Transport Across The Cell Membrane
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Phagocytosis
Active transport involving the formation of membrane- bound vesicles to engulf solid particles
Pinocytosis
Active transport involving the formation of membrane- bound vesicles/vacuoles to engulf liquid particles
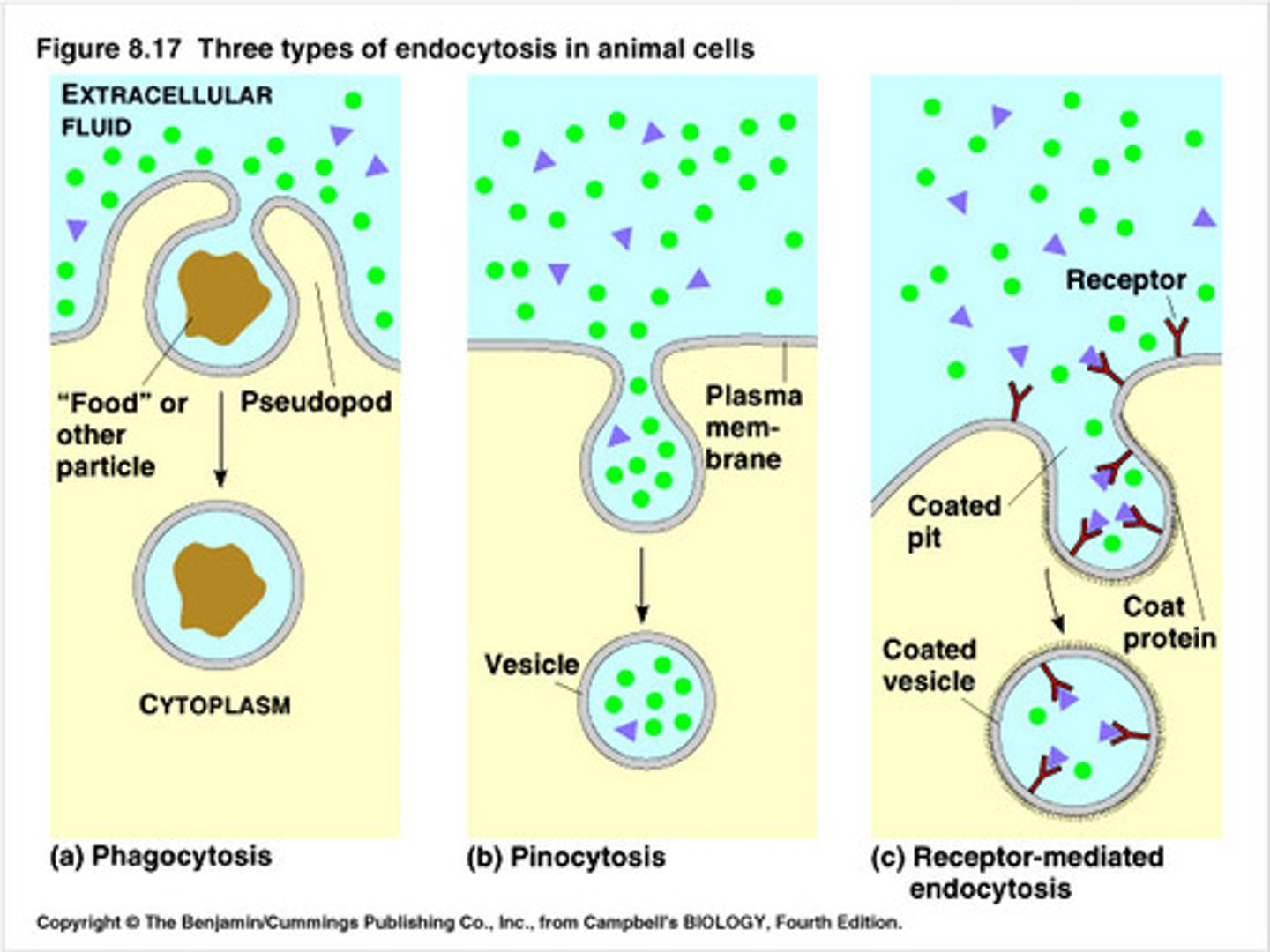
