Biosynthesis of Steroids and Amino Acid Catabolism
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
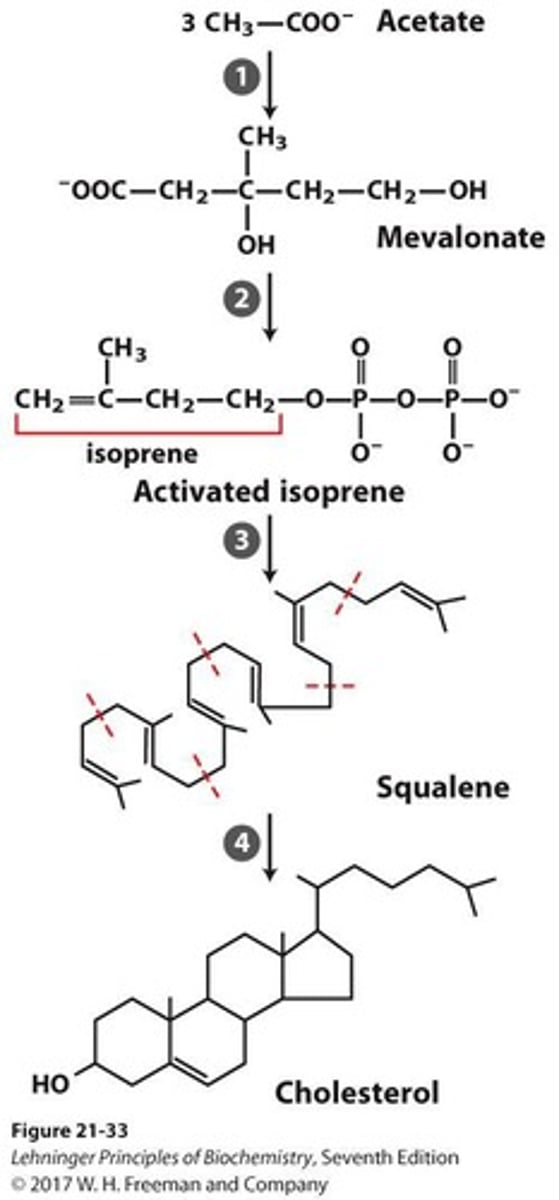
Isoprene
