UGA CBIO 3010 - Upper Limbs
1/258
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
259 Terms
What is the most flexible joint in the body?
Glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint)
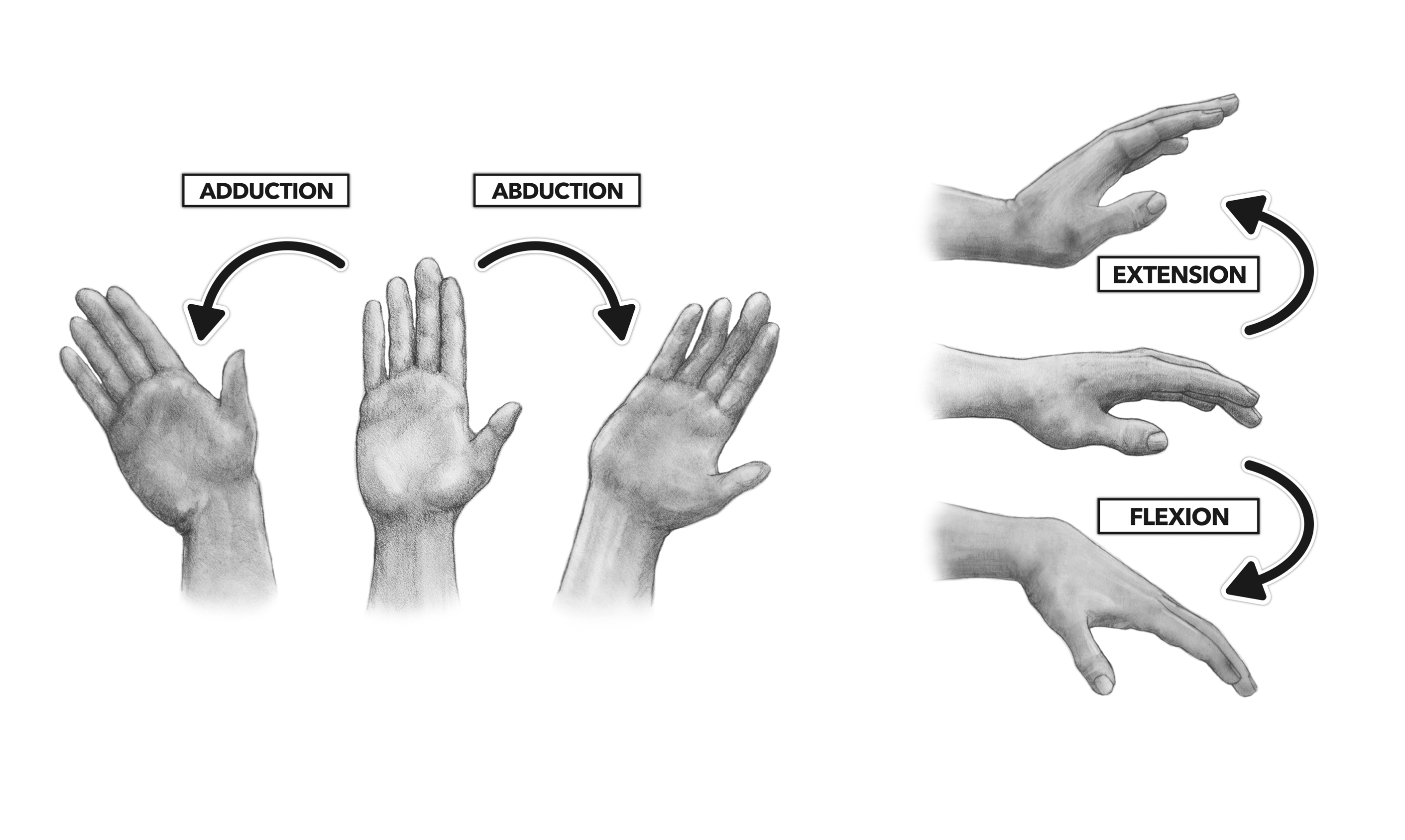
What movements can the glenohumeral joint do?
1. flexion/extension
2. abduction/adduction
3. medial/lateral rotation
4. circumduction
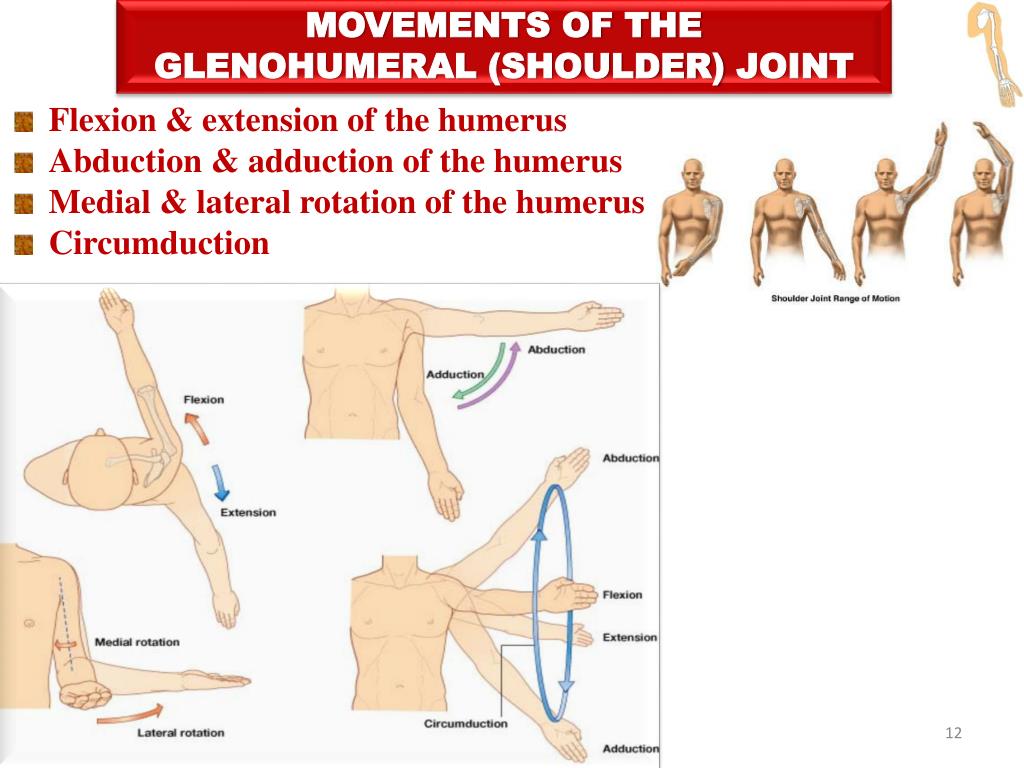
What is the difference between extension and abduction?
Abduction is the movement away from the midline of the body.
Extension is the straightening of limbs (increase in angle) at a joint.
What is circumduction movement?
combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction that allows the joint to move in a circular manner
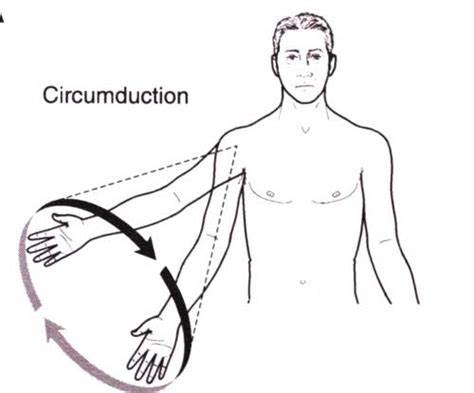
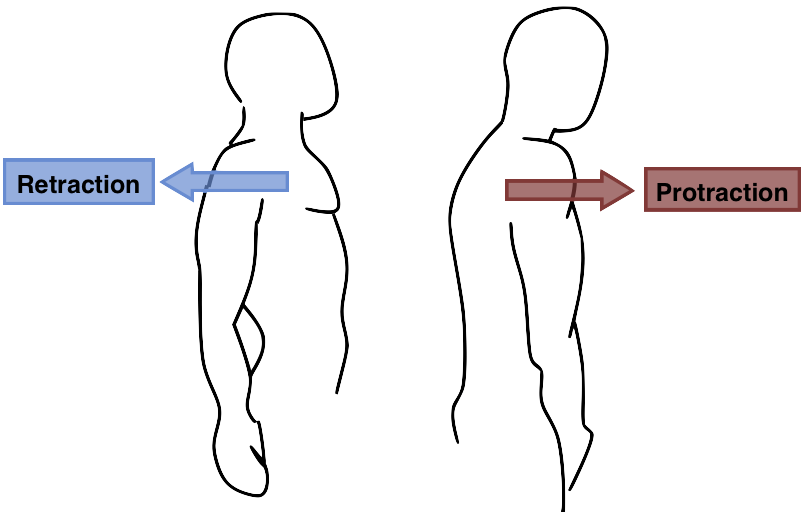
What is the difference between protraction and retraction?
PROTRACTION: moving a bone forward on the frontal plane
RETRACTION: moving a bone backwards on the frontal plane
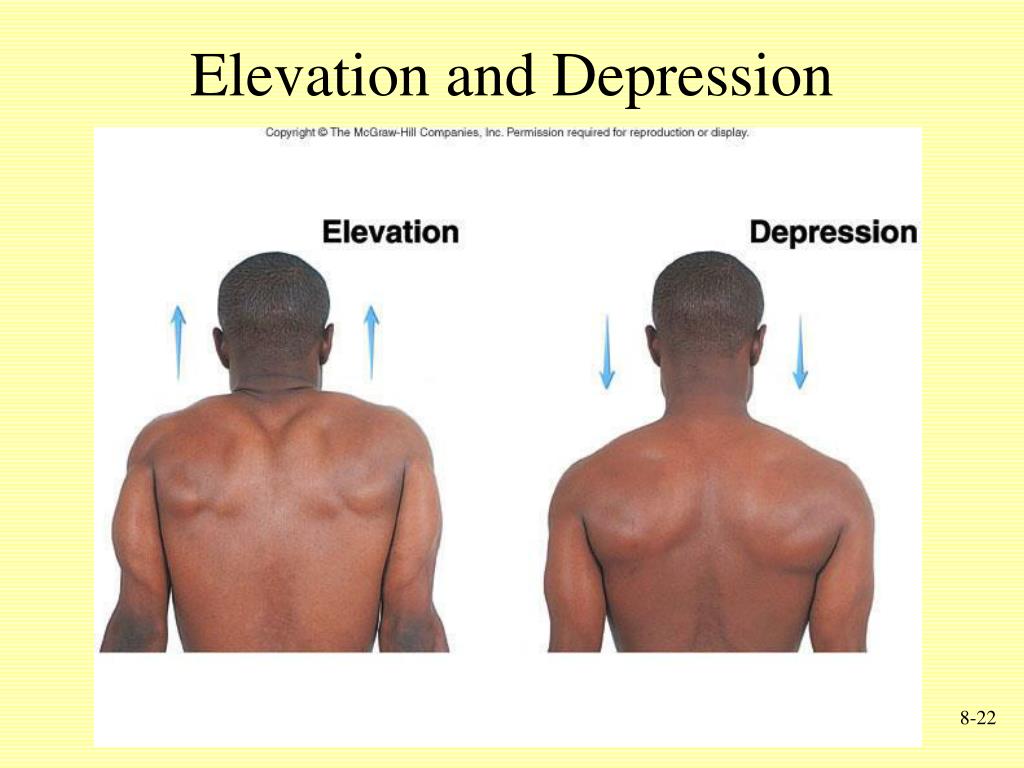
What is the difference between elevation and depression?
