Week 8 Anatomy Misc
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
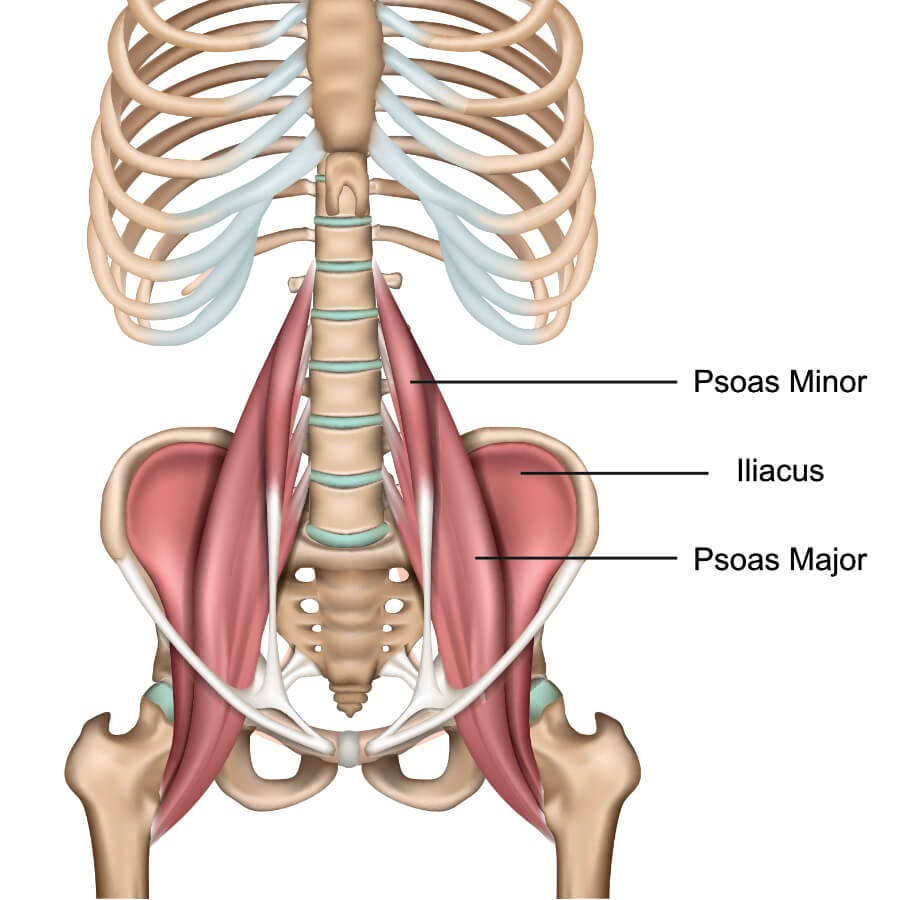
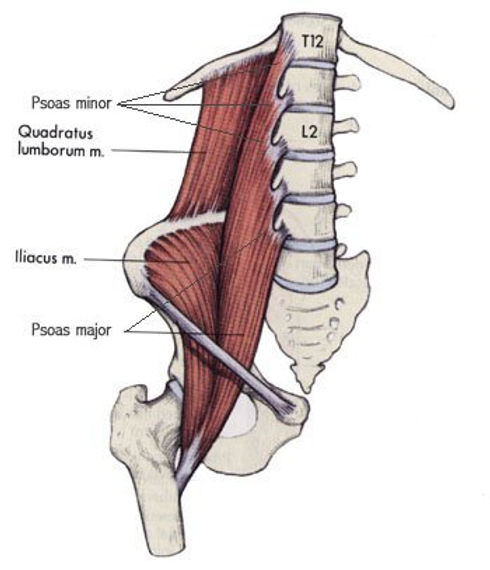
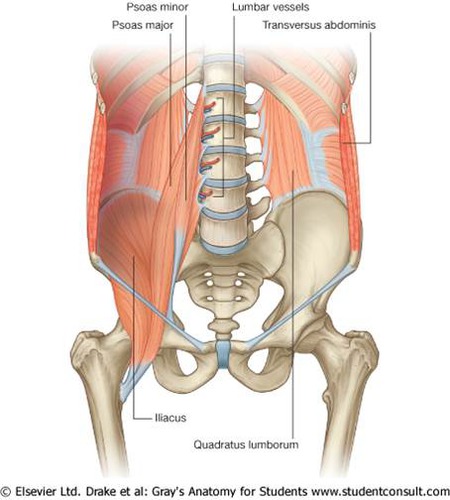
psoas major
flexes thigh (inferiorly)
flexes vertebral column (superiorly)
anterior rami of spinal nerves L1-L3
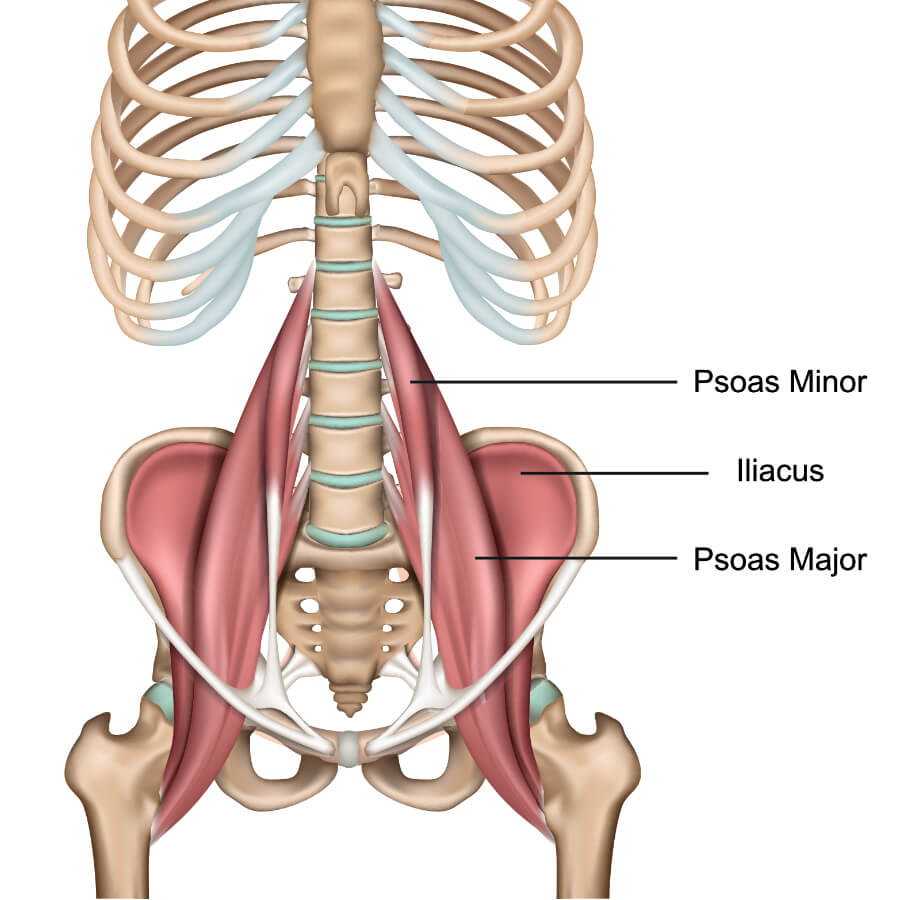
psoas minor
weak trunk flexor
anterior rami of spinal nerve L1
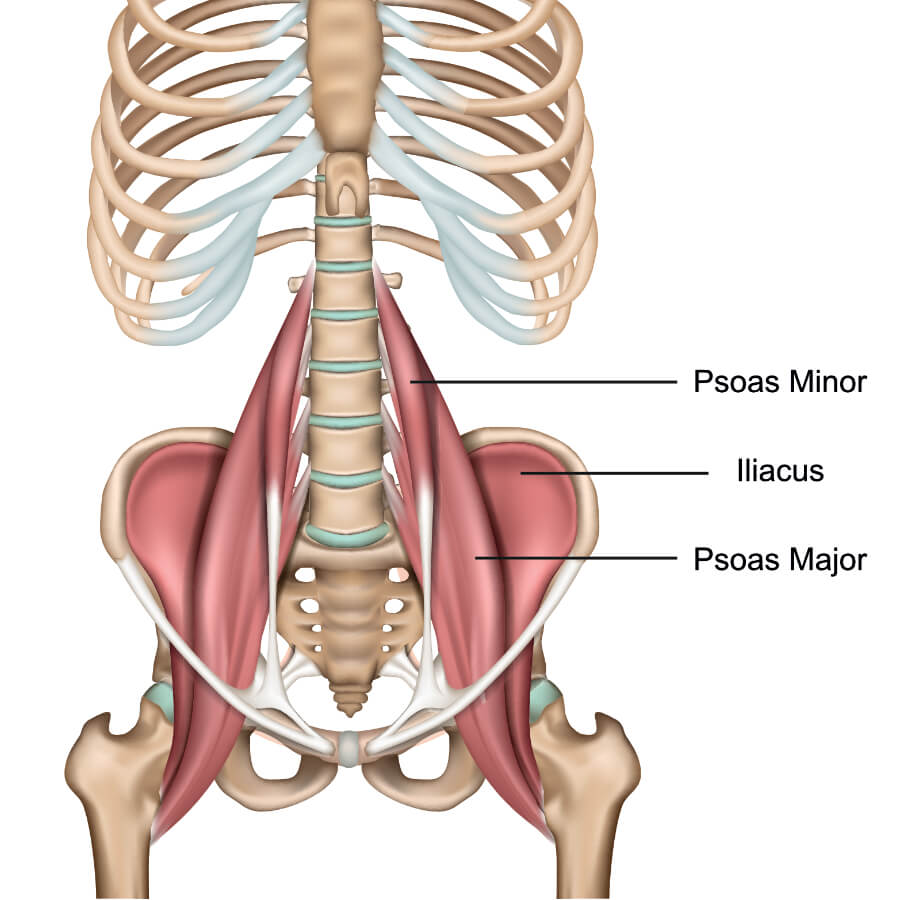
