AP Bio - Unit 7: Evolution (speciation)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:15 PM on 3/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
1
New cards
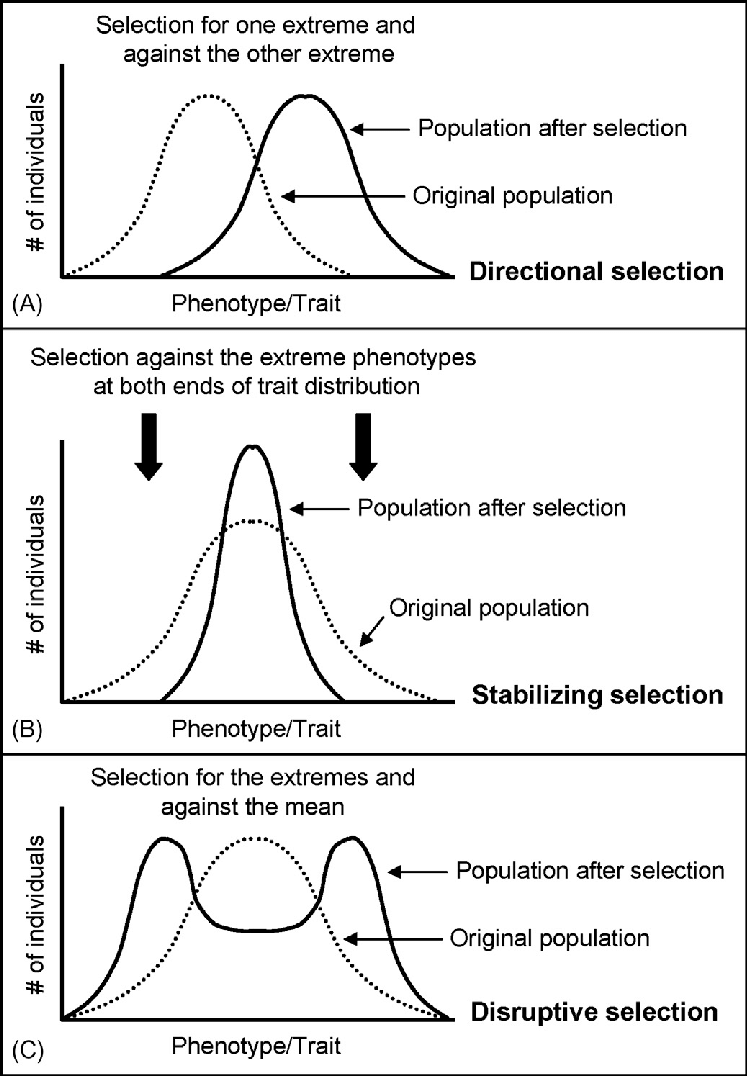
types of population selection
Directional, stabilizing, and disruptive
2
New cards
Species
A group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring
3
New cards
Hardy-Weinberg meaning and equation
Genetic variation will stay consistent across generations in the absence of disturbances
p = dominant
q = recessive
phenotypic frequency:
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
Allele Frequency:
p + q = 1
p = dominant
q = recessive
phenotypic frequency:
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
Allele Frequency:
p + q = 1
4
New cards
speciation
The formation of a new and distinct species in the course of evolution
5
New cards
2 Types of speciation
Allopatric and sympatric
6
New cards
Allopatric Speciaiton
One species is separated by geographic environments they undergo allopatric speciation. If they were to meet again in the future they would not interbreed
e.g. california salamanders
e.g. california salamanders
7
New cards
Sympatric Speciation
Even though both populations inhabit the same area, a new species evolves through pre-zygotic isolation
8
New cards
Types of pre-zygotic isolation
Gamete Isolation
* gametes cant fuse/fertilize
Behavioral Isolation
* courtship displays and different
Mechanical Isolation
* Incompatible sex organs
Temporal Isolation
* mating timing becomes different (nocturnal vs diurnal)
Habitat Isolation
* different habitats in the same location
* gametes cant fuse/fertilize
Behavioral Isolation
* courtship displays and different
Mechanical Isolation
* Incompatible sex organs
Temporal Isolation
* mating timing becomes different (nocturnal vs diurnal)
Habitat Isolation
* different habitats in the same location
9
New cards
post-Zygotic isolation
prevents the creation of a fertile offspring
10
New cards
Advantages of hybridization
favorable traits, survival of endangered species
11
New cards
Disadvantages of hybridizaiton
low zygotic viability (severe abnormalities, fails to mature), infertility, low adult viability (low survival rate because traits arent suited for any environment)
12
New cards
Micro evolution vs Macro evolution
micro: evolution in a short period of time (couple of generations)
macro: evolution over a long period of time
macro: evolution over a long period of time