Introduction to bias, cofounding and effect modification
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Asking questions about…
How studies are conducted
How data has been collected
How results have been interpreted
What results really mean
Overall implications of the study
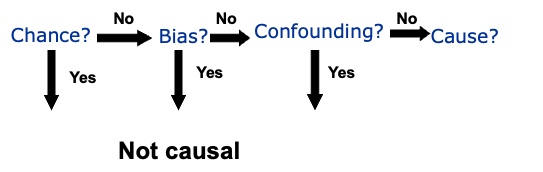
Did the estimate occur due to:
What is Bias?
Bias is a systematic error in data
Bias consistently pulls the risk estimate away from its true value
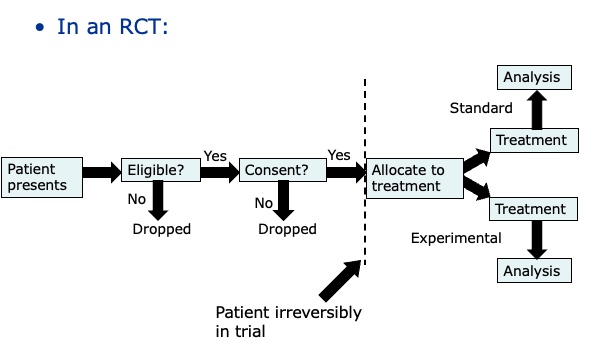
Where could bias occur in a RCT?
No blinding - can be focus on new treatment
narrow no generalised population
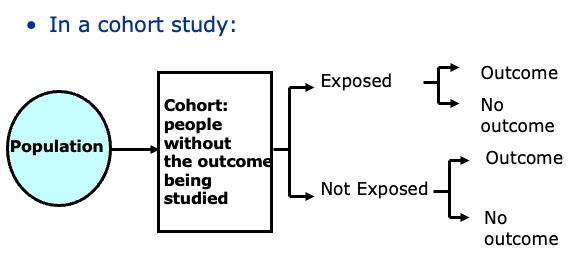
Where could bias occur in cohort study?
particular people choose
Where could bias occur in a case-control study?
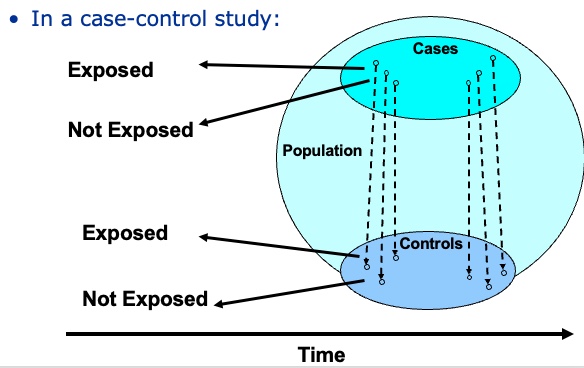
What example of bias can you think of?
Think about
Data collection methods
Participants
Older people, cohort study, electronic data, case control study, interviews, all patients, questionnaires, randomised controlled trials
Length of follow up, interviewer bias, misclassification of exposure, data source limitations, who volunteers?
Measurement bias, non-compliance, recall bias, selecting controls who aren’t controls, selecting cases who aren’t cases
Volunteer bias
Studies only include those who choose to participate
Are people who volunteer to take part different from those who do not?
What are the different types of information bias?
Interviewer bias
Misclassification of exposure
Recall bias
Measurement bias
What are the different types of selection bias?
Who volunteers?
Selecting controls who aren’t controls
Selecting cases who aren’t cases
Summarise the key points about Bias.
The introduction of a systematic error in the study
At the point of study design
Cannot be eliminated at point of analysis
Can be in terms of
Selection of study subjects
Exposure classification
Outcome classification
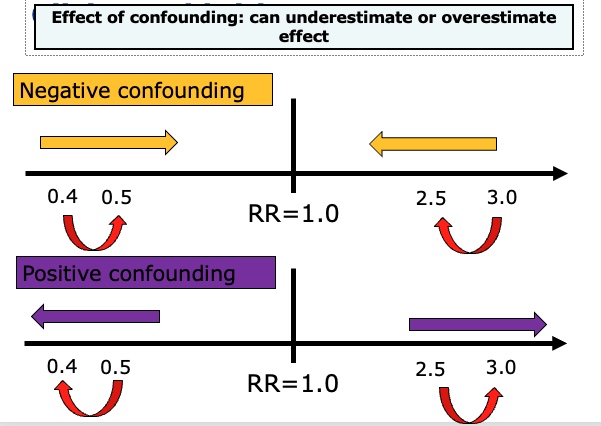
Can result in over- or underestimated risks
Non-differential Misclassification
Misclassification to same degree for all groups
Differential Misclassification
Misclassification different between groups
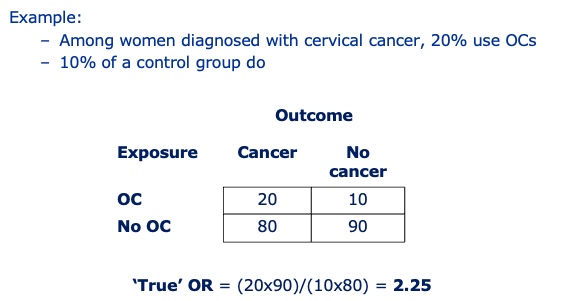
What happens to our results if 10% of exposures are misclassified (non-differential)?
