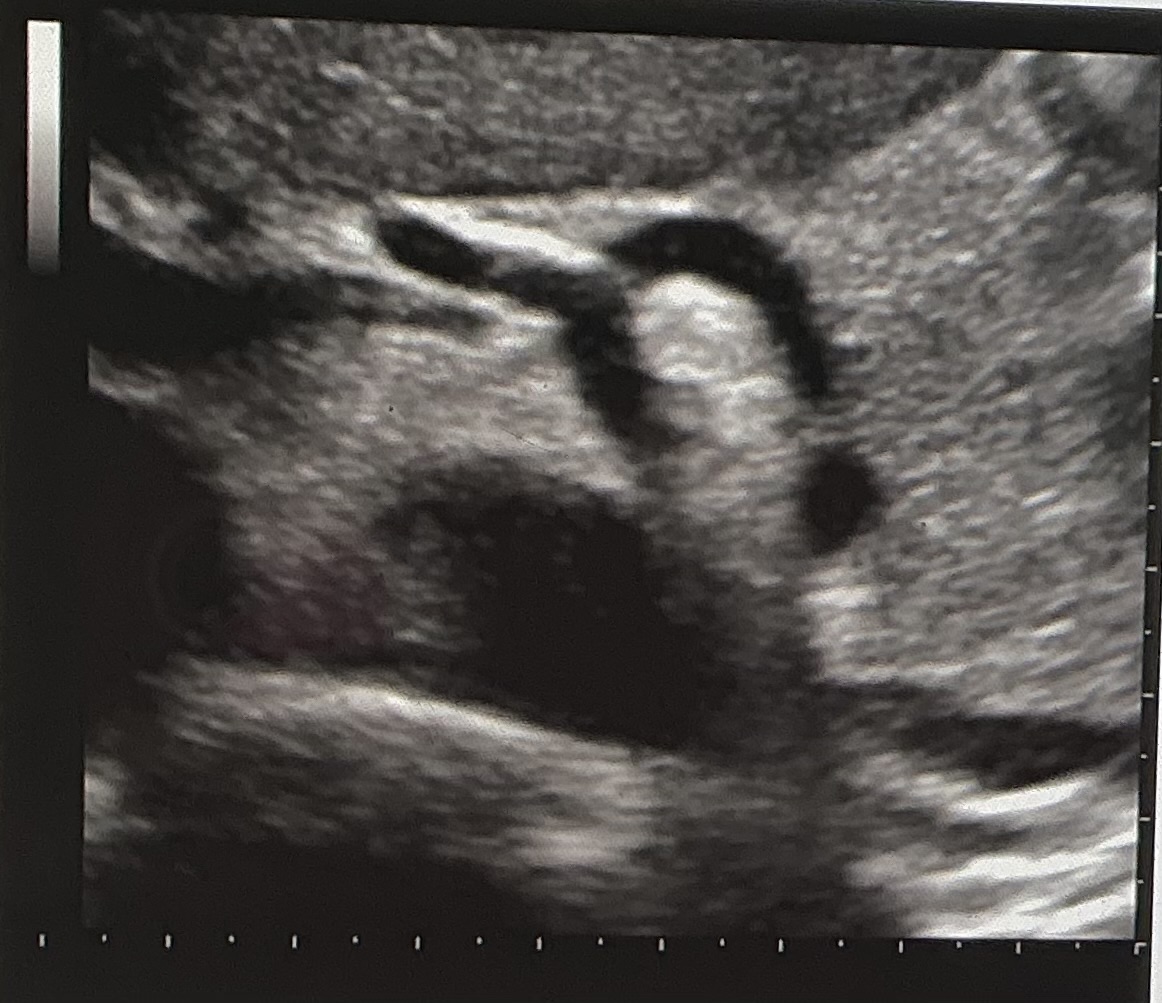
The sonographic image displayed is in which of the following orientations
transverse
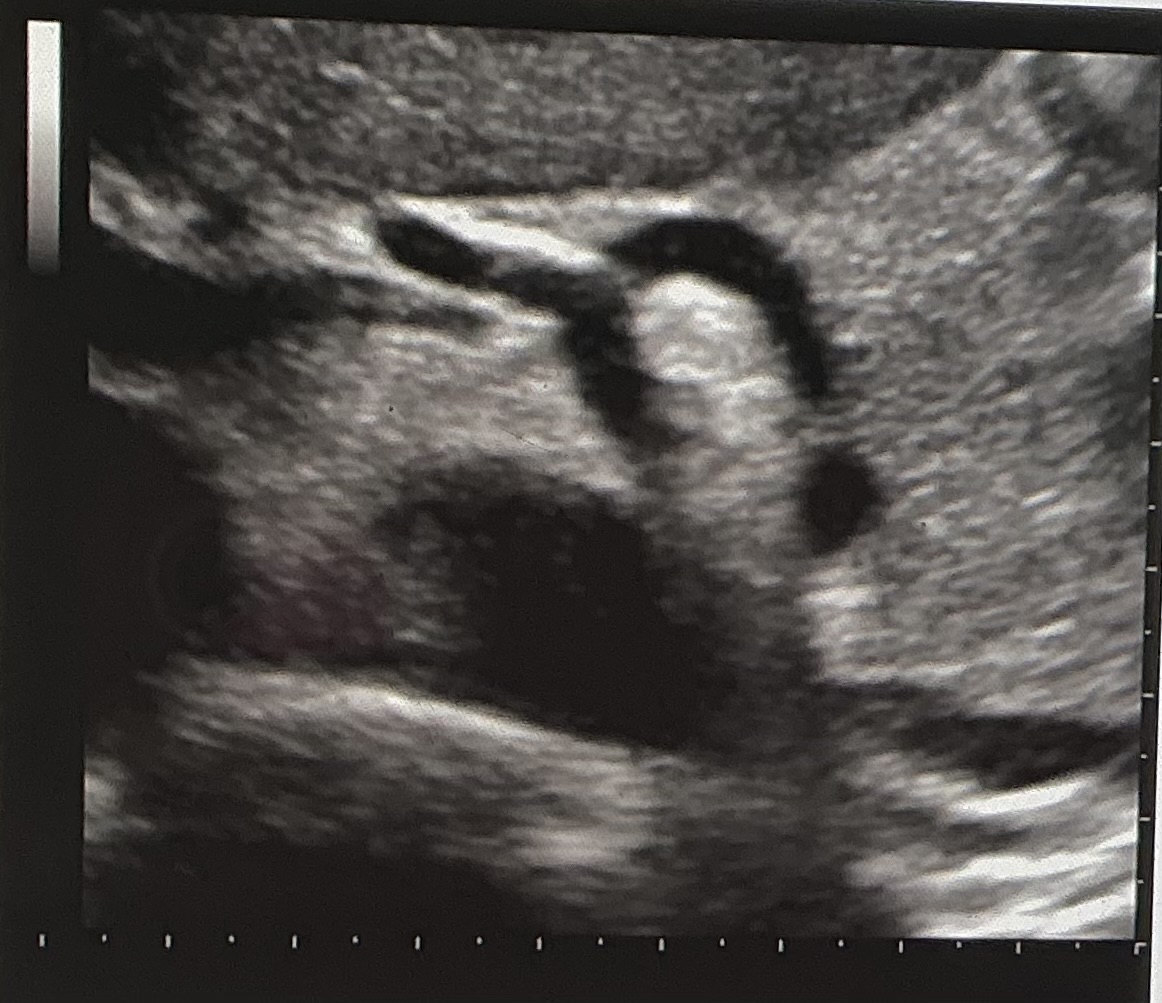
What vascular structure is visualized?
