Bio 201 Rio Salado Exam 1 With complete verified solutions + Rationales
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Explain the principle of complementarity.
Anatomy and physiology are inseparable because function always reflects structure examples.) bones support and protect body organs because they contain hard mineral deposits and, blood flows in one direction through the heart because the heart has valves that prevent back flow.
Levels of structural organization (in order of increasing complexity)
1) Chemical Level- At this level atoms, tiny building blocks of matter combine to form molecules such as water and proteins.
2) Cellular Level- All cells have some common functions, but individual cells vary widely in size and shape, reflecting their unique functions in the body.
3) Tissue Level- Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function
4) Organ Level- Organs are made up of different tissues.
5) Organ (System) level- Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely.
6) Organismal Level- The human organism is made up of many organ systems.
11 Organ systems of the body (major functions)
1) Integumentary System- Forms the external body covering.
2) Skeletal System- Protects and supports body organs.
3) Muscular System- Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expressions.
4) Lymphatic System- Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to the blood
5) Respiratory System- Keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
6) Digestive System- Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells.
7) Nervous System- Fast acting control system of the body.
8) Endocrine System- Glands secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use.
9)Cardiovascular System- Blood vessels transport blood, which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients , wastes, etc.
10) Urinary System- Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body.
11) Reproductive System- Overall function is production of offspring.