ELEVATION: shrug your shoulders up on the frontal plane
DEPRESSION: shrug your shoulders down on the frontal plane
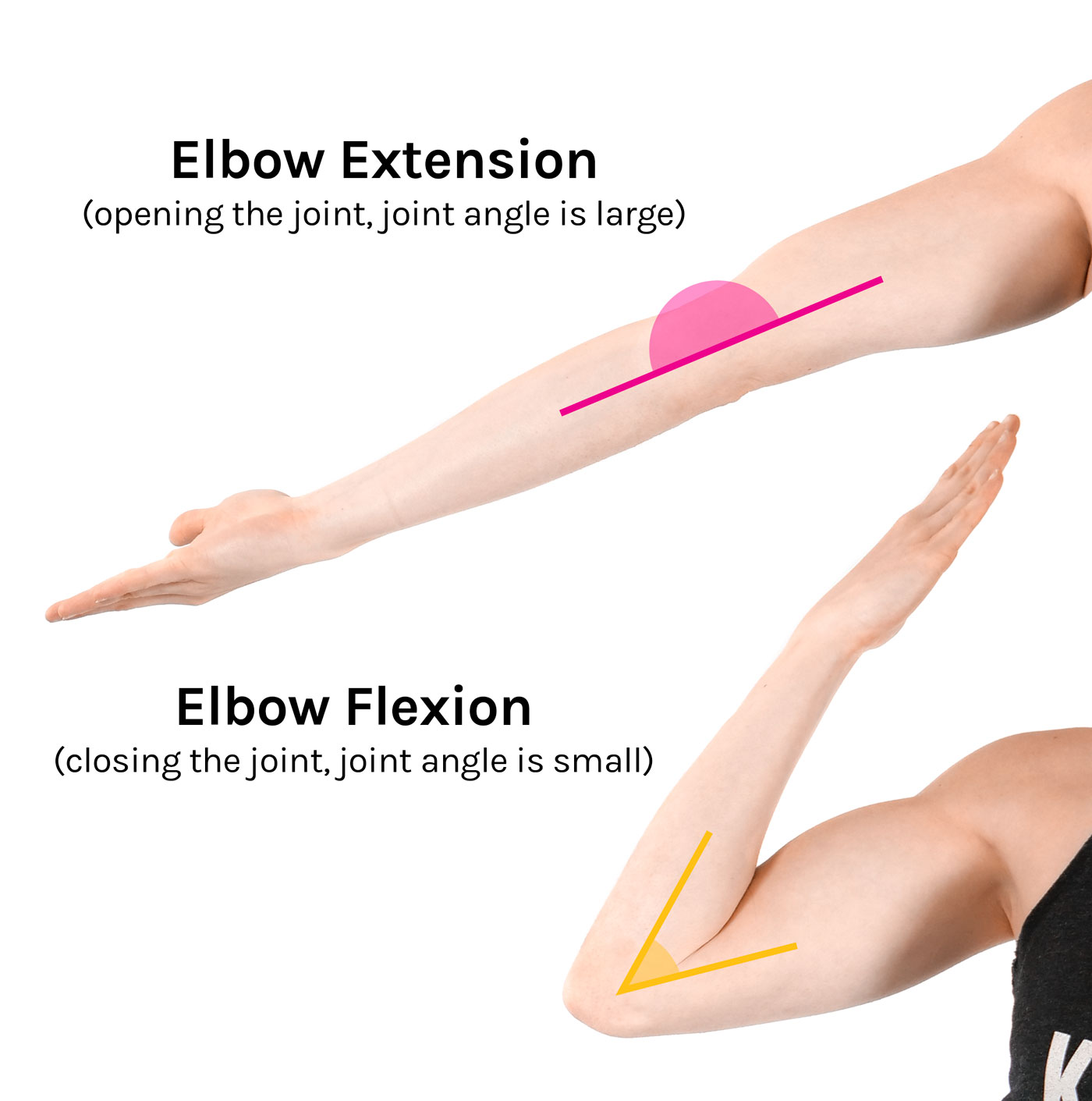
What are the primary movements of the elbow?
flexion/extension
What are the primary movements of the forearm?
pronation/supination
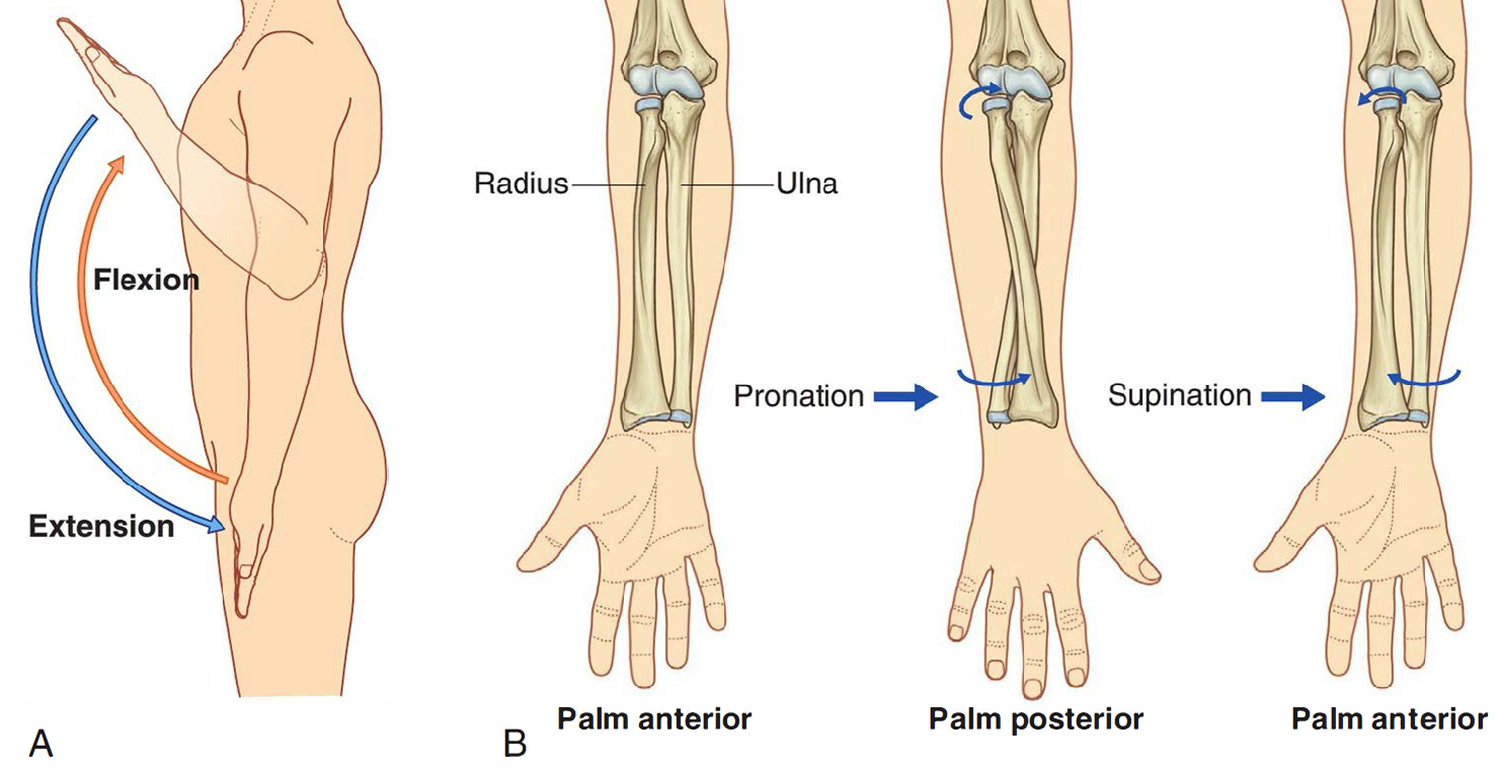
What is the pronation movement?
turning the forearm (the radius) so that the palm is down
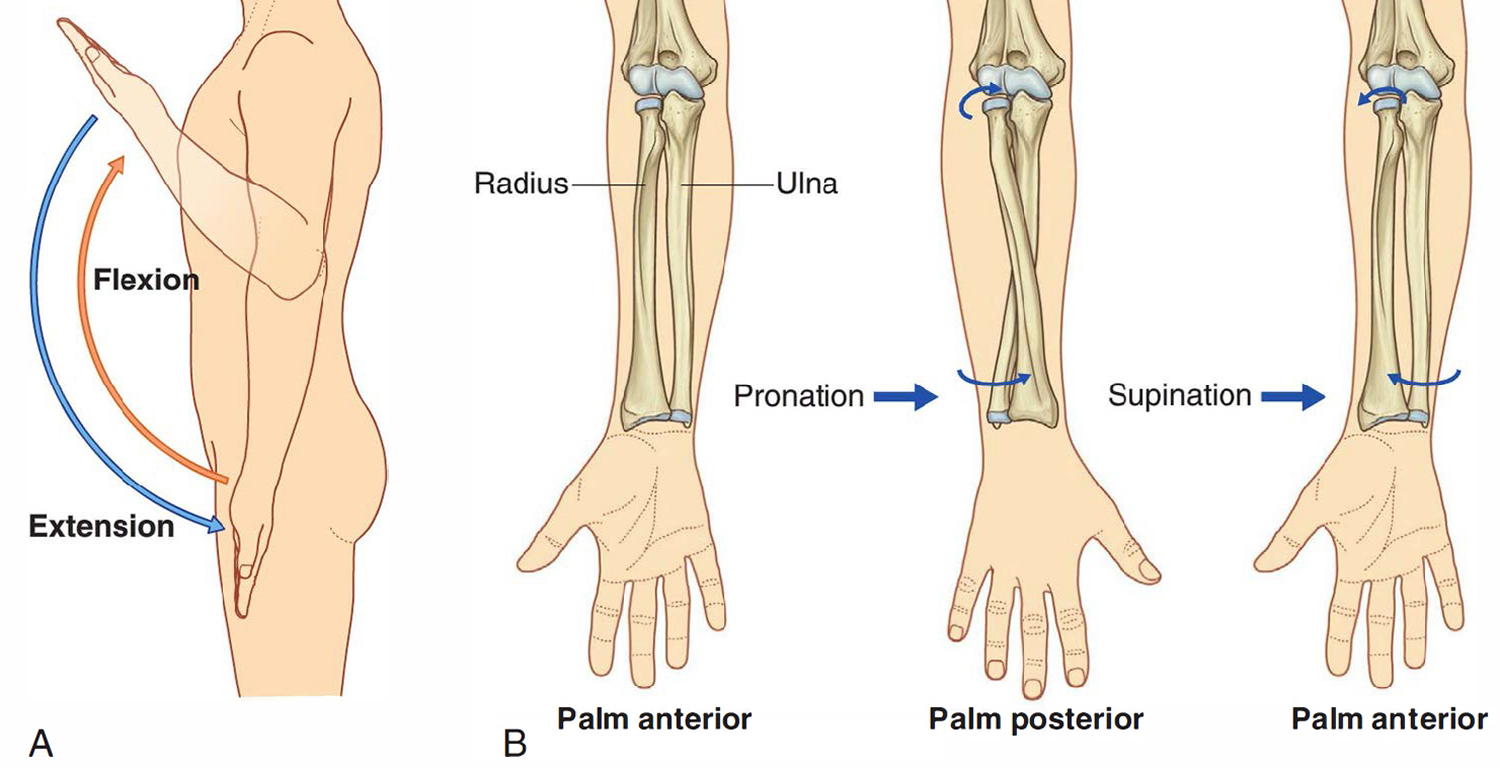
What is the supination movement?
turning the forearm (radius) so the palm is up
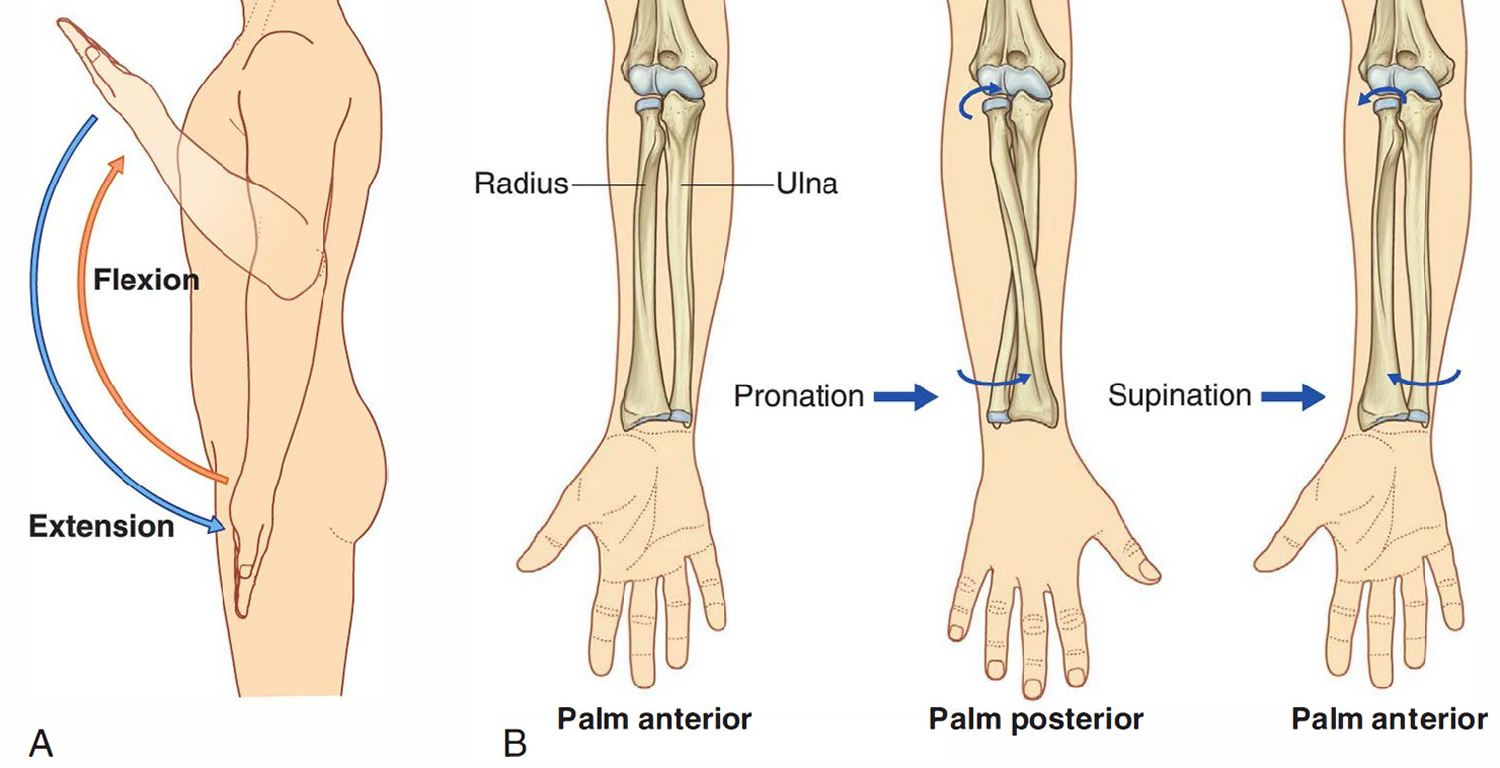
What are the movements of the wrist?
flexion/extension
abduction/adduction
What are the major divisions of the upper limb?