Five-carbon building block for steroid synthesis.
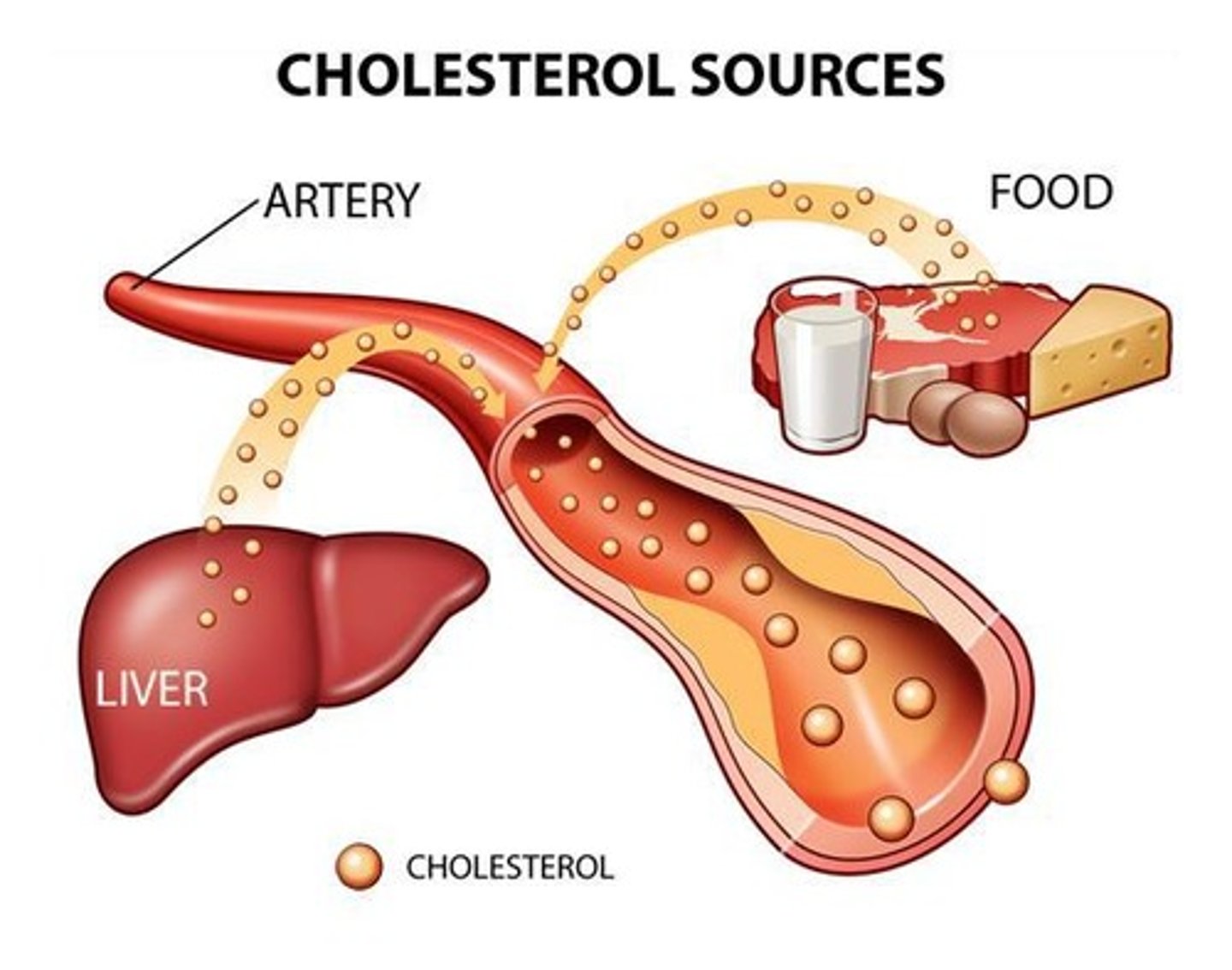
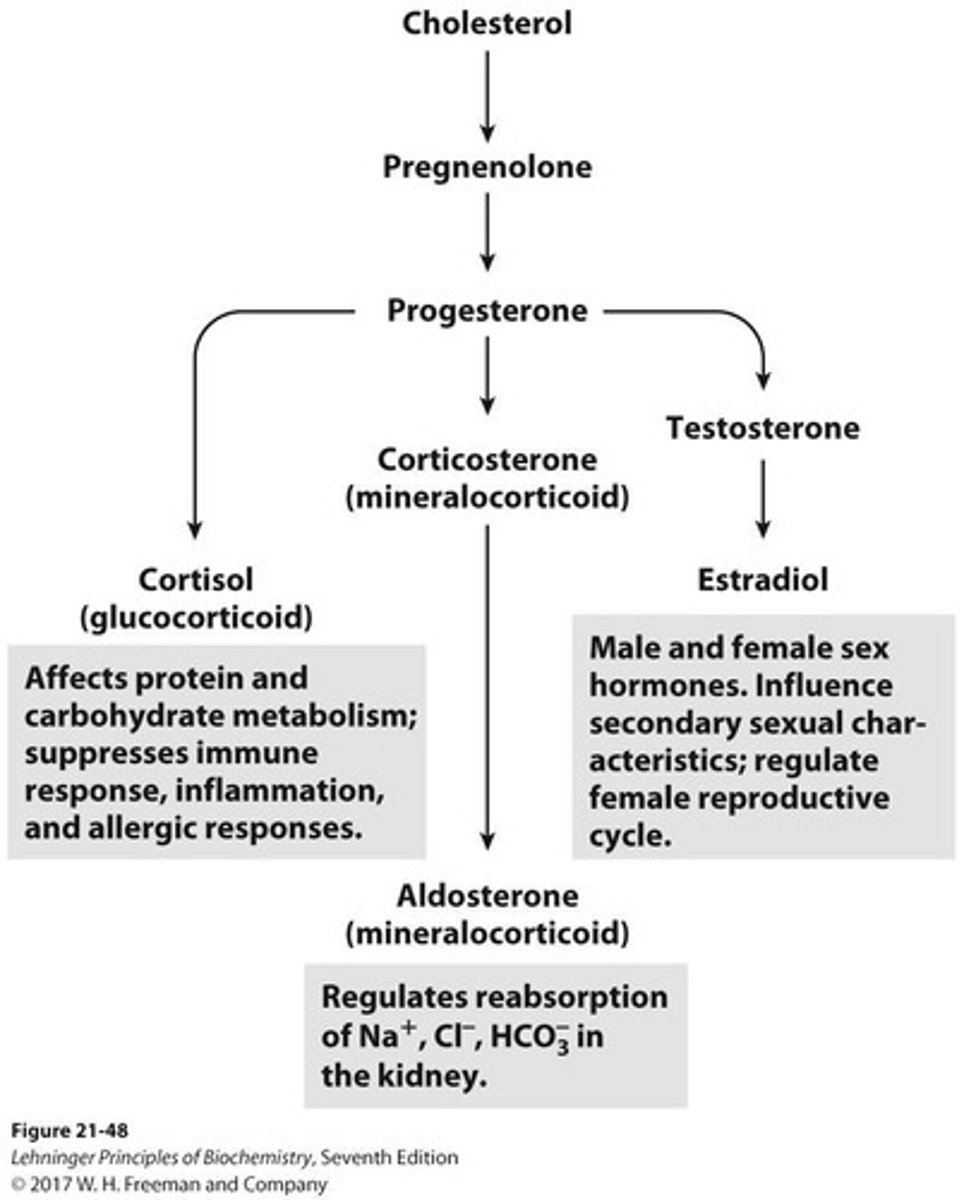
Cholesterol
A sterol synthesized from isoprene units.
