Lab 5: gymnosperms
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Gymnospores are:
“naked seeds”. vascular plant with seeds that do not develop within an ovary
Dominant generation of gymnosperms
Sporophyte
What are the 4 phyla of gymnosperms?
1) cycads
2) gnetophyta
3) ginkgoes
4) conifers
Derived trait of gymnosperms (and angiosperms)
seeds
Seeds are:
Multicellular structure with embryo, food reserves, and protective coat
Benefits of seeds over spores
multicellular
germinate deeper in soil
more reserves for growth
What are the types of heterospores?
microspores: male (smaller)
megaspores: female (bigger)
Microspores form what?
Pollen (male gametophytes)
What are found inside the female ovule?
megaspore that produces archegonia (female gametophyte)
What carries sperm to the egg?
pollen tube (no swimming)
Adaptations of gymnosperms
vessels
vascular cambium (or lateral meristem)
cone arrangment/structure of gymnosperms
What does the vascular cambium do?
produces wood to allow for bigger/taller growth
Differentiate monoecious and dioecious
monoecious: one house (one plant has male/female reproductive structures)
dioecious: two houses (male/female reproductive structures on different plants)
What kind of reproductive structure system do cycads have?
Dioecious
Cycads produce:
cones (gymnosperm)
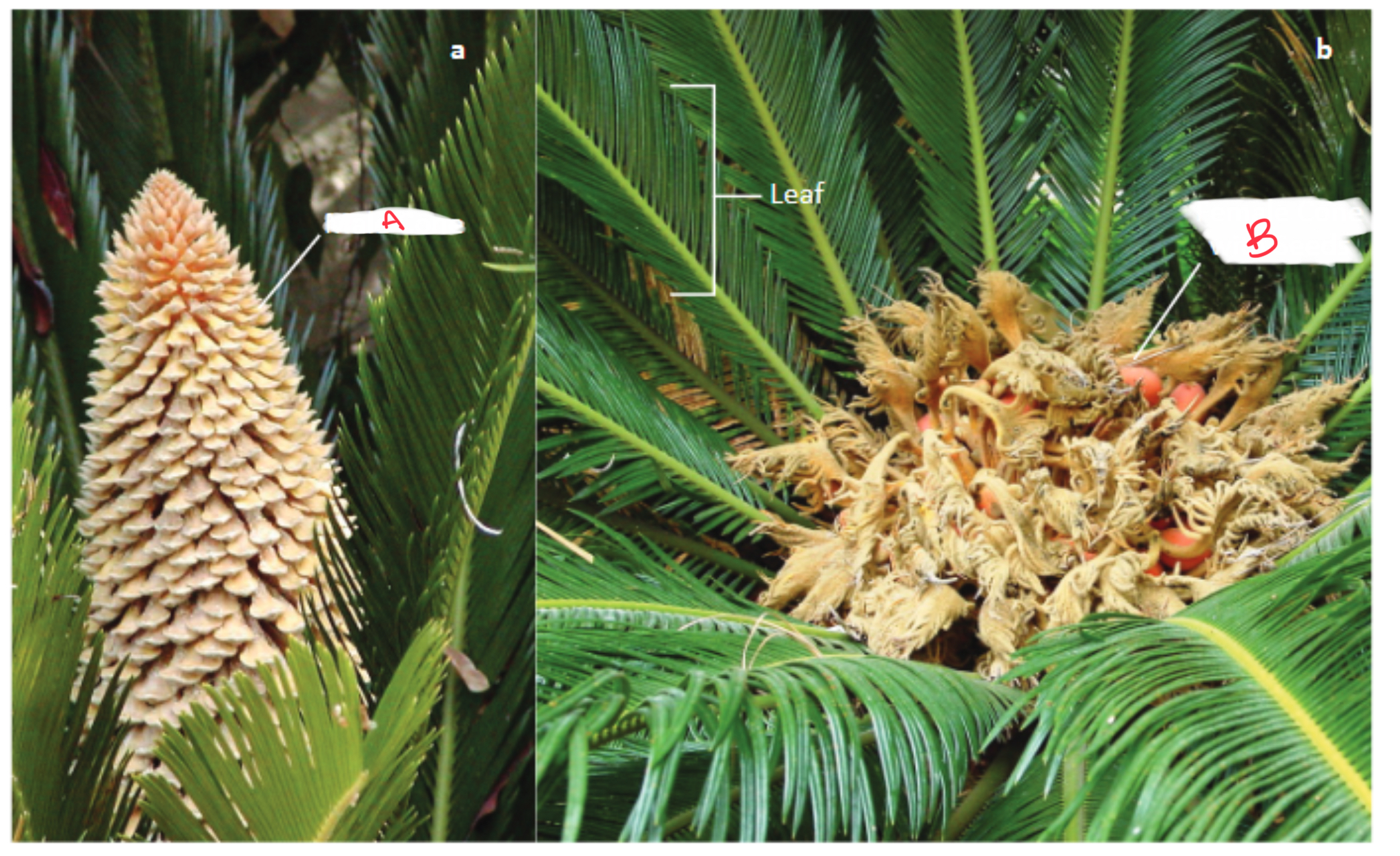

Identify the organism and the structures indicated
Cycad
a) male cone
b) female cone (with seeds)
What kind of reproductive structure system do ginkgoes have?
dioecious
Leaf structure of ginkgoes
deciduous and dichotomously veined leaves
Why are ginkgoes called the “living fossil”?