receptor mediated cytosis
Active transport involving the formation of membrane-bound vesicles/ vacuoles to engulf specific particles according to membrane receptors
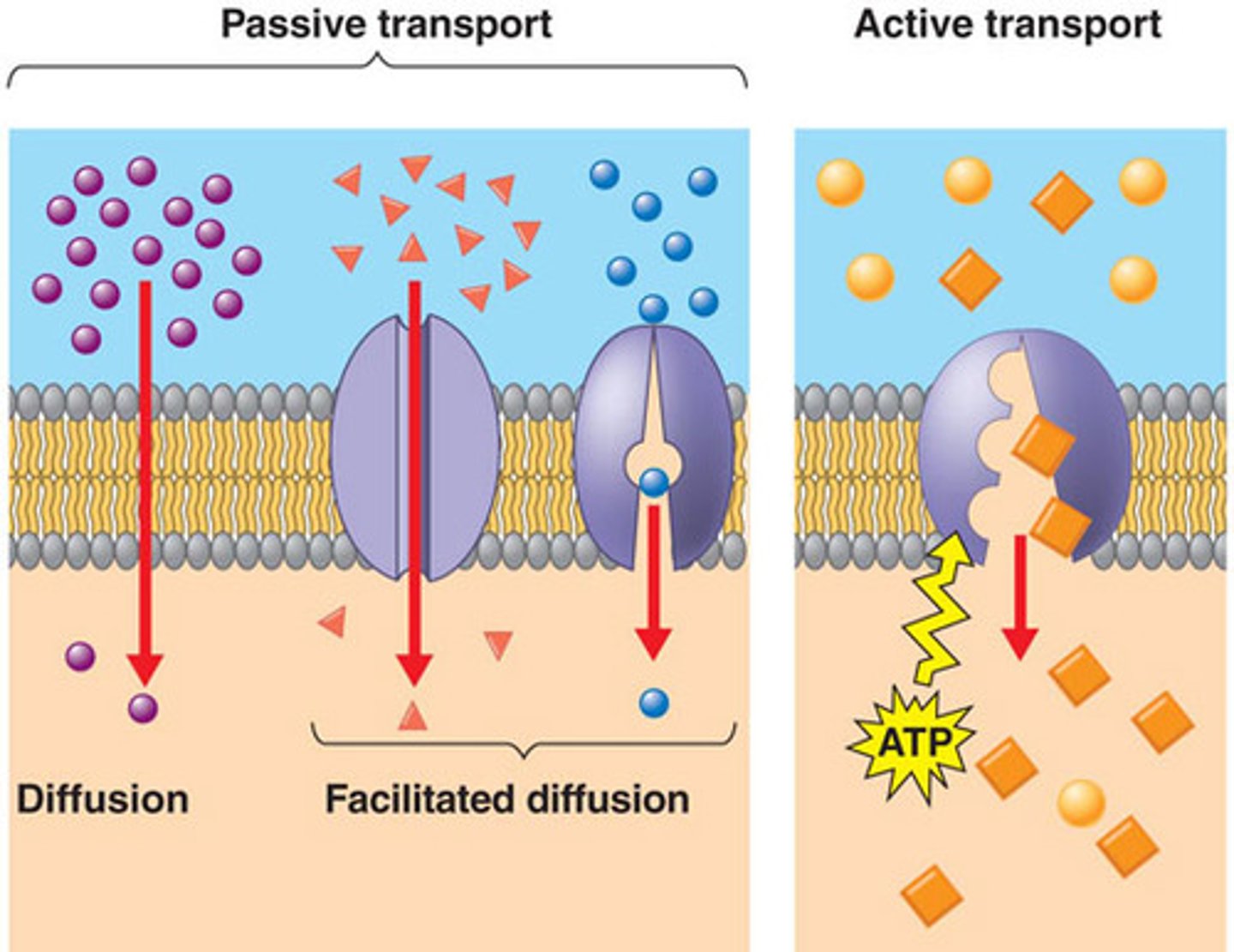
facilitated diffusion
diffusion assisted by proteins in cell membrane- for molecules that can't move through phospholipids
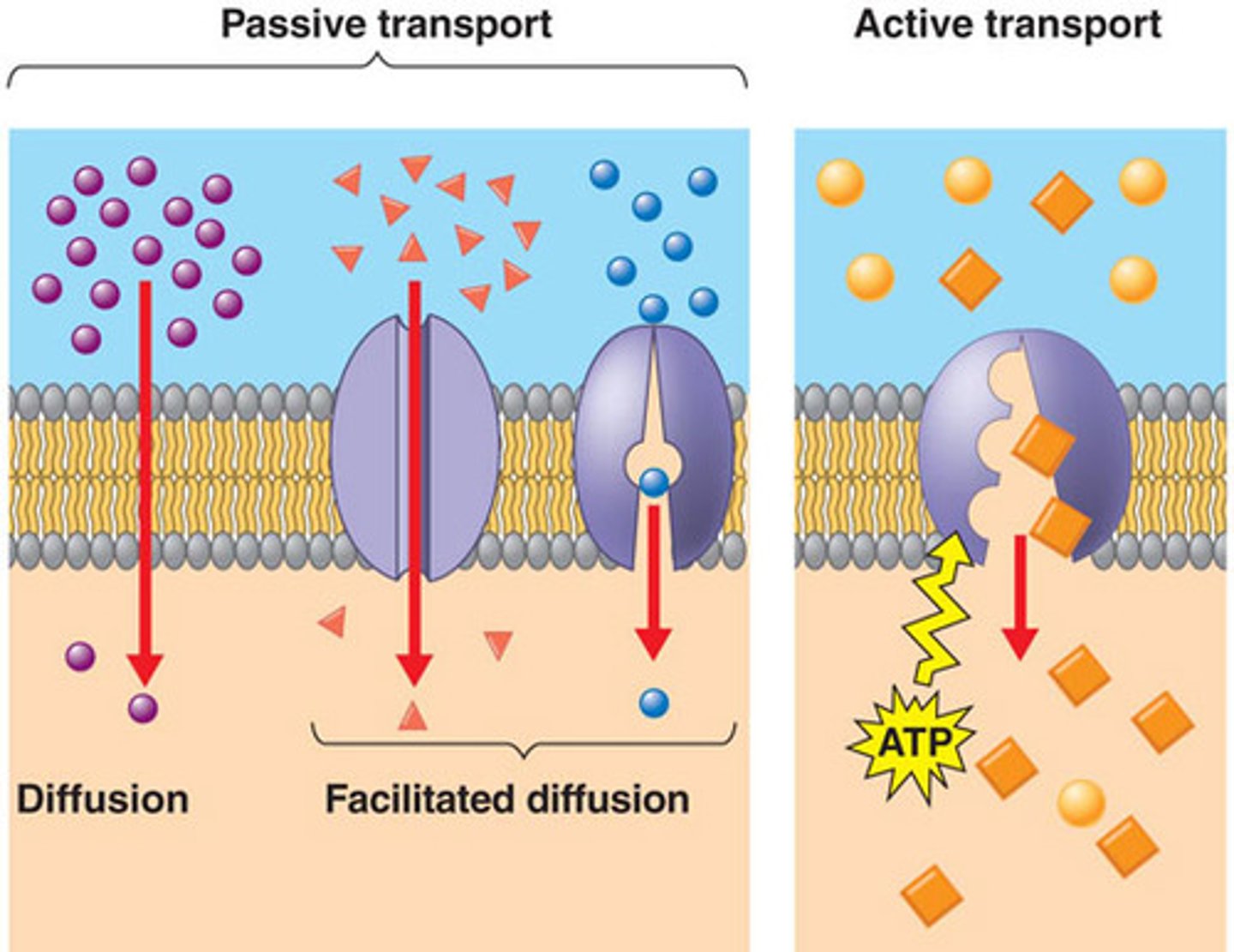
