Antigen
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Substance that stimulates antibody formation and has the ability to bind to an antibody or to T lymphocyte antigen receptor but may not be able to trigger immune response
Antigen
The recognition of antigen by T cells and B cells is fundamentally different:
B cells:
T cells:
B cells: recognize soluble antigen when it binds to their membrane-bound antibody
T cells: recognize peptides (antigen) combined with MHC molecules on the surface of APC
The smallest part of an antigen that is seen by B cell receptors and T cell receptors
Epitopes
Epitopes are discrete regions of molecules called _
antigenic determinants
Different lymphocytes, each with different receptors, recognize different epitopes on the same antigen:
B cells:
T cells:
B cell receptor: free-soluble molecules, surface bound molecules, degraded fragments of antigen
T cell receptors: peptide-MHC molecule combinations presented on the surface of APC
3 Functional Categories of Antigens
Haptens
Immunogens
Tolerogens
Functional Categories of Antigens
Complete antigens
Antigens that induce immune response either by producing antibody or sensitized lymphocytes which in turn react specifically with immunogens that produced them
Immunogens
Functional Categories of Antigens
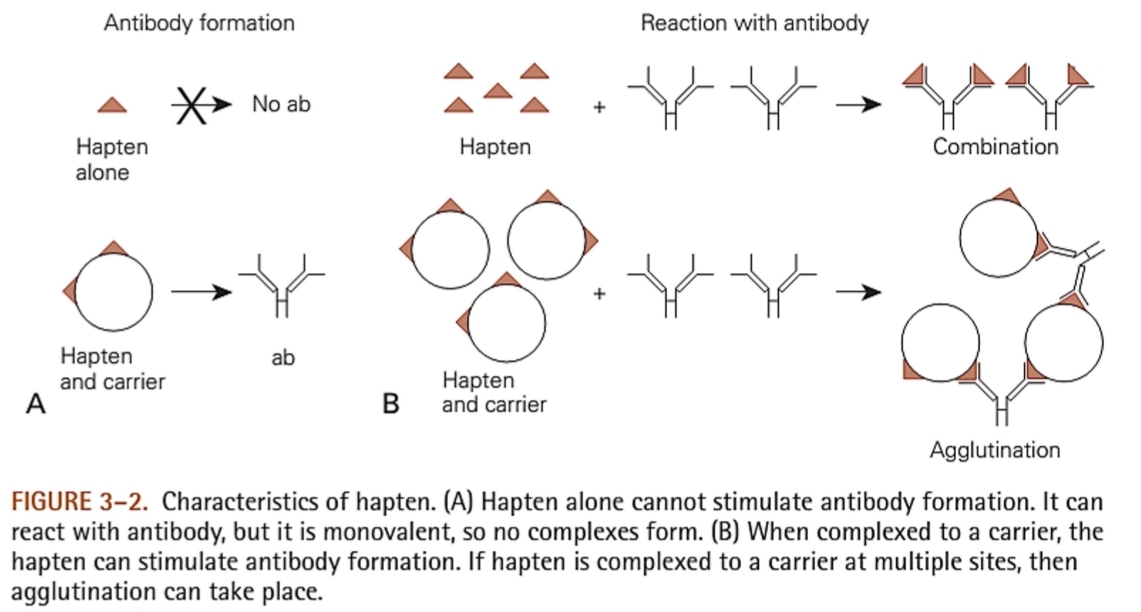
Partial antigens
Small molecular weight substances that are antigenic, but incapable by themselves of inducing specific immune response
Lack immunogenicity but can react with specific antibody when bound to an immunoge (carrier/larger molecule)
Haptens
Characteristics of Hapten
Functional Categories of Antigens
Antigens which induce immune unresponsiveness in normal condition
During development of immune repertoire, tolerance to self molecules and cells develop first.
Therefore there is no immune response against the self-tissue in normal, healthy state
Tolerogens
3 Cellular Antigens of Immunologic Importance
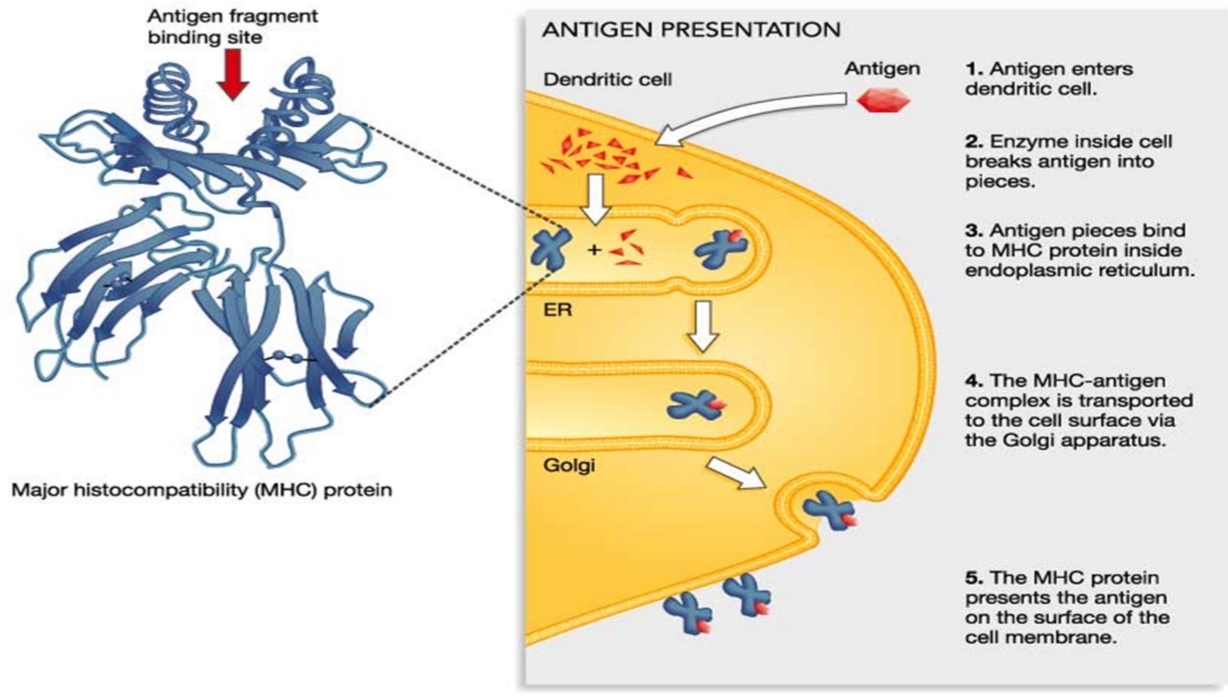
Major Histocompatibility Complex
Autoantigens
Blood Group Antigens
Cellular Antigens of Immunologic Importance
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
→Found on _
→Also known as _
→Present peptide antigens to _
→Determines _
→Genes coding MHC molecules > _
→Found on NUCLEATED CELLS
→Also known as HUMAN LEUKOCYTE ANTIGEN (HLA)
→Present peptide antigens to T-CELLS
→Determines HISTOCOMPATIBILITY
→Genes coding MHC molecules > CHROMOSOME 6
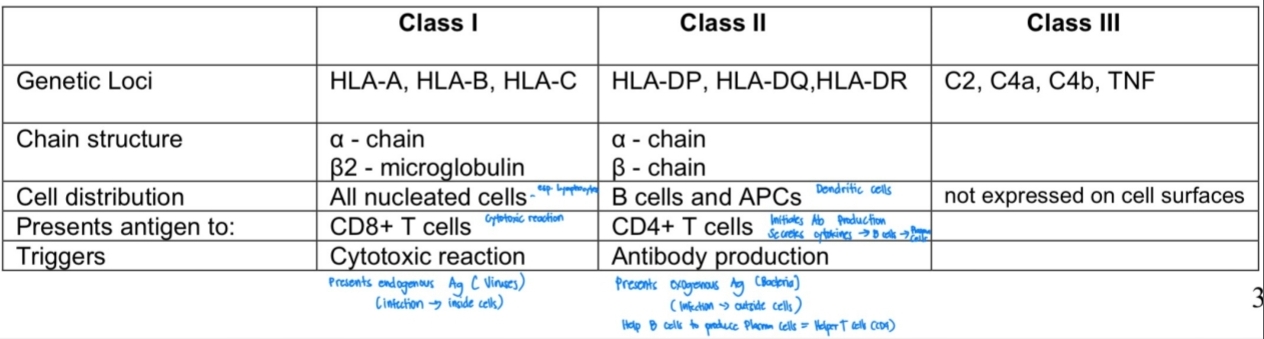
Classes of MHC
HLA Allelles and their disease association
HLA-B27
Ankylosing spondylitis
(a chronic inflammatory arthritis, primarily affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints, causing pain, stiffness (worse with rest, better with activity), fatigue, and potentially leading to spinal fusion (ankylosis), resulting in a hunched posture)
HLA Allelles and their disease association
HLA-DR2
Good Pasteur Syndrome
(a rare autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own collagen in the lungs and kidneys, causing inflammation, bleeding (hemorrhage) in the lungs, and glomerulonephritis (kidney inflammation) leading to potential kidney failure and respiratory issues like coughing up blood and shortness of breath)
HLA Allelles and their disease association
HLA-DR3
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
(a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs, causing widespread inflammation affecting joints, skin, kidneys, brain, heart, and more)
HLA Allelles and their disease association
HLA-DR4
Rheumatoid arthritis
(chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, primarily the synovium (joint lining), causing painful swelling, stiffness, and potential damage to cartilage, bone, and joints, often in the hands, wrists, and feet, symmetrically.)
HLA Allelles and their disease association
HLA-DQ2, HLA-DQ8
Celiac disease
(autoimmune disorder where gluten (in wheat, barley, rye) triggers the immune system to attack the small intestine, damaging villi and preventing nutrient absorption, leading to digestive issues)
HLA Allelles and their disease association
HLA-B51
Behcet's disease
(rare, chronic auto-inflammatory disorder causing systemic vasculitis—blood vessel inflammation—that leads to recurrent, painful mouth and genital ulcers, skin lesions, and eye inflammation)
HLA Allelles and their disease association
HLA-B58
Myasthenia gravis
(chronic autoimmune disease causing fluctuating weakness in voluntary muscles, especially eyes, face, throat, arms, and legs, due to faulty nerve-to-muscle communication. It's caused by the immune system attacking acethycholine receptors, leading to fatigue with activity and improvement with rest_)
HLA Allelles and their disease association
HLA-DR, HLA-DQ
Type 1 DM
Multiple sclerosis - a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks myelin, the protective sheath around nerves in the brain and spinal cord, disrupting nerve signals and causing varied neurological symptoms like vision problems, fatigue, numbness, weakness, balance issues, and cognitive changes.
Cellular Antigens of Immunologic Importance
Autoantigens
→ Also called _
→The evolution of a recognition system that can recognize and destroy non-self material must also have safeguards to prevent damage to self antigens
→Failure to recognize self antigens can result is _
→ Also called SELF ANTIGENS
→The evolution of a recognition system that can recognize and destroy non-self material must also have safeguards to prevent damage to self antigens
→Failure to recognize self antigens can result is AUTOANTIBODIES
Cellular Antigens of Immunologic Importance
Blood Group Antigens
→Widely distributed throughout the (3)
→A _ may result when foreign RBC antigens are introduced to a host
→Certain antigens (_) are structural components of the RBC membrane. If these are missing, RBC membrane is defective resulting in hemolytic anemia
→Widely distributed throughout the TISSUES, BLOOD CELLS, BODY FLUIDS
→A TRANSFUSION REACTION or HDN may result when foreign RBC antigens are introduced to a host
→Certain antigens (RH SYSTEM) are structural components of the RBC membrane. If these are missing, RBC membrane is defective resulting in hemolytic anemia
Chemical Nature of Antigens

Determinants of Immunogenecity (7)
Molecular weight
Chemical complexity
Foreignness
Antigenic determinants (Epitopes)
Genetic constitution of the host
Susceptibility to Tissue Enzymes
Dosage, Route, and Timing of Antigen
Substance administered with an antigen or immunogen to increase the immune response
Adjuvants
Adjuvants
Precipitates antigen to increase its _ and enhance antigen presentation and phagocytosis
Stimulates _
Activates macrophage and enhance phagocytosis and expression of co-stimulator such as _
Used in _
Precipitates antigen to increase its SIZE and enhance antigen presentation and phagocytosis
Stimulates LOCAL INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE
Activates macrophage and enhance phagocytosis and expression of co-stimulator such as MHC CLASS II
Used in IMMUNIZATION
Antigen Receptors (2)
The immune system depends upon receptors and the ligands bound by them for its function
Preformed receptors - innate immune system
Somatically generated receptors - adaptive immune system
Allow a quick response to confer some protection while adaptive immune system prepares to respond
Pre-formed receptors
6 Types of Pre-Formed Receptors
Pattern Recognition Receptors
Toll-like Receptors
Killer Activation Receptors
Killer Inhibition Receptors
Complement Receptors
Fc Receptors
Pre-Formed Receptors
Recognize broad structural motifs (similarities in design) that are not present within the host and are generally found on microbes
Pattern Recognition Receptors
Pre-Formed Receptors
Pattern Recognition Receptors
→Present in _
→Recognize _ which include combinations of sugars, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids broadly associated microbes
→PRR binding to PAMPs trigger various forms of _ intended to destroy the pathogens
→Present in SOLUBLE FORMS or on HOST CELL SURFACES
→Recognize PAMPs which include combinations of sugars, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids broadly associated microbes
→PRR binding to PAMPs trigger various forms of INFLAMMATION intended to destroy the pathogens
Pre-Formed Receptors
Toll-like receptors
In humans, PRRs also include TLRs that are present on a variety of host cells