Thought to be extinct / only one living species: ginkgo biloba
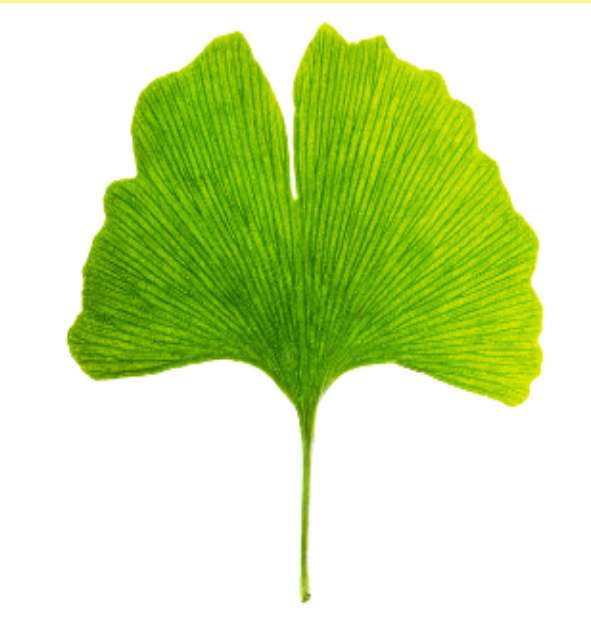

Identify the species that this leaf comes from
ginkgo
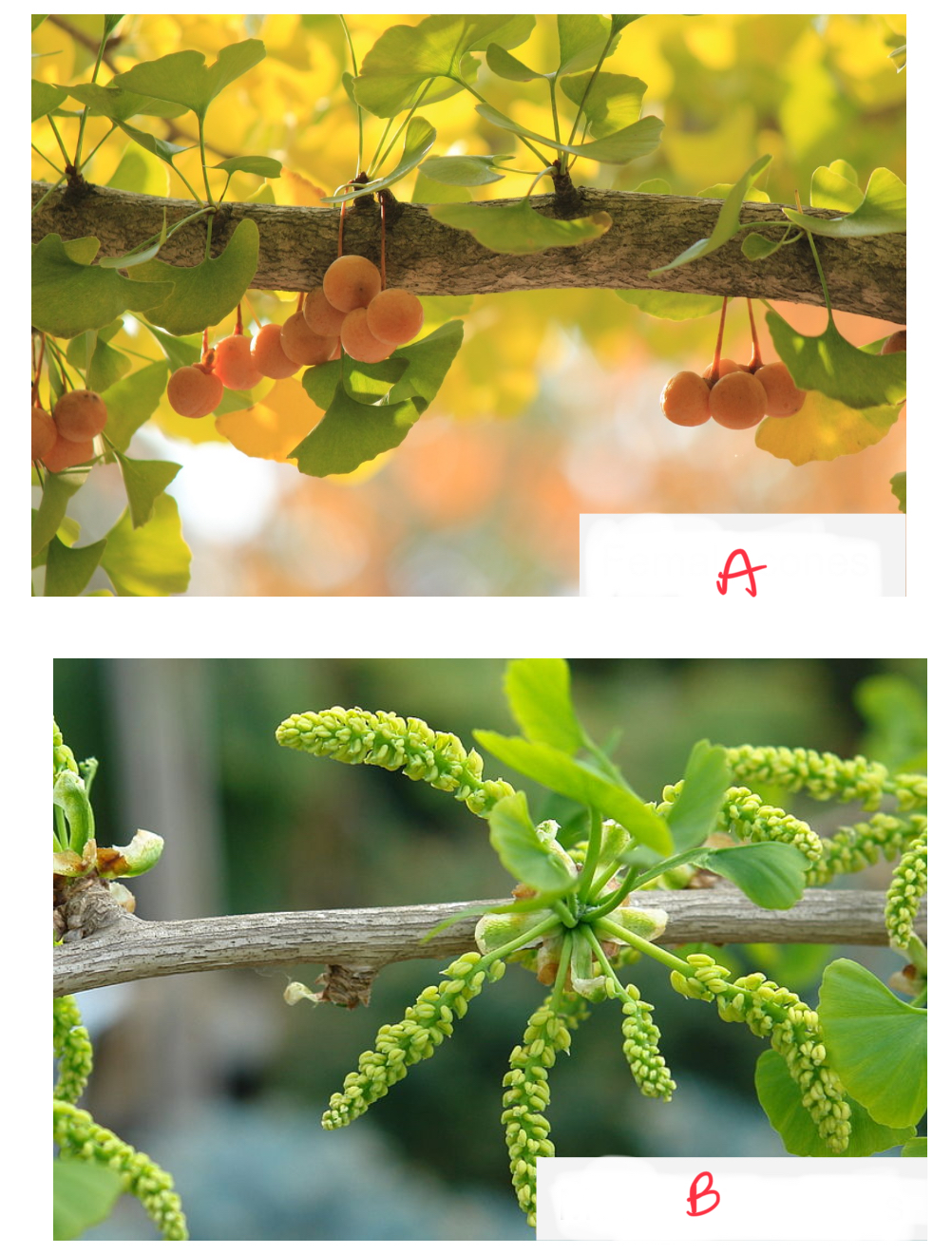

Identify the organism and the structures indicated
Ginkgo biloba
a) female cones
b) male pollen cones