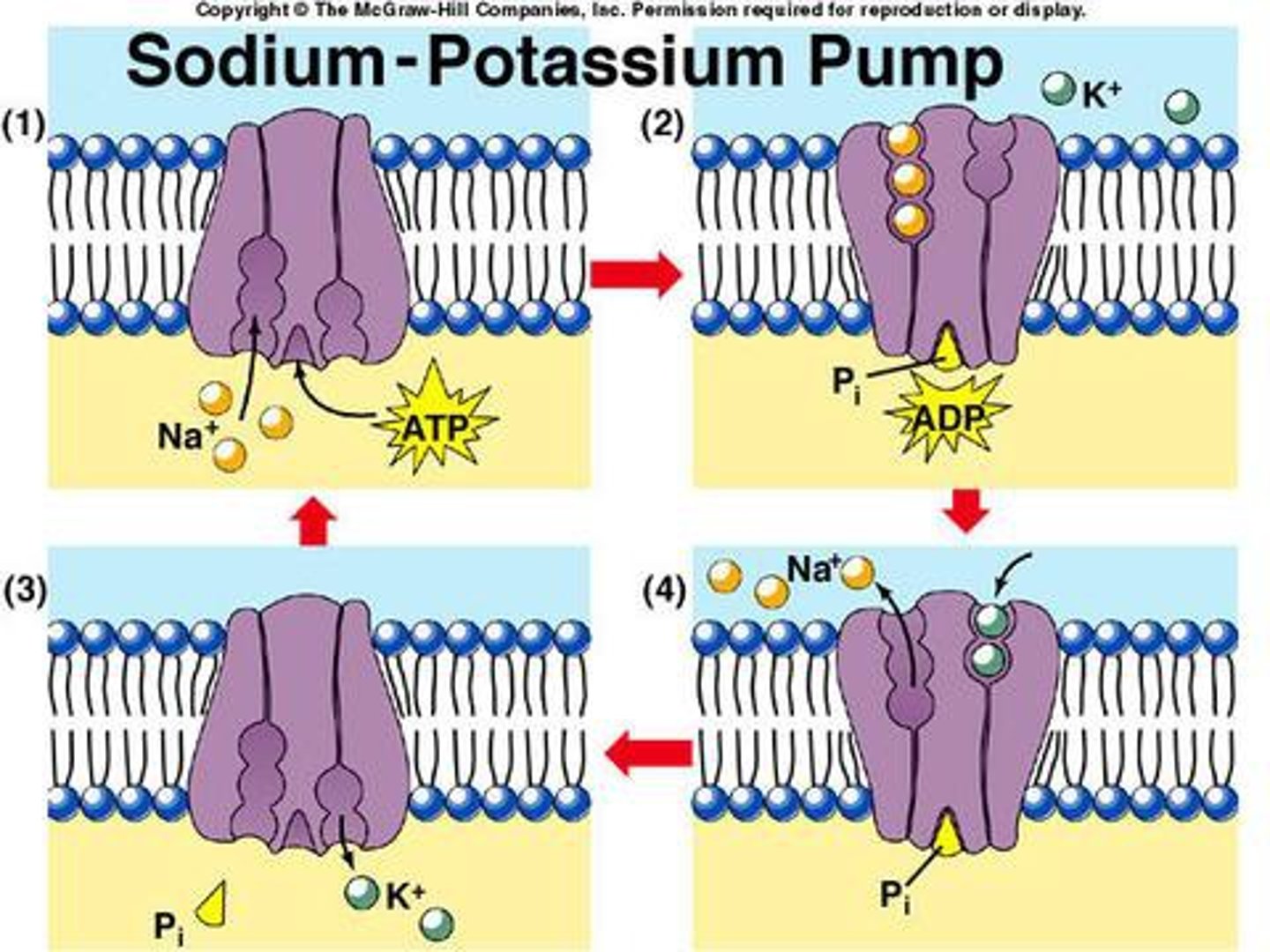
adenosine tri phosphate (ATP)
The energy which is used to transport molecules through cell membrane
permeability
allowing liquids or gases to pass through it.
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves a solute against its concentration gradient
Chanel mediated diffusion (facilitated diffusion)