celiac axis and branches
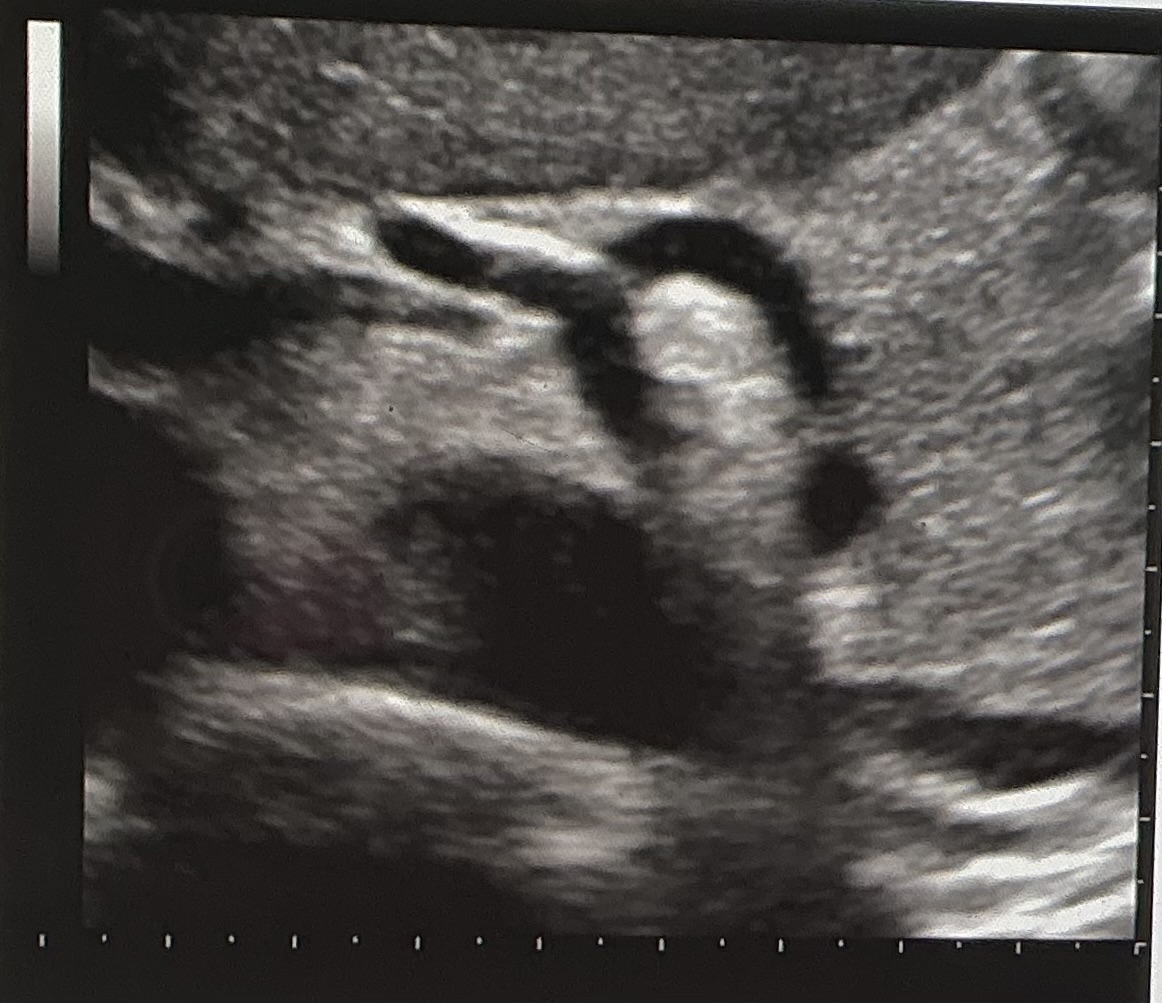
If you are scanning your patient in the transverse plane at the level demonstrated in the image, which way would you slide your transducer to see the SMA?
