Fluoroquinolone Pharmacology: Key Terms & Definitions | Quizlet
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
MOA of fluoroquinolones
inhibition of DNA replication/translation by preventing the relaxation of supercoiled DNA
MOA of Sulfonamides
Inhibits nucleotide precursor biosynthesis
MOA of Rifampin and Fidaxomicin
inhibits RNA synthesis by inhibiting bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
What was the molecule that lead to the discovery of quinolones?
Nalidixic acid
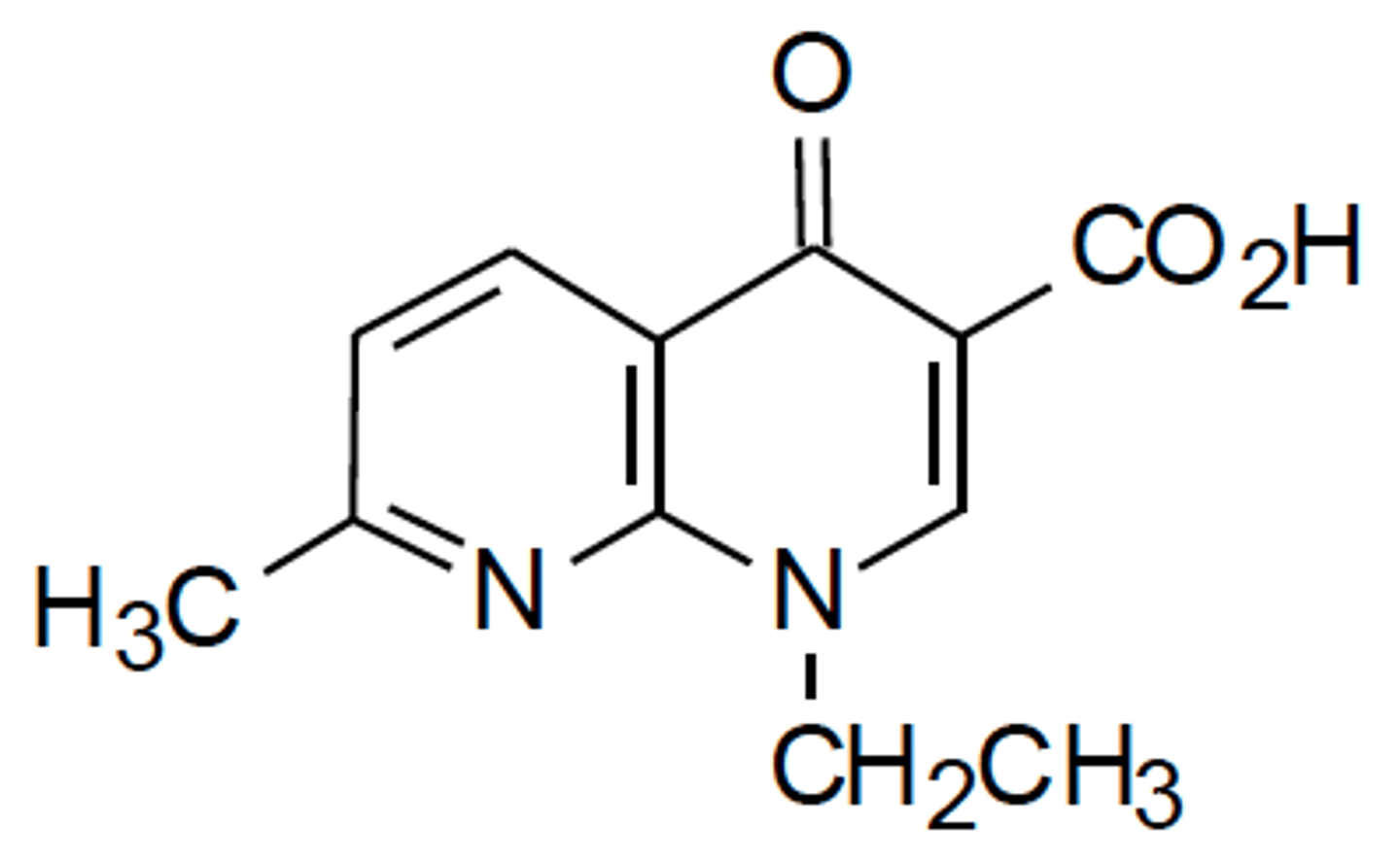
Are quinolones bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
bactericidal
What is the pharmacophore of quinolones?
