Organic Nomenclature and IUPAC Nomenclature
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Alkane
a hydrocarbon containing only single covalent bonds
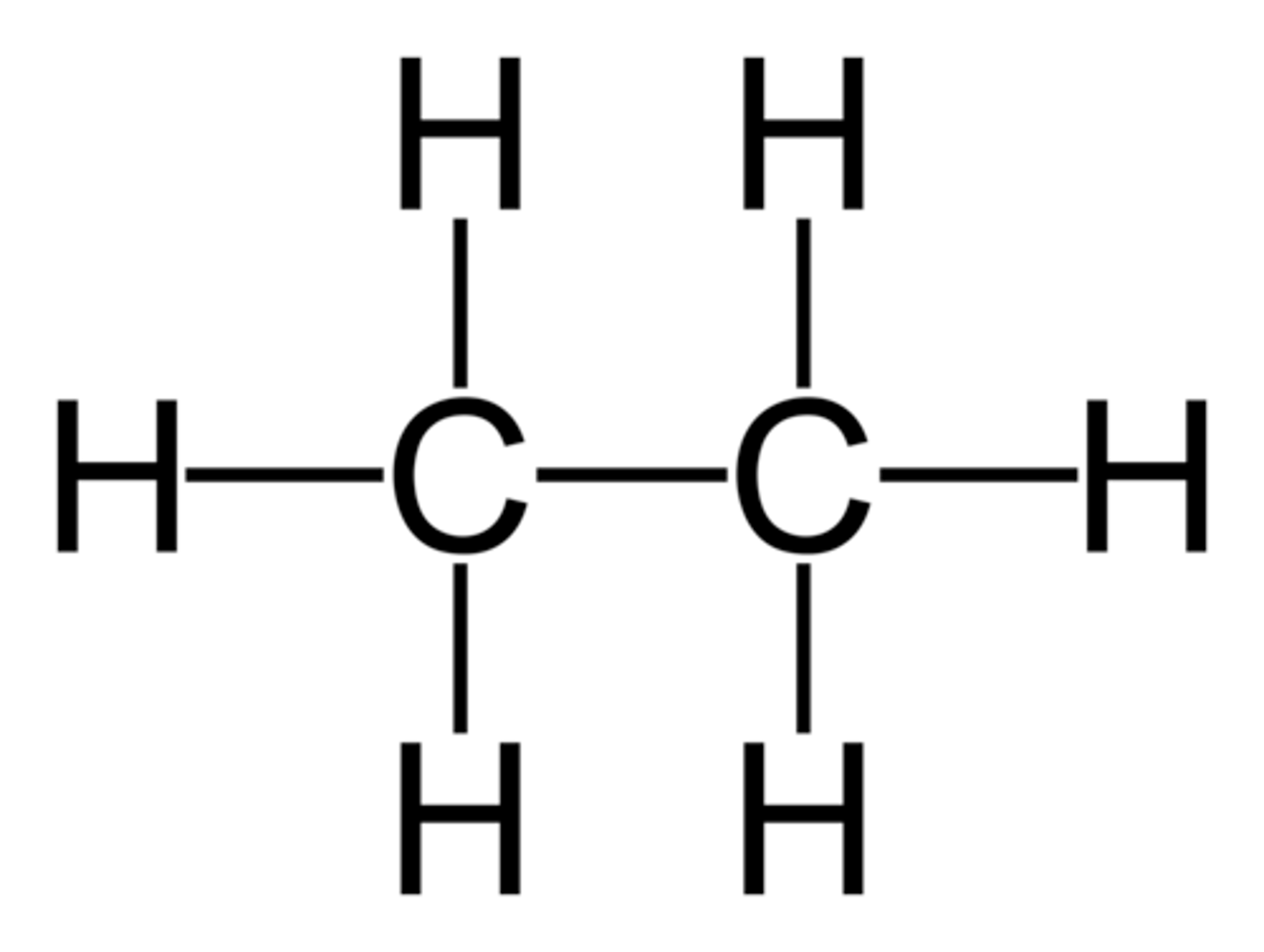
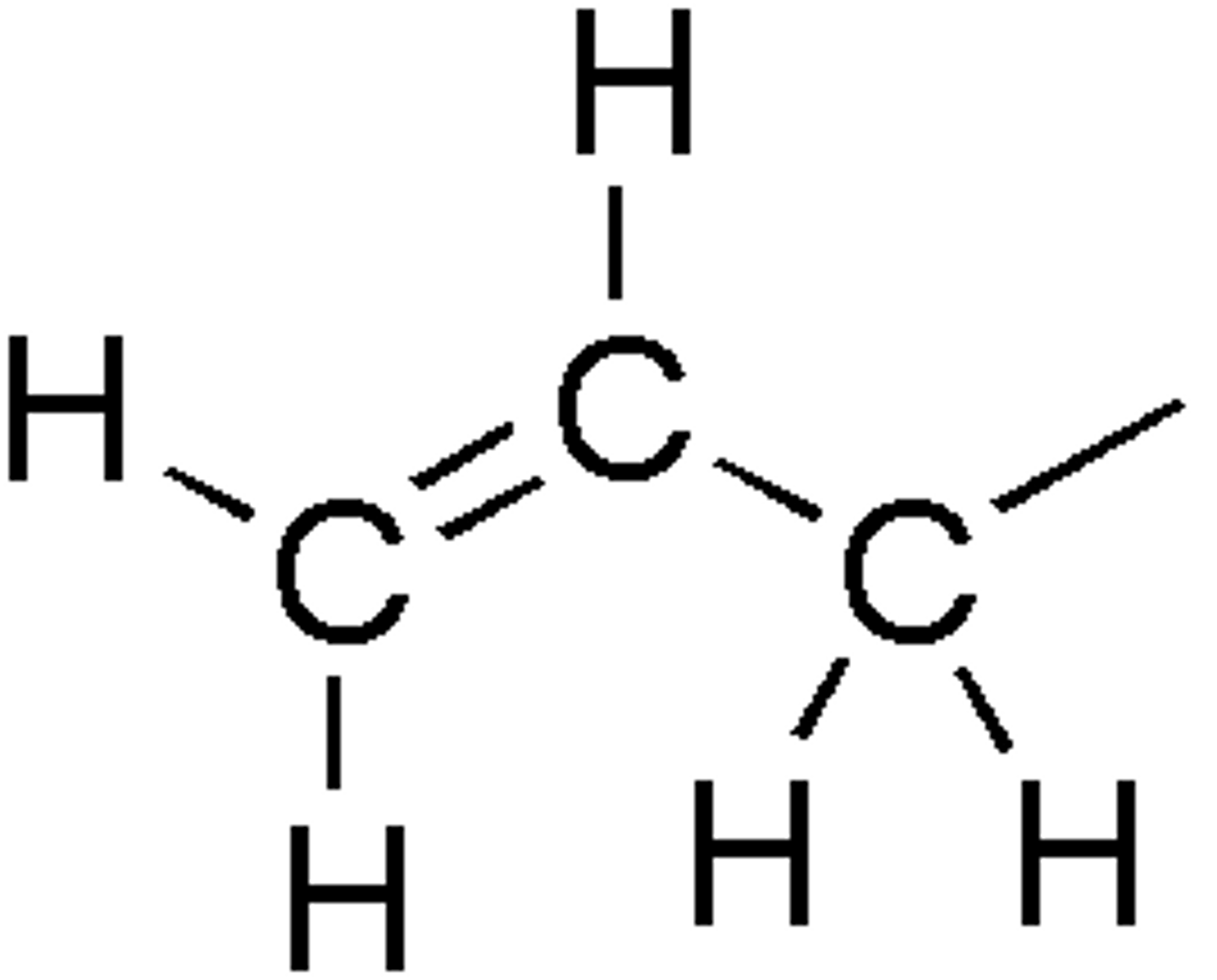
Alkene
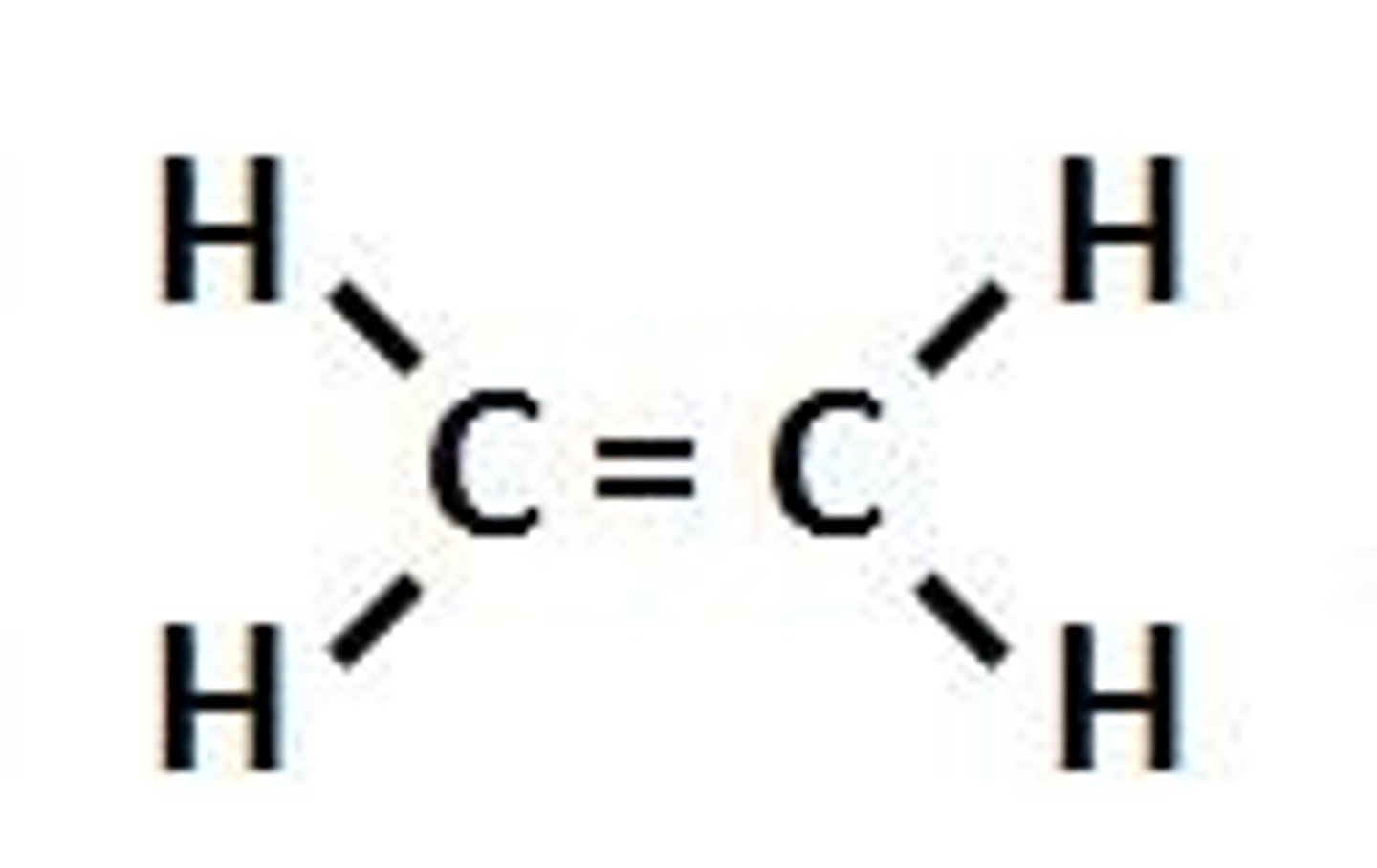
Alkyne
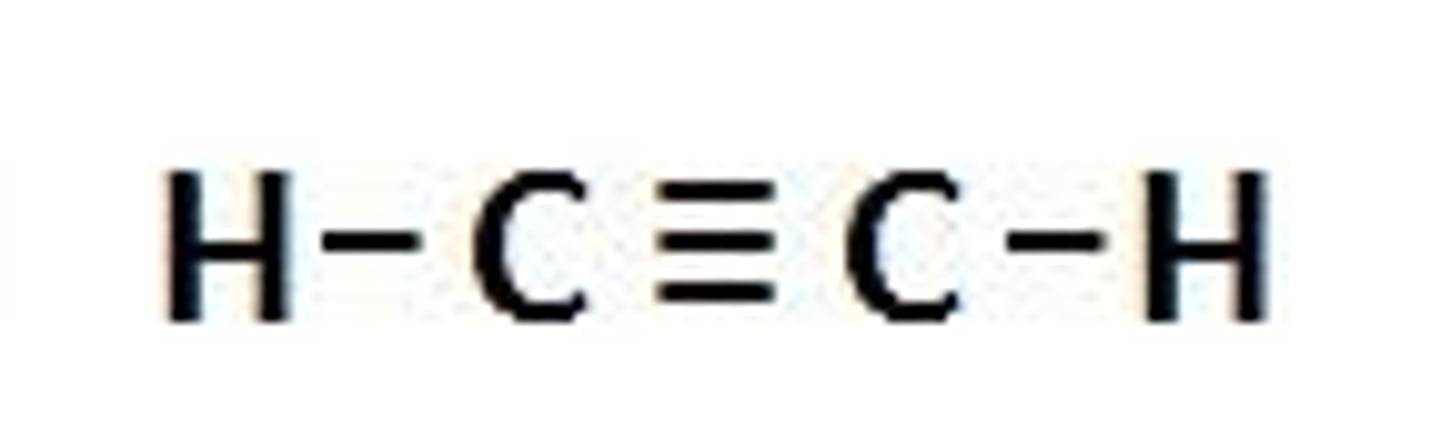