- shoulder
- arm
- forearm
- hand
What is considered the "shoulder"?
region of attachment of upper limb to trunk
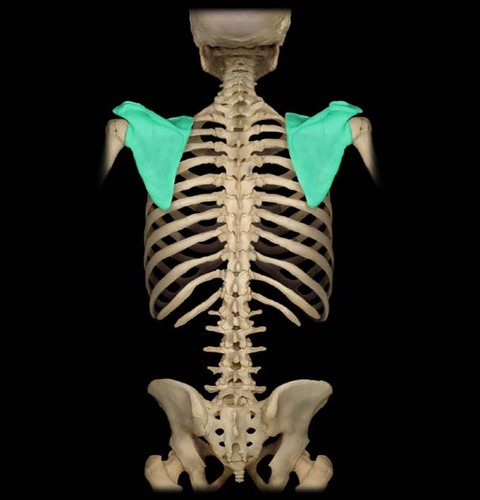
(T/F) The shoulder is sometimes called the coracoidal region.
False - it is sometimes call the ACROMIAL region
What is considered the "arm"?
shoulder to elbow
What is the difference between Latin terms "brachium" and "brachial"?
Brachium is a noun, and brachial is an adjective
What is considered the "forearm"?
elbow to wrist
What is the difference between Latin terms "antebrachium" and "antebrachial"?
Antebrachium is a noun, and antebrachial is an adjective
What is considered the "hand"?
remaining section distal to the wrist

What is the difference between Latin terms "manus" and "manual"?
Manus is a noun, and manual is an adjective
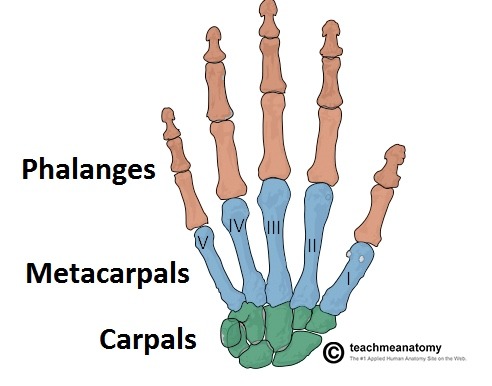
What is the difference between digits and phalanges?
The entire finger is a DIGIT, but the bones INSIDE of them are PHALANGES
(T/F) “Phalanx” is the singular form.
True - the plural is “phalanges”
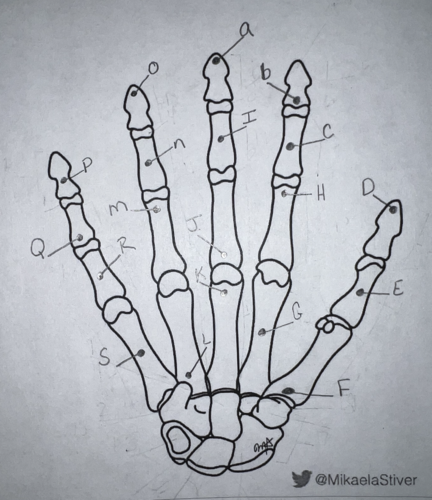
Using the long form, what is the name of this carpal? (labeled “E”)
proximal phalanx of the first digit
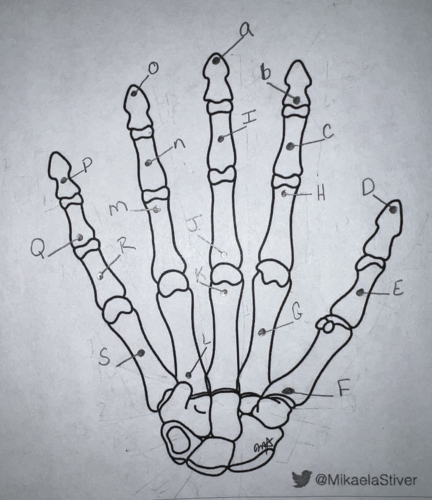
Using the long form, what is the name of this carpal? (labeled “C”)
middle phalanx of the first digit (first middle phalanx refers to INDEX finger)
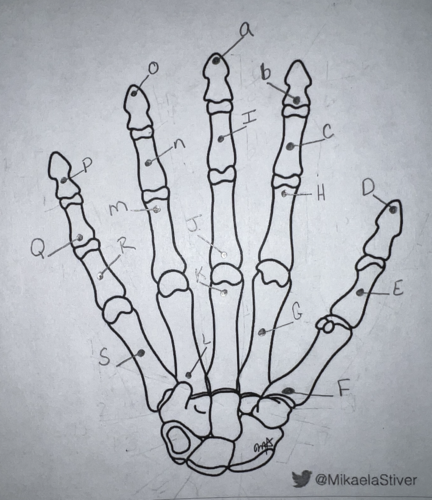
Using the short form, what is the name of this carpal? (labeled “N”)
third middle phalanx
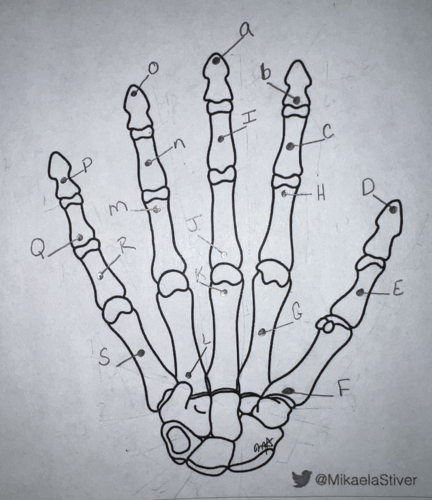
Using the short form, what is the name of this carpal? (labeled “P”)
fifth distal phalanx
What are the transitional areas of the upper limb?
- axilla
- cubital fossa
- carpal tunnel
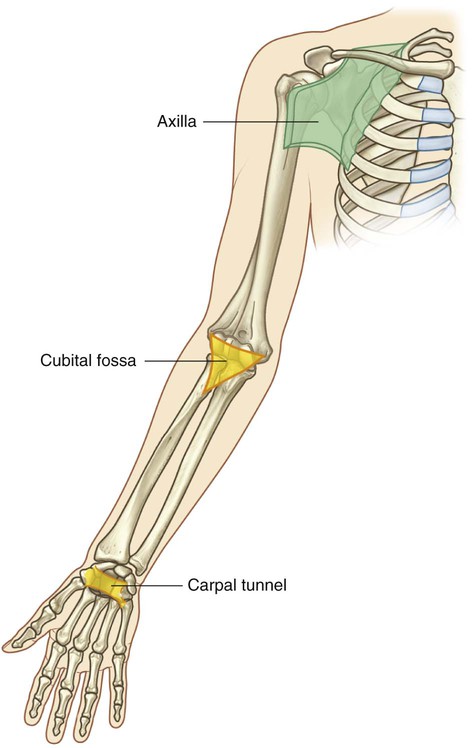
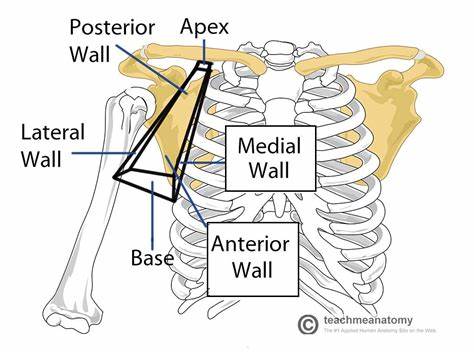
What makes up the axilla transitional area?
- muscles and bones of the shoulder (posterior wall)
- lateral surface of thoracic wall (medial wall)
- apex (point) opens directly to neck
- base (floor) formed by skin of armpit
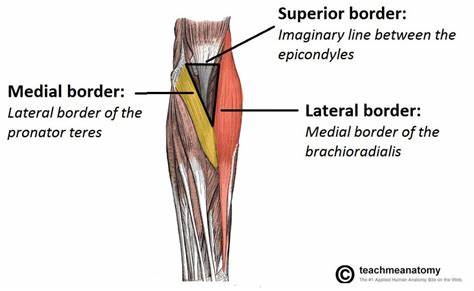
What makes up the cubital fossa transitional area?
Triangular region formed by muscles on anterior of elbow joint
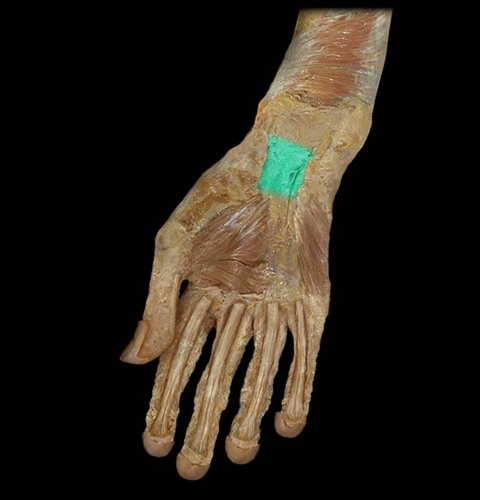
What makes up the carpal tunnel transitional area?
Essentially the wrist, with all of the nerves and tendons
(T/F) Axilla is the same as your armpit.
False - The axilla is the space UNDER the skin of your armpit
When muscles taper off and attach to the bones, what are they called?
Tendons
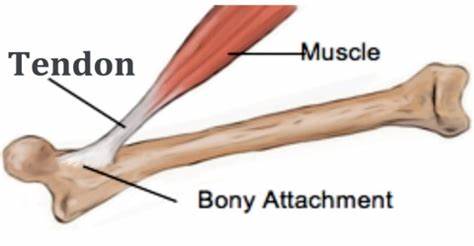
(T/F) Arteries are most vulnerable in transitional areas of the upper limb.
True - any injuries to these areas are paid more attention to
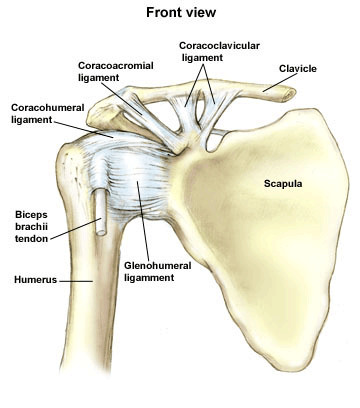
What are the bones that make up the shoulder joint?
- scapula
- clavicle
- humerus
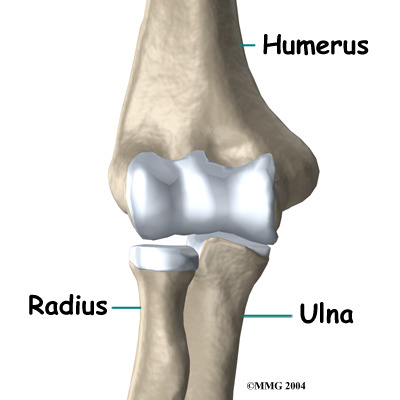
What are the bones that make up the elbow joint?
