radiology partial- respiratory, cardio
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
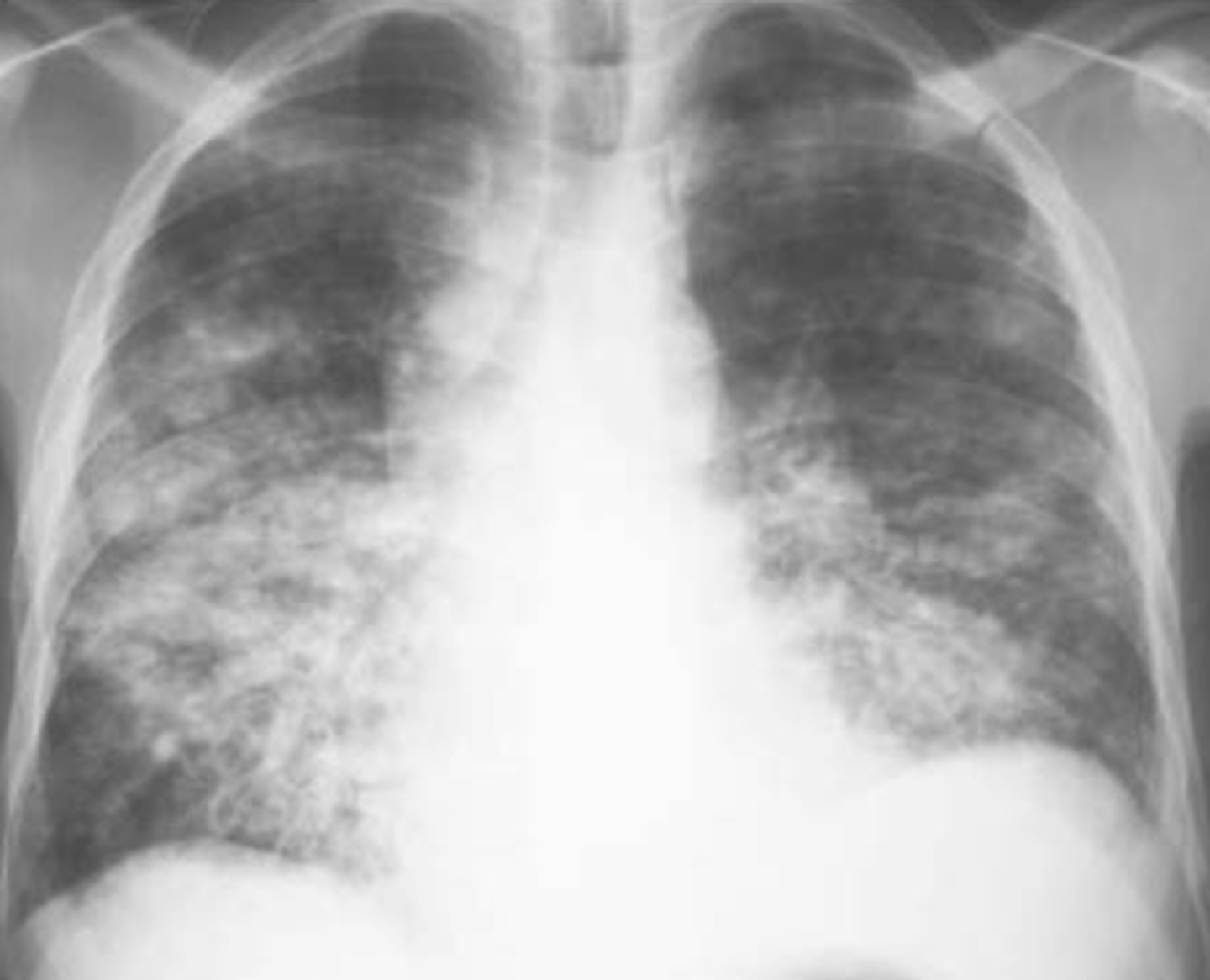
bronchopneumonia on CXR
Diffuse and patchy
Lobar pneumonia is usually caused by:
Streptococcus pneumonia
Phases of lobar pneumonia
congestion, red hepatization, gray hepatization, resolution
Lobar pneumonia on chest x-ray
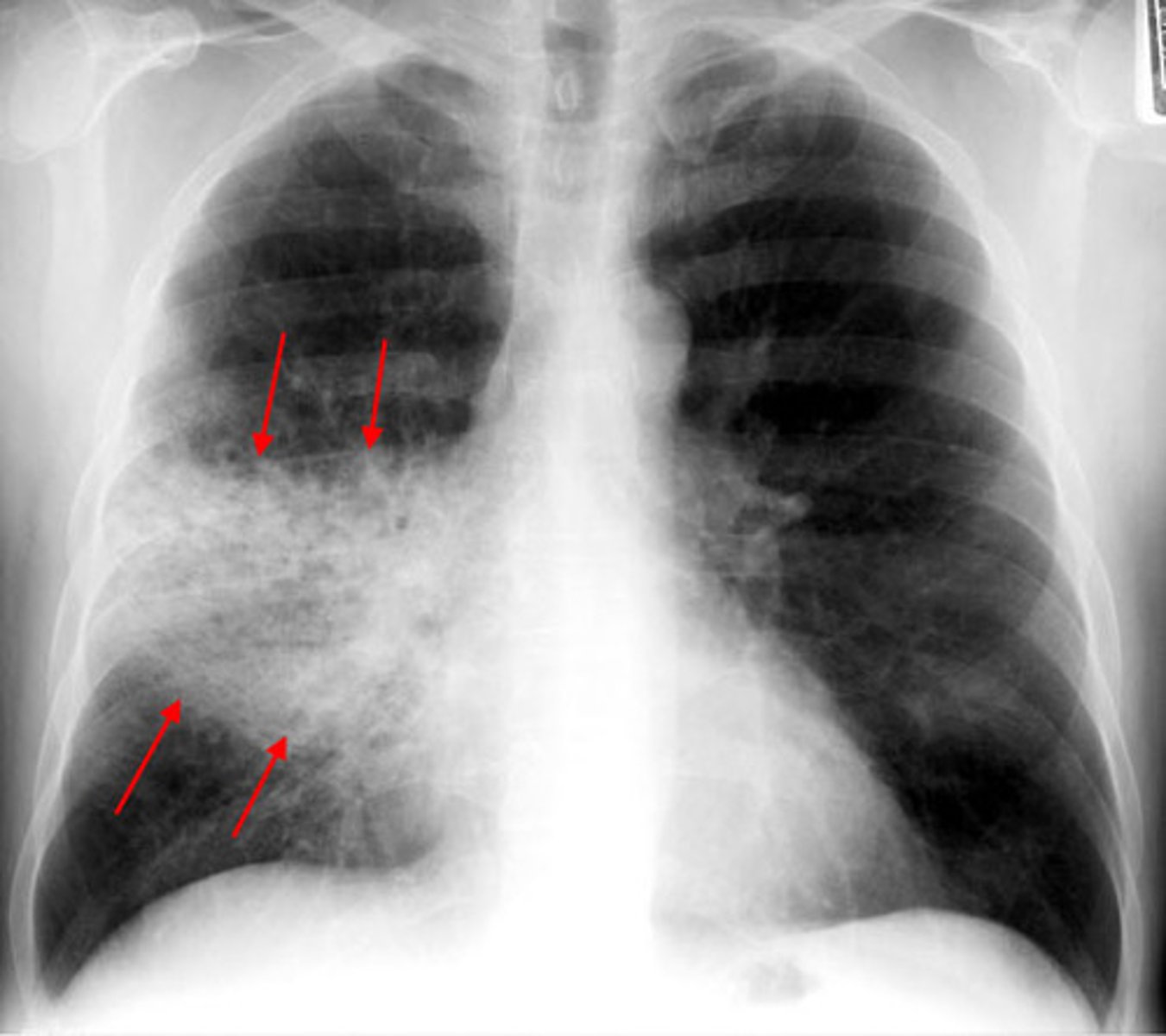
bronchopneumonia refers to