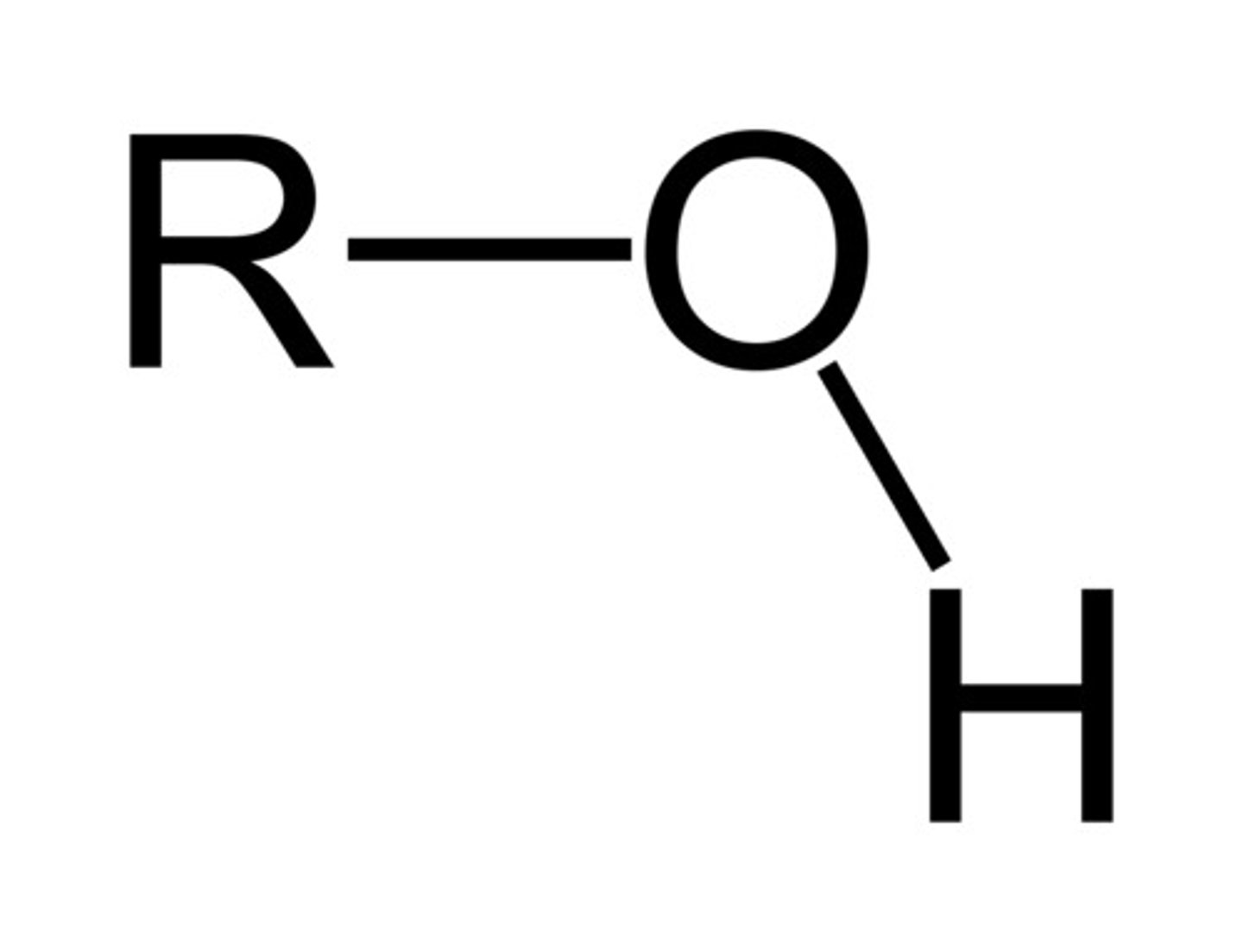
Alcohol
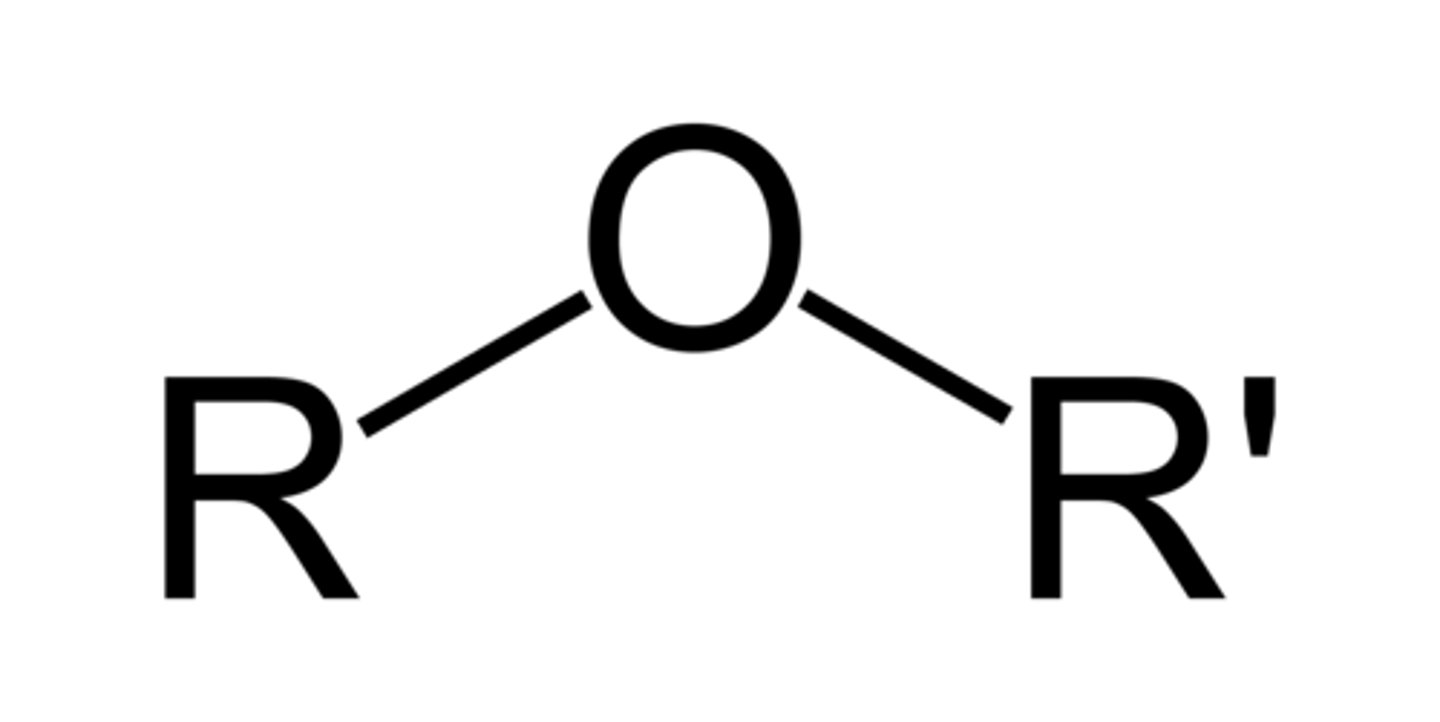
Ether
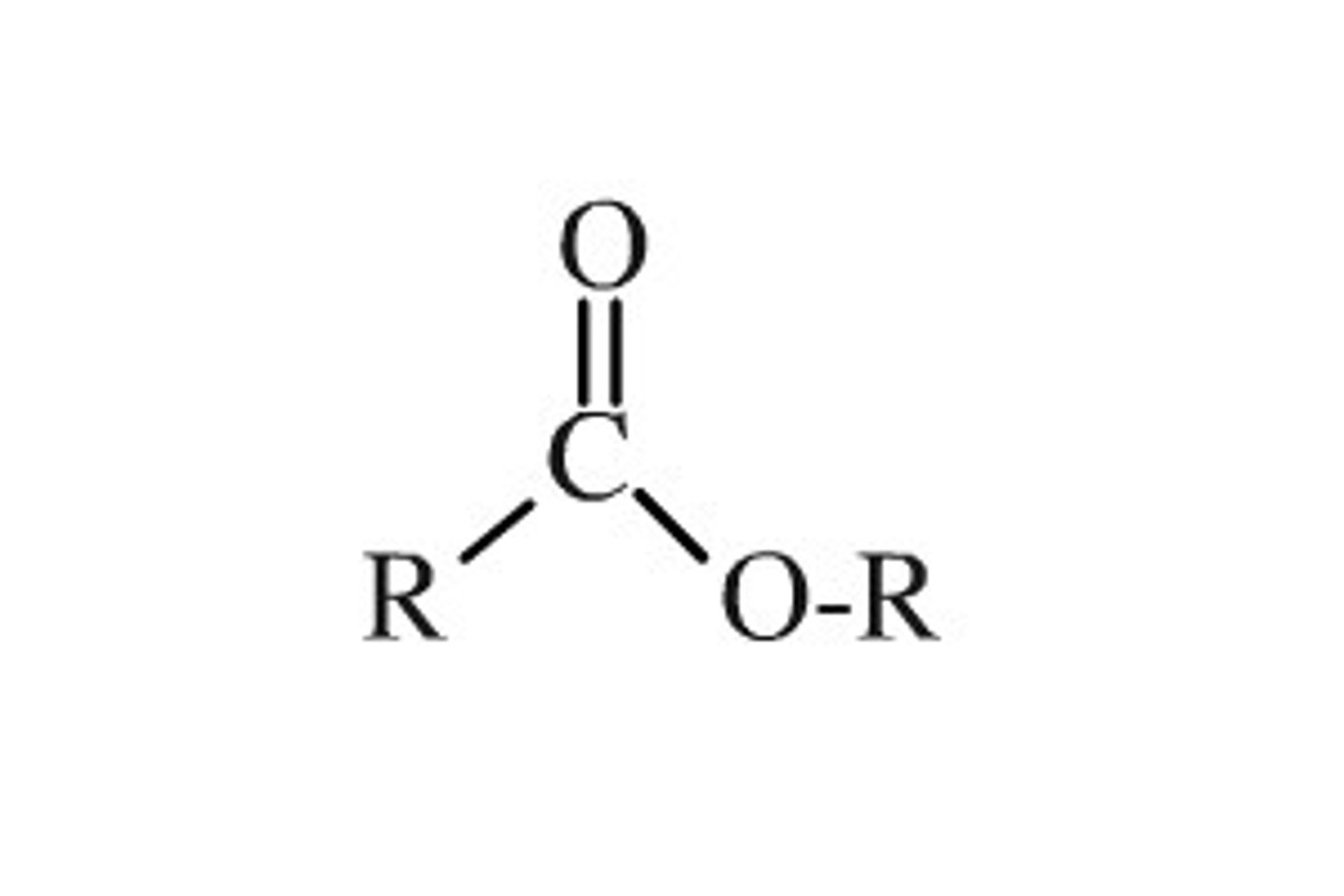
Ester
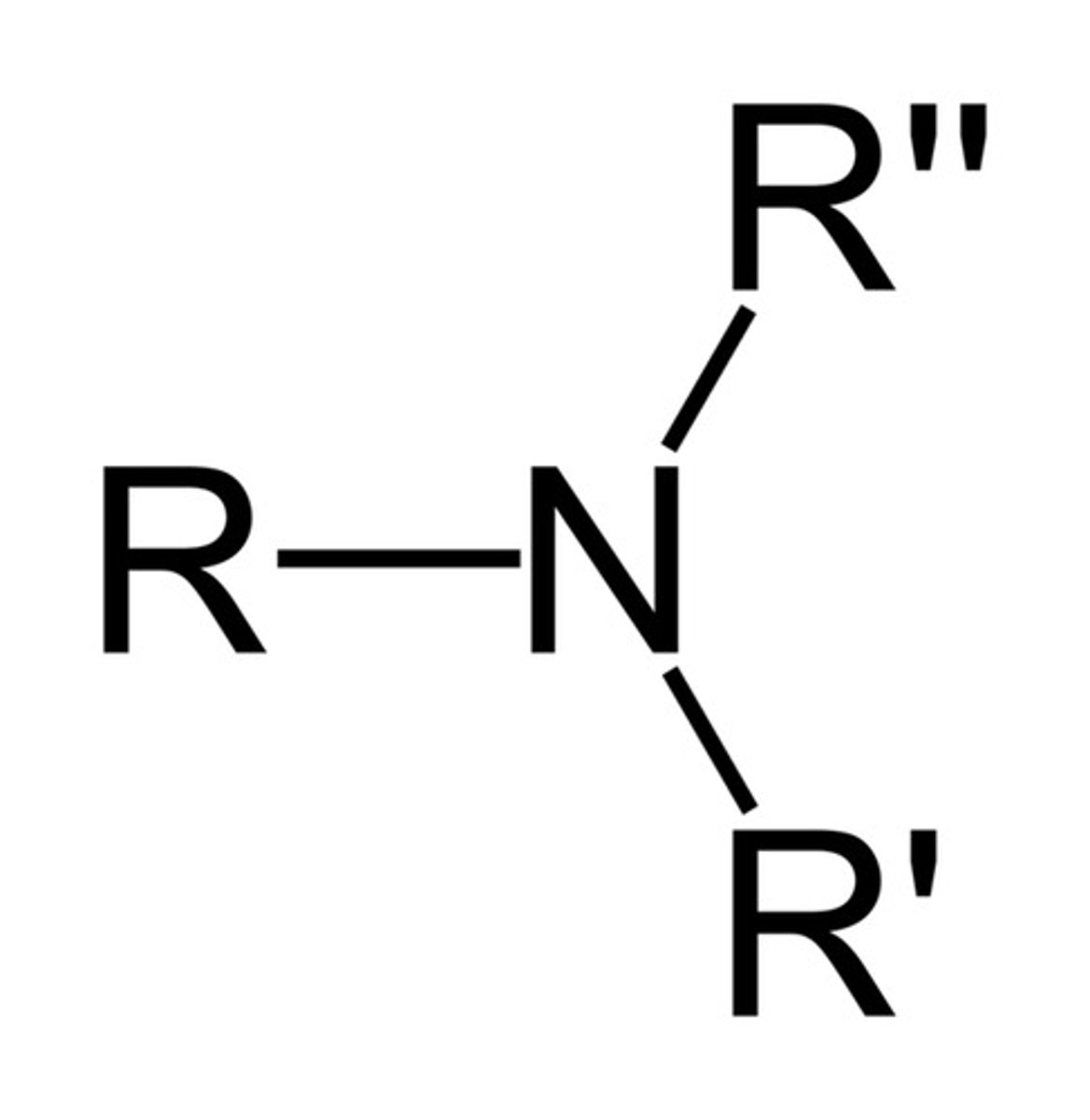
Amine
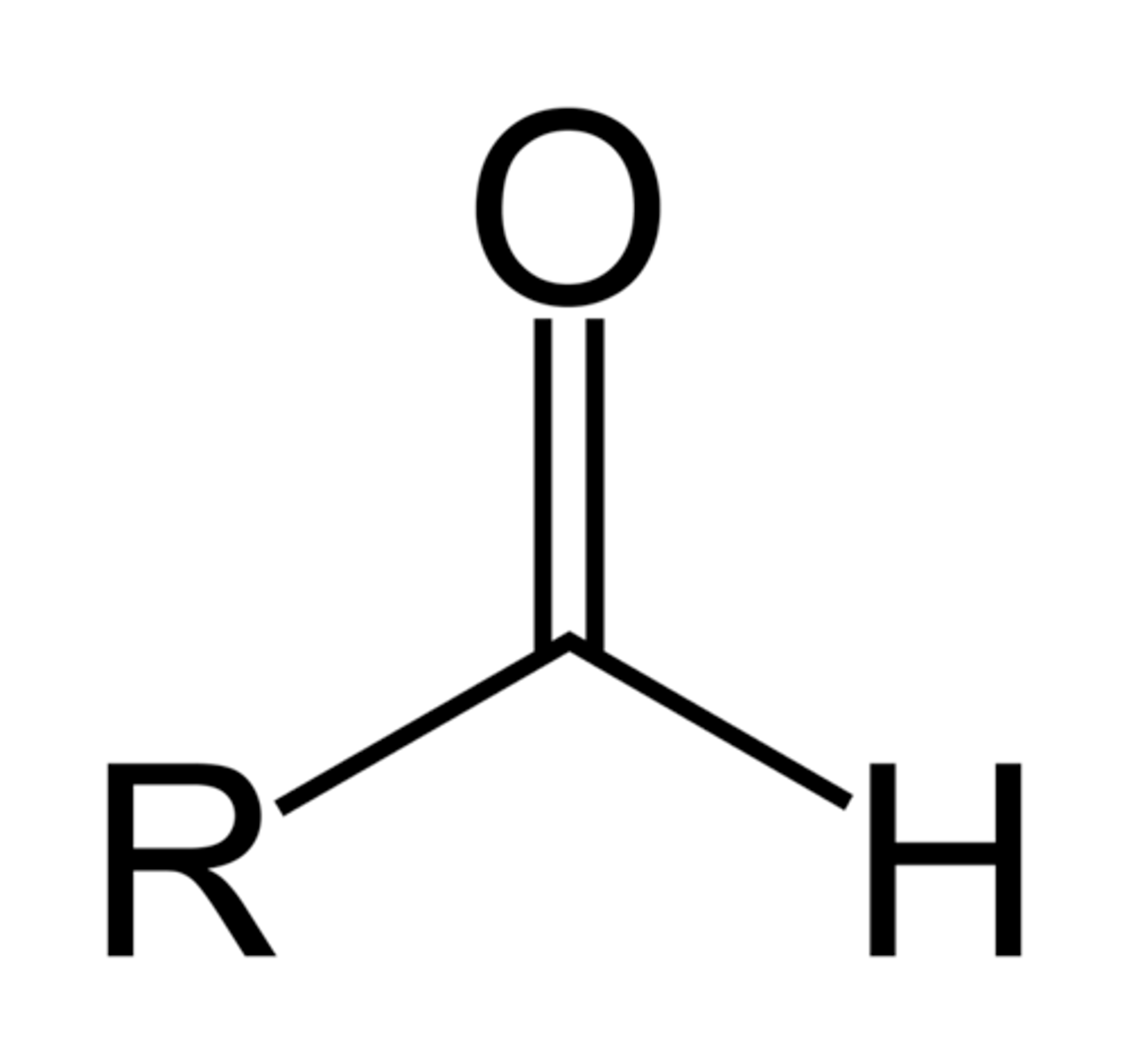
Aldehyde
Ketone
An organic compound with a carbonyl group of which the carbon atom is bonded to two other carbons.