iliacus
flex thigh, stabilize hip joint
femoral nerve
quadratus lumborum
extends and laterally flexes vertebral column
anterior rami of spinal nerves L1-L4
transversus abdominis
compress and support abdominal viscera; flex and rotate trunk
thoracoabdominal nerve T7-T11; subcostal nerve, and L1
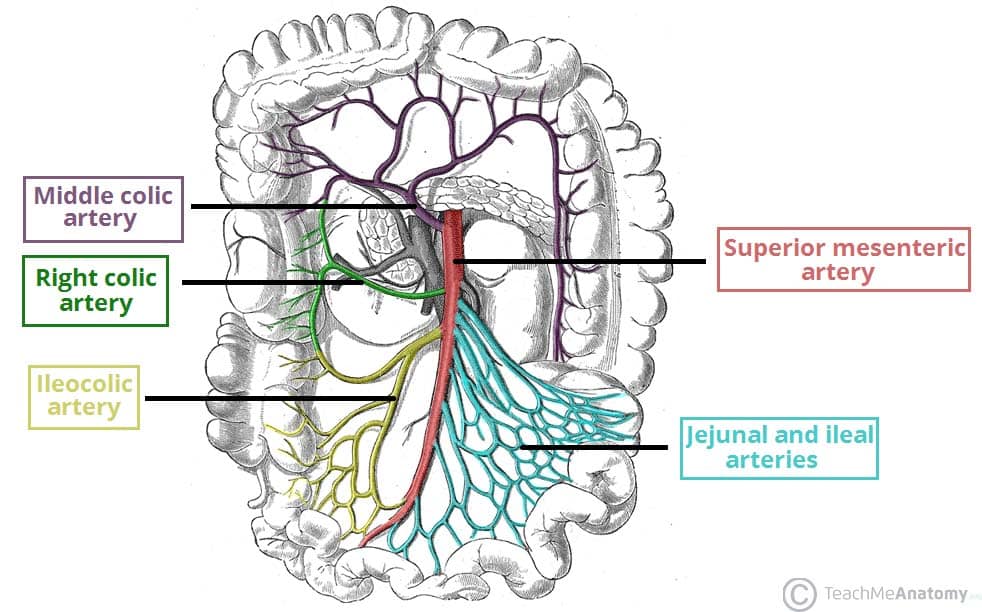
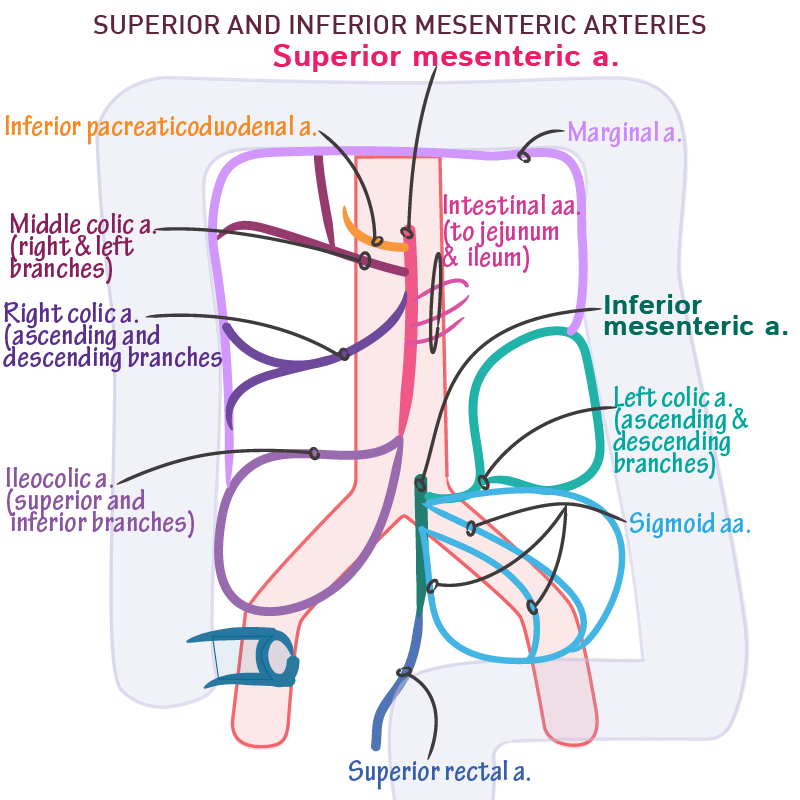
superior mesenteric artery
supplies foregut
inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
supply head of pancreas and proximal loop of duodenum
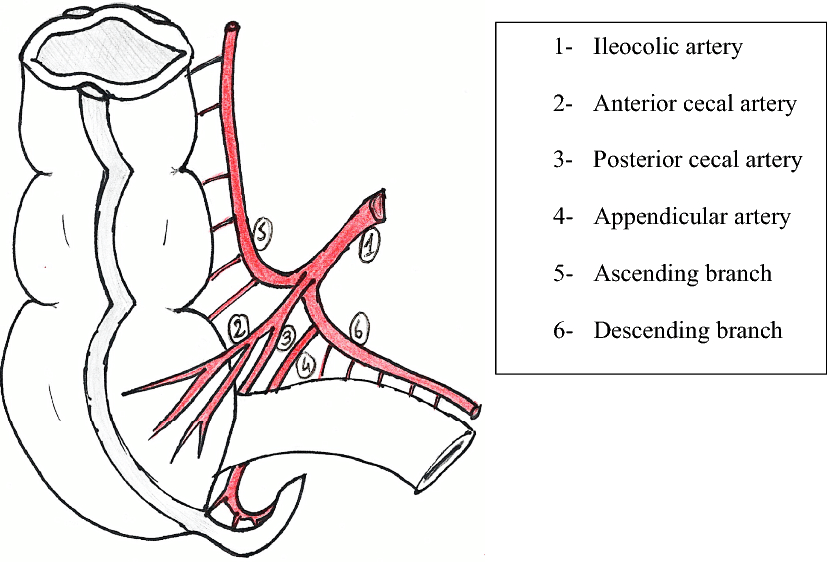
ileocolic artery
supplies cecum, distal ileum, and ileocecal junction
branch - appendicular a. (supplies vermiform appendix)
arterial arcades
a division of the intestinal arteries (jejunal and ileal)
supplies jejunum and ileum
vasa rectum
a division of arterial arcades
