EXAM I HEARING TESTS
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
audiology birthplace
WWII military hospitals
Parents of audiology
Otology, speech language pathology
Father of audiology
Raymond Carhart
Unit of frequency
Hz
Unit of Pressure
Pa
Unit of Force
Newton (N)
Impedance
resistance to the flow of energy, combining resistance and reactance in a syste
dB SPL
referenced to 20 µPa; used to measure actual sound pressure in ai
dB HL
referenced to average normal hearing; used in audiograms to show hearing thresholds.
dB SL
measures sound relative to a person’s threshold; used in testing speech or tones above threshold.
longitudinal wave
a wave where particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of wave trave
Transverse wave
a wave where particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
Measurable attributes of a soundwave
Frequency, amplitude, phase
Psychological correlates of physical soundwave attributes
Pitch, loudness
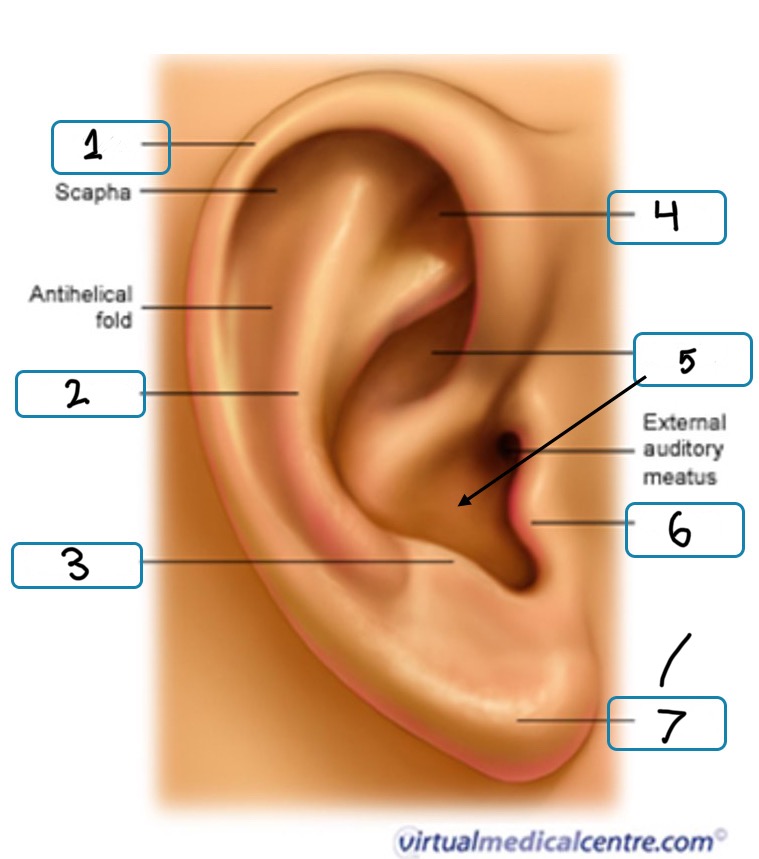
What is number 1
Helix
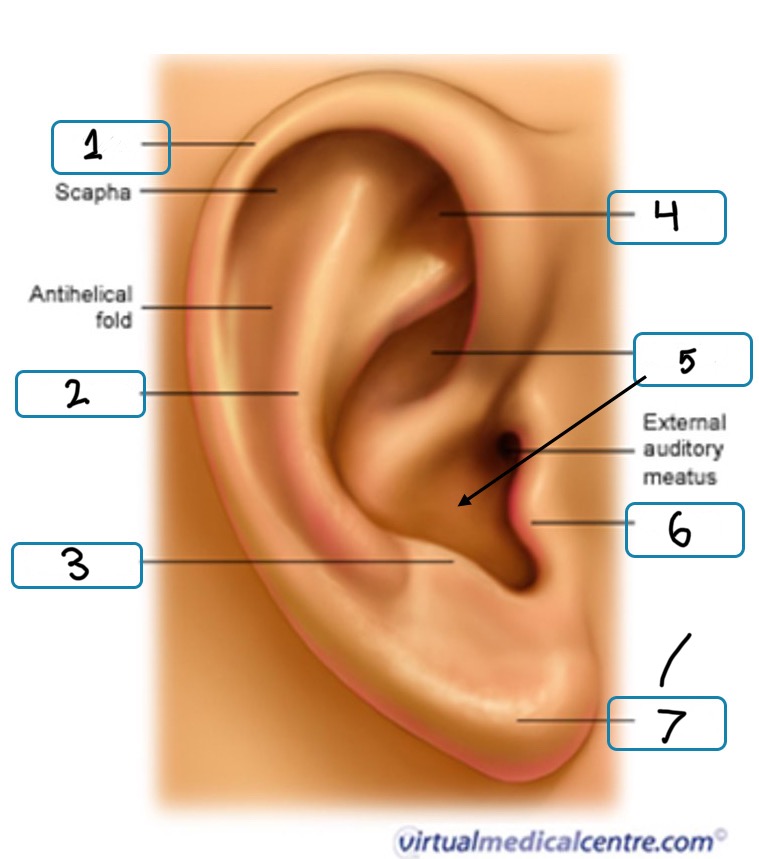
What is number 2
Antihelix
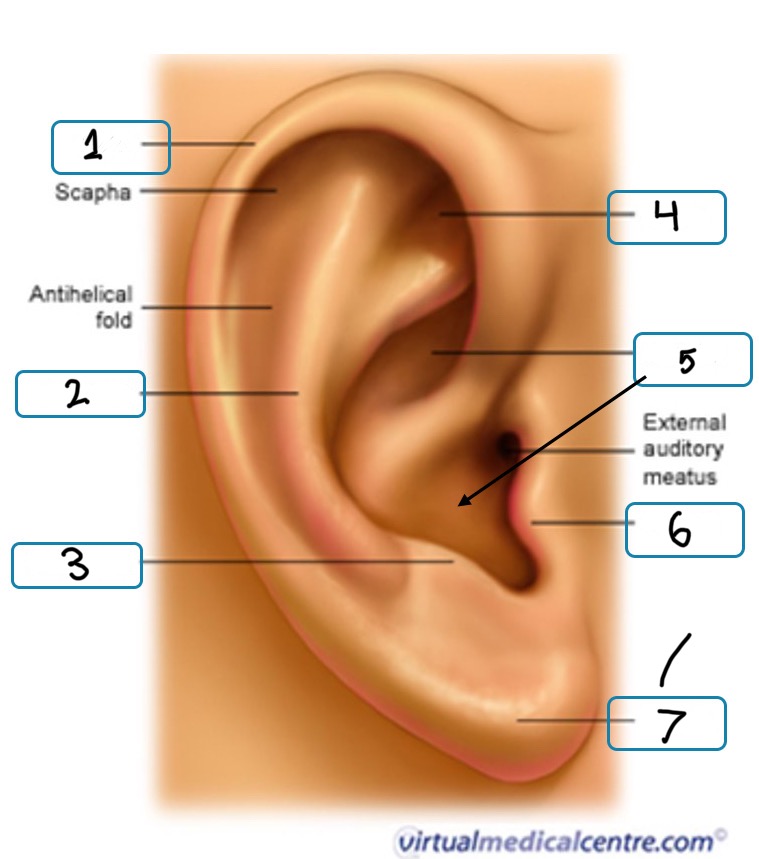