Gnetophyta reproduction:
gymnospermous
Gnetophyte: welwitschia
mostly underground, but 2 leaves. African deserts, moisture from fog
Gnetophyte: ephedra
photosynthetic stems. Medicinal purposes by Native Americans and settlers
Gnetophyte: Gnetum
Tropical, includes vines and trees
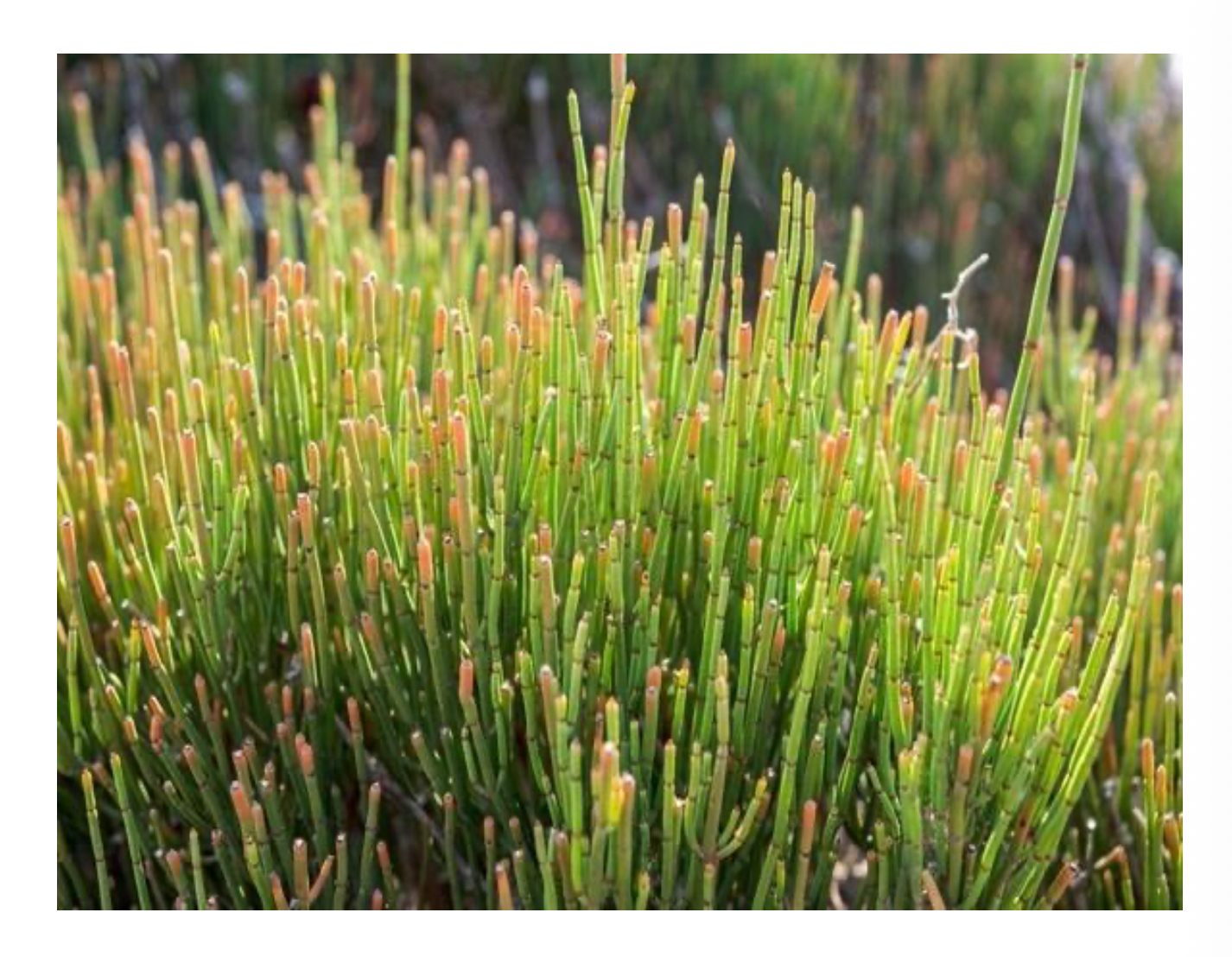

Identify the organism depicted
Ephedra
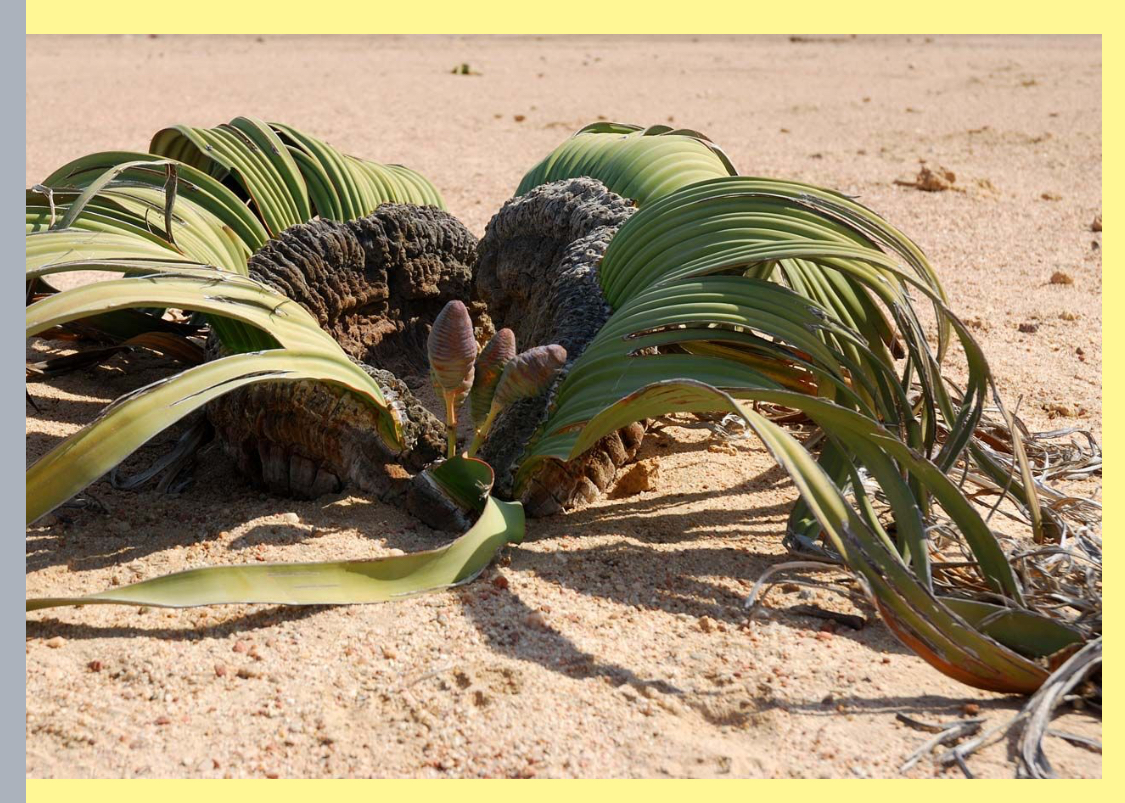

Identify the organism depicted
Welwischia
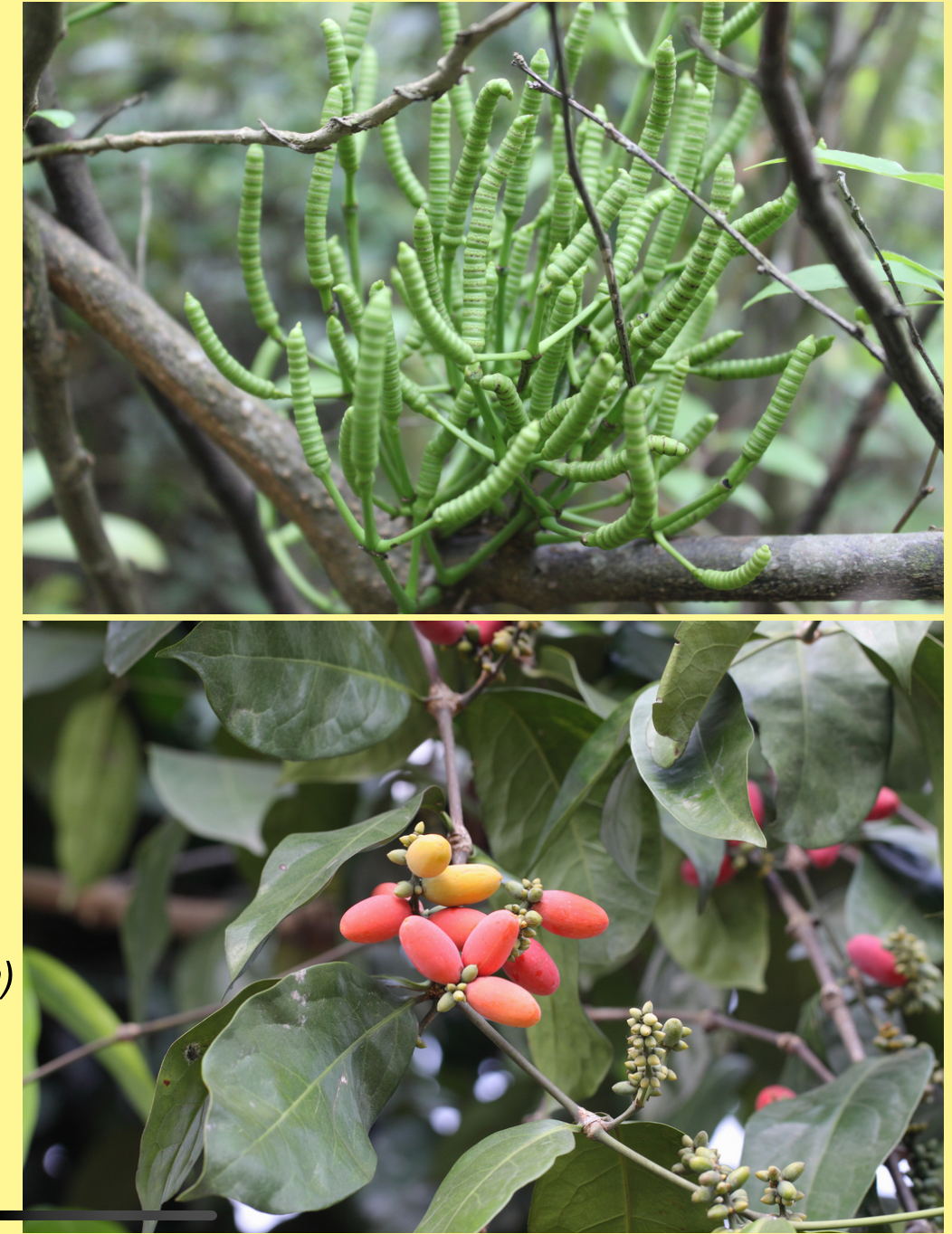

Identify the organism depicted
Gnetum
Conifer pines reproductive structures:
pollen (male) cones small