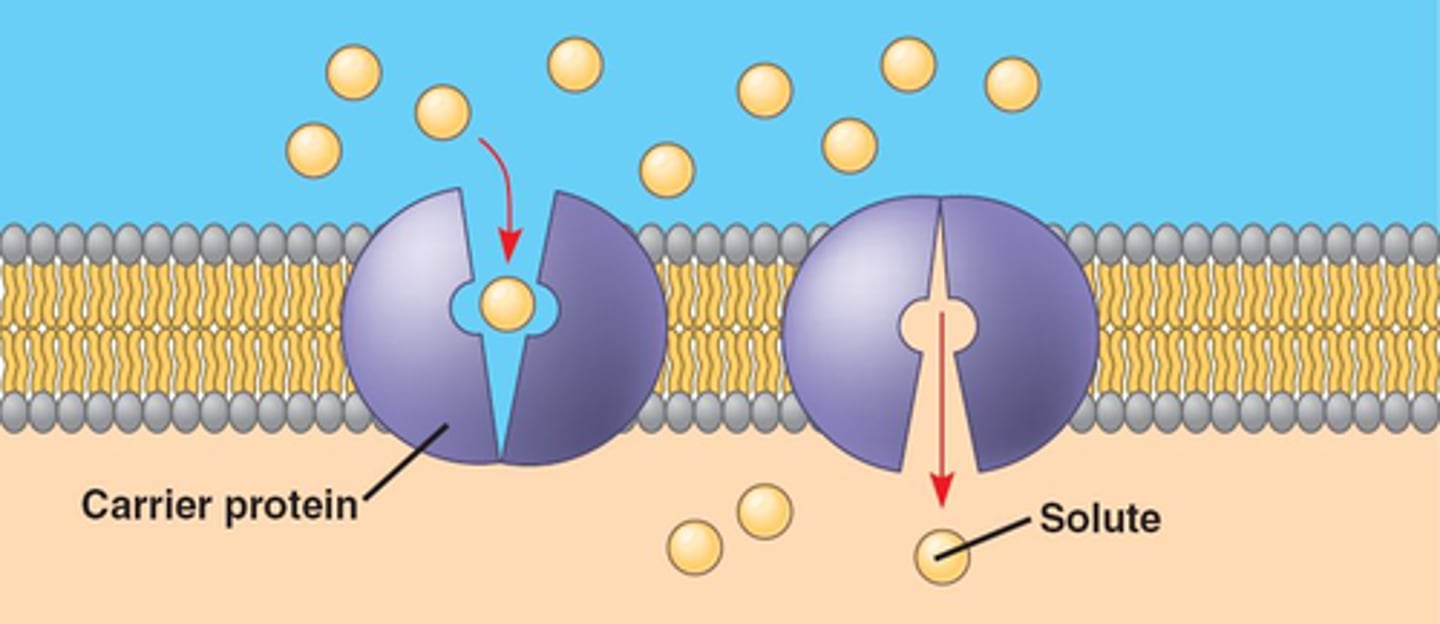
Carrier mediated diffusion (facilitated diffusion)
when protein channels changes shapes to let a molecule through
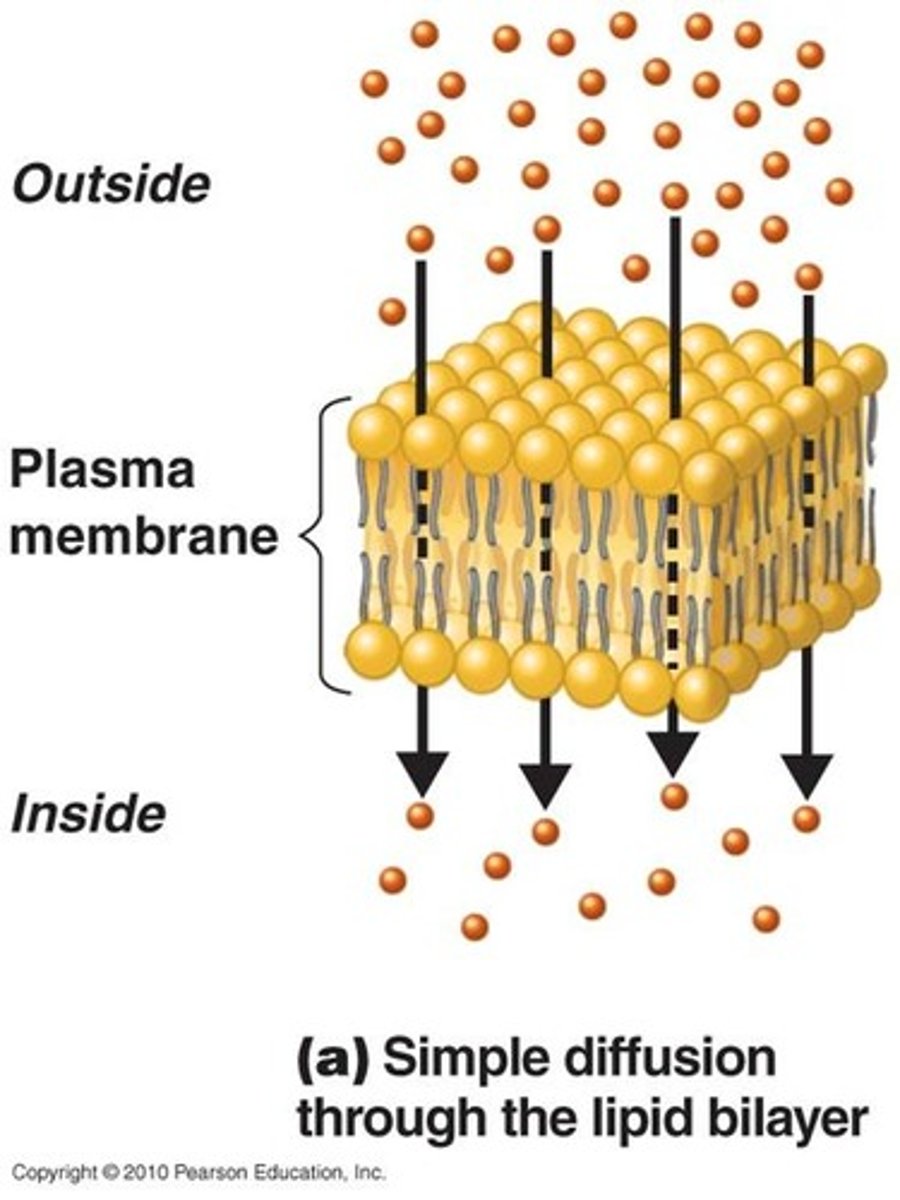
(simple) diffusion
When molecules move directly through cell membrane, going down their concentration gradient (from high to low)
Pumps (active transport)