4-pyridone ring with a 3-carboxylic acid group
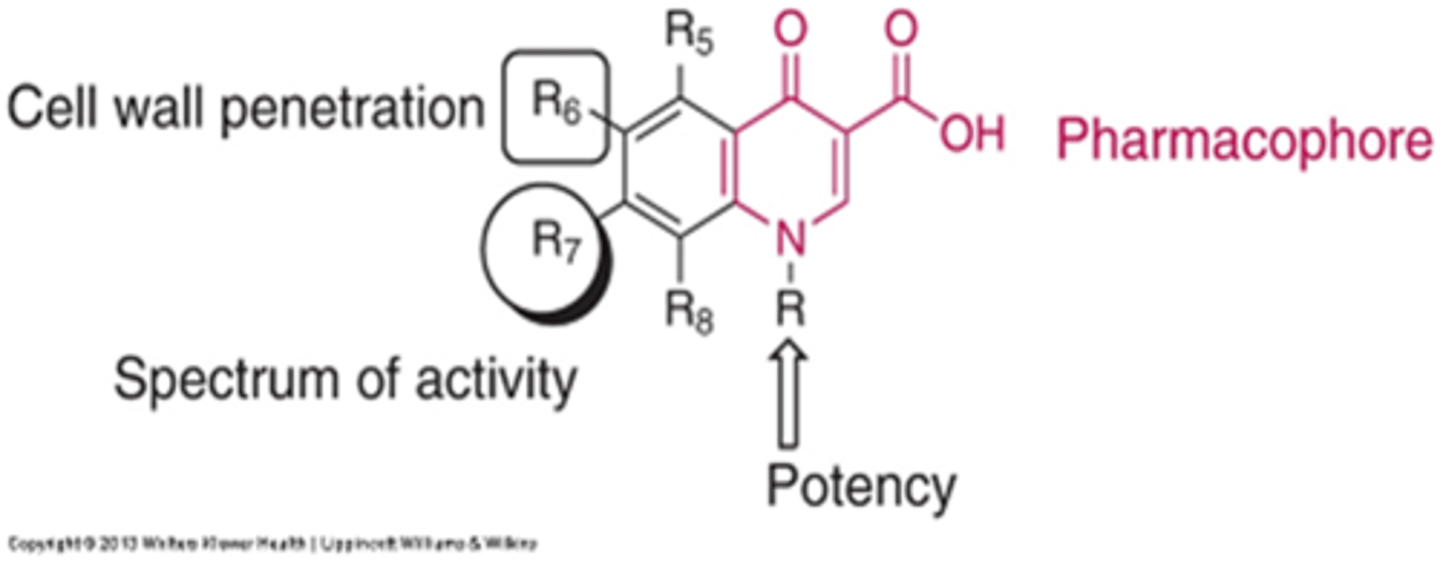
What part of the quinolone structure allows for cell wall penetration?