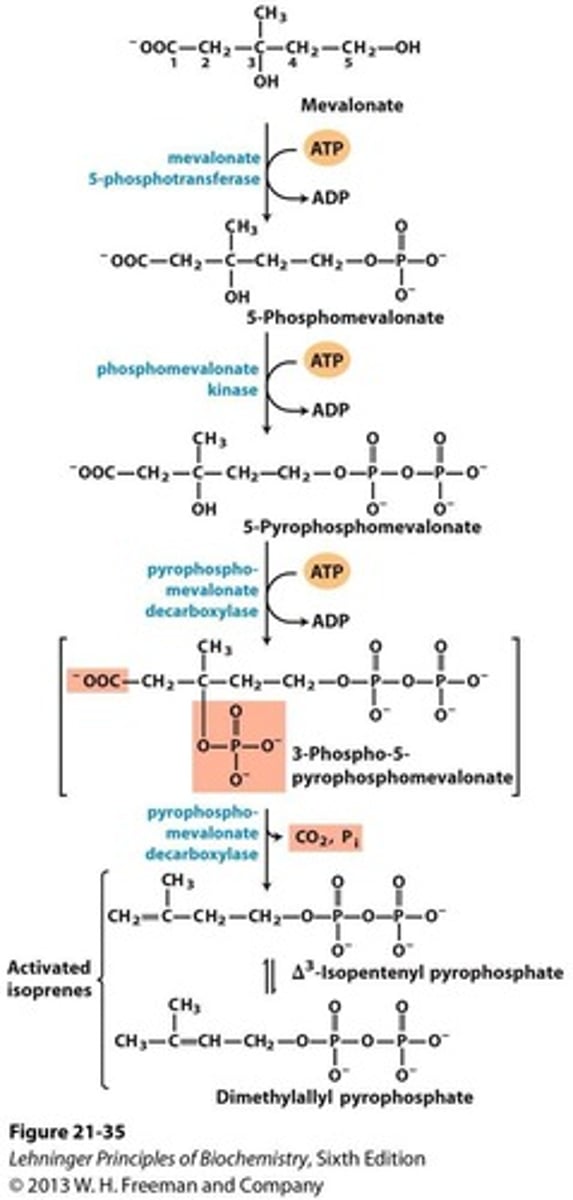
Mevalonate
Intermediate formed from acetyl-CoA in cholesterol biosynthesis.
HMG-CoA
Precursor to mevalonate in cholesterol synthesis.
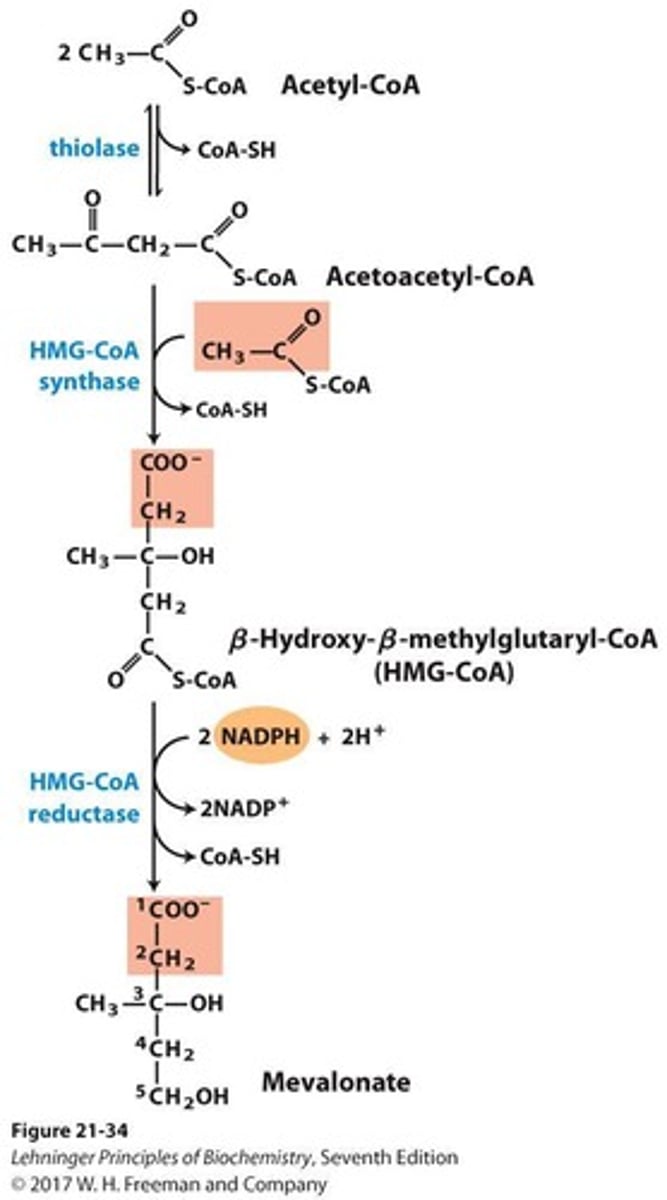
HMG-CoA reductase
Key enzyme targeted by cholesterol-lowering drugs.