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
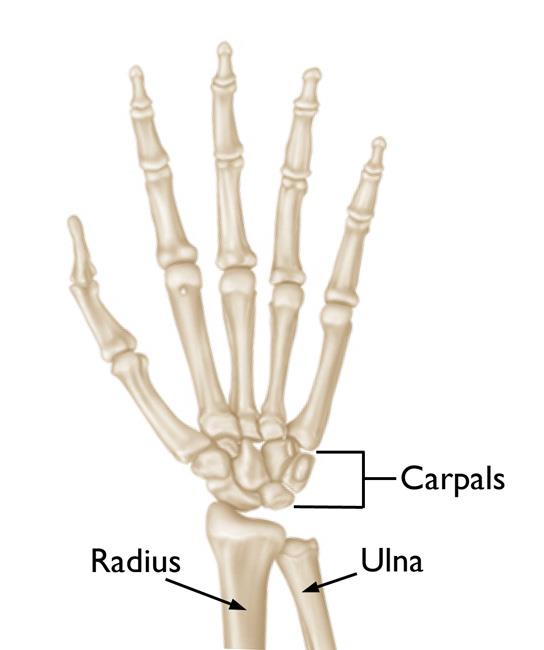
What are the bones of the wrist joint?
- radius (primarily)
- proximal carpals
What are the bones of the hand? (general)
- carpals
- metacarpals
- phalanges
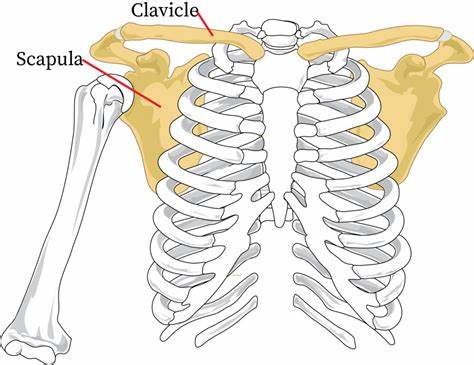
What is the purpose of the pectoral girdle?
attach the upper limbs to the axial skeleton; act as an anchor
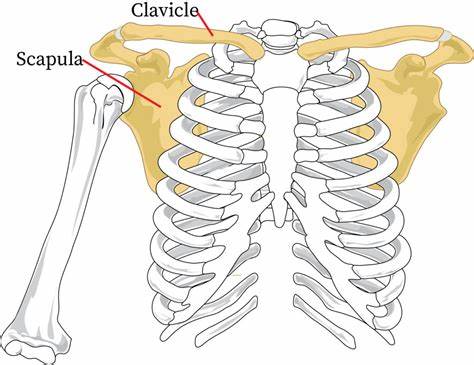
What bones make up the pectoral girdle?
clavicle and scapula
Where is the glenoid cavity (fossa)?
Shallow divot on the lateral side of scapula
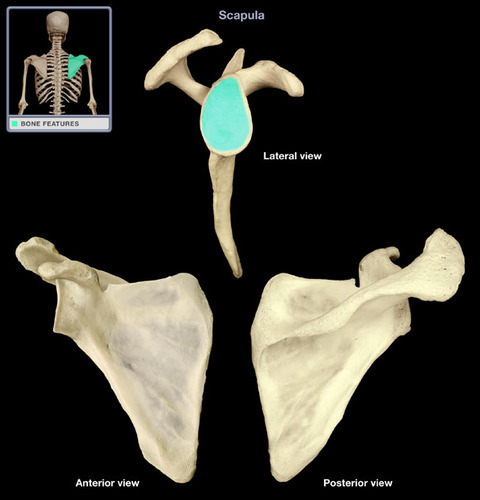
What does the glenoid cavity articulate with?
proximal end (head) of the humerus
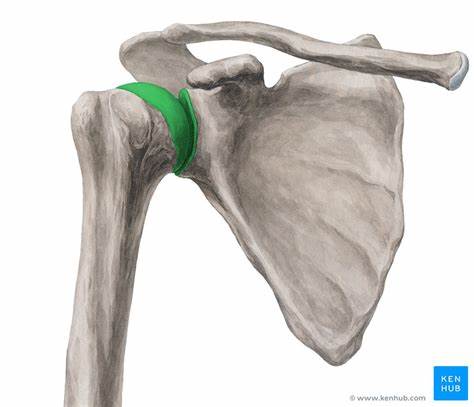
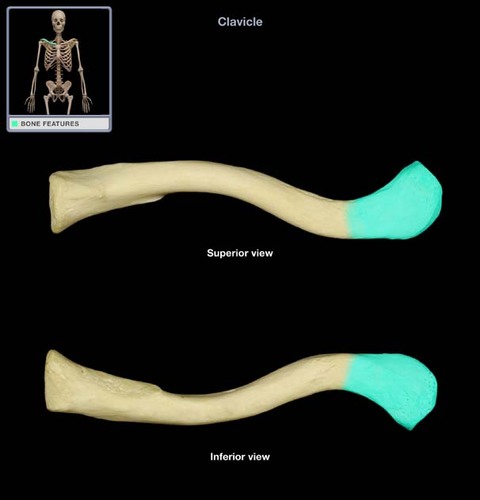
What thing(s) does the clavicle articulate with?
- manubrium of the sternum (medial end of clavicle)
- acromion of the scapula (lateral end of clavicle)
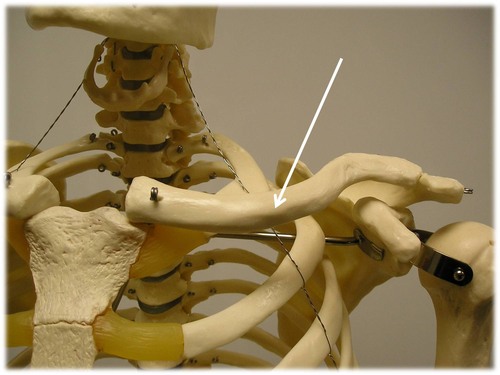
(T/F) The manubrium articulates with the medial end of the clavicle.
True
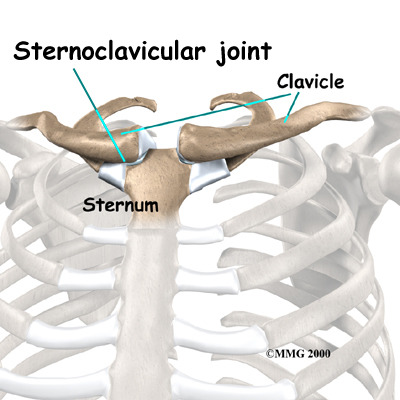
Which side is the medial end of the clavicle?
side of the clavicle closest to the median; a bit rounder/flat end
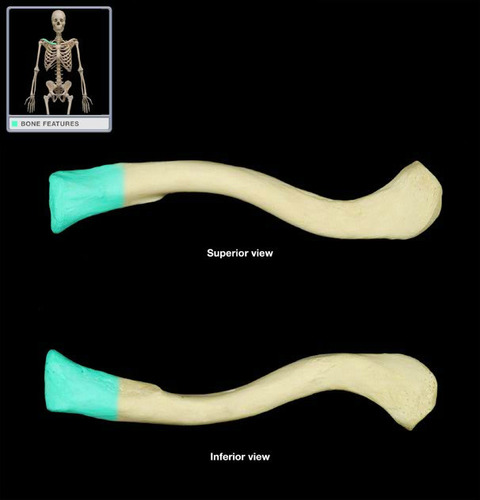
(T/F) The acromion of the scapula articulates with the medial end of the clavicle.
False - it articles with the lateral end of the clavicle
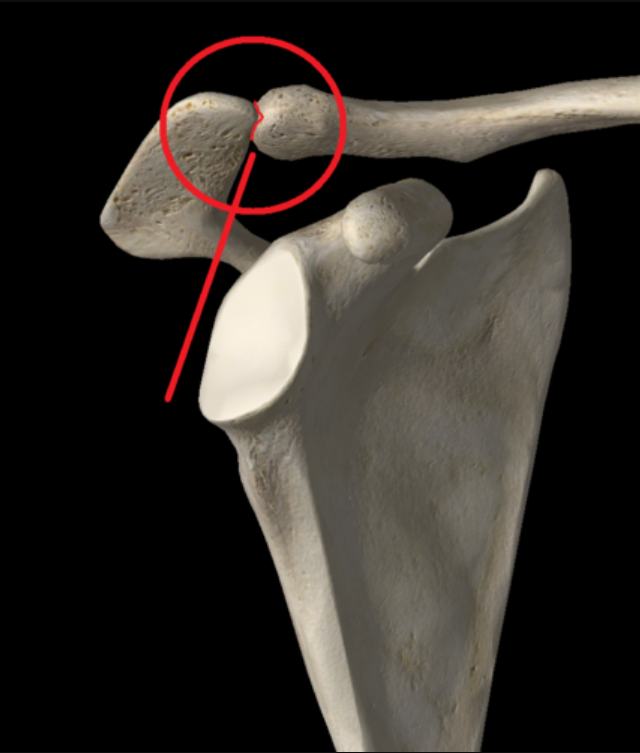
Which side is the lateral end of the clavicle?
The side of the clavicle closest to the sides; a bit thinner
(T/F) The clavicle has direct articulation with the humerus.
False - it does NOT
What are the processes of the scapula?
1) Spine of scapula
2) Coracoid process
3) Acromion process
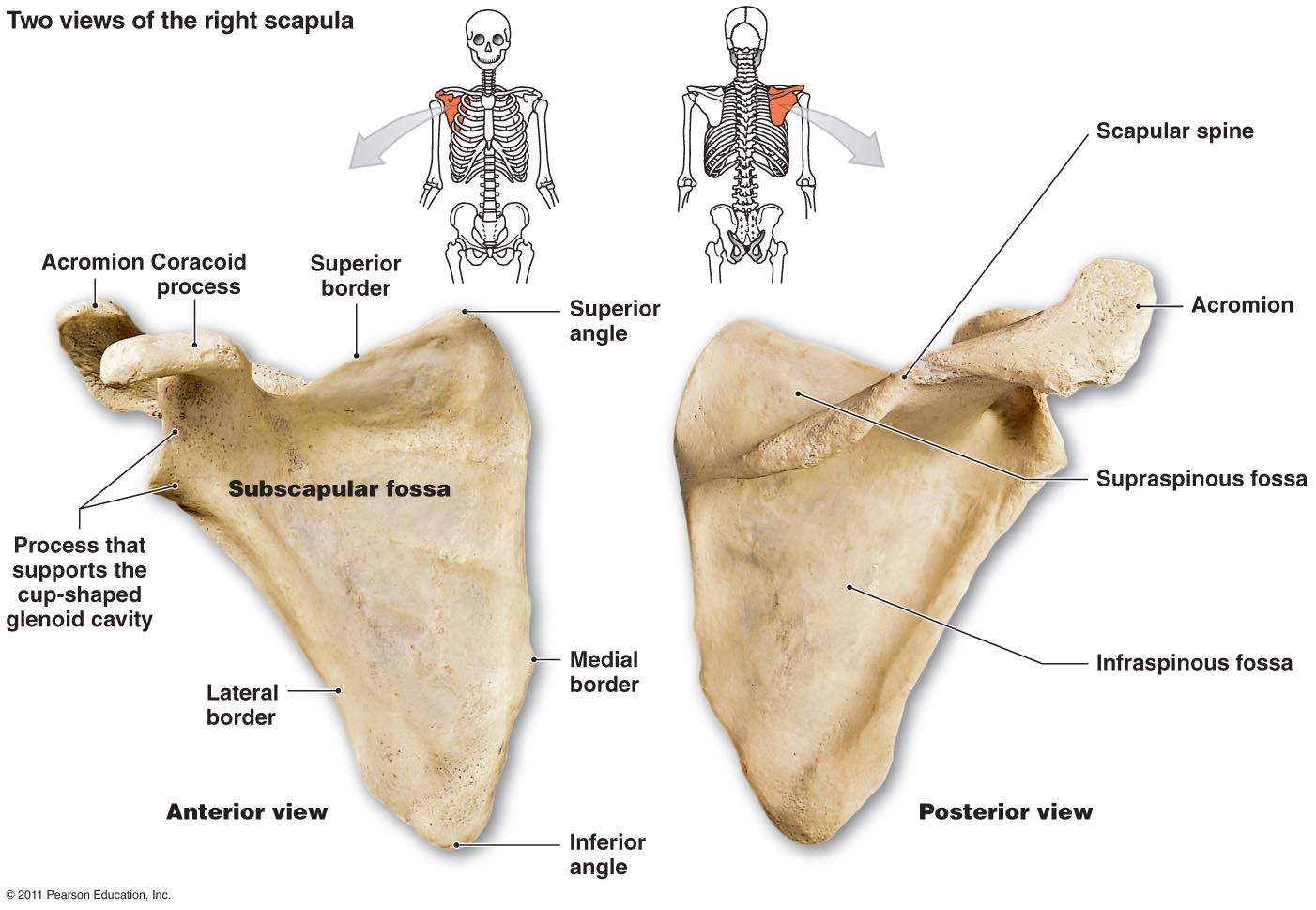
Where is the spine of the scapula located?