Flourine at C6
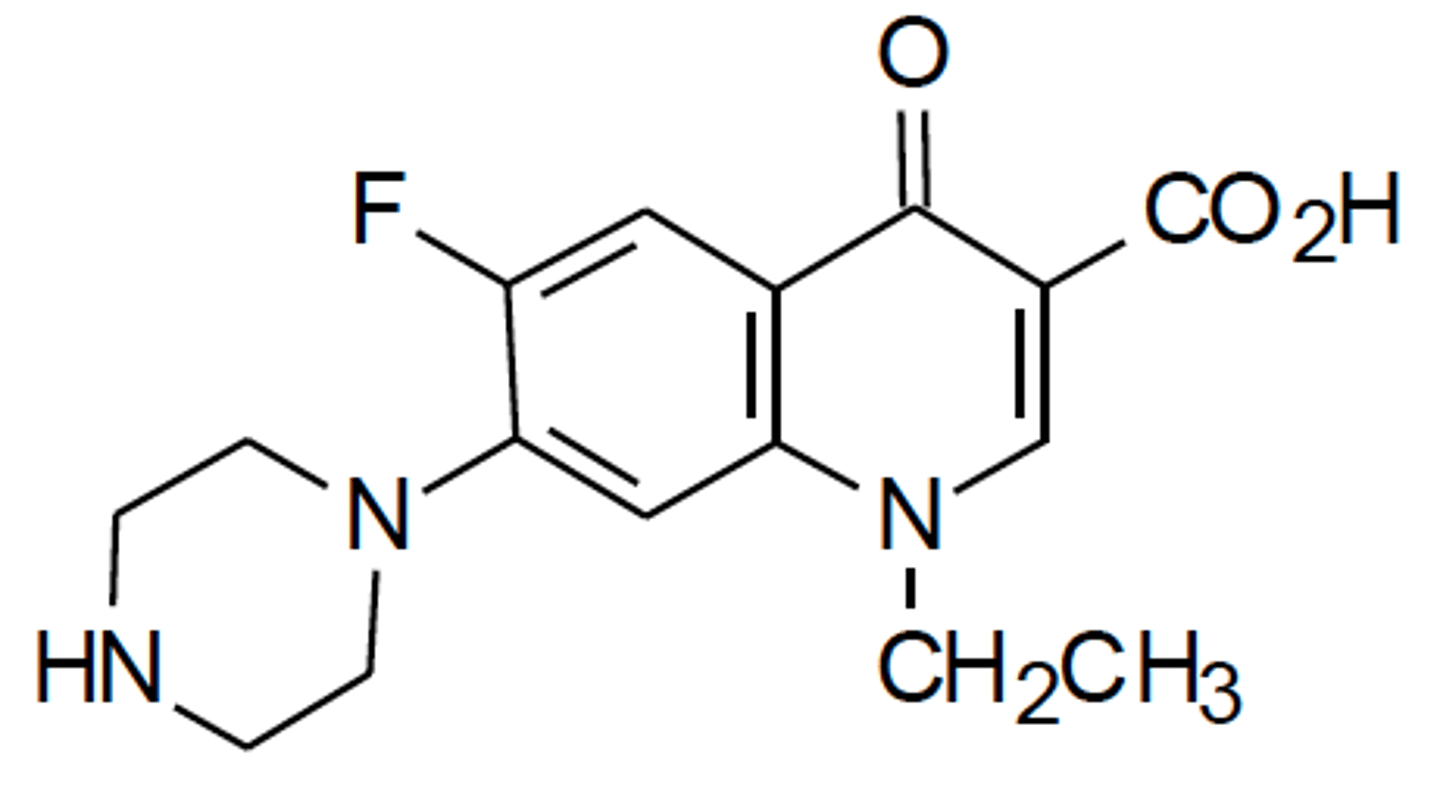
Elimination of what bond in a Quinolone eliminates its activity?