closest blood vessels to the jejunum and ileum
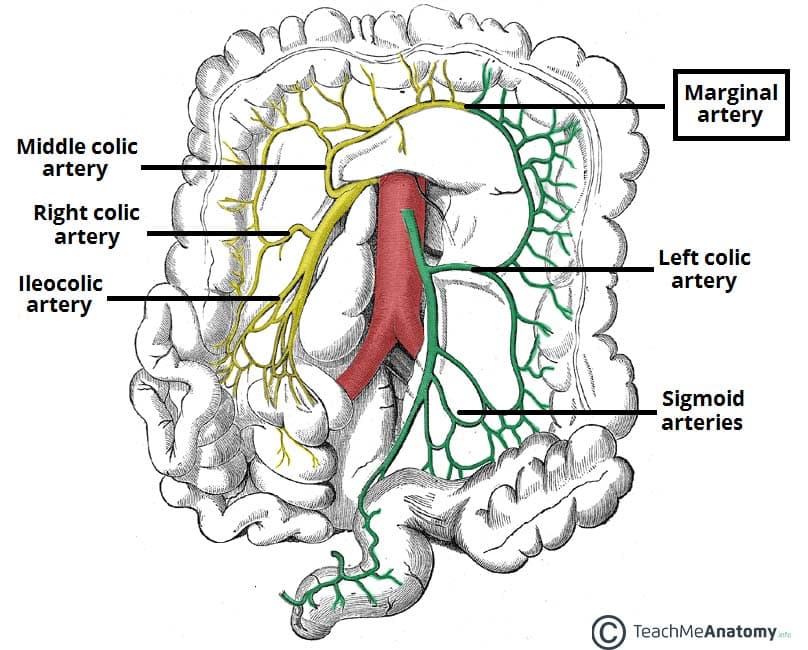
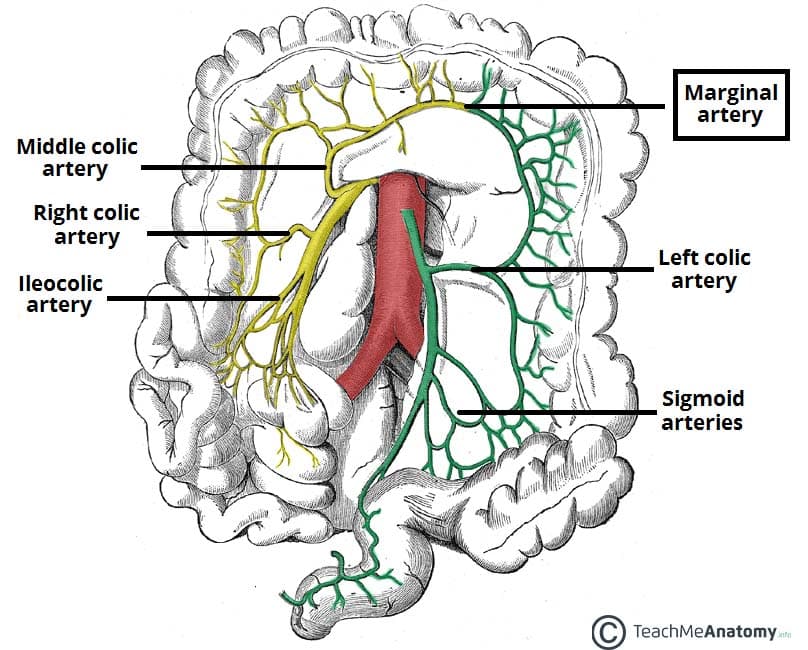
right colic artery
superior and inferior division
supplies ascending colon
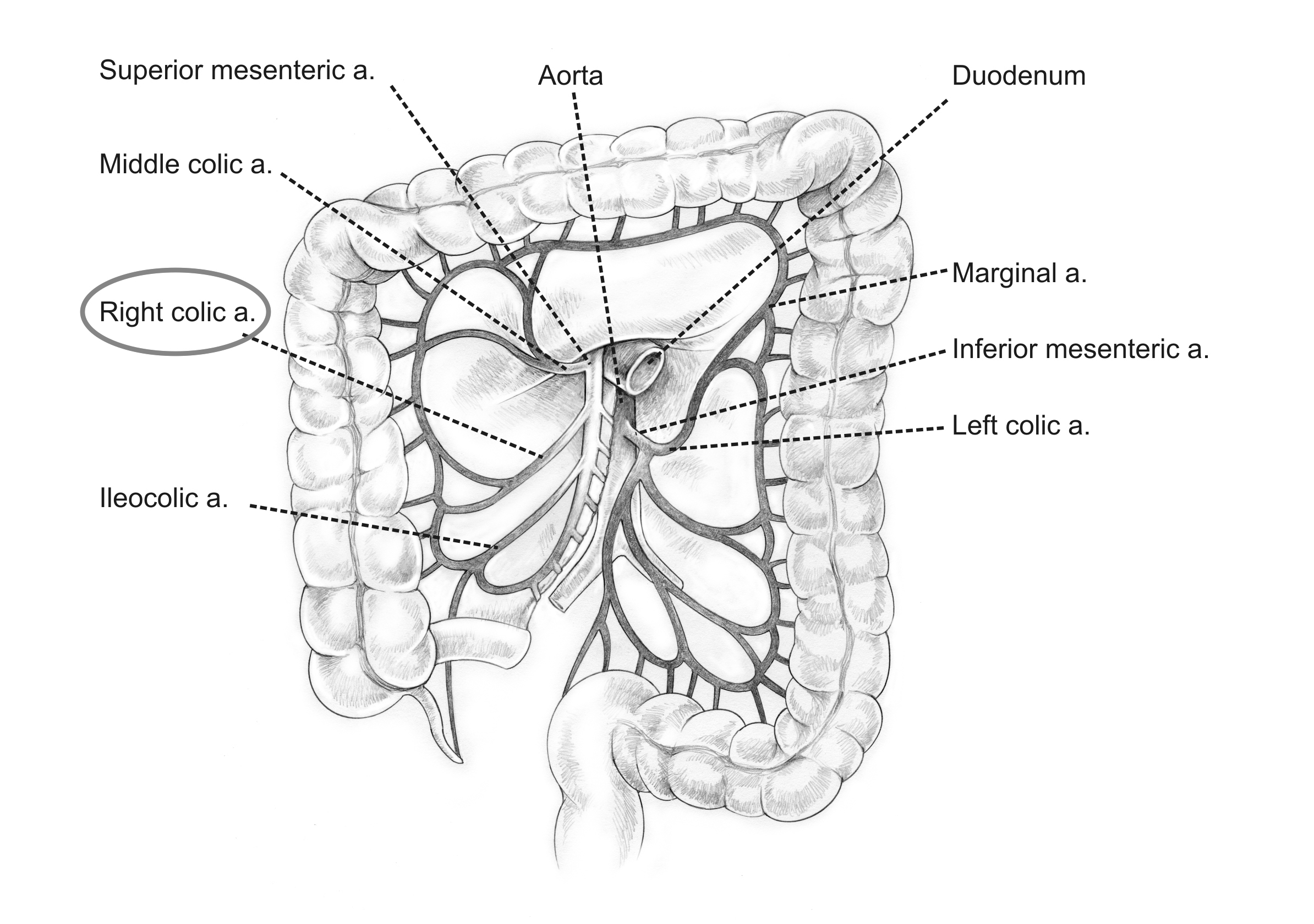
middle colic artery
left and right branches divisions
supplies transverse colon
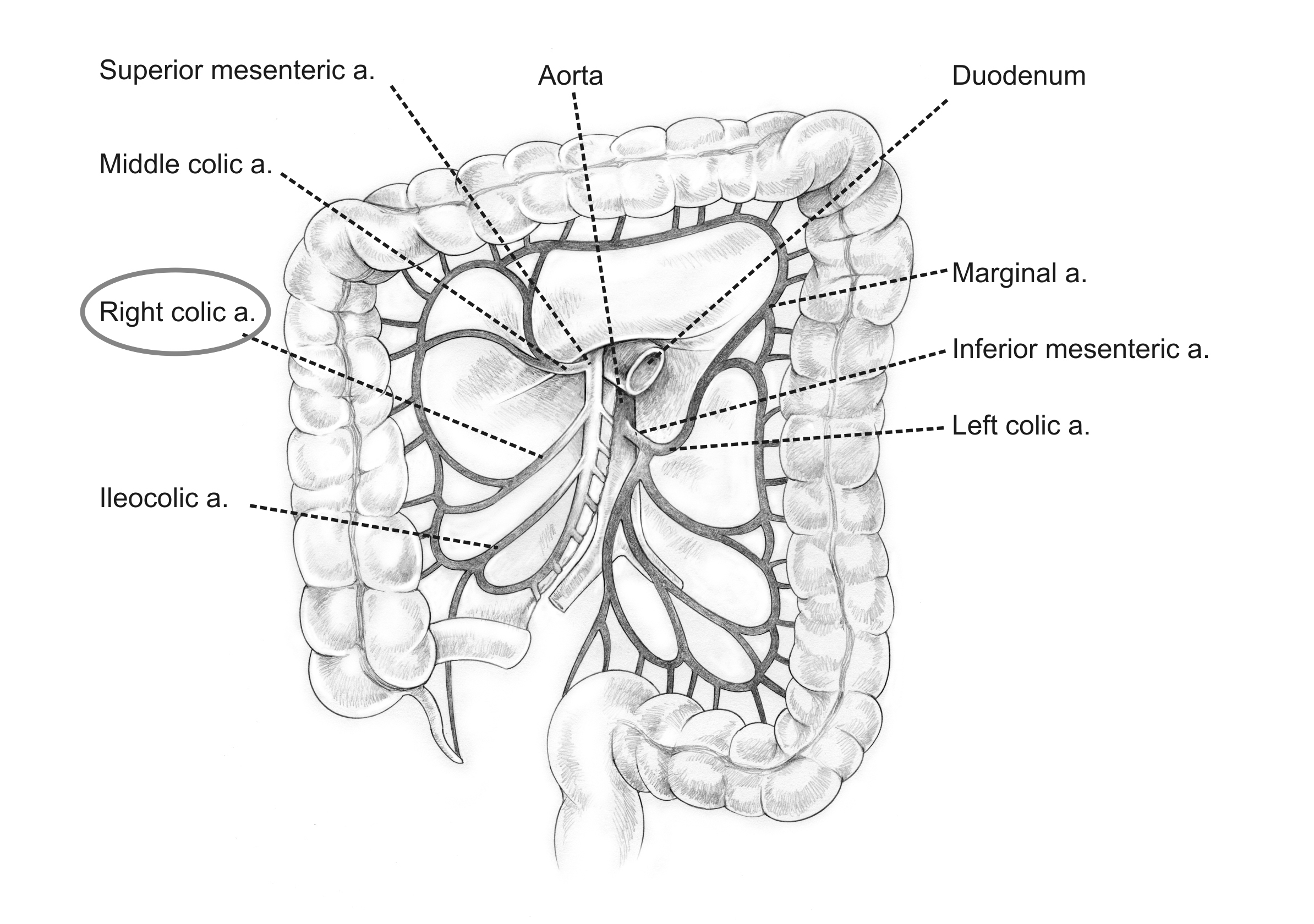
inferior mesenteric artery
divisions: left colic a., sigmoidal aa., superior rectal a.