posterior side
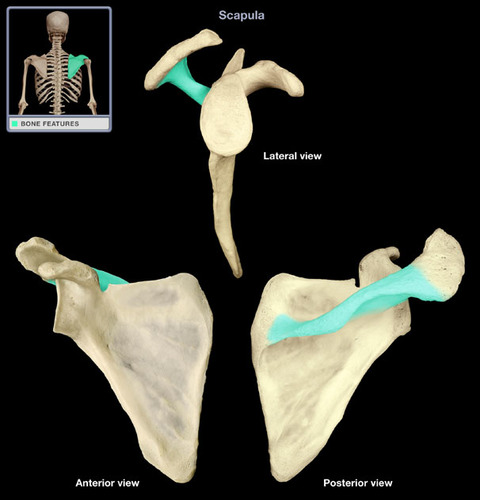
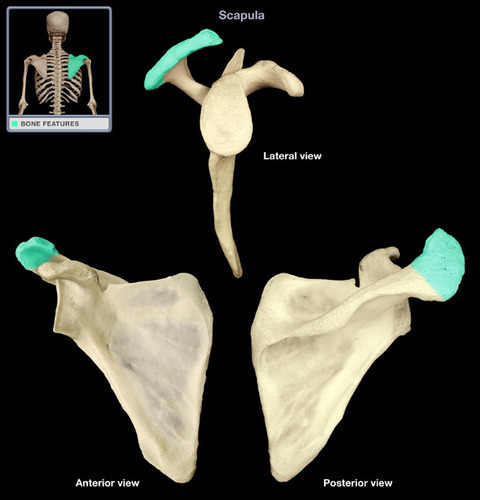
Where is the acromion process located?
tip of scapula, on the posterior lateral side, connected ridge with the spine of the scapula
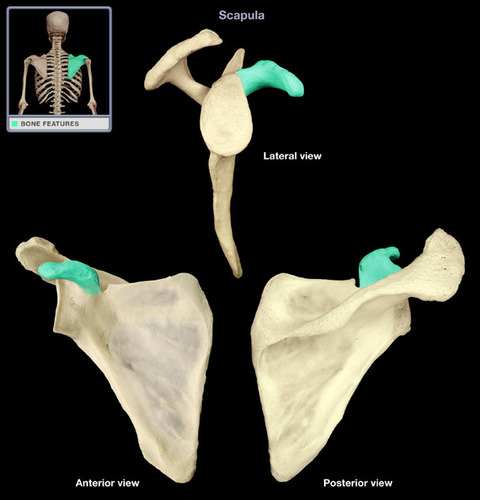
Where is the coracoid process?
tip of scapula, on the anterior lateral side
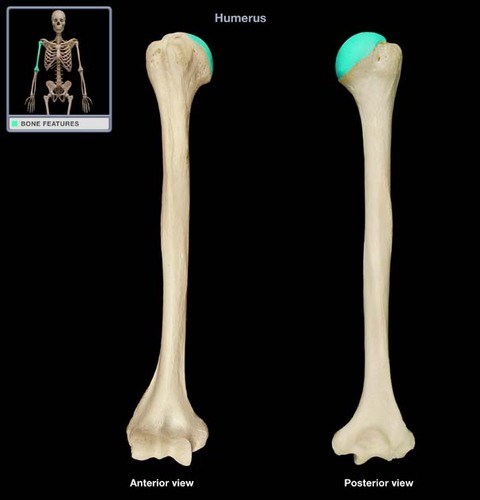
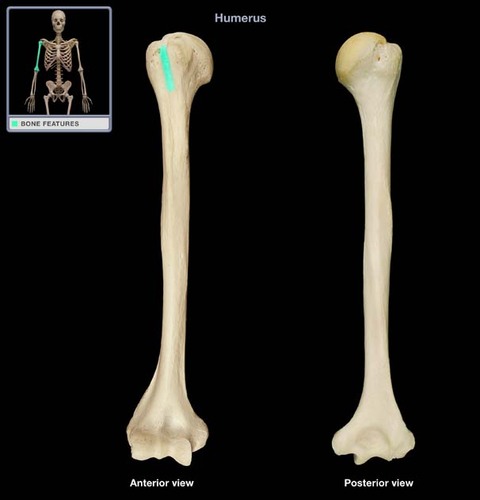
Where is the head of the humerus?
proximal end (closer to the scapula)
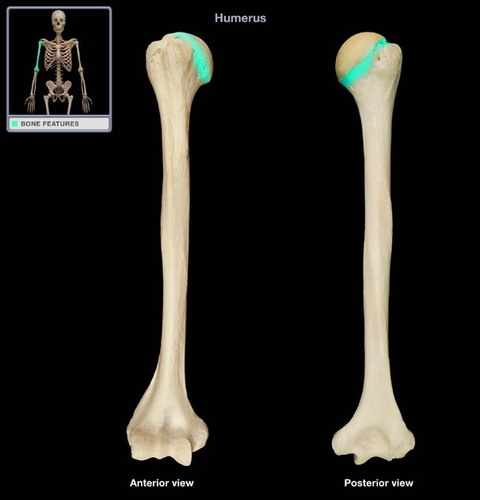
Where is the anatomical neck of the humerus?
right under the head
Where is the surgical neck of the humerus?
- falls right below the greater and lesser tuberosities
- the place where humeral fractures most commonly occur
- important location of arteries and nerves that surgeons want to avoid
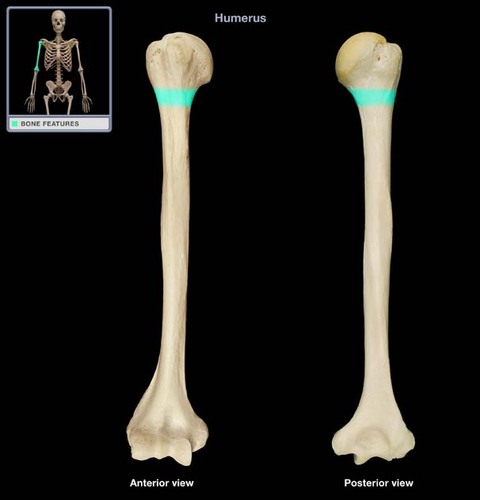
Where is the greater tubercule on the humerus?
located more laterally on the humerus
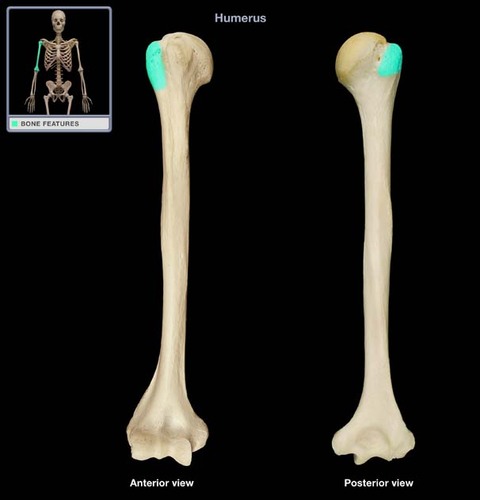
Where is the lesser tubercule on the humerus?
located laterally, but more frontal
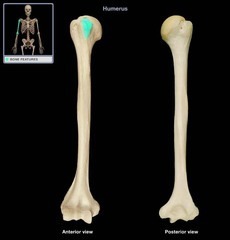
Where is the intertubercular sulcus on the humerus?
Groove in between the greater and lesser tubercles
What is the purpose of the intertubercular sulcus?
Groove for the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii
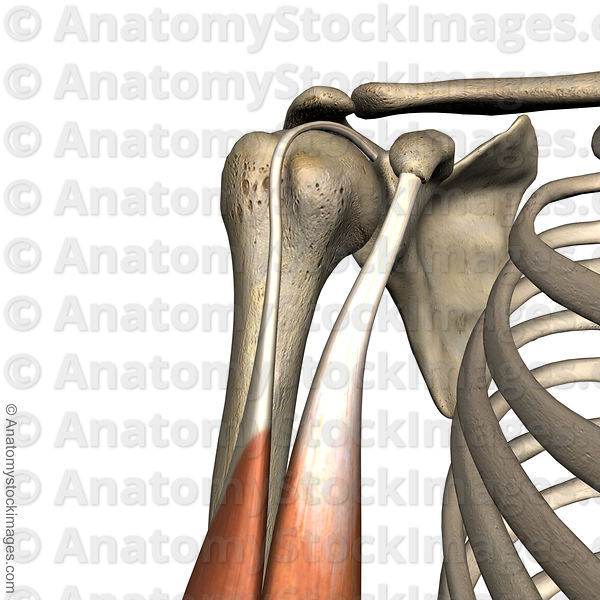
What muscles make up the rotator cuff?
SITS
- Subscapularis
- Infraspinatus
- Teres minor
- Supraspinatus
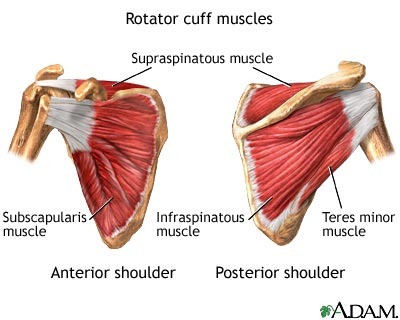
Where is the supraspinatus located?
posterior side of scapula, superior to spine of scapula
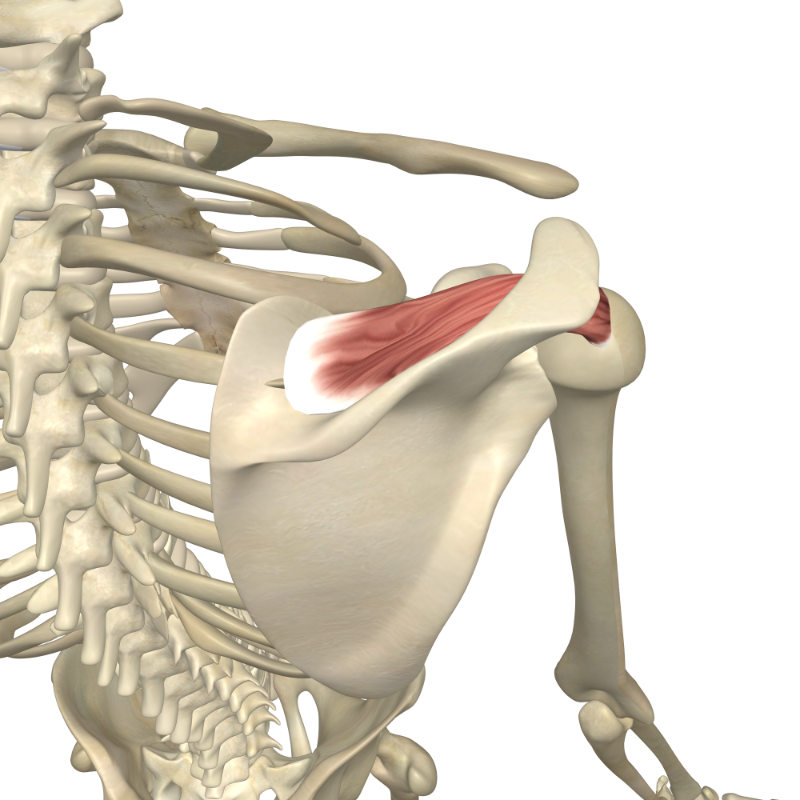
What are the origin and insertion points of the supraspinatus muscle?
