Chapter 5: Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels (Human Bio)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Identify the two components of the cardiovascular system.
The heart (pumps blood), and blood vessels (which blood flows).
Summarize the functions of the cardiovascular system.
Transport: It helps transport oxygen in and carbon dioxide from metabolism out. That, as well as nutrients from the digestive system and hormones from the endocrine system.
Homeostasis: It helps maintain homeostasis for a variety of internal conditions, including temperature, pH balance, and water and electrolyte levels.
Explain the function of the lymphatic system in circulation.
It helps the cardiovascular system. Lymphatic vessels collect excess interstitial fluid and return it to the cardiovascular system. The fluid naturally collects in the tissues. Eventually, it creates a lymph.
Describe the structure and function of the three types of blood vessels.
Arteries: Vessel that transports blood from the heart.
Capillaries: Smallest of the blood vessels in the circulatory system; site of the majority of nutrient and fluid exchange with tissues.
Vein: Vessel that transports blood back to the heart; often has valves due to the low pressure of blood.
Identify the structures and chambers of the human heart.
Septum: Wall between two cavities; in the human heart, a septum separates the right side from the left side. Lies within the heart
Atria: The upper chambers of the heart, either the left atrium or the right atrium, that receive blood.
Ventricle: Cavity of an organ, such as a lower chamber of the heart or the ventricles of the brain.
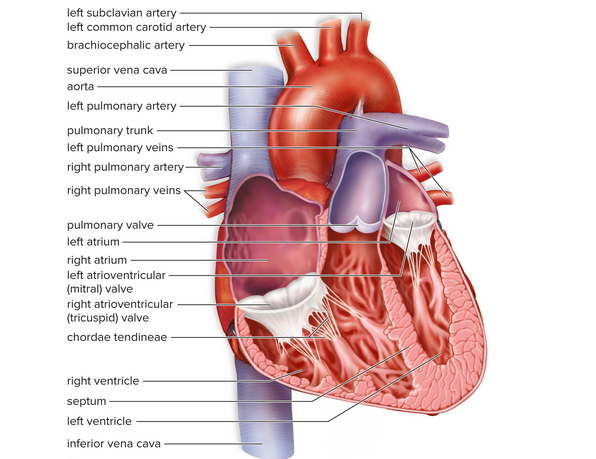
Describe the flow of blood through the human heart.
De-oxygenated blood enters the right atrium, moves through the right ventricle, and is pumped into the lungs. Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium, then to the left ventricle, and is finally pumped out the body.
Explain the internal and external controls of the heartbeat.
There is a pacemaker (SA Node) that send out an electrical impulse. The AV Node receives the signal from the impulse and delays it so the heart can fully pump blood before the next beat.
Understand how pulse relates to heart rate.
Pulse rate indicates the heart rate because the arterial walls pulse whenever the left ventricle contracts.
Explain how blood pressure differs in veins, arteries, and capillaries.
Veins: It’s faster than capillaries but depends on skeletal muscles, breathing and valves in veins.
Arteries: It is pressure of blood against the wall of a blood vessel. Happens in the brachial artery of the arm.
Capillaries: Blood moves slowly through the capillaries as there are more capillaries than arterioles.
Distinguish between systolic and diastolic pressure.
Systolic Pressure: Arterial blood pressure during the systolic phase of the cardiac cycle.
Diastolic Pressure: Arterial blood pressure during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle.
Compare blood flow in the pulmonary and systemic circuits.
Pulmonary Circuit: Circulates it through the lungs.
Systemic Circuit: To the needs of body tissues.
Identify the major arteries and veins of both the pulmonary and systemic circuits.
Pulmonary Circuit: Right Atrium → Right Ventricle → Pulmonary Trunk → Right and Left Pulmonary Arteries → Arterioles → Pulmonary Capillaries → Pulmonary Venules → Left Atrium.
Systemic Circuit: Aorta, Superior and Inferior Venae Cavae.
Compare oxygen content of blood in the arteries and veins of the pulmonary and systemic circuits.
Pulmonary: Starts oxygen-poor and ends oxygen-rich.
Systemic: Starts oxygen-rich and ends oxygen-poor.
Explain the location and purpose of the hepatic portal system.
It’s located near the liver and digestive tract. It drains blood that’s rich in glucose, amino acids, and other nutrients absorbed from the small intestine and sends it to the liver to use.
Explain what happens to the excess fluid that leaves the capillaries.
It is reabsorbed into the lymphatic system.
Explain underlying causes of cardiovascular disease in humans.
Alcohol Abuse: Drinking more than 1-2 drinks per day.
Resveratrol: The questionable belief that red wine helps with the heart, without considering other factors.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Intake of foods high in saturated fat (red meat, cream, butter) and trans fats (most kinds of margarine, commercially baked goods, and deep fried foods).
Vitamin D Deficiency: Lack of vitamin D leads to an increased rates of strokes, heart attacks, and hypertension.
Summarize how advances in medicine can treat cardiovascular disorders.
Advances in medicine can help treat clots by using a drug and clogged arteries by a bypass surgery with incorporated technology and stents/inflated balloons.