‘Estimated’ OR = (26x82)/(74x18) = 1.60
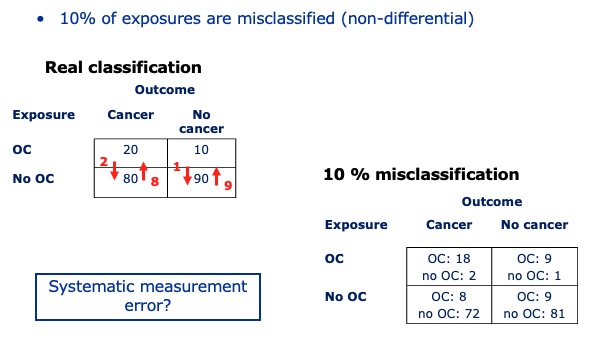
Non-differential misclassification will
underestimate effect (for two exposure categories)
would push all results closer to 1
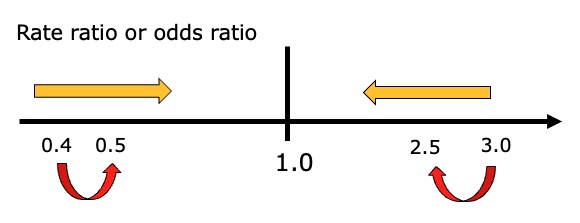
Differential misclassification can bias result in
either direction
What is Cofounding?
The distortion of a risk estimate due to the mixture of the people in the study population
A confounder is a risk factor for the…
disease and is correlated with the exposure independent of disease
How can we determine cofounding?
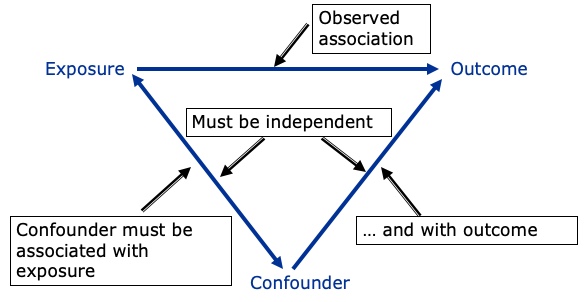
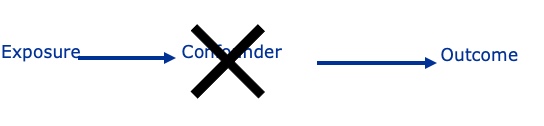
If in the causal pathway then not a…
cofounder
Give examples of cofounder.
Age, gender, smoker
The indication for prescription is one of the most important factors to consider when…
evaluating medication exposures
A factor’s ability to be a confounder is entirely dependent on whether it is…
unevenly distributed between the study groups
What is Channelling?
Where a drug is prescribed to a group of patients because of
a characteristic of the drug
a characteristic of that group of patients
usually is a new drug
Often the drug
Has a claim of a better side-effect profile
Is heavily marketed
How can you control for cofounding using randomisation?
Evenly distribute confounders between study groups
How can you control for cofounding using restriction?
Gives much more control but cannot study variation between levels of that factor
How can you control for cofounding using matching?
Each case is paired with a control subject(s) for specified constraints e.g. confounding factor(s)
Can be difficult to find a match
Risk of over-matching
Can’t determine the association with a factor that is used for matching
Only controls for the criteria that have been matched on
How can you control for cofounding using analysis of data?
Stratified analysis
Separating out factors so any mixture of their effect is removed
Can be used for one or two factors
Multivariate analysis
Takes into account a number of factors simultaneously
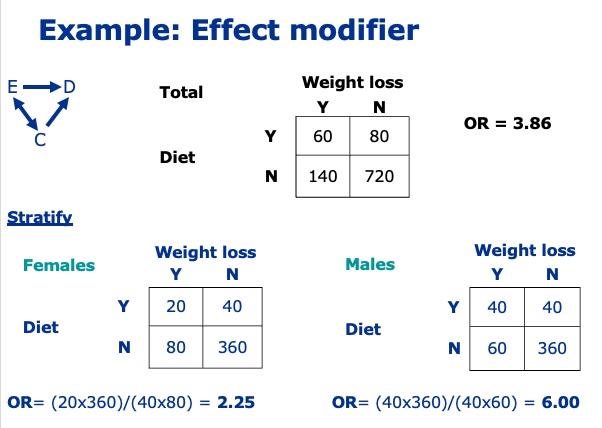
What is Effect modifier?
Effect modification occurs when the effect of the exposure is different in different groups of the population
A factor that modifies the effect of a putative causal factor under study
There is no average ‘true value’
Give an example of effect modifier.
Confounding distorts…
data
Unmeasured confounding is the most serious limitation in observational studies
Equal ‘estimated’ OR indicates…
cofounder
Effect of confounding: