Chapter 1: Study of Human Sexuality
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the key components of Sexual Literacy?
Sexual Well-Being, Holistic Sexuality, Sexual Selfhood, Sexual Negotiation, Sexual Empowerment.
What are the three aspects of achieving Sexual Well-Being?
Pleasure, Protection, Purpose in life.
What is Emotional Literacy in the context of sexuality?
Knowing what to say, how to name body parts, and how to protect oneself.
Who was John Kellogg and what was his controversial practice?
John Kellogg was a sexologist known for performing circumcision without anesthesia to 'cure' masturbation.
What was the contribution of Charles Darwin to sexology?
He explained how sex contributes to the diversity of life.
What terms did Richard von Krafft-Ebing coin in his studies?
Fetishism and perversions.
Who was Magnus Hirschfeld and what did he contribute to?
He used surveys and helped found the homosexual rights movement in Germany.
What was Havelock Ellis known for?
He was an authority on the treatment of sexual problems in heterosexual marriages and had an open marriage with a feminist wife.
What is Sigmund Freud's theory about early desires?
He proposed that our earliest desires and fantasies revolve around conflicted sexual attraction to the opposite-sex parent.
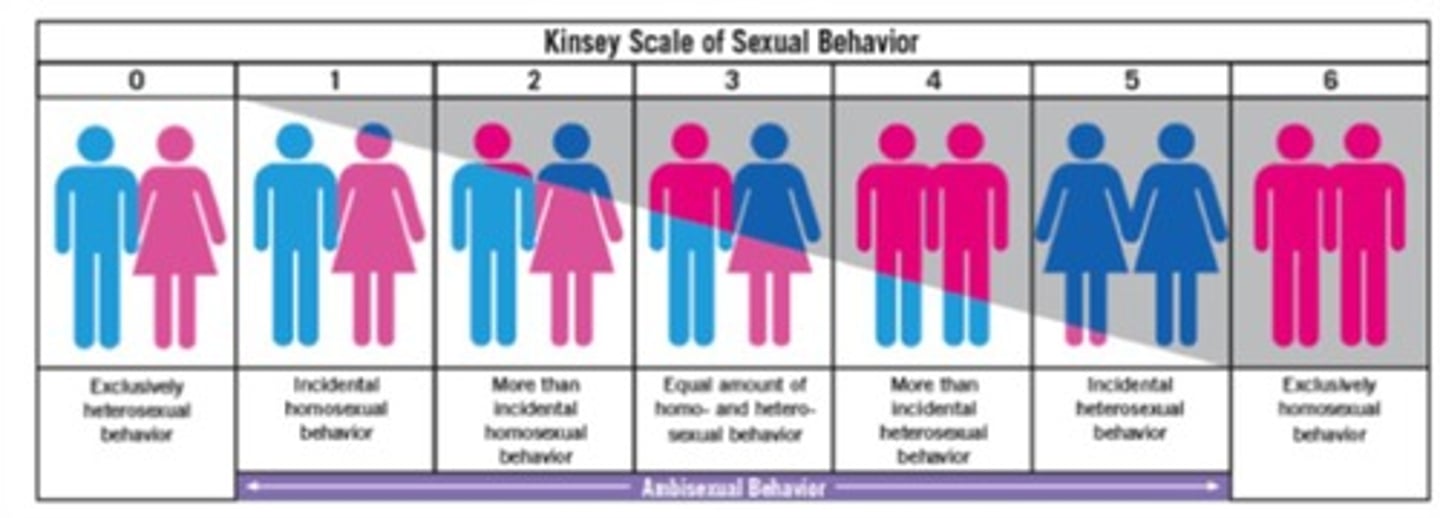
What is the significance of Alfred Kinsey in sex research?
He pioneered the scientific survey study and developed the sexuality continuum.
What did Masters & Johnson discover about women's sexual response?
They discovered that women could have multiple orgasms.
What were the goals of the National Health and Social Life Survey (NHSLS)?
To include ethnic diversity, identify changes in sexuality, and study the role of pleasure in sexual behavior.
What are the ethical considerations in studying sexuality?
Protecting research participants, ensuring anonymity, verifying truthful results, and preventing harm.
What are the benefits of sex research?
Reduction of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), unintended pregnancies, and improvement in mental & physical health and sexual well-being.
What is the purpose of interdisciplinary goals in sex research?
To better understand and predict human sexual behavior and influence laws and policies.
What does intersectionality address?
The combination of social identities and social inequality, promoting social justice.
What is qualitative research focused on?
Meaning and context, often using small or nonrandom samples.
What distinguishes quantitative research?
It focuses on sample design with large representative or random samples.
What is a case study in sex research?
An in-depth study of a single individual or very small group, analyzing personal records.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of direct observation in research?
Advantages include observing natural behaviors; disadvantages include potential observer influence and self-selection bias.
What is the aim of experimental research?
To examine how changes in independent variables influence dependent variables, establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
What are universal human rights in the context of sexuality?
Rights that ensure accessibility and respect for individuals' sexual health and well-being.