actively move molecules against their concentration gradients
passive transport
Does not require energy to transport a solute (down the concentration gradient)
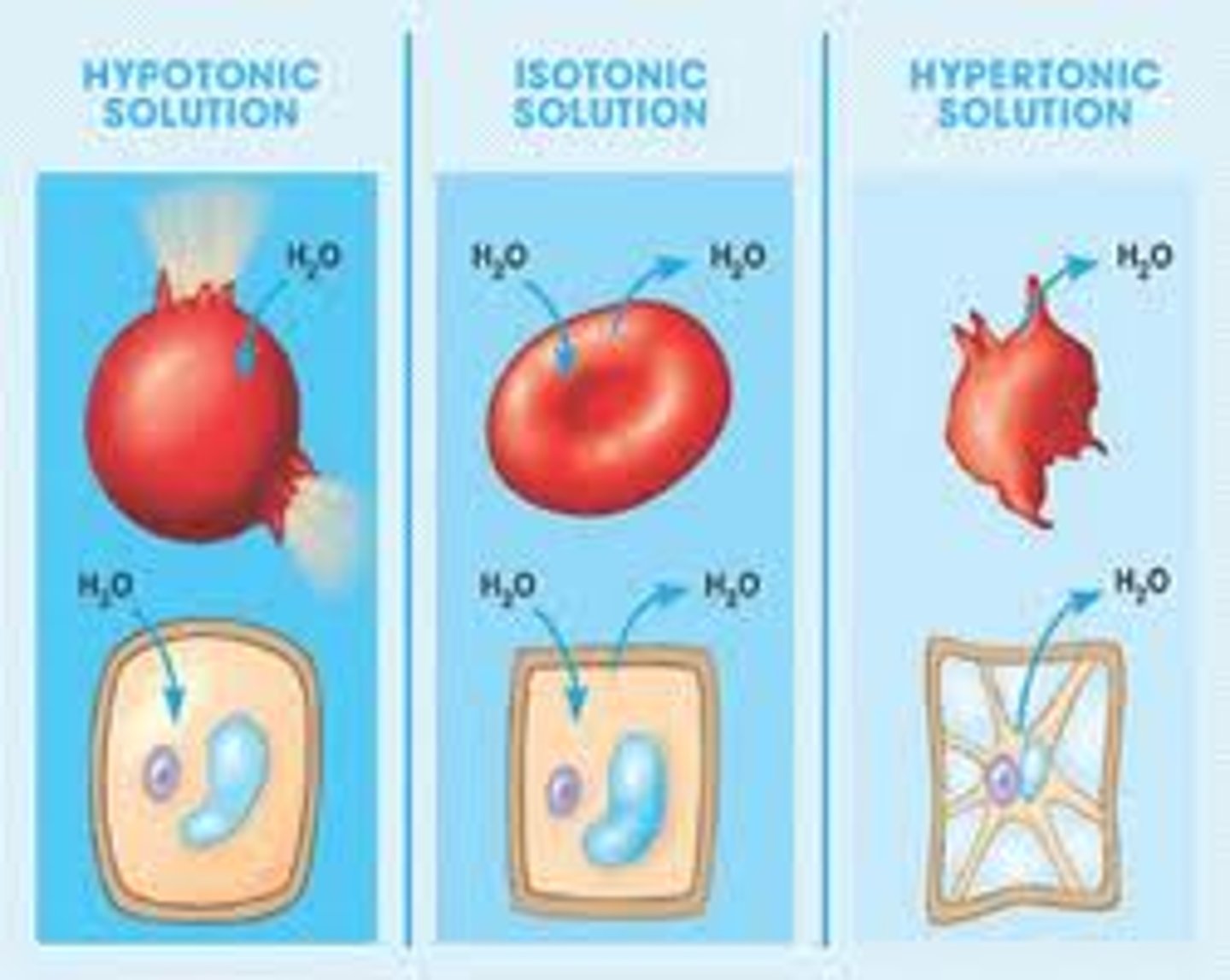
Hypotomic
when water moves outside the cell because solute concentrate is lower outside the cell than inside- diffusion
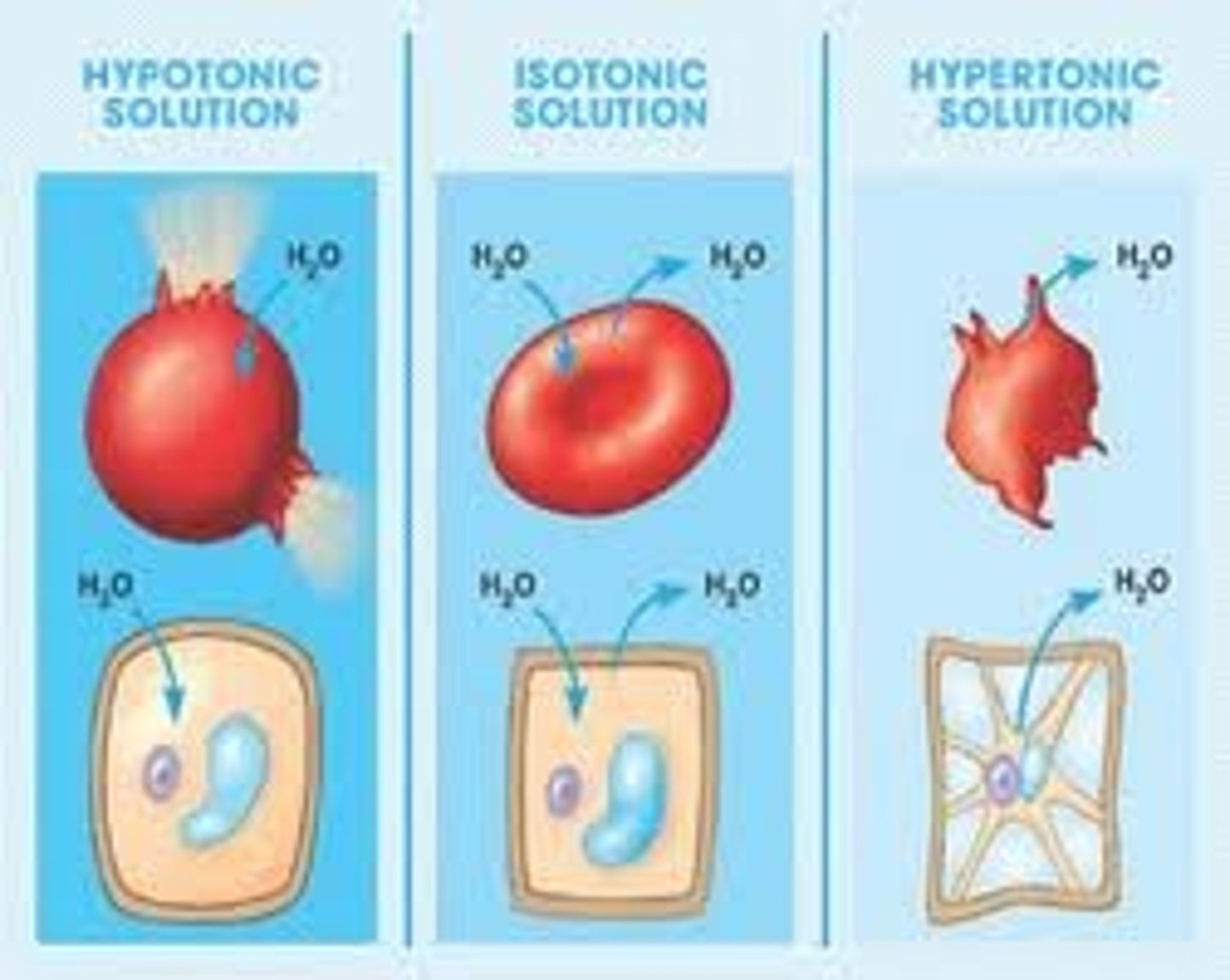
isotonic