supplies descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum
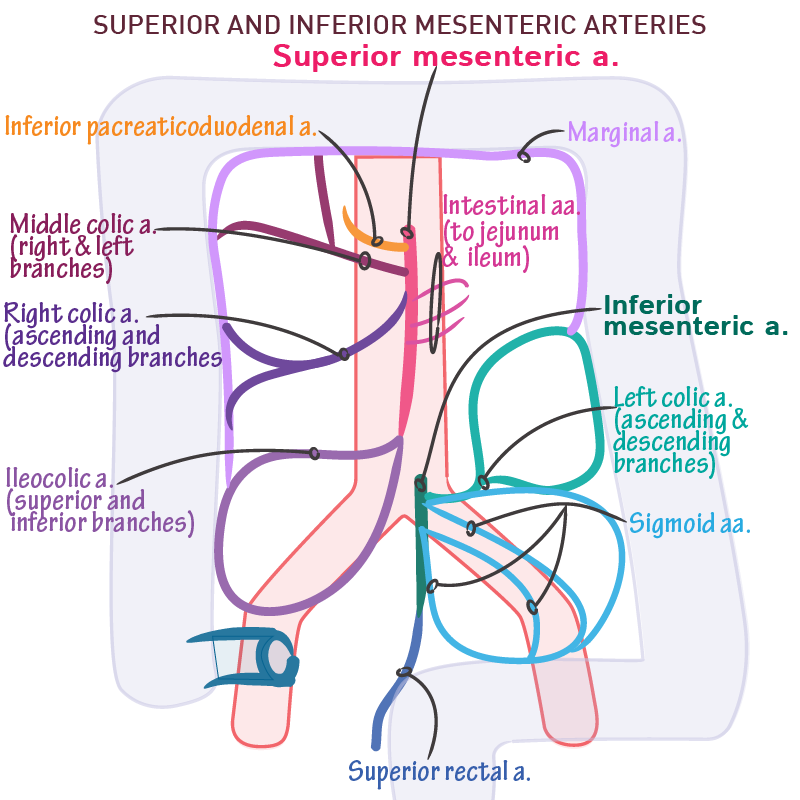
left colic artery
ascending and descending branch
supplies descending colon
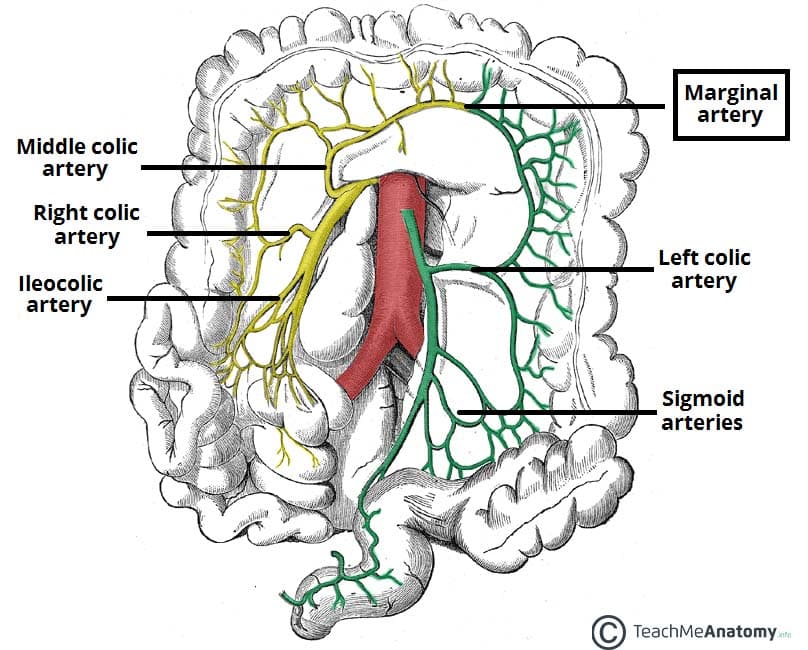
sigmoidal arteries
supply descending colon and sigmoid colon
superior rectal artery
supplies rectum (duh)
marginal artery
originates from superior and inferior mesenteric arteries - what connects them
supplies the large intestine
what 3 anastomoses are observed in the mesenteric arteries?
superior posterior pancreaticoduodenal a. with inferior posterior pancreaticoduodenal a.
superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal a. with inferior anterior pancreaticoduodenal a.
arterial arcade - anastomoses of jejunal and ileal arteries
what are some more anastomoses?
ileocolic with right colic
right colic with middle colic
middle colic with marginal
marginal with left colic
left colic with sigmoidal
superior mesenteric vein
receives blood from large intestine, small intestine, appendix, stomach, pancreas and brings them to hepatic portal vein
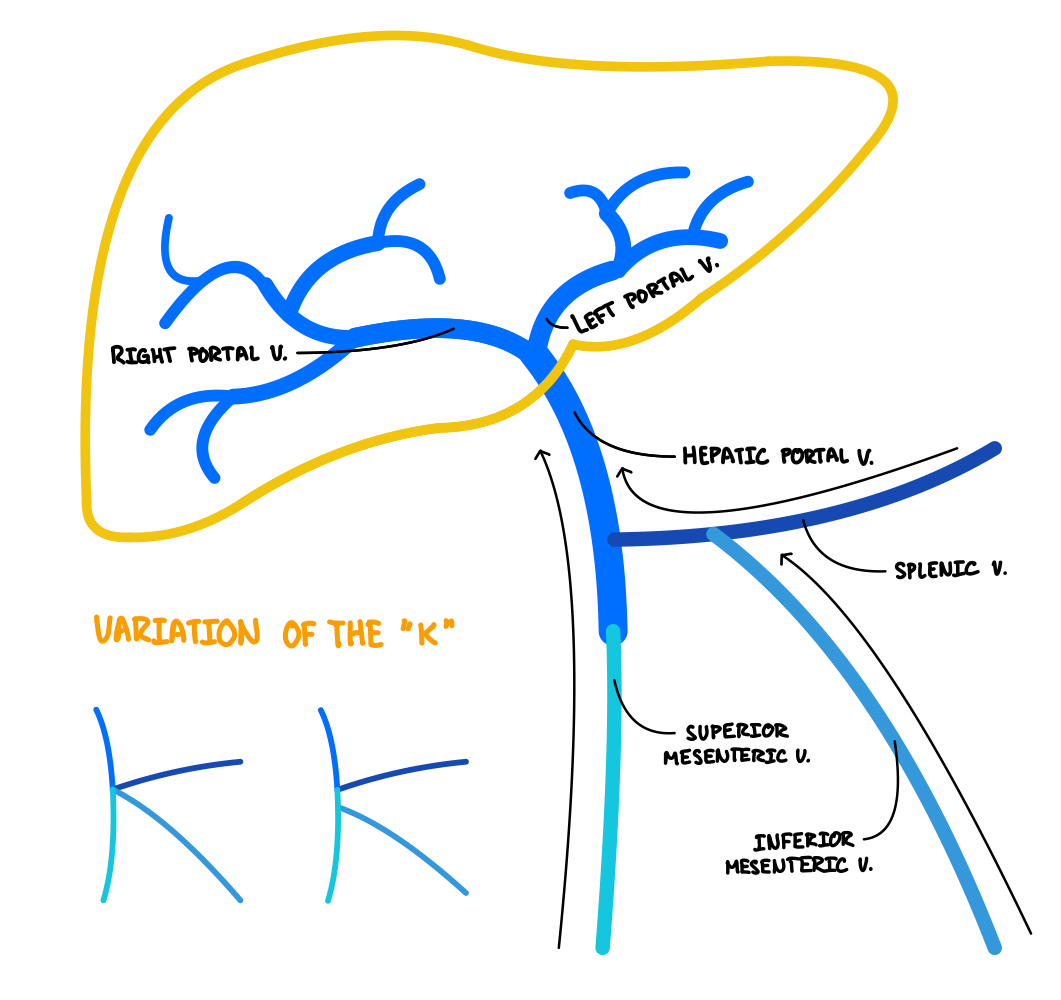
inferior mesenteric vein
receives blood from sigmoid colon, rectum, large intestine and brings it to splenic vein
(sometimes can branch onto superior mesenteric vein or hepatic portal vein)
abdominal aorta divisions
inferior phrenic aa.