inferiorly
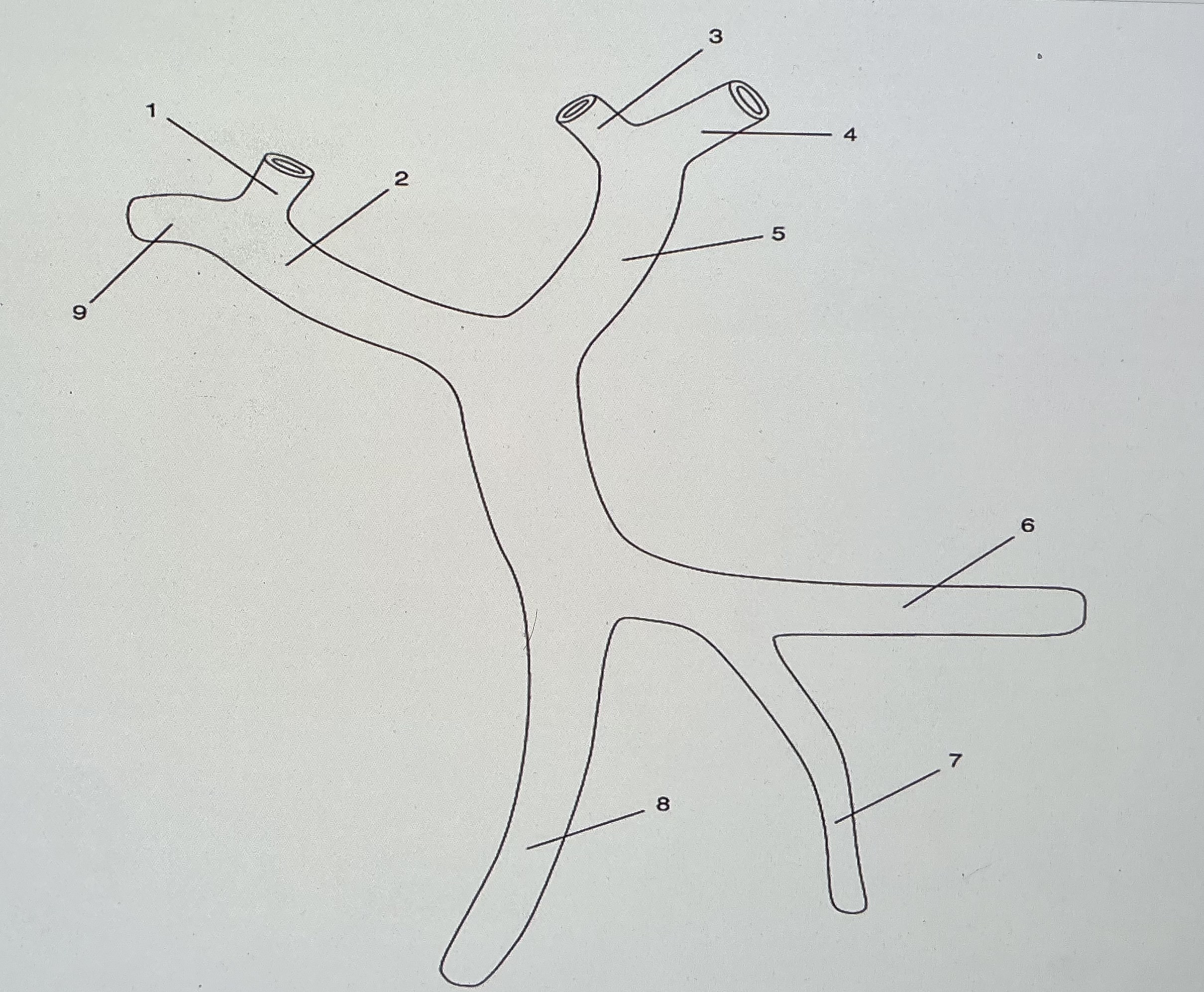
On the diagram, what do numbers 3 and 4 refer to?
medial and lateral branches of the left portal vein
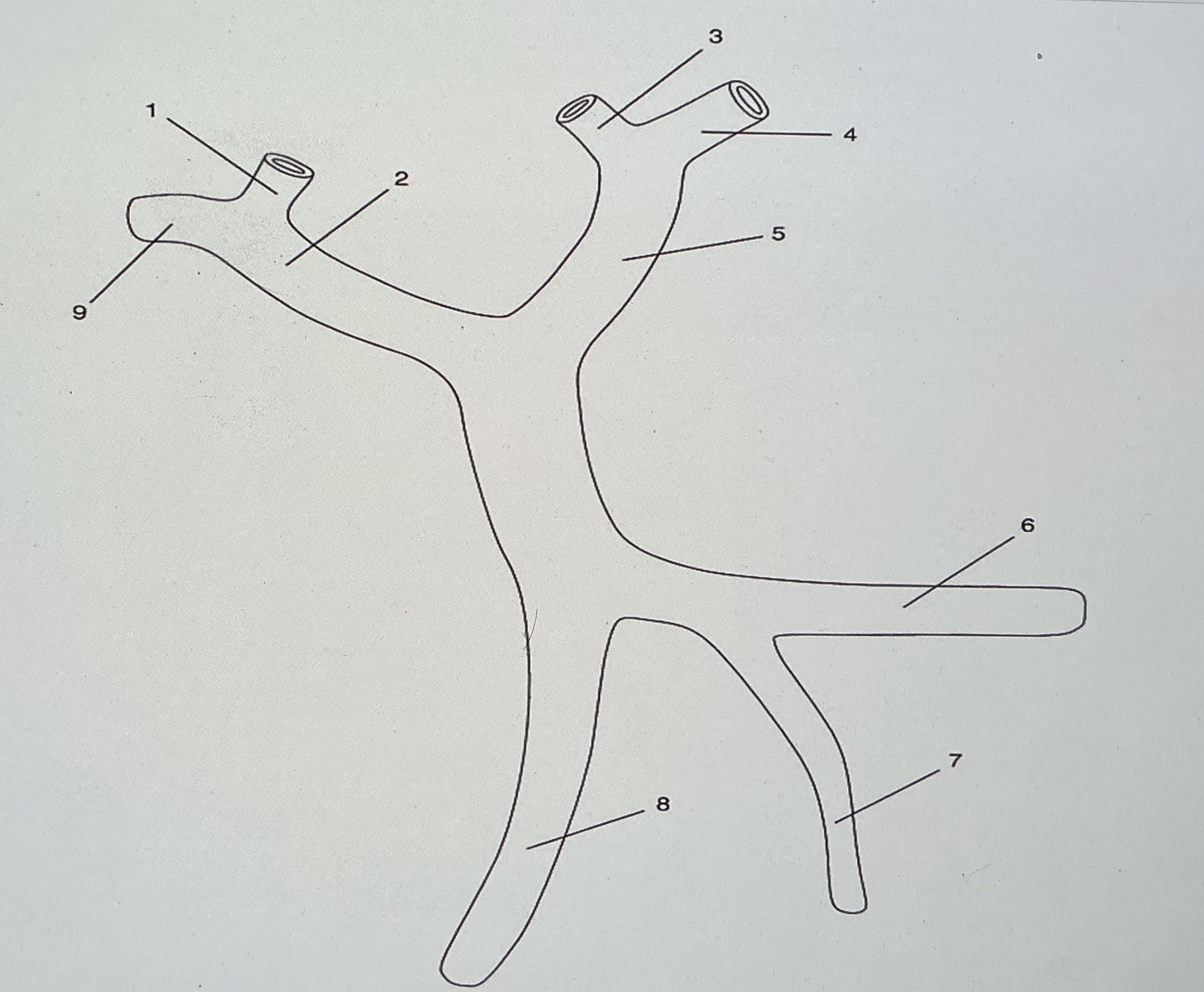
What do #6 and @7 refer to?
splenic vein and IMV
Which numbers on the diagram/image indicate portal venous structures?