focal/patchy areas of consolidated acute suppurative inflammation in one or more lobes. Usually, it involves lower lobes (basal) bilaterally.
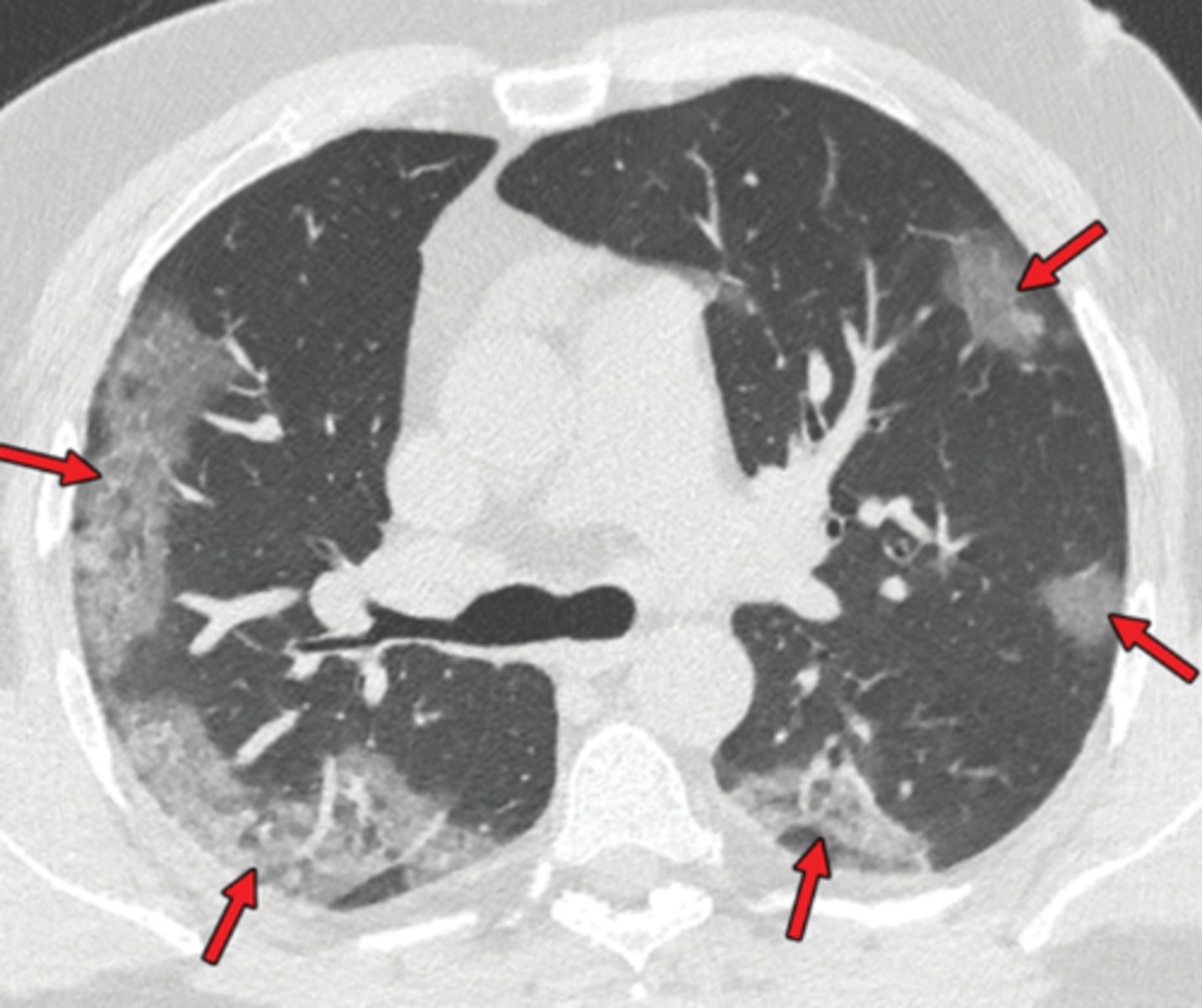
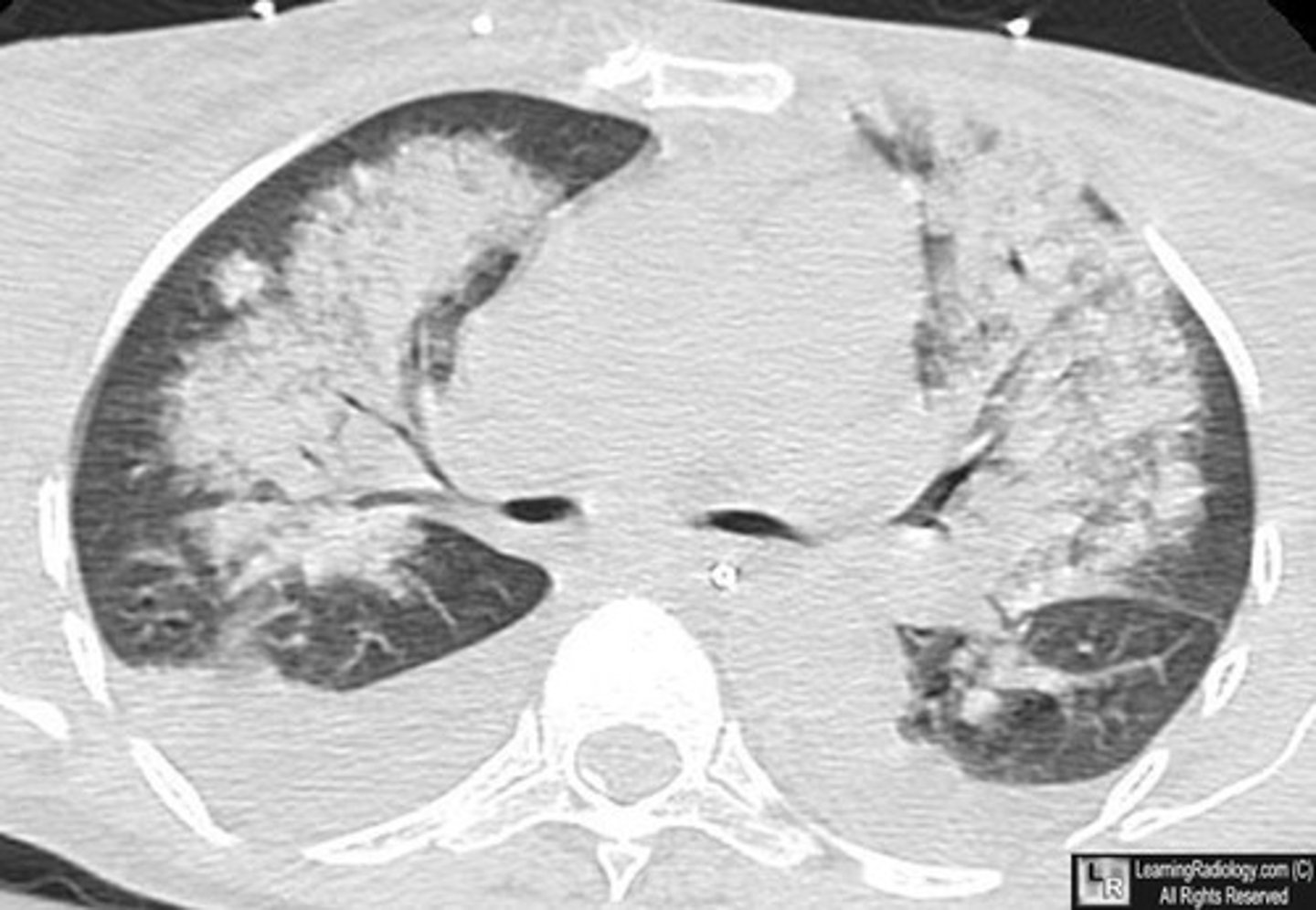
COVID-19 CT findings
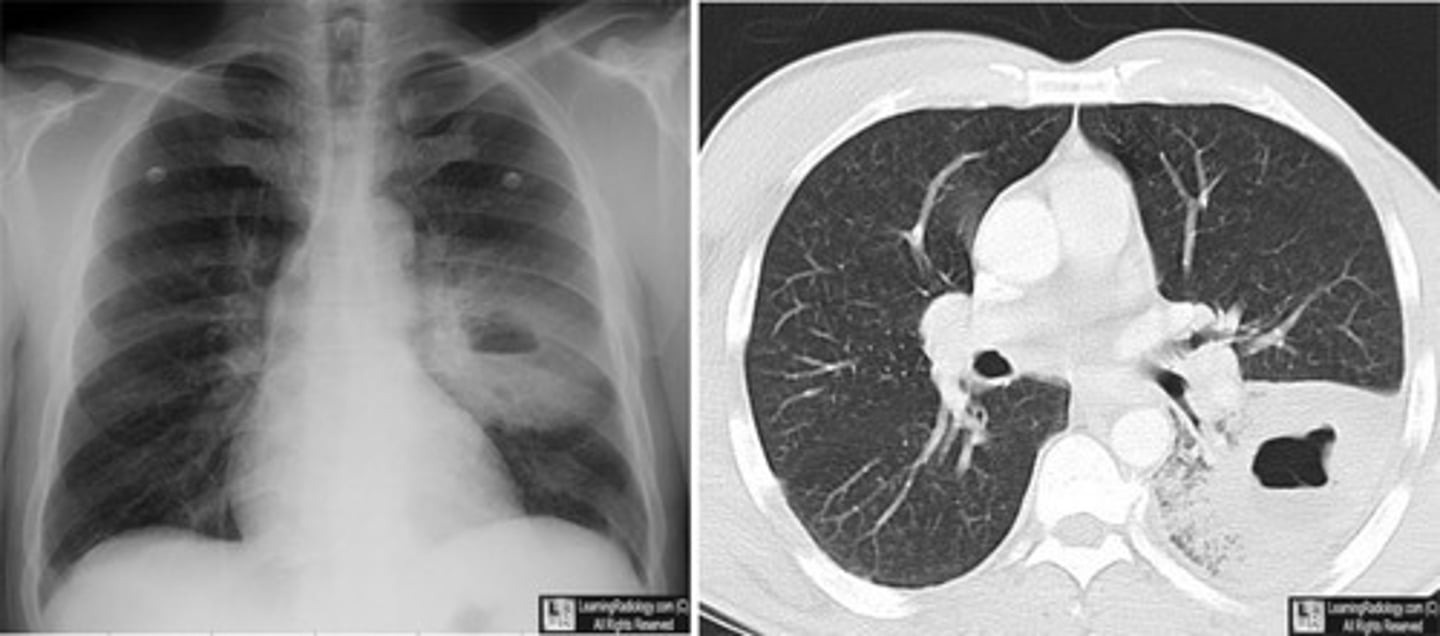
Pulmonary abscess on CXR and CT
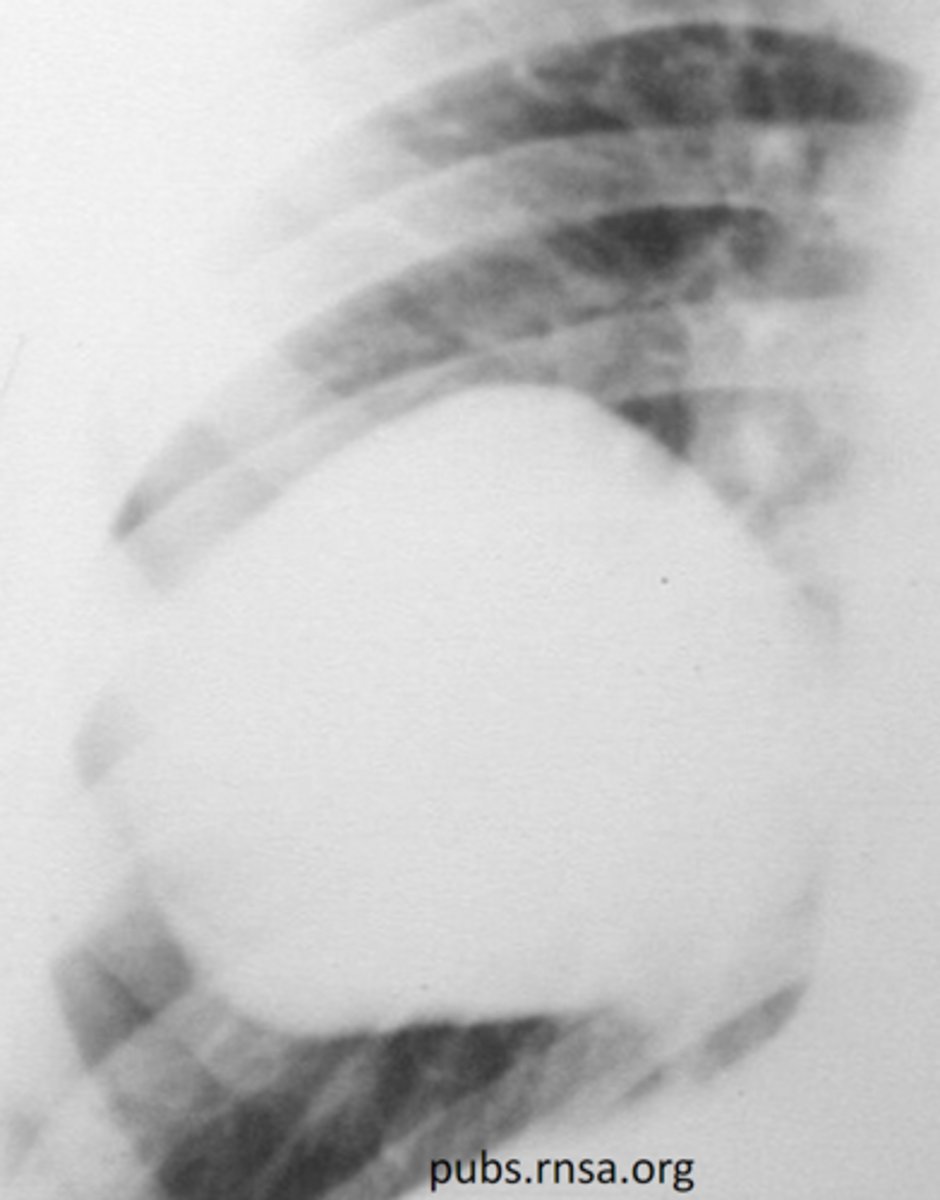
cyst on CXR
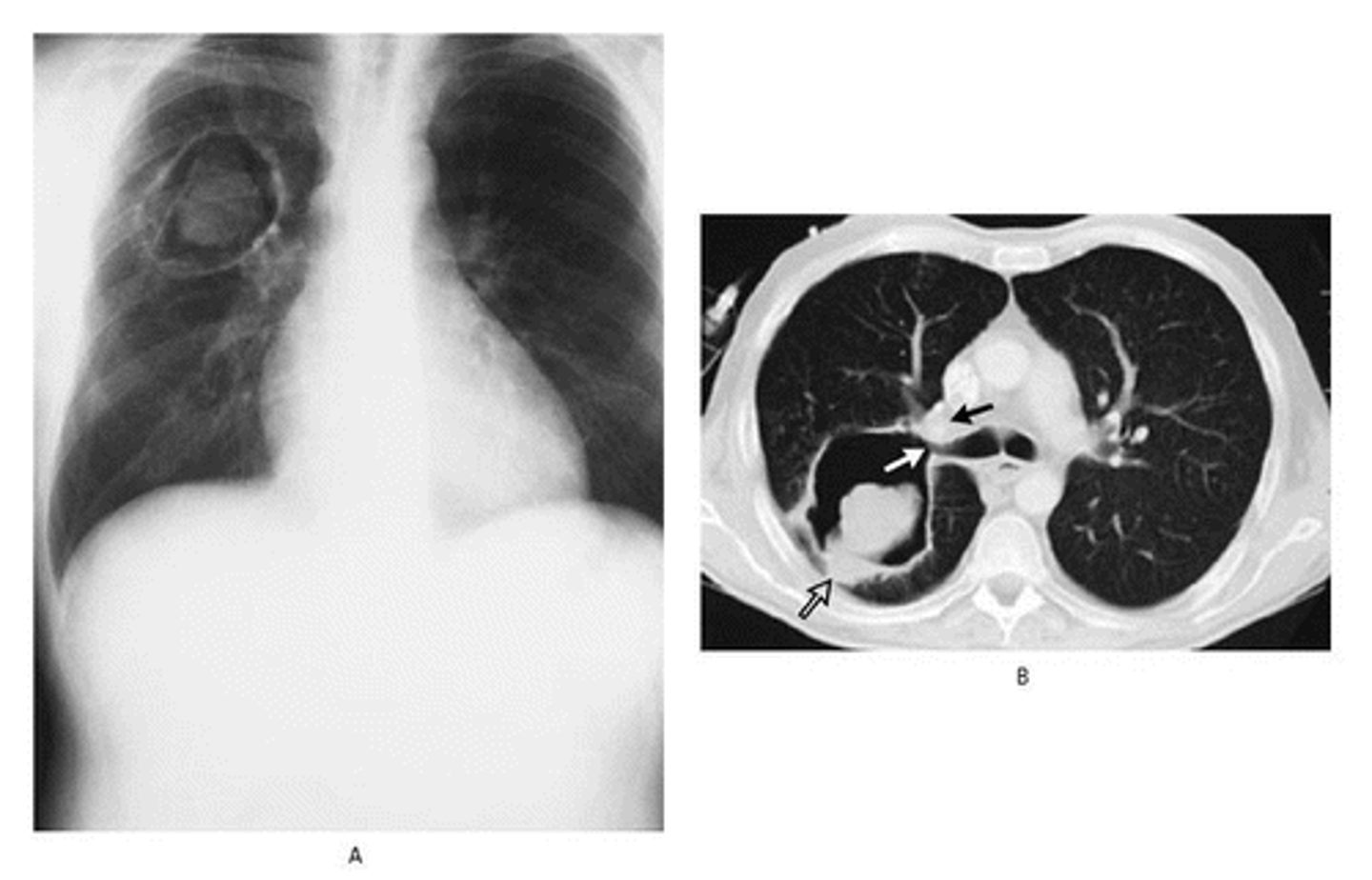
Pulmonary aspergillosis on CXR and CT
The formation of a "fungus ball" within preexisting cavities