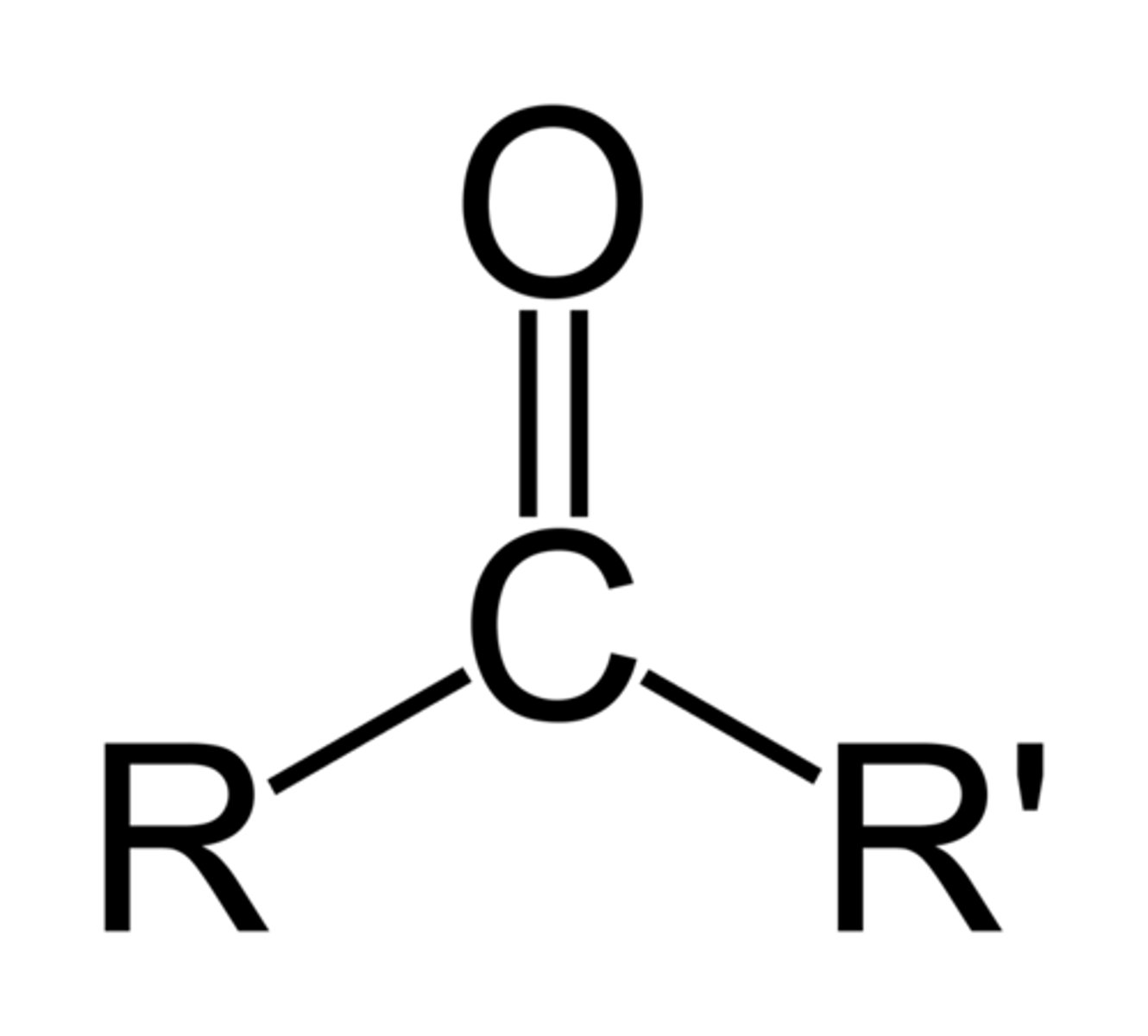
Alkoxy
is an -OR group, an alkyl (or aryl) groupatttached to an oxygen atom.
Alkyl group
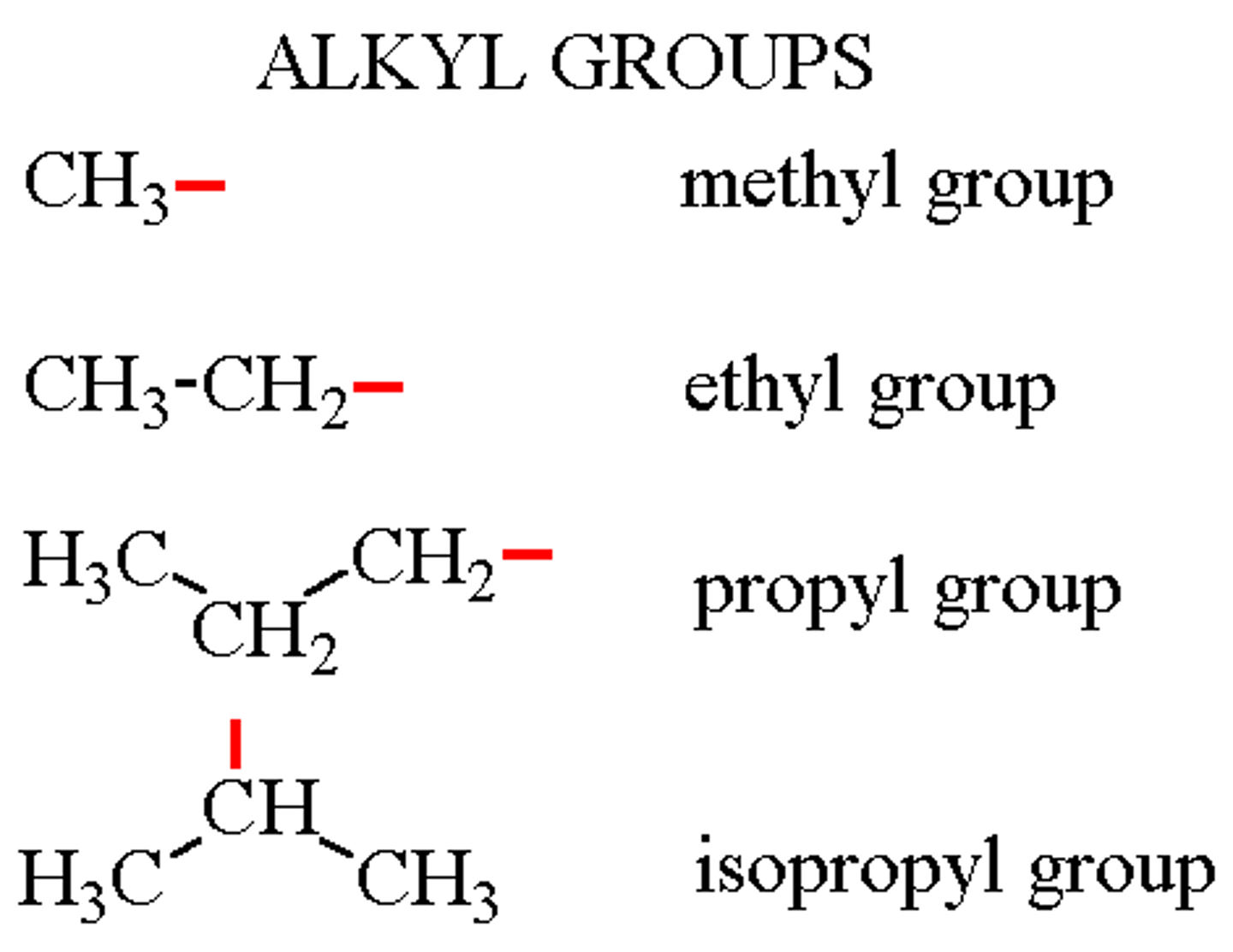
Carbonyl
carbon atom with a double bond to an oxygen atom
Hydroxyl
A functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom joined to an oxygen atom by a polar covalent bond. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water and are called alcohols.
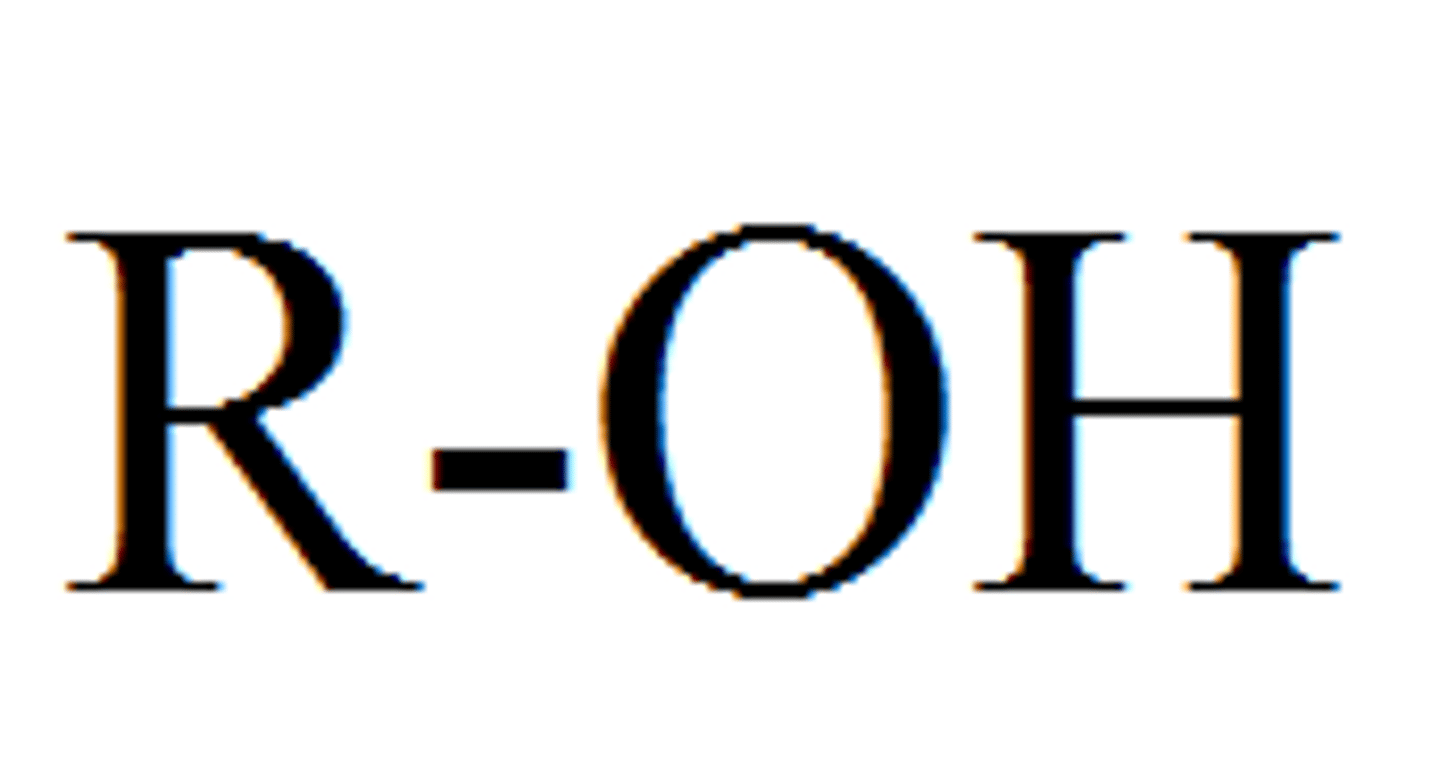
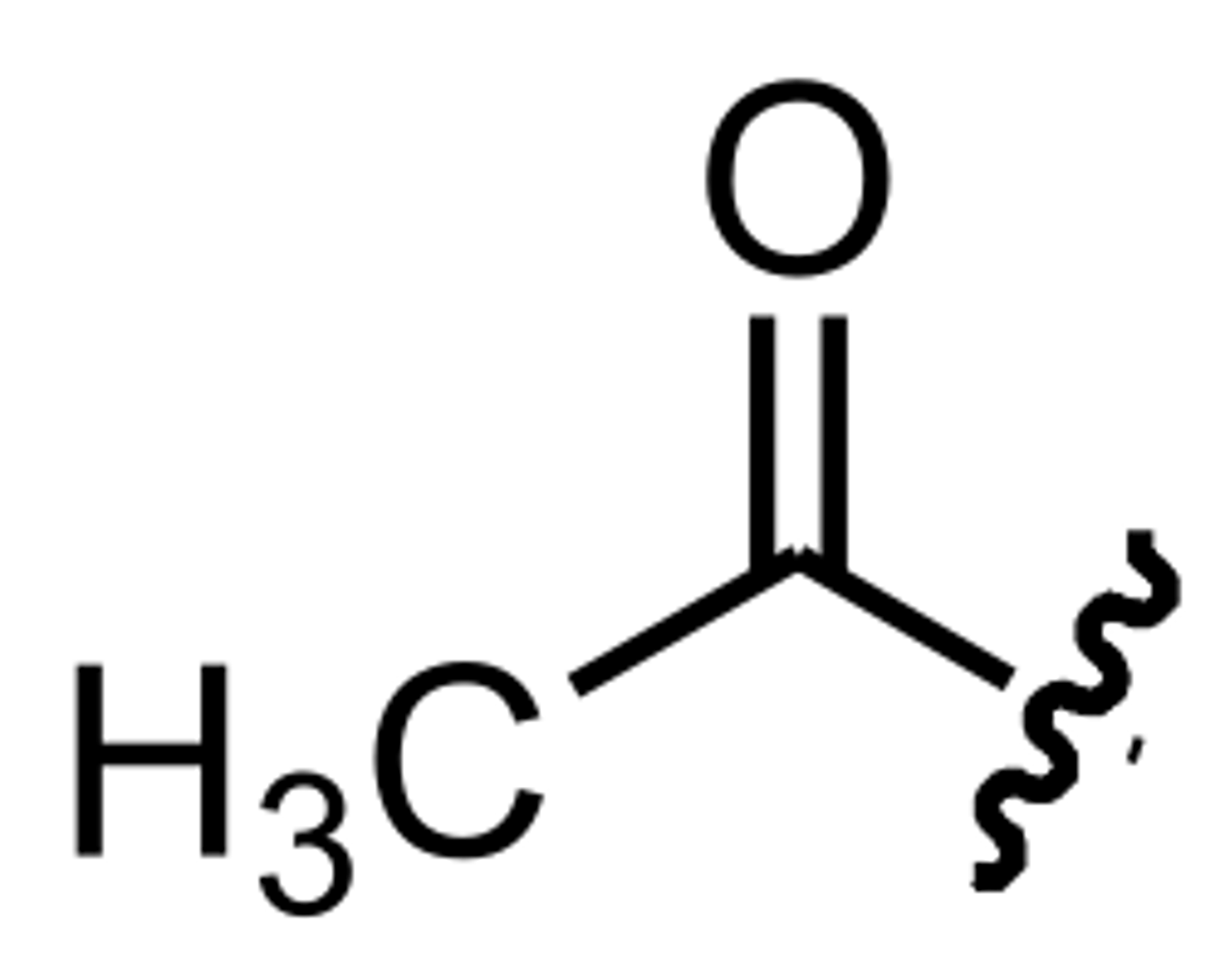
Acetyl
In organic chemistry, acetyl is a functional group, the acyl with chemical formula CH3CO. It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac (not to be confused with the element actinium). The acetyl group contains a methyl group single-bonded to a carbonyl.
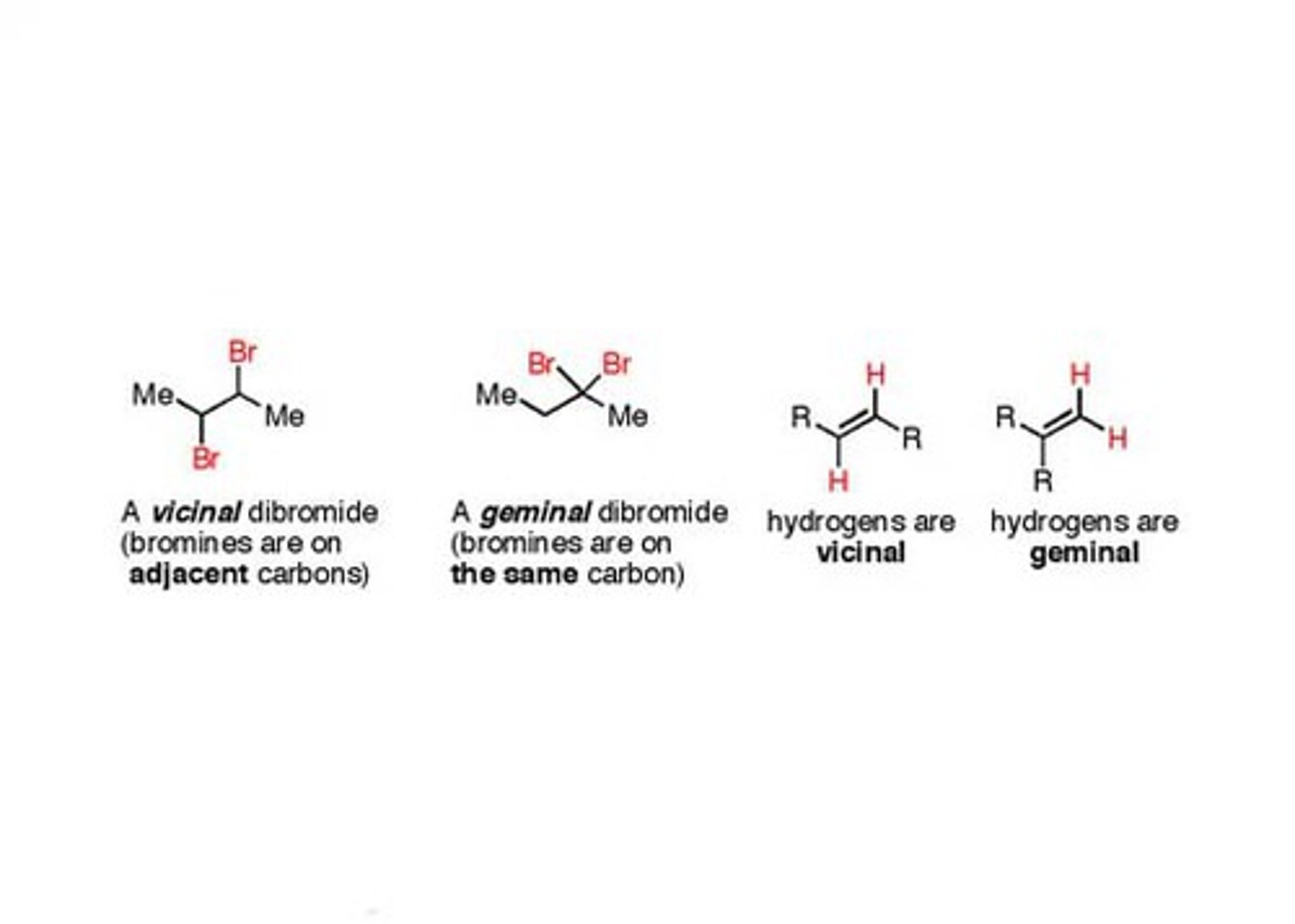
Gem-/Vic-
Vicinal on 2 different adjacent carbons
Geminal- on same carbon
Tosyl
a compound containing the functional group -SO3C6H4CH3, derived from toluenesulfonic acid.
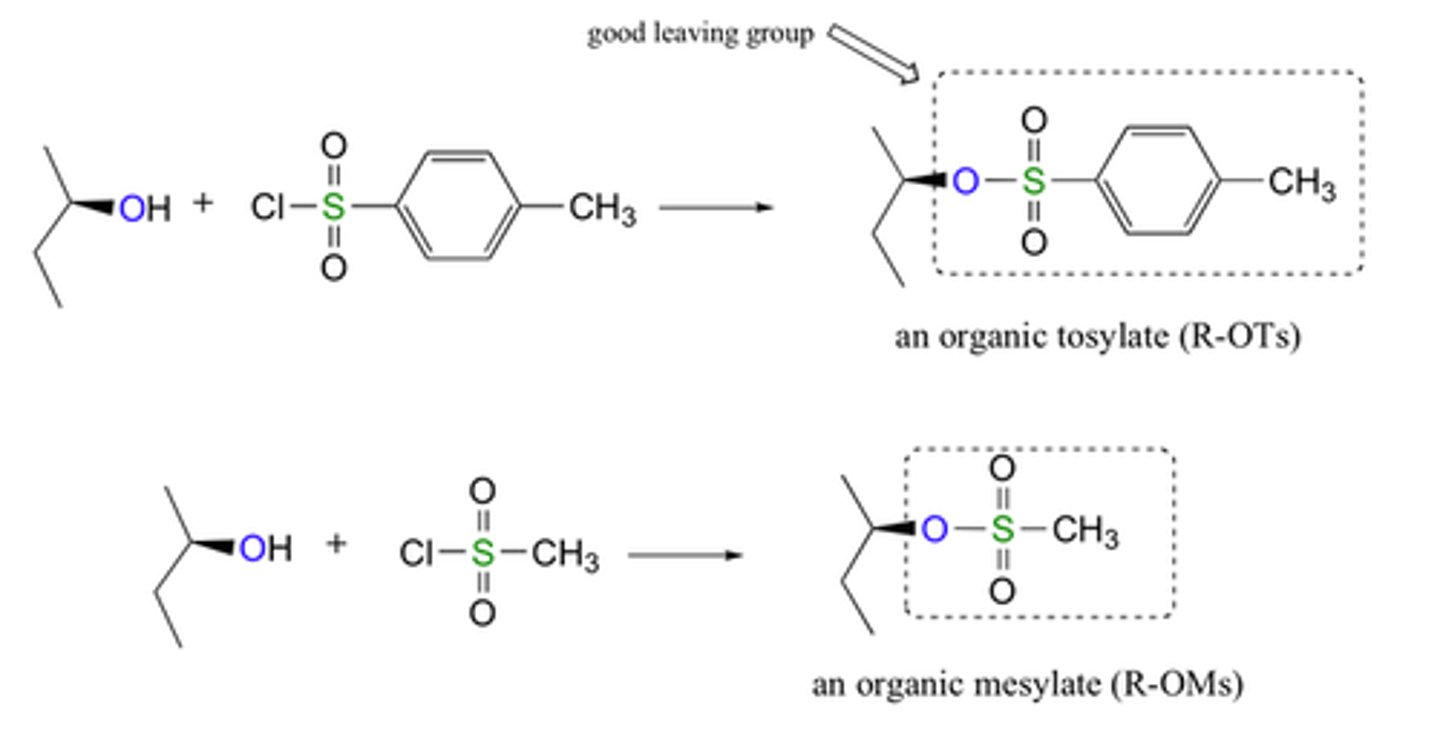
Mesyl
a compound containing the functional group -SO3CH3, derived from methanesulfonic acid.
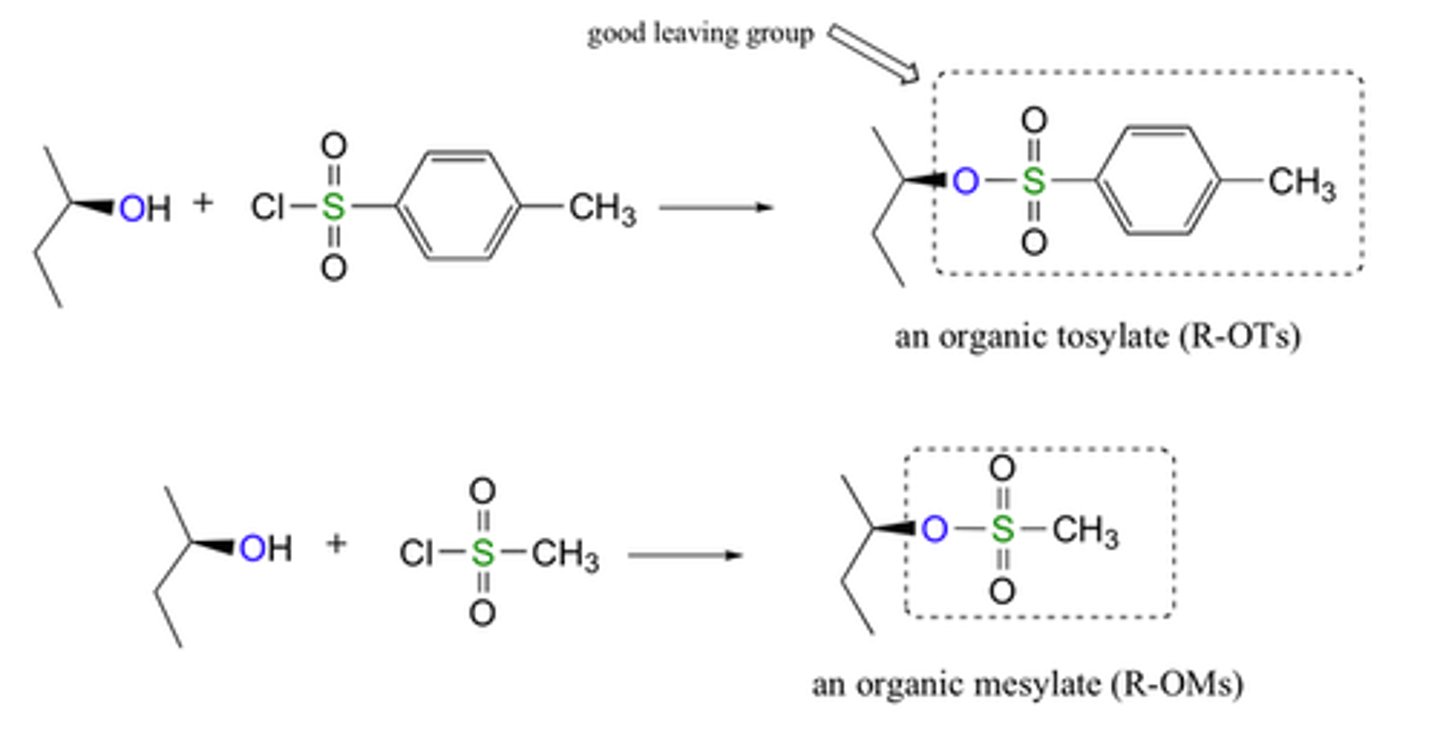
Carboxylic Acid
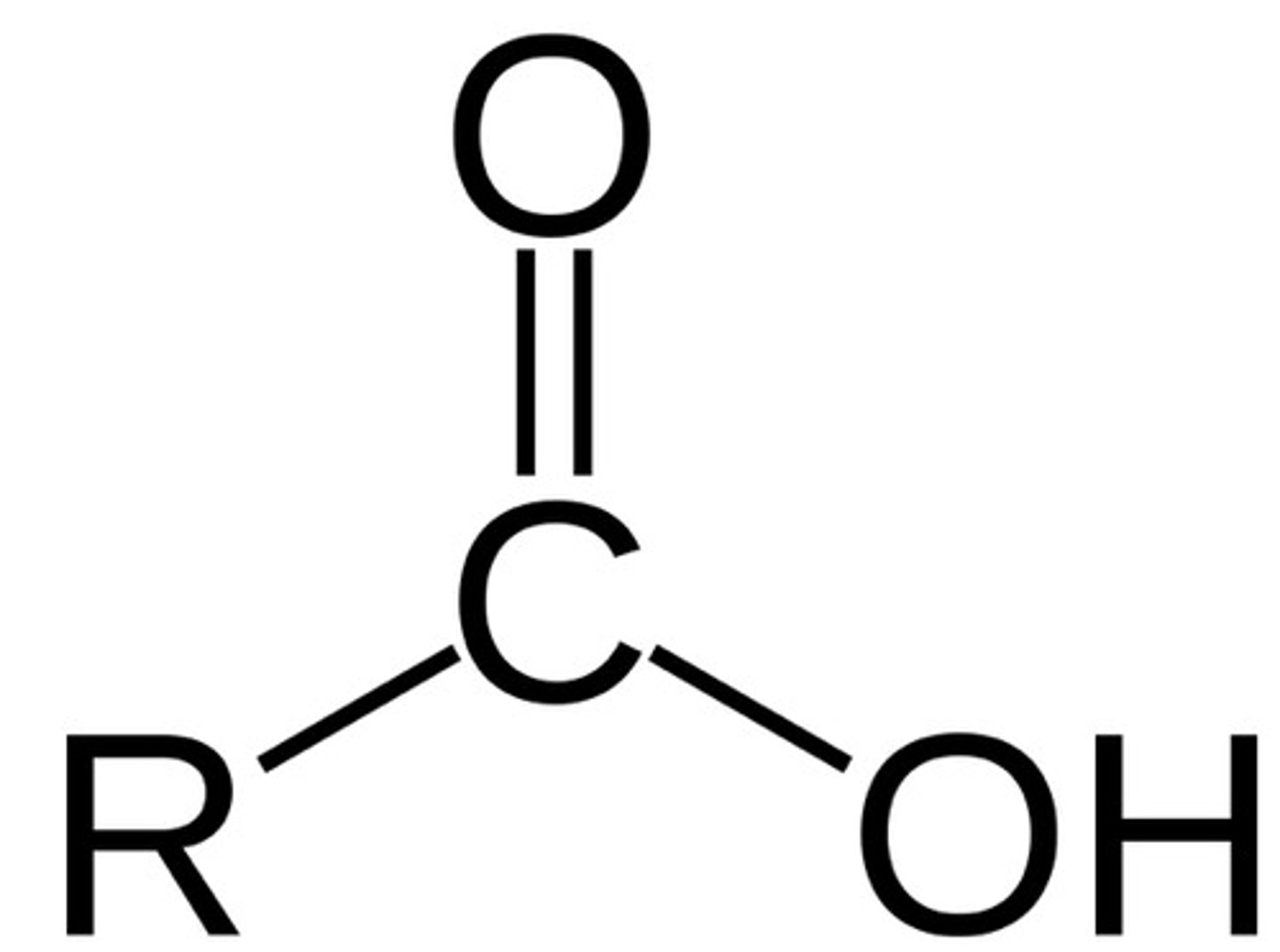
Amide (think of amino acid strucutre)
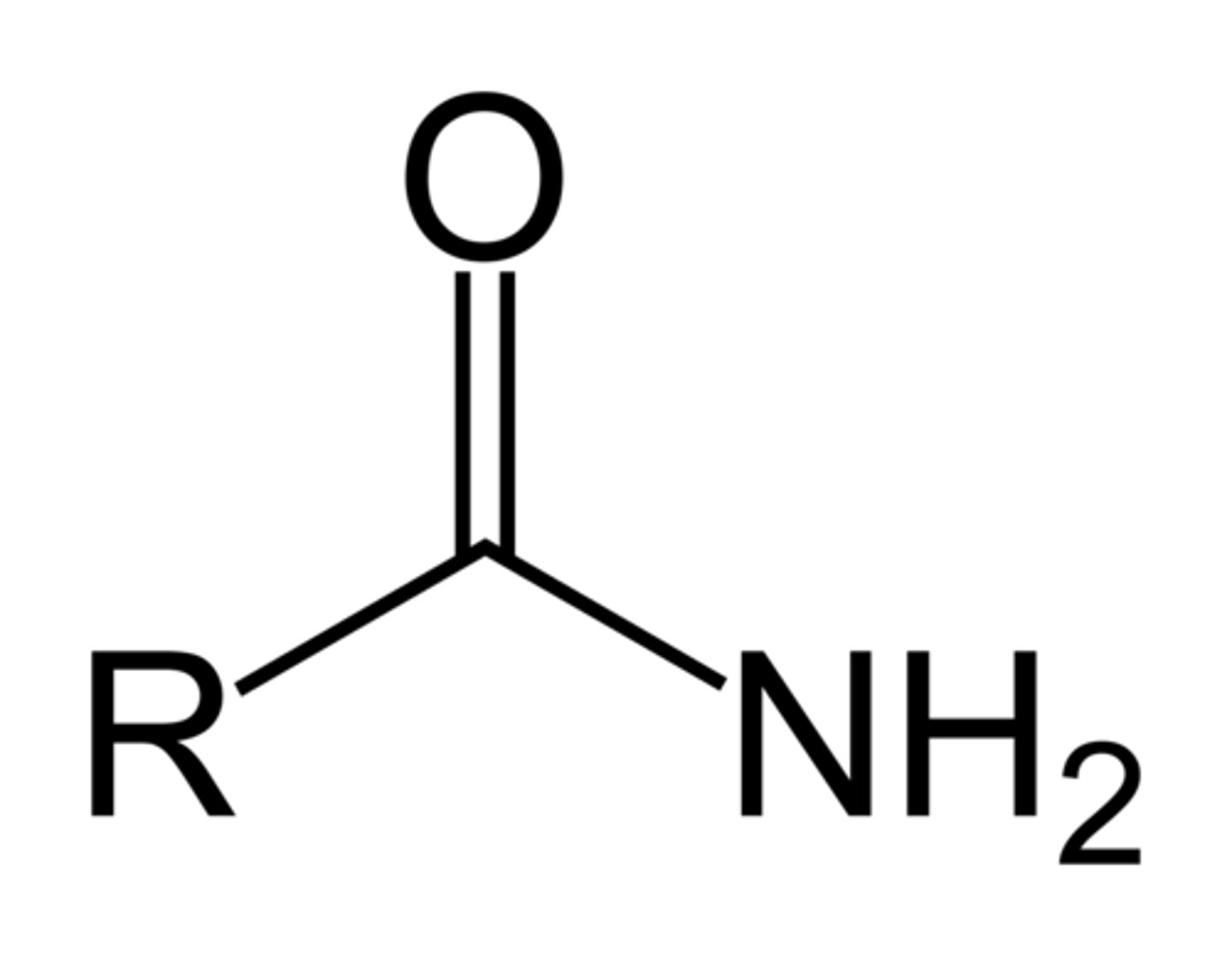
Anhydride
A functional group containing two carbonyls separated by an oxygen atom (RCOOCOR); often the condensation dimer of a carboxylic acid.
Aryl
organic halide in which the halogen atom is attached to an aromatic ring, such as a benzene ring
Halogens (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine) are nonmetal elements that are highly electronegative and reactive.
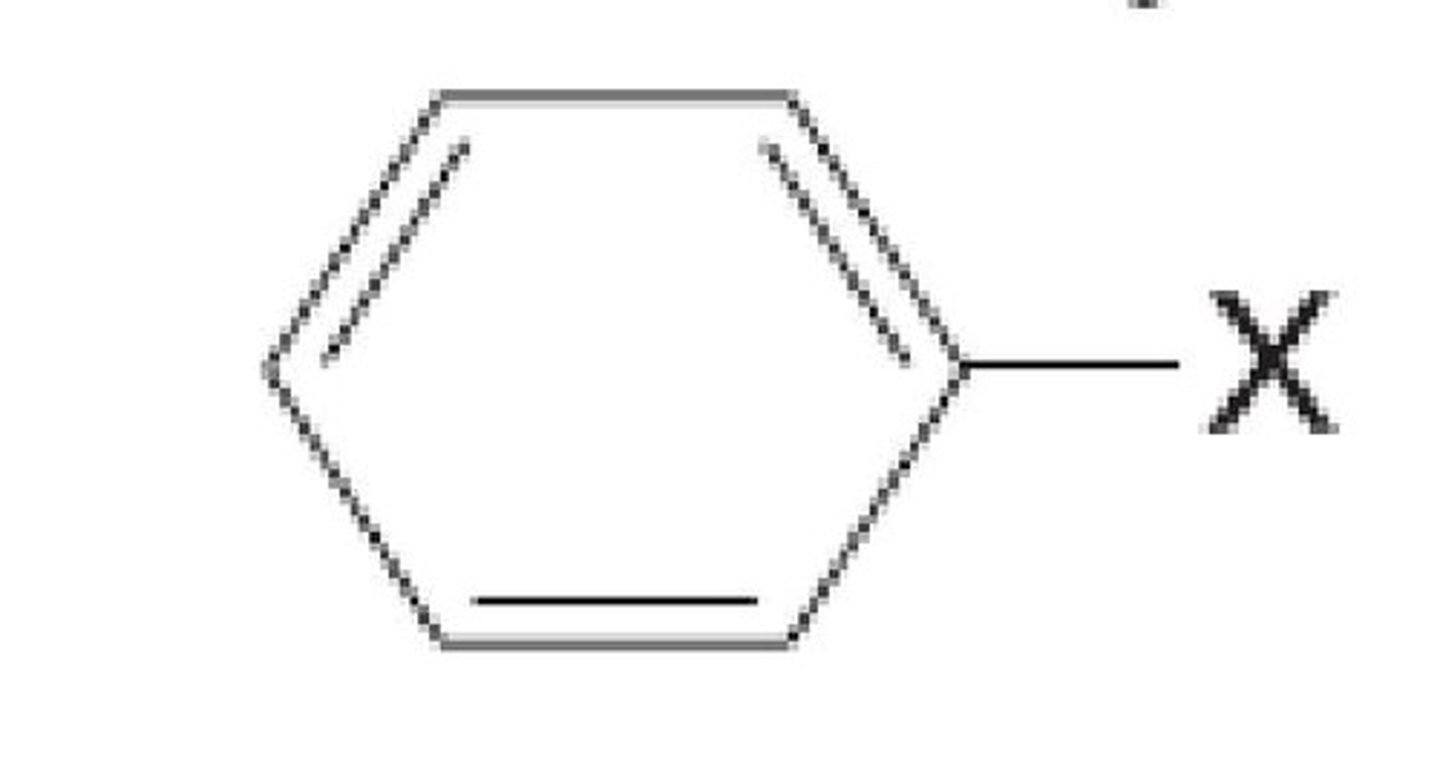
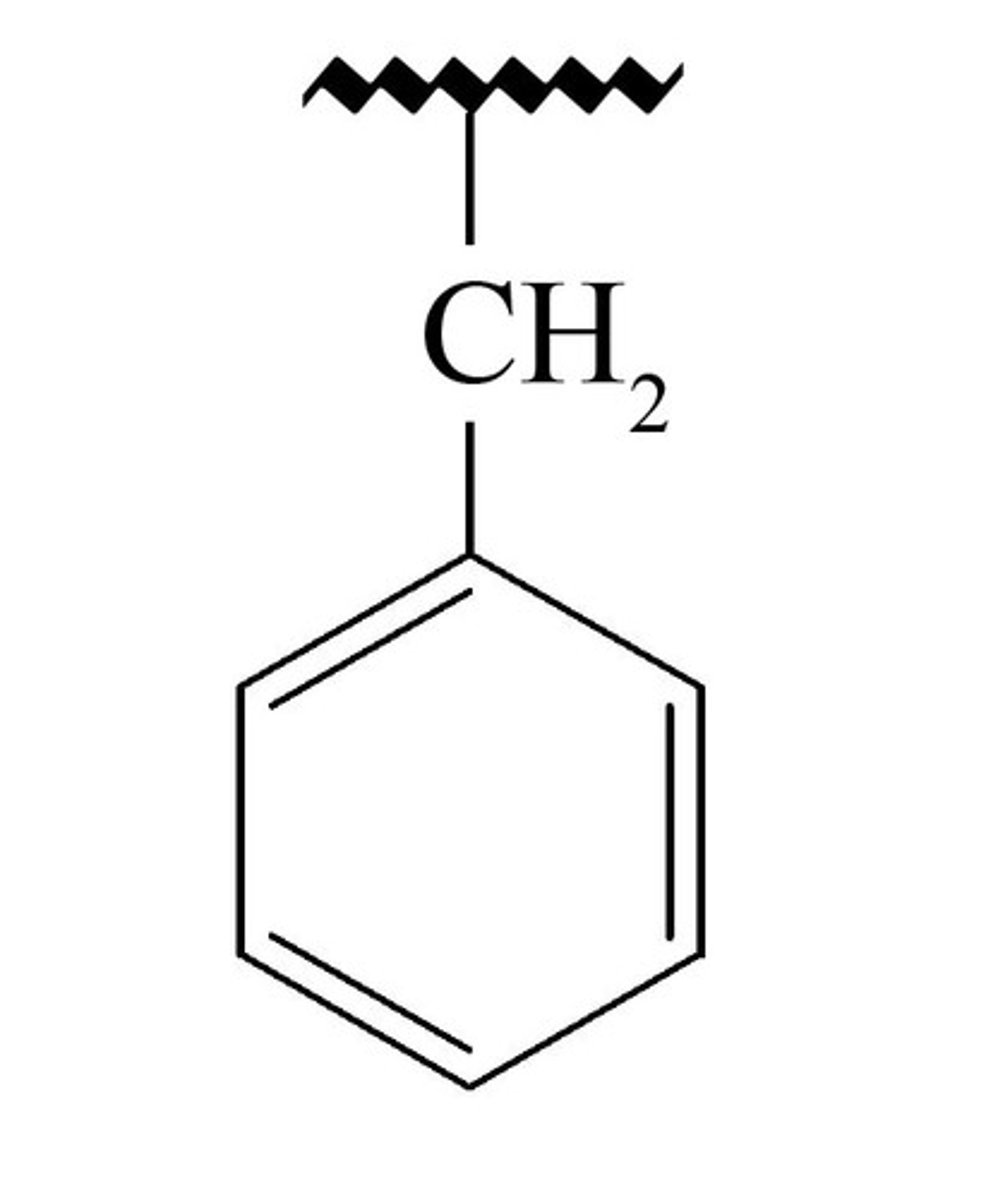
Benzyl
benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure C6H5CH2-. Benzyl features a benzene ring attached to a CH2 group.
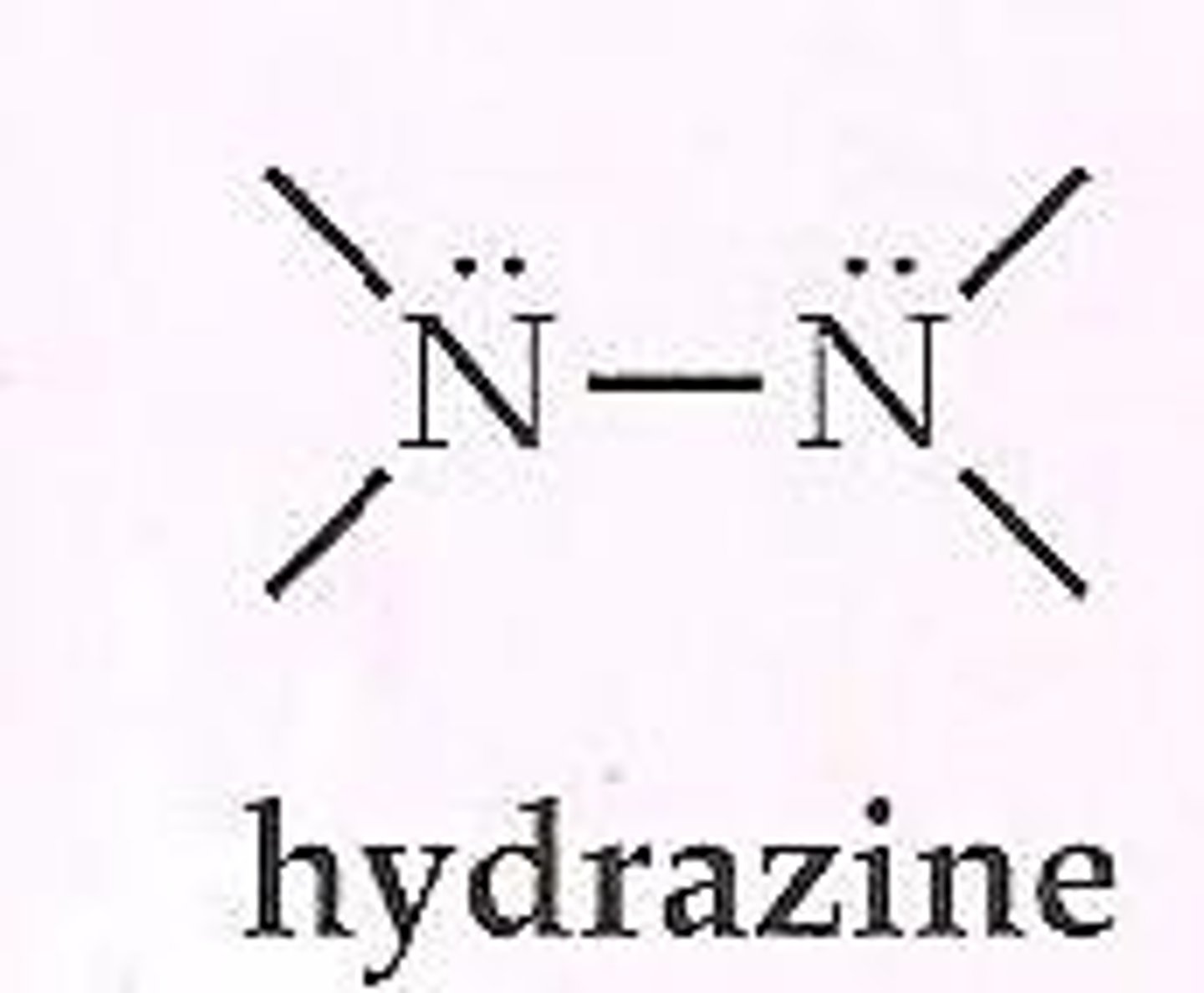
Hydrazine
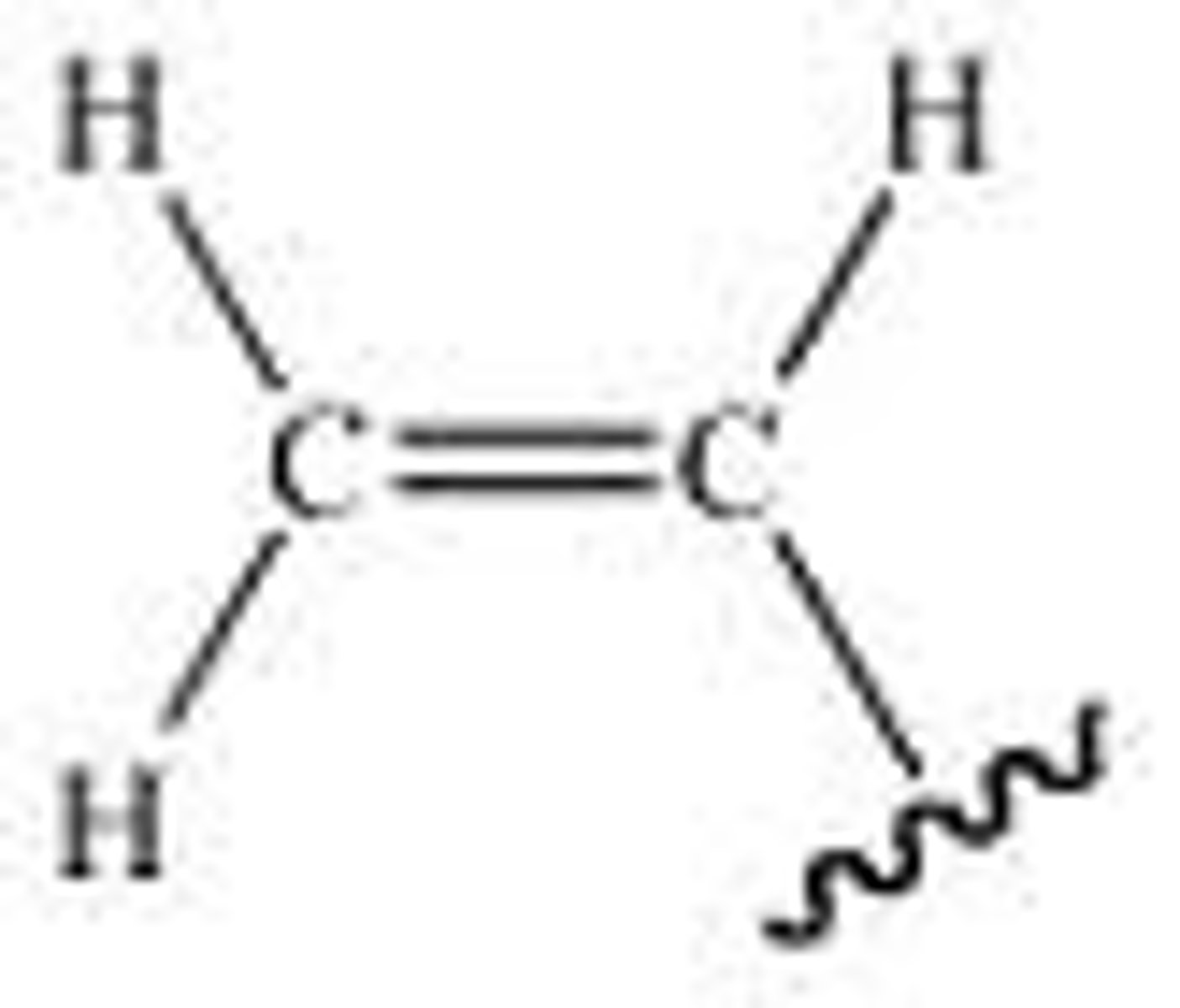
Vinyl
vinyl or ethenyl is the functional group −CH=CH2, namely the ethylene (IUPAC ethene) molecule (H2C=CH2) minus one hydrogen atom. The name is also used for any compound containing that group, namely R−CH=CH2 where R is any other group of atoms.
Allyl
An allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula H2C=CH-CH2R, where R is the rest of the molecule
Nitrile
A nitrile is an organic chemical that contains a cyano functional group (subunit), CN-, in which the carbon and nitrogen atoms have a triple bond i.e. C≡N-. The general chemical formula of a nitrile is RCN, where R is the organic group.
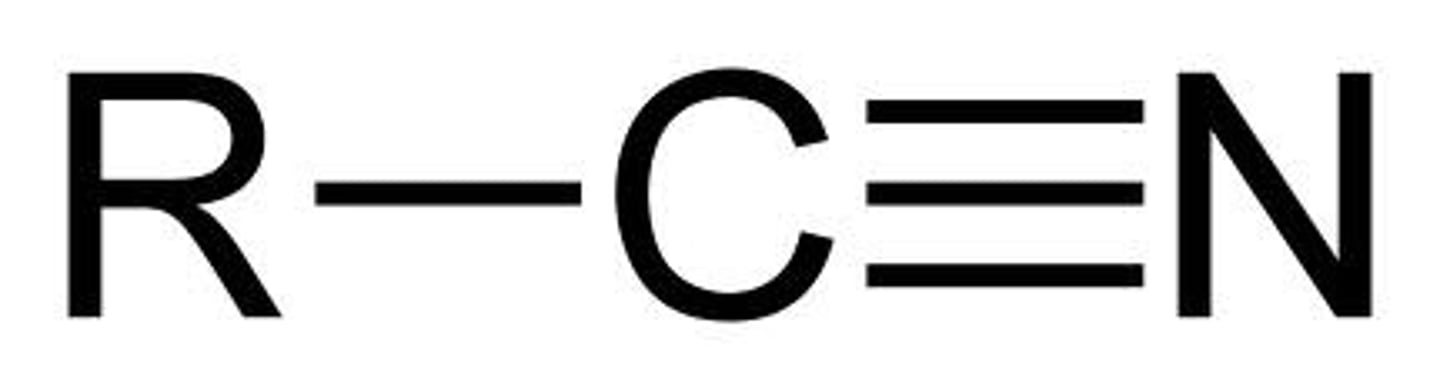
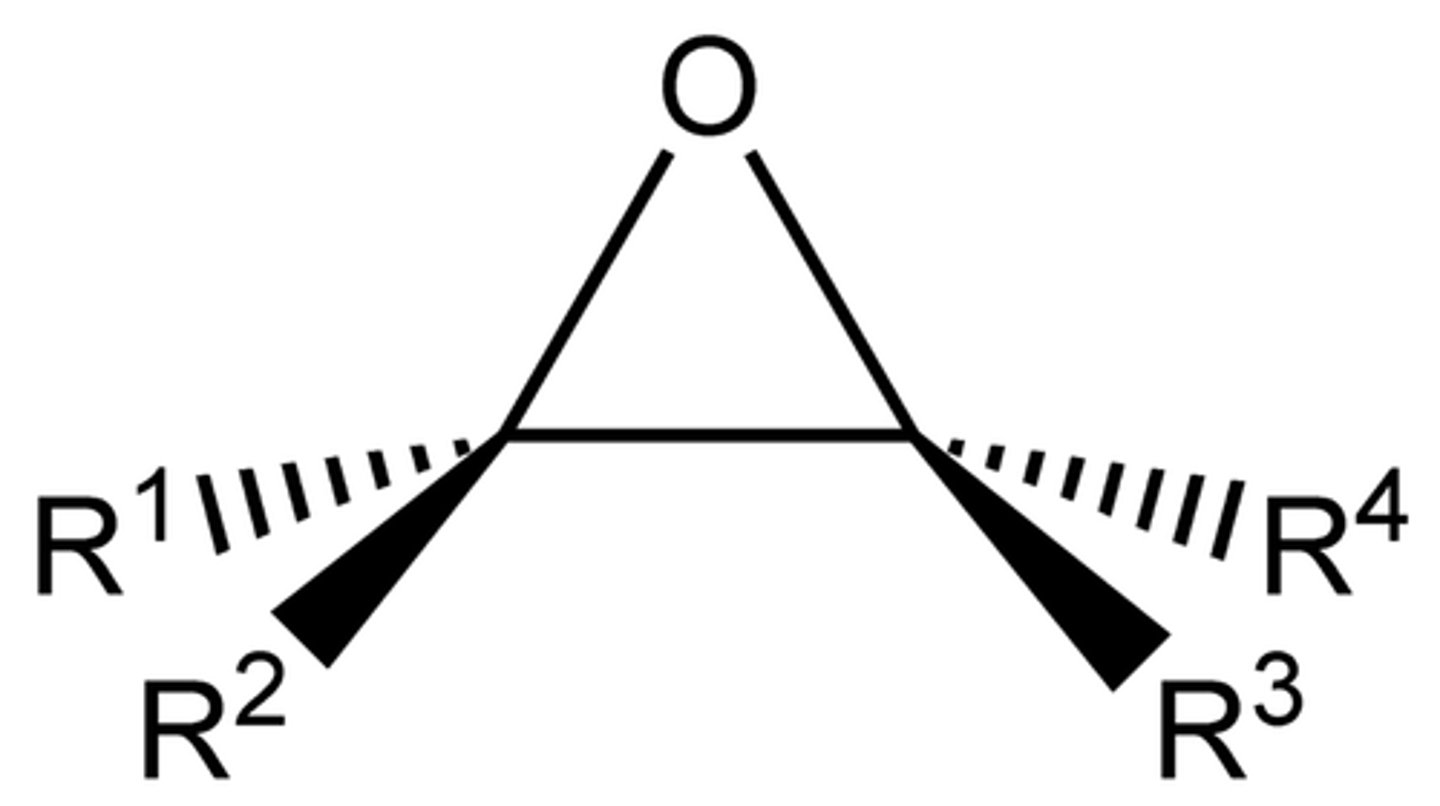
Epoxide
`
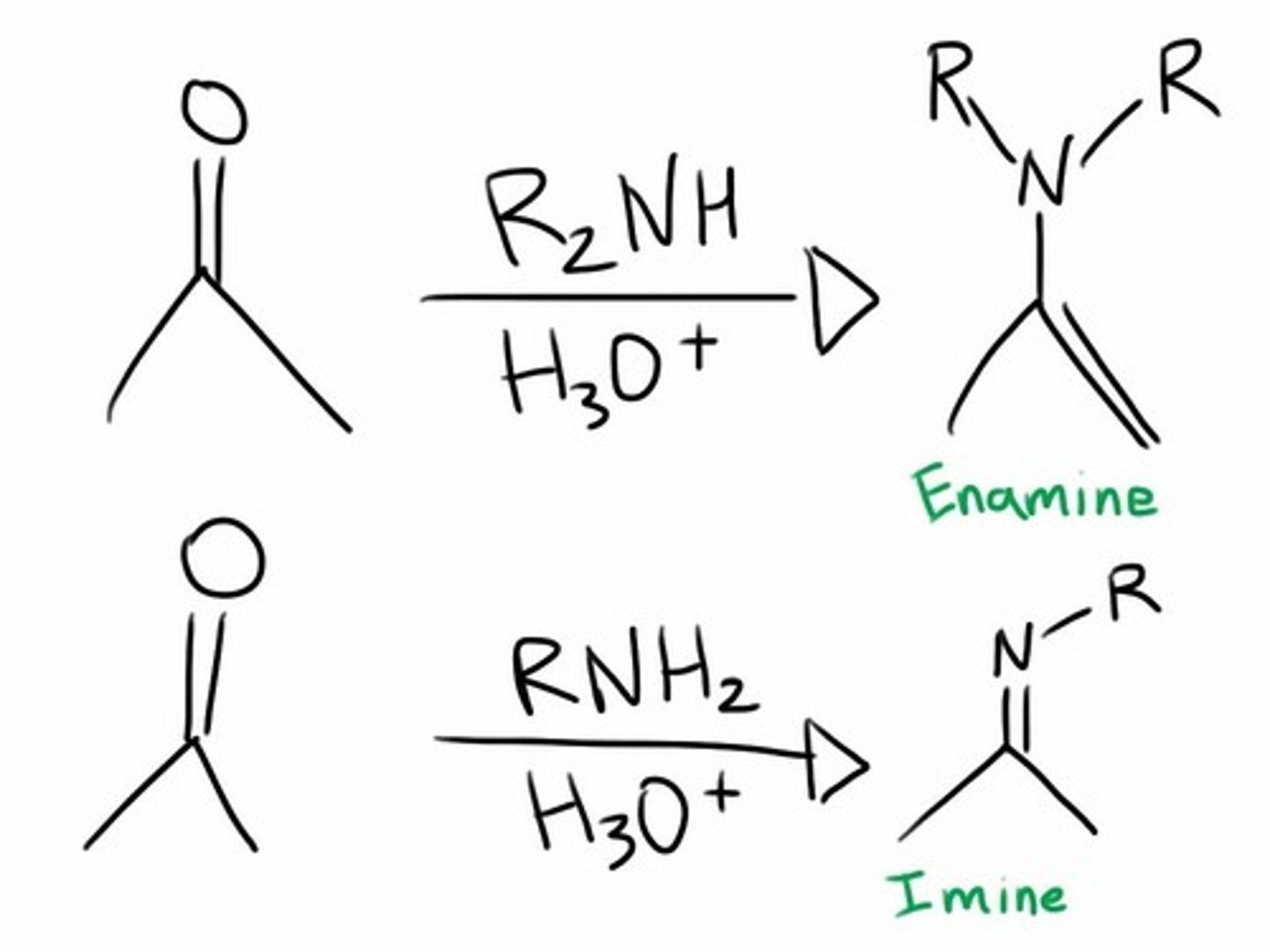
Enamine/Imine
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine. Enamines are considered to be nitrogen analogs of enols. If one of the nitrogen substituents is a hydrogen atom, H, it is the tautomeric form of an imine.
Acyl
a functional group derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid,[1] including inorganic acids. It contains a double bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group.
![<p>a functional group derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid,[1] including inorganic acids. It contains a double bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/aecca386-2213-4d38-89bc-8ab7ff37356f.png)
Aromatic
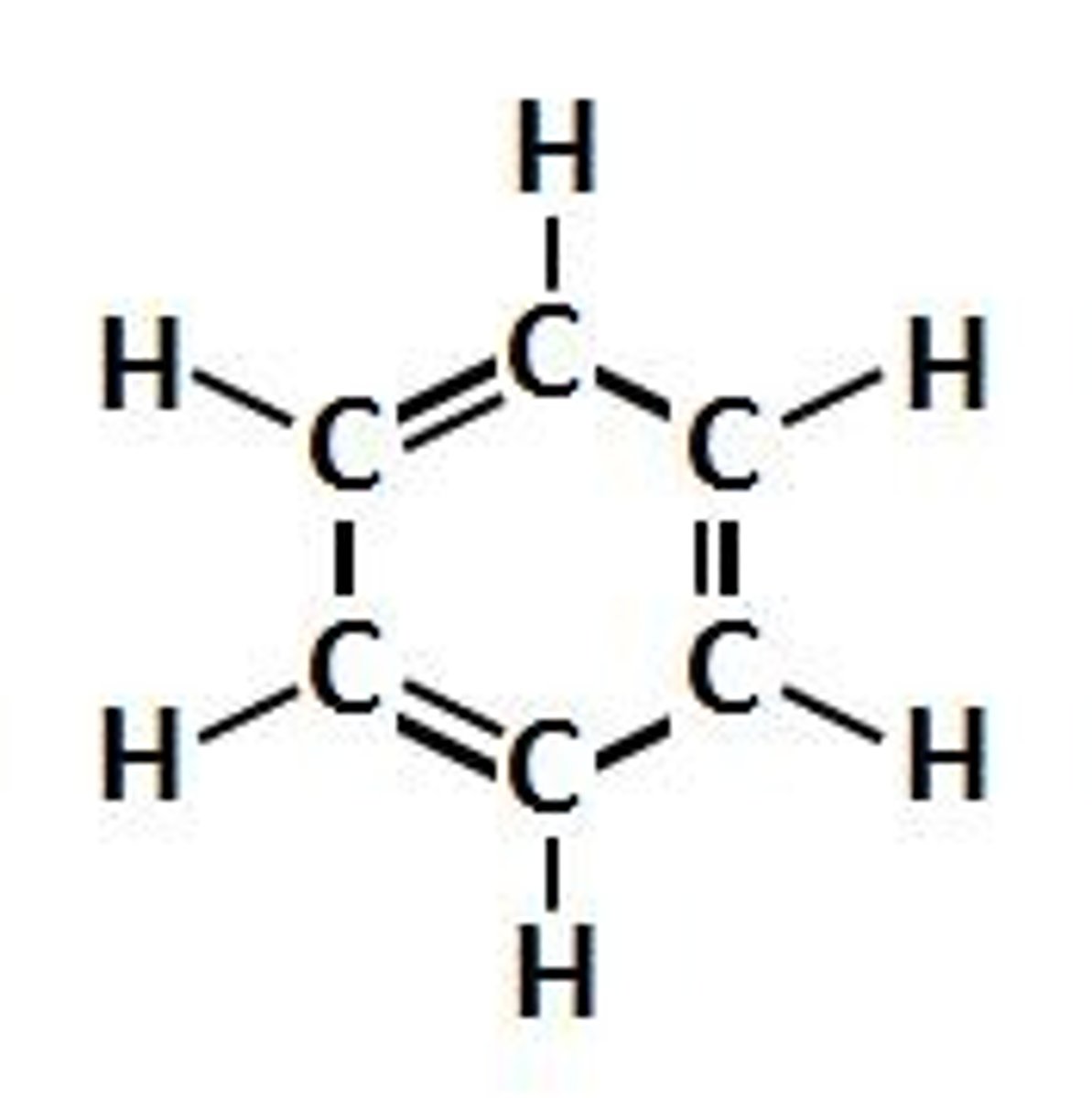
Aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons (compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds also known as non-aromatic compounds.
Aliphatics can be cyclic, but only aromatic compounds contain an especially stable ring of atoms, such as benzene.
Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like Hexane, or unsaturated, like Hexene and Hexyne. Open-chain compounds (whether straight or branched) contain no rings of any type, and are thus aliphatic.
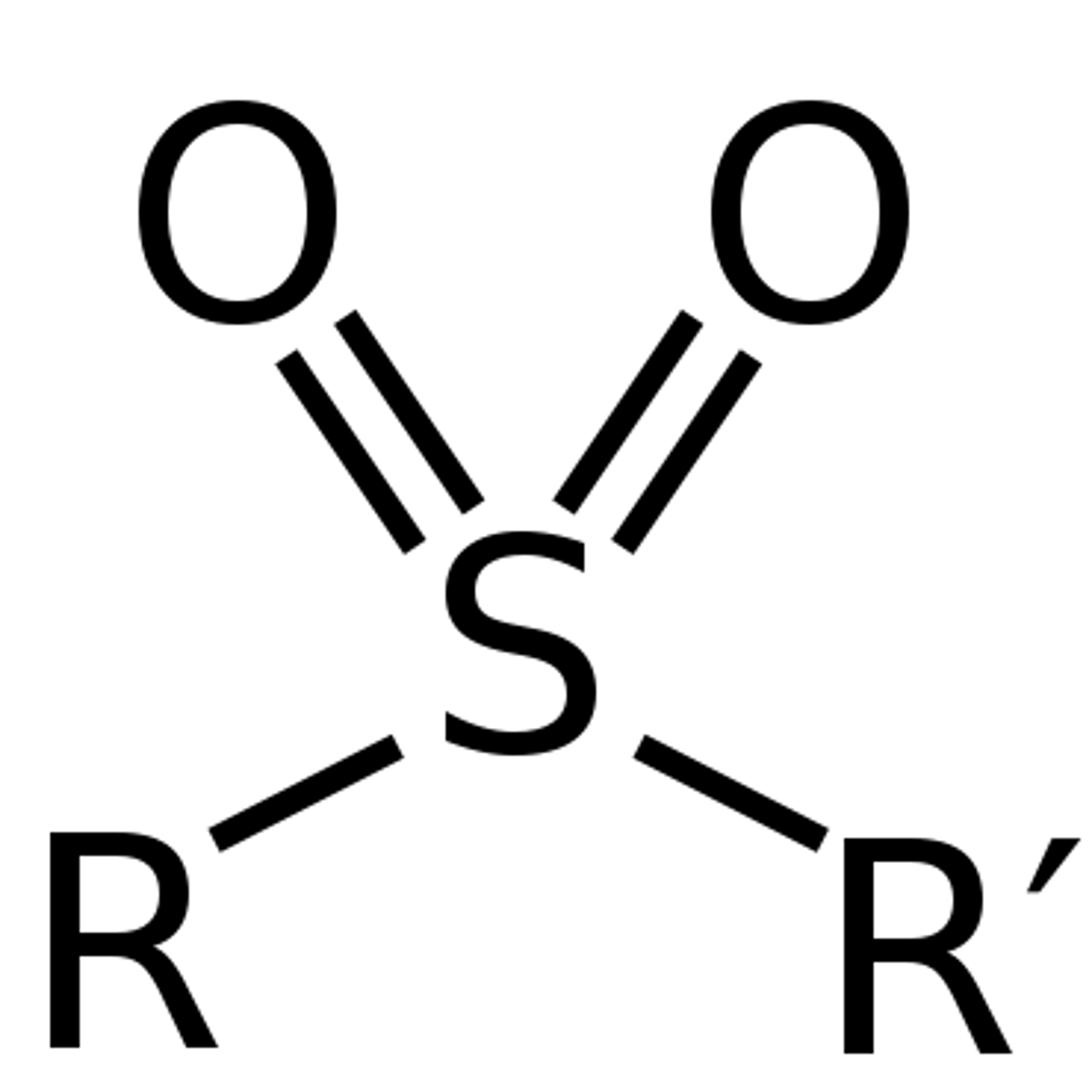
Sulphone
an organic compound containing a sulfonyl group linking two organic groups.
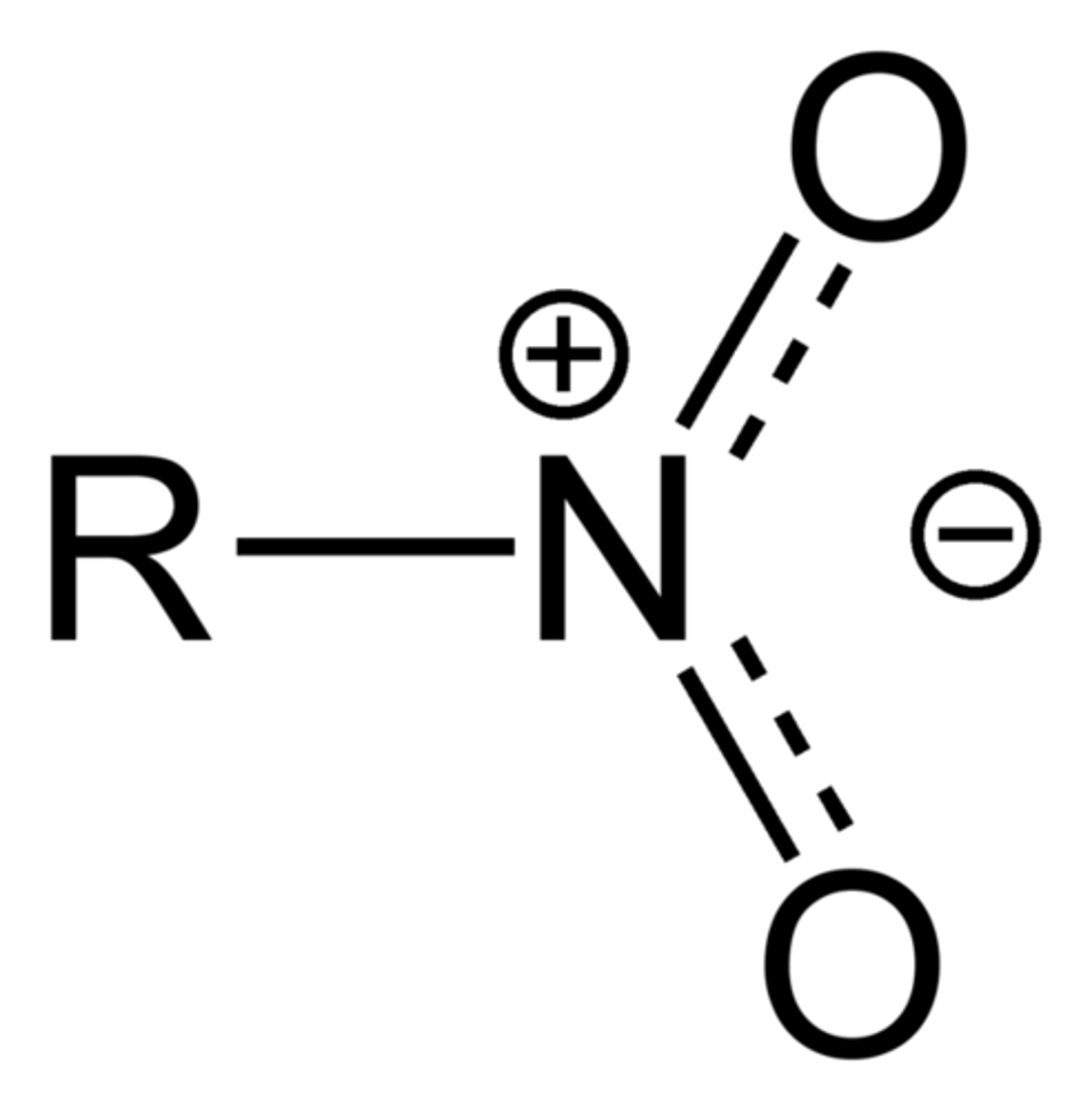
Nitro
Nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (−NO2). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing
Acetal
An acetal is a functional group with the following connectivity R2C(OR')2, where both R' groups are organic fragments.
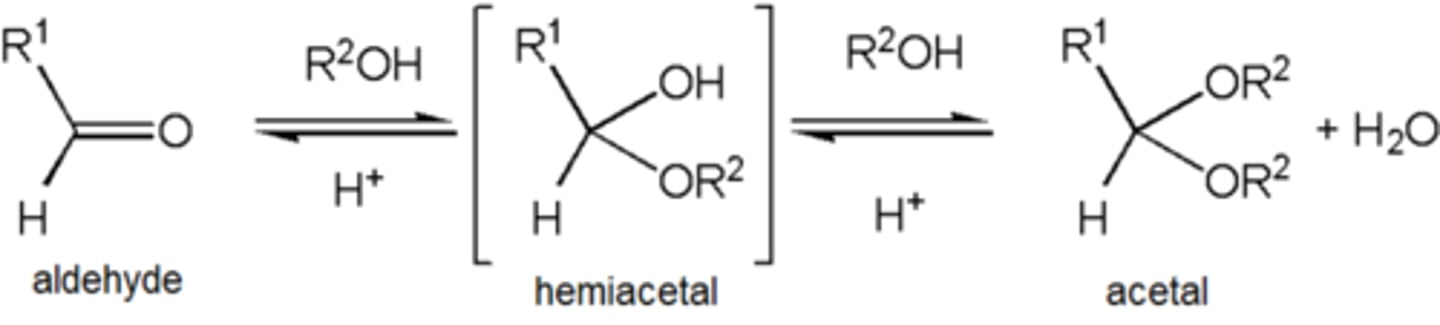
Ketal
term ketal is sometimes used to identify structures associated with ketones rather than aldehydes and, historically, the term acetal was used specifically for the aldehyde cases.
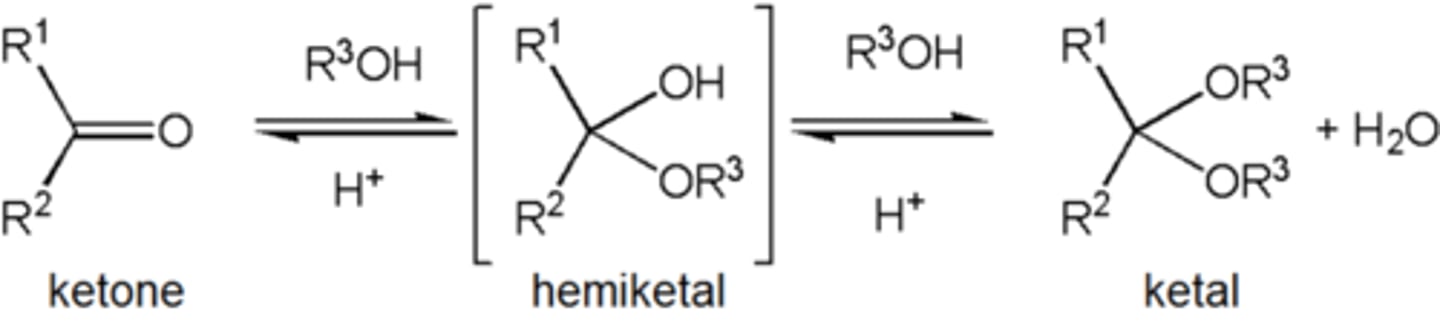
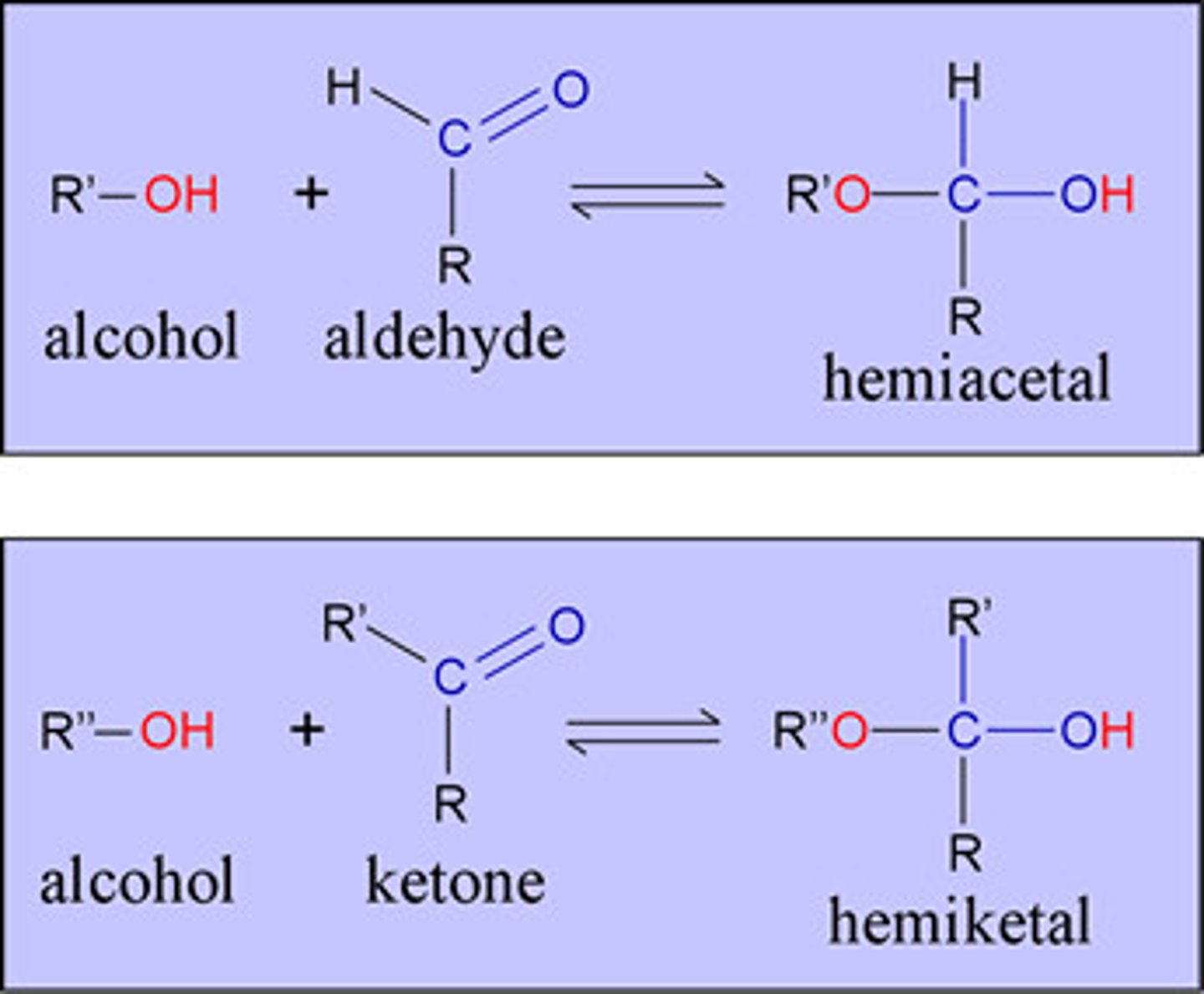
Hemiacetal
A functional group that contains a carbon atom bonded to one -OR group, one -OH group, an alkyl chain, and a hydrogen atom.
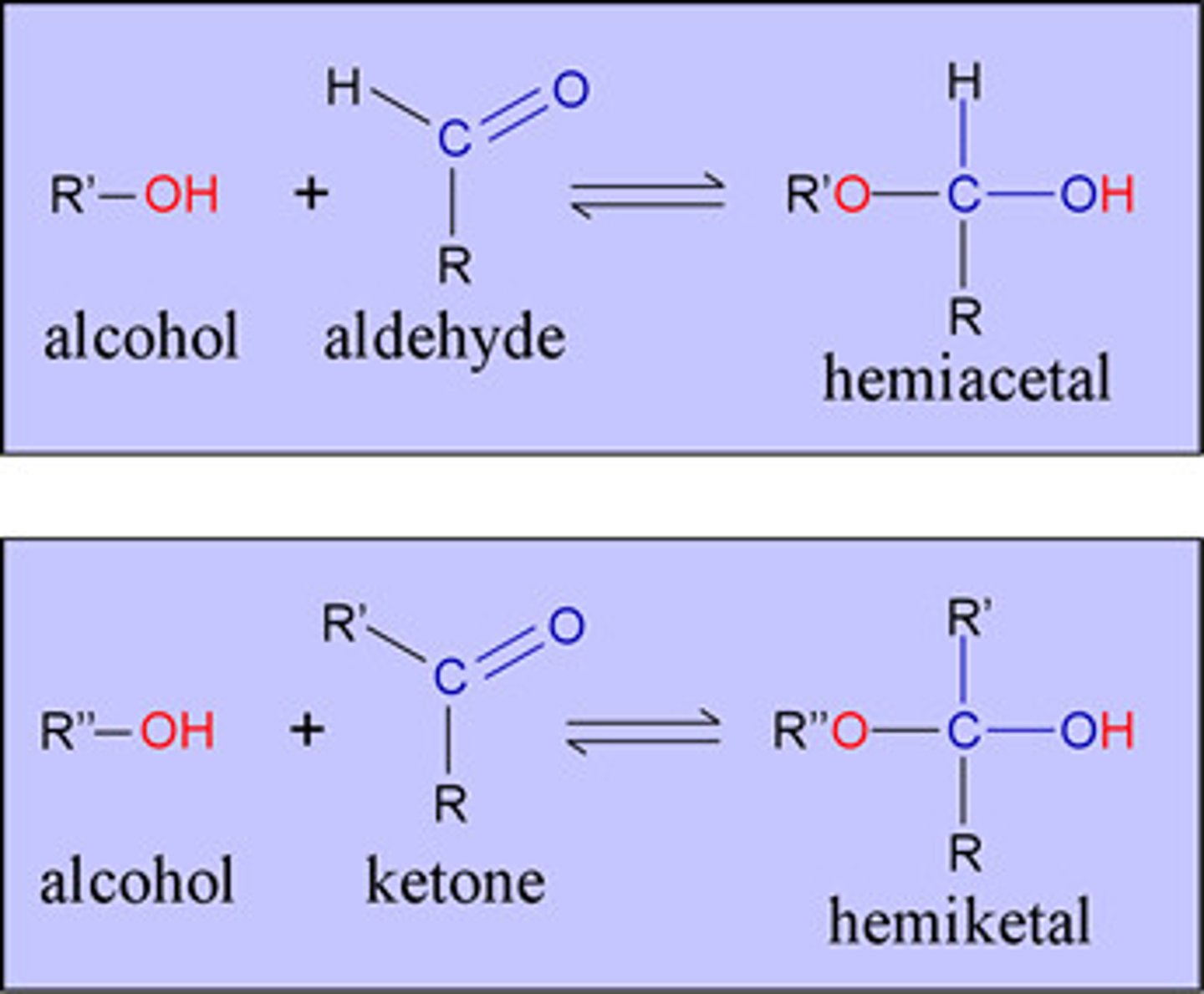
Hemiketal
A carbon atom bonded to two alkyl groups, an -OR group, and an -OH group
Meth
1
eth
2
prop
3
but-
4
pent-
5
hex-
6
hept-
7
oct-
8
non-
9
dec-

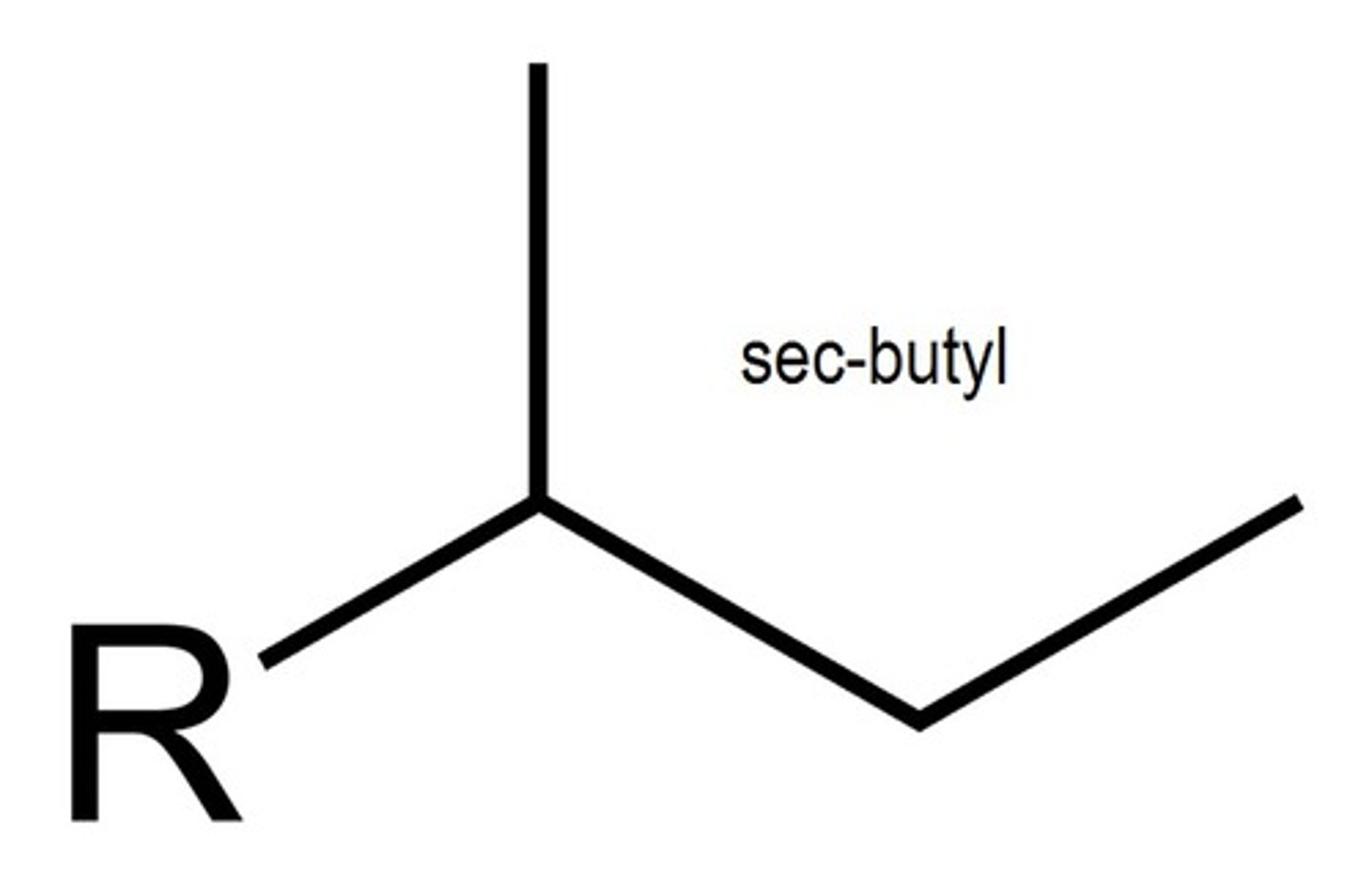
sec-butyl
isopropyl
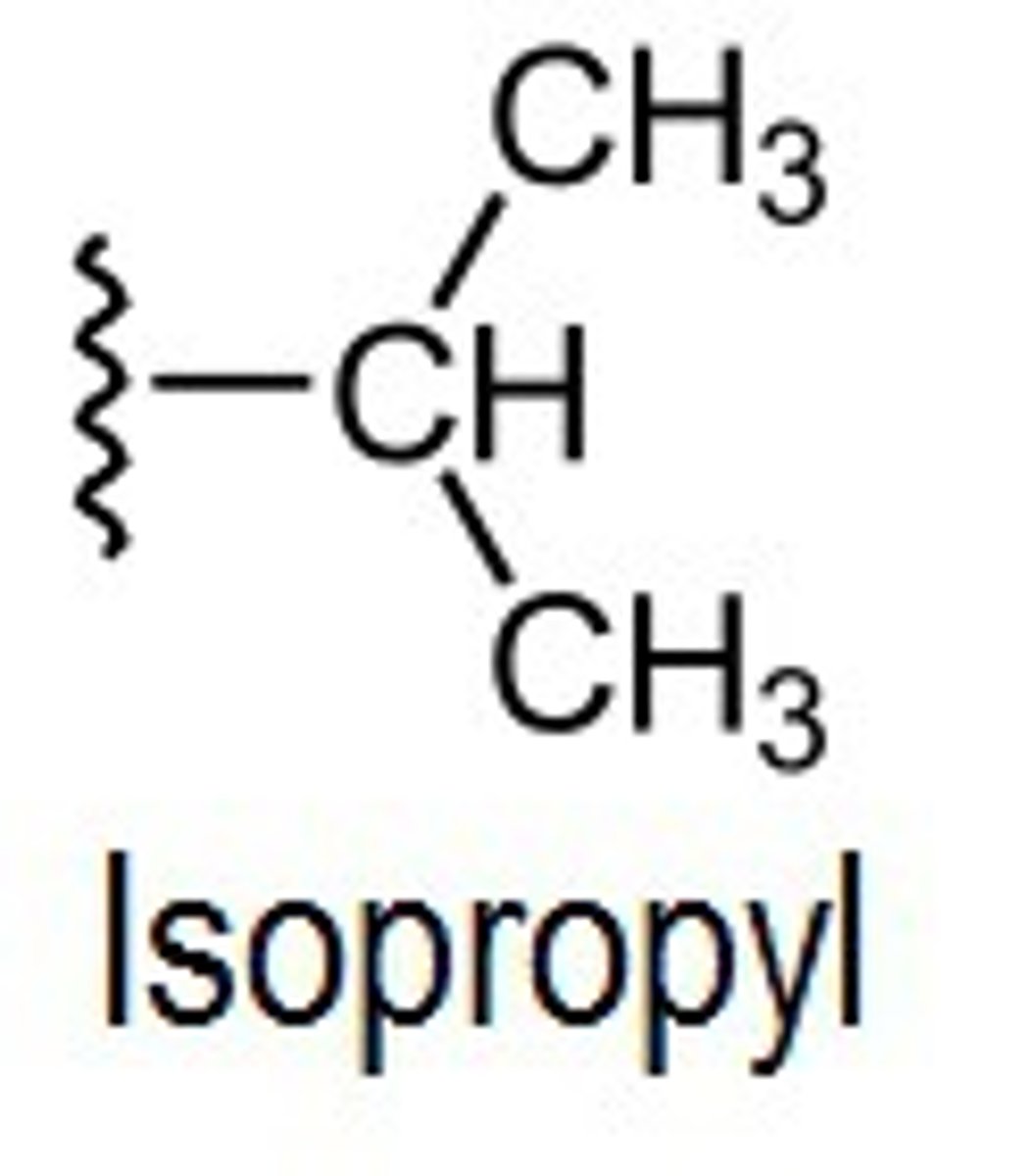
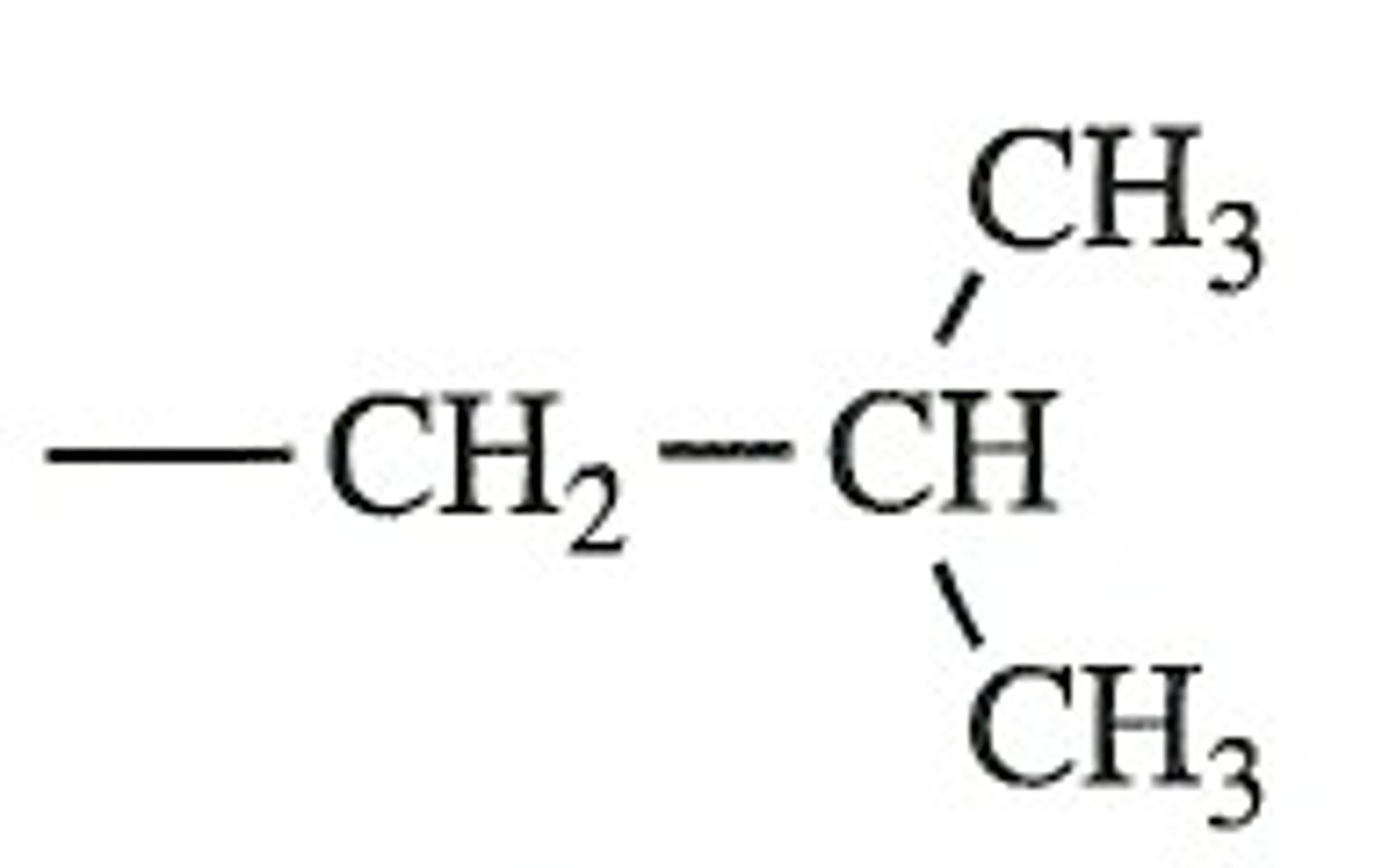
isobutyl
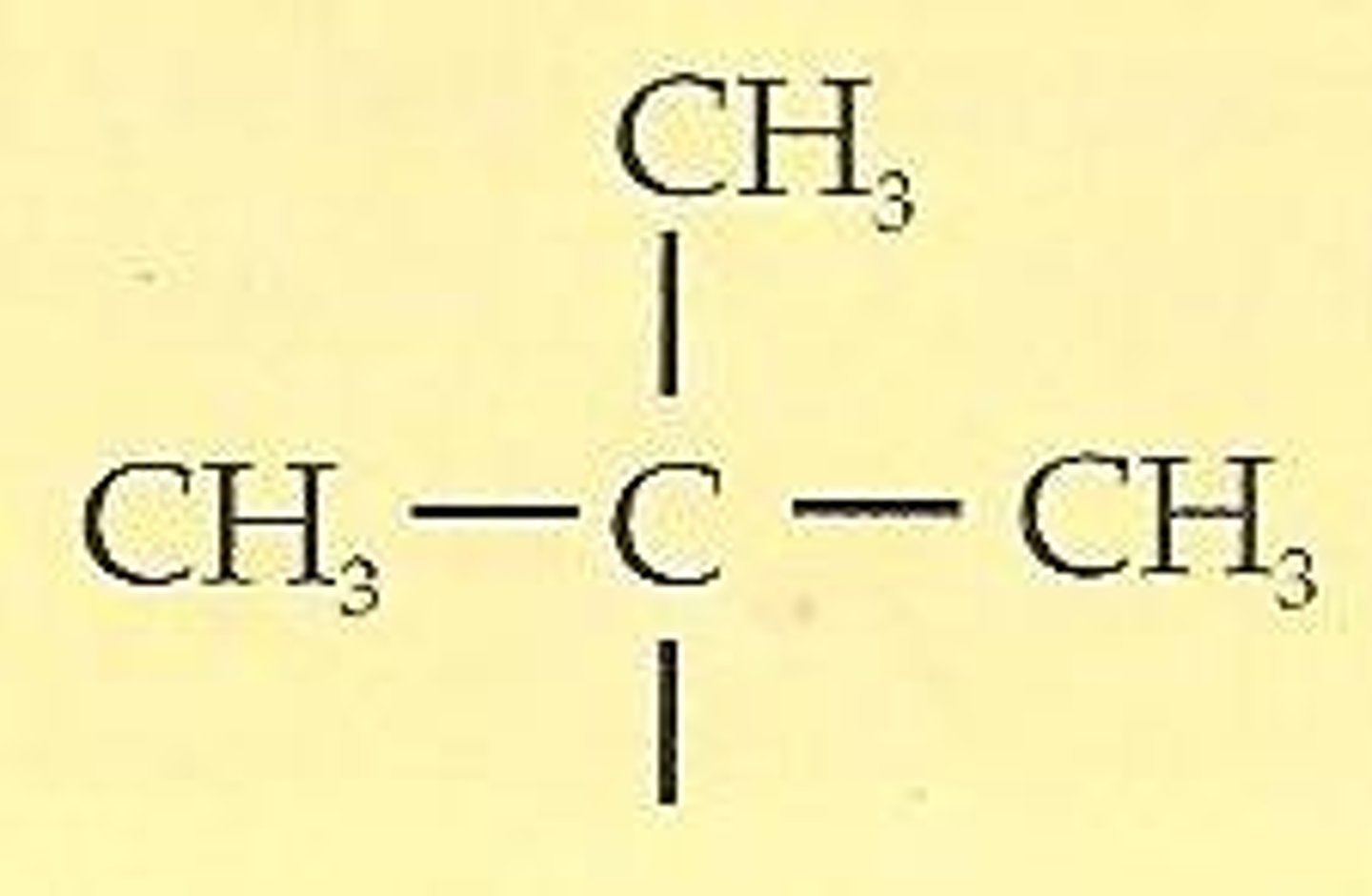
tert-butyl
IUPAC RULES
IUPAC Rules:
1) Find the longest carbon chain.
• If there is a tie, the one with the most substituents is the parent chain.
2) The terminal carbon closest to a substituent is numbered #1.
• If there is a tie, look at the second substituent.
3) Order the substituents alphabetically and give each one a number to match the carbon to which it is attached
4) If more than one of the same substituent is present, use the prefixes di, tri, tetra, etc. (i.e., 2,2- dimethylbutane).
5) When to use hyphens:
• Hyphens are placed before and after substituent numbers, but NOT between standard prefixes.
6) Rules for alphabetizing:
• Do NOT consider the prefix when alphabetizing the substituents if:
1) it represents a number (di-, tri-, etc.) or 2) it includes a hyphen (sec-, tert-, etc.). Do alphabetize other prefixes (isopropyl, isobutyl, etc.).