Lesson 12: Transmission of Mendelian traits in Humans
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is autosomal inheritance?
Genes on chromosomes 1–22, not related to sex.
What is Sex-linked inheritance?
Traits from genes on X or Y chromosomes.
Types of Autosomal Inheritance
Dominant and recessive
Types of Sex-linked inheritance
X-chromosomal domninat/recessive, Y-chromosomal, mitochondrial
Symbols of pedirgrees
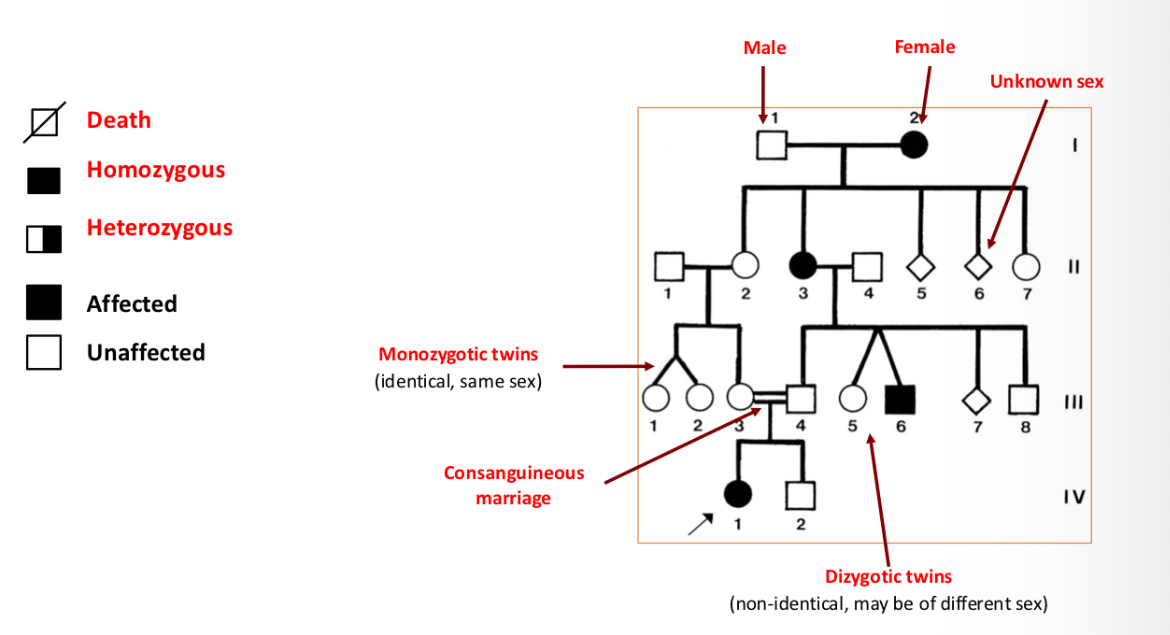
When is Autosomal dominant observable phenotypically?
Phenotypically observable both in homozygous and heterozygous
Criteria of autosomal dominant inheritance
-Every generation has a phneotypical affected person
-Affected parents get not affected kids
-independent of the sex of the progenitor
-Not affected individuals will not transmit
-Each affected individual has an affected parent
AA + aa → 100% of offspring
Aa + Aa → 75%
Aa + aa → 50%
Autosomal recessive
for the trait to be observed, the allele gene responsible for it must be in homozygosis
Possible genotypes and their status
AA = healthy
Aa = carrier heterozygous
aa = ill
Homozygosis aa
Can only transmit the trait to the offspring with carrier (heterozygous) 50% or another homozygous 100%
Heterozygous Aa - carriers
Do not show the trait but can transmit it
With another carrier 25%, with a recessive homozygous 50%
Criteria of recessive autosomic inheritance
-not affected progenitors get affected offspring
-independent of the sex of the progenitor
-trait not observed in all generations
What is incidence risk?
Probability that the first child inherits a genetic disease
- When it is known that there is a risk of transmitting a genetic disease
What is the recurrence risk?
Probability that the following children will also inherit the disease
- When one or more children have been born with the disease
What is consanguinity?
Mating among individuals from the same family (having a common ancestor)
How is a genetically identical twin painted and a non identical?

Does it matter if a dominant disease is homozygous or heterozygous?
Yes homozygous geno- and phenotype expression is way more severe
Carriers of genes of recessive diseases
-clinically normal
-can cause reduced levels of enzymatic activity
What genes do Sex chromosomes carry?
Sex genes, that determine the sexual phnemotype of the individual and non sex genes
Which Segments of sex chromosomes contain genes are transmitted like autosomal genes?
BC

Which Segments are hemizygous?
AB and CD
X-linked inheritance
• In men: hemizygosis
• In women: homozygosis or heterozygosis
• It can be dominant or recessive
Criteria for X-linked dominant
-appears in females with double frequency than in males
-sick father → every daughter sick
-will not transmit to son
-heterozygous woman has 50% chance of transmitting
Criteria for x-linked recessive
-male → hemizygosis
-male more affected than females
-sick woman → sick son
-not transmitted from male to male
Y linked inheritance
Affected father → affected son
-woman never affected
-only few y linked diseases because its small
Mitochondrial
Males will suffer but never transmit it