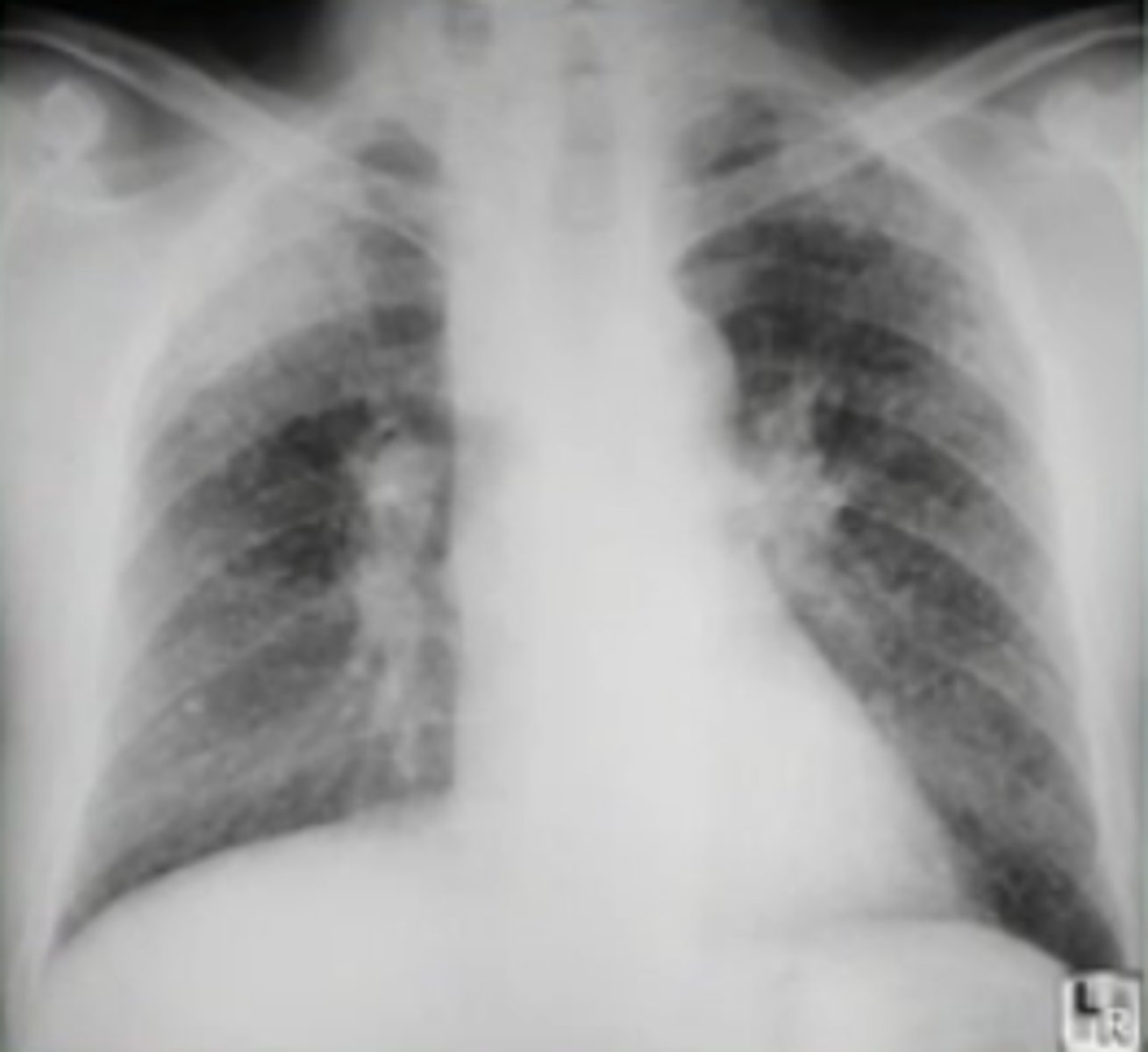
Pulmonary silicosis on CXR
nodular densities and eggshell calcifications of hilar nodes
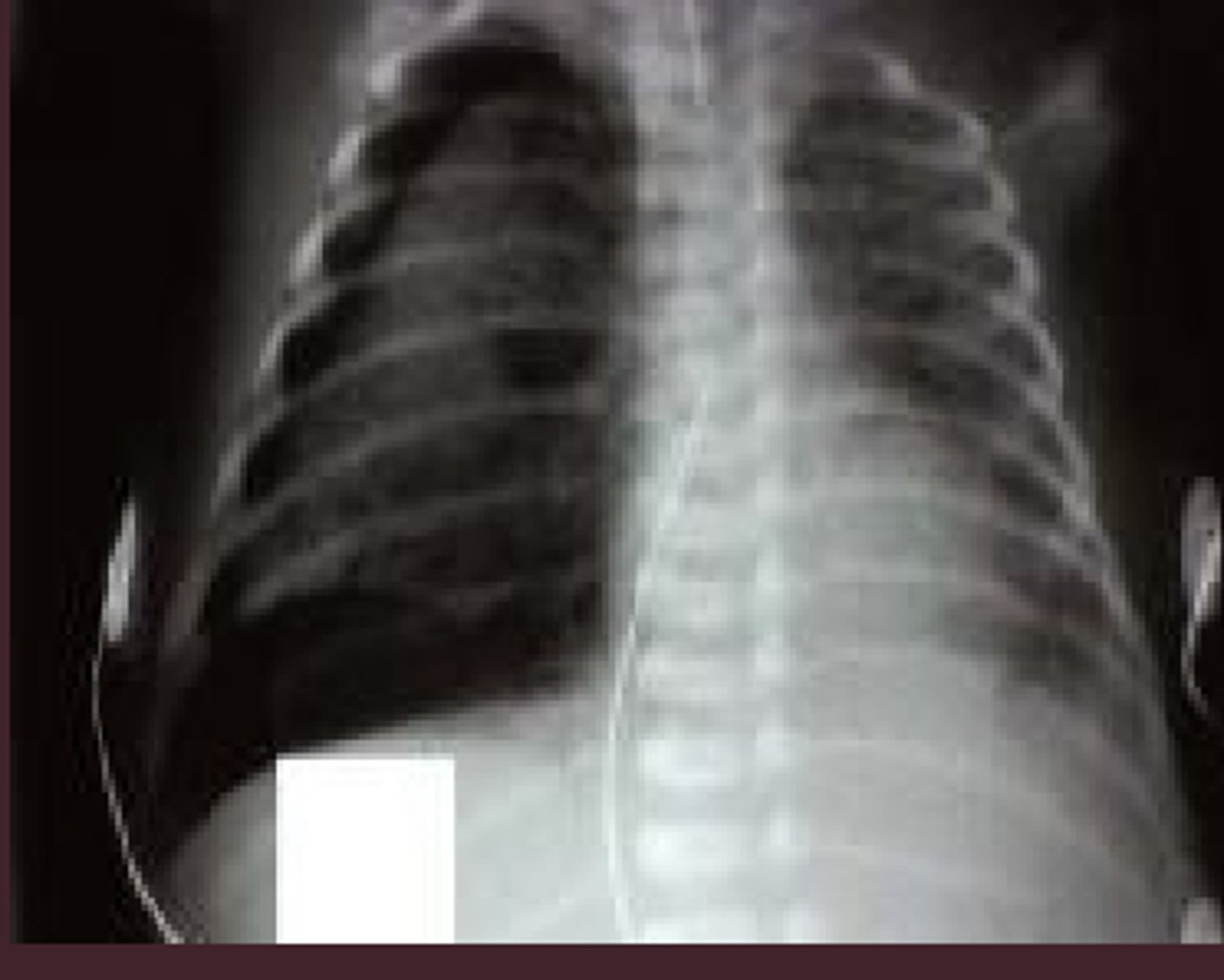
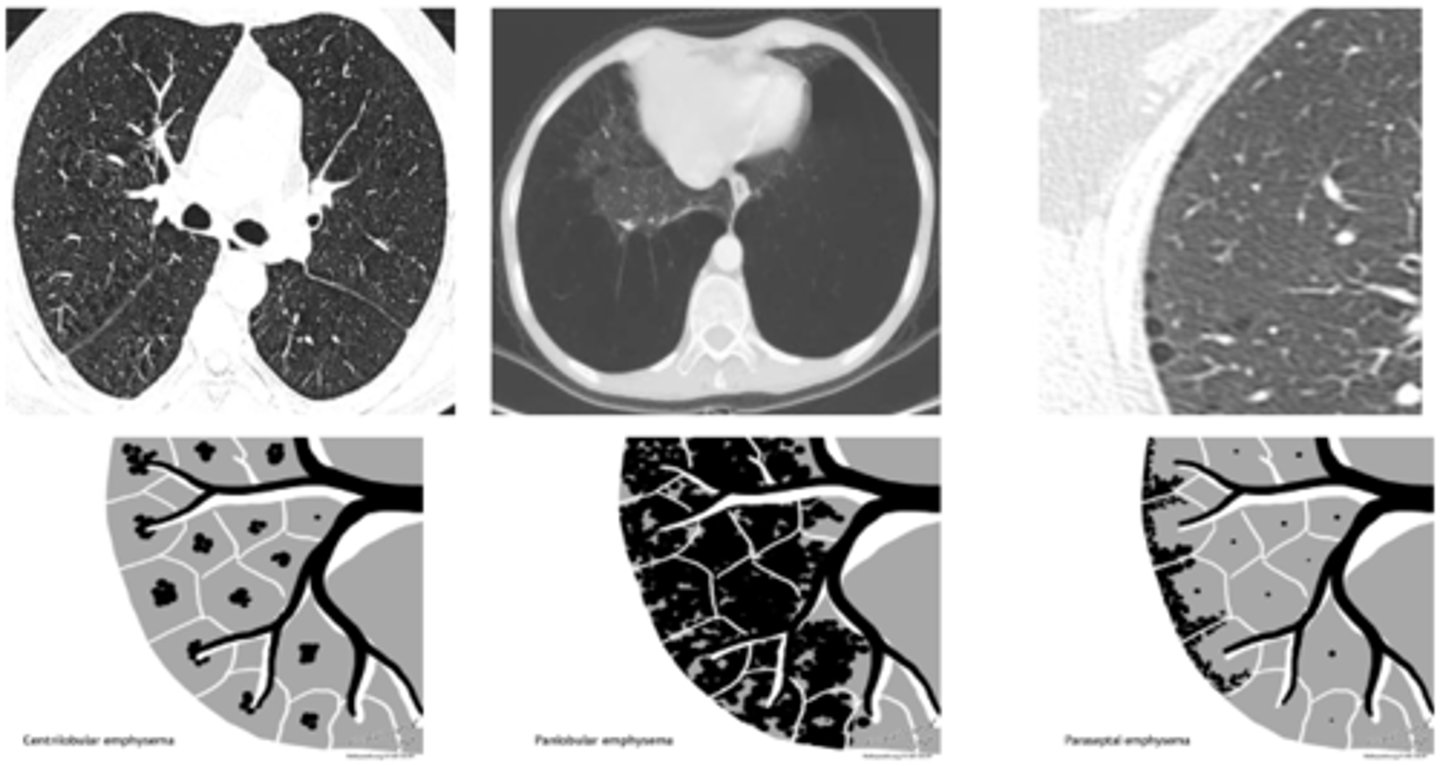
pulmonary emphysema on CXR
horizontal ribs
pulmonary emphysema on CT
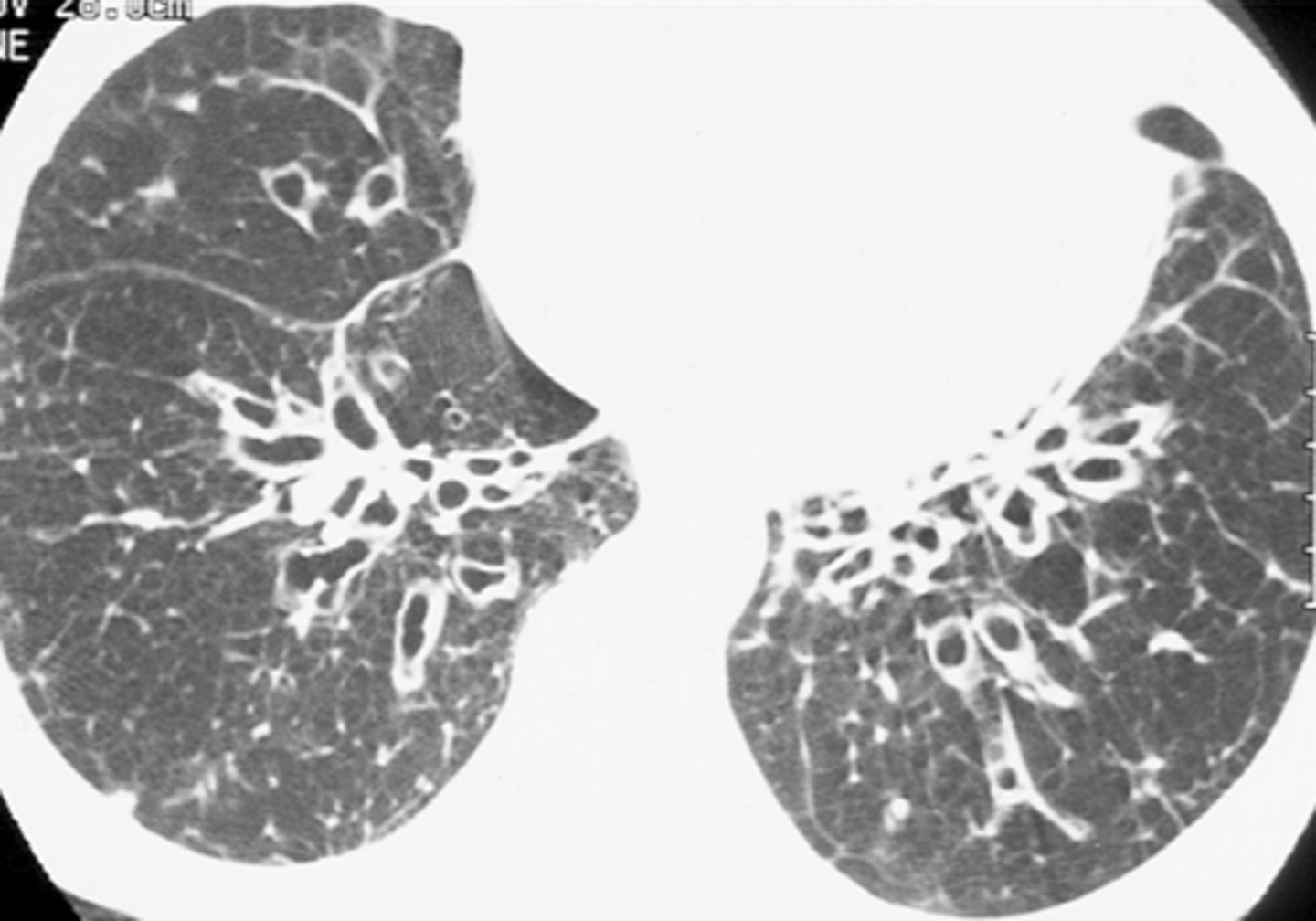
bronchiectasis
abnormal dilation of the bronchi with accumulation of mucus
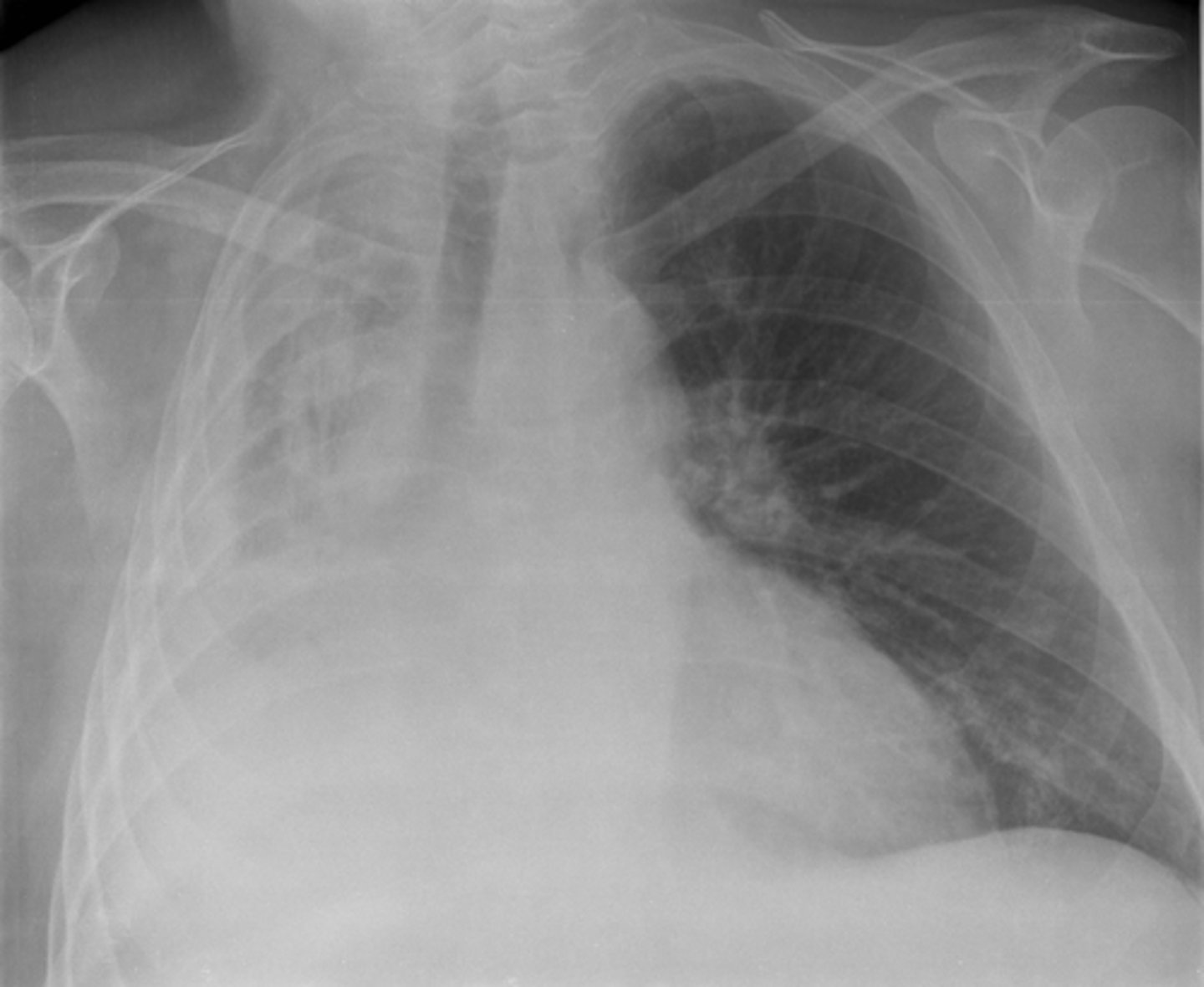
Right pulmonary atelectasis
a complete or partial collapse