ORIGIN: supraspinous fossa of scapula
INSERTION: greater tubercle of humerus
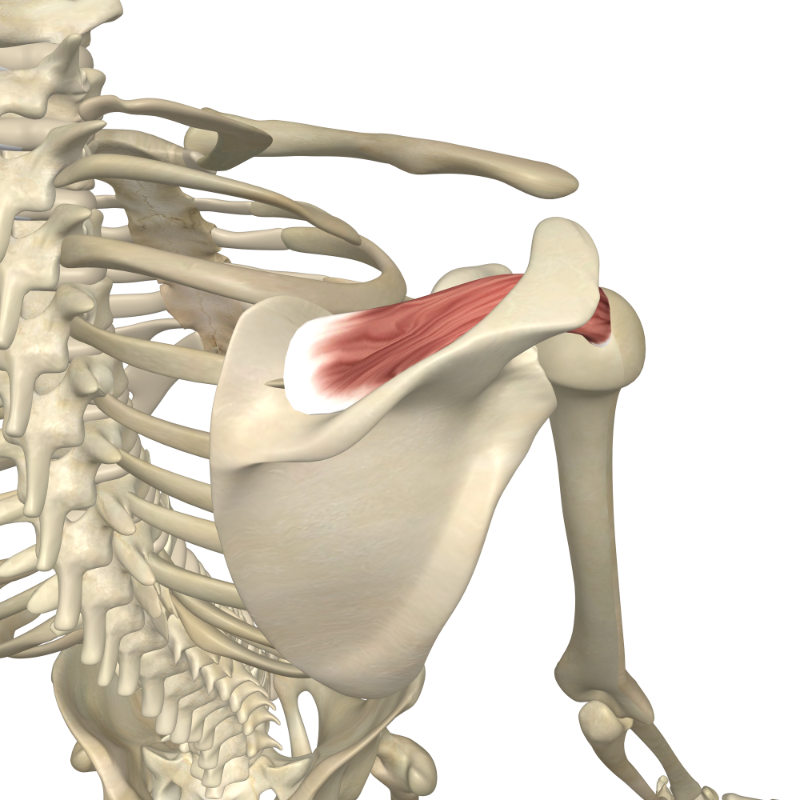
Where is the infraspinatus located?
posterior side of scapula, inferior to spine of scapula
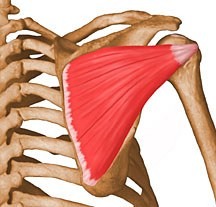
What are the origin and insertion points of the infraspinatus muscle?
ORIGIN: infraspinous fossa of scapula
INSERTIONS: greater tubercle of humerus
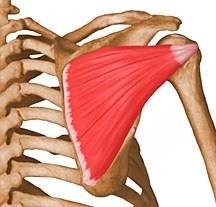
Where is the teres minor located?
lateral border of scapula, inferior to infraspinatus
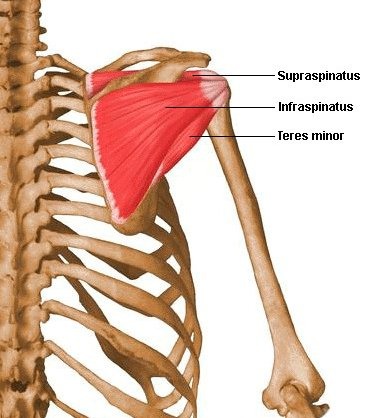
What are the origin and insertion points of the teres minor muscle?
ORIGIN: lateral border of scapula
INSERTION: greater tubercle of humerus
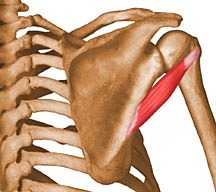
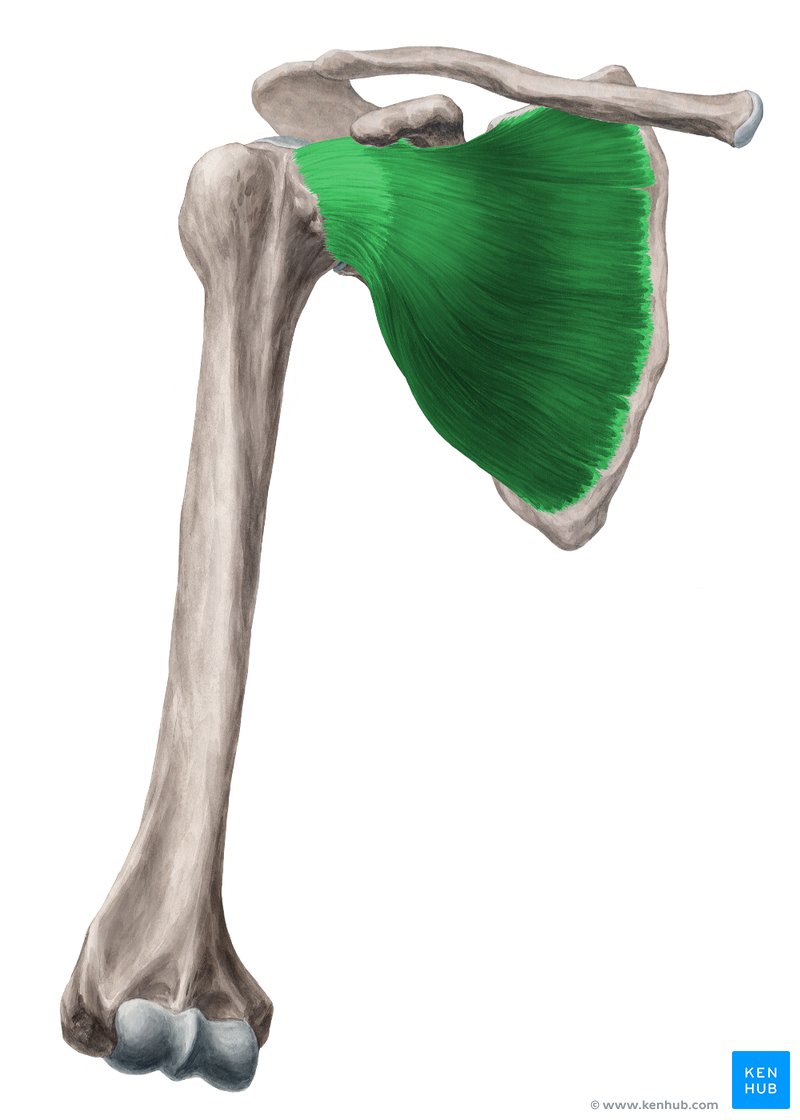
Where is the subscapularis located?
anterior side of scapula
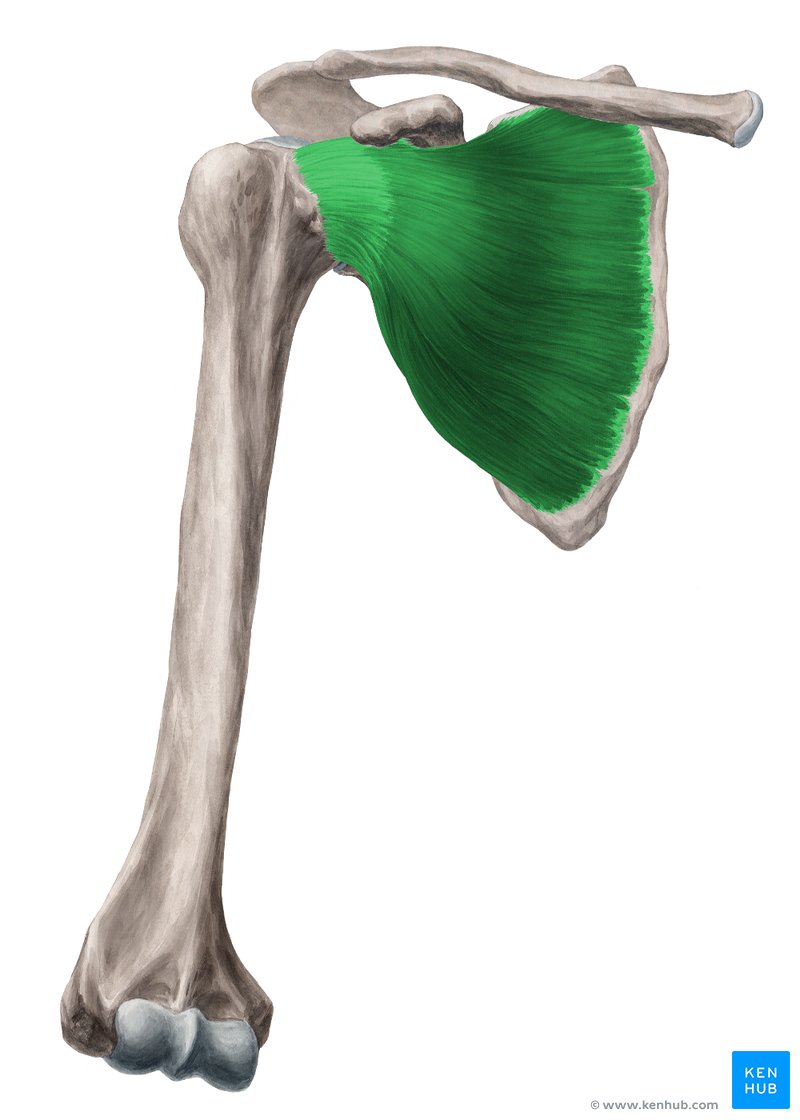
What are the origin and insertion points of the subscapularis muscle?
ORIGIN: subscapular fossa of scapula
INSERTION: less tubercle of humerus
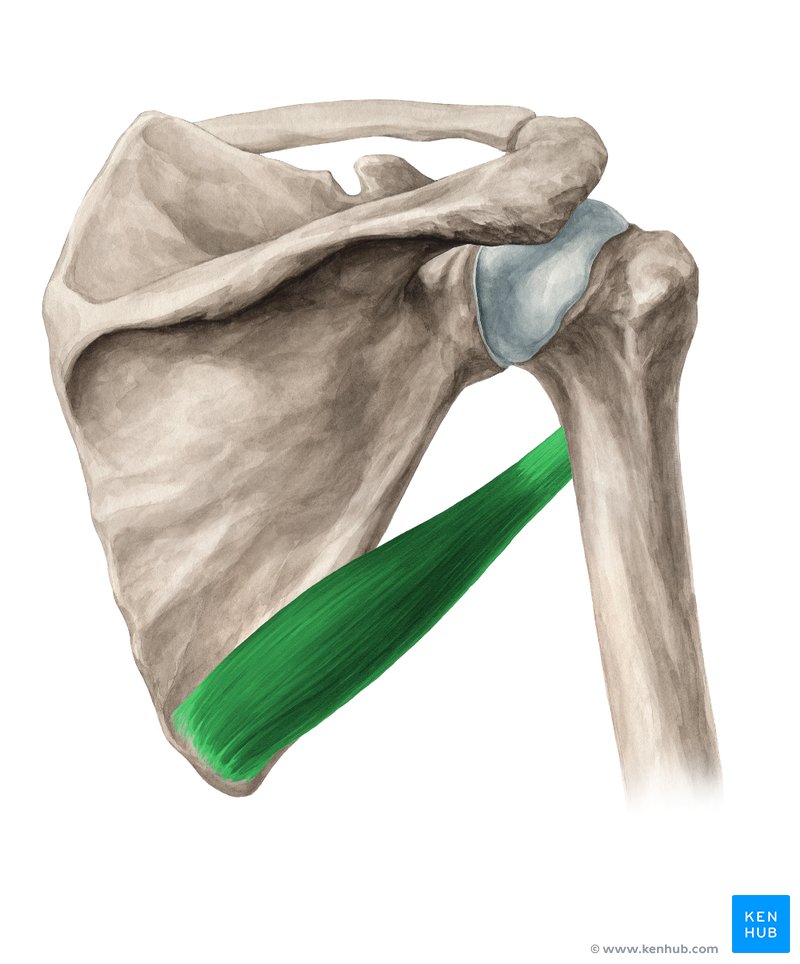
Where is the teres major located?
lower part of lateral border of scapula, inferior to teres minor
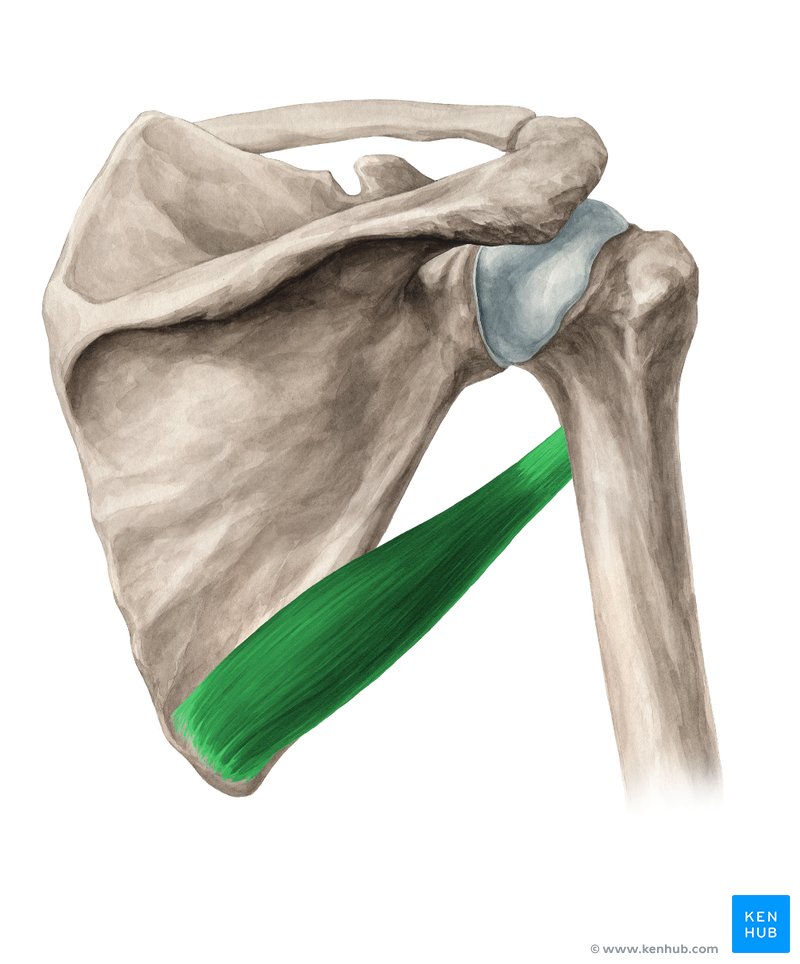
What are the origin and insertion points of the teres major muscle?