2,3 double bond
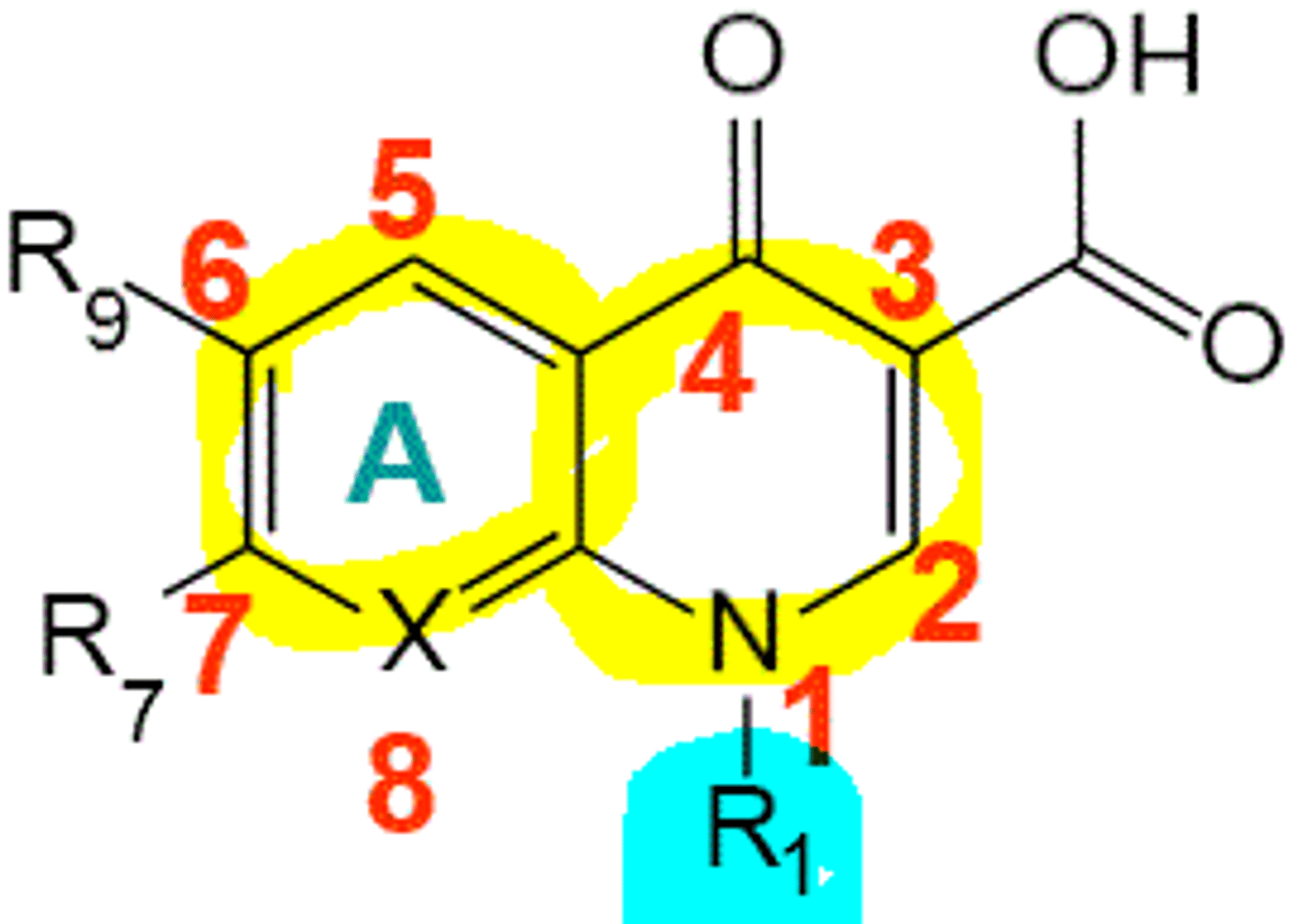
What substitution at C7 improves gram negative activity of quinolones?