primary tuberculosis
initial infection of tuberculosis, Ranke complex
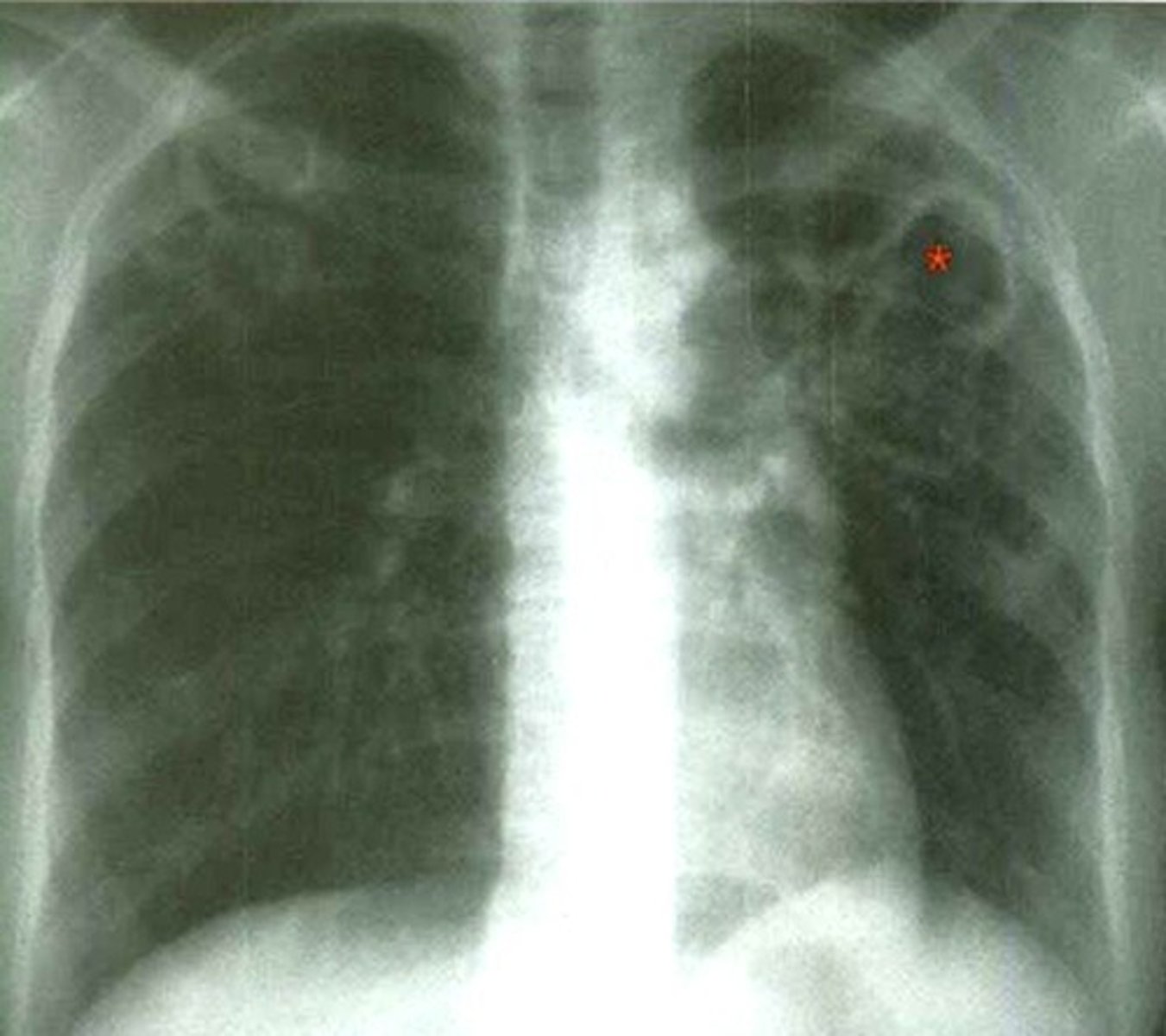
Ranke complex TB
primary lesion, lymphangitis, hilar lymphadenopathy
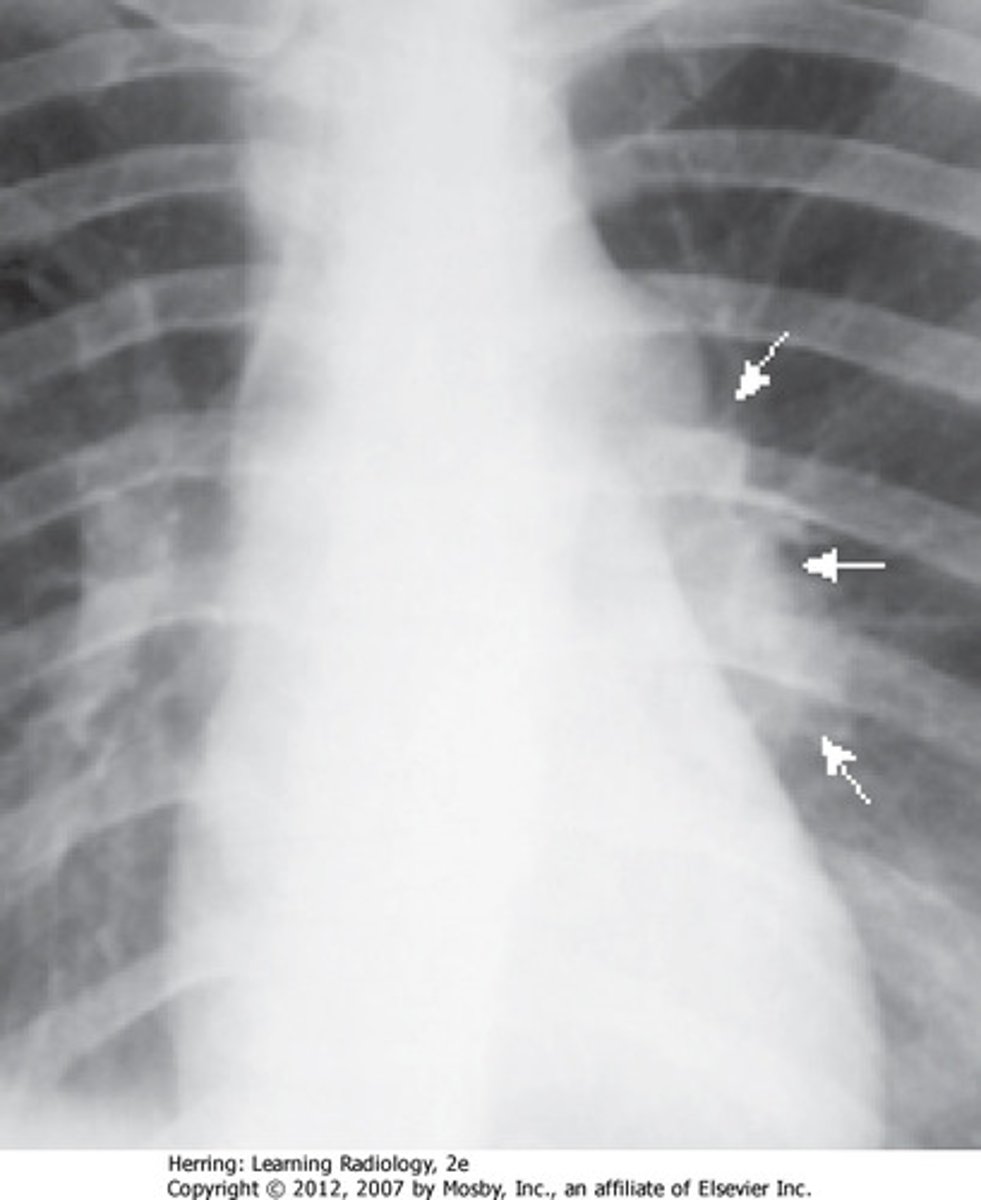
Assman infiltrate is characteristic of
secondary TB
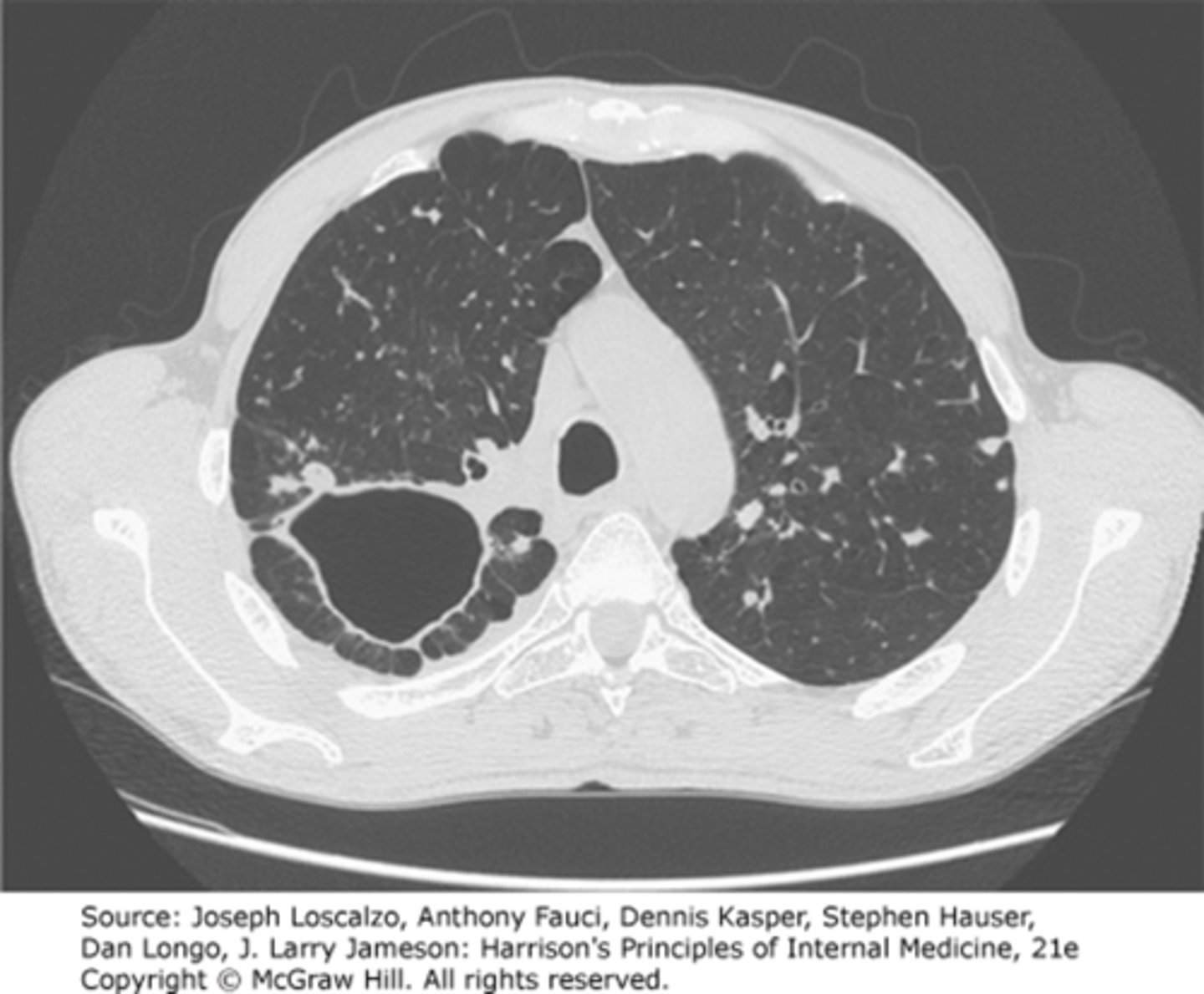
secondary TB and cavitation
TB cavity on CT
Lung cancer types
- right parahilar
- left apical, Pancoast-Tobias Syndrome
pulmonary sarcoma
