GTPase's
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
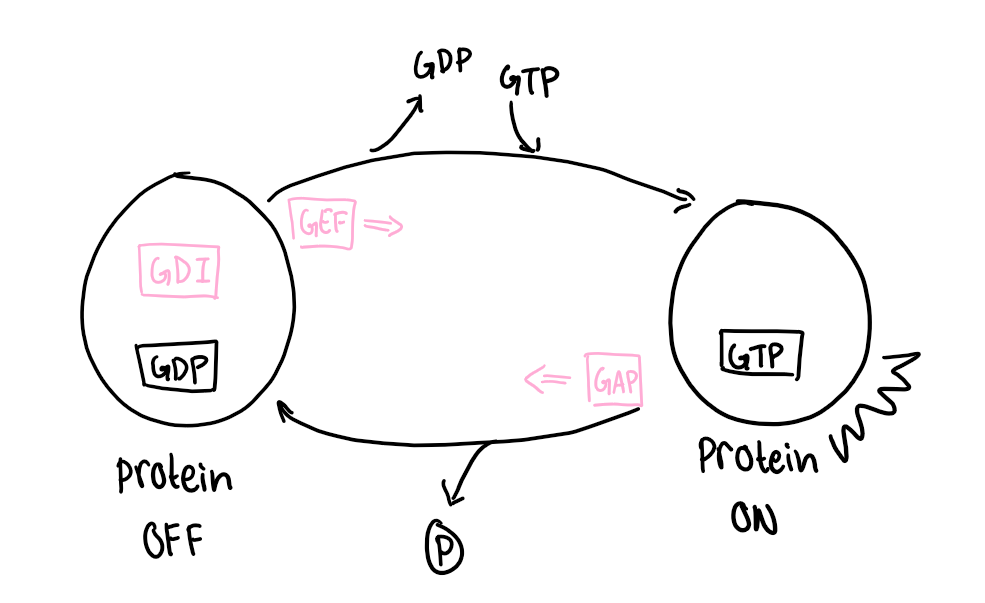
GTPase
small, catalytic proteins that have the ability to bind guanine nucleotides
GTPase when bound to GTP is what (inactive or active)
active conformation
GTPase when bound to GDP is what (inactive or active)
inactive conformation
bound GTP is naturally hydrolyzed into what
GDP
GEFs
guanine nucleotide exchange factors
precisely controls GTPase activation
stimulate the exchange of GDP for GTP
pushes GTPases into their active conformation
GAPs
GTPase activating proteins
stimulate the rapid hydrolysis of GTP to GDP
pushes GTPases into their inactivate conformation
GDIs
guanosine dissociation inhibitors
bind to GTPases and prevent the release of GDP
maintain GTPases in their inactive conformation
GTPase switch diagram/picture
what are the two types of G-proteins
monomeric and heterotrimeric/trimeric
different types of monomeric GTPases
Ras
Rho
ARF
Rab
Ran
G-proteins
trimeric GTPases
3 subunits: alpha, beta, and gamma
alpha subunit behaves like a monomeric GTPase
inactive when bound to GDP
active when bound to GTP
what is Gs
a stimulatory G-protein
stimulates an effector protein
what is a Gi
an inhibitory G-protein
inhibits an effector protein
what are the 3 classes of transmembrane receptors
gated ion channels
enzyme-couple receptors
G-protein coupled receptors
dimer signaling molecules are what
stronger than single molecule signaling
what is cross-phosphorylation
when activated kinase domains phosphorylate and increase each other’s activity