ORIGIN: inferior angle of scapula & lower portion of lateral border of scapula
INSERTION: medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus
What are the five stabilizing ligaments of the shoulder?
- superior glenohumeral ligament
- middle glenohumeral ligament
- inferior glenohumeral ligament
- coracohumeral ligament
- transverse humeral ligament
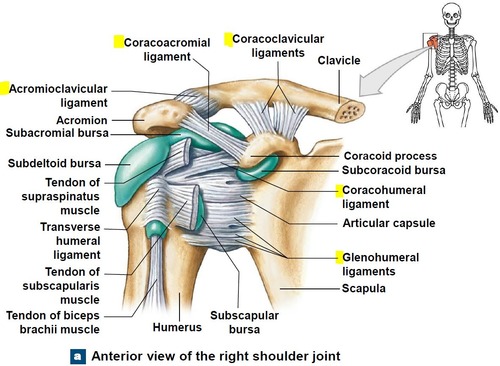
Where is the superior glenohumeral ligament located? What is its purpose?
Extends from supraglenoid tubercle of scapula to the proximal aspect of the lesser tubercle of humerus
along with the coracohumeral ligament, it supports the rotator cuff and prevents inferior translation (downward movement) of the humeral head, especially during shoulder adduction
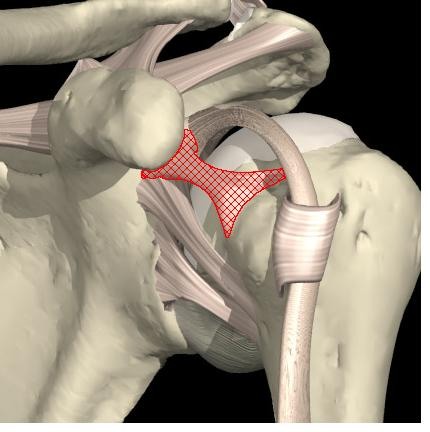
Where is the middle glenohumeral ligament located? What is its purpose?
Extends from anterior glenoid margin of the scapula (just inferior to the superior GH ligament) to less tubercle of humerus
stabilizes the shoulder capsule around ball-and-socket joint and limits external rotation, especially when the arm is in an abducted position
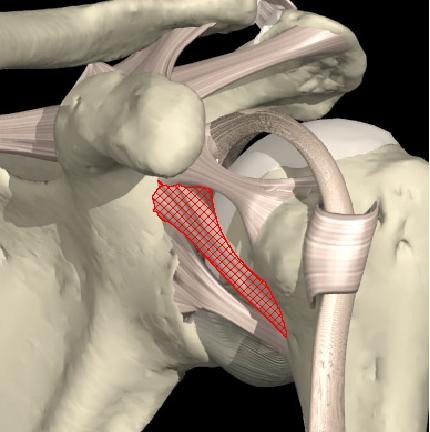
Where is the inferior glenohumeral ligament located? What is its purpose?
extends from the glenoid labrum to inferomedial part of the humeral neck
it is the strongest of the GH ligaments, it stabilizes the humeral head when the arm is abducted above 90 degrees
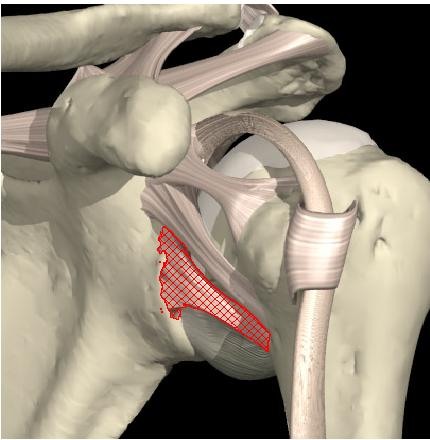
Where is the coracohumeral ligament located? What is its purpose?
Extends between coracoid process to both the lesser and greater humeral tubercles
strengthens the upper part of the shoulder capsule around ball-and-socket joint
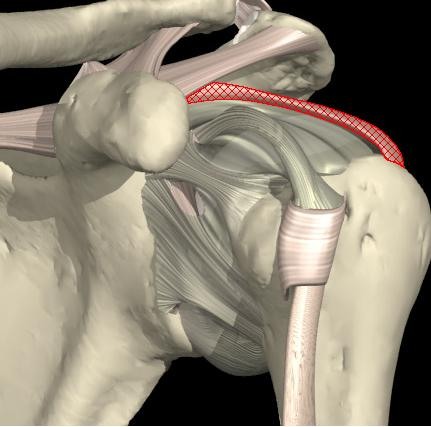
Where is the transverse humeral ligament located? What is its purpose?
bridges between the greater and lesser humeral tubercules
holds the long head of the biceps tendon into position in the intertubercular groove
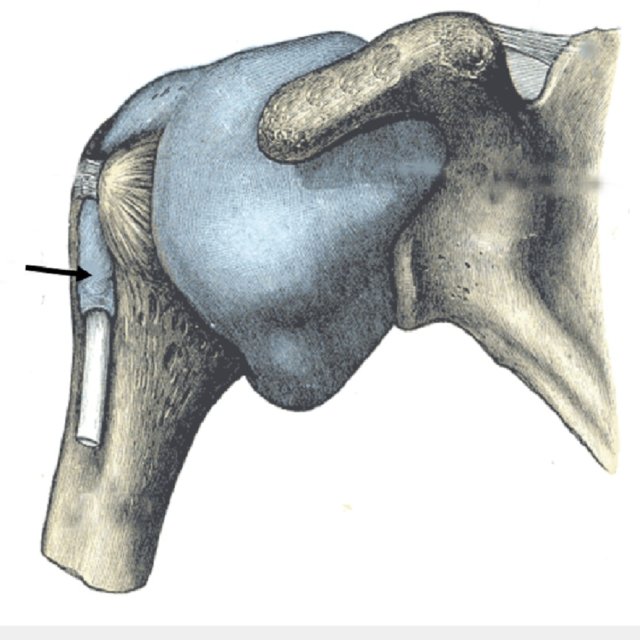
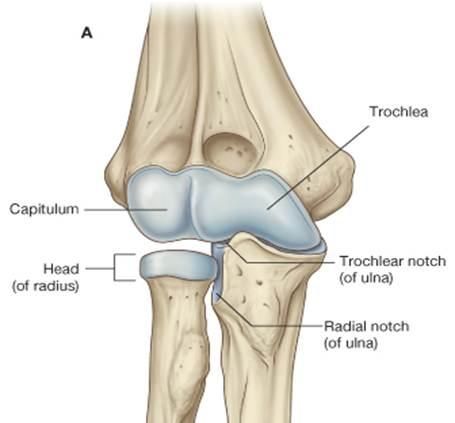
What articulation(s) allow for flexion and extension of the elbow?
1. trochlea of humerus & trochlear notch of ulna
2. capitulum of humerus & head of radius
Where is the articulation between the trochlea of humerus and trochlear notch of ulna?
- distal & medial side of humerus
- proximal end (hook) of ulna
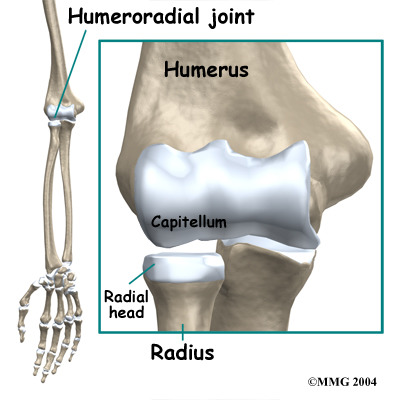
Where is the articulation between the capitulum of humerus and head of radius?
- distal & lateral side of humerus
- proximal end (stump) of radius
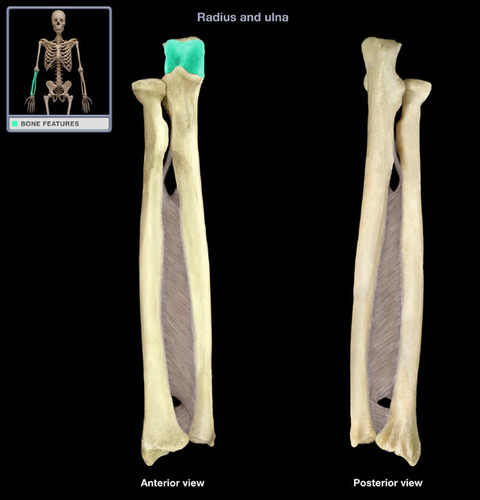
Where is the trochlear notch of ulna?
proximal end (hook) of ulna
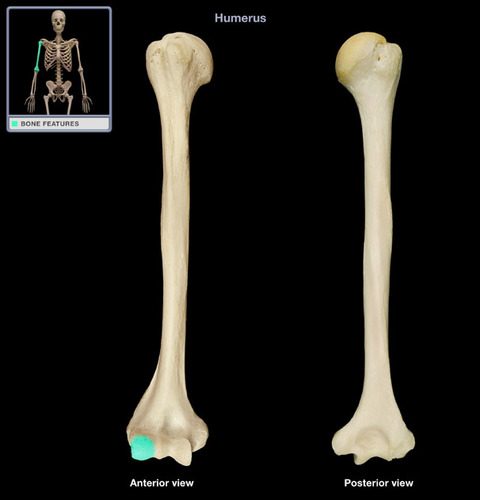
Where is the trochlea of the humerus?
distal & medial side of humerus
Where is the capitulum of the humerus?
distal & lateral side of humerus
Where is the head of the radius?
proximal end (stump) of radius
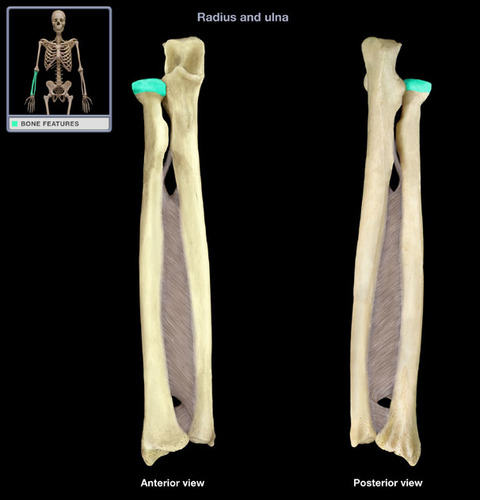
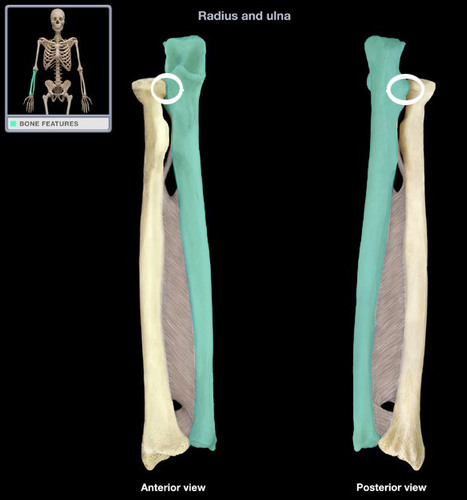
What articulation(s) allow for pronation and supination of the forearm?
head of radius & radial notch of ulna
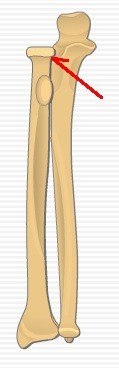
Where is the articulation between the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna?