Negative and Positive Feedback Mechanisms
Negative Feedback Mechanisms- In these systems, the output shuts off the original stimulus or reduces intensity. Examples: Regulation of body temperatures; Withdrawal Reflex in which the hand is jerked away from a painful stimulus such as a broken glass; As blood volume drops, the hypothalamus of the brain is stimulated to release ADH to the blood.
Positive Feedback Mechanisms- The result or response enhances the original stimulus so that the activity is accelerated. Examples: Homeostatic mechanisms are the enhancement of labor contractions during birth and blood clotting.
Homeostatic Imbalance and Disease.
Most disease can be regarded as a result of the disturbance of homeostasis, which is known as homeostatic imbalance. Any abnormal condition is known as homeostatic imbalance.
Anatomical Terminology
Refer to page 12-18
9 Regions of Abdominopelvic Regions
1) Right Hypchondriac Region (Top right) Organ: Liver Gallbladder
2) Right Lumbar Region (Middle Right) Organs: Ascending Colon of large intestine
3) Right Iliac (inguinal) region- Cecum
4) Epigastric Region (middle top) Organs: Stomach
5) Umbilical Region (middle middle) Organs: Small intestine and Transverse colon of large intestine.
6) Hypogastric (pubic) region (Bottom middle) Organs: Urinary Bladder
7) Left Hypochondriac Region (Top left) Organs: Diaphragm
8) Left Lumbar Region (Middle Left) Organs: Descending colon of large intestine.
9) Left Illiac (inguinal) region (Bottom Left) Organ: Initial part of sigmoid colon
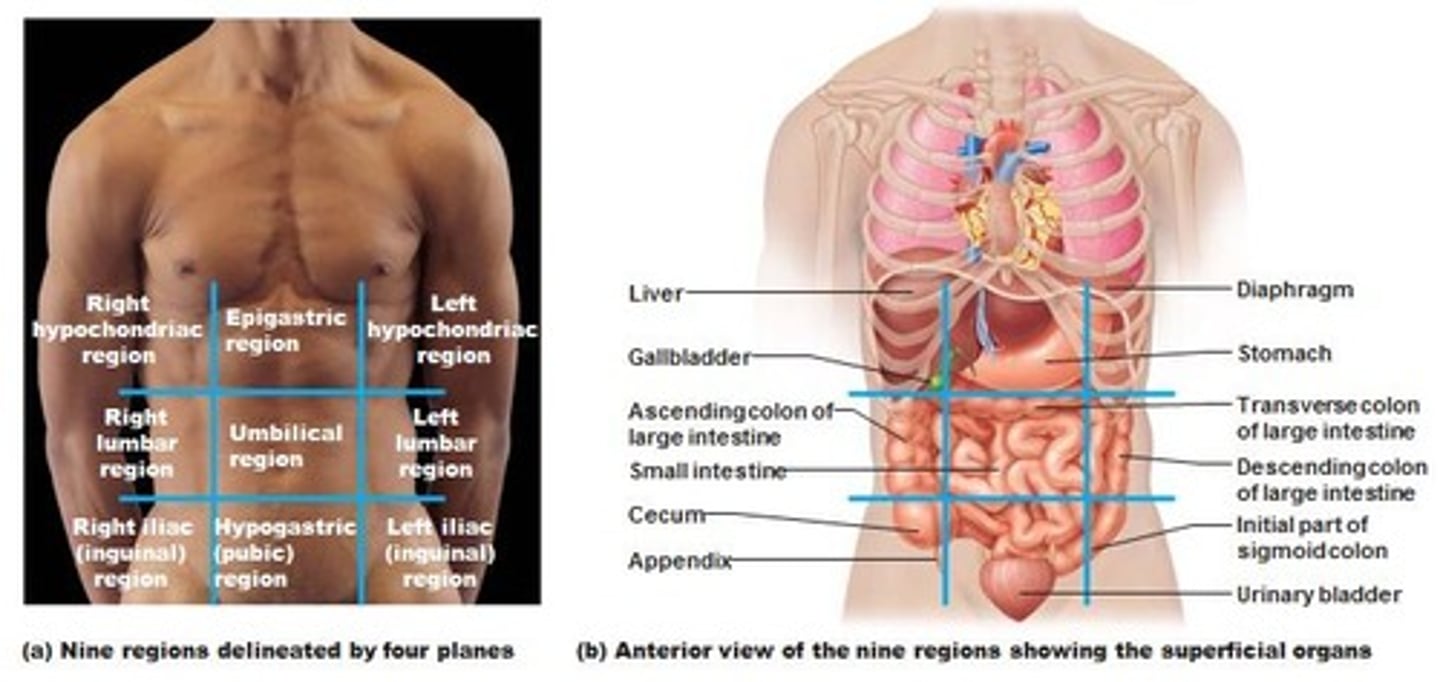
Four Abdominopelvic Quadrants
1) Right upper Quadrant
2) Left upper quadrant
3) Right lower Quadrant
4) Left lower quadrant
Structure of the Generalized Cell
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosome, golgi body, mitochondrion, lysosome. For picture refer to page 66.
Epithelial Tissue (Simple squamous)