heterocyclic
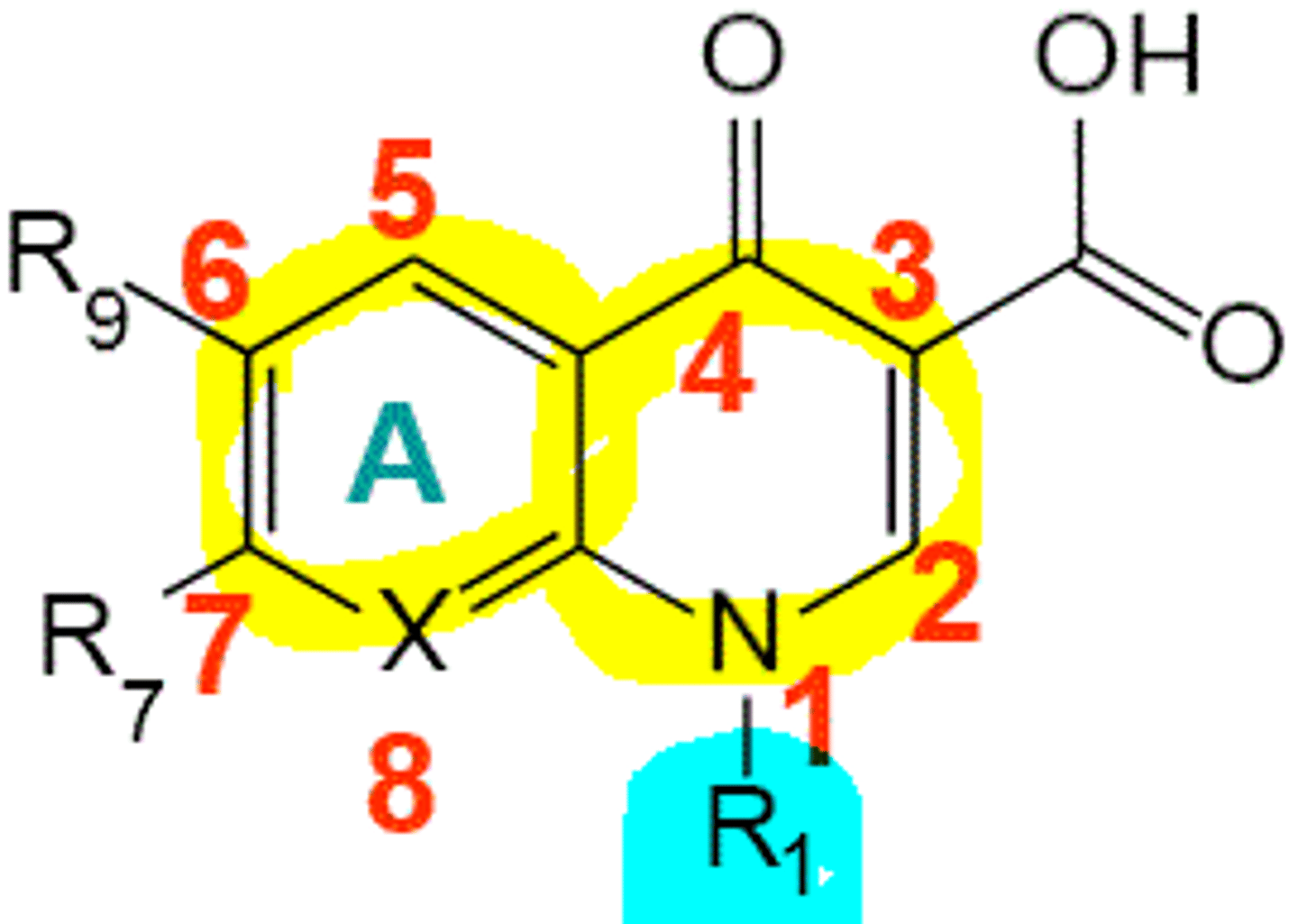
What positions on a quinolone affect its gram positive potency?
R1 alkyl group
R2 substitutions
2nd gen fluoroquinolones
Ciprofloxacin
Ofloxacin
3rd gen fluoroquinolones
Levofloxacin
Gatifloxacin
Gemifloxacin
4th gen fluoroquinolones
Moxifloxacin
Besifloxacin
Delafloxacin
new Fluoroquinolone with a 4 membered N-ring at the C7 position (azetidine)
1st gen quinolones spectrum of activity
limited to gram negatives
2nd gen quinolones spectrum of activity
Limited to gram negatives and atypicals
Which quinolones cover Pseudomonas?