2 and 4
What branch of the MPV is shown in the image?
left
What are the names of the smaller branches of the vessel shown?
left medial and left lateral portal veins
Which blood vessel courses anterior to the aorta and posterior to the SMA?
LRV
Which blood vessel courses more anteriorly, renal arteries or renal veins?
veins
All of the following are lower extremity arteries except:
greater saphenous artery
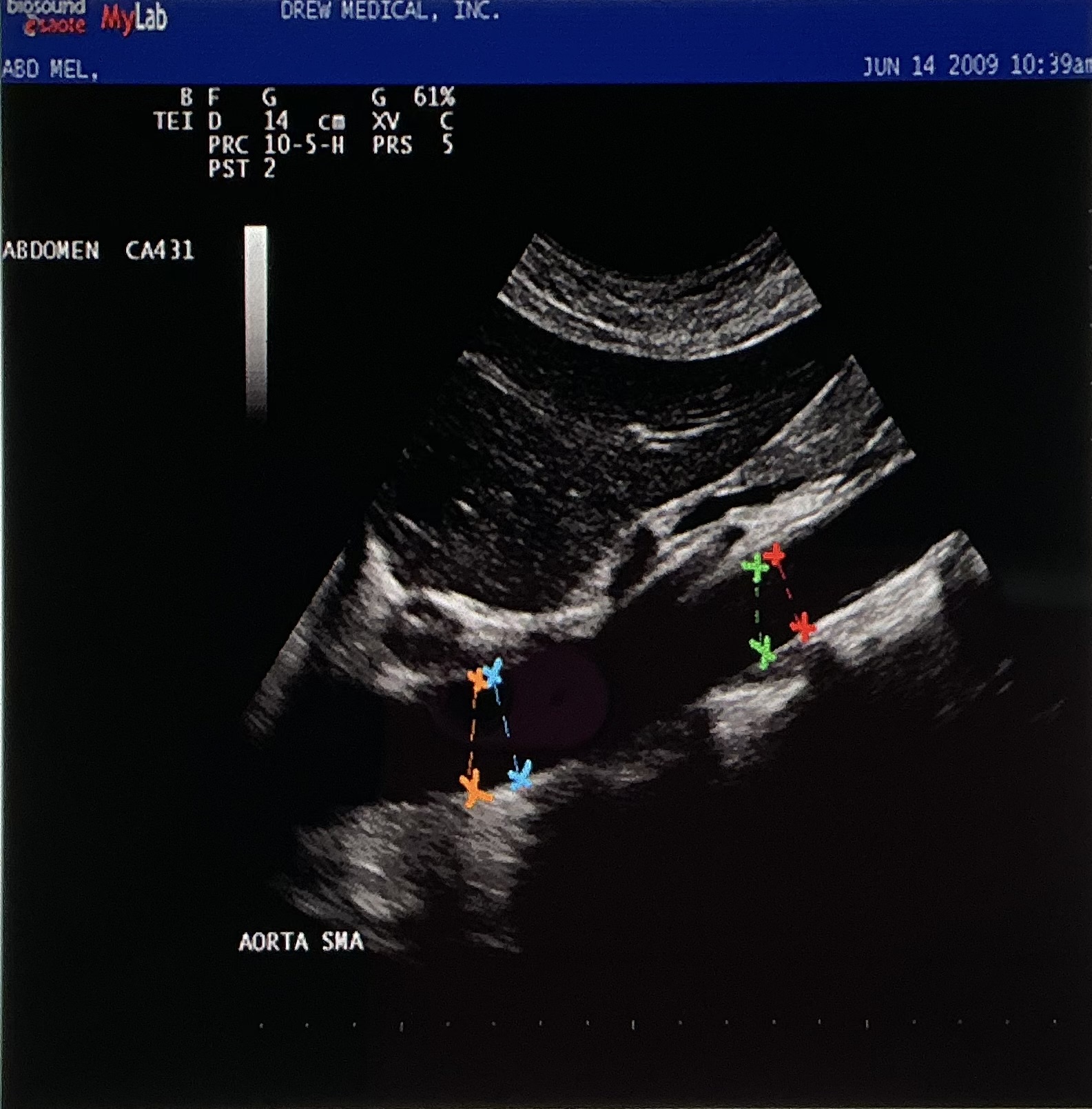
Which of the following colors of cursors are demonstrating a CORRECT AP measurement of the mid aorta segment on the image?
red
What vascular landmark divides the aorta into proximal and mid segments?