What is number 3
Antitragus
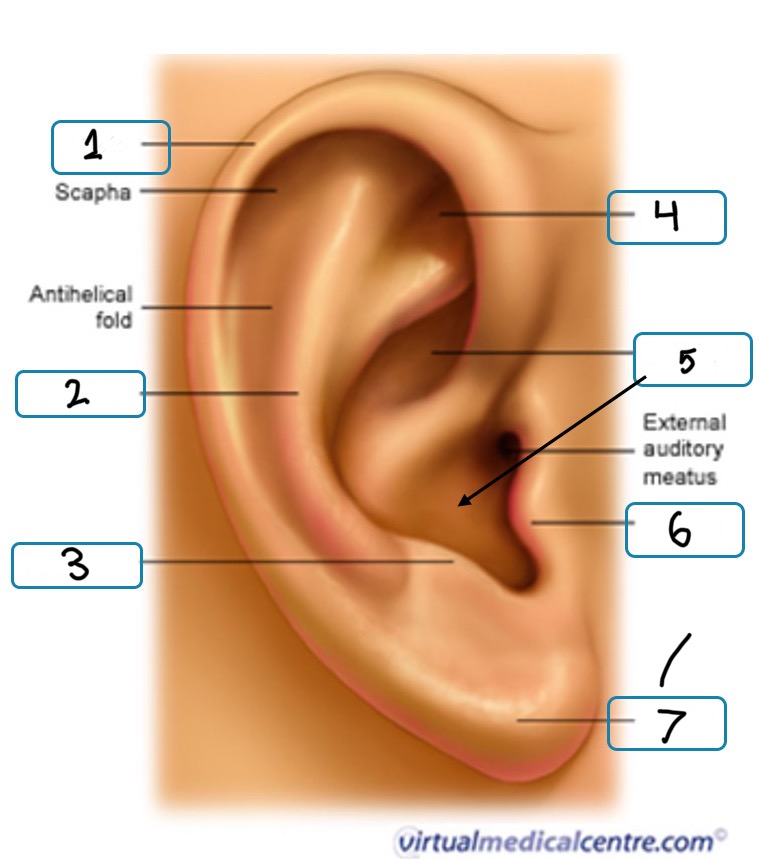
What is number 4
Fossa
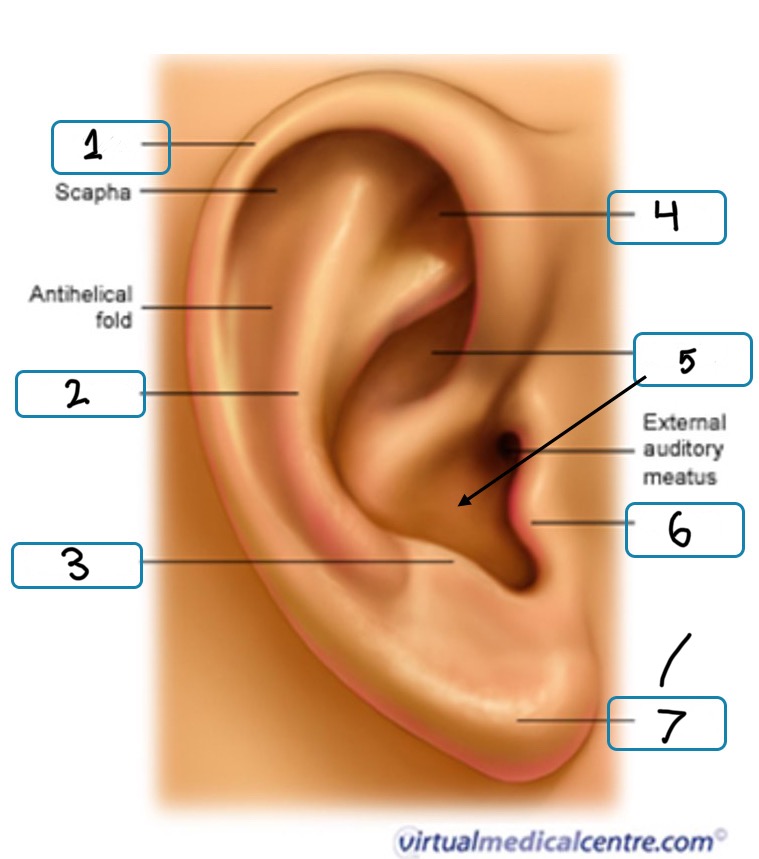
What is number 5
Concha
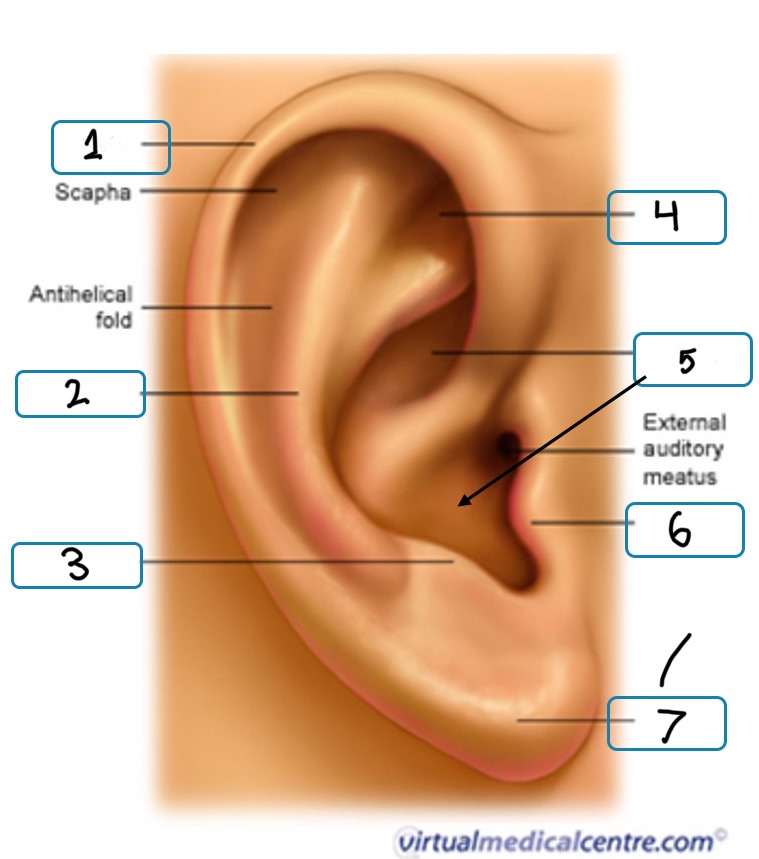
What is number 6
Tragus
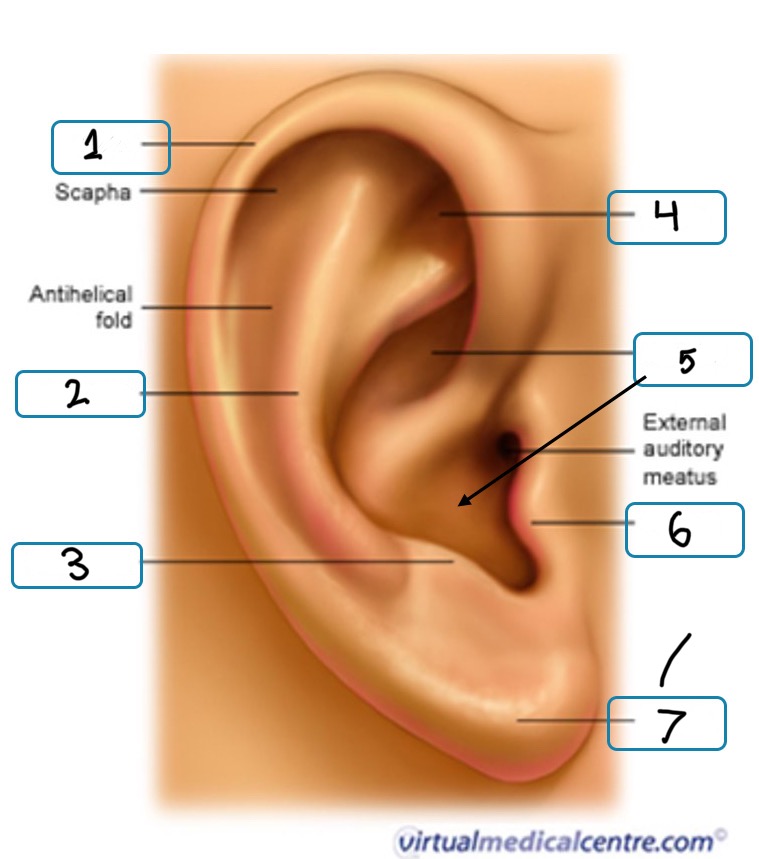
What is number 7
Lobule
Air bone gap
the difference between air conduction and bone conduction hearing thresholds.
What does an air bone gap suggest
a gap indicates a conductive hearing loss, meaning sound is not efficiently conducted through the outer or middle ear
Otoscopy landmarks
Manubrium, umbo, cone of light, annulus
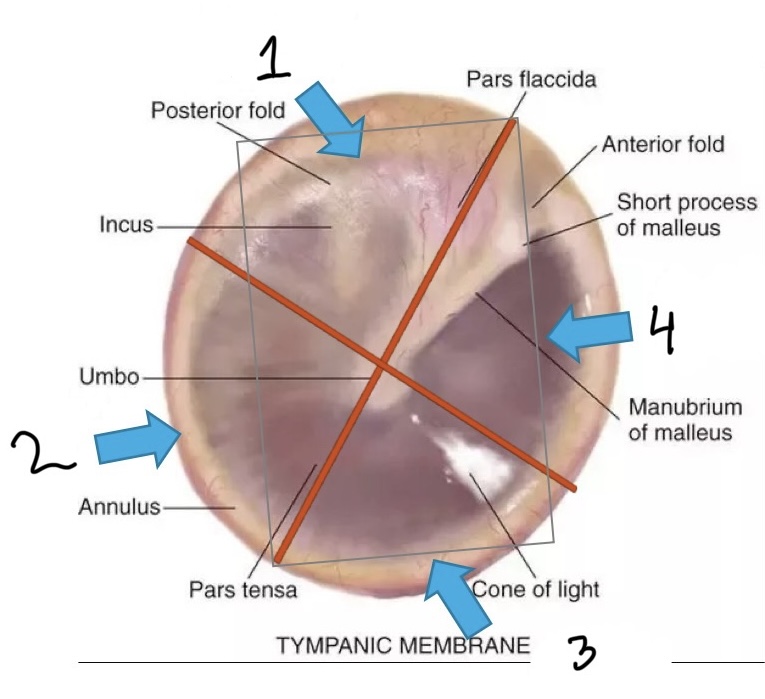
From 1-4, what quadrants are these?
Posterior superior, posterior inferior, anterior inferior, anterior superior
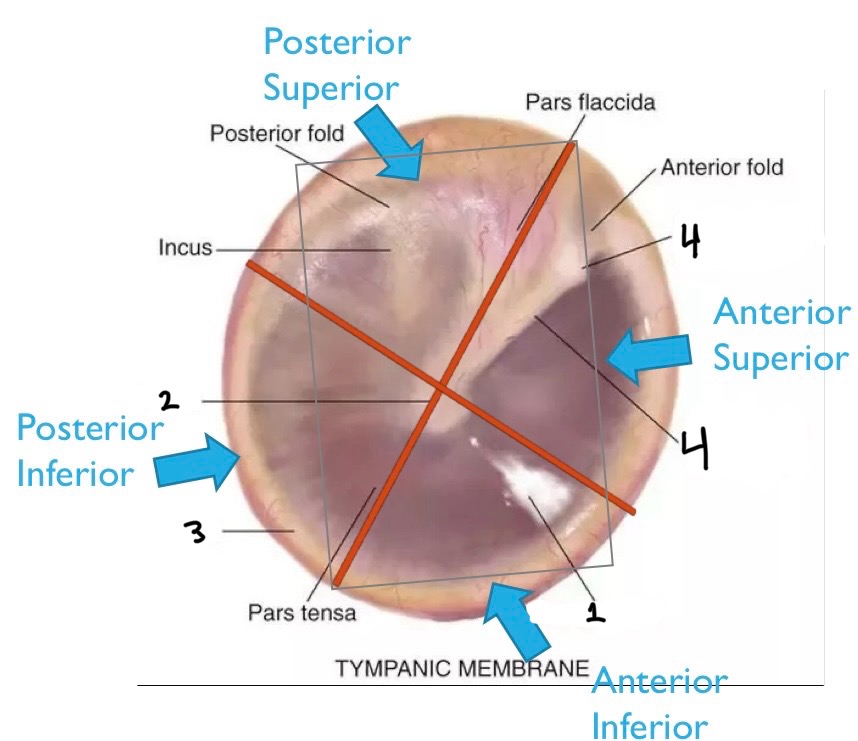
What is number one?
Cone of light
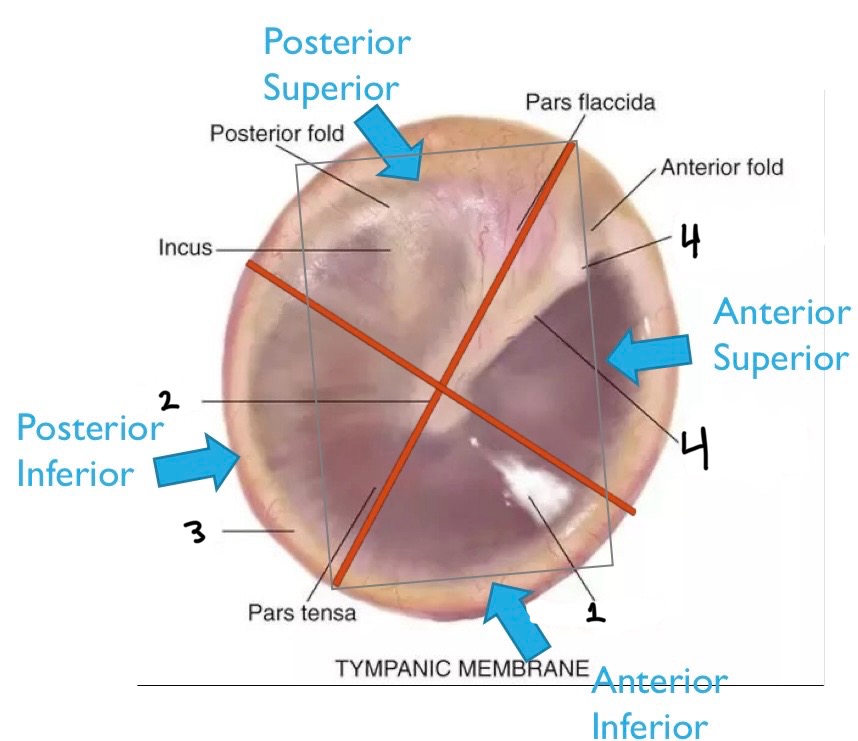
What is number two?
Umbo
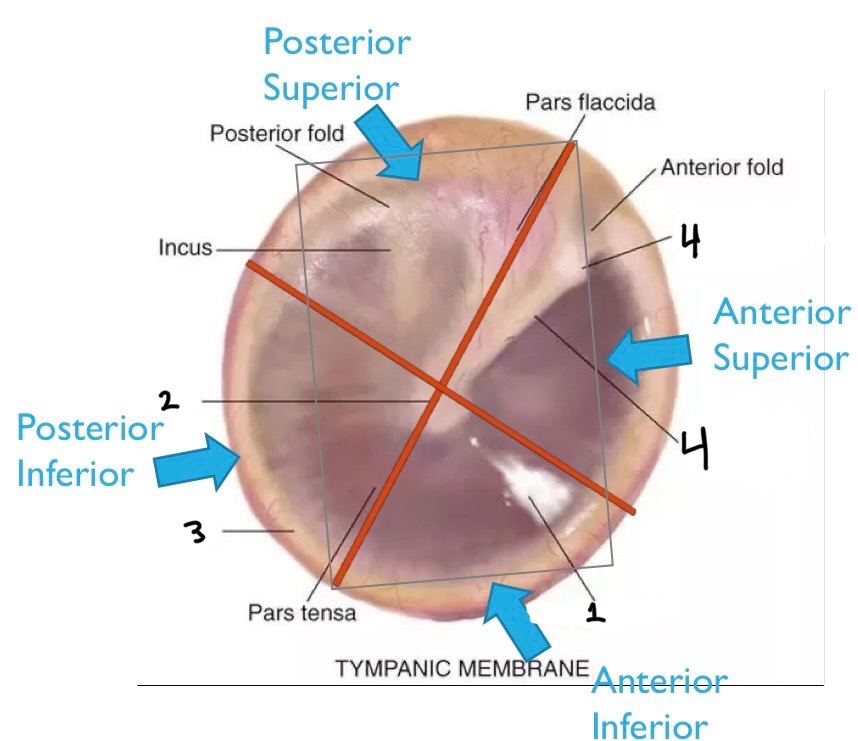
What is number three?
Annulus
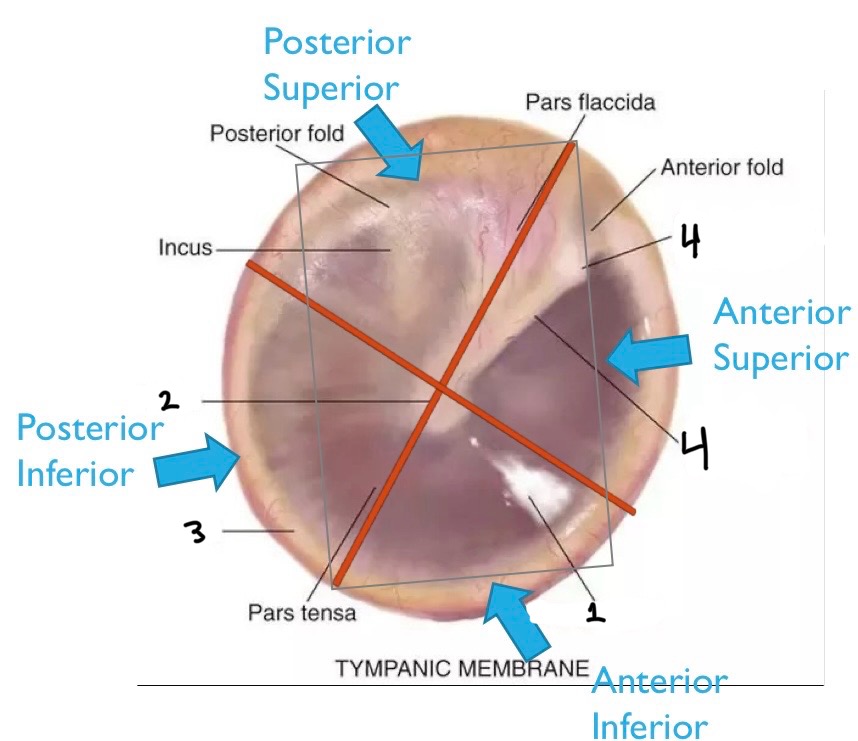
What is number four?
Malleus
Rinne test
Compares air vs bone conduction
Weber test
Checks lateralization
Bing test
Tests occlusion effect, negative result indicates conductive loss
Talk forward button
Lets clinician talk to client
Frequency selector switch
changes the pitch of the tone presented
Attenuator
Controls intensity of sound
Interrupter switch
Controls duration of signal
Output transducer
Converts oscillator electric energy to acoustic or vibratory energy
Interval size of standard frequencies on an audiogram
250, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000, 8000 Hz
Squares on an audiogram
5 dB on y axis and one octave on x axis
x axis of audiogram
Frequency from low to high
Y axis of audiogram
loudness from soft to loud
which ear do we test first
worse ear, in lieu of that right ear
frequencies tested in order
1000, 2000, 3000, 6000, 4000, 8000, 1000, 500, 250
What is PTA
Pure tone average, average of hearing thresholds
How is PTA measured
Averaging air conduction thresholds at 500, 1000, 2000 hz
When do you use 2 frequencies for PTA
One of the three frequencies is significantly worse
Threshold
the softest level of sound a person can hear at least 50% of the time during testing.
false positive
Raising hand even when they cannot hear anything
False negative
They can hear but do not respond
BC vs AC
BC is always better or equal
Calibration checks
Daily listening checks, behavioral checks, electroacoustic checks
Electroacoustic calibration technique
Set audiometer to 70 dB, check 70 dB + RETSPLs for earphones and RETFLs for bone vibrators
Pros and cons of forehead transducer placement
Easier to place, less variable results, more comfortable— con is that greater intensity is required to stimulate normal thresholds
Pinna disorders
Anotia, microtia, trauma to pinna, cancer
External auditory canal disorders
Atresia, stenosis, external otitis, excessive cerulean, collapsing ear canal
Tympanic membrane disorders
Perforations