when water does not move anywhere because solute concentrate outside the cell is the same as inside the cell
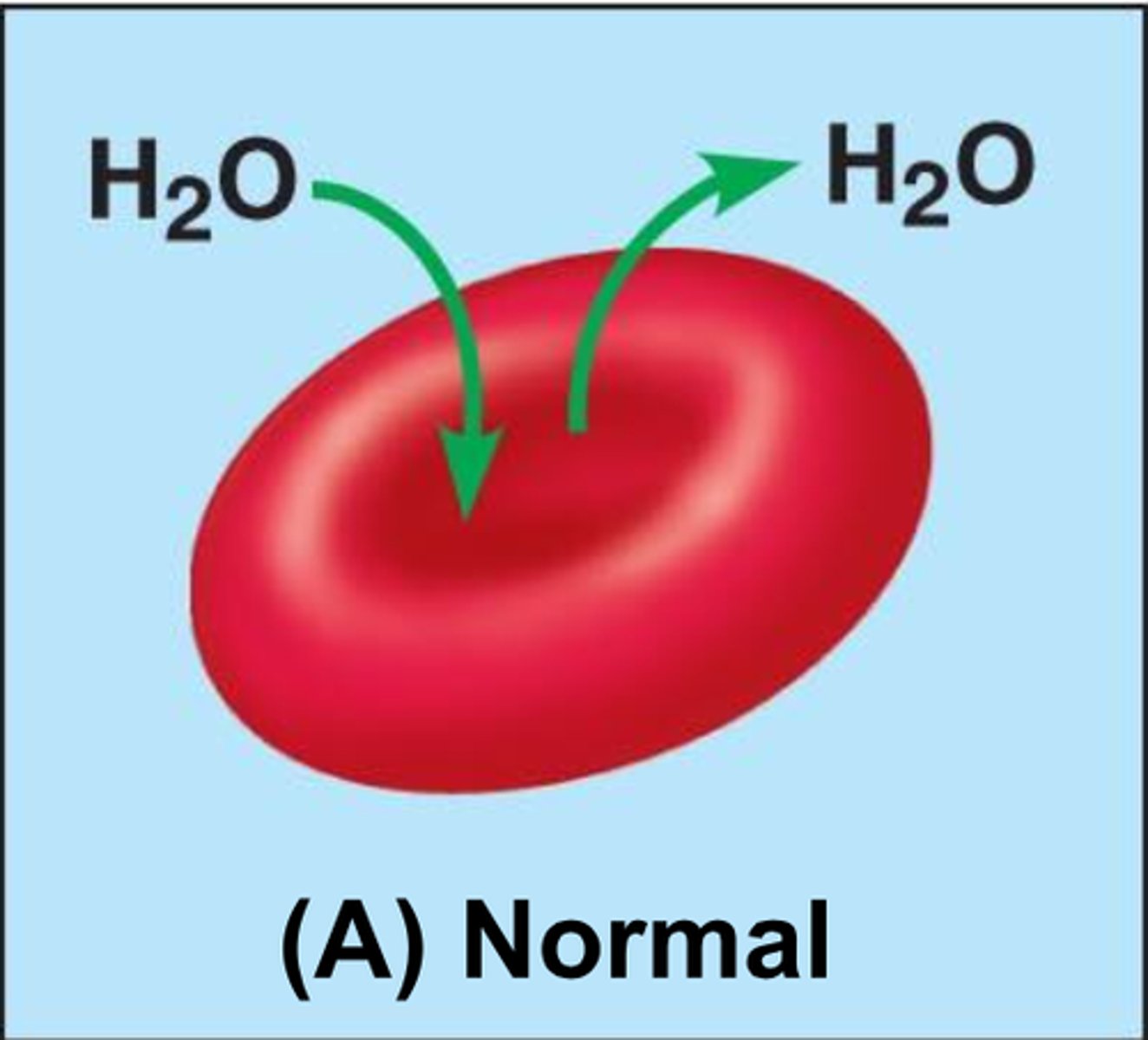
hypertonic
when water moves inside the cell because solute concentrate inside the cell is less than outside the cell
Osmosis
diffusion of water, when the solute cannot easily cross the membrane any other way