cancer that metastasizes to the lung from another part of the body
Fibrinothorax on CXR
trachea pull to the same side, minimal aerated lung parenchyma visible
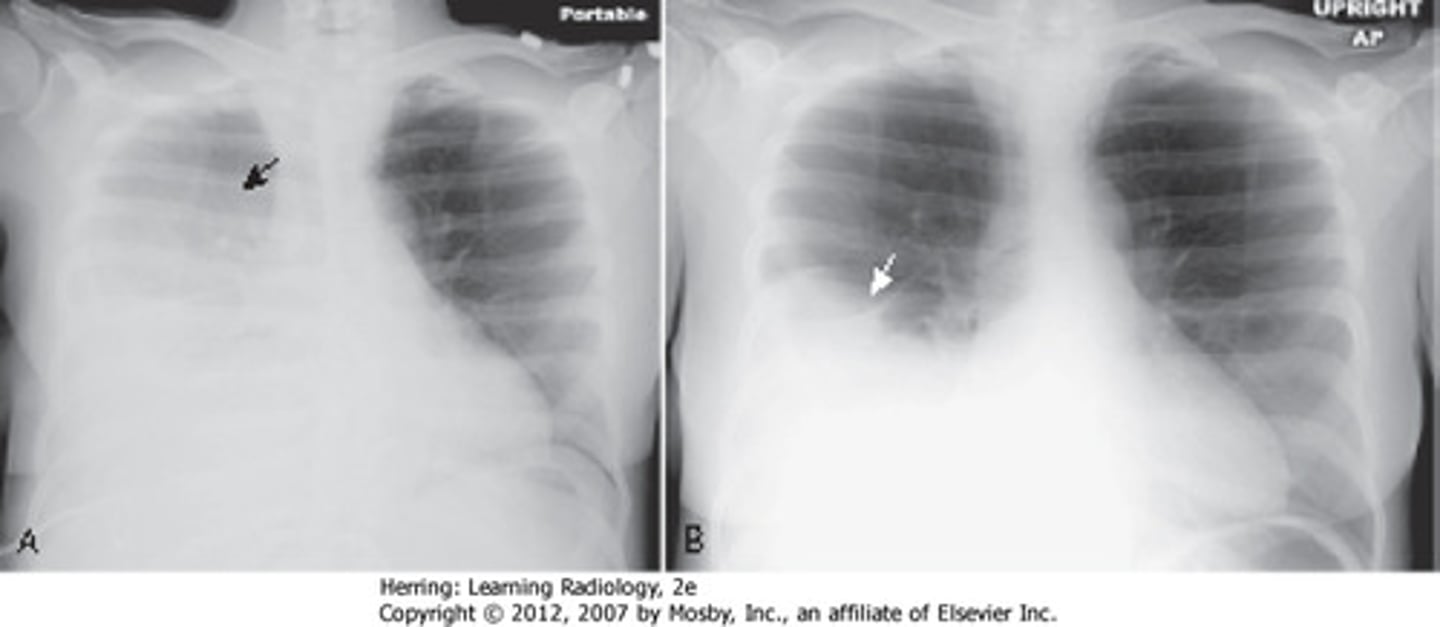
pleural effusion on CXR
trachea affected (pushed to opposite side), Damoiseau line
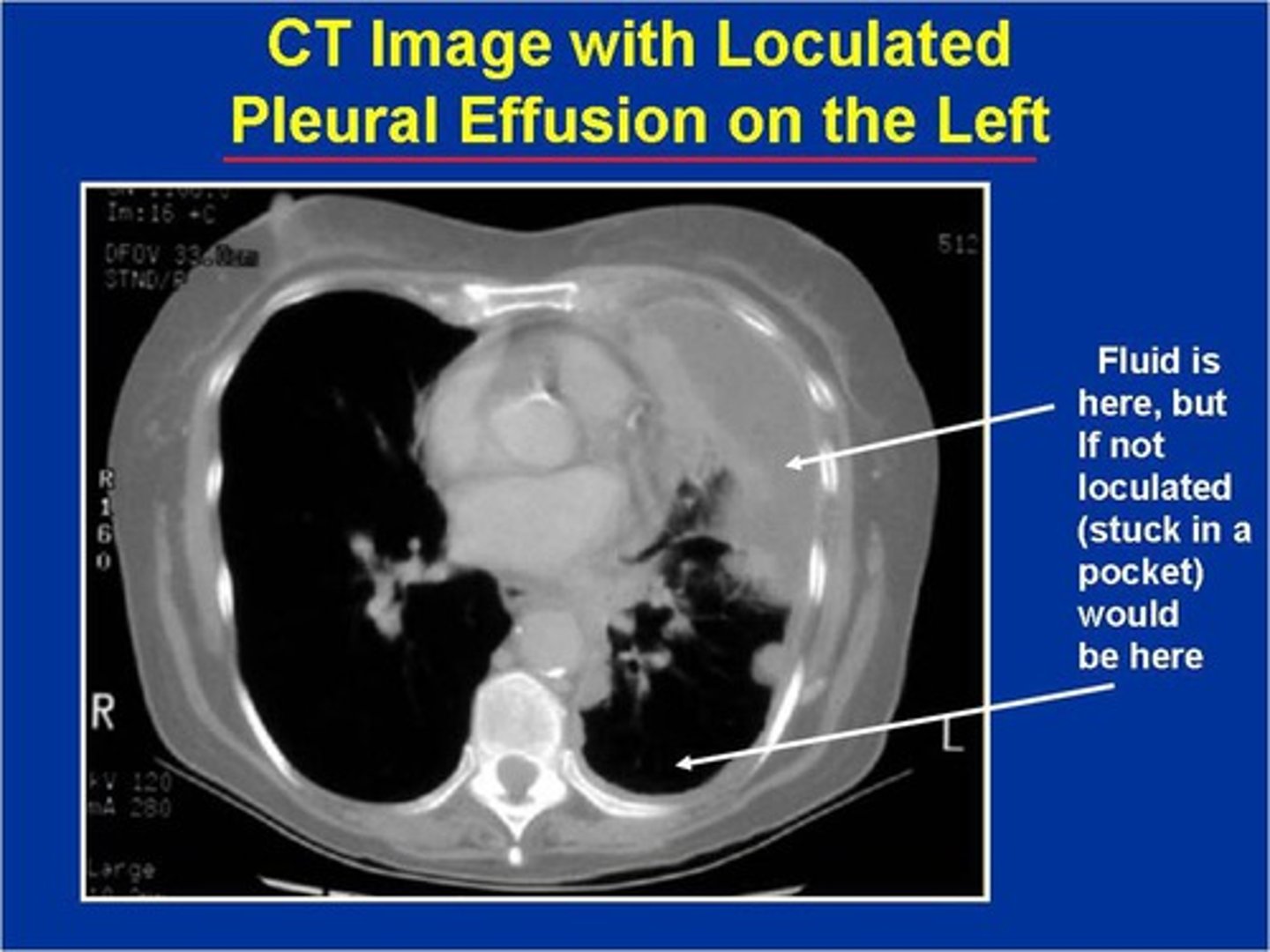
pleural effusion on CT
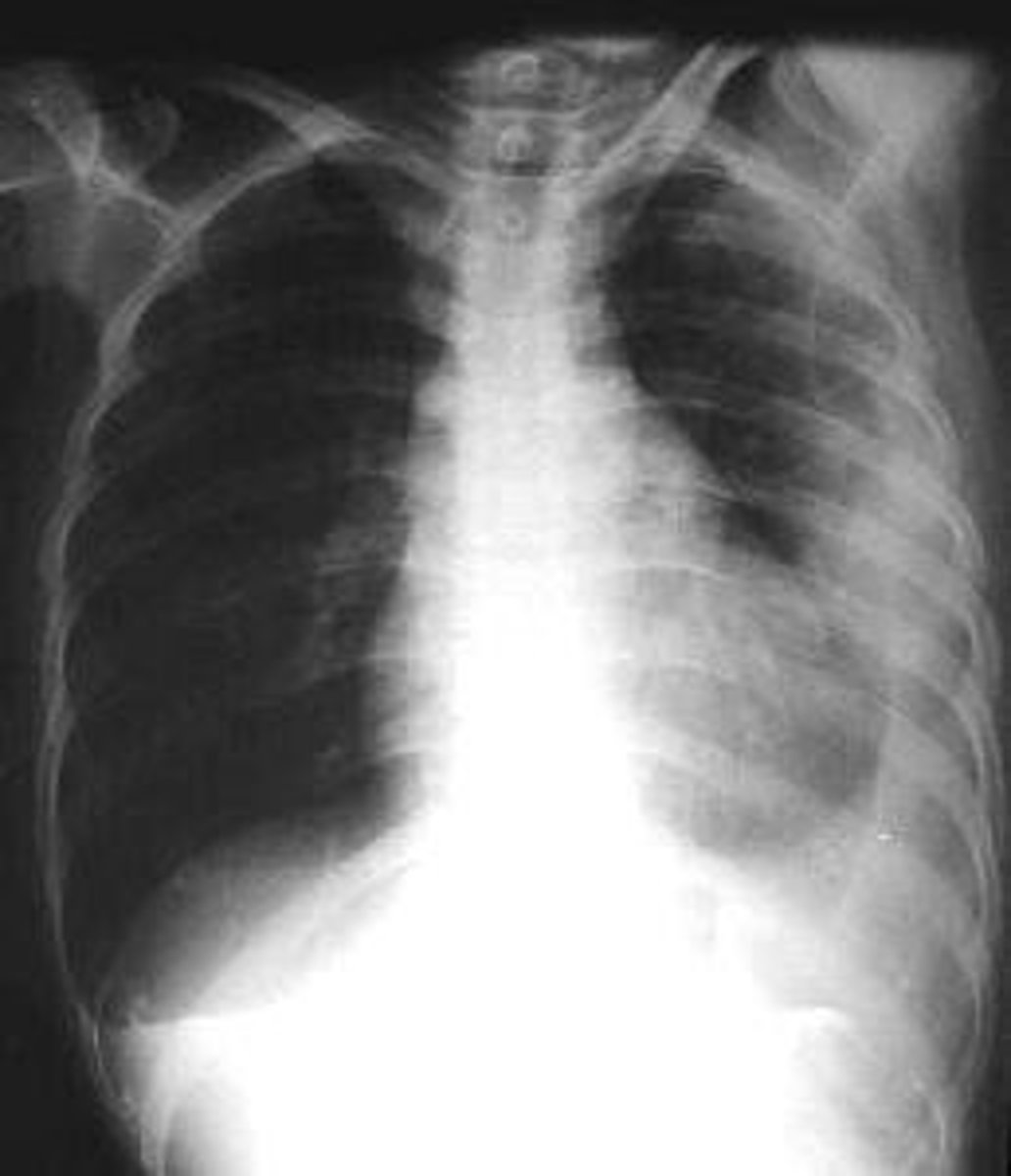
Hemothorax
blood in the pleural cavity
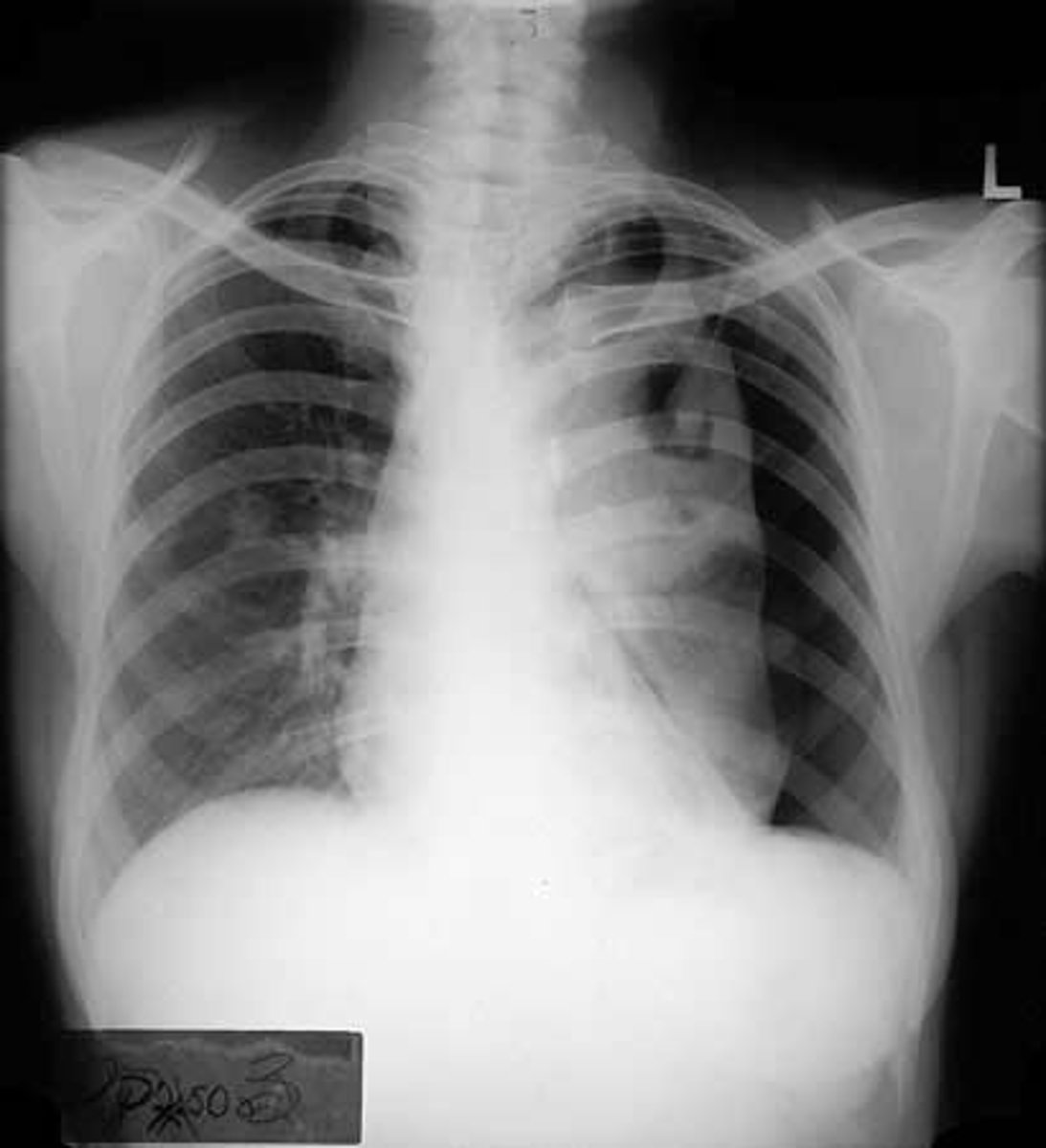
Pneumothorax CXR findings