Ciprofloxacin
Levofloxacin
3rd gen quinolones spectrum of activity
Gram positive (strep)
Gram negative
Atypicals
4th gen quinolones spectrum of activity
Gram positive
Gram negative
Atypicals
Anaerobes
What are the bacterial resistance mechanisms to quinolones?
Altered target
Decreased accumulation
Quinolones ADRs
Athropathy
QT prolongation
Hypo/hyperglycemia
GI upset
Photosensitivity
What are the contraindications of quinolones?
<18 y/o
pregnancy
Myasthenia gravis
Sulfonamides
Sulfamethoxazole
Silver Sulfadiazine
Sulfisoxazole
The amino and sulfonyl groups of a Sulfonamide antibiotic should be at what two positions?
1,4 - para positions
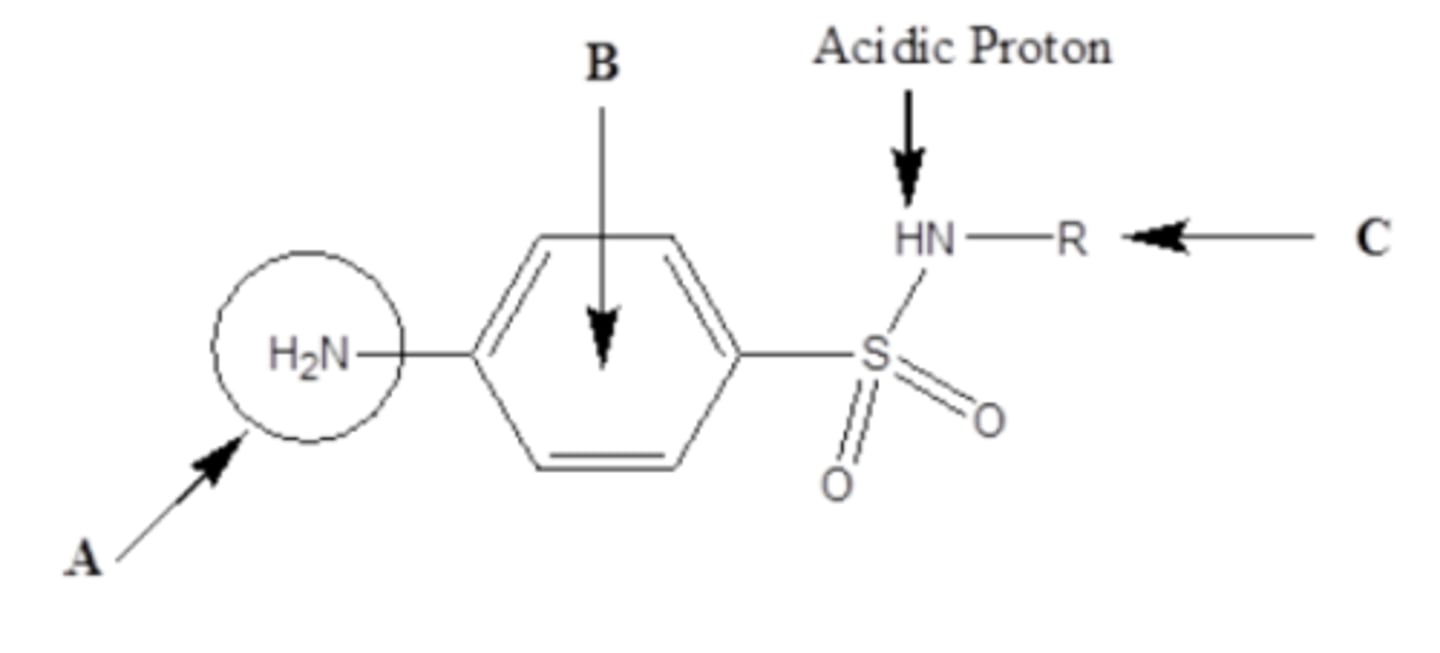
Monosubstitution at what position on a quinolone increases its activity?