seed (female) cones large
Conifer forms of leaves:
1) needle-like
2) scale-like
3) awl-like
Conifer growth kinds:
1) primary growth: growth in height
2) secondary growth: growth in girth (xylem)
Conifer seed breakdown:
embryo (2n) and food (1n gametophyte tissue) inside a seed coat
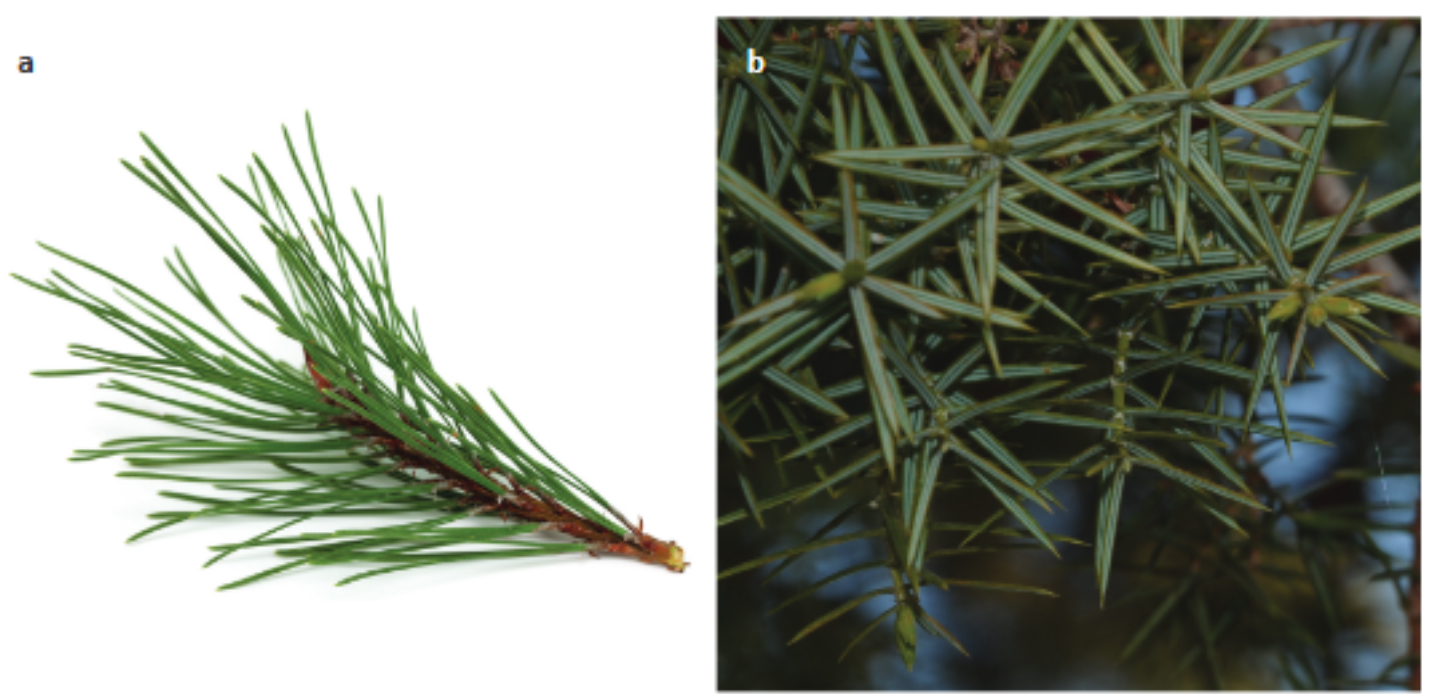