-Hyper-translucent (black) area at site of pneumothorax
- Shift of mediastinum toward the unaffected side
- Lung collapse
- air in the pleural cavity caused by a puncture of the lung or chest wall
Pneumothorax on CT
collapsed lung, more prominent markings on non-collapsed sign
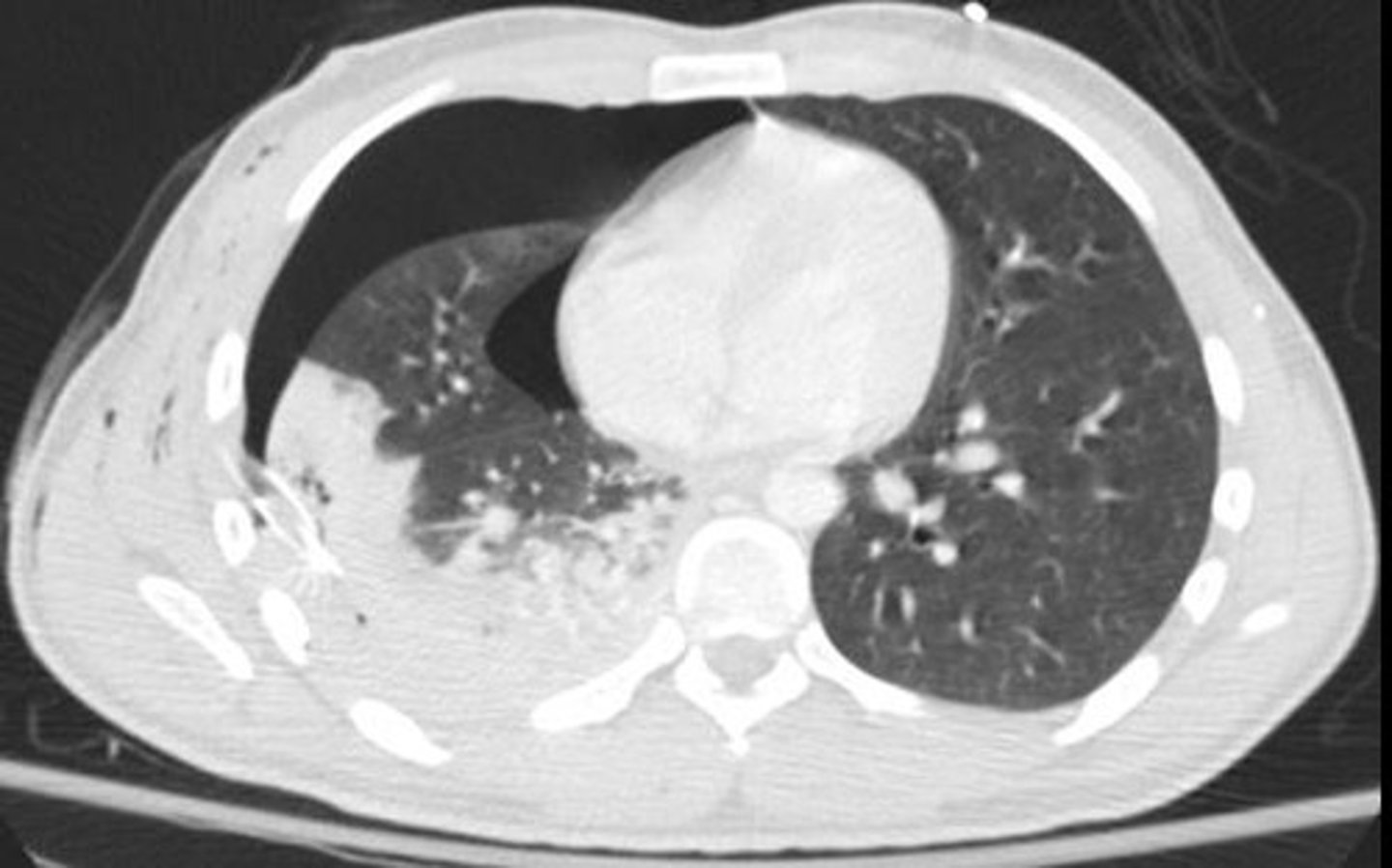
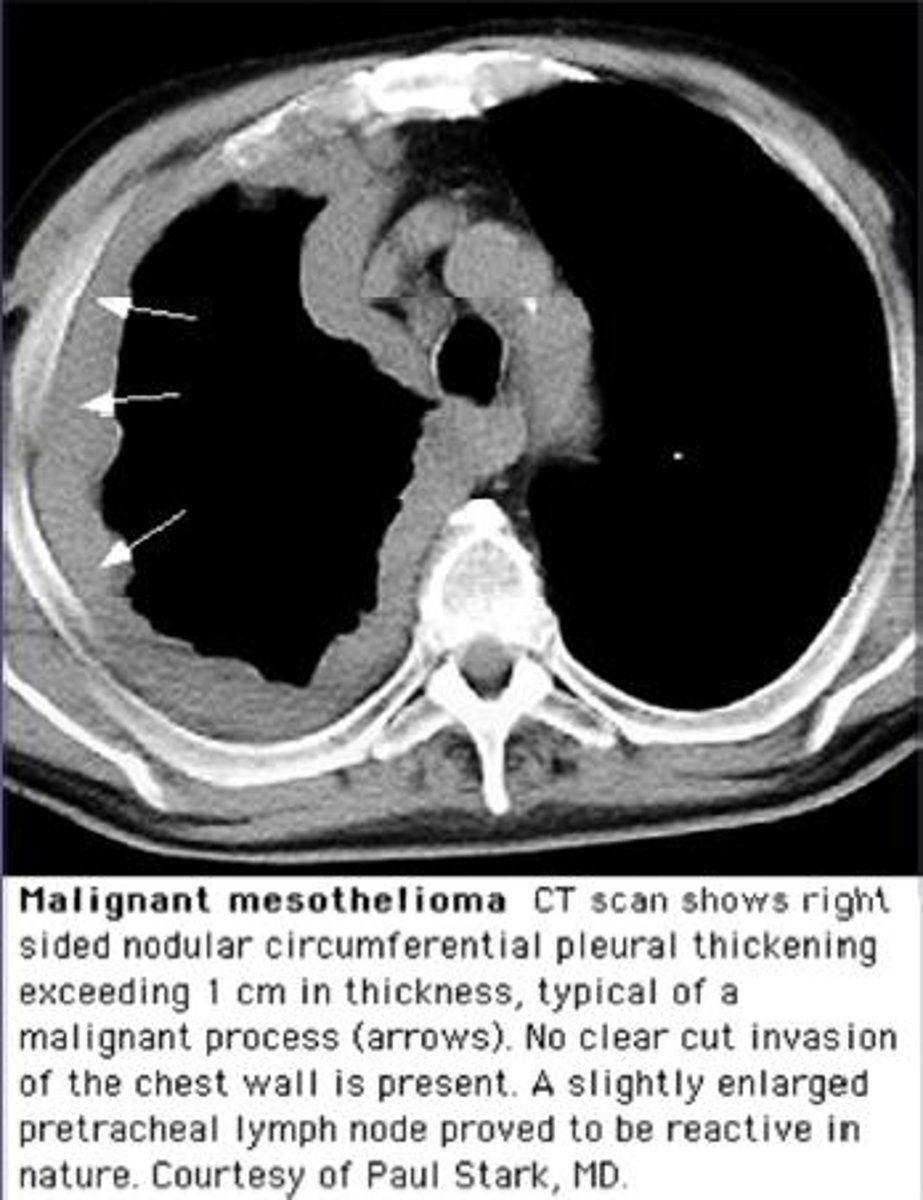
Mesothelioma
Rare malignant tumor arising in the pleura and associated with asbestos exposure.
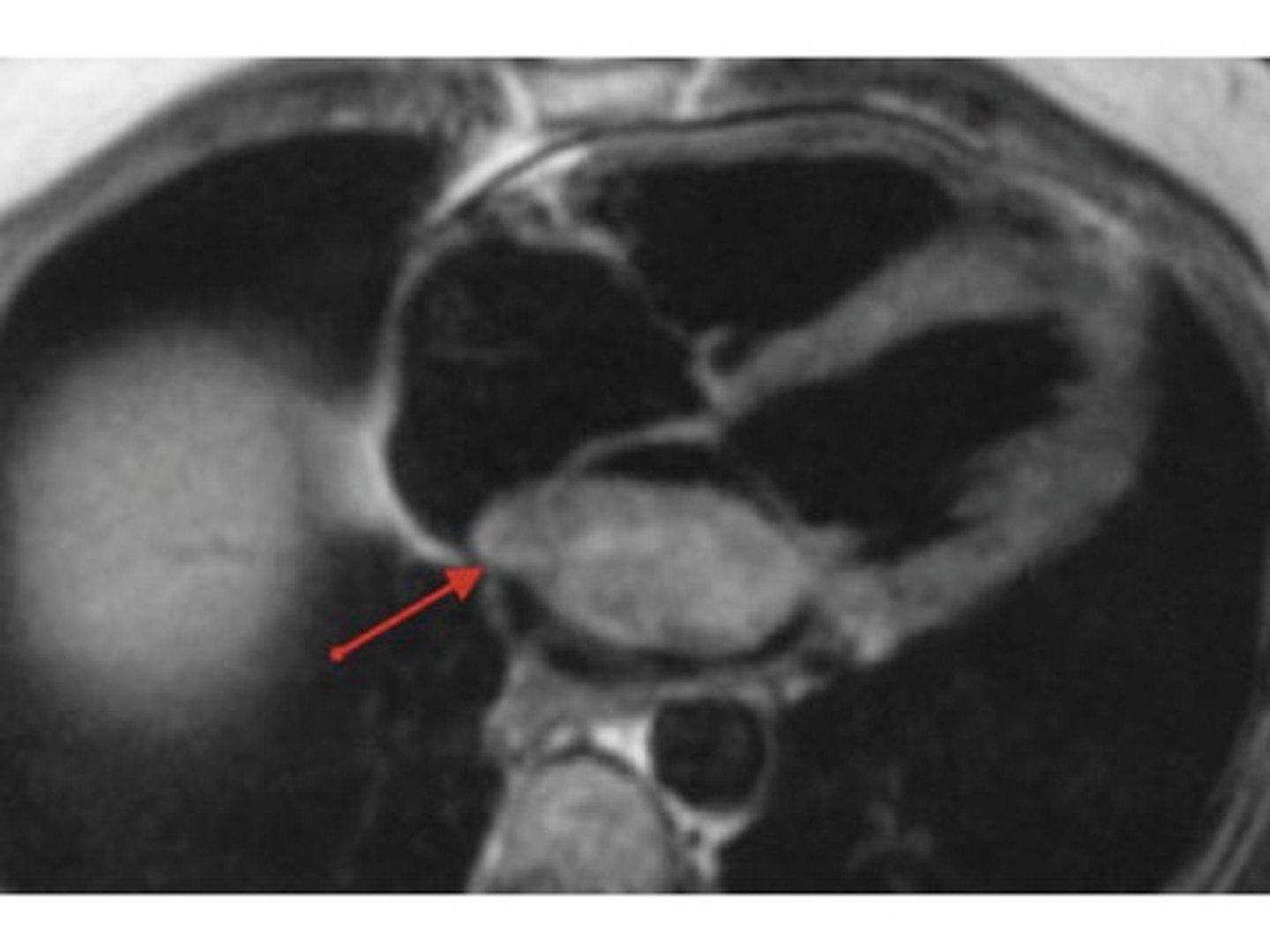