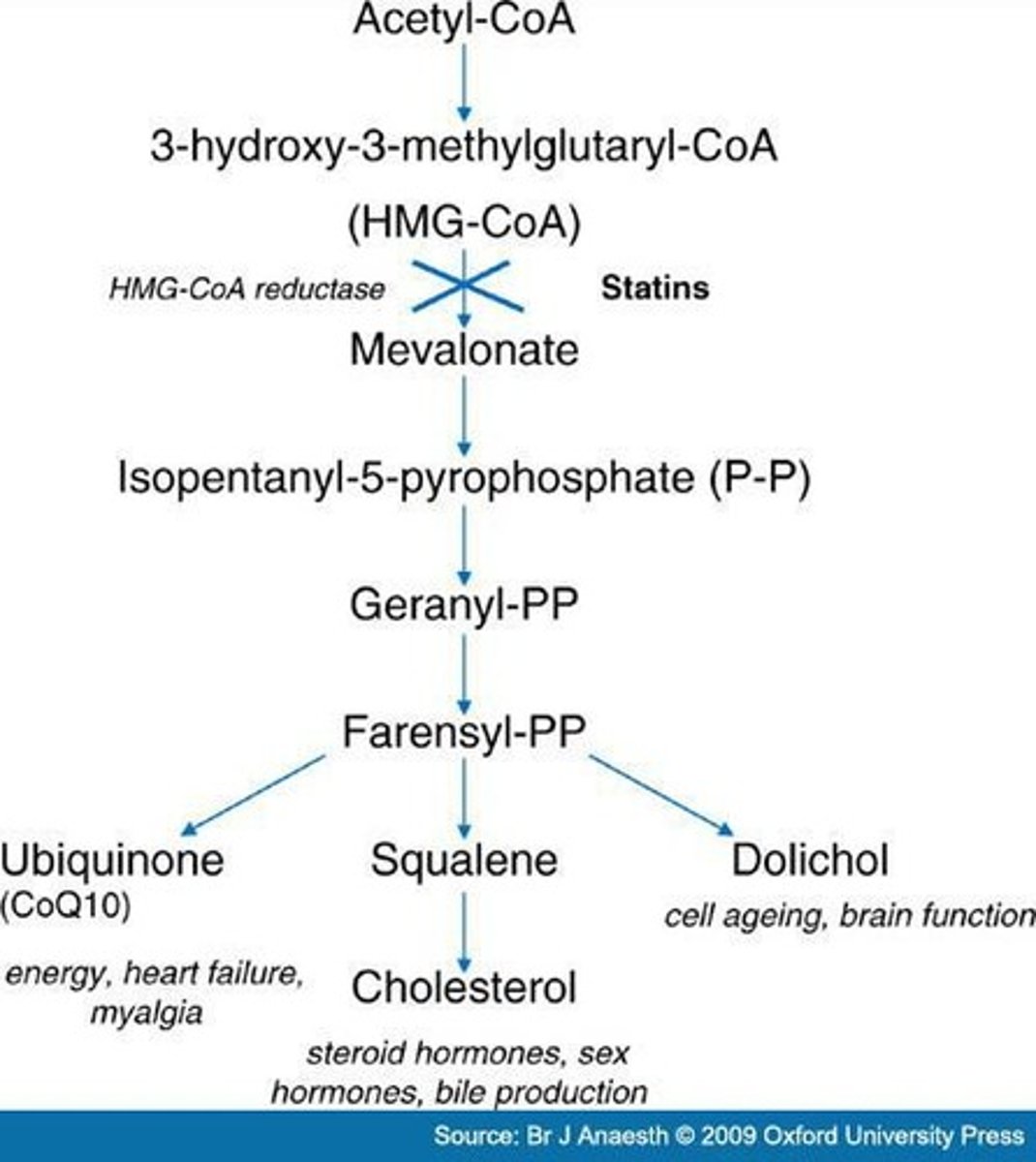
Squalene
30-carbon linear precursor to cholesterol.
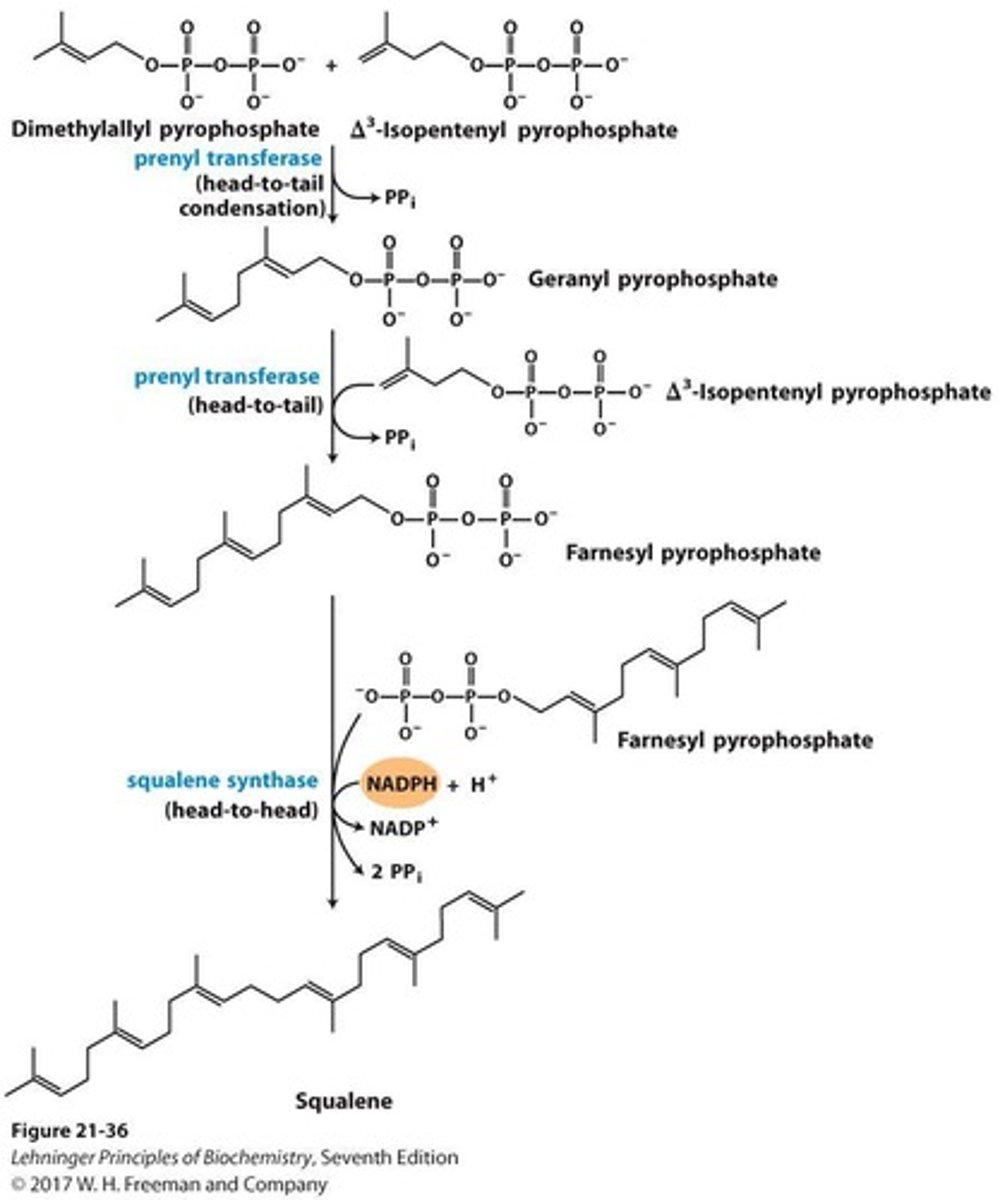
Geranyl pyrophosphate
10-carbon intermediate formed from isoprenes.