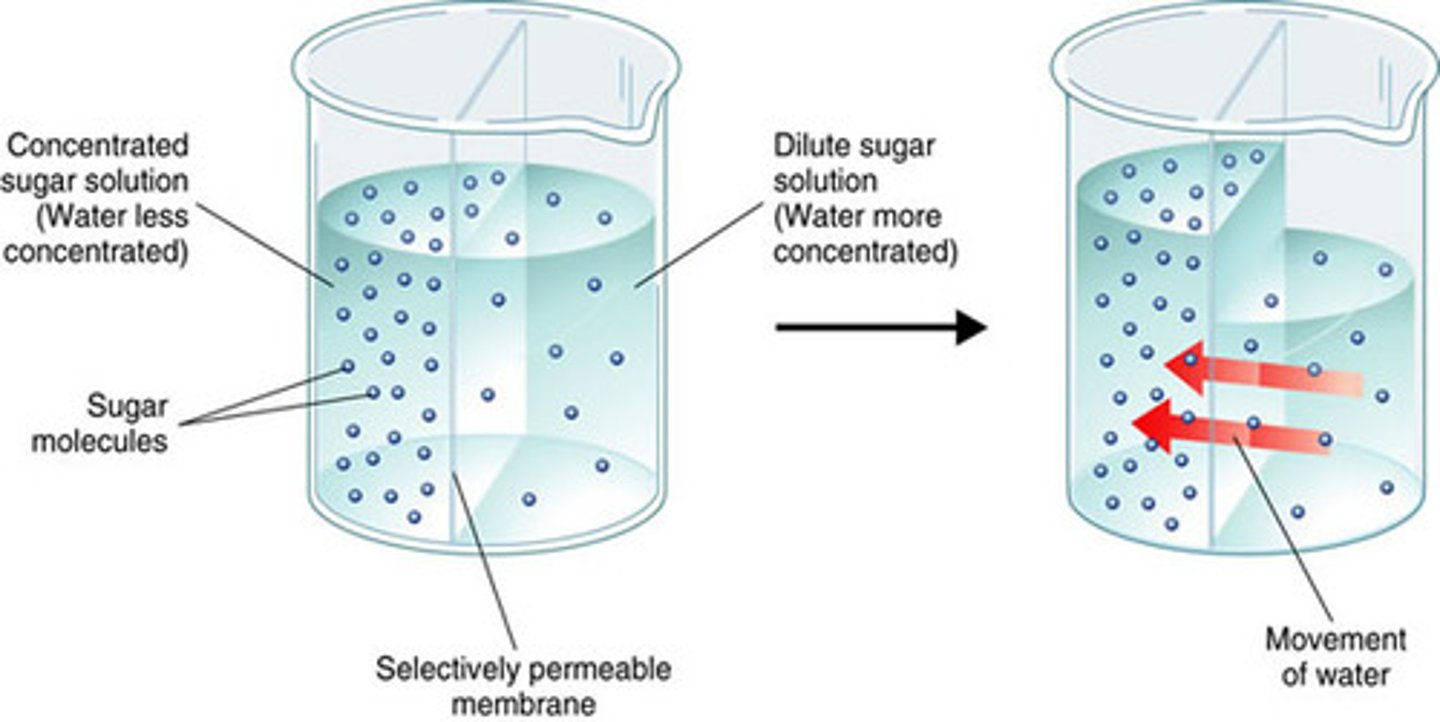
concentration gradient
slope from high to low relative amounts of solute and solvents
Endocytosis (cytosis)
membrane infolds to bring substances into the cell
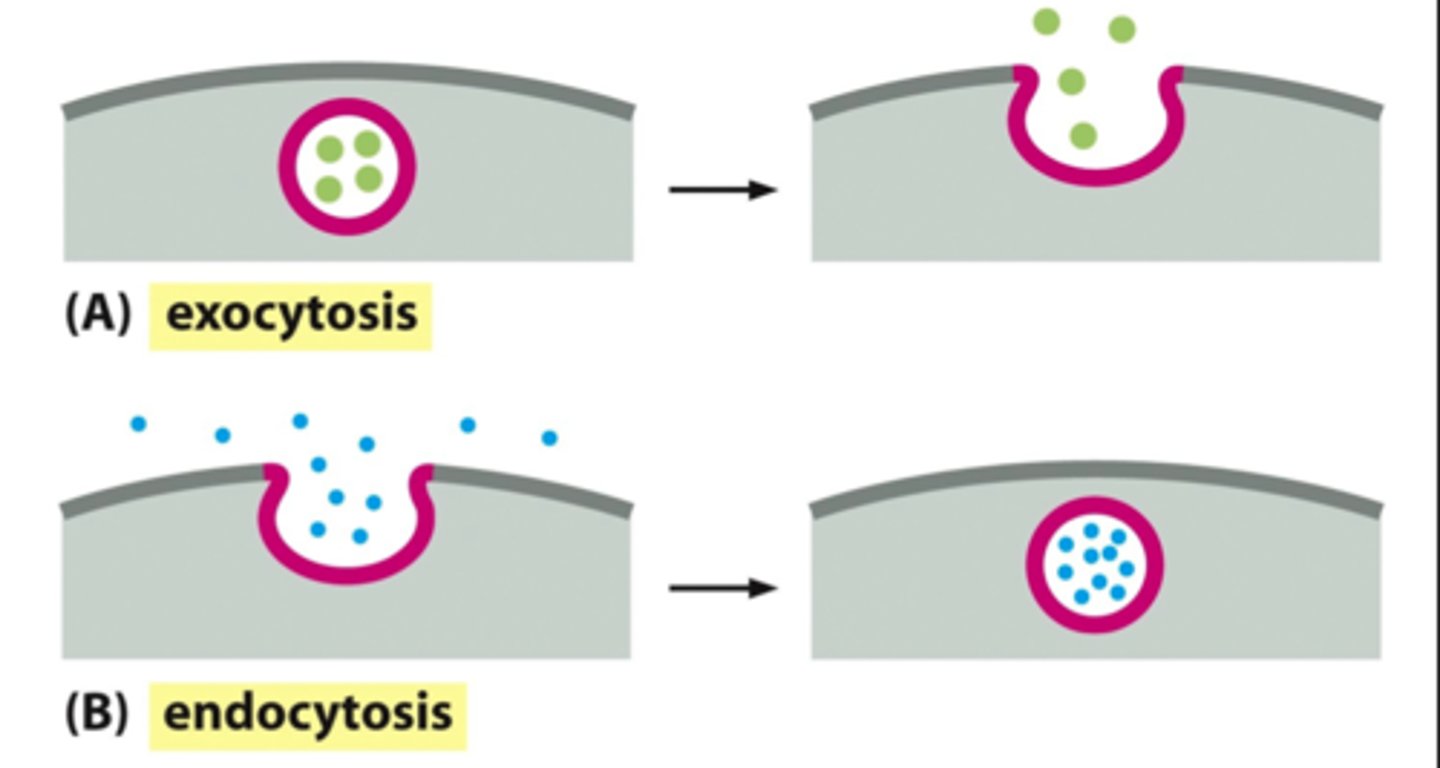
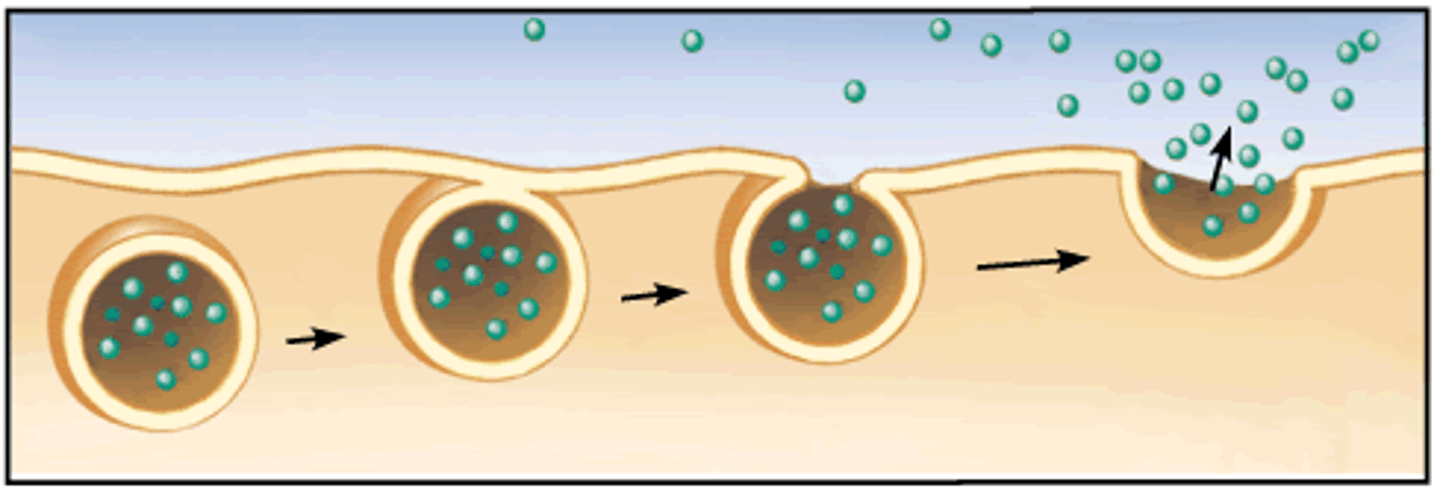
Exocytosis
membrane outfolds to move substances out of the cell