Description: Single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped central nuclei and sparse cytoplasm. Simplest of the epithelia.
Function: Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration. Secretes lubricating substances in serosae
-Forms walls of air sacs of the lungs and lines blood vessels
-It contributes to
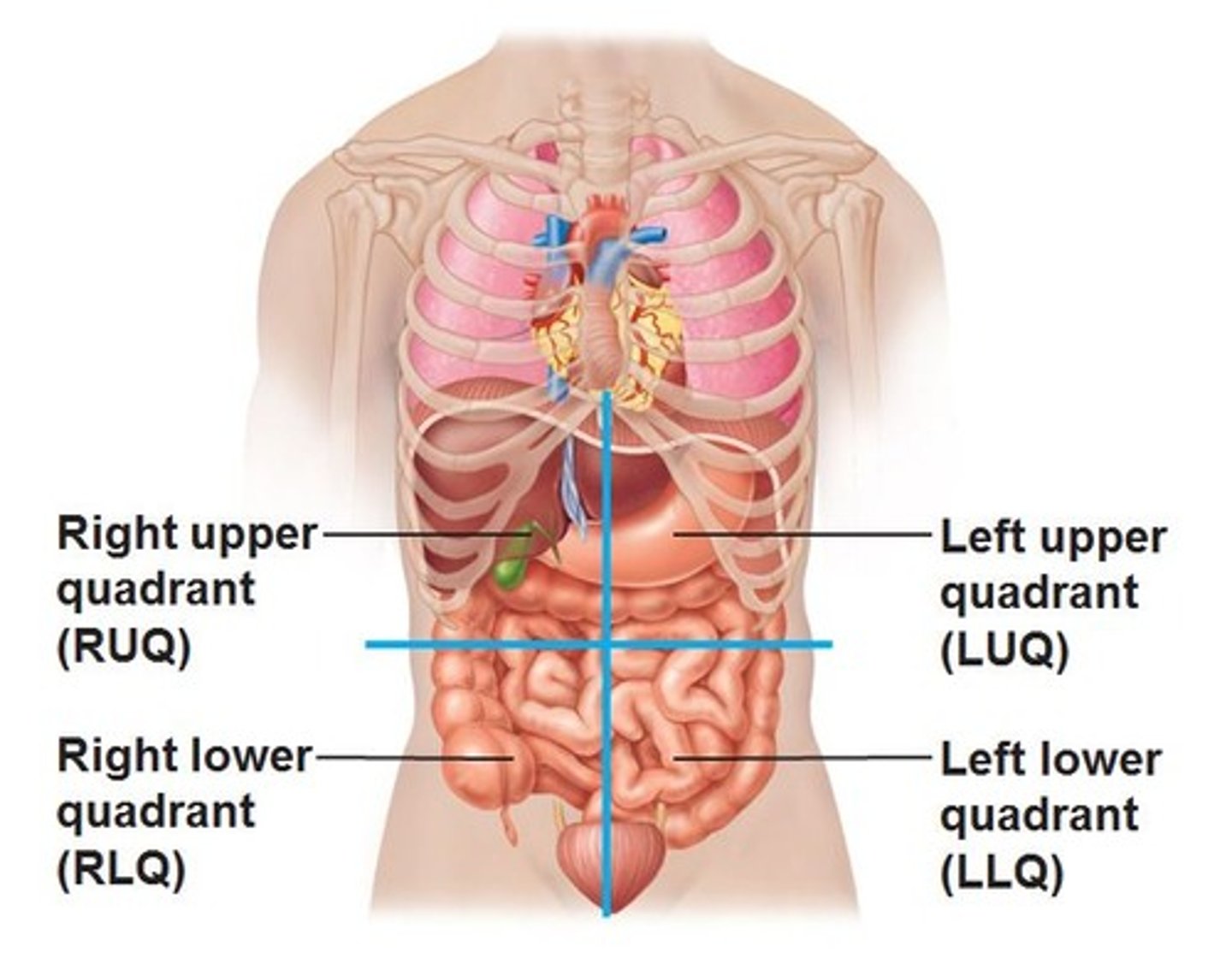
Nervous Tissue Characteristics
Description: Neurons are branching cells cell processes that might be quite long extend from the nucleus-containing cell body. Also contributing to nervous tissue are non irritable supporting cells.
Function: Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands) which control their activity.
Location: Brain, spinal cord, and nerves
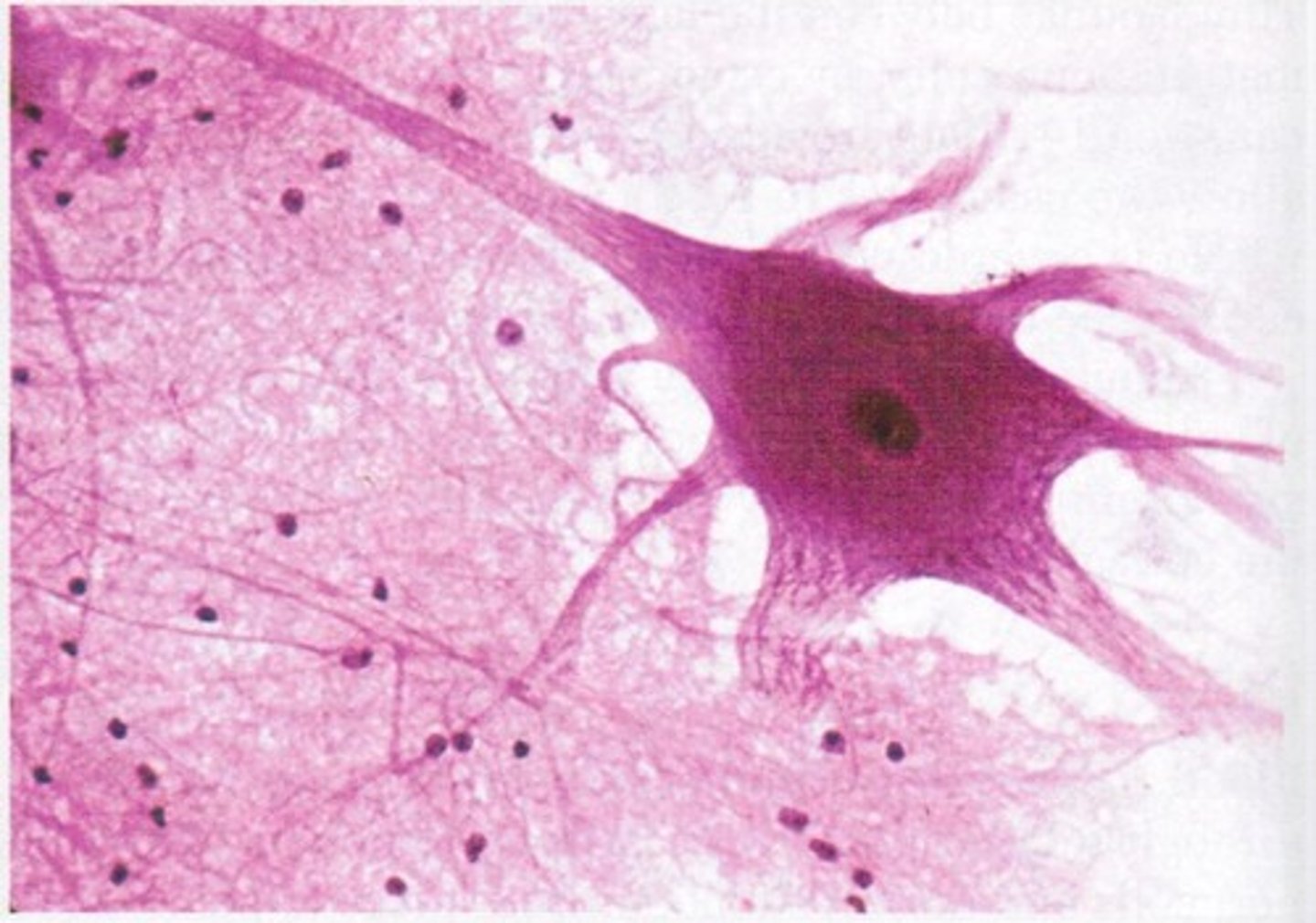
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Description: long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells; obvious striations
Function: voluntary movement; locomotion, manipulate of the environment; facial expression; voluntary control