Identify the leaf form depicted
Needle-like

Identify the leaf form depicted
Scale-like

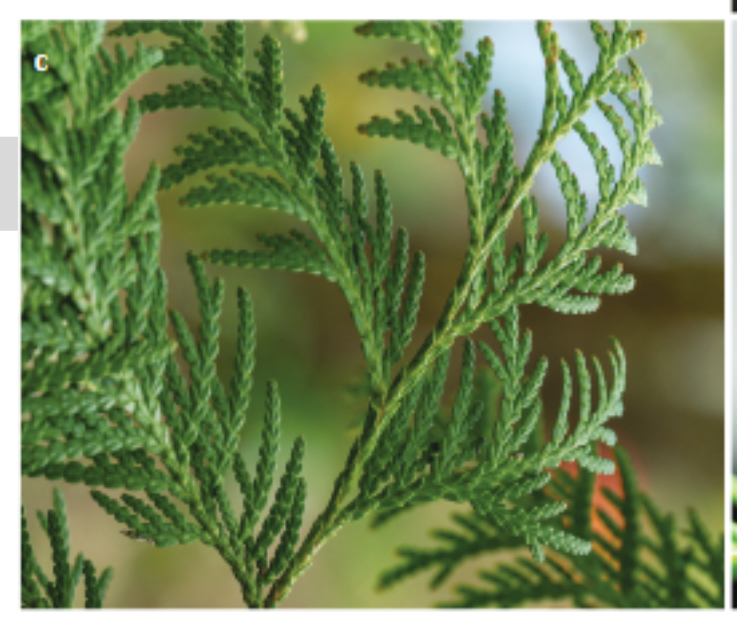
Identify the leaf form depicted
Awl-like
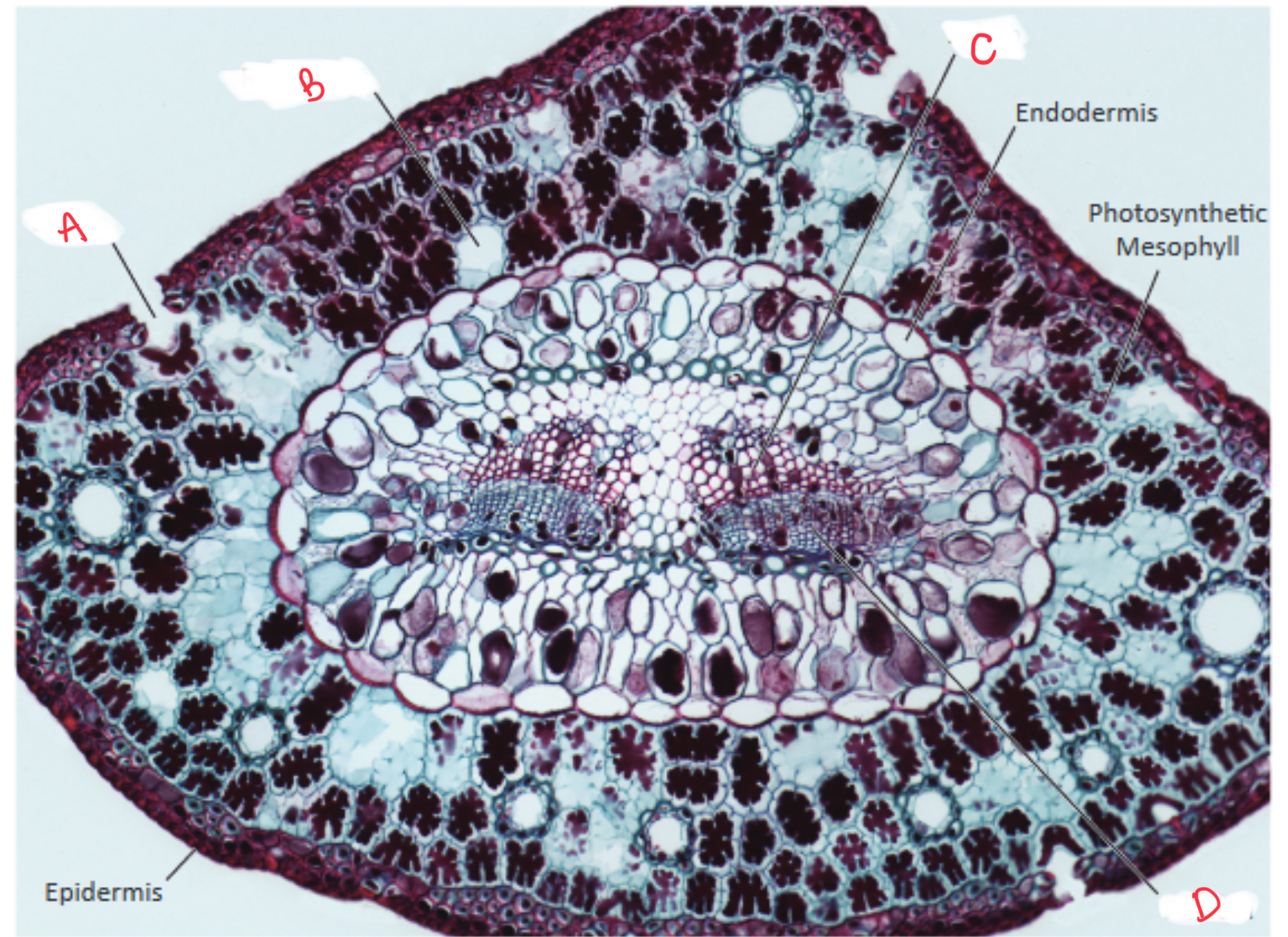
This cross section is of a(n) _________. Identify the structures
pine needle