What are the three things cell membranes are made from?
1. Phospholipids (lipid bilayer) (the basic building block of the cell membrane)
2. Proteins (can act as receptors and help transport molecules inside or outside the cell)
3. Cholesterol (keeps fluidity of the membrane stable)
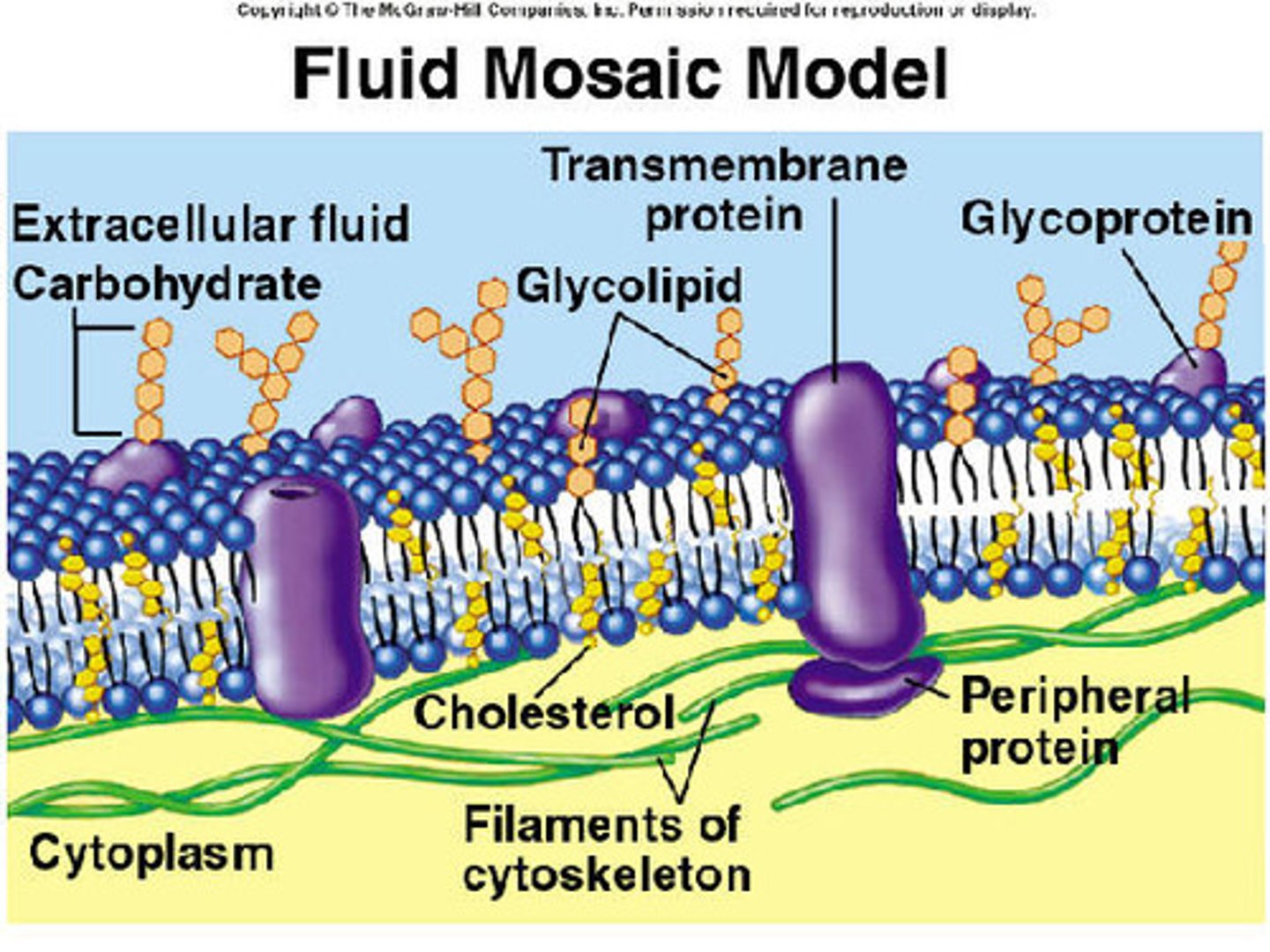
The role of lipids in cell membrane structure