N1
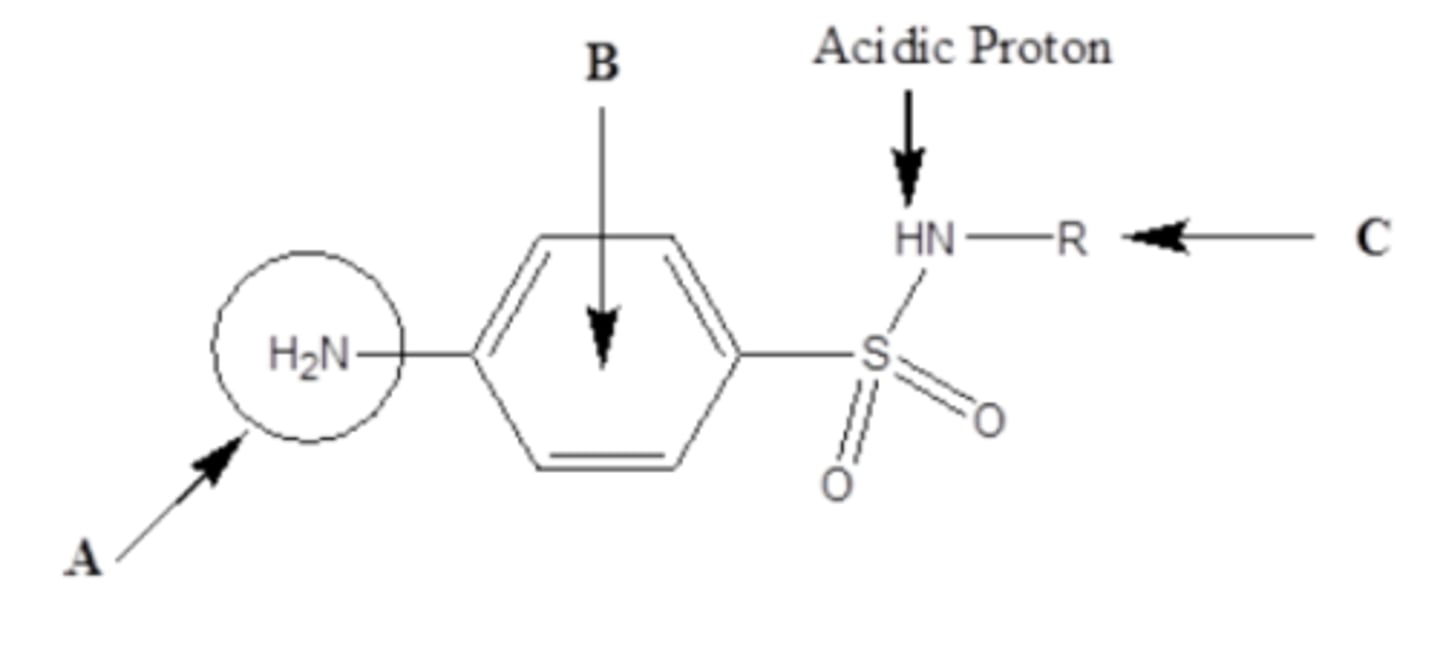
Sulfonamides spectrum of activity
Gram positive (including MRSA)
Gram negative
ADRs of Sulfonamides
GI upset
Photosensitivity
Hypersensitivity
SJS
Crystalluria
DHFR Inhibitors
Trimethoprim
Pyrimethamine
MOA of DHFR Inhibitors
inhibit dihydrofolate reductase (sequential blocking)
Sequential blocking
synergistic activity as a result of sequential step in the synthesis of the folic acid pathway
ADRs of Trimethoprim
Rash
Increased SCr
Hyperkalemia
Rifampin MOA
Inhibits DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (bactericidal)
ADRs of Rifampin
Discoloration of body fluids
Hepatotoxicity
GI disturbances
Rifampin spectrum of activity
Mycobacterial infections
Fidaxomicin spectrum of activity
gram positive anaerobes (primarily clostridioides)