celiac trunk
renal aa.
suprarenal aa.
gonadal aa.
lumbar aa.
common iliac aa.
inferior phrenic artery
division of superior suprarenal artery
supplies inferior thoracic diaphragm
renal arteries
division of inferior suprarenal artery
supplies kidneys
middle suprarenal artery
originates from abdominal aorta
supplies suprarenal (adrenal) gland
inferior suprarenal artery
origins from renal arteries
supplies suprarenal (adrenal) gland
gonadal arteries (testicular/ovarian)
supply testes/ovaries
often tore off when abdominal cavity is dissected
halfway btwn superior and inferior mesenteric arteries
lumbar arteries
supplies quadratus lumborum and psoas minor
usually four on each side on posterior aorta
common iliac arteries
supply abdominal wall and lower limb
right gonadal vein
comes from testes/ovaries
drains into IVC
left gonadal vein
comes from gonads
drains into renal vein
renal veins
come from interlobar veins of kidney
drains into IVC
right suprarenal vein
comes from adrenal gland
drains into IVC
left suprarenal vein
comes from adrenal gland
drains into renal vein
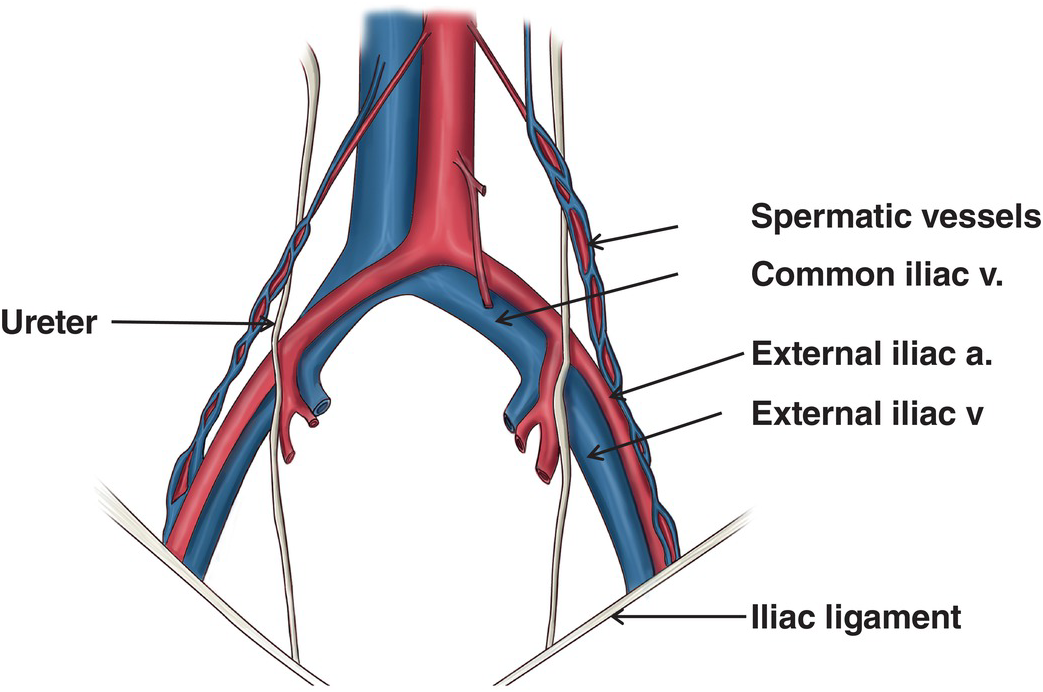
subcostal nerve
T12
motor to external obliques and skin of abdominal wall
iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal
T12-L1
iliohypogastric - remains above the inguinal ligament; more superior
ilioinguinal nerve travels through the inguinal canal
genitofemoral
L1-L2
lateral femoral cutaneous
L2-L3
lateral thigh sensation
femoral nerve
L2-L4
knee jerk and cremaster reflex
obturator nerve
L2-L4
femoral vs genital branch of genitofemoral nerve
femoral - sensory; descends along the psoas major muscle, passing beneath the inguinal ligament to reach the thigh; more lateral
genital - sensory and motor; travels toward the inguinal canal and enters it. In males, it accompanies the spermatic cord; in females, it accompanies the round ligament of the uterus