SMA
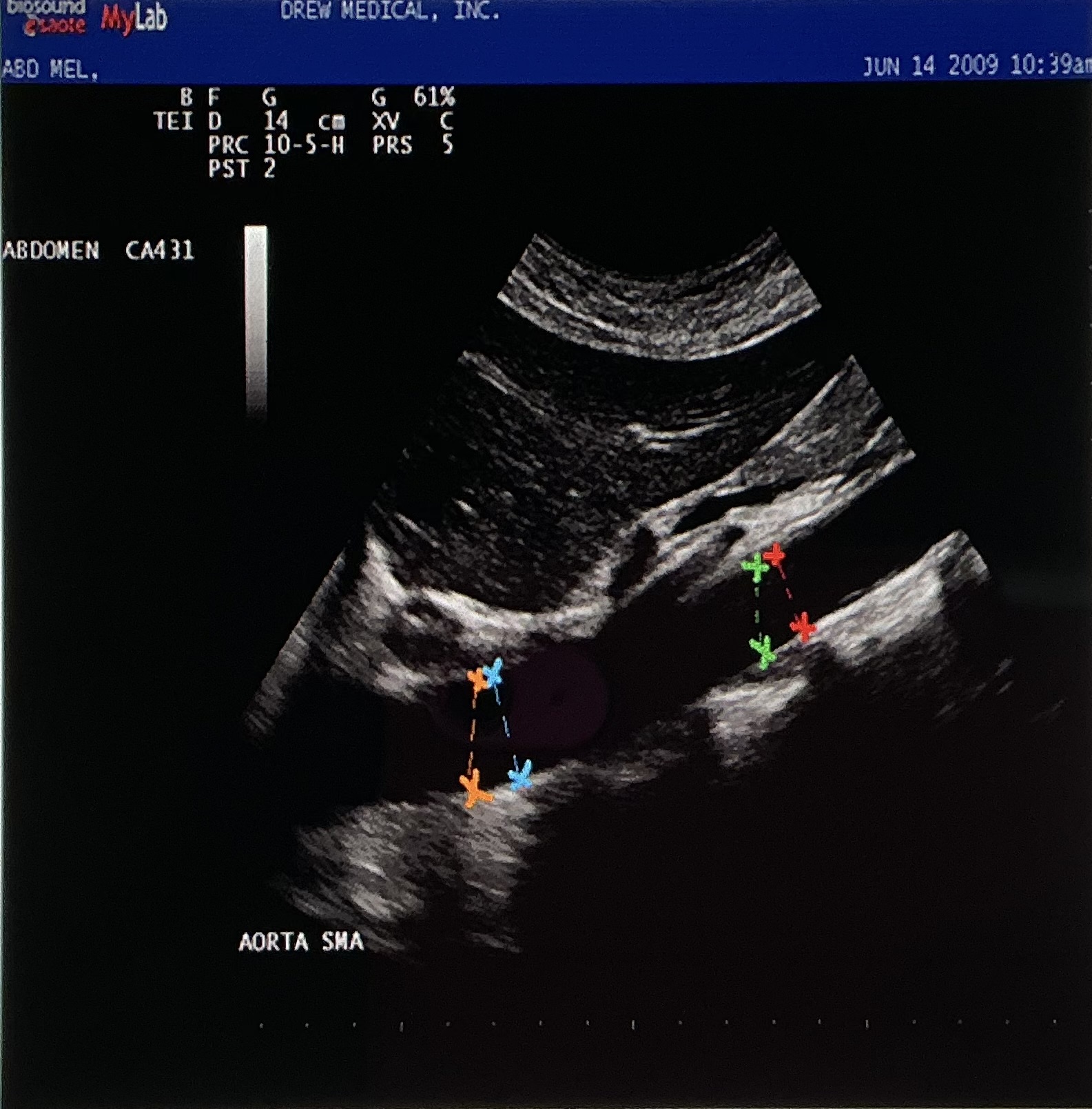
The image is demonstrating the aorta from what probe orientation?
longitudinal
When scanning the upper abdominal vessels what would be the preferred prep for the patient?
NPO for at least 6-8 hours prior
Describe the location and relationship to other liver structures of the following: the right hepatic vein, the right posterior portal vein, the left hepatic vein, and the ligamentum teres.
right hepatic vein: separates and drains the anterior and posterior segments of the right lobe
left hepatic vein: separates and drains the medial and lateral segments of the left lobe
right posterior portal vein: supplies the caudate lobe with blood
ligamentum teres: divides the medial and lateral left lobe portions
Name two ligaments that can be seen in the liver and describe the anatomic relationship to the liver.
ligamentum venosum separates the caudate lobe from the left lobe, and it marks the left anterolateral border of the caudate lobe. Travels within the transverse fissure