Location: in skeletal muscles, attached to bones or occasionally to the skin
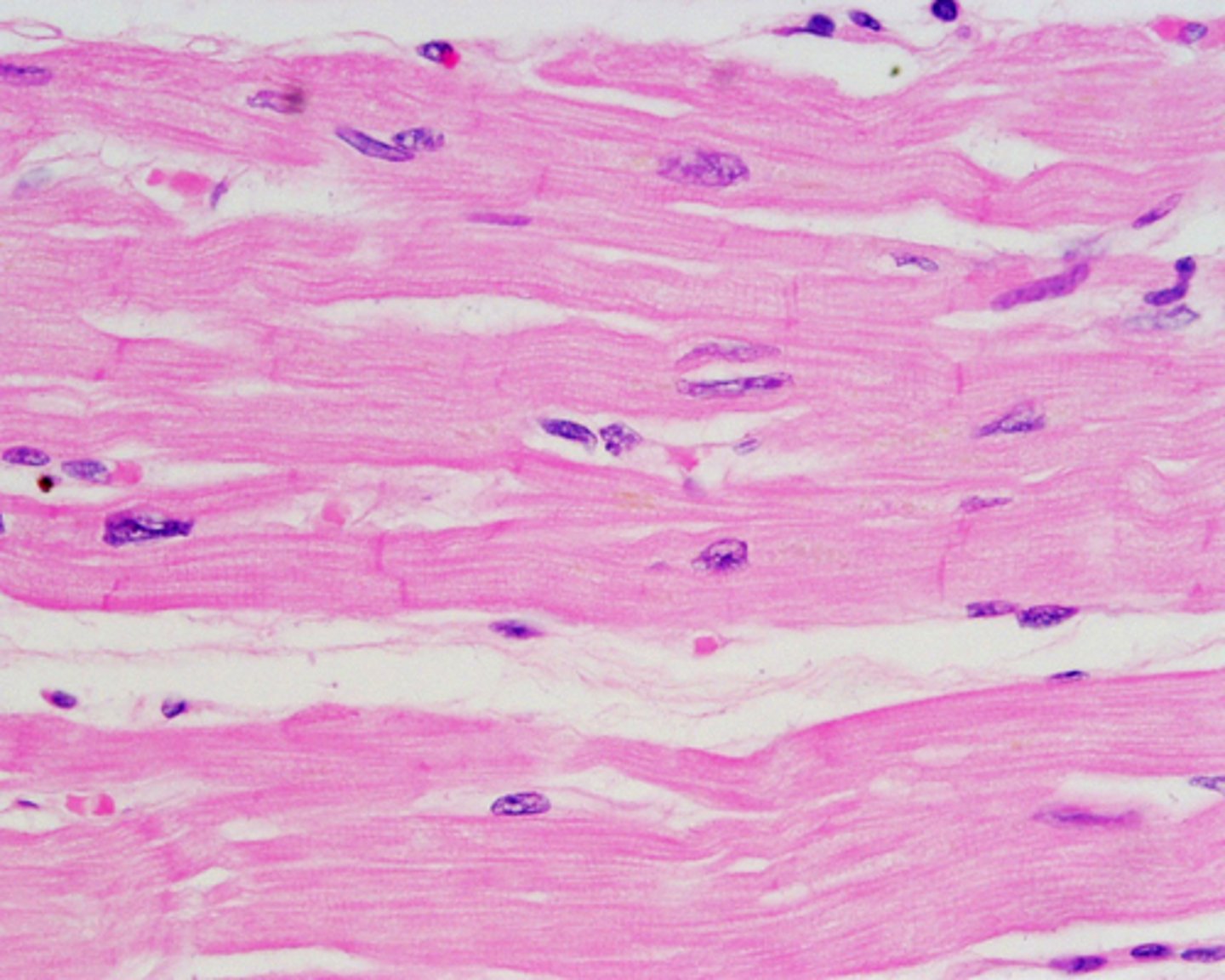
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Description: branching, striated, generally uninucleate cells that interdigetiate at specialized junctions
Function: as it contracts, it propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control
Location: walls of the heart
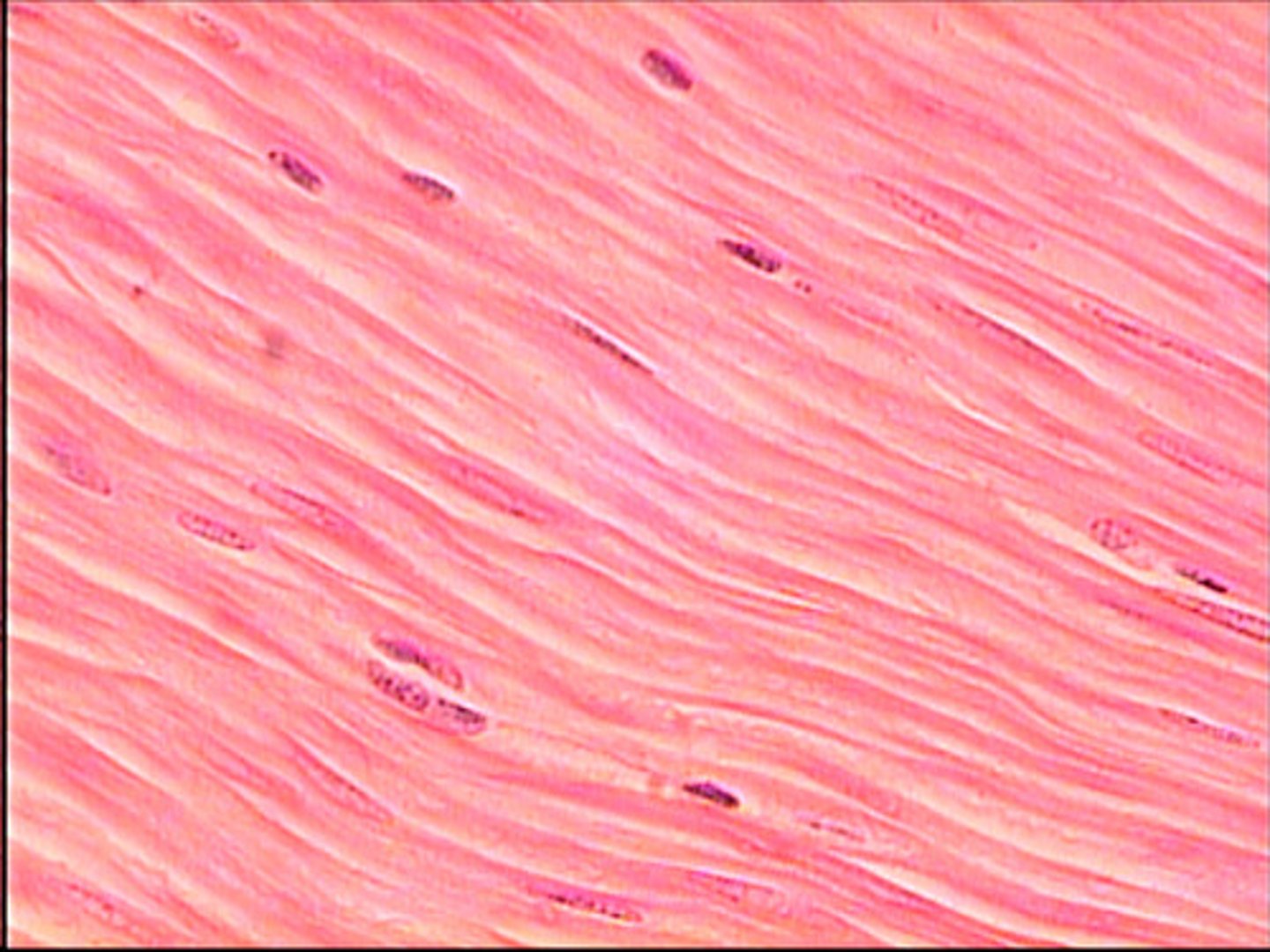
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Description: Spindle-shaped cells with a central nuclei ; no striations; cells arranged closely to form sheets
Function: propels substances or objects along internal passage ways; involuntary control
Location: mostly in walls of hollow organs
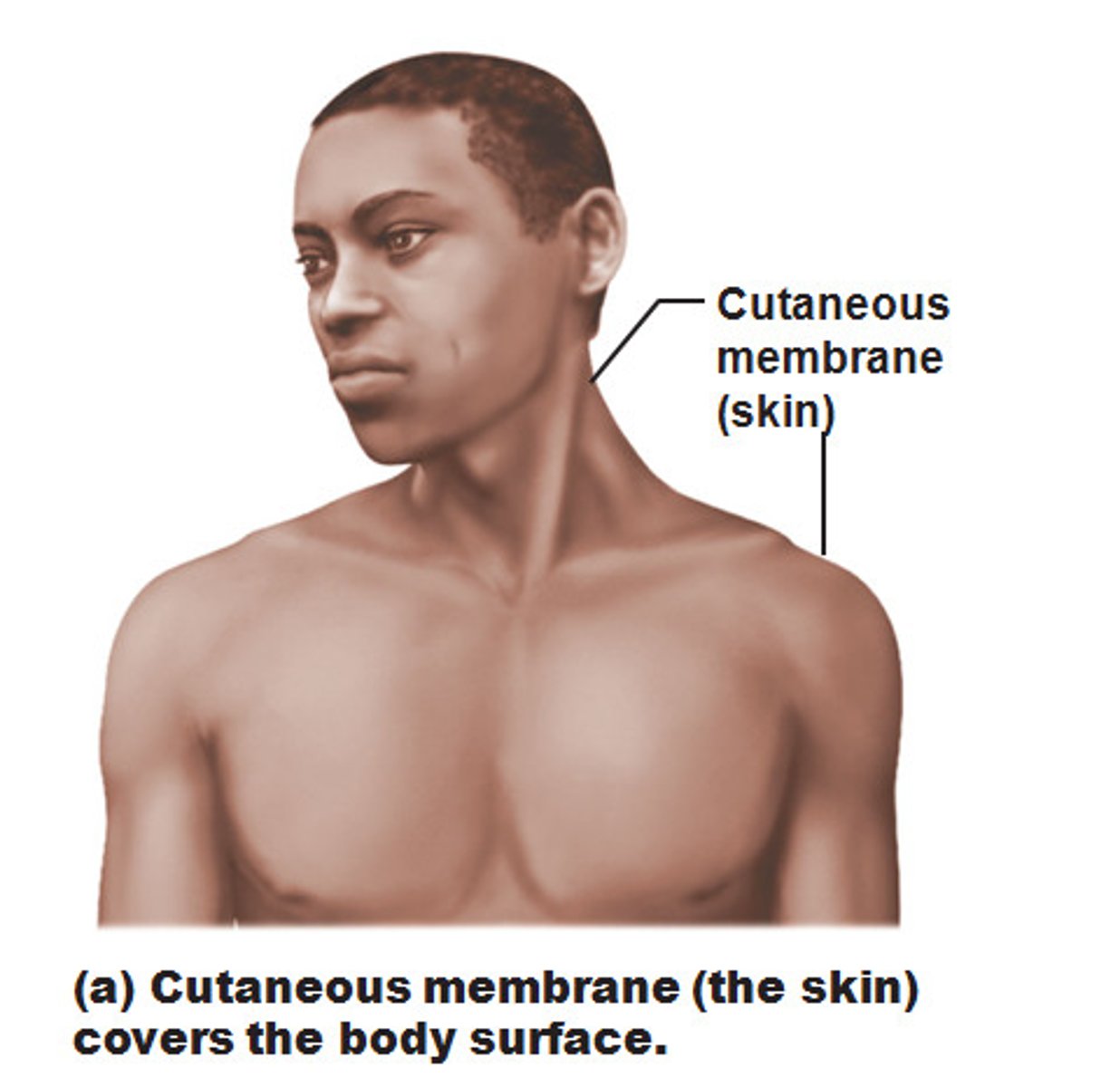
Cutaneous Membrane
skin, organ system consisting of a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium firmly attached to a thick layer of dense irregular connective tissue
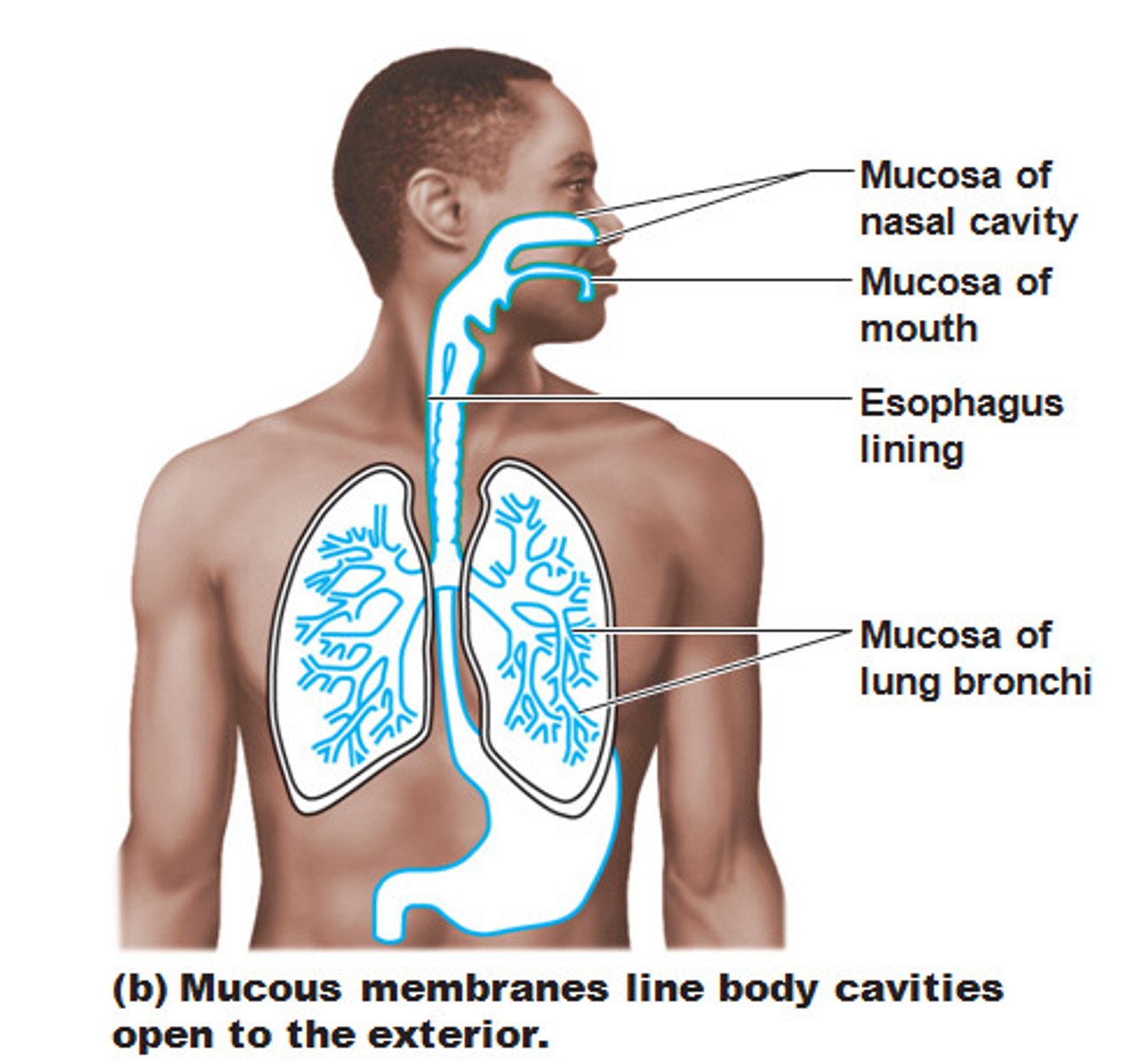
Mucous Membranes