a) stoma
b) resin duct
c) xylem
d) phloem
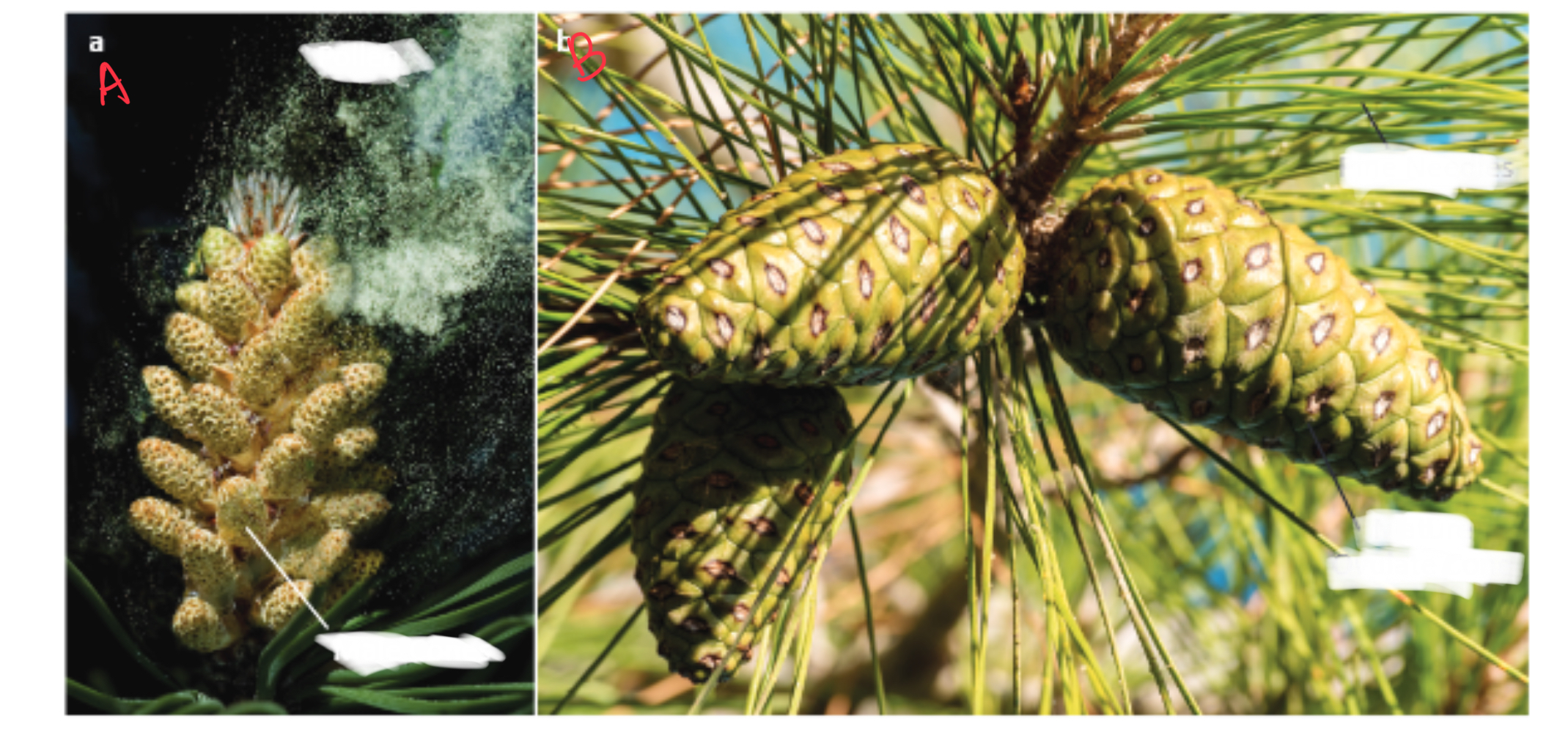

Distinguish the two types of cones depicted:
a) male cone (with pollen)
b) female cone (seeds)
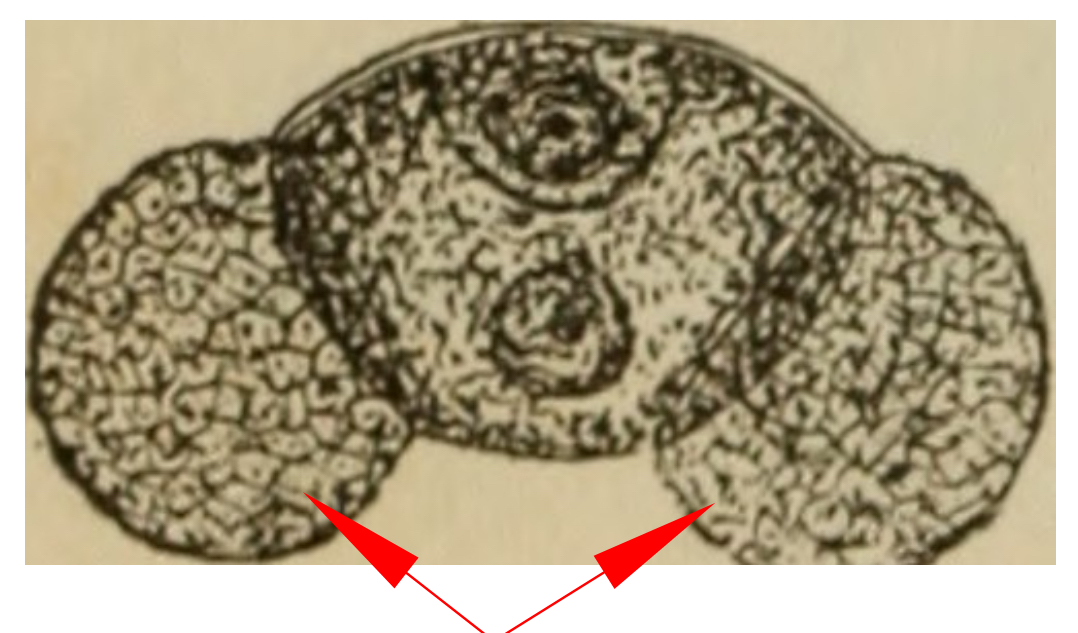
This cross section is of a(n) _________. Identify the structures indicated by the red arrows