Farnesyl pyrophosphate
15-carbon intermediate formed from two isoprenes.
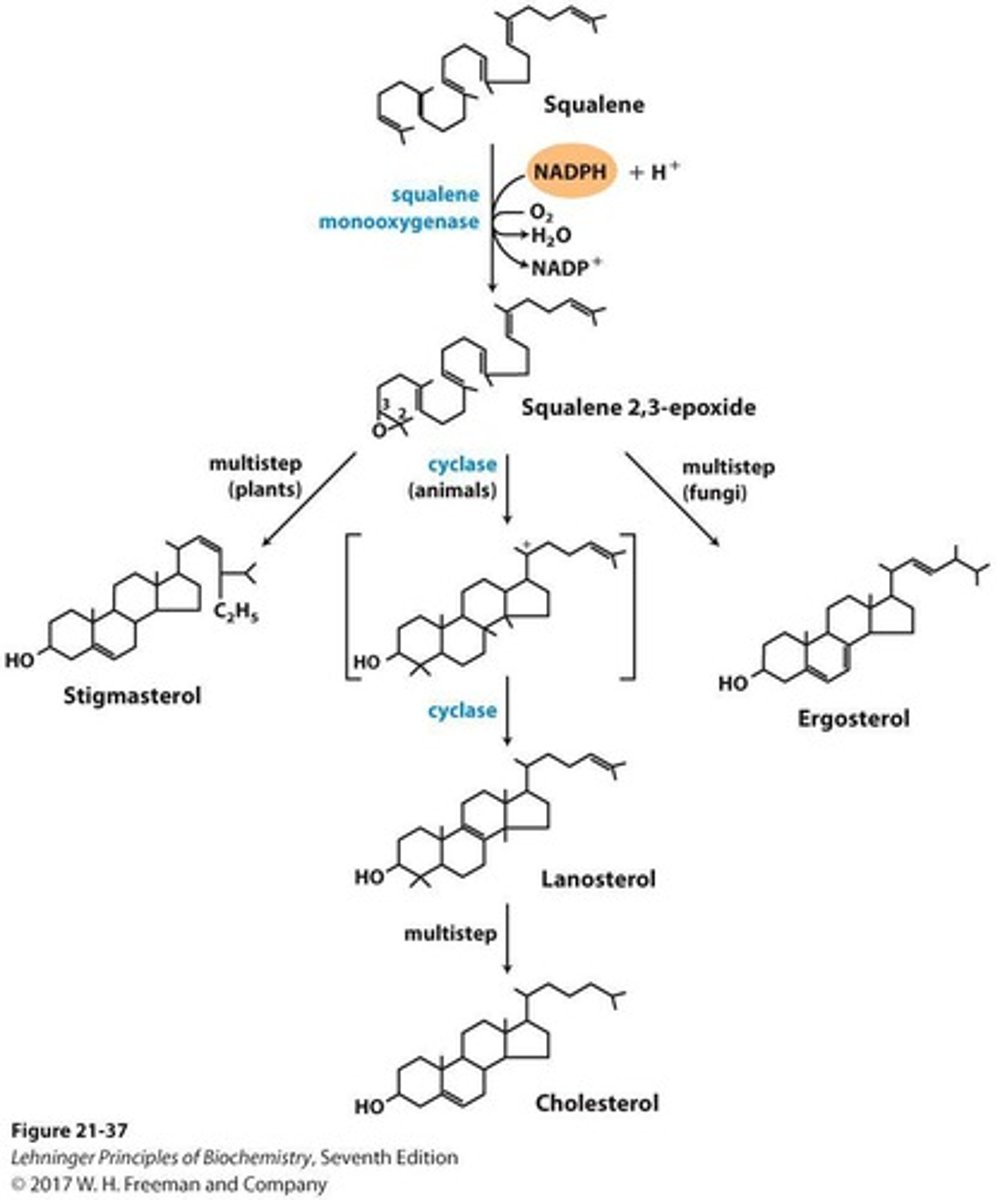
Squalene monooxygenase
Enzyme that converts squalene to squalene epoxide.
