Fermentation
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A metabolic process that produces chemical energy from carbohydrates without the use of oxygen
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
The core goal of fermentation is to
Replenish NAD +
In fermentation pyruvate is ___ and NADH is ___ (oxidized or reduced)
Reduced ; oxidized
Fermentation occurs when there is:
A lack of oxygen available
Human cells and some bacteria undergo
Lactic acid fermentation
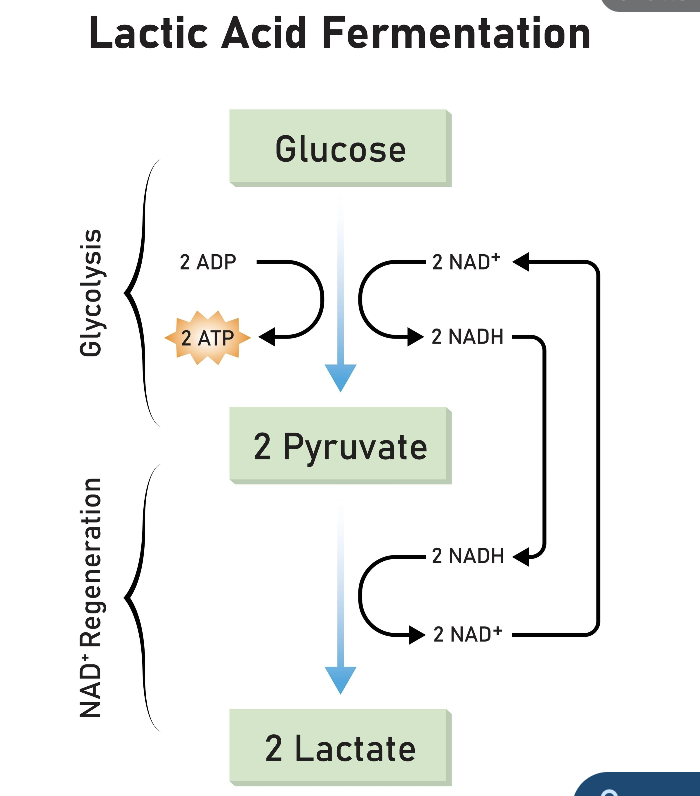
Lactic acid fermentation turns
Pyruvate into lactic acid
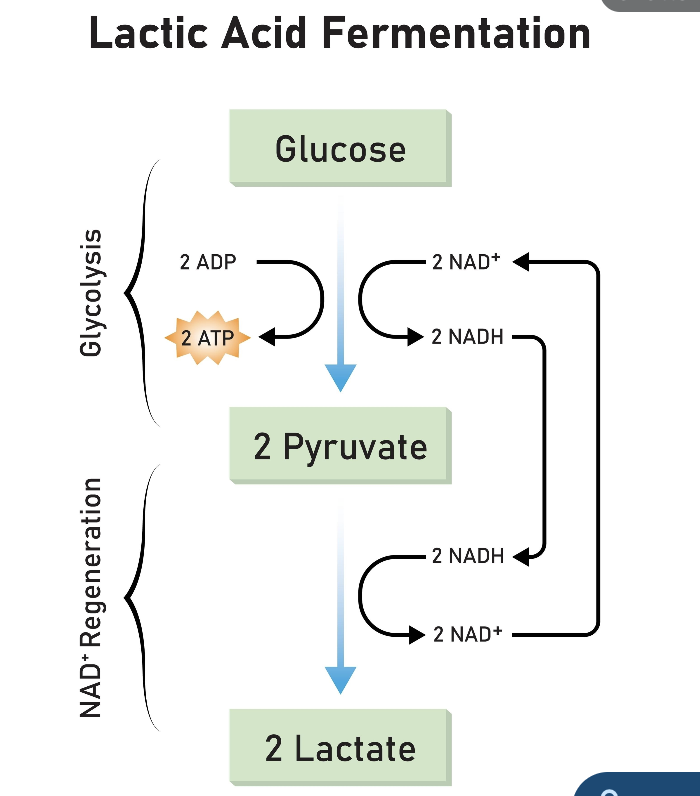
This fermentation is done by yeast and some bacteria
Alcohol fermentation
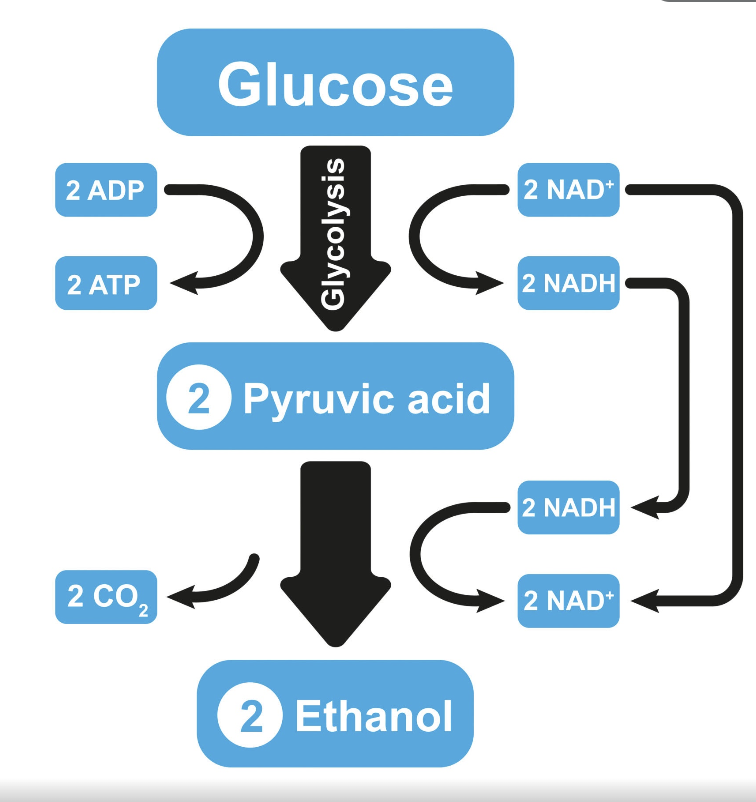
Alcohol fermentation turns
Pyruvate to CO2 and ethanol
Fermentation itself yields how many ATP per glucose?
0
Where does fermentation take place in the cell?
Cytoplasm
Enzyme that catalyzes lactic acid fermentation
Lactate dehydrogenase
Enzymes that catalyze alcohol fermentation
Pyruvate decarboxylase
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Lactate produced in the muscle travels through the blood to the liver, where it is converted back into Pyruvate and then into Glucose via Gluconeogenesis. This glucose is then sent back to the muscle.
This is known as the:
The Cori Cycle
Cancer cells often perform high rates of glycolysis followed by lactic acid fermentation even in the presence of oxygen (aerobic glycolysis)
This is known as:
The Warburg Effect
These cells lack mitochondria and rely exclusively on anaerobic glycolysis for energy
Red blood cells / erythrocytes