falciform ligament and the ligamentum teres are located within the left intersegmental fissure, which divides the medial and lateral segments of the left lobe. The falciform ligament divides the right and left lobes, and ends at the ligamentum teres inferiorly.
Describe the relationship of the hepatic artery, the common bile duct, and the portal vein.
They form the portal triad.
The hepatic artery is anterior and medial to the portal vein
the CBD is lateral to the portal vein
They enter the liver at the porta hepatis.
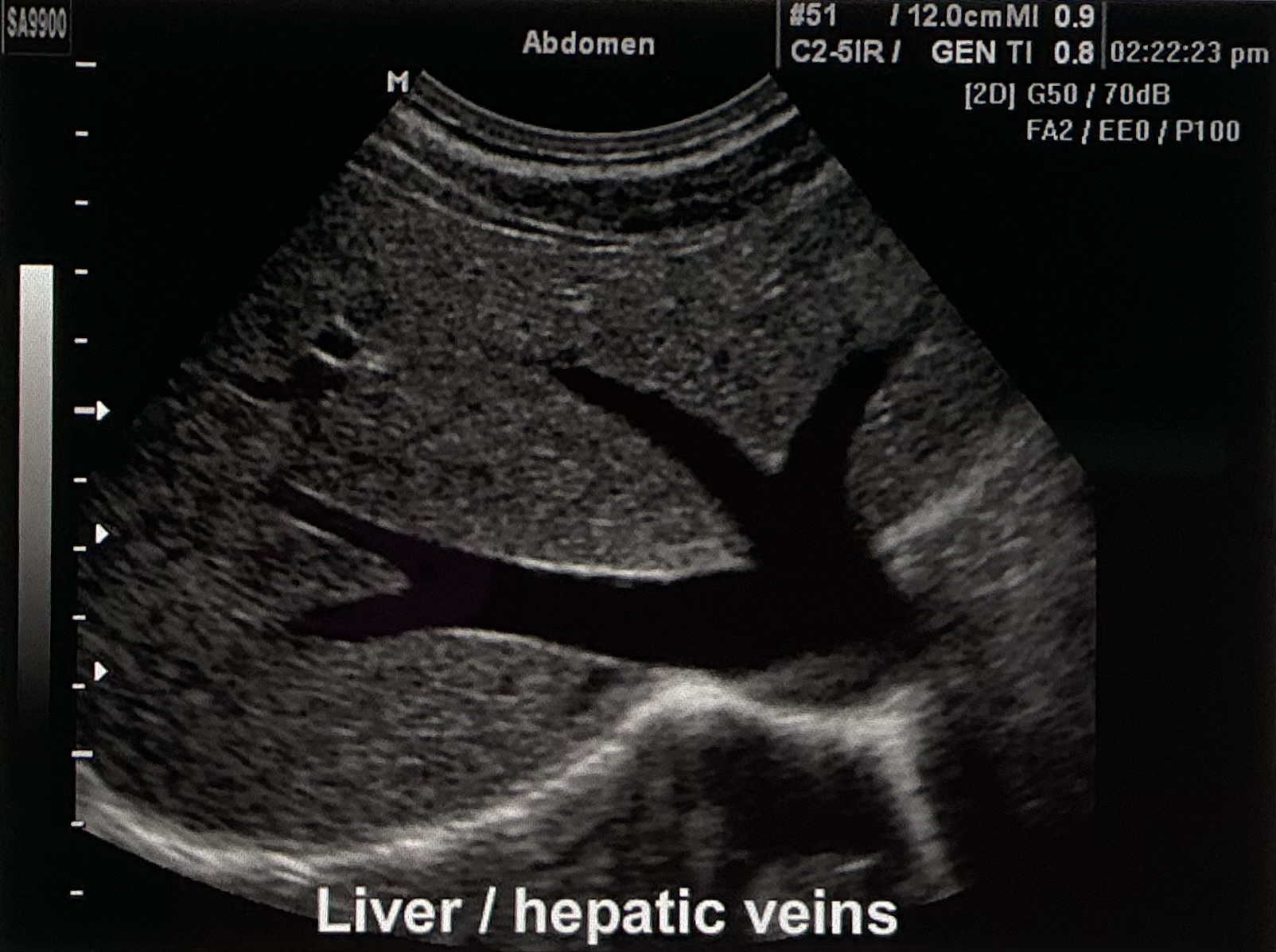
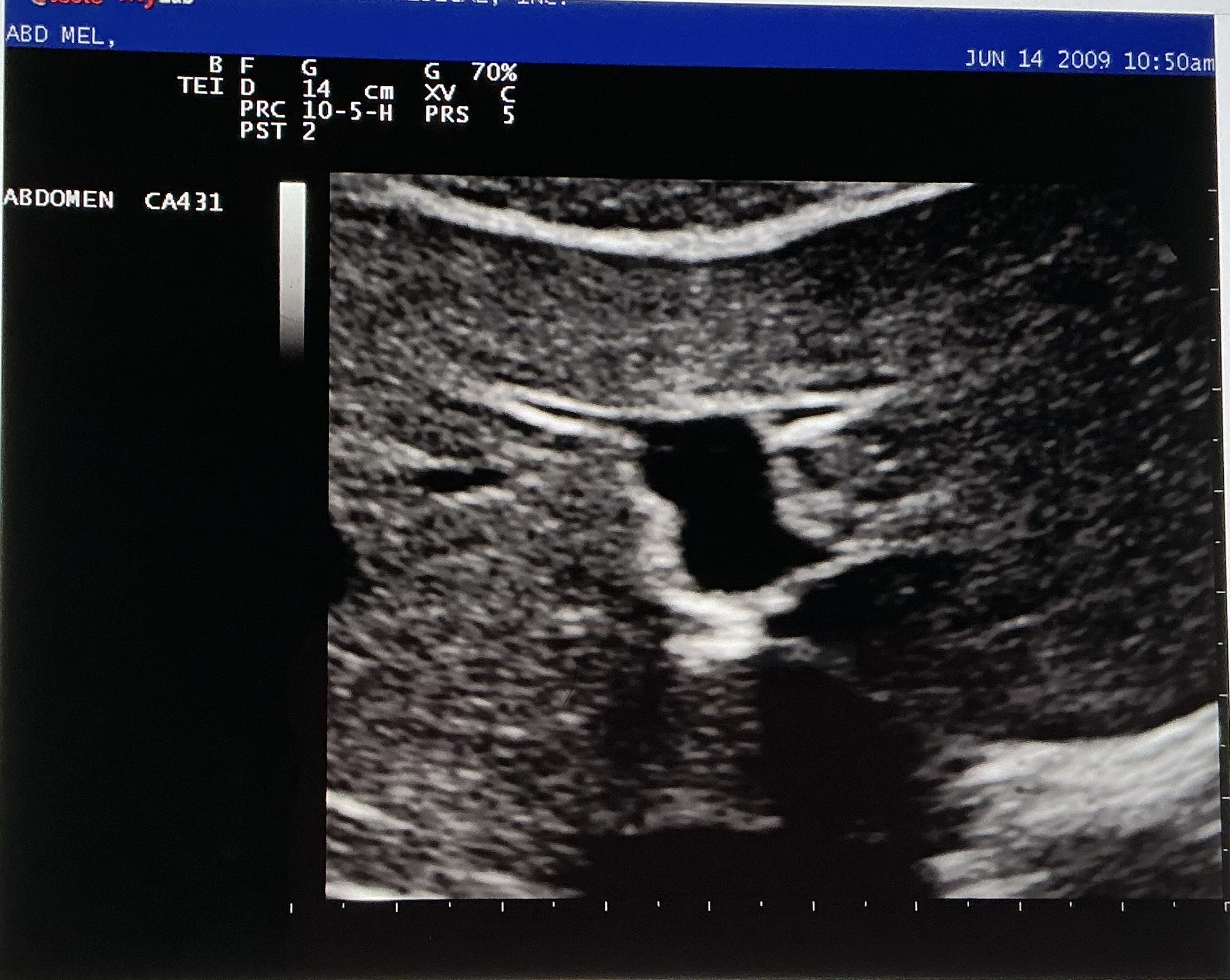
Describe the sonographic appearance of this image.
Left lobe of the liver, specifically the hepatic veins.
The liver tissue appears homogenous and hyperechoic to the vessels. It is bordered by an echogenic line, which is the diaphragm. The hepatic veins appear anechoic throughout, and they are hypoechoic to the surrounding tissue.
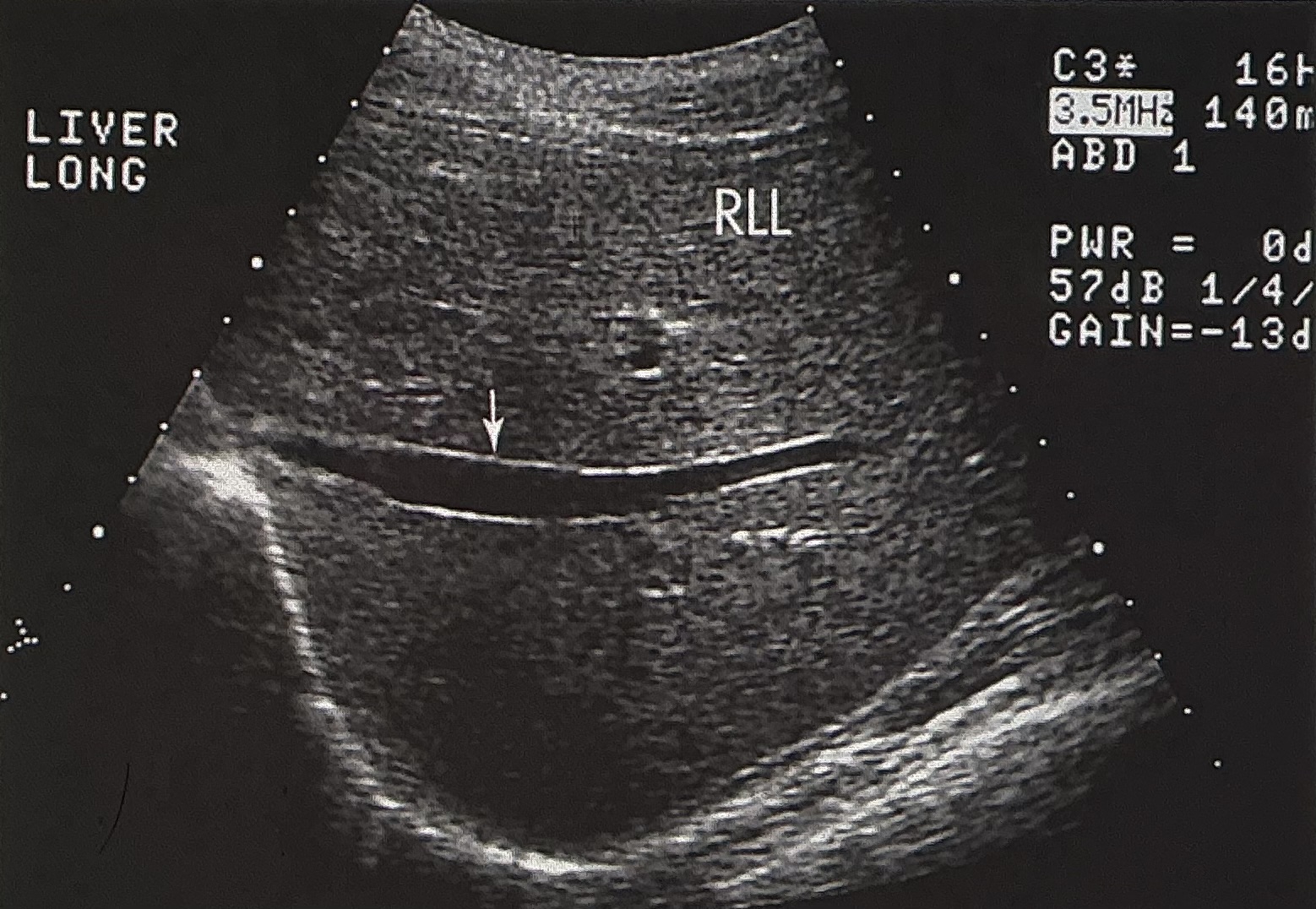
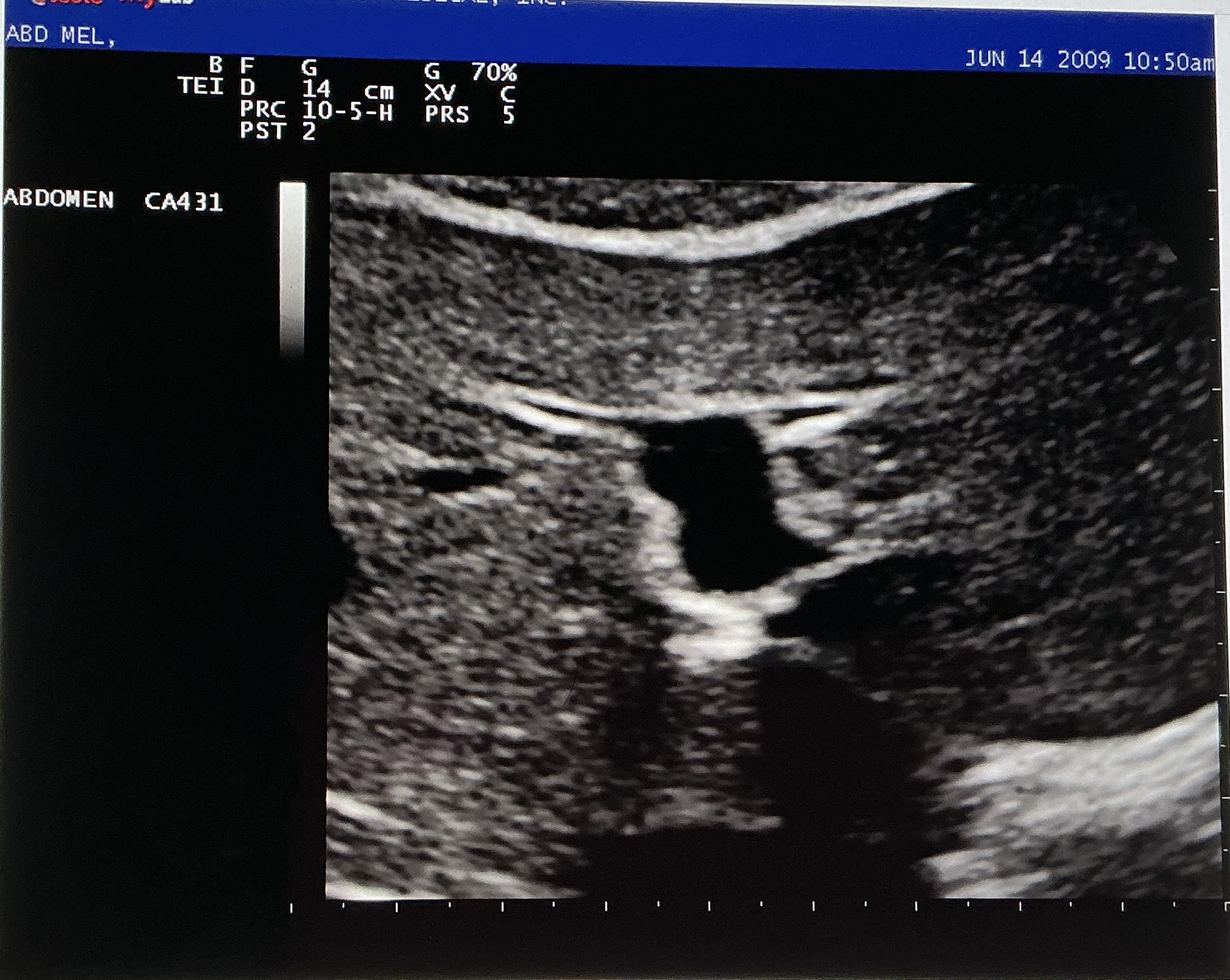
Name and describe this image: Include scan plane, and name the structure identified by the white arrow.
longitudinal image of the right lobe of the liver
the structure is the right portal vein
liver tissue appears homogenous throughout and is hyperechoic to the vessel’s lumen. The vessel is anechoic, with echogenic borders.
The liver occupies a major portion of the:
right hypochondrium
The IVC and its visible branches are primarily evaluated to detect
intraluminal thrombosis or tumor invasion
All of the following are ligaments of the liver EXCEPT:
bare area
On the left anteriorly, the ligamentum teres divides the
medial from the lateral left lobe
The caudate lobe is bordered posteriorly by the _____ and anteriorly by the ______.
IVC; left portal vein
The main portal vein enters the _______ and divides into left and right portal veins.
porta hepatis
The main lobar fissure is seen as an echogenic line connecting the ______ to the ______.
gallbladder; right portal vein
The portal triad consists of
CBD, HA, PV
The common hepatic duct is ______ to the portal vein.
anterior
All of the following are divisions of the gallbladder EXCEPT
cystic duct
Which of the following is not a probe position for a Gallbladder Fast Exam
low/lateral view
The right and left hepatic ducts emerge from the right lobe of the liver in the porta hepatis and unite to form the:
common hepatic duct
The hepatic duct is joined by the ____ to form the ____.
cystic duct; common bile duct
The distal duct lies ____ with the anterior wall of the IVC.
parallel
The cystic duct connects the _____ of the gallbladder with the common hepatic duct to form the ____.
neck; CBD
The function of the gallbladder is:
reservoir for bile
The bright linear echo within the liver connecting the gallbladder and the right or main portal vein is the:
main lobar fissure
The ____ branch of the hepatic artery can be seen between the common duct and the portal vein as a small circular structure.
right
The common bile duct is joined by the main pancreatic duct. Together they open through the ____ into the duodenal wall.
ampulla of Vater
The Mickey mouse sign contains which of the following structures…
HA, CBD, PV
The walls of the portal vein are ____ when compared to the liver parenchyma
hyperechoic
“Shotgun sign” seen in the liver parenchyma is indicative of:
dilated biliary ducts
What vein brings oxygen enriched blood to the liver?
portal vein
The portal triad is made up of the CBD, PV, and what other structure?
hepatic artery
Within the liver, which is one of the ligaments that divides the right lobe from the left lobe?
main lobar fissure
A contracted gallbladder packed with stones will give the ____ sign
WES
On ultrasound, a gallstone appears
hyperechoic with posterior shadowing
A benign growth that protrudes from the wall of the gallbladder is called a
polyp
A patient presents to the ER with acute RUQ pain. Upon examination you find that the gallbladder wall measures 4 mm and there are stones within the gallbladder, and some fluid is seen anterior to the gallbladder. The most likely diagnosis would be:
acute cholecystitis with cholelithiasis
Causes of gallbladder wall thickening include everything EXCEPT:
deep vein thrombosis
What are the common signs and symptoms of biliary disease?
RUQ pain
jaundice
nausea
joint pain
fatigue
fever
Low level, nonshadowing echoes in the dependent portion of the gallbladder can be described as
biliary sludge
The GB is located on the
posterior and inferior portion of the right lobe of the liver
The left and right hepatic ducts join at approximately the level of
porta hepatis
The cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the
common hepatic duct
The common bile duct extends from the point where the cystic duct joins the
common hepatic duct
The overall length of the GB is
highly variable
Bile enters the intestinal tract at the
ampulla of Vater
The _____ supplies blood to the GB and liver
proper hepatic artery
The intrahepatic ducts run alongside of the
portal vein and hepatic arteries
The three landmarks that may be helpful in locating the GB on a longitudinal image are
PV, main lobar fissure, and the right kidney
What anatomic structures are included in the GI tract?
mouth
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small intestines
liver/GB
pancreas
large intestines
rectum
anus
Name and describe the location of the two ducts of the pancreas.
Duct of Wirsung: main pancreatic duct runs through the body and tail of the pancreas. Connects to the CBD + enters duodenum through Ampulla of Vater
Duct of Santorini: accessory duct located closer to head of pancreas and CBD. Joins Duct of Wirsung to join CBD
Name and describe two normal variants of the pancreas.
Ectopic pancreas: found outside of normal location, closer to stomach or intestines
Annular pancreas: ring of pancreatic tissue covers the duodenum (C-loop portion)
Normal measurements of the pancreas.
length: 12-18 cm
head: 2-3 cm
body: 2-3 cm
neck: 1.5-2.5 cm
tail: 1-2 cm
Explain the term Courvoiser’s gallbladder
Enlargement of the GB caused by a slow progressive obstruction of the distal CBD from an external mass (such as adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head)
The hepatic duct is joined by the _____ to form the ____.
cystic duct; CBD
The head of the pancreas lies in the:
lap of the duodenum
The head of the pancreas is inferior to the:
caudate lobe
The _____ is the anterolateral border of the pancreatic head
gastroduodenal artery
The tail of the pancreas is found:
anterior to the left kidney, near the splenic hilum
The primary pancreatic duct is the
duct of Wirsung
The duct of Santorini is a/an:
accessory duct to the pancreas
The splenic artery is considered to be the:
superior border of the pancreas
The pancreas is reflective in its sonographic appearance because of
fat between the lobules
Approximately 2% of the pancreatic gland is endocrine
false
The largest component of pancreatic juice is hydrochloric acid.
false
The _____ is a posteromedial projection of the pancreas head.
uncinate process
Pancreatic juice from the acini cells are drained by ______,
intercalated ducts
Transverse scanning plane images best demonstrate the ______ section of the pancreas.
longitudinal
Sagittal scanning plane images best demonstrate the _____ section of the pancreas.
axial
A normal pancreatic duct variant that enters the duodenum is called the ______.
duct of Santorini
The muscle that surrounds the ampulla through which the main pancreatic duct enters the duodenum is called the
sphincter of Oddi