Lanosterol
Cyclization product of squalene in animals.
Ergosterol
Cyclization product of squalene in plants.
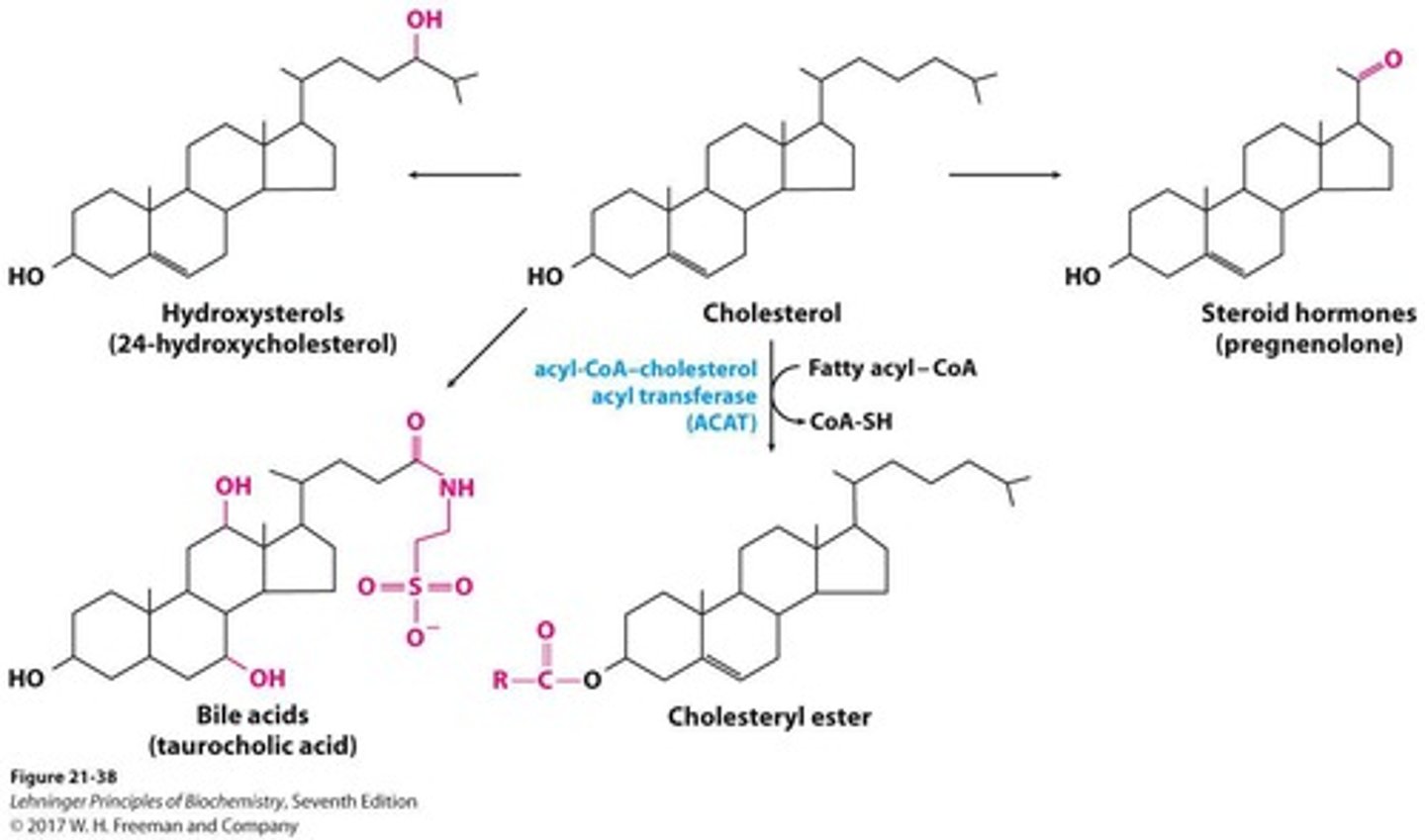
Bile acids
Cholesterol derivatives that emulsify fats.