cardiac tumor on CT
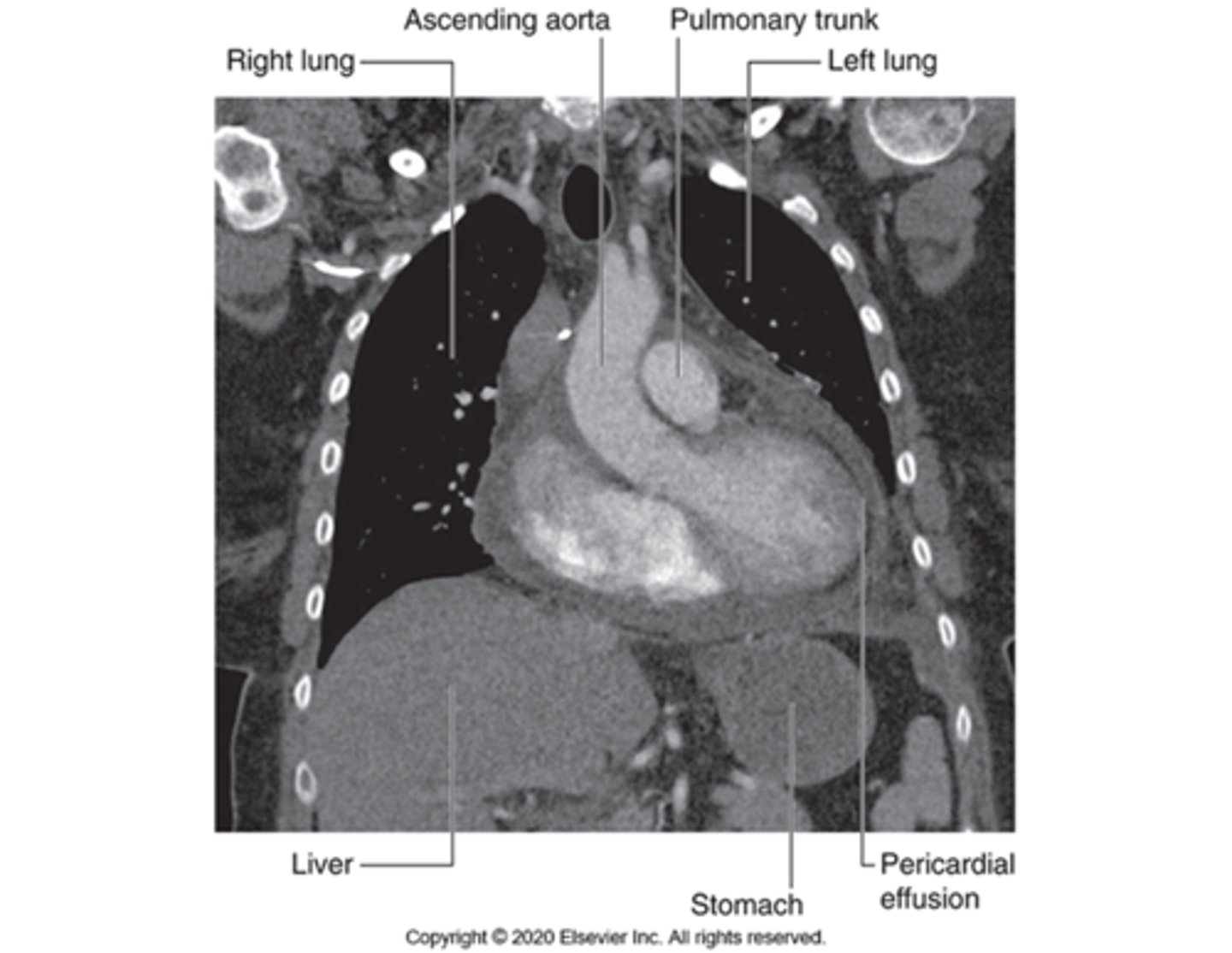
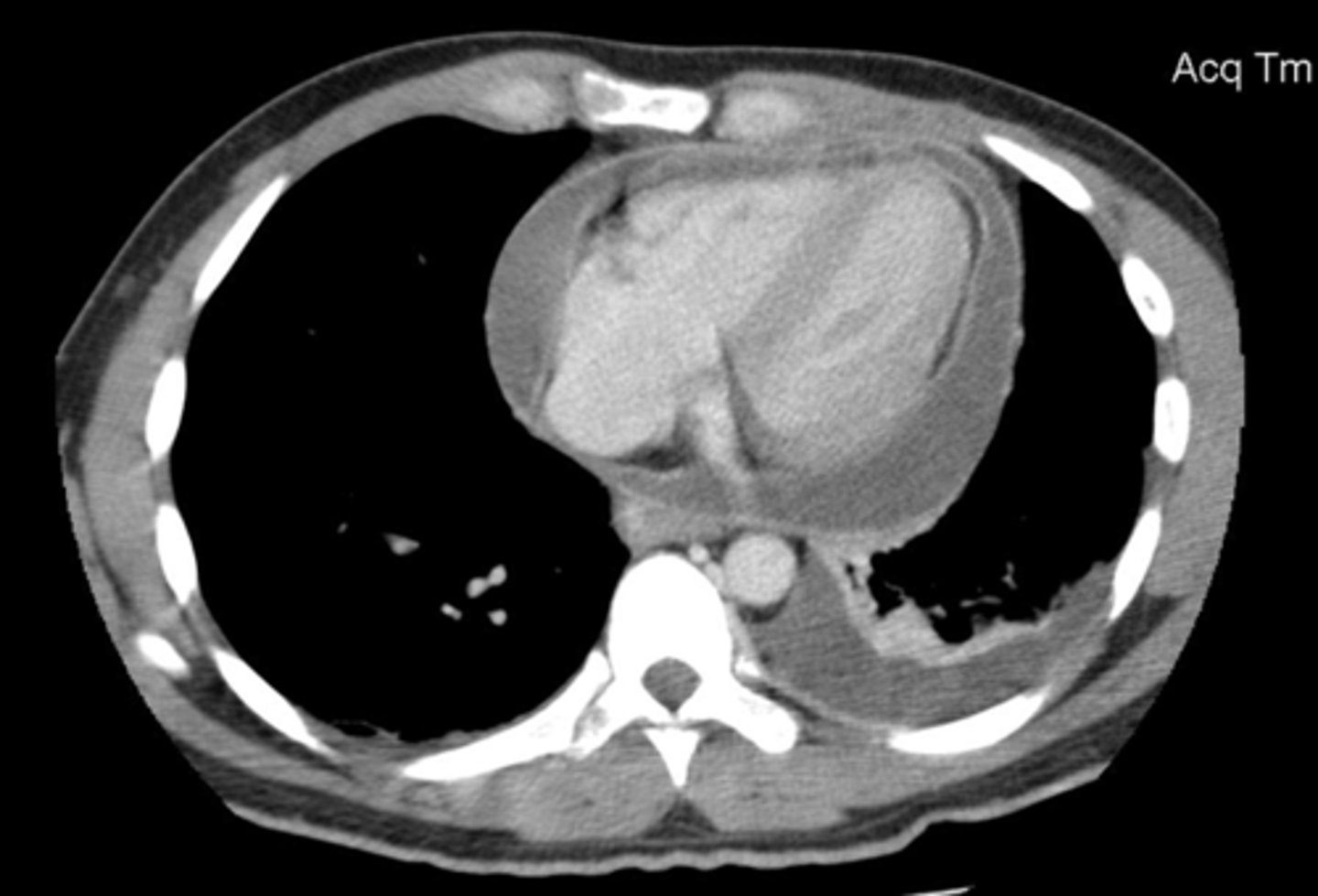
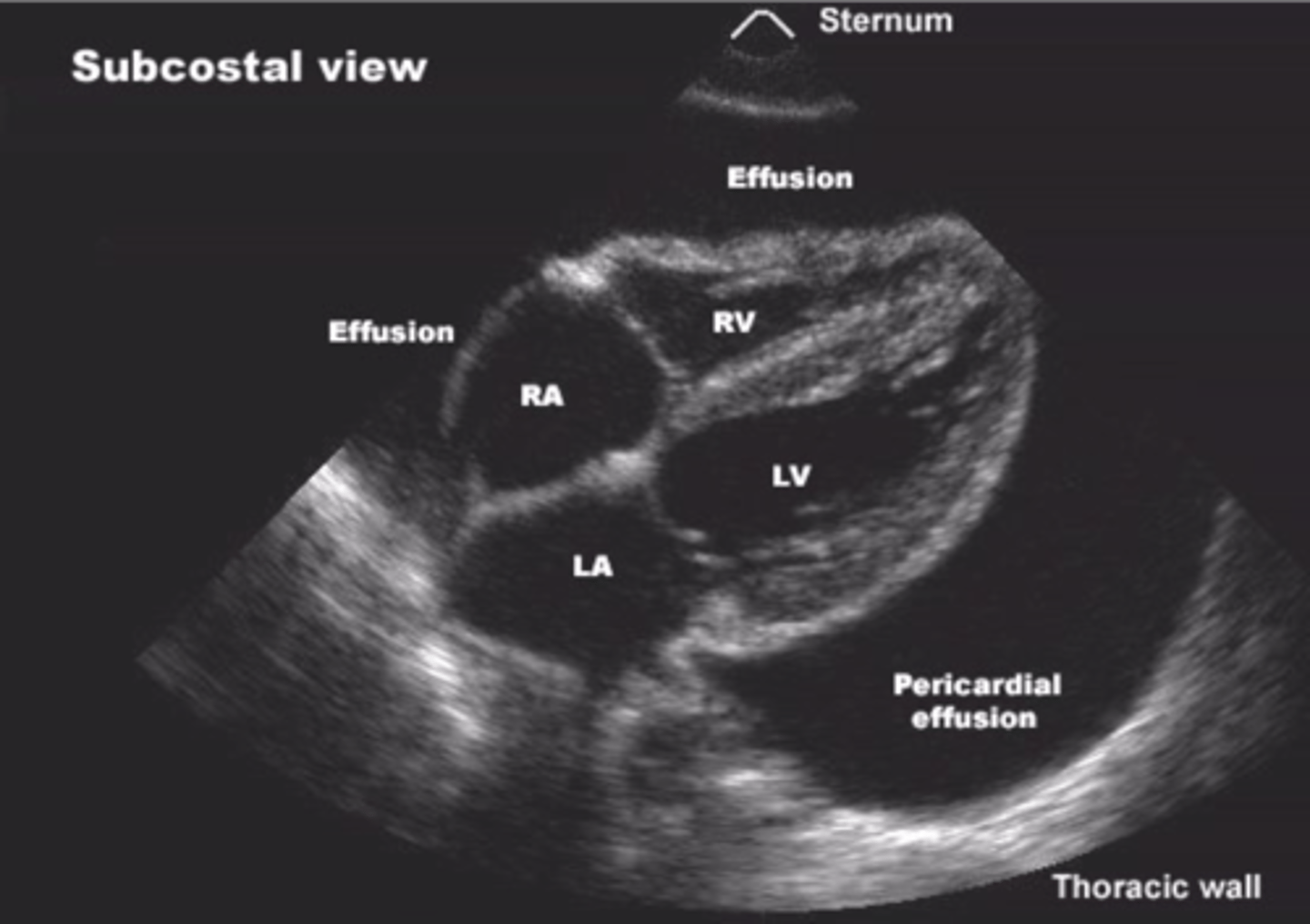
pericardial effusion on CT
accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity
Aortic dissection
wall splits apart
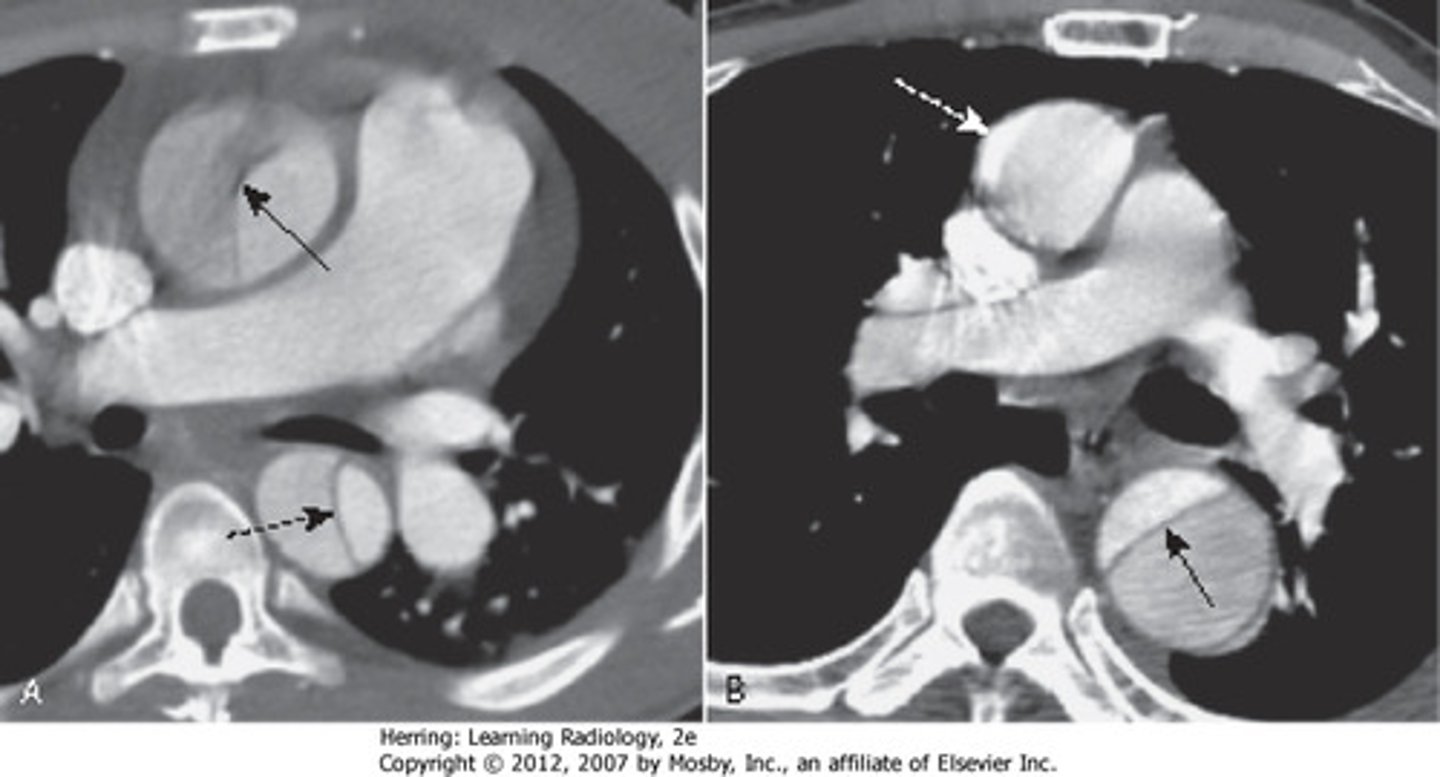
pulmonary hypertension on CXR
enlarged pulmonary arteries
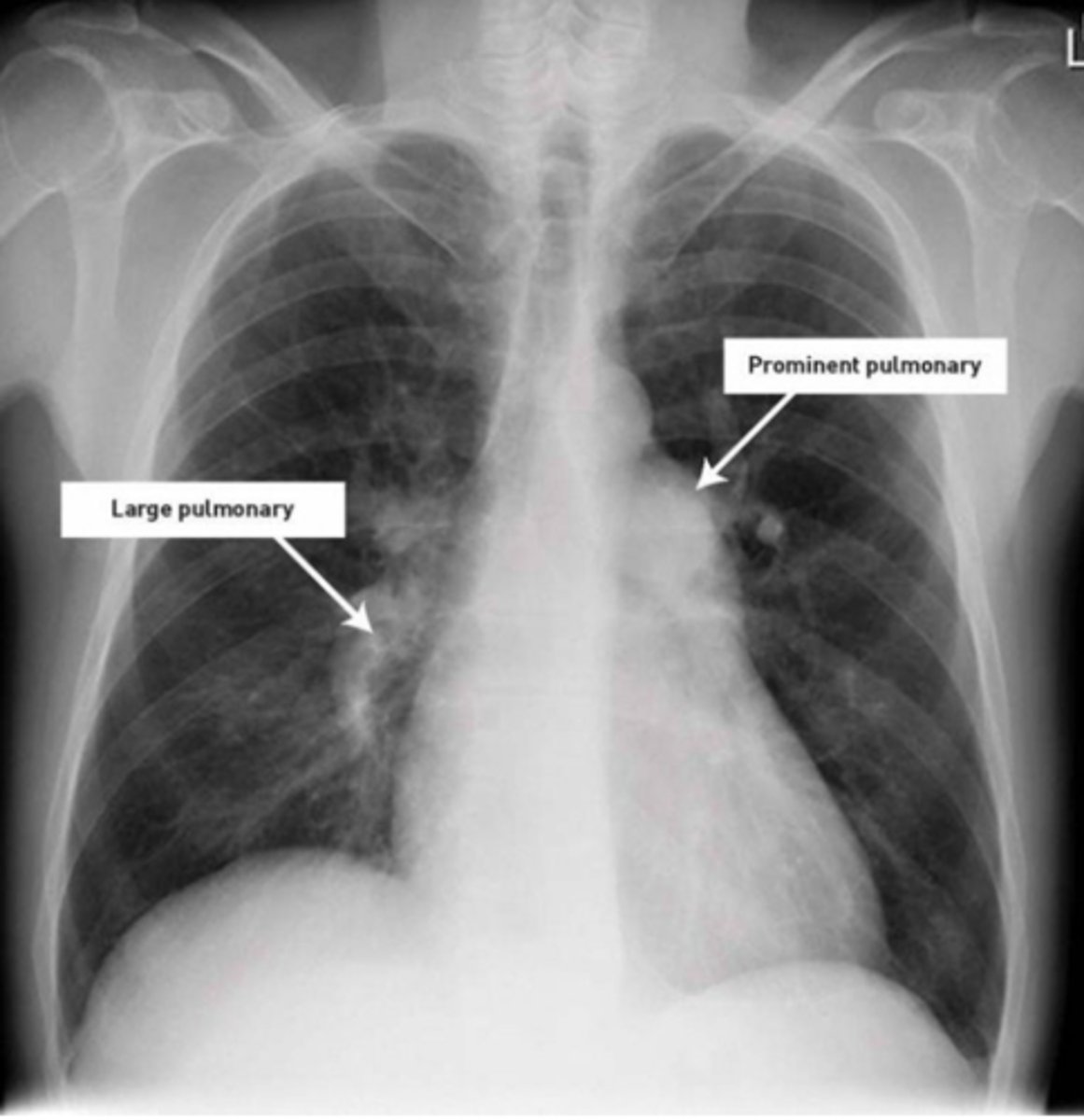
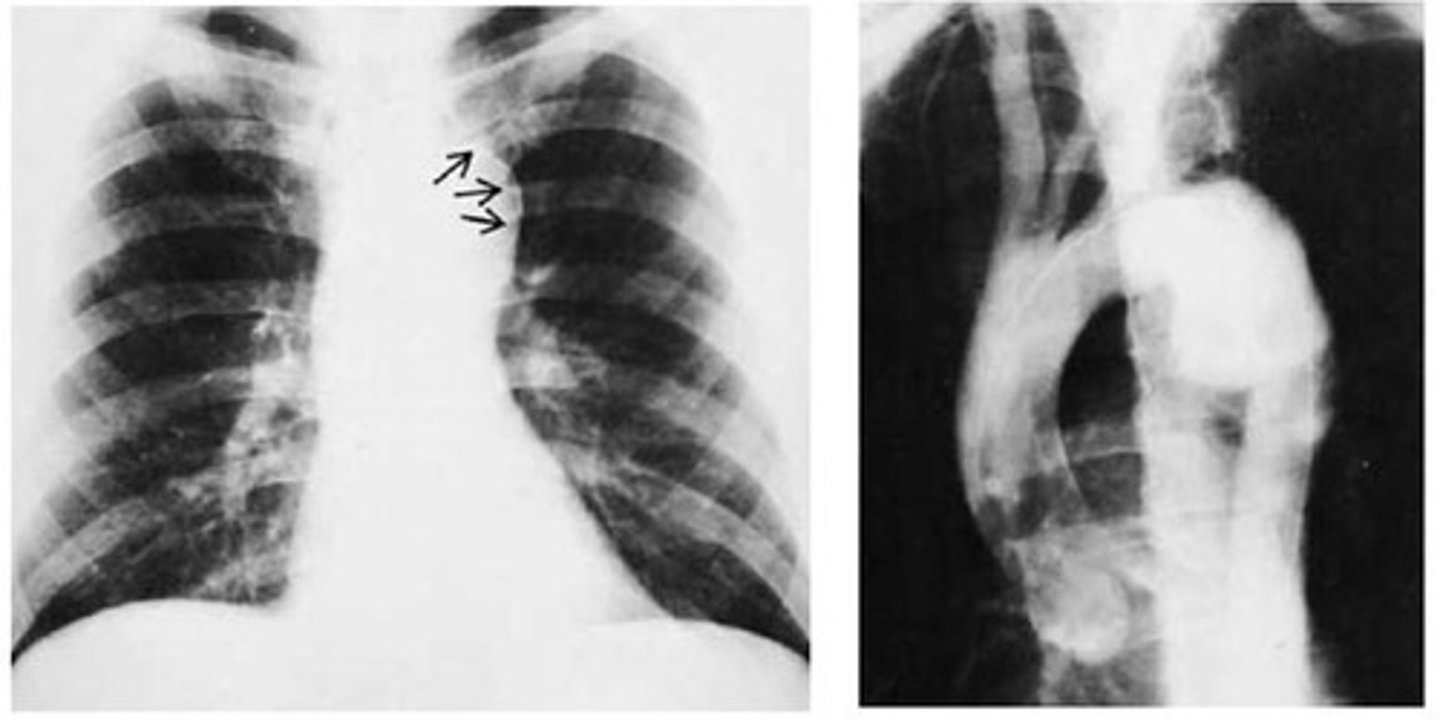
Aortic arch aneurysm on CXR