→ binding to TLR mediates the generation of defensive responses like _ ( to promote inflammation, attraction of macrophages, PMNs, NK cells, and dendritic cells to the site of infection)
cytokine release
Pre-Formed Receptors
Receptors found on NK cells capable of detecting alterations in host cells infected by pathogens (viruses)
Killer ACtivation Receptors
Pre-Formed Receptors
Killer Activation Receptors
→Recognize presence of stress-related molecules (_ and _) expressed by host cells that are unhealthy or abnormal for various reasons
→Binding of _ or _ to KAR induces the NK cells to attach and destroy the targeted host cells
→Recognize presence of stress-related molecules (MICA & MICB) expressed by host cells that are unhealthy or abnormal for various reasons
→Binding of MICA or MICB to KAR induces the NK cells to attach and destroy the targeted host cells
Pre-Formed Receptors
Receptors used by NK cells to monitor MHC class I molecules normally displayed on cell surfaces of all nucleated cells in the body
Killer Inhibition Receptors
Pre-Formed Receptors
Killer Inhibition Receptors
→Many processes, including cancers or viral infections, decrease the number of _ molecules displayed on the surface of affected cells
→Once bound to target cells via KARs, NK cells use KIRs to assess MHC class I expression on that cell
MHC class I
Pre-Formed Receptors
Certain complement components or fragments bind to microbial surfaces and tag microbes for destruction by other elements of the immune system
Complement Receptors
Pre-Formed Receptors
Complement Receptors
→Cell surface-bound complement receptors on phagocytic cells and B cells recognize these bound complement fragments and facilitate binding, ingestion, and internal degradation of tagged microbes
---------------------------
Pre-Formed Receptors
Expressed on the surface of phagocytic cells to recognize and bind epitope-engaged antibodies
Fc Receptors
Pre-Formed Receptors
Fc receptors
→Epitope binding by (3) triggers a conformational change in the _ portion of the antibody
→Binding results to _ of epitope-antibody-FcR complex
→Epitope binding by IgA, IgG, or IgM triggers a conformational change in the TAIL or Fc portion of the antibody
→Binding results to PHAGOCYTOSIS of epitope-antibody-FcR complex
Specialized receptors of the adaptive immune system that are regenerated anew in the lymphocytes of every individual through somatic chromosomal rearrangements and mutations
Somatically Generated Receptors
Somatically Generated Receptors (2)
B cell Receptors (BCR)
T cell Receptors (TCR)
Somatically Generated Receptors
Composed of monomeric IgG ssociated with disulfide-linked heterodimers Igα and Igβ
B Cell Receptors
Somatically Generated Receptors
B Cell Receptors
→When a BCR binds to an epitope, the specialized cytoplasmic tails of _ initiate an intracellular signalling cascade that may lead to B cell activation
→Some activated B cells, terminally differentiate into _ which secrete Igs
Igα and Igβ
plasma cells
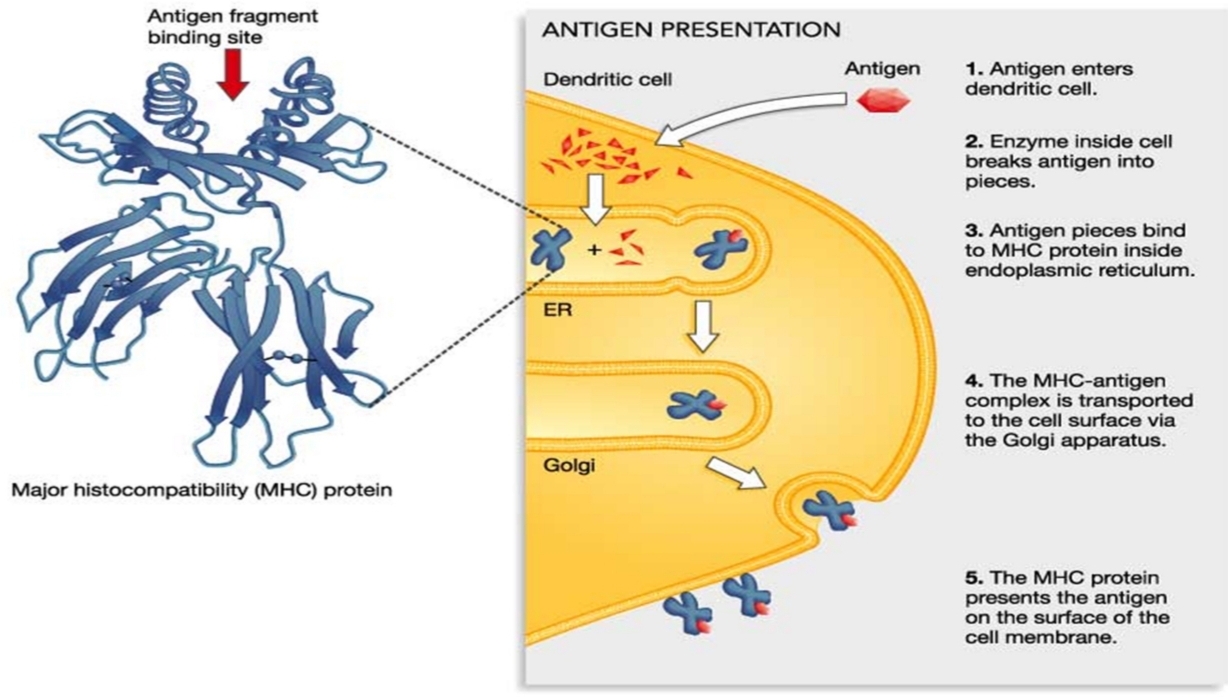
Somatically Generated Receptors
Structurally similar to Igs
Heterodimers with an αβ or γδ chain pair
T Cell Receptors
Somatically Generated Receptors
T Cell Receptors
→Membrane bound receptors and recognize antigen combined with _
→Associated with _ which links TCR with intracellular signalling molecules
→_ or _, an accessory molecule, acts as co-receptor for TCR
MHC molecules
CD3
CD4 or CD8
T Cell receptor