Taurocholic acid
Bile acid that aids in fat digestion.
Hypercholesterolemia
Condition of elevated cholesterol levels in blood.
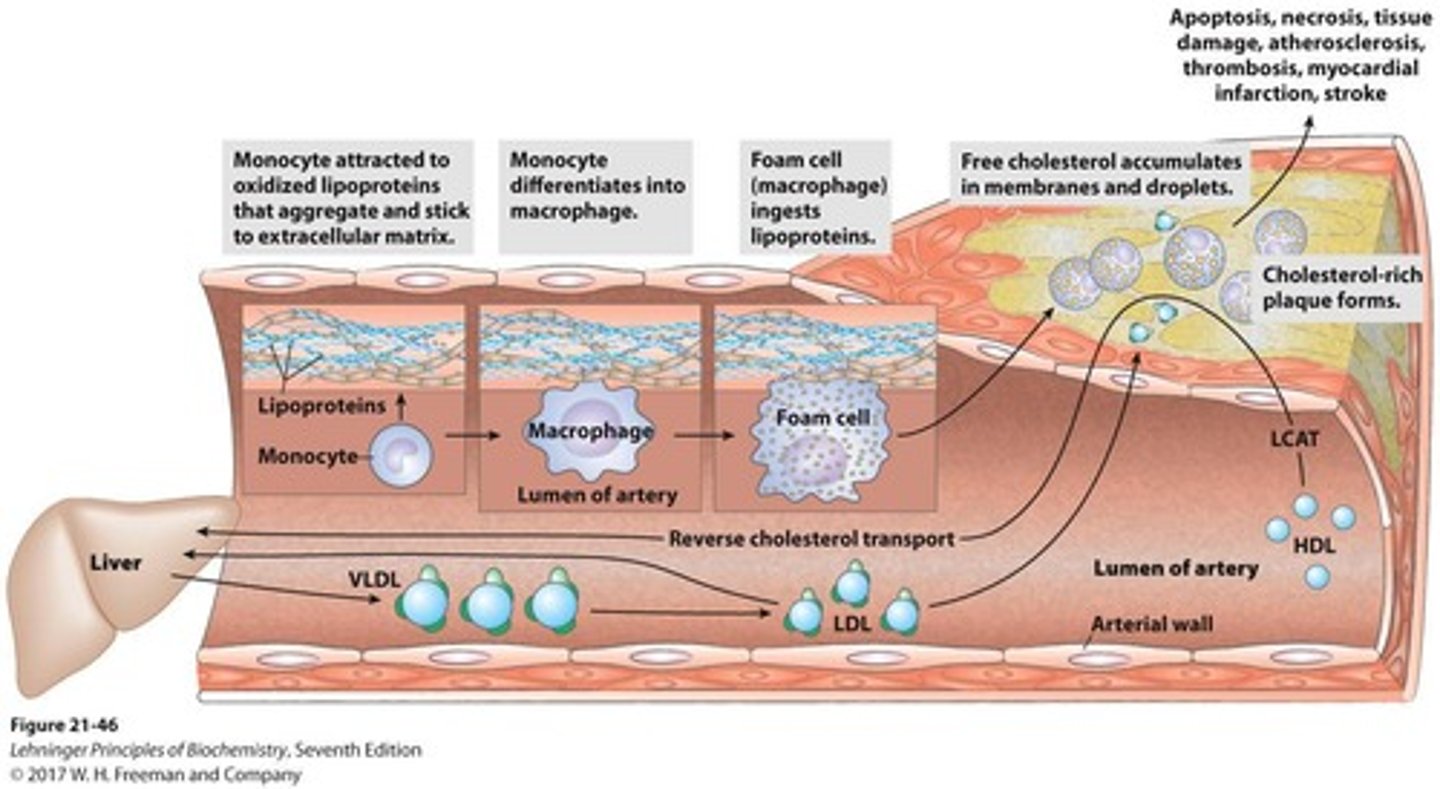
LDL-cholesterol
Low-density lipoprotein associated with heart disease.
HDL-cholesterol
High-density lipoprotein protective against heart disease.
Atherosclerosis
Plaque buildup in arteries linked to high LDL.
Statins
Drugs that inhibit HMG-CoA reductase activity.
Cholesteryl esters
Cholesterol molecules esterified with fatty acids.
Biliary cholesterol
Cholesterol secreted into bile for fat digestion.
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP)
Activated isoprene intermediate in cholesterol biosynthesis.
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP)
Another activated isoprene involved in synthesis.
Nitrogen Fixation
Conversion of N2 to NH3 by bacteria.
Urea Cycle
Process converting ammonia to urea for excretion.
Nitrogen Importance
Essential for nucleic acids and proteins.
Cofactors
Molecules aiding enzyme function, e.g., NAD, FAD.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Genetic disorder affecting phenylalanine metabolism.
Oxidation States of Nitrogen
Different forms of nitrogen with varying oxidation levels.
Nitrate
NO3-, highest oxidation state of nitrogen.
Nitrite
NO2-, intermediate oxidation state of nitrogen.
Ammonia
NH3, lowest oxidation state of nitrogen.
Nitrogen Cycle
Biochemical transformations of nitrogen in ecosystems.
Nitrification
Conversion of ammonia to nitrite and nitrate.
Assimilation
Incorporation of nitrogen into organic compounds.
Denitrification
Reduction of nitrate to N2 under anaerobic conditions.
Nitrogenase Complex
Enzyme complex facilitating nitrogen fixation.
Exergonic Reaction
Reaction releasing energy, e.g., nitrogen fixation.
ATP Consumption
About 16 ATP used per nitrogen molecule fixed.
Dinitrogenase Reductase
Enzyme transferring electrons in nitrogen fixation.
Dinitrogenase
Enzyme catalyzing reduction of nitrogen to ammonia.
Leghemoglobin
Protein binding O2 in nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Ferredoxin
Electron carrier in nitrogen fixation process.
Flavodoxin
Alternative electron carrier in nitrogen fixation.
Mo-FeS Cage
Structure coordinating nitrogen in nitrogenase complex.
NH3 Production
Excess ammonia released to soil by organisms.
Non-essential Amino Acids
Humans synthesize 11 amino acids internally.
Essential Amino Acids
Nine amino acids must be obtained from diet.
Amino Acid Synthesis
Bacteria and plants synthesize all 20 amino acids.
Nitrogen Sources
Glutamate or glutamine provide nitrogen for synthesis.
Metabolic Precursors
Seven precursors form scaffolds for amino acid synthesis.
Amino Acid Oxidation
Carnivores meet 90% energy needs from amino acids.
Microbial Fuel Source
Microorganisms scavenge amino acids for energy.
Herbivore Energy Needs
Amino acids meet only small fraction of energy.
Plant Amino Acid Use
Plants degrade amino acids for other metabolites.
Protein Hydrolysis
Dietary proteins are broken down into amino acids.
Pepsin Function
Pepsin cuts proteins into peptides in the stomach.
Trypsin and Chymotrypsin
These enzymes further digest peptides in the intestine.
Peptide Degradation
Aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidases convert peptides to amino acids.
Gastric Gland Secretions
HCl, pepsinogen, and gastrin are secreted in stomach.
Pancreatic Enzyme Synthesis
Pancreas synthesizes many digestive enzymes for protein breakdown.
Zymogen Granules
Zymogens are stored in membrane-enclosed transport particles.
Amino Acid Absorption
Absorbed through epithelial cells in intestinal mucosa.
Amino Acid Catabolism
Fates include recycling or oxidation for energy.
Urea Cycle
Removes amino group during amino acid oxidation.
Nitrogen Excretion in Aquatic Vertebrates
Ammonia released via diffusion or active transport.
Urea Excretion
Terrestrial vertebrates excrete nitrogen as less toxic urea.
Uric Acid Excretion
Birds and reptiles excrete nitrogen as insoluble uric acid.
Human Nitrogen Excretion
Humans excrete both urea and uric acid.
Ammonia Toxicity
Ammonia must be kept at low blood concentrations.
Bacterial Ammonium Production
Bacteria in intestines produce significant NH4+.
Aminotransferases
Enzymes catalyzing amino group transfer.
Transamination
Transfer of an amine to a metabolite.
α-Ketoglutarate
Common acceptor for amino groups.
Glutamate
Trafficable amino acid generated from transamination.
PLP (Pyridoxal Phosphate)
Cofactor derived from vitamin B6 for aminotransferases.
Nucleophilic Attack
Mechanism linking PLP to enzyme via lysine.
Glutamate Dehydrogenase
Enzyme removing ammonia from glutamate.
Oxidative Deamination
Ammonia removal process in mitochondrial matrix.
Electron Acceptors
NAD+ or NADP+ used in deamination.
Urea
Final product of ammonia processing for excretion.
Transdeamination
Combination of transamination and oxidative deamination.
Glutamine
Ammonia carrier formed from glutamate.
Glutamine Synthetase
Enzyme catalyzing glutamine formation from glutamate.
Glutaminase
Enzyme liberating ammonium ion from glutamine.
Glycolysis
Anaerobic energy production pathway in muscles.
Pyruvate
Product of glycolysis, convertible to alanine.
Alanine
Transport molecule for ammonia and pyruvate.
Glucose-Alanine Cycle
Cycle transporting alanine and ammonia to liver.
Carbamoyl Phosphate
Captures free ammonia in urea cycle's first step.
Citrulline
Product formed from ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate.
Argininosuccinate
Intermediate formed in the urea cycle.
Fumarate
Released during arginine formation from argininosuccinate.
Ornithine
Regenerated in the final step of urea cycle.
Arginase
Enzyme that cleaves arginine, producing urea.
Ornithine
Substrate for the urea cycle's next round.
Carbamoyl phosphate synthase
Activated by N-acetylglutamate for urea synthesis.
N-acetylglutamate
Activator formed from glutamate and acetyl-CoA.
High-protein diet
Increases expression of urea cycle enzymes.
Starvation
Stimulates protein breakdown for energy.
Ketogenic amino acids
Converted to ketone bodies; includes Leu, Ile, Thr.