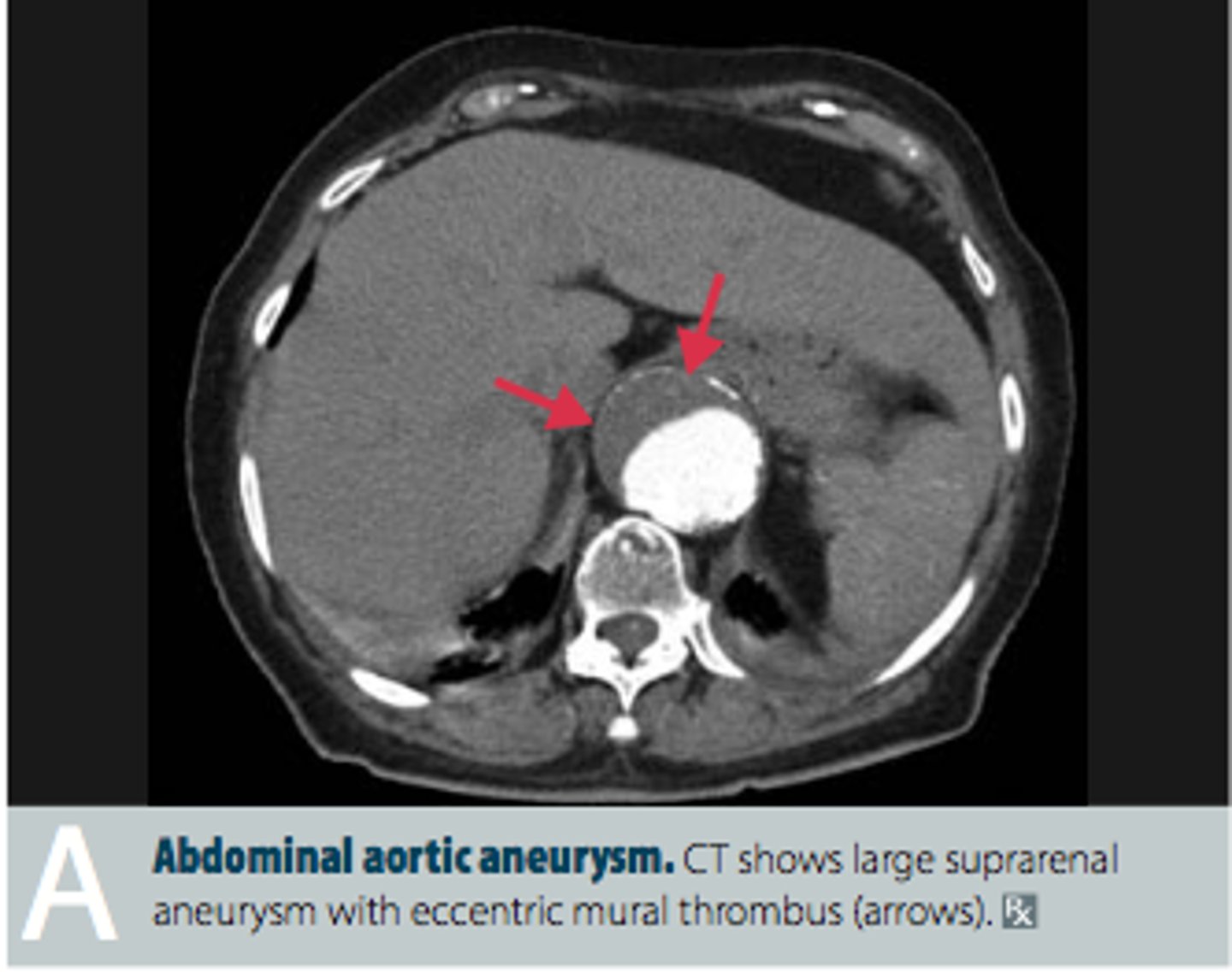
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
localized dilation of abdominal aorta
Pulmonary edema on CT
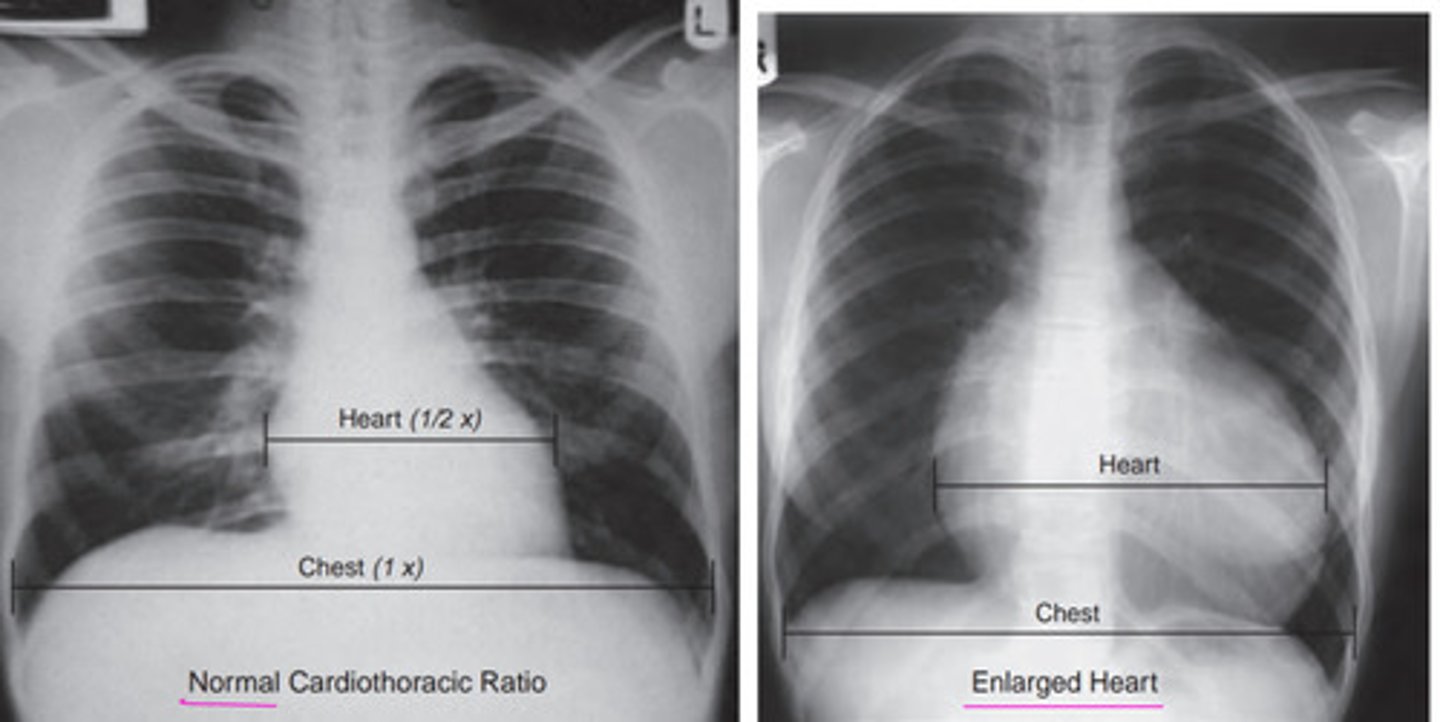
Abnormal cardiothoracic ratio
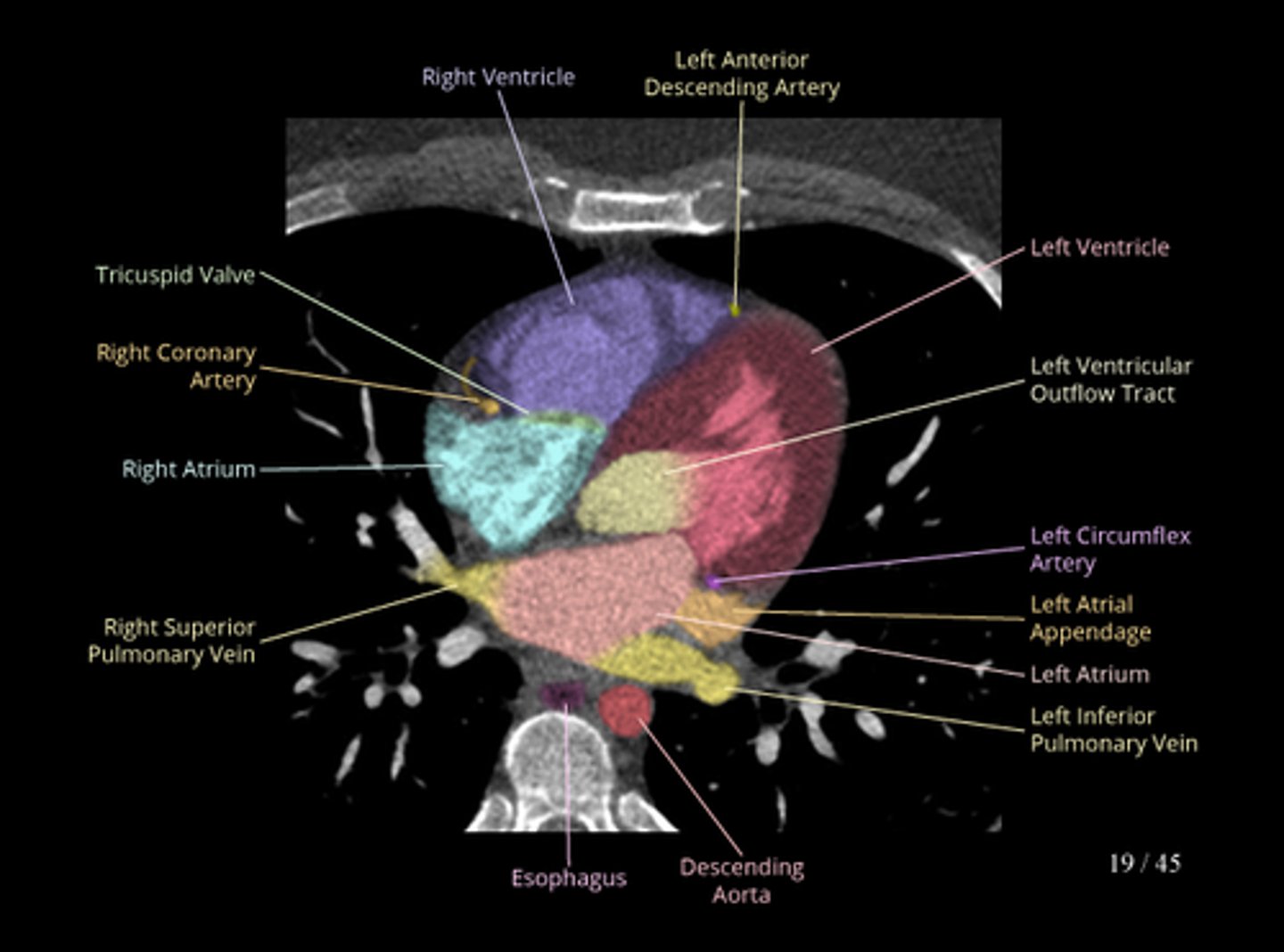
CT Heart Scan
Ultrasound of heart
echocardiogram, echo
Heart MRI
Diagnostic procedure that uses strong magnets and radio waves to produce images of the heart. Is non invasive and safer than other tests.