- proximal end (stump) of radius
- proximal end of ulna on its lateral side (closest to radius)
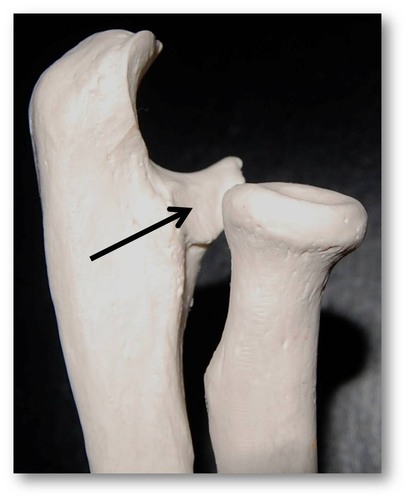
Where is the radial notch of the ulna?
proximal end of ulna on its lateral side (closest to radius)
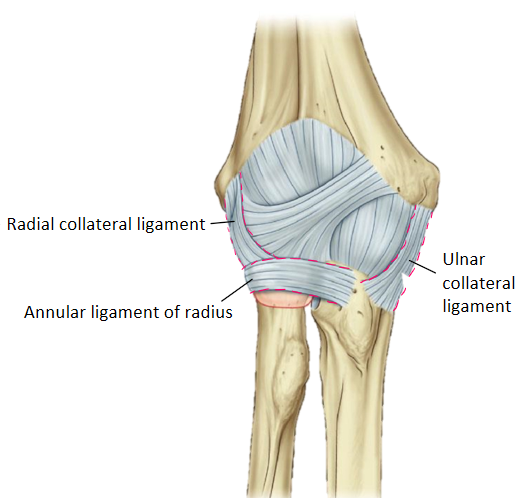
What are the stabilizing ligaments of the elbow?
- radial (lateral) collateral
- ulnar (medial) collateral
- annular ligament of radius
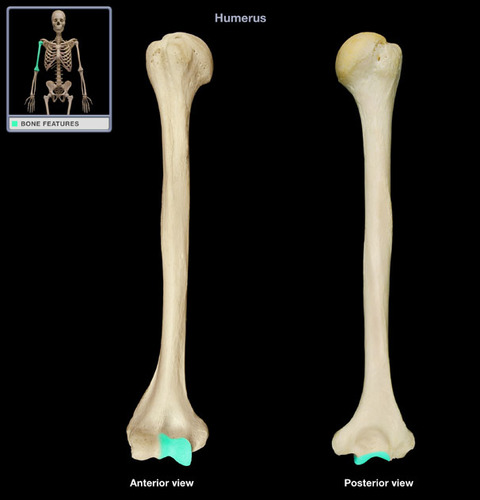
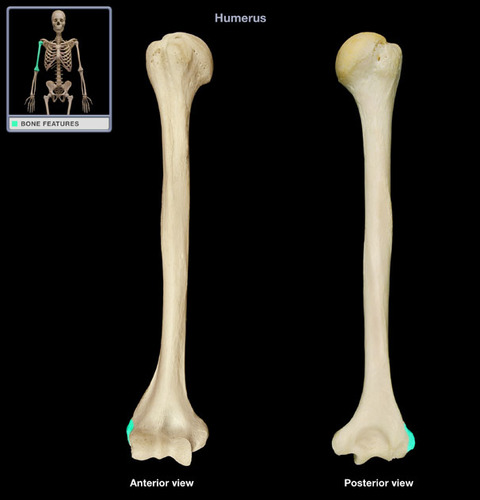
Where is the lateral epicondyle of the humerus located?
A bony projection on the lateral side of the humerus on its distal end
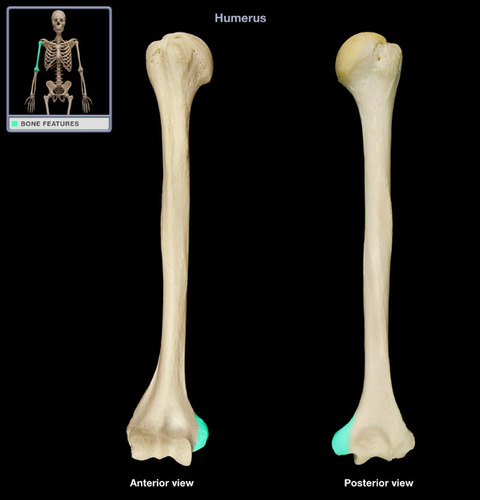
Where is the medial epicondyle of the humerus located?
A bony projection on the medial side of the humerus on its distal end
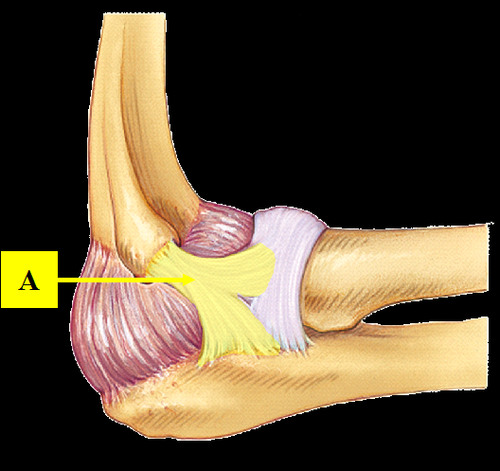
Where is the radial collateral ligament located?
Attaches from lateral epicondyle of humerus to annular ligament of the radius
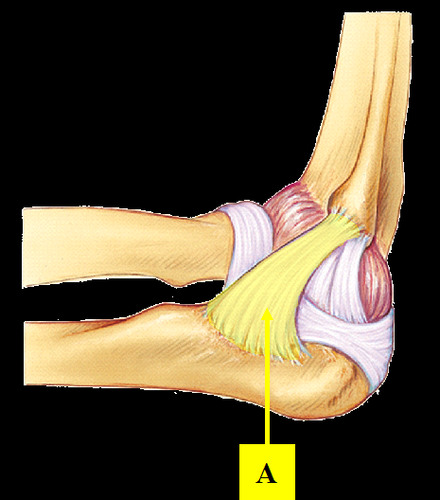
Where is the ulnar collateral ligament located?
extends from the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the coronoid process of the ulna
Where is the coronoid process of the ulna?
v-shaped tip on the anterior side of the proximal end of the ulna
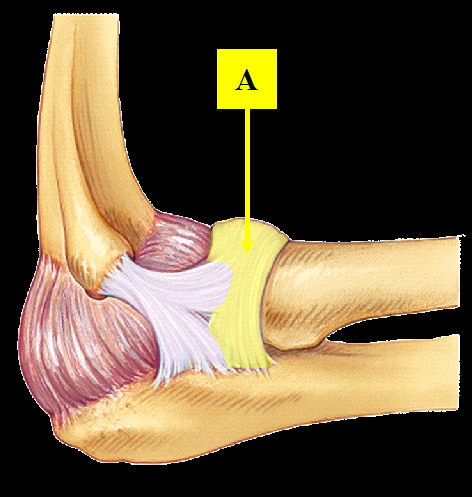
Where is the annular ligament of the radius located?
extends from the anterior margin of the radial fossa of the ulna, encircles the radial head, and attaches to the posterior margin of the radial fossa (creates a ring)
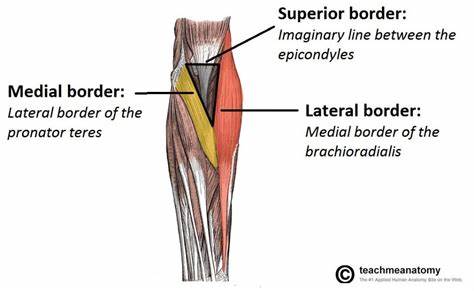
What are the boundaries of the cubital fossa?
- brachioradialis
- pronator teres
- line between lateral and medial epicondyles
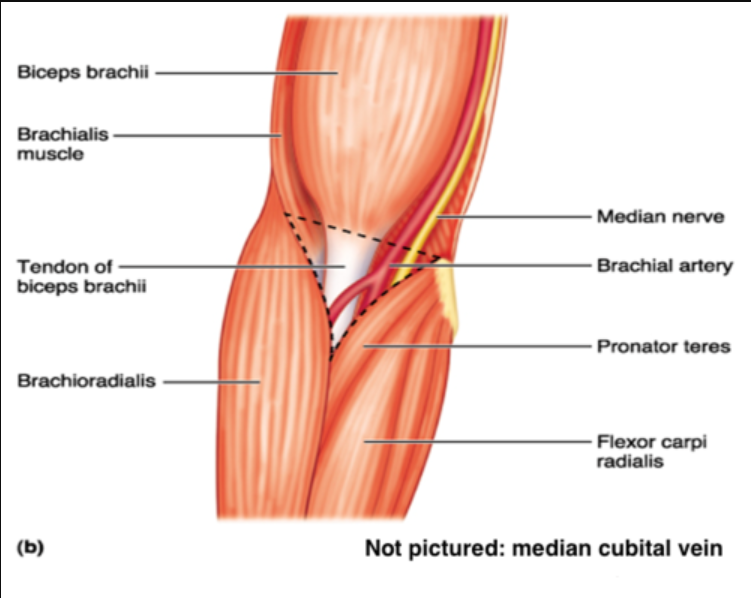
What are the contents of the cubital fossa?
- tendon of biceps brachii
- brachial artery
- median nerve
- (superficially) the median cubital vein
What are the forearm bones?
radius and ulna (radius is lateral to ulna in anatomical position)
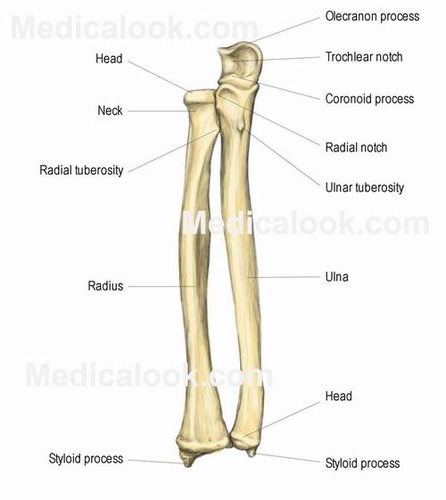
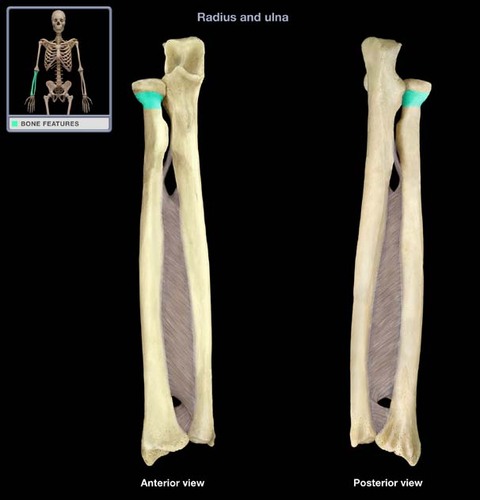
Where is the neck of the radius?
between head and radial tuberosity
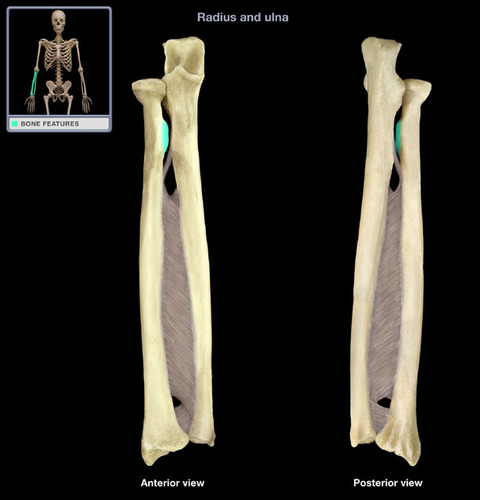
Where is the radial tuberosity?
Right below the head and neck of the radius, faces medially (towards ulna)
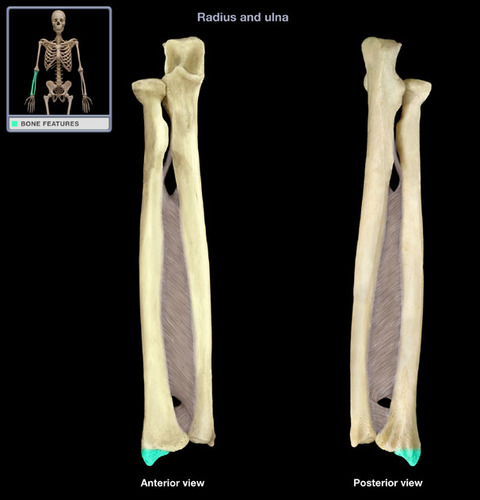
Where is the radial styloid process located?
projection on the distal end of radius
Where is the olecranon process located?
The proximal end of the ulna on the posterior side.
Where is the ulnar styloid process located?
distally and medially on the ulna