male pollen grain
wings (aid in pollen dispersal)
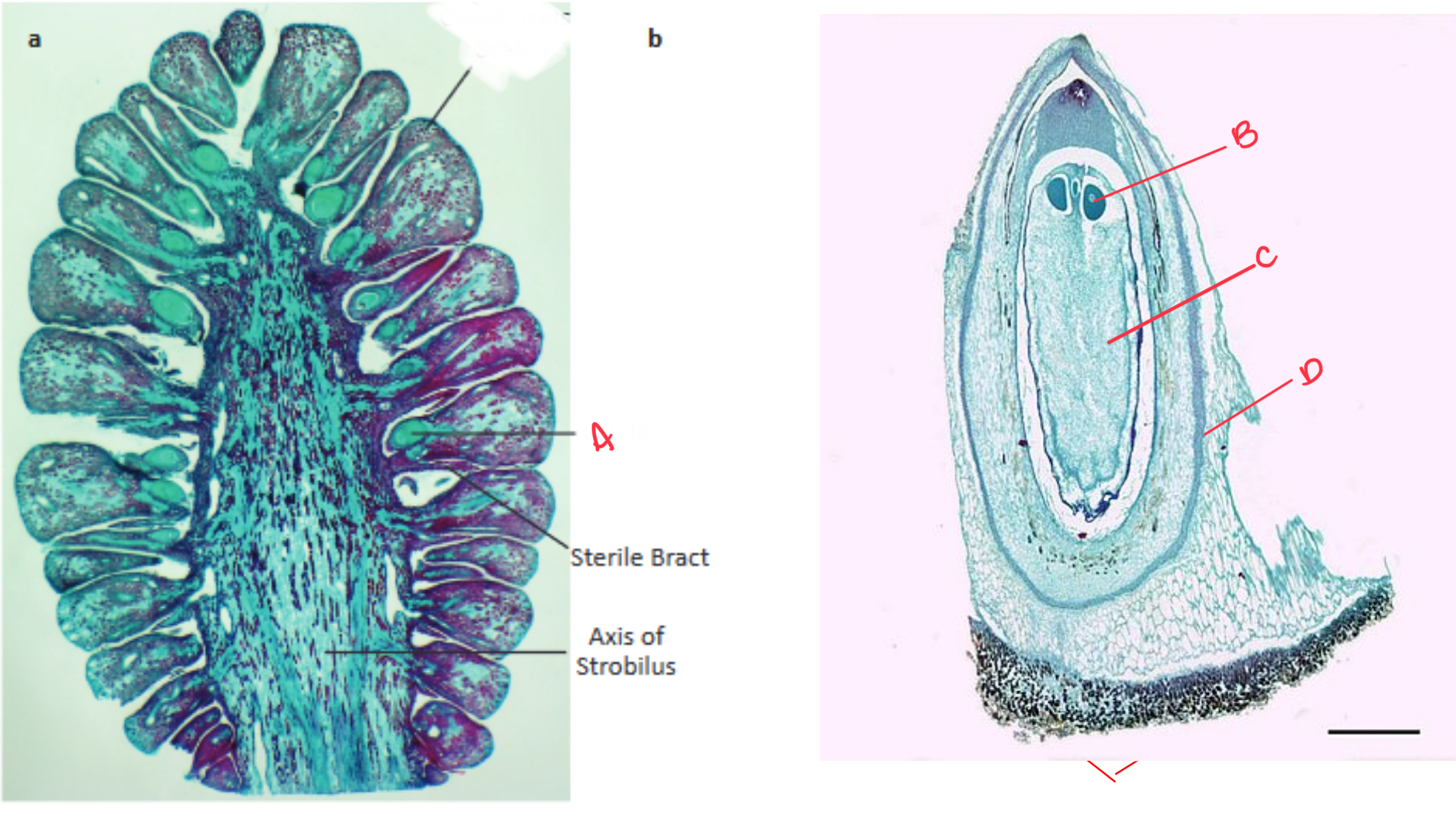
These cross sections are of a ____________ and a _________. Identify the structures indicated by the red arrows
female pine cone, ovule
a) ovule
b) archegonium
c) female gametophyte
d) integument