mesometrium
drape-like, largest portion of the broad ligament
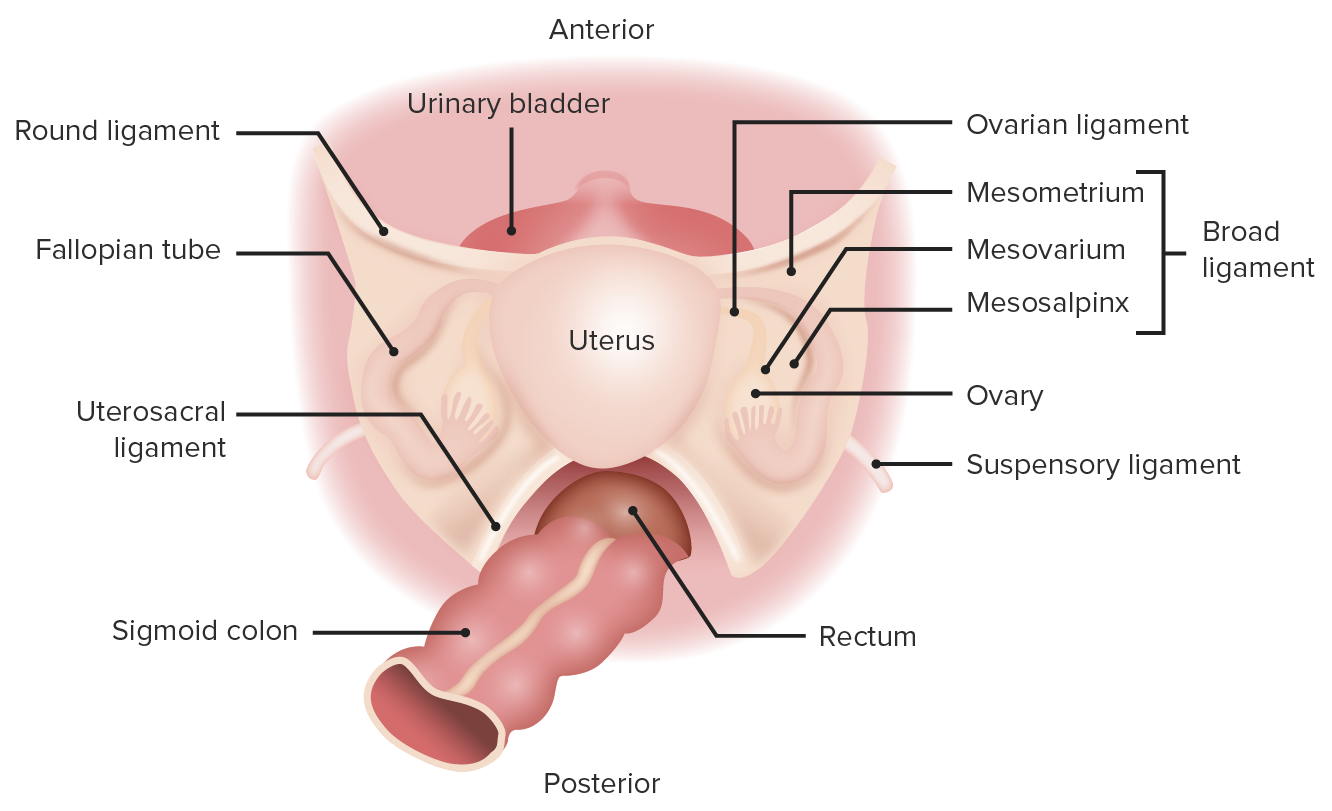
mesoalpinx
connects uterine tubes to ovaries
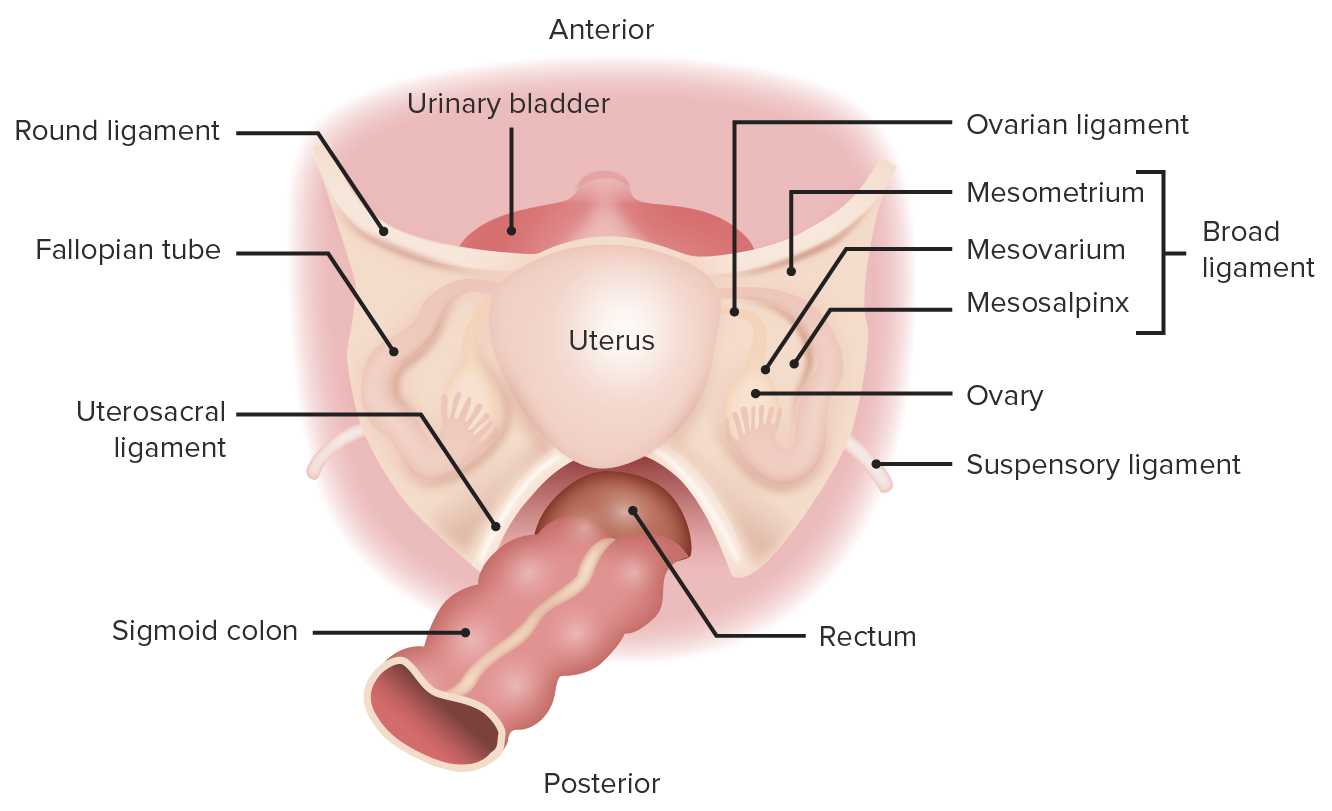
mesovarium
connects ovaries to broad ligament
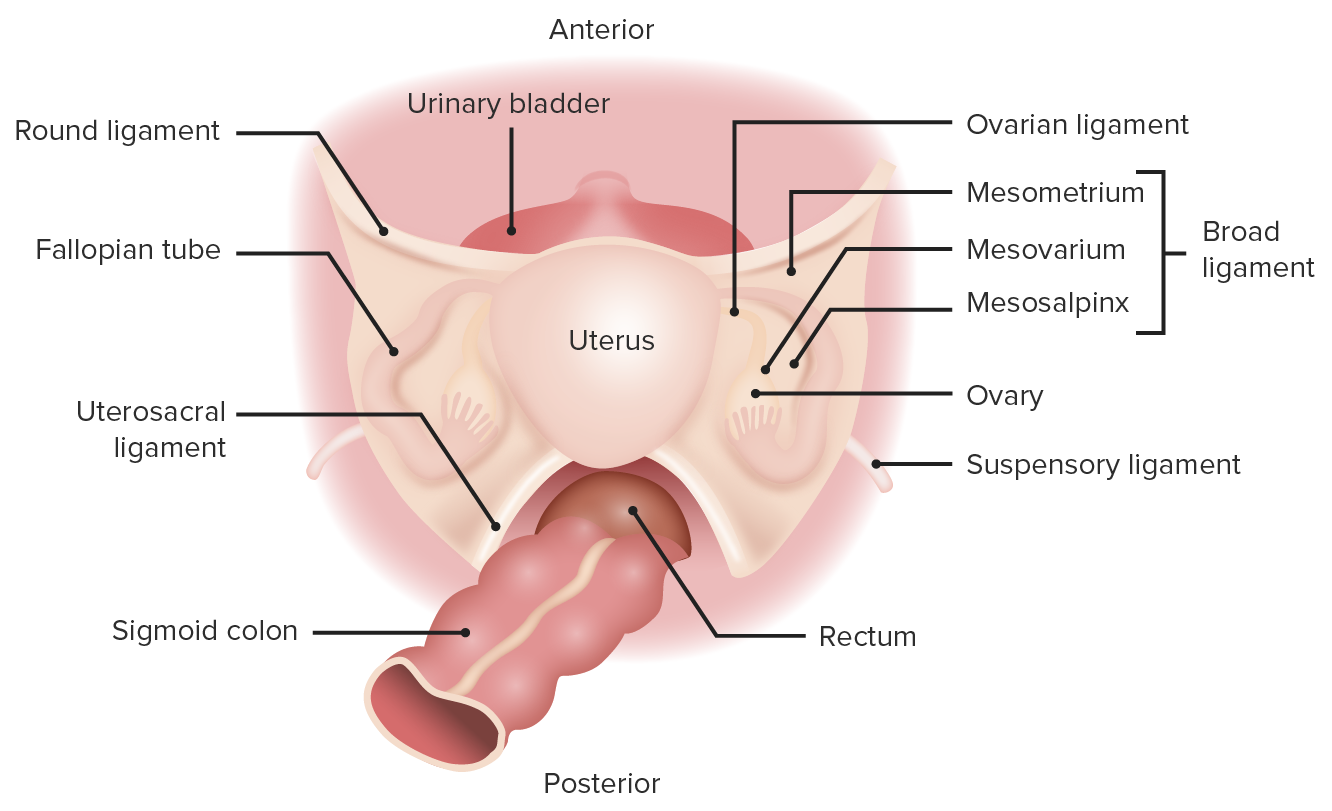
seminal vesicle
produces 2/3 fluid of sperm (fructose)
prostatic urethra
urethra and ejaculatory duct join up inside here
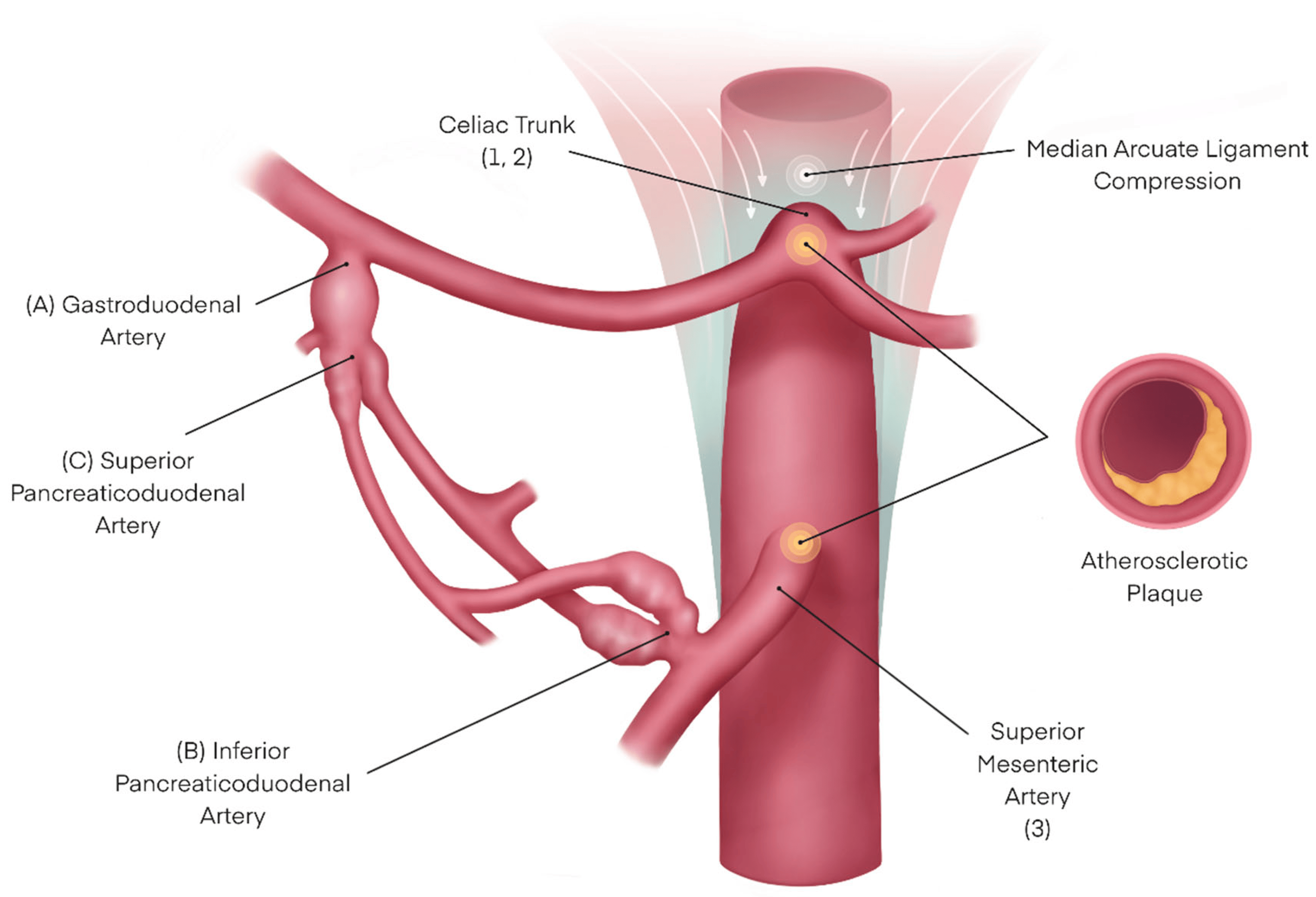
SMA syndrome
compression of the 3rd part of duodenum between the abdominal aorta and the superior mesenteric artery
fast weight loss
bilious vomiting
nutcracker syndrome
compression of your left renal vein, usually between your abdominal aorta and SMA
left renal vein crosses midline
the interior mesenteric vein is ____ to the IMA
left
splenic A and V are ___ the pancreas
behind
splenic flexure
watershed area with no direct blood supply
easier risk of necrosis
what separates the SMA and IMA
horizontal duodenum