lines body cavities that open to the exterior, such as those of hollow organs of the digestive, respiratory, and urogenital tracts (they are usually wet or moist)
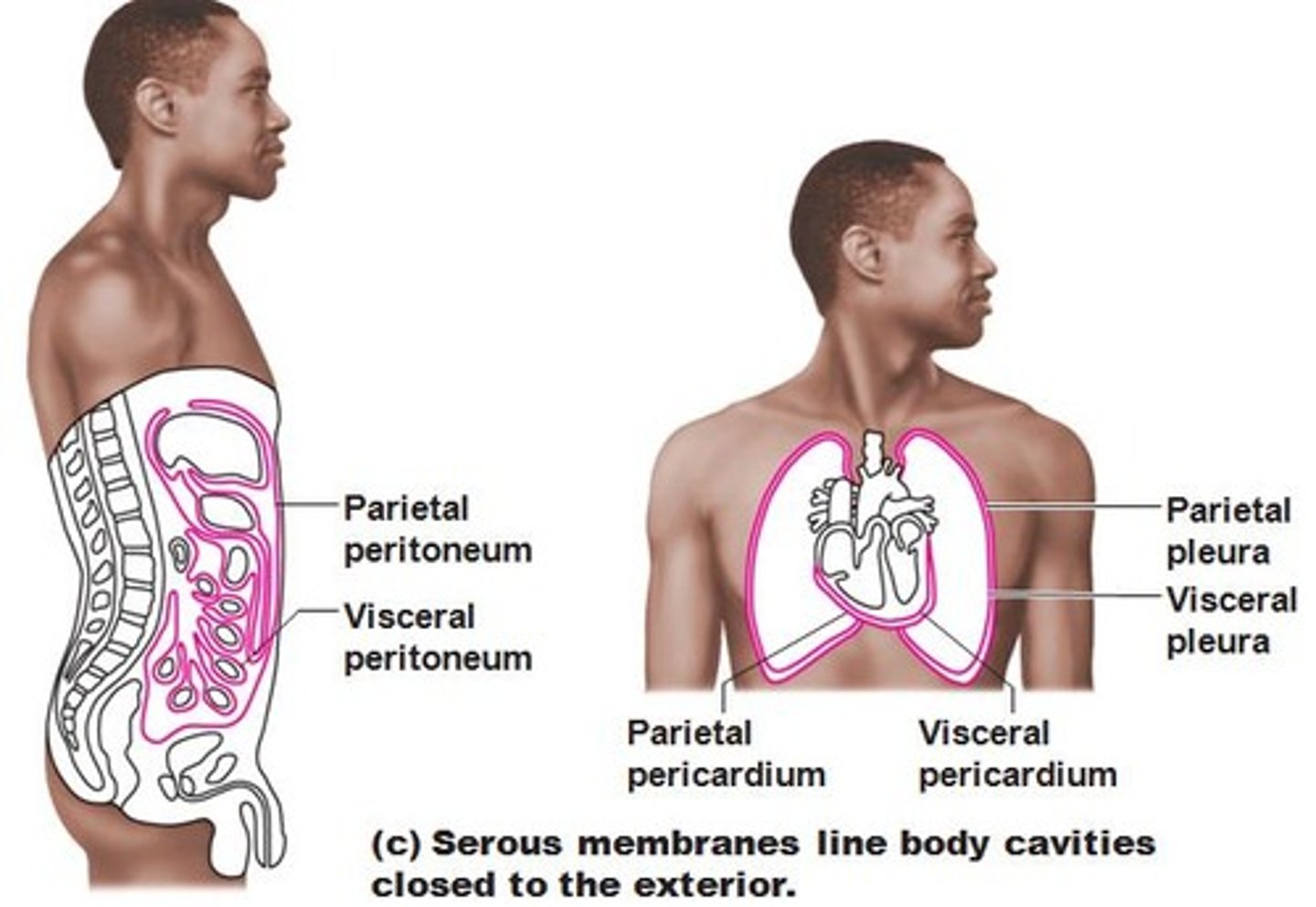
Serous Membranes
moist membranes found in closed ventral body cavities. consists of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of loose connective areolar tissue
Analyze the changes that occur in tissue from embryonic development throughout a person's lifetime.
First event of embryotic development is primary germ layers (ectotherm, mesotherm, and endotherm).
-They then specialize to form the 4 major tissues by second month of development.
-division of nerve cells stop during fetal period.
-only epithelia and blood-forming tissues are highly miotic.
-with age, epithelia thins breach prone, tissue repair and circulatory system is less efficient
-More DNA mutation = cancer.
melanin
protects the keratinocytes nuclei from the damaging affects of UV radiation
sweat glands (sudoriferous)
thermoregulation
eccrine sweat gland
produces true sweat; abundant on the palms of hand, soles of the feet, and forehead
Apocrine sweat gland
produce true sweat plus fatty substances and proteins; found in the axillary (armpit) and anogenital areas of the body
oil glands (sebaceous)
empty into hair follicles, they are simple alveolar glands; their oily, holocrine secretion is called sebum. Lubricates the skin and hair, prevents water loss from skin
hair follicle
arrector pili
smooth muscle cells associated with each hair follicle bundle of smooth muscle cells, pulls the hair follicle into an upright position, forms goosebumps due to cold temperature and fear
hair
Hair on skin senses insects before they sting or bite; Hair on scalp protects from physical trauma, heat loss, sunburn; eyelashes shield eyes; nose hairs filter particles in the air
nail
scalelike modification of the epidermis that forms a clear protective covering on the dorsal surface of a finger or toe